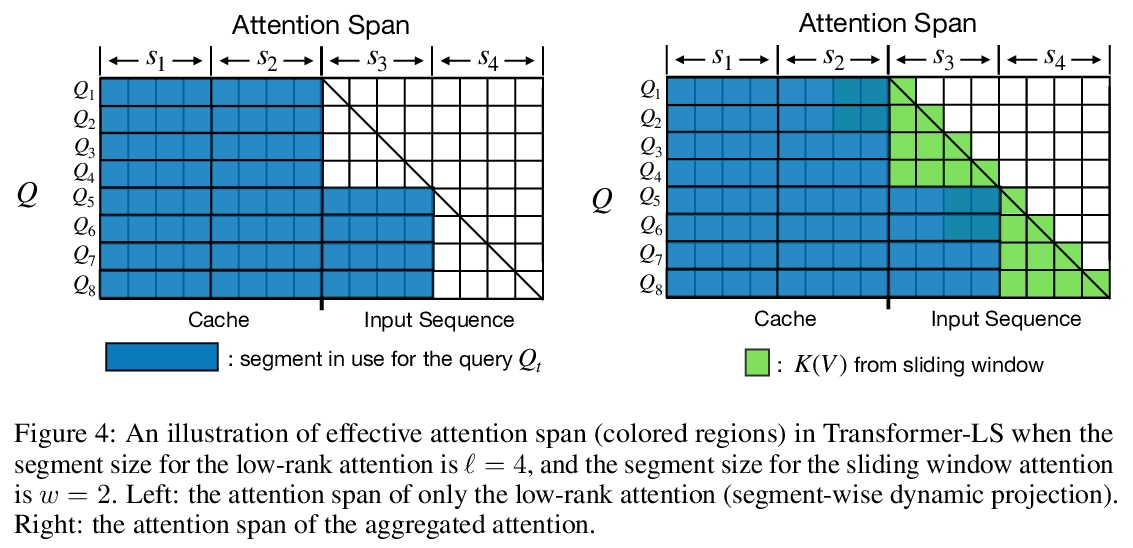
- 1、[CV] Long-Short Transformer: Efficient Transformers for Language and Vision
- 2、[LG] Rethinking Positional Encoding
- 3、[CV] Depth-supervised NeRF: Fewer Views and Faster Training for Free
- 4、[LG] Automating Generative Deep Learning for Artistic Purposes: Challenges and Opportunities
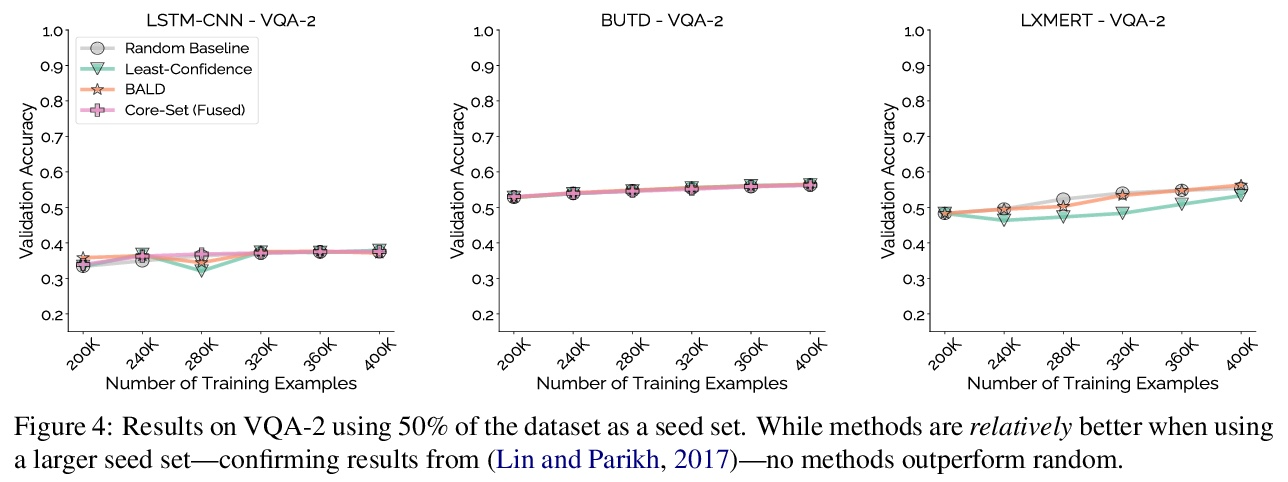
- 5、[CL] Mind Your Outliers! Investigating the Negative Impact of Outliers on Active Learning for Visual Question Answering
- [CV] iPOKE: Poking a Still Image for Controlled Stochastic Video Synthesis
- [LG] Prioritized training on points that are learnable, worth learning, and not yet learned
- [CV] Foreground-Aware Stylization and Consensus Pseudo-Labeling for Domain Adaptation of First-Person Hand Segmentation
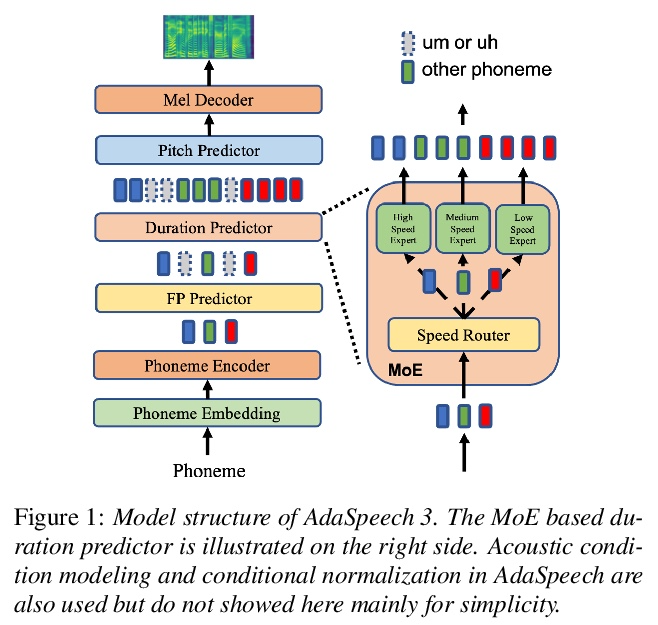
- [AS] AdaSpeech 3: Adaptive Text to Speech for Spontaneous Style
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CV] Long-Short Transformer: Efficient Transformers for Language and Vision
C Zhu, W Ping, C Xiao, M Shoeybi, T Goldstein, A Anandkumar, B Catanzaro
[NVIDIA & University of Maryland]
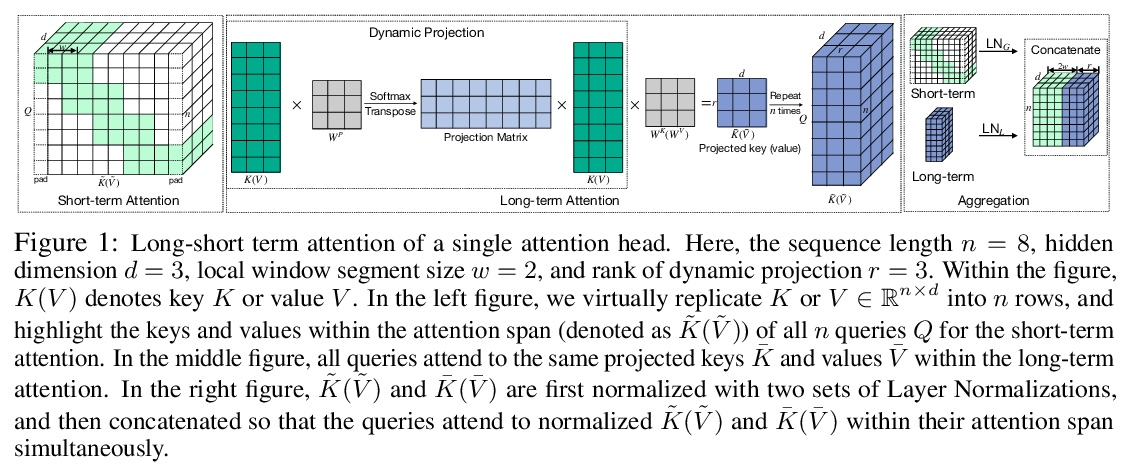
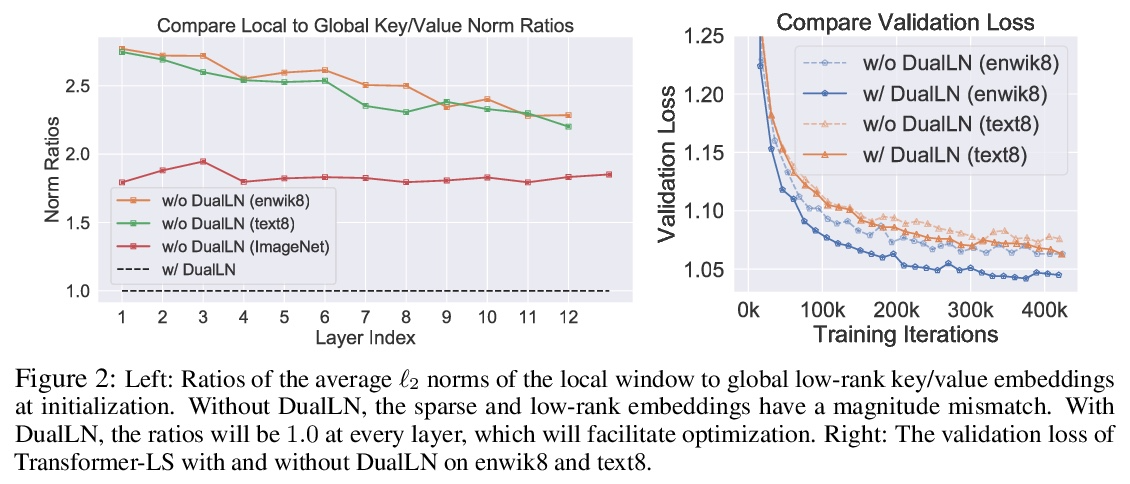
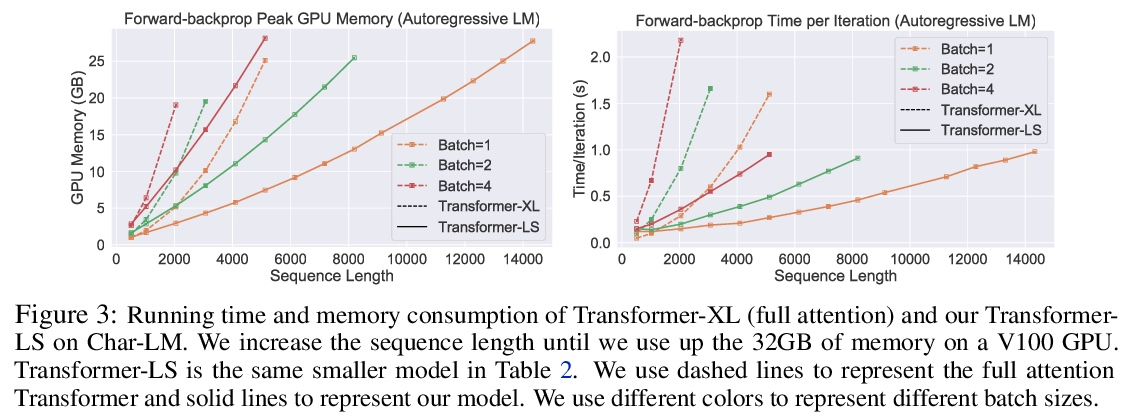
长-短Transformer:面向语言和视觉的高效Transformer。Transformer在语言和视觉领域都取得了成功。然而,将它们扩展到长序列(如长文档或高分辨率图像)是非常昂贵的,因为相对于输入序列的长度,自注意力机制具有二次的时间和记忆复杂度。本文中提出长短Transformer(Transformer-LS),一种高效的自注意力机制,用于语言和视觉任务的长序列建模,具有线性复杂度。该方法聚集了一种新的长程注意力和一种短程注意力,前者用动态投影来模拟远距离相关性,后者用来捕捉细粒度的局部相关性。提出一种双重归一化(DualLN)策略,已解决这两种注意力机制之间规模的不匹配,更有效地聚合局部和全局注意力。Transformer-LS可用于自回归和双向模型,没有额外的复杂性。该方法在语言和视觉领域的多个任务上都优于最先进的模型,包括Long Range Arena benchmark、自回归语言建模和ImageNet分类。例如,Transformer-LS在enwik8上用比以前的方法少一半的参数实现了0.97的测试BPC,同时速度更快,与相同硬件上的全注意力版本相比,能够处理3倍长的序列。在ImageNet上,可以获得最先进的结果(例如,仅在224×224的ImageNet-1K上训练的Top-1准确率为84.1%),同时在高分辨率图像上更具可扩展性。
Transformers have achieved success in both language and vision domains. However, it is prohibitively expensive to scale them to long sequences such as long documents or high-resolution images, because self-attention mechanism has quadratic time and memory complexities with respect to the input sequence length. In this paper, we propose Long-Short Transformer (Transformer-LS), an efficient self-attention mechanism for modeling long sequences with linear complexity for both language and vision tasks. It aggregates a novel long-range attention with dynamic projection to model distant correlations and a short-term attention to capture fine-grained local correlations. We propose a dual normalization strategy to account for the scale mismatch between the two attention mechanisms. Transformer-LS can be applied to both autoregressive and bidirectional models without additional complexity. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art models on multiple tasks in language and vision domains, including the Long Range Arena benchmark, autoregressive language modeling, and ImageNet classification. For instance, Transformer-LS achieves 0.97 test BPC on enwik8 using half the number of parameters than previous method, while being faster and is able to handle 3× as long sequences compared to its full-attention version on the same hardware. On ImageNet, it can obtain the state-of-the-art results (e.g., Top-1 accuracy 84.1% trained on 224× 224 ImageNet-1K only), while being more scalable on high-resolution images.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KnJb2CHrQ 
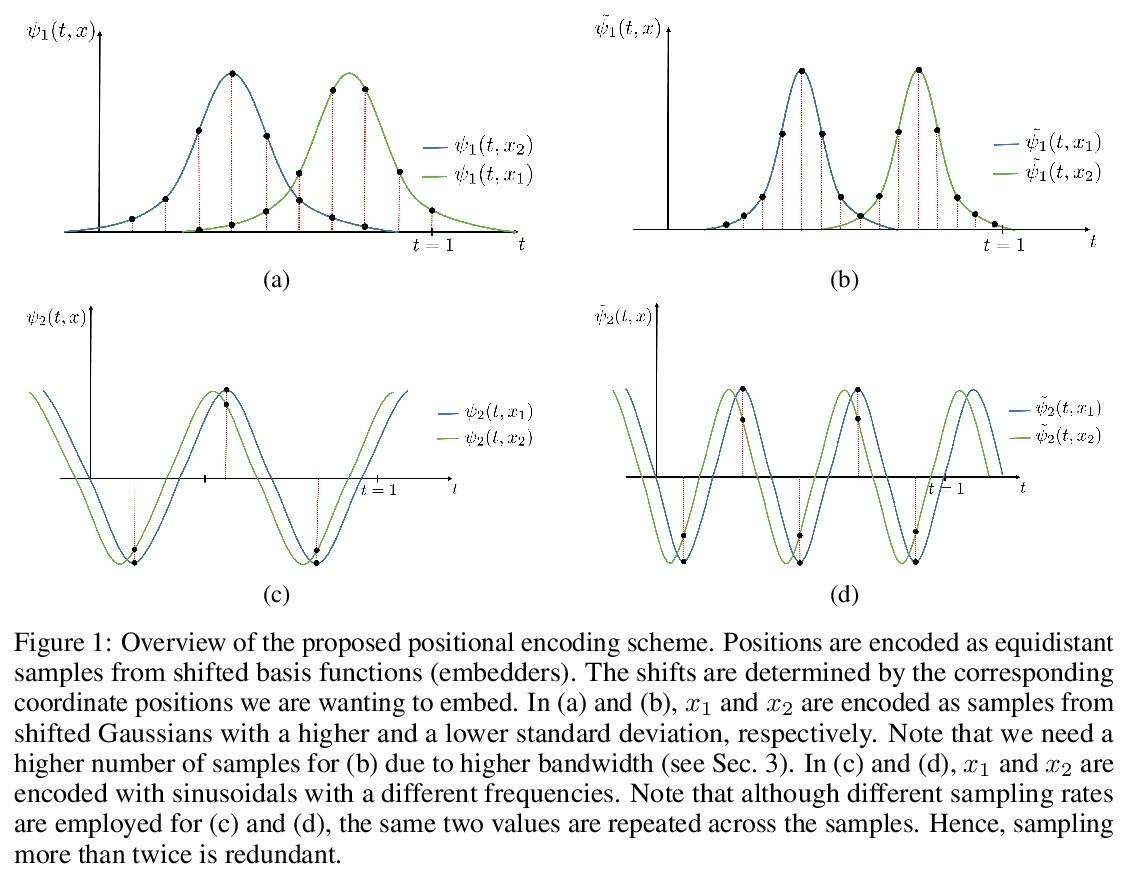
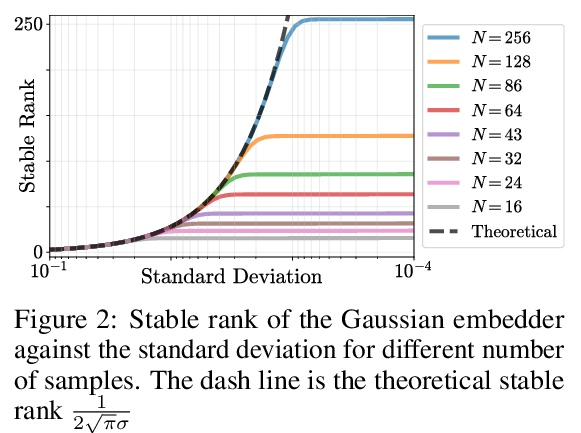
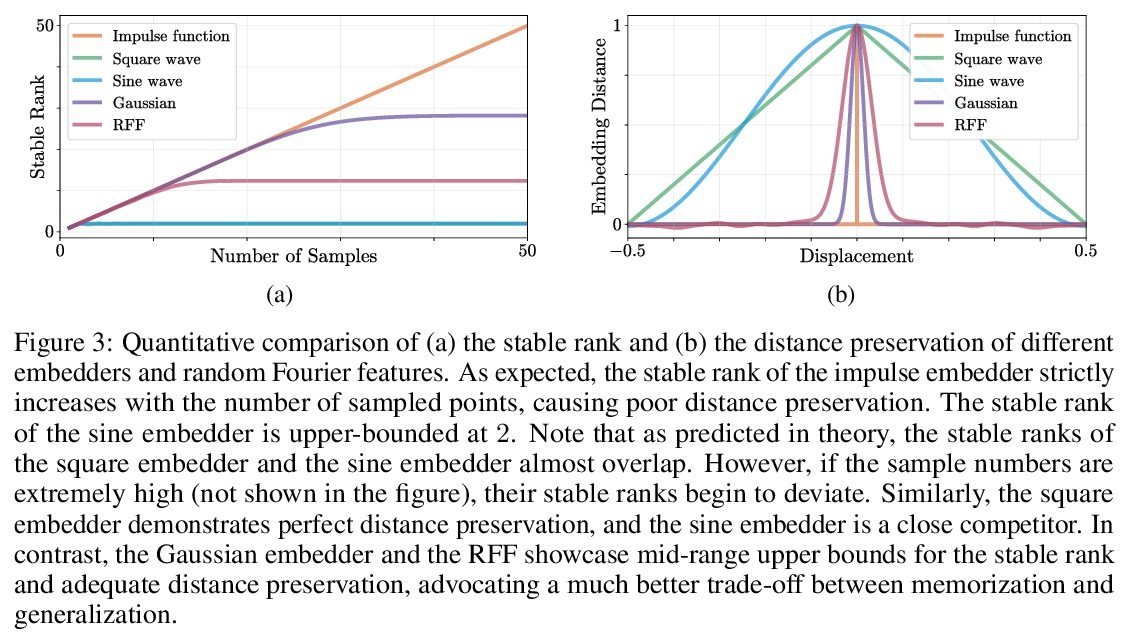
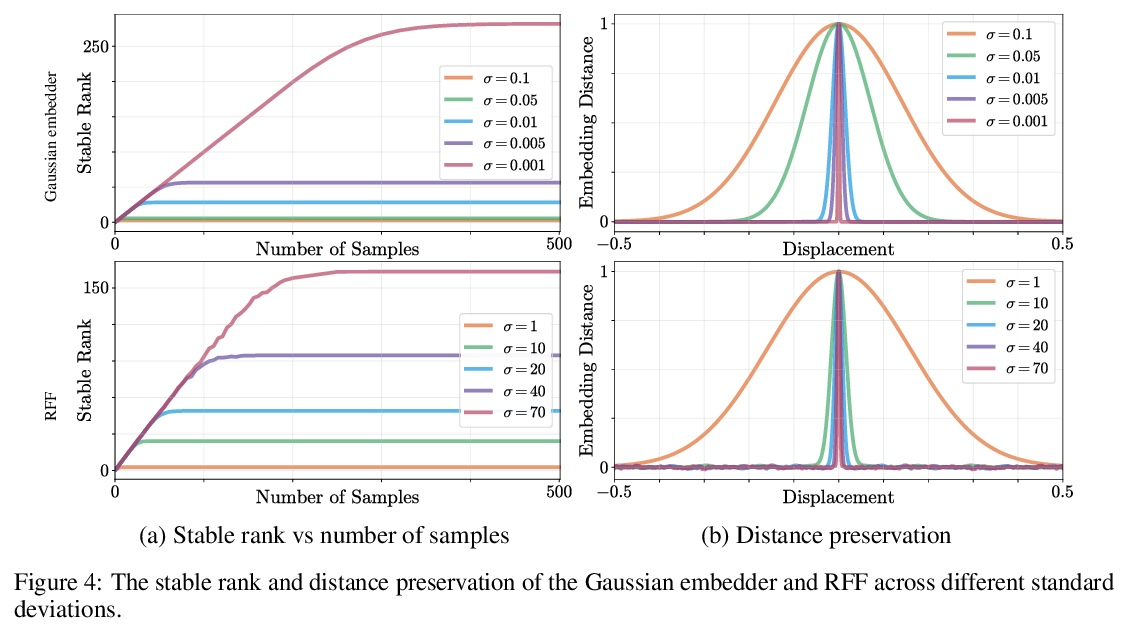
2、[LG] Rethinking Positional Encoding
J Zheng, S Ramasinghe, S Lucey
[University of Adelaide]
位置编码的反思。基于坐标的多层感知器通过将坐标位置编码为一系列的傅里叶特征,在保留高频信息方面受益匪浅。到目前为止,这些位置编码的有效性的理由只通过傅里叶的视角进行研究。本文试图扩大这种理解,表明其他非傅里叶嵌入函数确实可以用于位置编码,其性能完全由嵌入矩阵的稳定秩和嵌入坐标间距离保持两者的权衡决定。现在无处不在的位置傅里叶特征映射是满足这些条件的一个特例。提出了一个更普遍的理论来分析移位基函数方面的位置编码。推导了必要的理论公式,并从经验上验证了该理论主张在实践中是成立的。提出了一种新的位置编码机制,在某些约束条件下,可以将任意的连续信号作为潜嵌入器,使位置编码有更多的可解释性和更少的限制性,可用于各种计算机视觉任务。
It is well noted that coordinate based MLPs benefit greatly – in terms of preserving high-frequency information – through the encoding of coordinate positions as an array of Fourier features. Hitherto, the rationale for the effectiveness of these positional encodings has been solely studied through a Fourier lens. In this paper, we strive to broaden this understanding by showing that alternative non-Fourier embedding functions can indeed be used for positional encoding. Moreover, we show that their performance is entirely determined by a trade-off between the stable rank of the embedded matrix and the distance preservation between embedded coordinates. We further establish that the now ubiquitous Fourier feature mapping of position is a special case that fulfills these conditions. Consequently, we present a more general theory to analyze positional encoding in terms of shifted basis functions. To this end, we develop the necessary theoretical formulae and empirically verify that our theoretical claims hold in practice.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KnJfPh5jS 
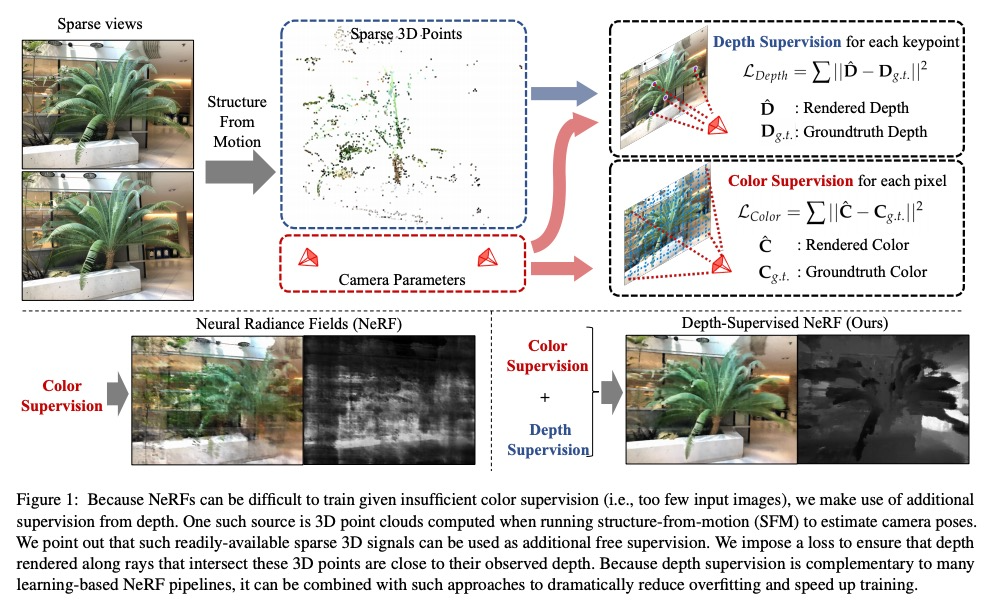
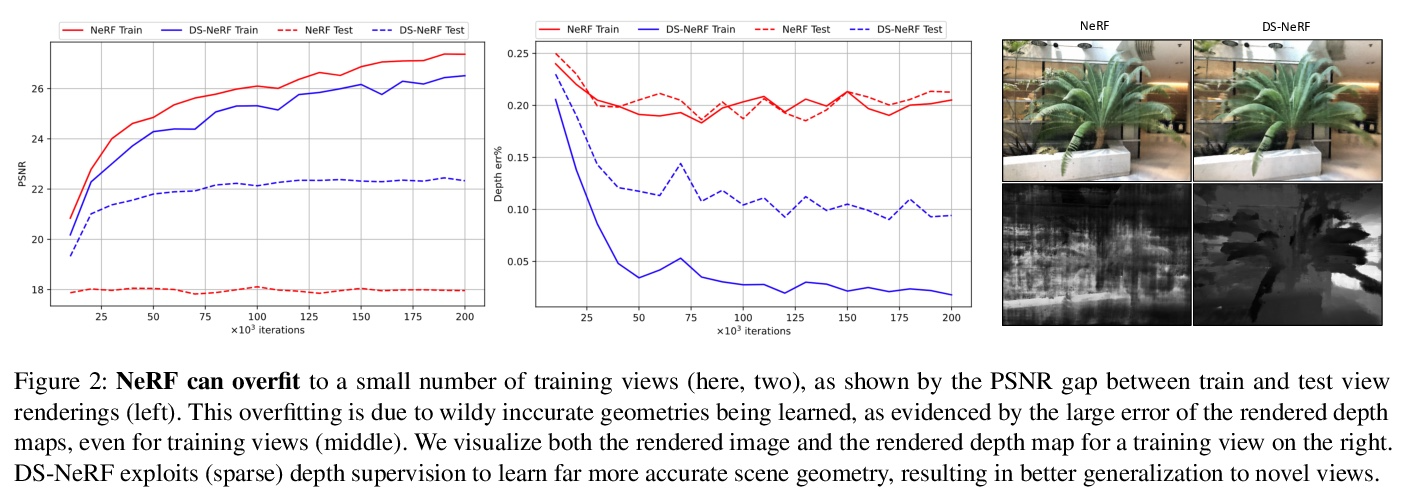
3、[CV] Depth-supervised NeRF: Fewer Views and Faster Training for Free
K Deng, A Liu, J Zhu, D Ramanan
[CMU & Google]
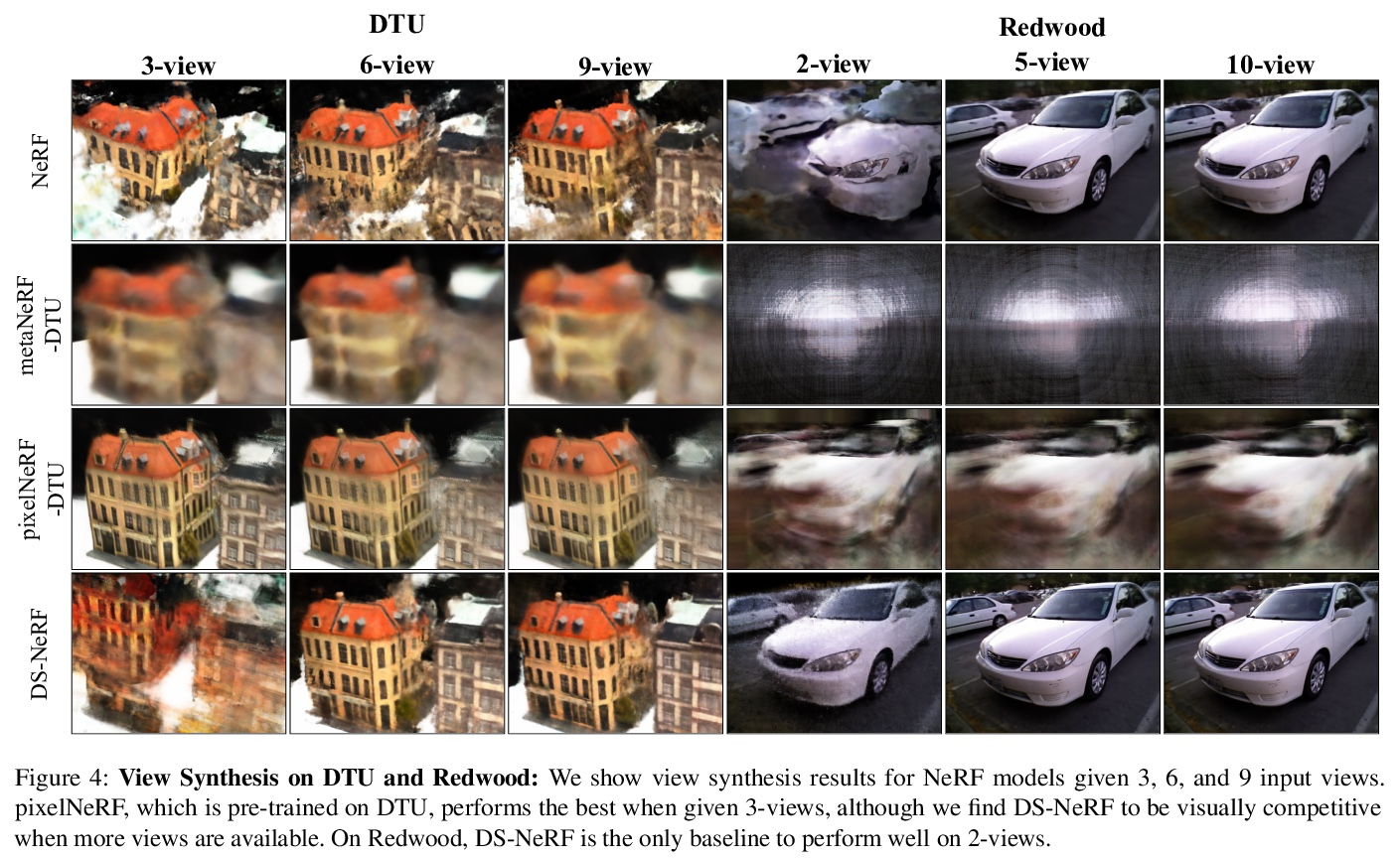
深度监督NeRF:更少的视图、更快的训练。神经辐射场(NeRF)模型的一个常见失败模式是,当给定的输入视图数量不足时,拟合出不正确的几何。本文提出深度监督神经辐射场(DS-NeRF),一种用来学习神经辐射场的损失,利用了现成的深度监督。其关键是,稀疏的深度监督可以用来正则化学到的几何,这是用NeRF有效渲染新视图的一个关键组成部分。利用了这样一个事实,即目前的NeRF管道需要具有已知摄像机位置的图像,这些位置通常是通过运行从运动中获得的结构(SFM)来估计的。最重要的是,SFM还能产生稀疏的三维点,在训练过程中可作为”免费”的深度监督:只需添加一个损失,以确保沿与这些三维点相交的射线渲染的深度接近观察到的深度。在较少的训练视图下,DS-NeRF可以渲染出更准确的图像,同时训练速度也提高了2-6倍。在真实世界的图像上只有两个训练视图的情况下,DS-NeRF明显优于NeRF以及其他稀疏视图的变体。所提出损失与这些NeRF模型兼容,证明深度是一个廉价且易用的监督信号。DS-NeRF支持其他类型的深度监督,如扫描的深度传感器和RGBD重建输出。
One common failure mode of Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) models is fitting incorrect geometries when given an insufficient number of input views. We propose DS-NeRF (Depth-supervised Neural Radiance Fields), a loss for learning neural radiance fields that takes advantage of readilyavailable depth supervision. Our key insight is that sparse depth supervision can be used to regularize the learned geometry, a crucial component for effectively rendering novel views using NeRF. We exploit the fact that current NeRF pipelines require images with known camera poses that are typically estimated by running structure-from-motion (SFM). Crucially, SFM also produces sparse 3D points that can be used as “free” depth supervision during training: we simply add a loss to ensure that depth rendered along rays that intersect these 3D points is close to the observed depth. We find that DS-NeRF can render more accurate images given fewer training views while training 2-6x faster. With only two training views on real-world images, DS-NeRF significantly outperforms NeRF as well as other sparse-view variants. We show that our loss is compatible with these NeRF models, demonstrating that depth is a cheap and easily digestible supervisory signal. Finally, we show that DS-NeRF supports other types of depth supervision such as scanned depth sensors and RGBD reconstruction outputs.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KnJmt9SzG 


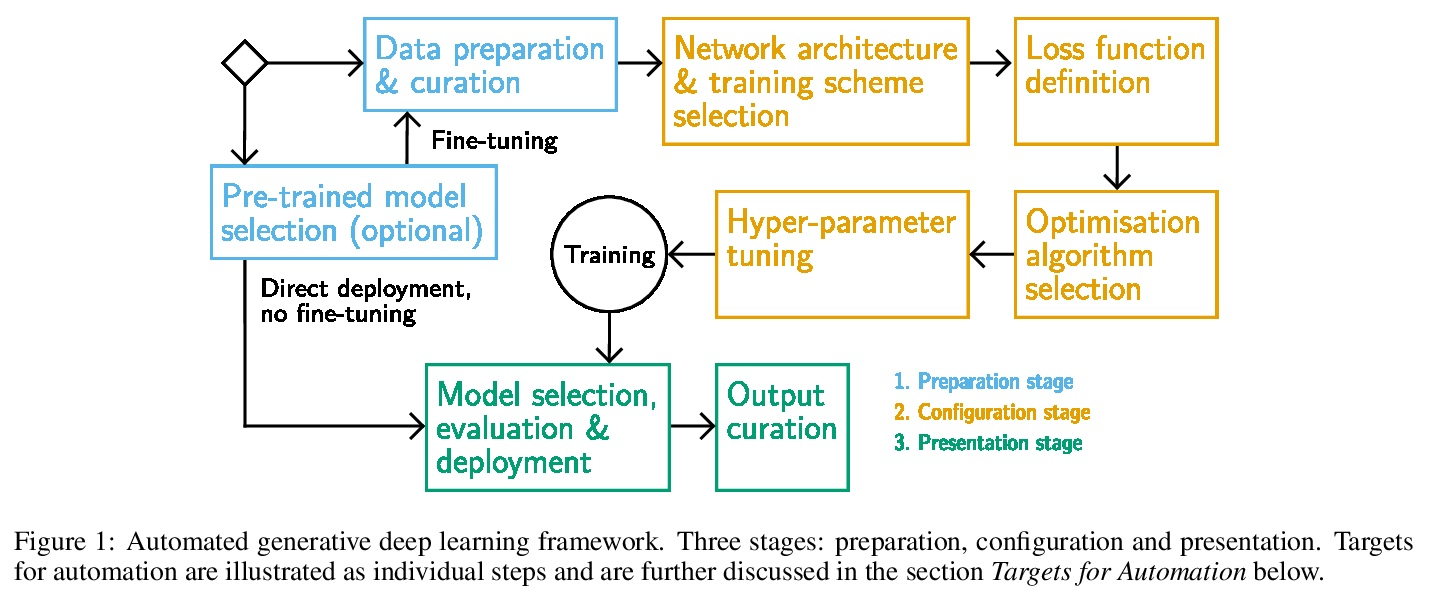
4、[LG] Automating Generative Deep Learning for Artistic Purposes: Challenges and Opportunities
S Berns, T Broad, C Guckelsberger, S Colton
[Queen Mary University of London & University of London & Aalto University]
面向艺术的自动化生成式深度学习:挑战与机遇。本文提出一种自动化生成式深度学习框架,特别关注艺术应用。该框架提供了将创造性的责任移交给生成系统的机会,作为自动化的目标。对于目标的定义,采用了自动化机器学习(AutoML)的核心概念和对生成式深度学习管道的分析,包括标准和艺术设置。为了激励该框架,本文认为自动化与增加生成系统的创造性责任的目标很一致,这是计算创造力研究的一个核心主题。将自动化理解为赋予生成式系统更多的创造性自主权的挑战,将用户与系统之间的互动框定为一个共同创造的过程。对自动化和创造性自主性之间关系的分析为该框架的发展提供了参考。一个说明性的例子显示了该框架如何在交出创造性责任的过程中给予启发和指导。
We present a framework for automating generative deep learning with a specific focus on artistic applications. The framework provides opportunities to hand over creative responsibilities to a generative system as targets for automation. For the definition of targets, we adopt core concepts from automated machine learning and an analysis of generative deep learning pipelines, both in standard and artistic settings. To motivate the framework, we argue that automation aligns well with the goal of increasing the creative responsibility of a generative system, a central theme in computational creativity research. We understand automation as the challenge of granting a generative system more creative autonomy, by framing the interaction between the user and the system as a co-creative process. The development of the framework is informed by our analysis of the relationship between automation and creative autonomy. An illustrative example shows how the framework can give inspiration and guidance in the process of handing over creative responsibility.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KnJq58RAM 
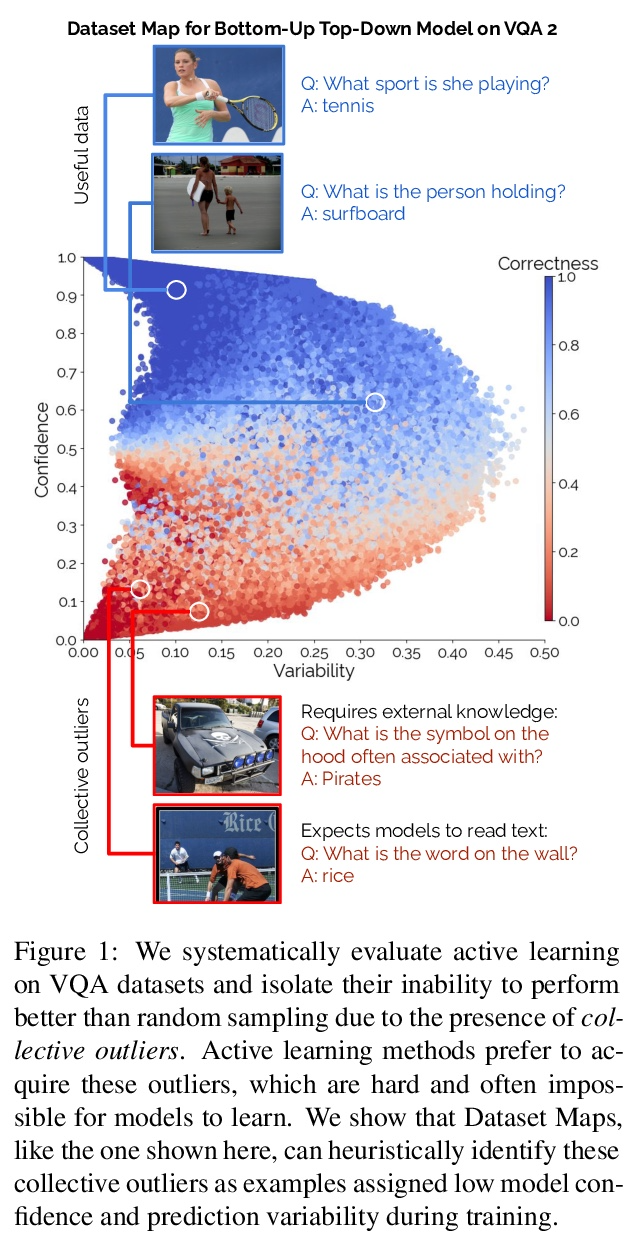
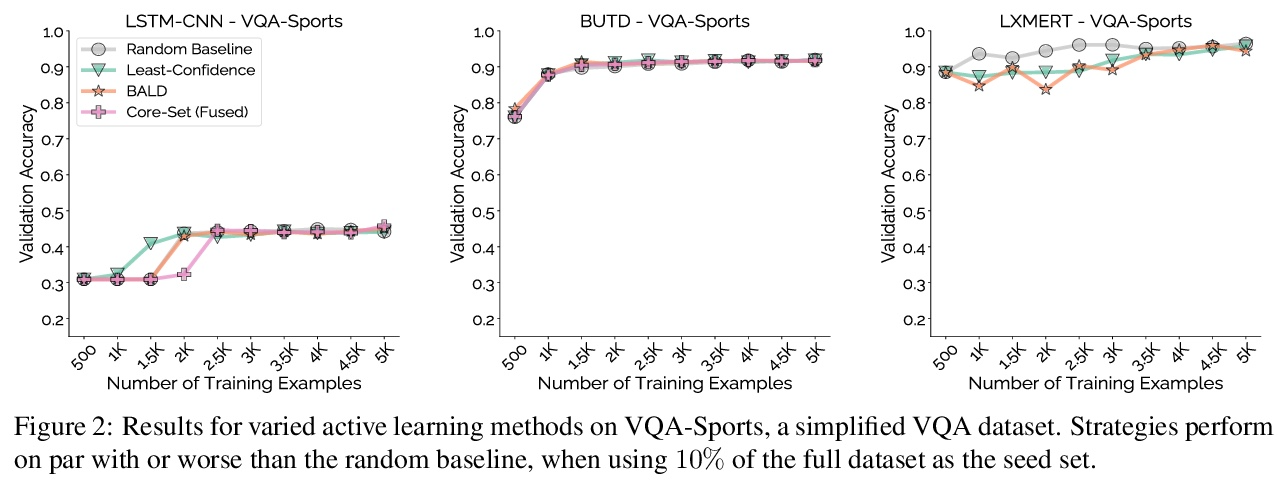
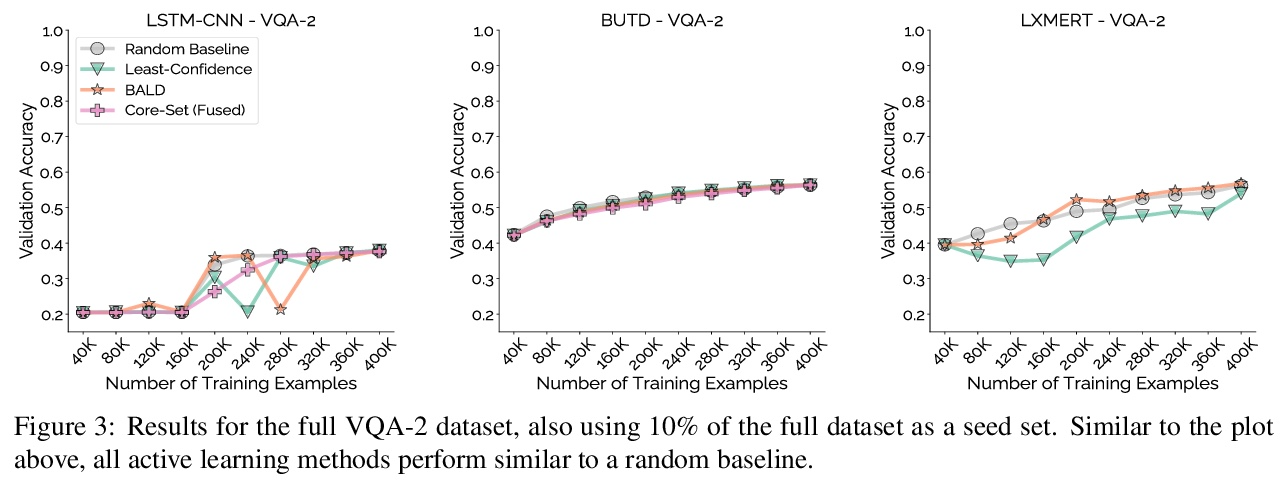
5、[CL] Mind Your Outliers! Investigating the Negative Impact of Outliers on Active Learning for Visual Question Answering
S Karamcheti, R Krishna, L Fei-Fei, C D. Manning
[Stanford University]
注意离群值!离群值对视觉问答主动学习的消极影响。主动学习有望缓解监督式机器学习的大量数据需求:它已经成功地将主题分类和物体识别等传统任务的样本效率提高了一个数量级。然而,与这一承诺形成鲜明对比的是:在视觉问答任务的5个模型和4个数据集中,各种主动学习方法都没有超过随机选择的效果。为了理解这种差异,本文在每样本基础上对8种主动学习方法进行了剖析,并将问题确定为协同离群值——主动学习方法喜欢获取但模型无法学习的样本群(例如,询问图像中的文本或需要外部知识的问题)。通过系统的消融实验和定性的可视化,验证了协同离群值是一个普遍现象,其造成了基于池的主动学习的退化。主动学习的样本效率随着主动学习池中协同离群值的减少而显著增加。最后讨论了在未来的工作中减轻这些离群值的影响,并提出了规范性建议。
Active learning promises to alleviate the massive data needs of supervised machine learning: it has successfully improved sample efficiency by an order of magnitude on traditional tasks like topic classification and object recognition. However, we uncover a striking contrast to this promise: across 5 models and 4 datasets on the task of visual question answering, a wide variety of active learning approaches fail to outperform random selection. To understand this discrepancy, we profile 8 active learning methods on a per-example basis, and identify the problem as collective outliers – groups of examples that active learning methods prefer to acquire but models fail to learn (e.g., questions that ask about text in images or require external knowledge). Through systematic ablation experiments and qualitative visualizations, we verify that collective outliers are a general phenomenon responsible for degrading pool-based active learning. Notably, we show that active learning sample efficiency increases significantly as the number of collective outliers in the active learning pool decreases. We conclude with a discussion and prescriptive recommendations for mitigating the effects of these outliers in future work.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KnJsxoZmD 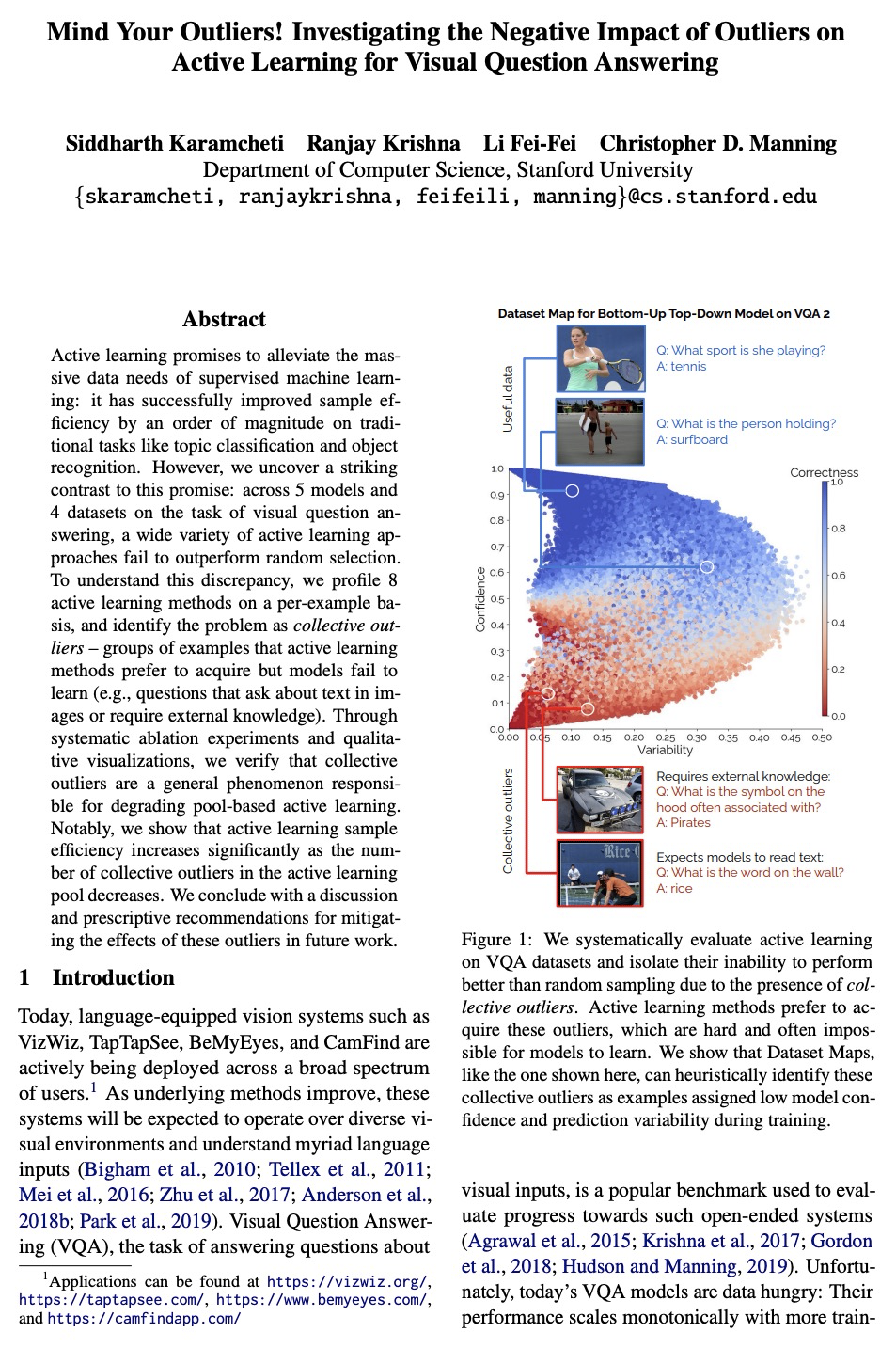
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
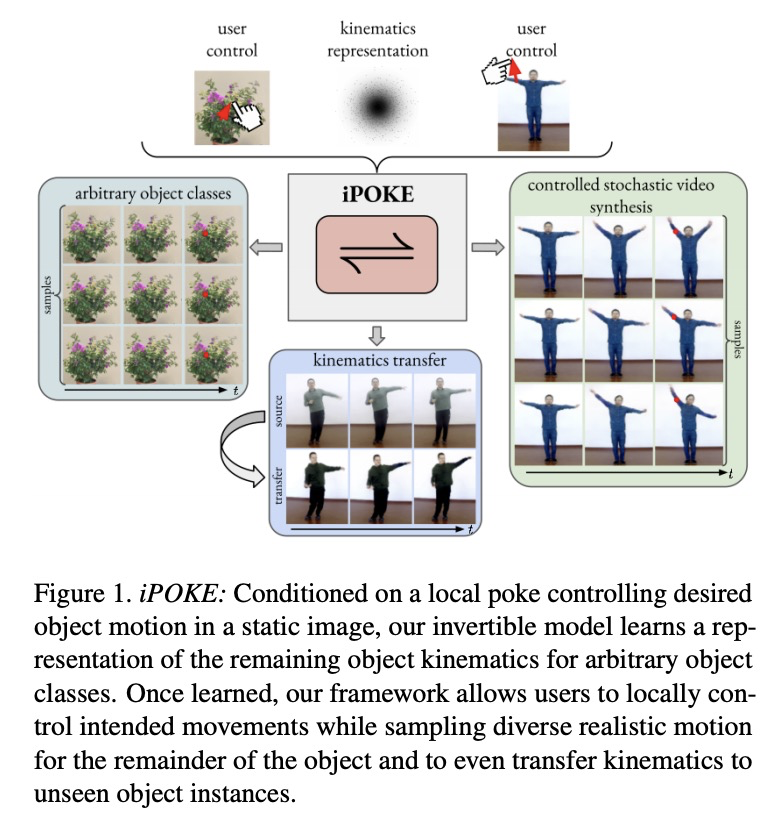
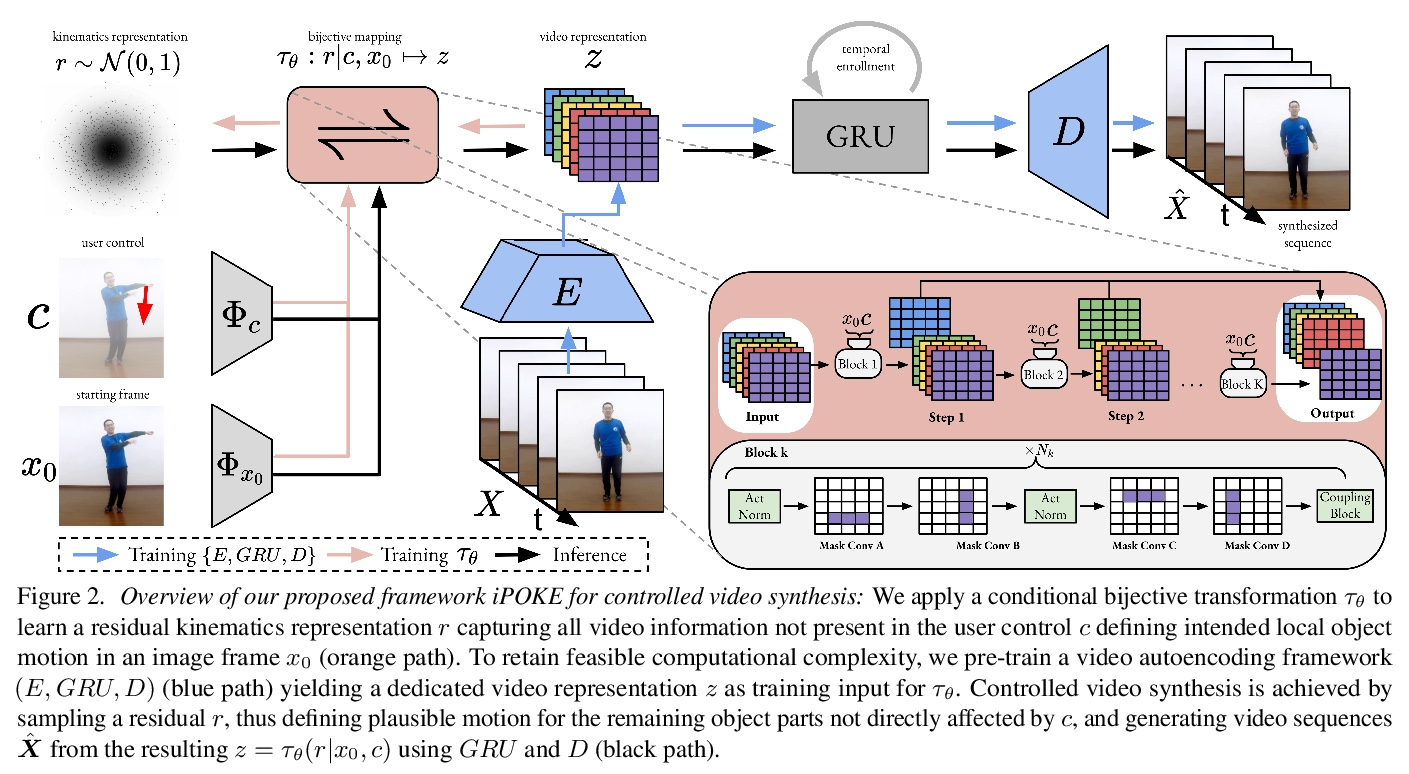
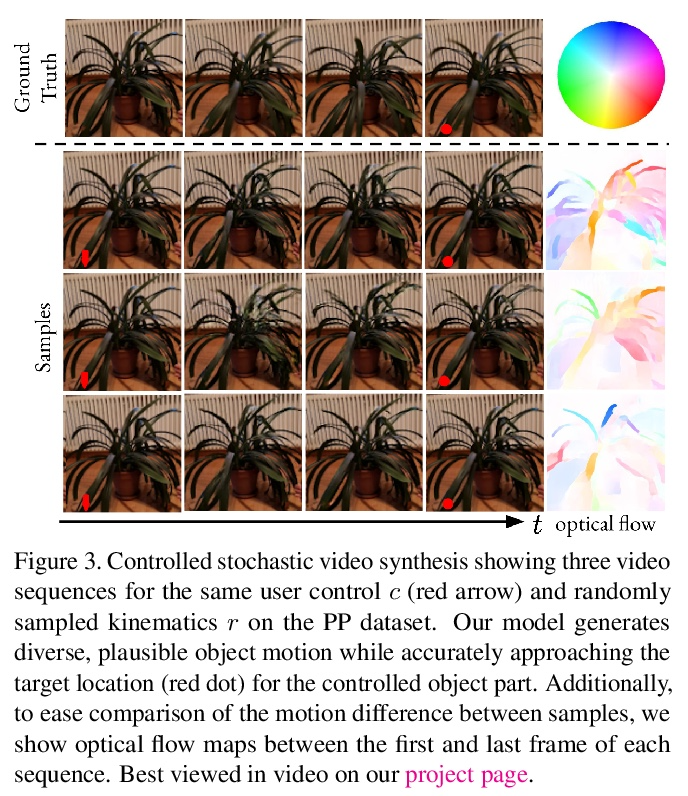
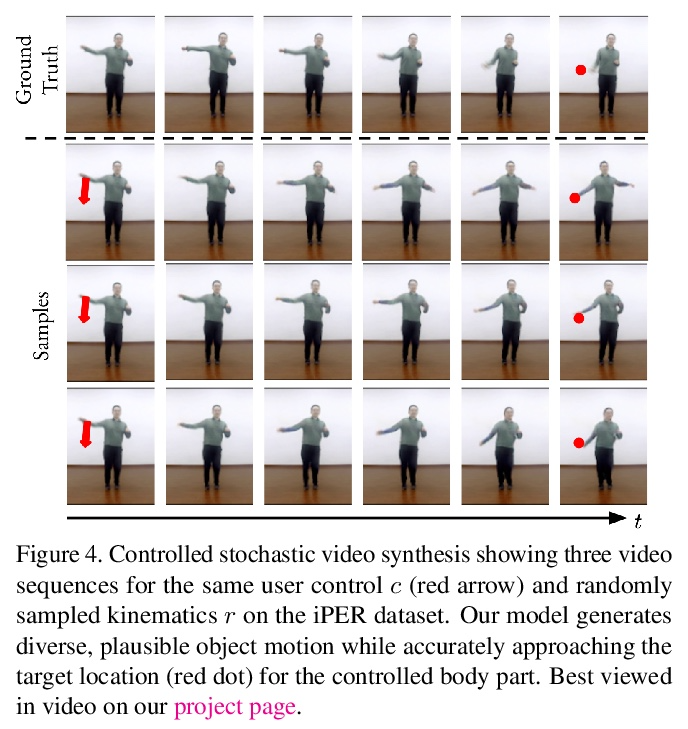
[CV] iPOKE: Poking a Still Image for Controlled Stochastic Video Synthesis
iPOKE(物体运动学的可逆预测):为受控随机视频合成戳动静止图像
A Blattmann, T Milbich, M Dorkenwald, B Ommer
[Heidelberg University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KnJwd91S2 
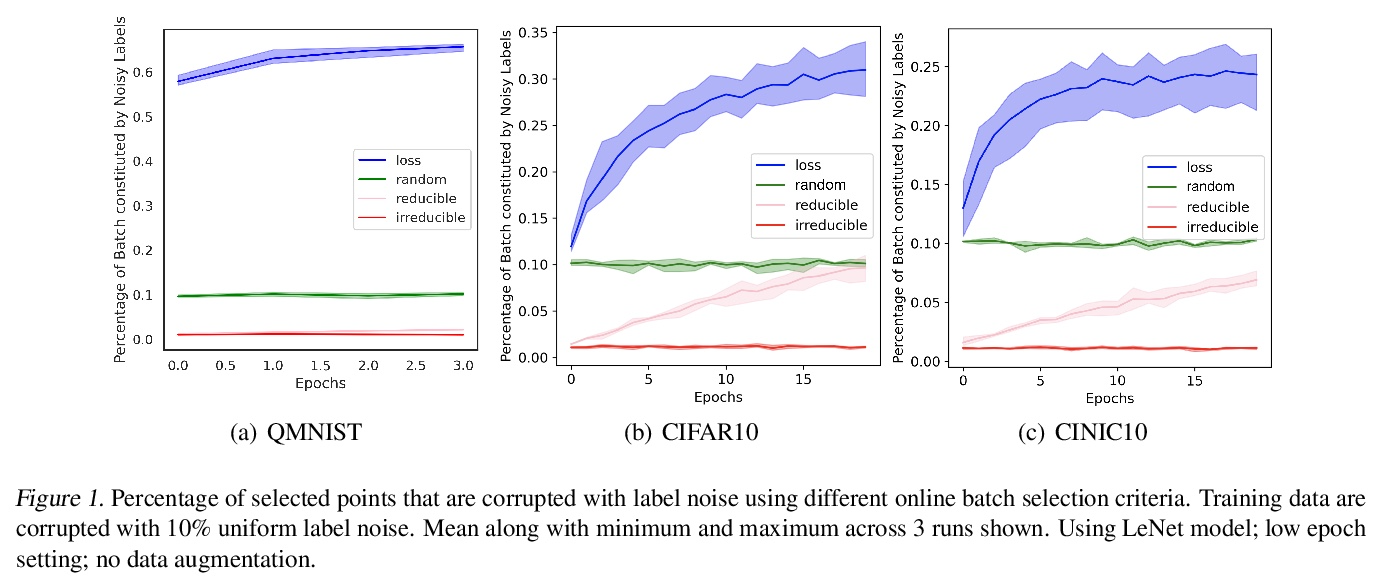
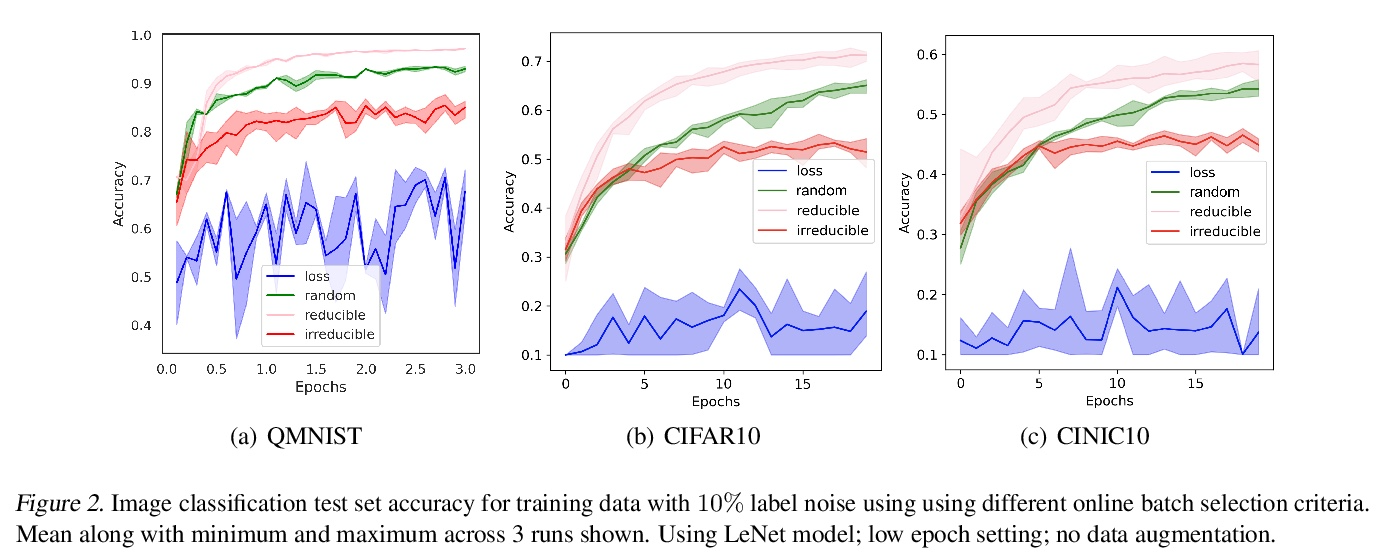
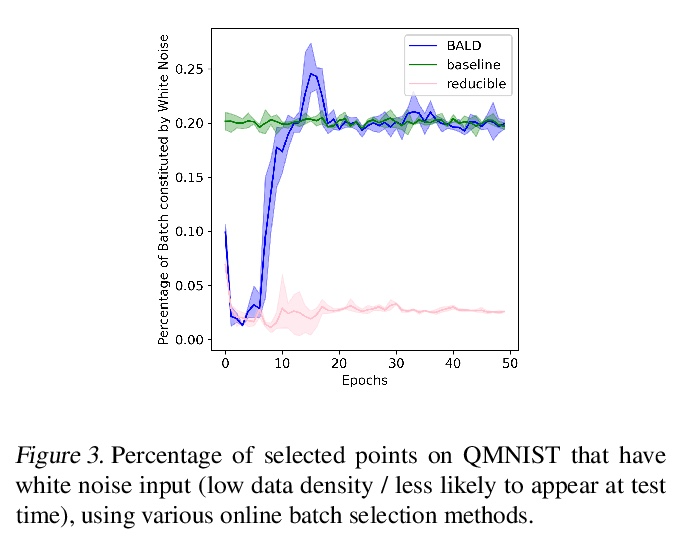
[LG] Prioritized training on points that are learnable, worth learning, and not yet learned
对可学、值得学和尚未学的点的优先训练
S Mindermann, M Razzak, W Xu, A Kirsch, M Sharma, A Morisot, A N. Gomez, S Farquhar, J Brauner, Y Gal
[University of Oxford & University of Toronto & Cohere]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KnJzef68q 
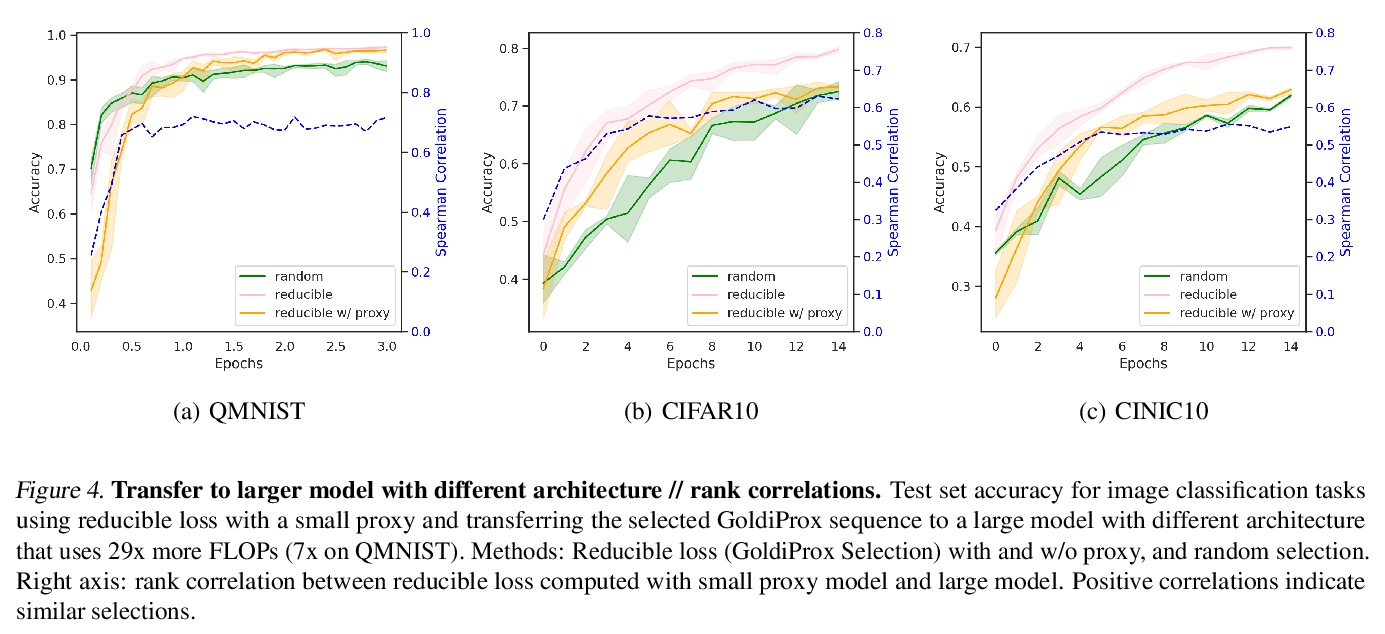
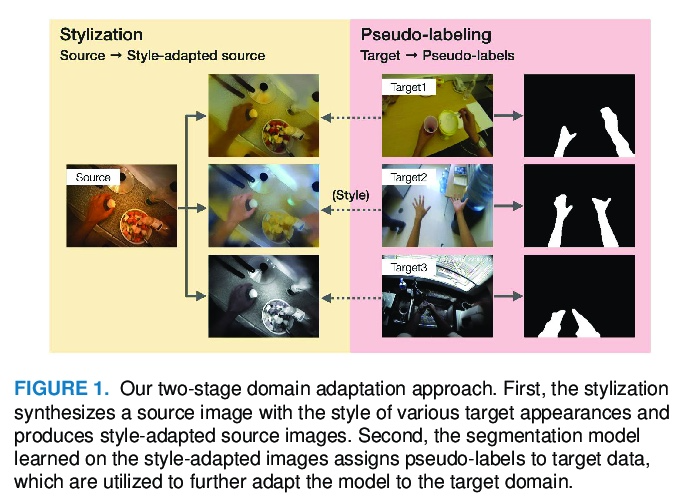
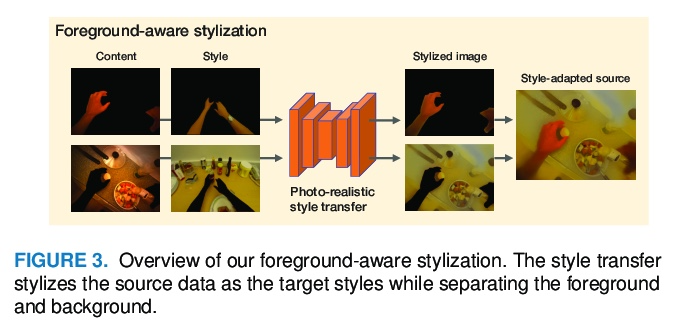
[CV] Foreground-Aware Stylization and Consensus Pseudo-Labeling for Domain Adaptation of First-Person Hand Segmentation
面向第一人称手分割域自适应的前景感知风格化和一致性伪标记
T Ohkawa, T Yagi, A Hashimoto, Y Ushiku, Y Sato
[The University of Tokyo & OMRON SINIC X Corporation]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KnJB1E3dO 


[AS] AdaSpeech 3: Adaptive Text to Speech for Spontaneous Style
AdaSpeech 3:文本到语音的自然风格自适应
Y Yan, X Tan, B Li, G Zhang, T Qin, S Zhao, Y Shen, W Zhang, T Liu
[Microsoft Research Asia & Microsoft Azure Speech & The Chinese University of Hong Kong]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KnJCJ6pHc