- 1、[CL] One Question Answering Model for Many Languages with Cross-lingual Dense Passage Retrieval
- 2、[AI] Predictive Coding: a Theoretical and Experimental Review
- 3、[LG] Efficient Neural Causal Discovery without Acyclicity Constraints
- 4、[CV] Self-supervised Multisensor Change Detection
- 5、[CV] Insights from Generative Modeling for Neural Video Compression
- [LG] Adaptable Agent Populations via a Generative Model of Policies
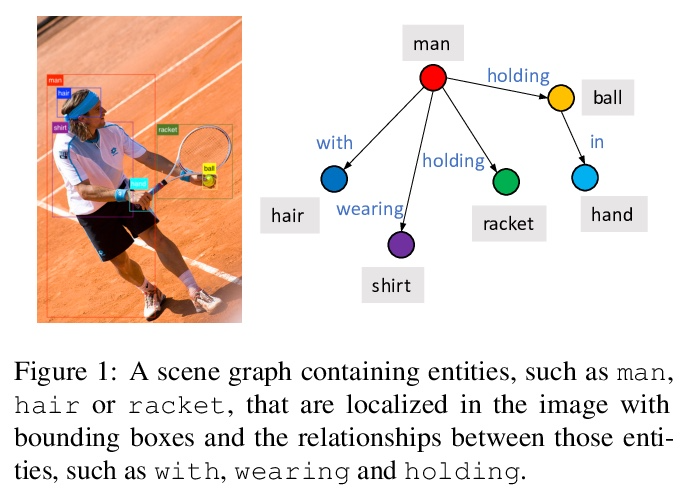
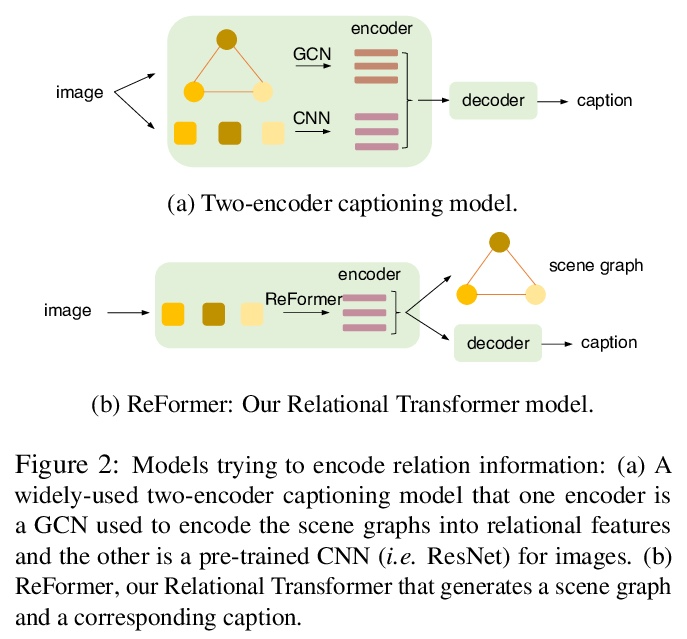
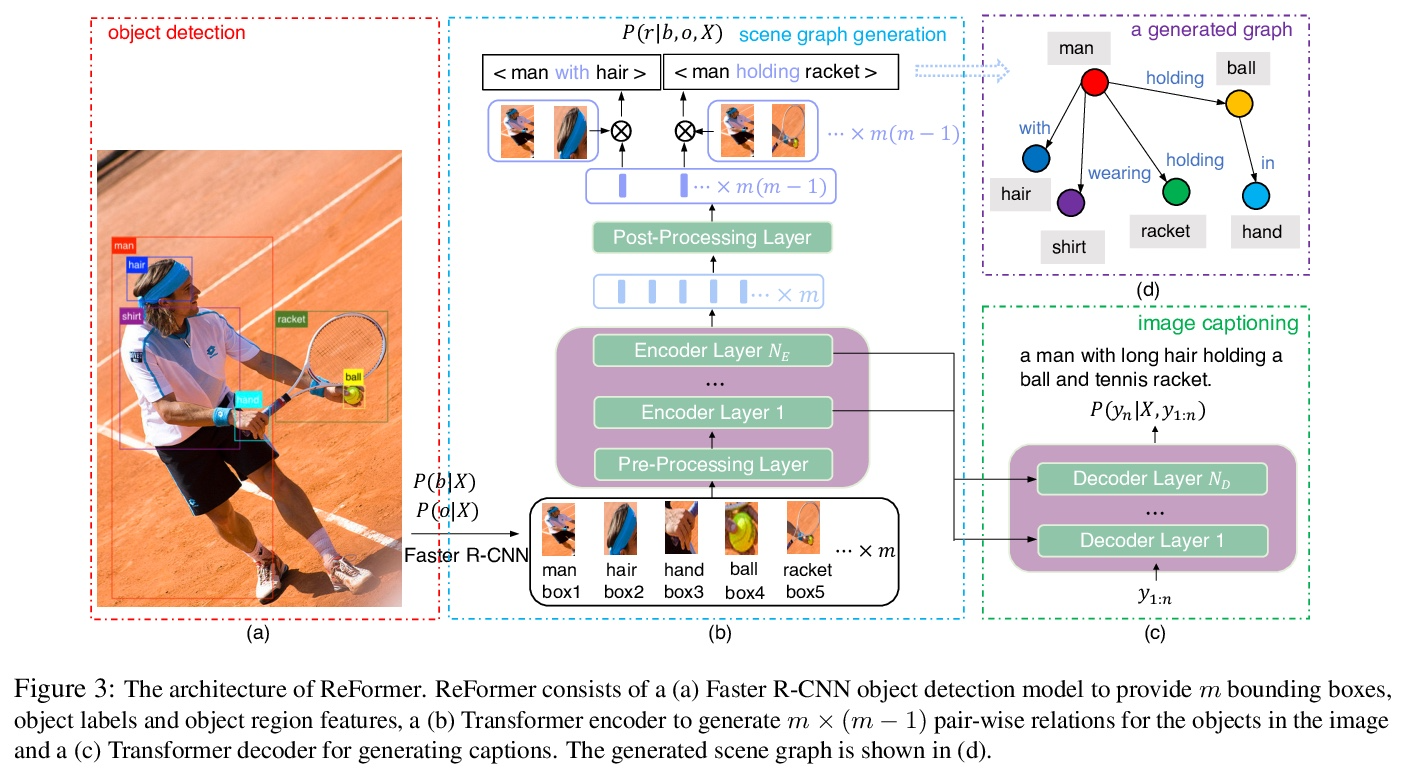
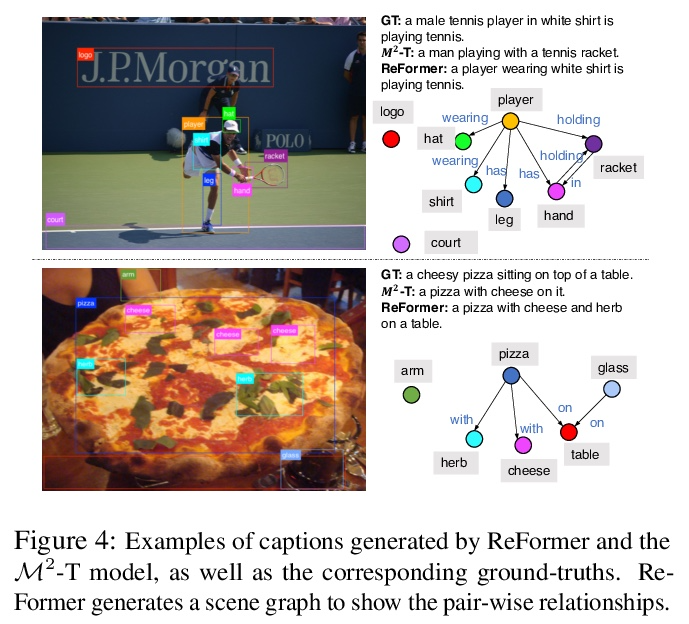
- [CV] ReFormer: The Relational Transformer for Image Captioning
- [LG] Revisiting IoT Device Identification
- [LG] Rotation Invariant Graph Neural Networks using Spin Convolutions
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CL] One Question Answering Model for Many Languages with Cross-lingual Dense Passage Retrieval
A Asai, X Yu, J Kasai, H Hajishirzi
[University of Washington]
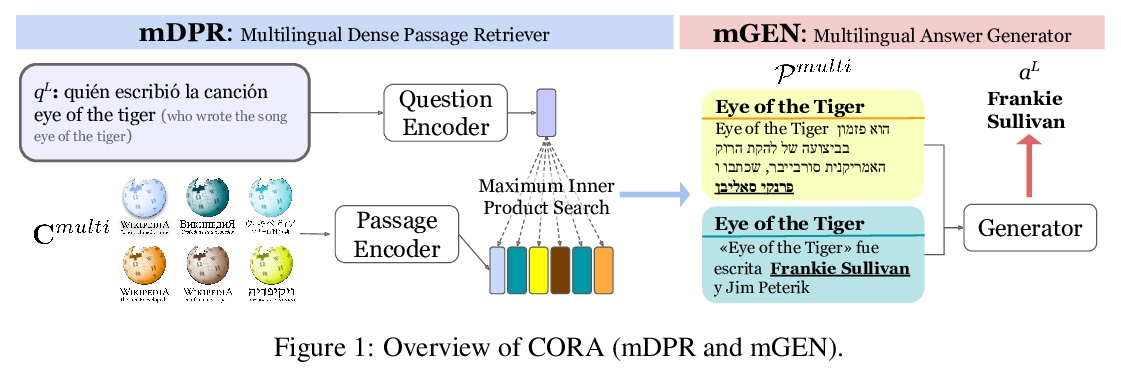
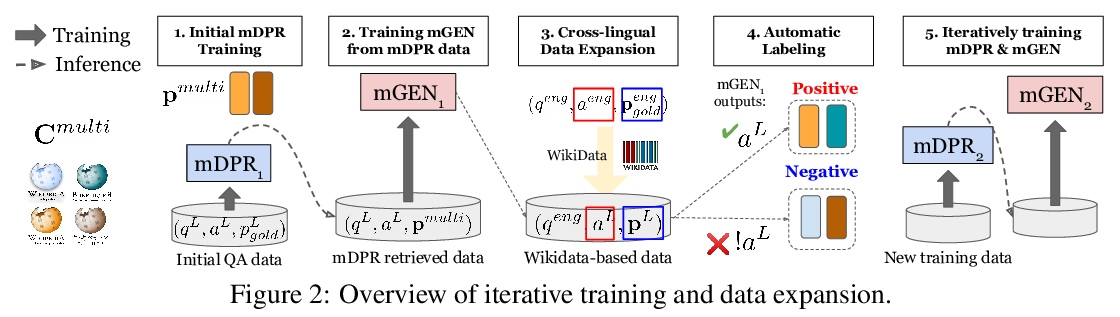
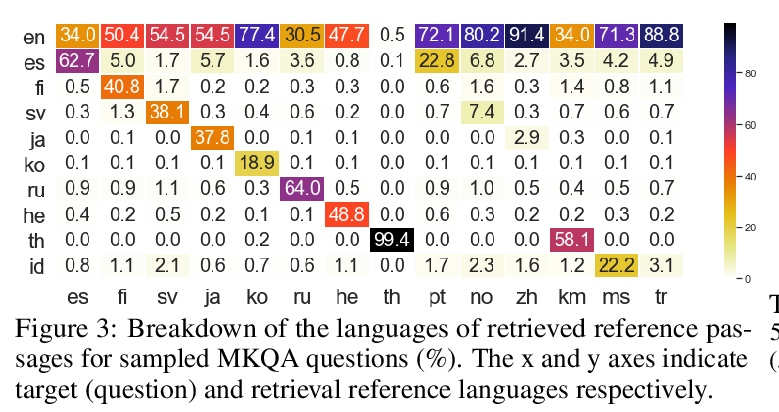
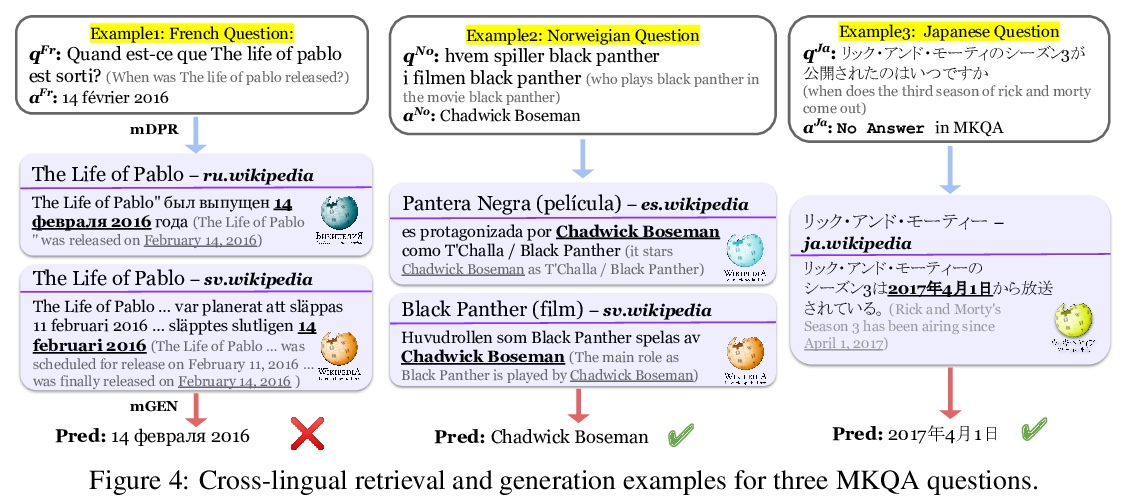
基于跨语言密集段落检索的多语言问答模型。本文提出CORA,一种跨语言开放式检索答案生成模型,即使在特定语言的标注数据或知识源不可用的情况下,也能回答多语言的问题。引入了一种新的密集段落检索算法,经训练可为问题跨语言检索文档。与多语言自回归生成模型相结合,CORA直接在目标语言中进行回答,不需要像之前的工作中使用任何翻译或语言内检索模块。提出一种迭代训练方法,自动将只有高资源语言的标注数据扩展到低资源语言。实验结果表明,CORA在26种语言的多语言开放问答基准上的表现大大超过了之前的技术水平,其中9种语言在训练期间未曾见过。分析表明,在多语言中,特别是在低资源环境下,跨语言检索和生成是非常重要的。
We present CORA, a Cross-lingual Open-Retrieval Answer Generation model that can answer questions across many languages even when language-specific annotated data or knowledge sources are unavailable. We introduce a new dense passage retrieval algorithm that is trained to retrieve documents across languages for a question. Combined with a multilingual autoregressive generation model, CORA answers directly in the target language without any translation or in-language retrieval modules as used in prior work. We propose an iterative training method that automatically extends annotated data available only in high-resource languages to low-resource ones. Our results show that CORA substantially outperforms the previous state of the art on multilingual open question answering benchmarks across 26 languages, 9 of which are unseen during training. Our analyses show the significance of cross-lingual retrieval and generation in many languages, particularly under low-resource settings.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrwY7aDgE 
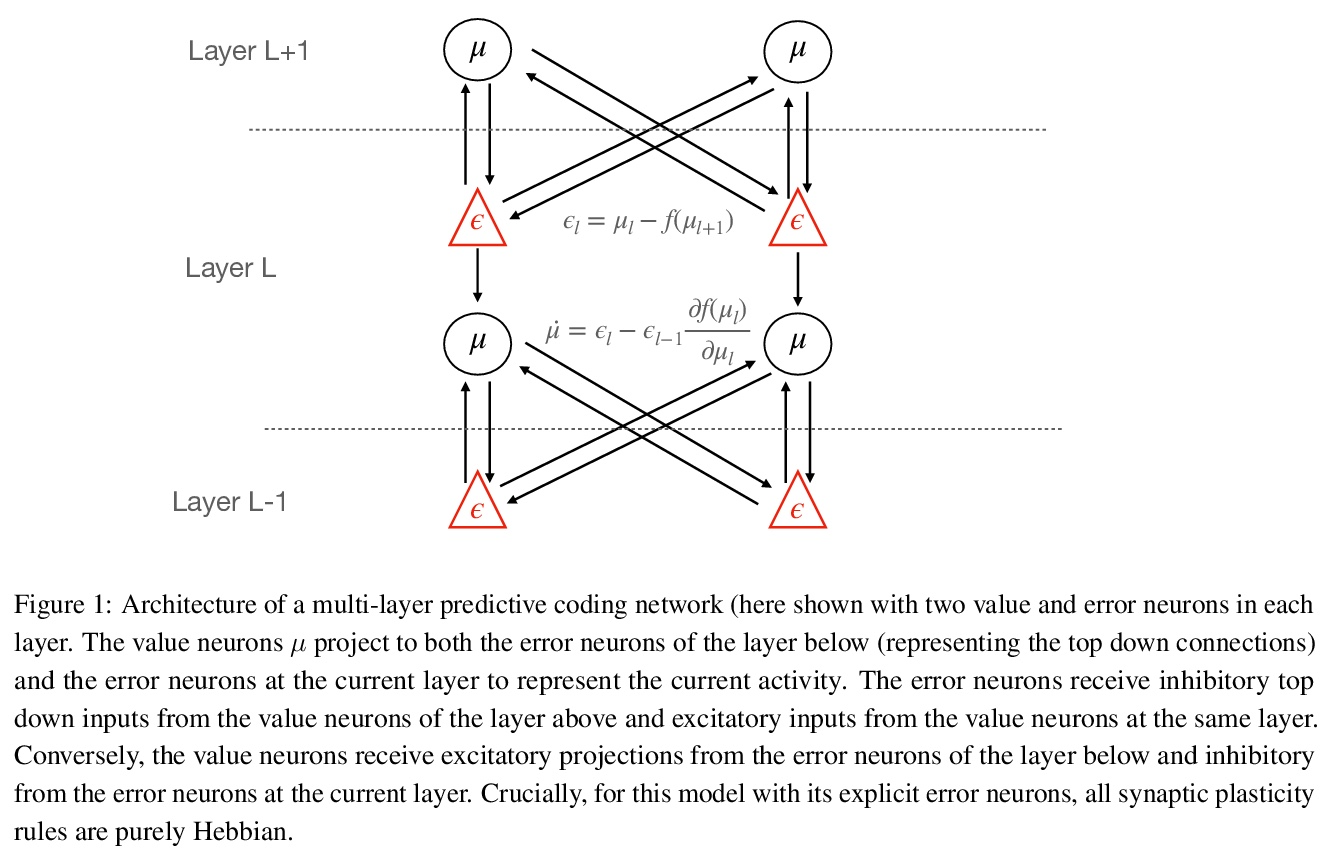
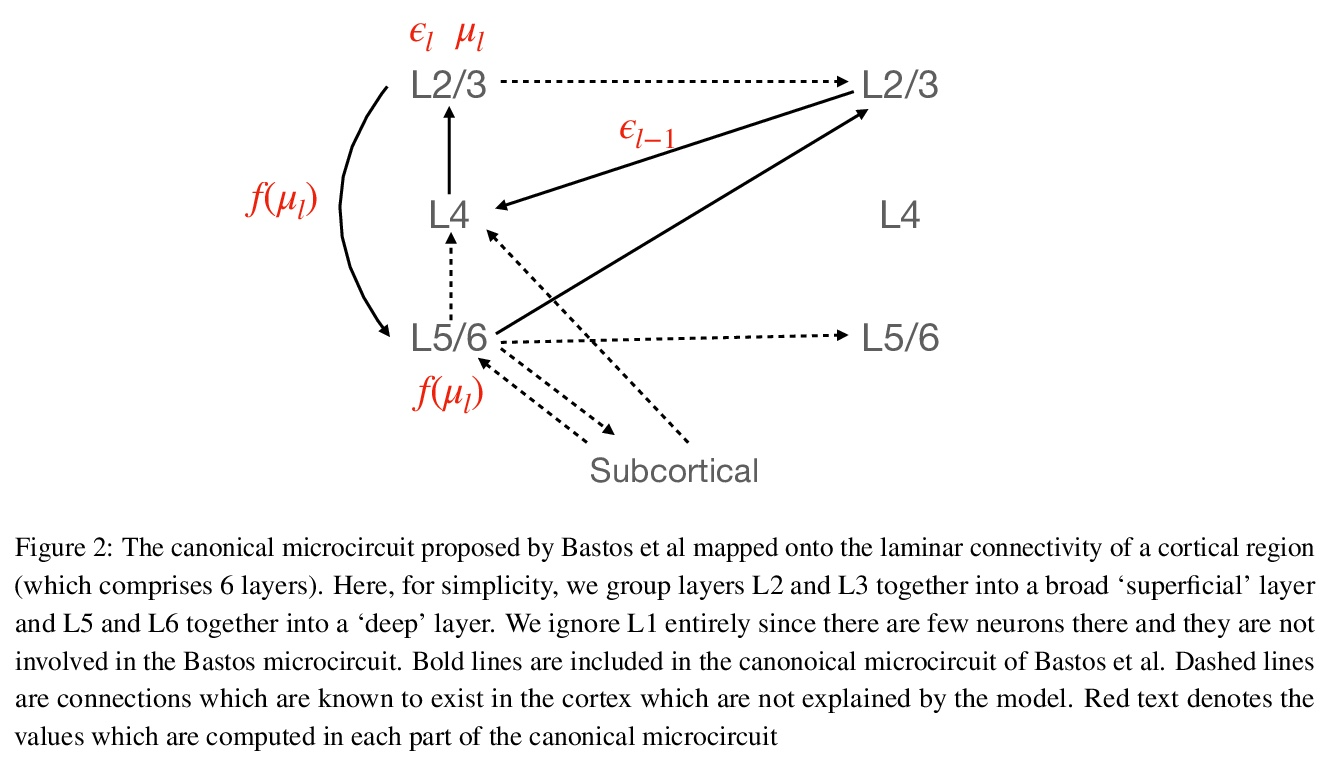
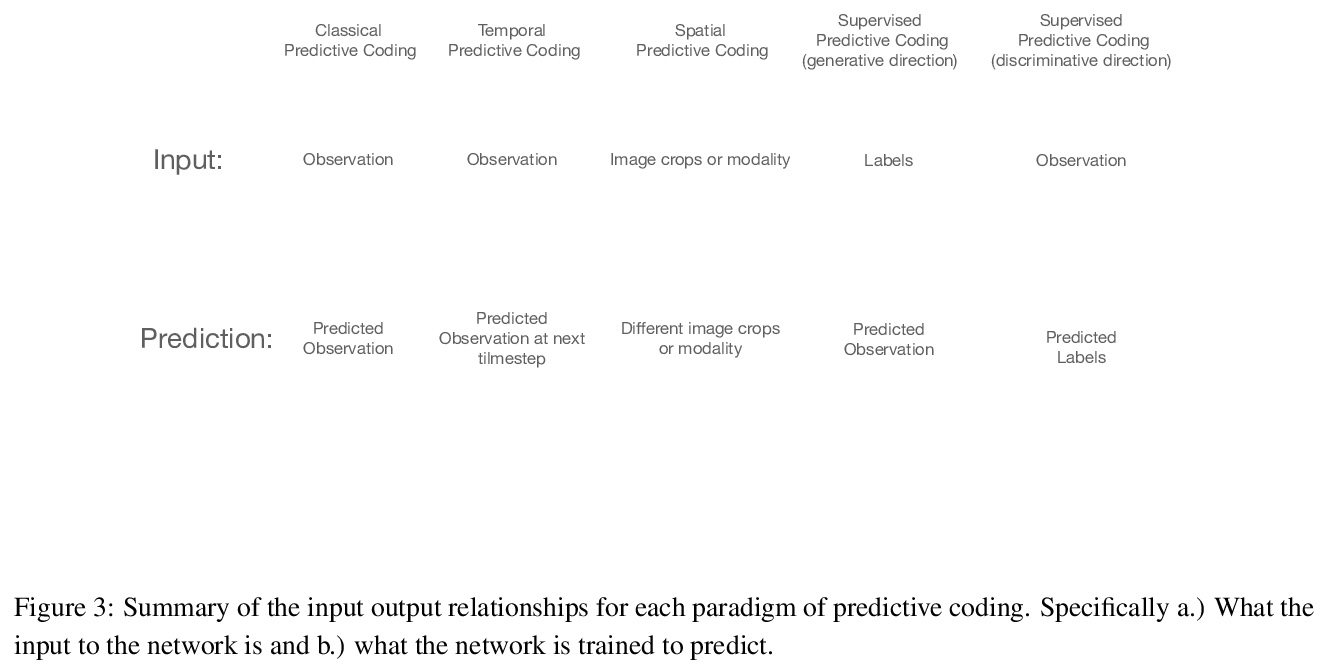
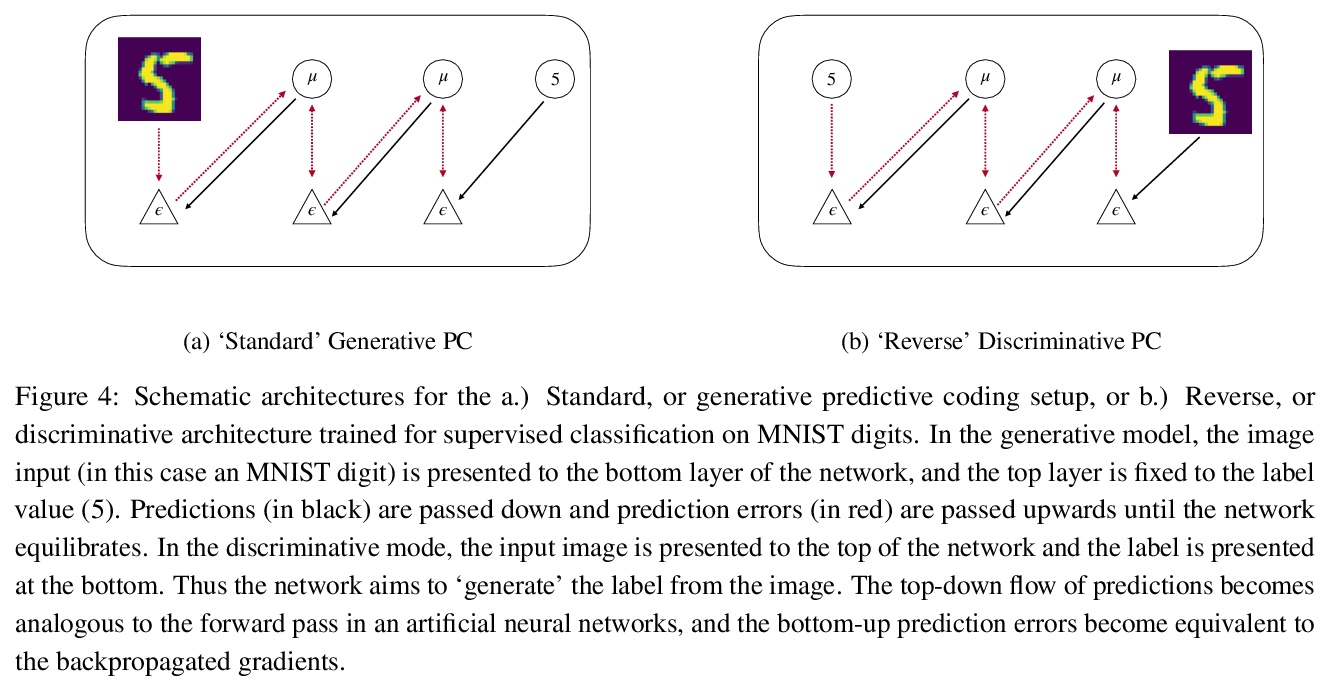
2、[AI] Predictive Coding: a Theoretical and Experimental Review
B Millidge, A Seth, C L Buckley
[University of Edinburgh & University of Sussex]
预测性编码:理论和实验综述。预测性编码为皮质功能提供了潜在的统一解释——假设大脑的核心功能,是使世界生成模型的预测误差最小化。该理论与贝叶斯脑框架密切相关,在过去20年里,在理论和认知神经科学领域获得了巨大的影响。在对预测性编码的改进和扩展的理论和数学模型进行实证检验的基础上,以及在评估其在大脑中实施的潜在生物学合理性和该理论所做的具体神经生理和心理预测的基础上,出现了大量研究。尽管预测性编码理论经久不衰,但是没有对预测性编码理论的全面回顾,特别是对该领域的最新发展。本文对预测性编码的核心数学结构和逻辑进行了全面回顾,补充了最近文献中的教程。回顾了该框架内广泛的经典和最新工作,从可以实现预测性编码的神经生物学现实的微电路,到预测性编码和广泛使用的误差反向传播算法之间的密切关系,以及调研预测性编码和现代机器学习技术之间的密切关系。
Predictive coding offers a potentially unifying account of cortical function – postulating that the core function of the brain is to minimize prediction errors with respect to a generative model of the world. The theory is closely related to the Bayesian brain framework and, over the last two decades, has gained substantial influence in the fields of theoretical and cognitive neuroscience. A large body of research has arisen based on both empirically testing improved and extended theoretical and mathematical models of predictive coding, as well as in evaluating their potential biological plausibility for implementation in the brain and the concrete neurophysiological and psychological predictions made by the theory. Despite this enduring popularity, however, no comprehensive review of predictive coding theory, and especially of recent developments in this field, exists. Here, we provide a comprehensive review both of the core mathematical structure and logic of predictive coding, thus complementing recent tutorials in the literature (Bogacz, 2017; Buckley, Kim, McGregor, & Seth, 2017). We also review a wide range of classic and recent work within the framework, ranging from the neurobiologically realistic microcircuits that could implement predictive coding, to the close relationship between predictive coding and the widely-used backpropagation of error algorithm, as well as surveying the close relationships between predictive coding and modern machine learning techniques.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Krx2CFqqo 
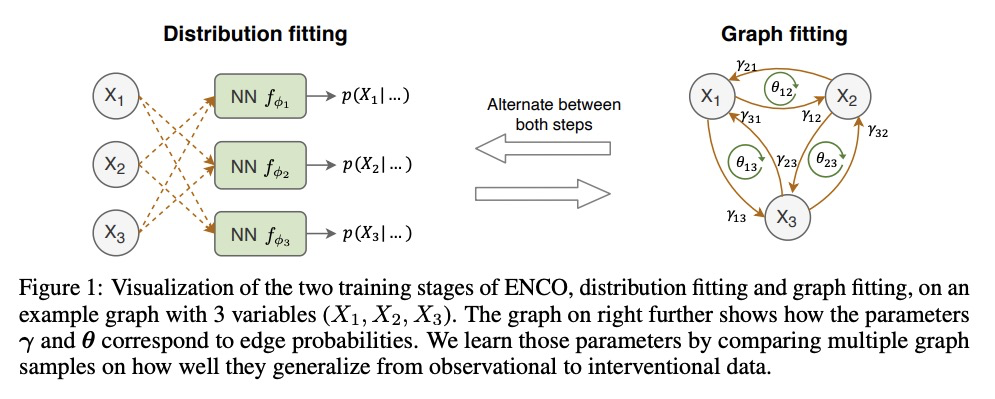
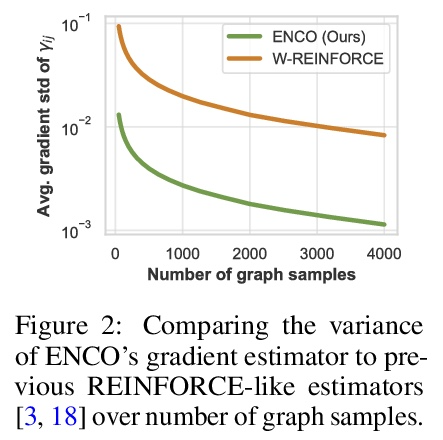
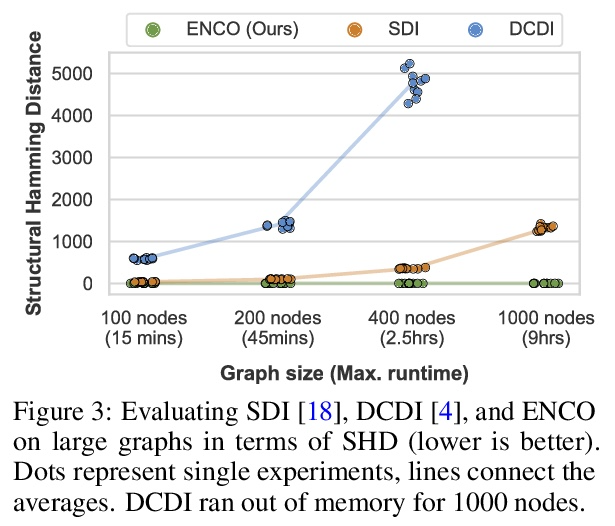
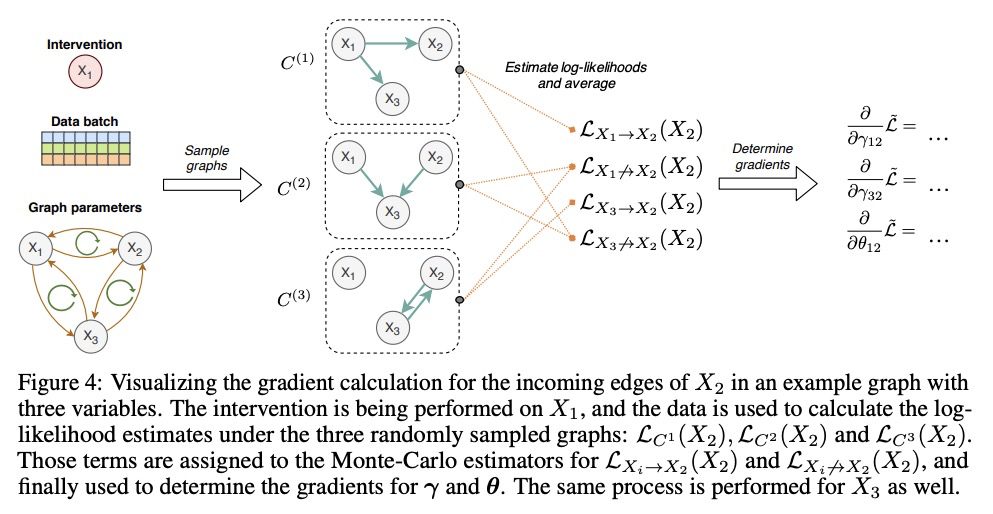
3、[LG] Efficient Neural Causal Discovery without Acyclicity Constraints
P Lippe, T Cohen, E Gavves
[University of Amsterdam & Qualcomm AI Research]
非无环约束高效神经因果发现。基于观察和干预数据的因果图模型结构学习,是许多科学领域的一个基本问题。一个有前途的方向是基于分数的连续优化方法,以数据驱动的方式有效地学习因果图。然而,到目前为止,这些方法需要约束优化,来强制执行无环或缺乏收敛保证。本文提出ENCO,一种利用观察和干预数据的有向、无环因果图的高效结构学习方法。ENCO将图的搜索表述为独立边缘可能性的优化,边缘方向被建模为一个单独的参数。可以在温和条件下提供ENCO的收敛保证,而不需要对无环得分函数进行约束。实验表明,ENCO可以有效地恢复具有数百节点的图,比之前可能的要大一个数量级,同时处理确定性变量和潜在的混杂因素。
Learning the structure of a causal graphical model using both observational and interventional data is a fundamental problem in many scientific fields. A promising direction is continuous optimization for score-based methods, which efficiently learn the causal graph in a data-driven manner. However, to date, those methods require constrained optimization to enforce acyclicity or lack convergence guarantees. In this paper, we present ENCO, an efficient structure learning method for directed, acyclic causal graphs leveraging observational and interventional data. ENCO formulates the graph search as an optimization of independent edge likelihoods with the edge orientation being modeled as a separate parameter. Consequently, we can provide convergence guarantees of ENCO under mild conditions without constraining the score function with respect to acyclicity. In experiments, we show that ENCO can efficiently recover graphs with hundreds of nodes, an order of magnitude larger than what was previously possible, while handling deterministic variables and latent confounders.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Krx62jfNh 
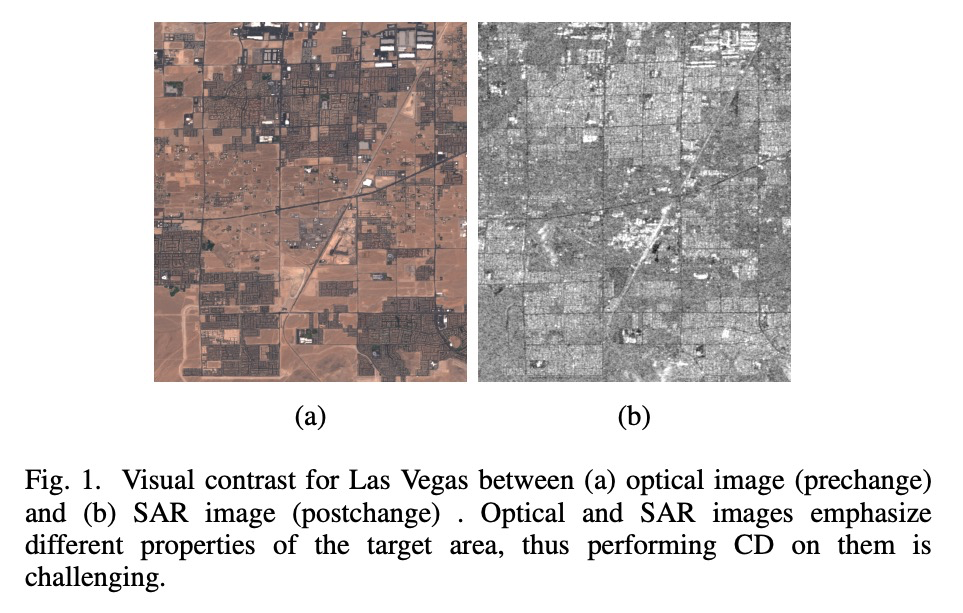
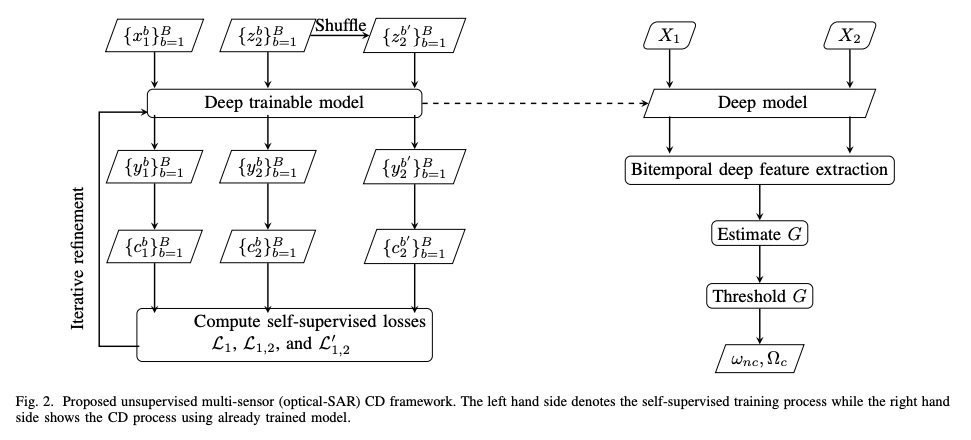
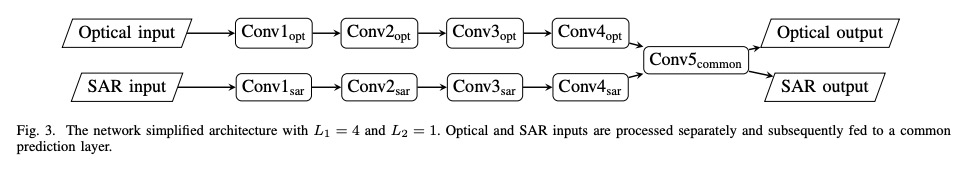
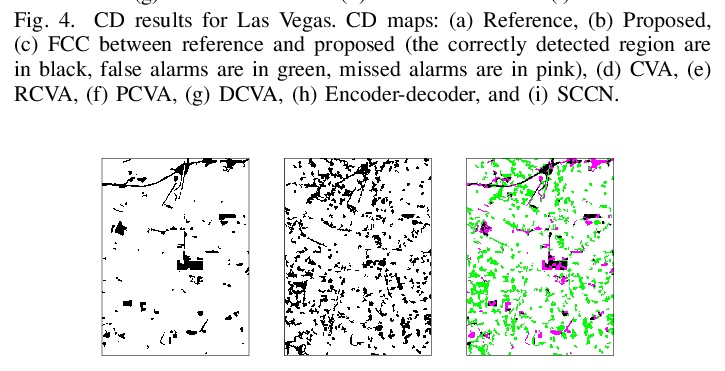
4、[CV] Self-supervised Multisensor Change Detection
S Saha, P Ebel, X X Zhu
[Technical University of Munich]
自监督多传感器变化检测。大多数变化检测方法,假定变化前和变化后的图像是由同一个传感器获取的。然而,在许多现实场景中,例如自然灾害,使用发生前和发生后的最新可用图像更为实际,这些图像可能是用不同的传感器获取的。特别是,对由光学和合成孔径雷达(SAR)传感器获取的图像的组合感兴趣。SAR图像看起来与光学图像有很大的不同,即使是在捕获相同的场景。除此之外,变化检测方法通常被限制为只使用目标图像对,没有标记数据,也没有额外的未标记数据。这种约束限制了传统的监督机器学习和无监督生成方法在多传感器变化检测中的应用范围。最近自监督学习方法的快速发展表明,其中一些方法甚至可以在只有少数图像的情况下工作。受此启发,本文提出一种多传感器变化检测的方法,只使用未标记目标双时空图像,通过深度聚类和对比学习,以自监督方式训练网络。在四个显示变化的多模态双时空场景中,对所提出的方法进行了评估,并证明了自监督方法的好处。
Most change detection methods assume that prechange and post-change images are acquired by the same sensor. However, in many real-life scenarios, e.g., natural disaster, it is more practical to use the latest available images before and after the occurrence of incidence, which may be acquired using different sensors. In particular, we are interested in the combination of the images acquired by optical and Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) sensors. SAR images appear vastly different from the optical images even when capturing the same scene. Adding to this, change detection methods are often constrained to use only target image-pair, no labeled data, and no additional unlabeled data. Such constraints limit the scope of traditional supervised machine learning and unsupervised generative approaches for multi-sensor change detection. Recent rapid development of selfsupervised learning methods has shown that some of them can even work with only few images. Motivated by this, in this work we propose a method for multi-sensor change detection using only the unlabeled target bi-temporal images that are used for training a network in self-supervised fashion by using deep clustering and contrastive learning. The proposed method is evaluated on four multi-modal bi-temporal scenes showing change and the benefits of our self-supervised approach are demonstrated.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrxcH6nSO 
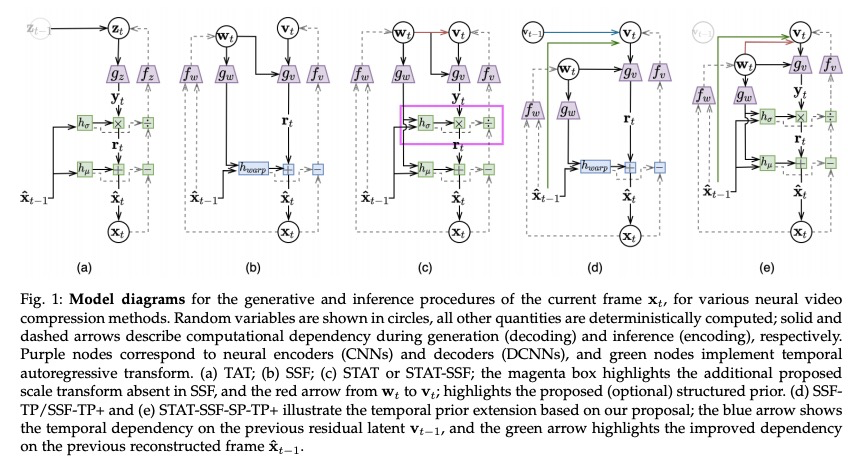
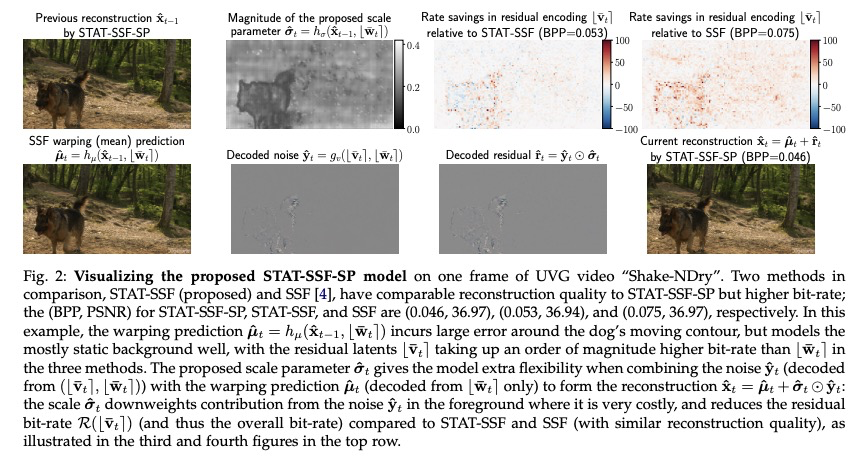
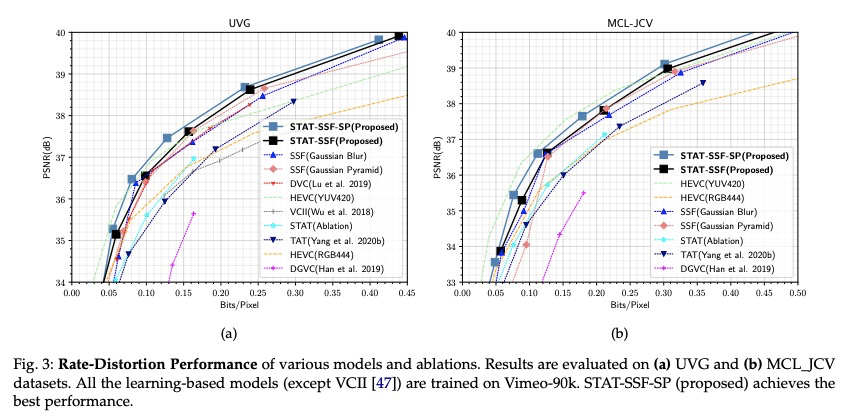
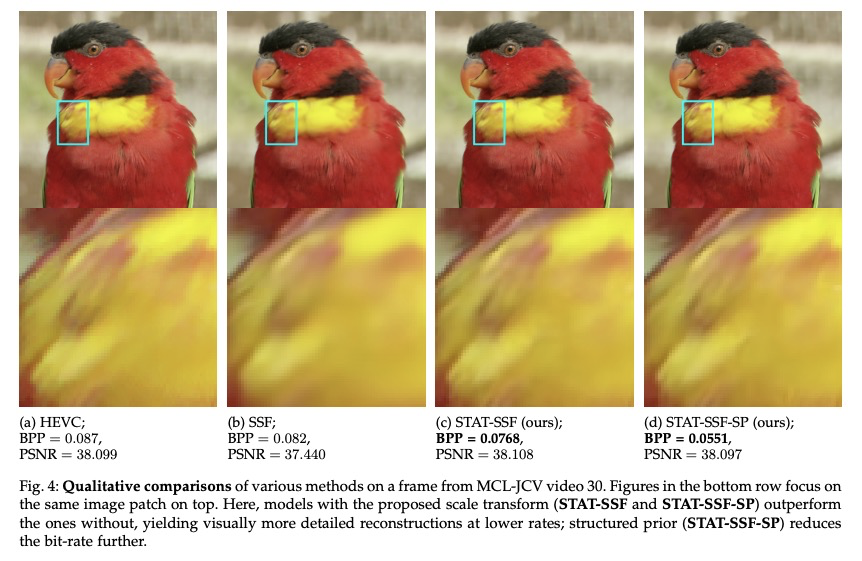
5、[CV] Insights from Generative Modeling for Neural Video Compression
R Yang, Y Yang, J Marino, S Mandt
[University of California Irvine]
生成式建模对神经视频压缩的启示。虽然最近的机器学习研究揭示了深度生成模型(如VAE)与学习型压缩中使用的速率-失真损失之间的联系,但这些工作大多集中在图像上。本文通过深度自回归和潜变量建模的视角,来看待最近提出的神经视频编码算法。将最近的神经视频编解码器作为广义随机时空自回归变换的实例,提出了受归一化流和结构化先验启发的进一步改进的新途径。提出几个架构,在全分辨率视频上产生最先进的视频压缩性能,并讨论了它们的权衡和消融。提出(i)改进的时间自回归变换,(ii)改进的具有结构化和时间依赖性的熵模型,以及(iii)所提出算法的可变比特率版本。由于所提出改进与一大类现有模型兼容,提供了进一步的证据,证明生成式建模的观点可以推进神经视频编码领域。
While recent machine learning research has revealed connections between deep generative models such as VAEs and rate-distortion losses used in learned compression, most of this work has focused on images. In a similar spirit, we view recently proposed neural video coding algorithms through the lens of deep autoregressive and latent variable modeling. We present recent neural video codecs as instances of a generalized stochastic temporal autoregressive transform, and propose new avenues for further improvements inspired by normalizing flows and structured priors. We propose several architectures that yield state-of-the-art video compression performance on full-resolution video and discuss their tradeoffs and ablations. In particular, we propose (i) improved temporal autoregressive transforms, (ii) improved entropy models with structured and temporal dependencies, and (iii) variable bitrate versions of our algorithms. Since our improvements are compatible with a large class of existing models, we provide further evidence that the generative modeling viewpoint can advance the neural video coding field.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Krxgt89y0 
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
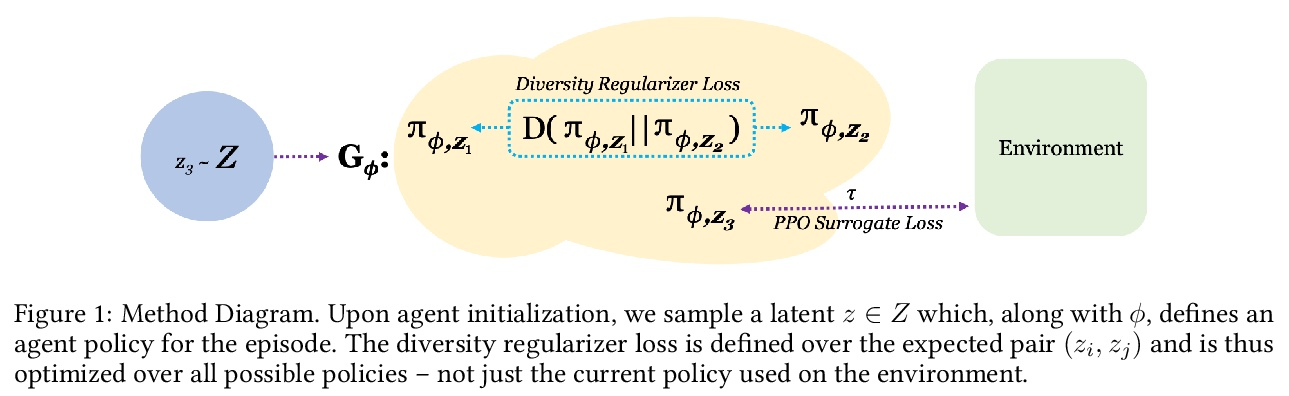
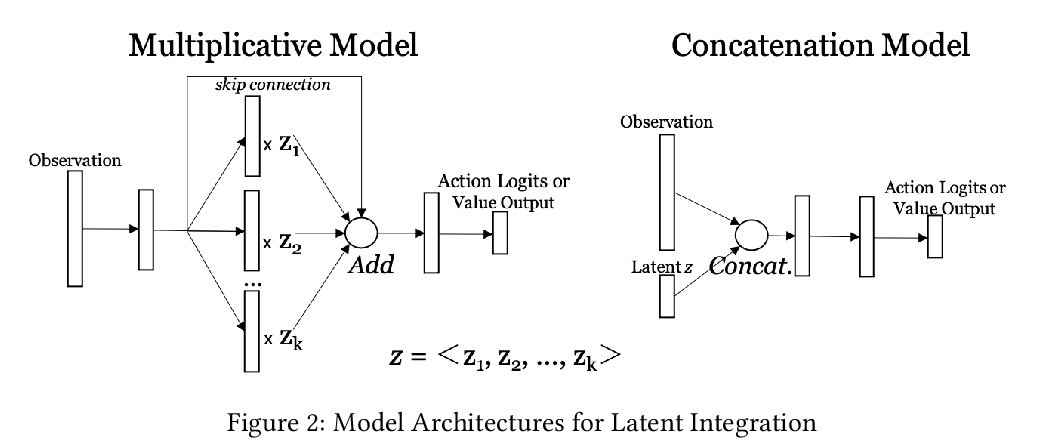
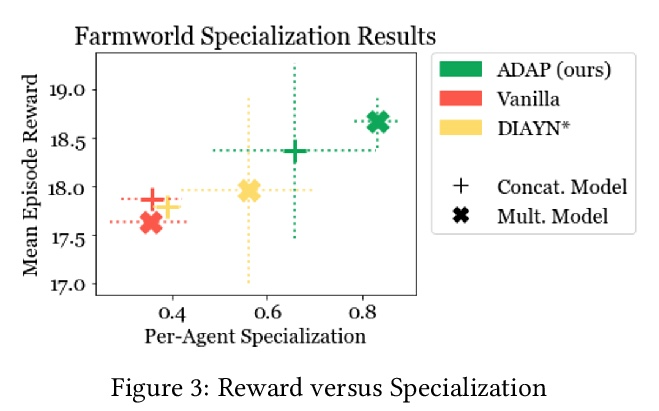
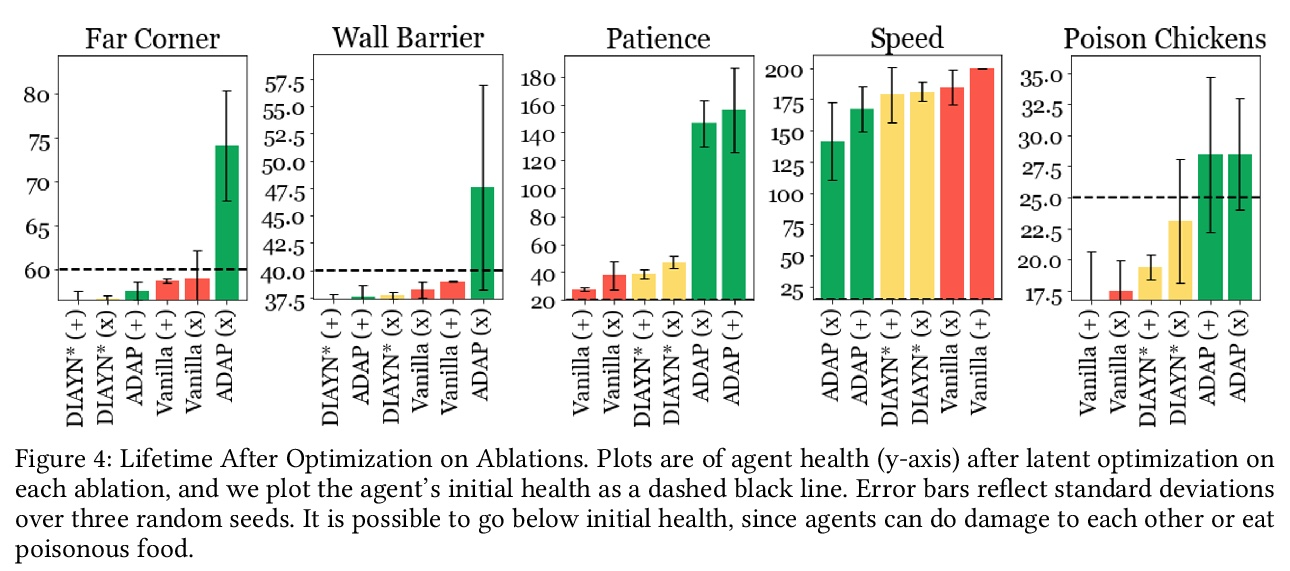
[LG] Adaptable Agent Populations via a Generative Model of Policies
基于策略生成模型的自适应智能体种群
K Derek, P Isola
[MIT]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Krxjqlt4a 
[CV] ReFormer: The Relational Transformer for Image Captioning
ReFormer:面向图像描述的关系Transformer
X Yang, Y Liu, X Wang
[Stony Brook University & Facebook]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrxlZiRpP 
[LG] Revisiting IoT Device Identification
再论物联网设备识别
R Kolcun, D A Popescu, V Safronov, P Yadav, A M Mandalari, R Mortier, H Haddadi
[University of Cambridge & University of York & Imperial College London]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrxnNhfUU 
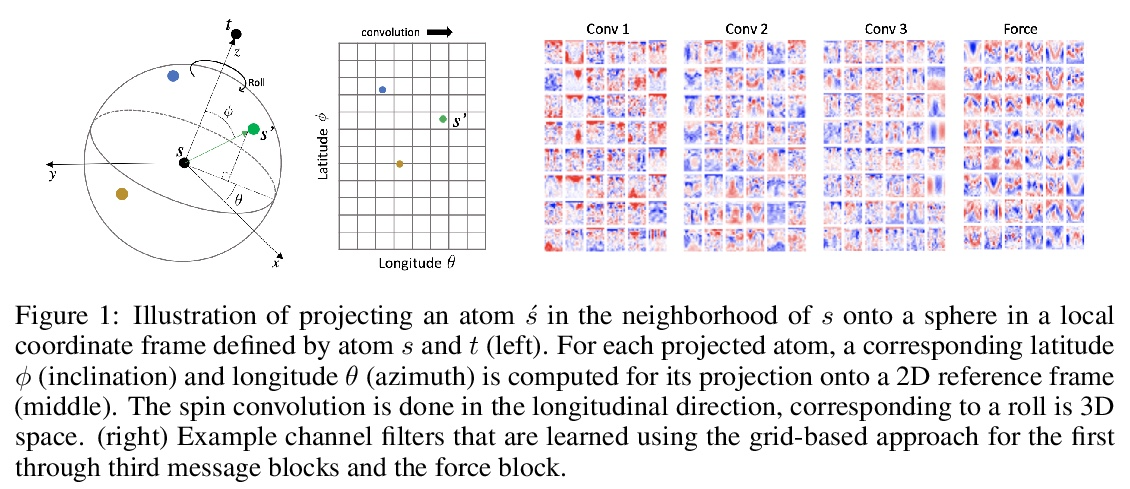
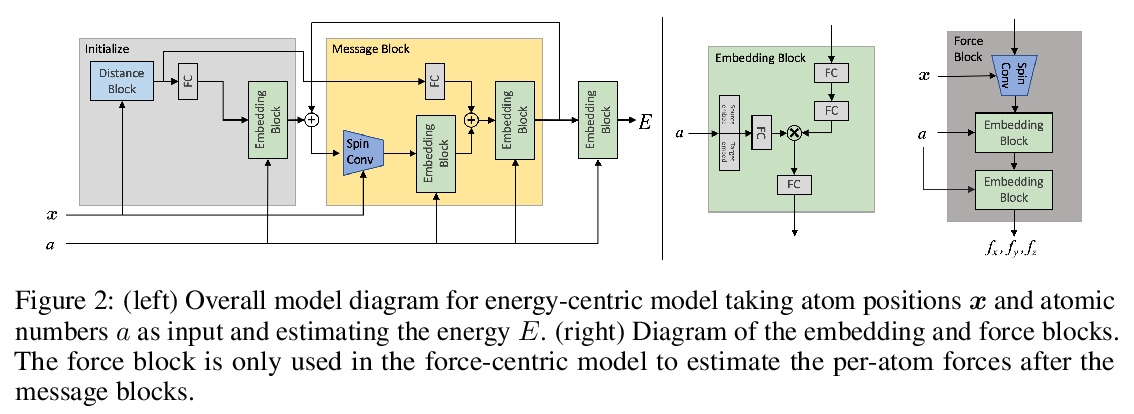
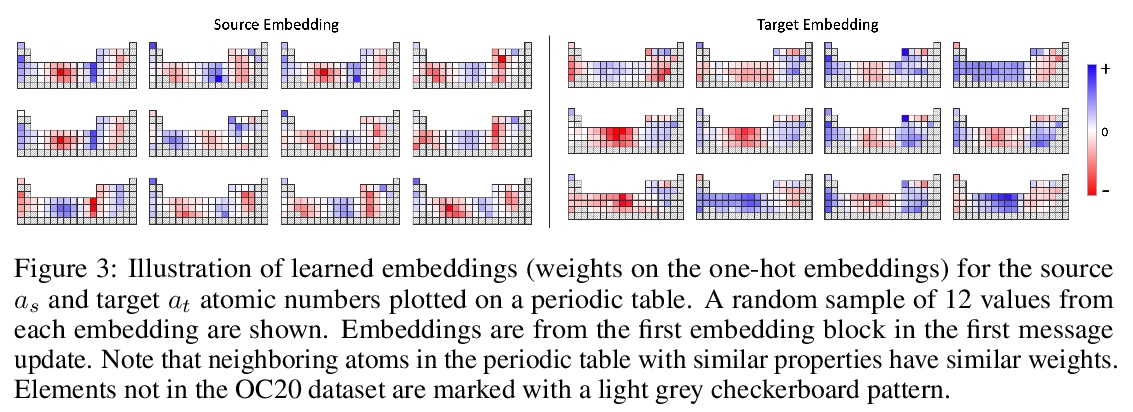
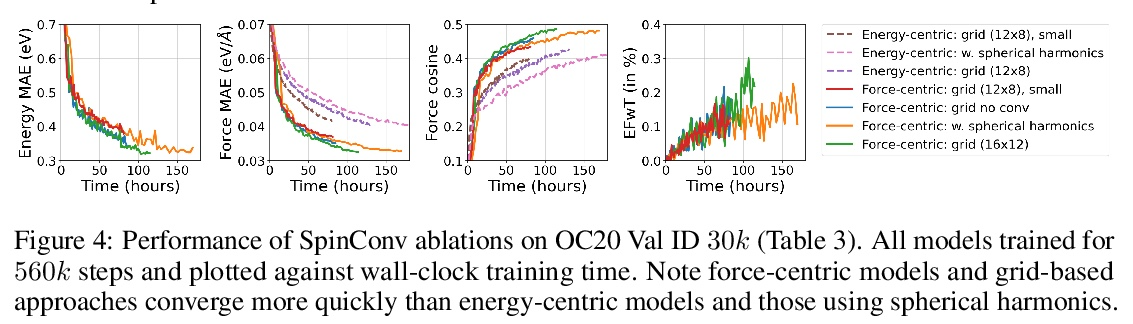
[LG] Rotation Invariant Graph Neural Networks using Spin Convolutions
基于自旋卷积的旋转不变图神经网络
M Shuaibi, A Kolluru, A Das, A Grover, A Sriram, Z Ulissi, C. L Zitnick
[CMU & Facebook AI Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Krxqq6iUB