- 1、[AI] Counter-Strike Deathmatch with Large-Scale Behavioural Cloning
- 2、[CL] QA-GNN: Reasoning with Language Models and Knowledge Graphs for Question Answering
- 3、[LG] Meta-Learning Bidirectional Update Rules
- 4、[CL] Sparse Attention with Linear Units
- 5、[CL] Hierarchical Learning for Generation with Long Source Sequences
- [CL] From partners to populations: A hierarchical Bayesian account of coordination and convention
- [LG] mlf-core: a framework for deterministic machine learning
- [CV] CodedStereo: Learned Phase Masks for Large Depth-of-field Stereo
- [CV] Adversarial Open Domain Adaption for Sketch-to-Photo Synthesis
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[AI] Counter-Strike Deathmatch with Large-Scale Behavioural Cloning
T Pearce, J Zhu
[Tsinghua University]
“反恐精英”死亡竞赛的大规模行为克隆。提出一种仅利用像素输入玩第一人称射击游戏CS GO的AI智能体,一个深度神经网络,在死亡竞赛游戏模式中等难度设置下,采用类似人类的游戏风格,表现优于游戏中基于规则的机器人。与之前许多游戏不同,CS GO没有API,算法必须实时训练和运行。这就限制了可生成的on-policy数据的数量,使许多强化学习算法无法使用。通过使用行为克隆——从在线服务器上爬取人类游戏记录,主要是以旁观者身份加入游戏得到的游戏画面,在这些大规模含噪数据上进行训练(规模达到400万帧,70小时,与ImageNet相当),在较小的高质量专家演示数据集上进行微调,其规模比之前在FPS游戏中的模仿学习工作大一个数量级。得到的智能体可在瞄准训练模式达到略逊于最强玩家(CSGO前10%玩家)的水平,在死亡竞赛游戏模式中等难度下达到内置AI(CSGO内置的基于规则的机器人)水平。这是到目前为止游戏行为克隆领域规模最大的作品之一,也是最早解决没有API支持的现代视频游戏的工作之一。
This paper describes an AI agent that plays the popular first-person-shooter (FPS) video game `Counter-Strike; Global Offensive’ (CSGO) from pixel input. The agent, a deep neural network, matches the performance of the medium difficulty built-in AI on the deathmatch game mode, whilst adopting a humanlike play style. Unlike much prior work in games, no API is available for CSGO, so algorithms must train and run in real-time. This limits the quantity of on-policy data that can be generated, precluding many reinforcement learning algorithms. Our solution uses behavioural cloning - training on a large noisy dataset scraped from human play on online servers (4 million frames, comparable in size to ImageNet), and a smaller dataset of high-quality expert demonstrations. This scale is an order of magnitude larger than prior work on imitation learning in FPS games.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbpHEC7jw




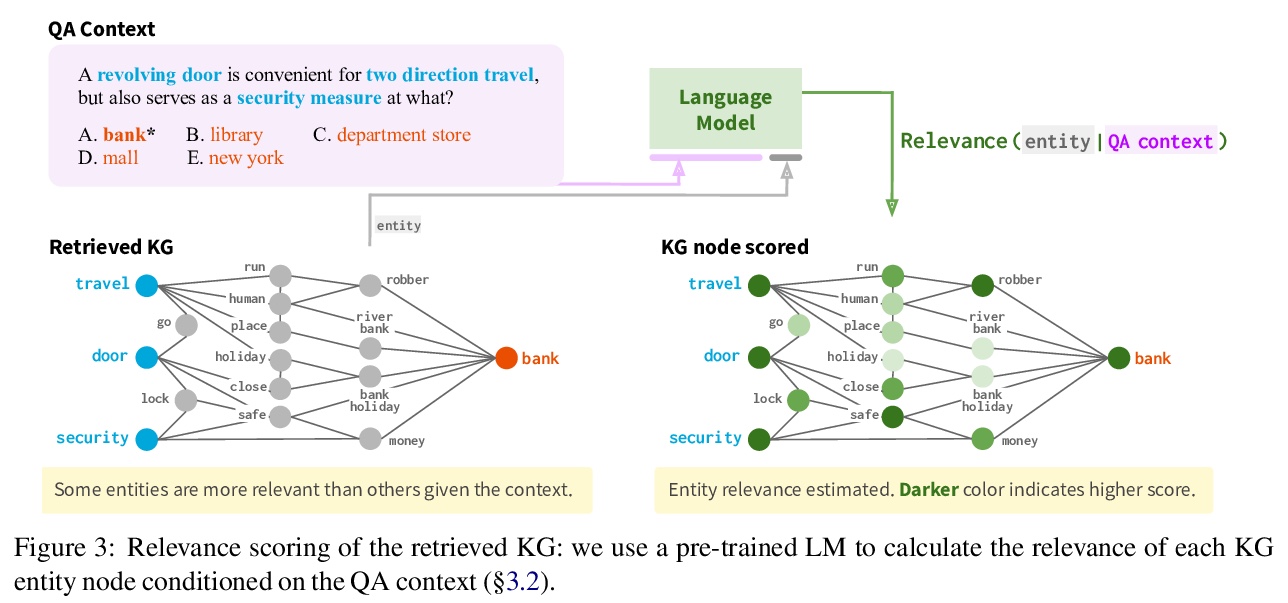
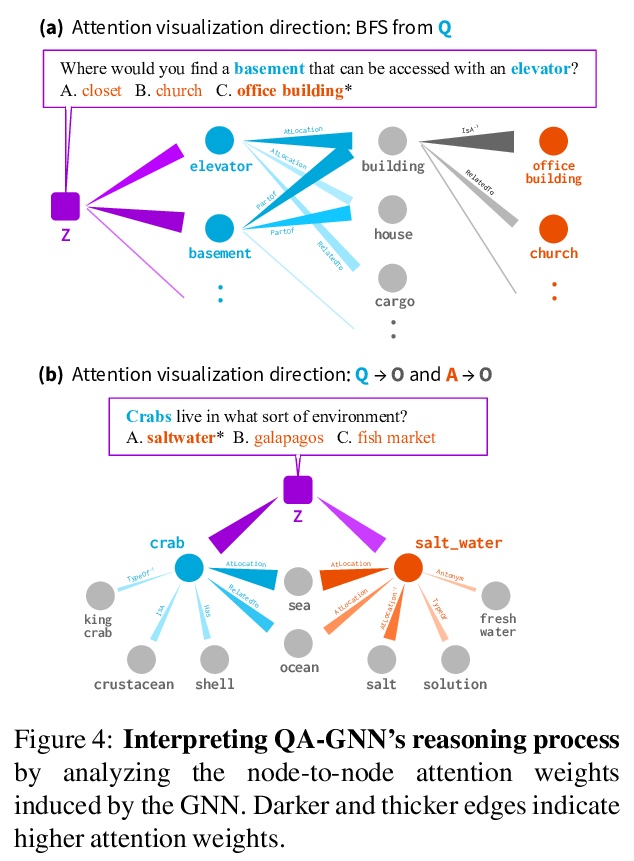
2、[CL] QA-GNN: Reasoning with Language Models and Knowledge Graphs for Question Answering
M Yasunaga, H Ren, A Bosselut, P Liang, J Leskovec
[Stanford University]
QA-GNN:面向问答的基于语言模型和知识图谱推理。用来自预训练语言模型(LM)和知识图谱(KG)的知识回答问题,存在两个主要挑战:给定一个QA的上下文(问题和答案选择),需要从大型知识图谱中识别相关知识,并对QA上下文和知识图谱进行联合推理。本文提出一种新的端到端问答LM+KG模型QA-GNN,通过两个关键创新来解决以上挑战:相关性评分,用语言模型估计知识图谱节点相对于给定QA上下文的重要性,提出了对知识图谱上信息进行加权的通用框架;联合推理,将QA上下文和知识图谱连接起来形成一个联合图,成为工作图,将两个模态统一为一个图,用基于注意力的GNN模块进行推理,通过基于图的消息传递交互更新它们的表示。在CommonsenseQA和OpenBookQA数据集上对QA-GNN进行了评价,展示了它比现有语言模型和语言模型+知识图谱模型的改进,QA-GNN在某些形式的结构化推理上表现出了更高的性能(例如,正确处理问题中的否定和实体替换)。
The problem of answering questions using knowledge from pre-trained language models (LMs) and knowledge graphs (KGs) presents two challenges: given a QA context (question and answer choice), methods need to (i) identify relevant knowledge from large KGs, and (ii) perform joint reasoning over the QA context and KG. Here we propose a new model, QA-GNN, which addresses the above challenges through two key innovations: (i) relevance scoring, where we use LMs to estimate the importance of KG nodes relative to the given QA context, and (ii) joint reasoning, where we connect the QA context and KG to form a joint graph, and mutually update their representations through graph-based message passing. We evaluate QA-GNN on the CommonsenseQA and OpenBookQA datasets, and show its improvement over existing LM and LM+KG models, as well as its capability to perform interpretable and structured reasoning, e.g., correctly handling negation in questions.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbpSaxUi8

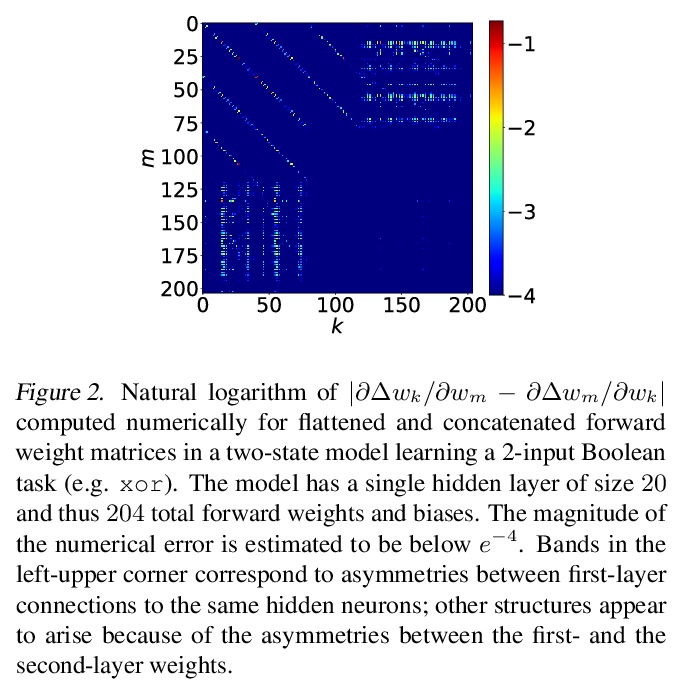
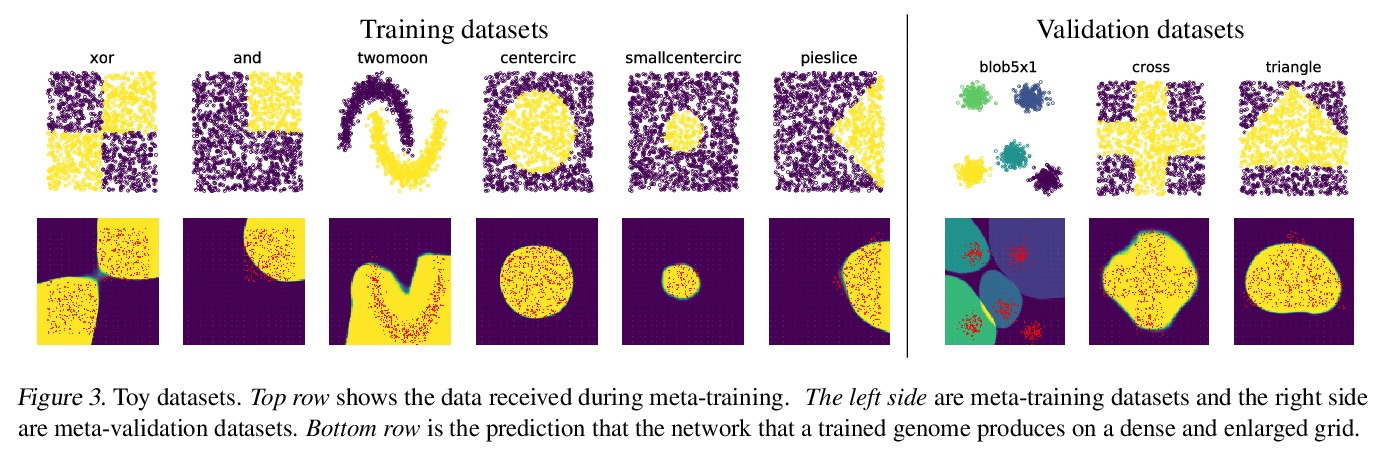
3、[LG] Meta-Learning Bidirectional Update Rules
M Sandler, M Vladymyrov, A Zhmoginov, N Miller, A Jackson, T Madams, B A y Arcas
[Google Research]
元学习双向更新法则。提出了一种新的广义神经网络,其中神经元和突触保持多种状态。神经网络中经典的基于梯度的反向传播,可看作是双状态网络的一个特例,其中一个状态用于激活,另一个状态用于梯度,更新规则来自链式法则。在广义框架中,网络既没有梯度的显式概念,甚至不接受梯度。突触和神经元用双向Hebb式的更新法则进行更新,该规则由一个共享的低维”基因组”进行参数化。这种基因组可以从头开始学习,用传统的优化技术,或进化策略,如CMA-ES。结果的更新法则可泛化到未见任务中,对一些标准的计算机视觉和合成任务,其训练速度比基于梯度下降的优化器更快。
In this paper, we introduce a new type of generalized neural network where neurons and synapses maintain multiple states. We show that classical gradient-based backpropagation in neural networks can be seen as a special case of a two-state network where one state is used for activations and another for gradients, with update rules derived from the chain rule. In our generalized framework, networks have neither explicit notion of nor ever receive gradients. The synapses and neurons are updated using a bidirectional Hebb-style update rule parameterized by a shared low-dimensional “genome”. We show that such genomes can be meta-learned from scratch, using either conventional optimization techniques, or evolutionary strategies, such as CMA-ES. Resulting update rules generalize to unseen tasks and train faster than gradient descent based optimizers for several standard computer vision and synthetic tasks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kbq4LtKjA

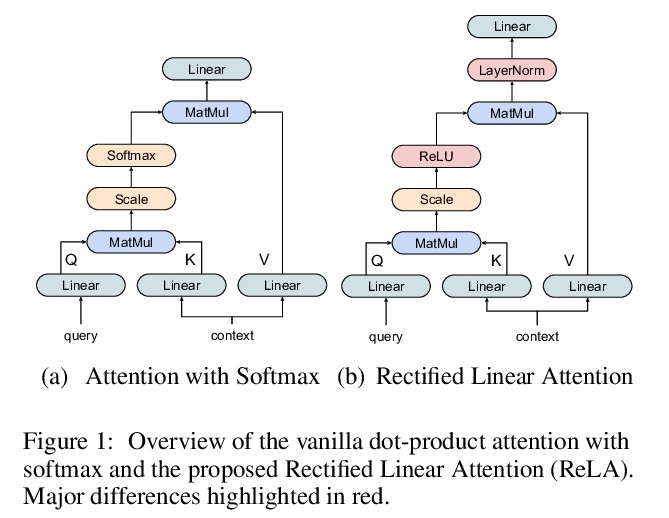
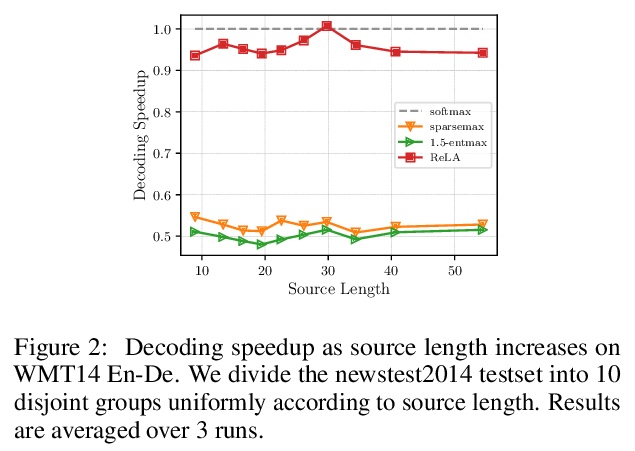
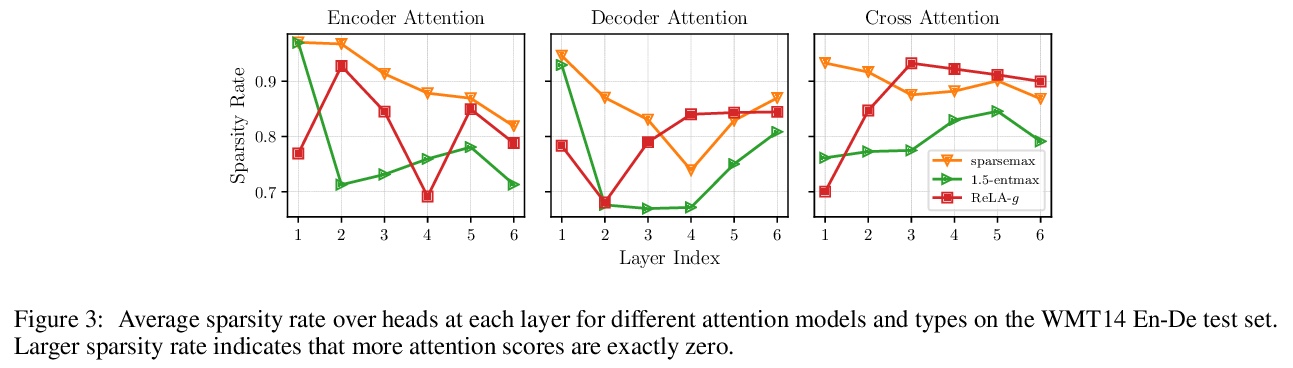
4、[CL] Sparse Attention with Linear Units
B Zhang, I Titov, R Sennrich
[University of Edinburgh & University of Zurich]
线性单元稀疏注意力。提出了整流线性注意力(ReLA),一种新的非softmax稀疏注意力模型,避免了注意力的分类分布假设,可自动学习稀疏注意力,具有很高的灵活性和效率。由于使用ReLU作为激活函数,修剪了所有的负注意力得分,产生了稀疏注意力。为稳定模型训练,在注意力输出中增加了一个归一化层,用专门的初始化或门控结构,比之前提出的稀疏注意机制更容易实现和更高效。将ReLA应用于Transformer,并在五个机器翻译任务上进行了实验,ReLA实现了相当的翻译性能,训练/解码速度与SATT相似,比稀疏softmax基线快得多。分析表明,ReLA提供了高稀疏率、高头部多样性,在源-目标词对齐方面比所有基线都要好。
Recently, it has been argued that encoder-decoder models can be made more interpretable by replacing the softmax function in the attention with its sparse variants. In this work, we introduce a novel, simple method for achieving sparsity in attention: we replace the softmax activation with a ReLU, and show that sparsity naturally emerges from such a formulation. Training stability is achieved with layer normalization with either a specialized initialization or an additional gating function. Our model, which we call Rectified Linear Attention (ReLA), is easy to implement and more efficient than previously proposed sparse attention mechanisms. We apply ReLA to the Transformer and conduct experiments on five machine translation tasks. ReLA achieves translation performance comparable to several strong baselines, with training and decoding speed similar to that of the vanilla attention. Our analysis shows that ReLA delivers high sparsity rate and head diversity, and the induced cross attention achieves better accuracy with respect to source-target word alignment than recent sparsified softmax-based models. Intriguingly, ReLA heads also learn to attend to nothing (i.e. ‘switch off’) for some queries, which is not possible with sparsified softmax alternatives.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kbq8wkFRN
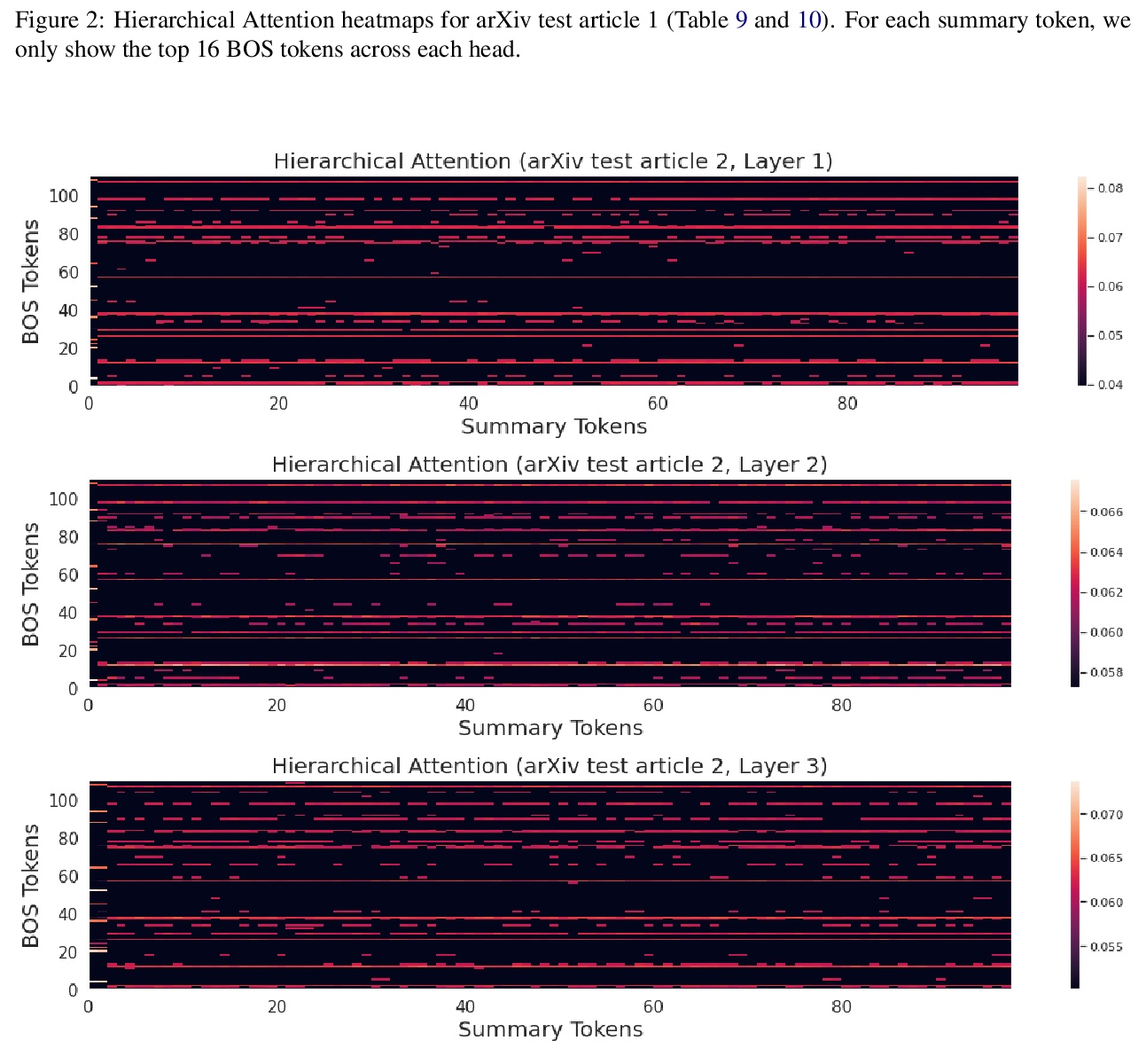
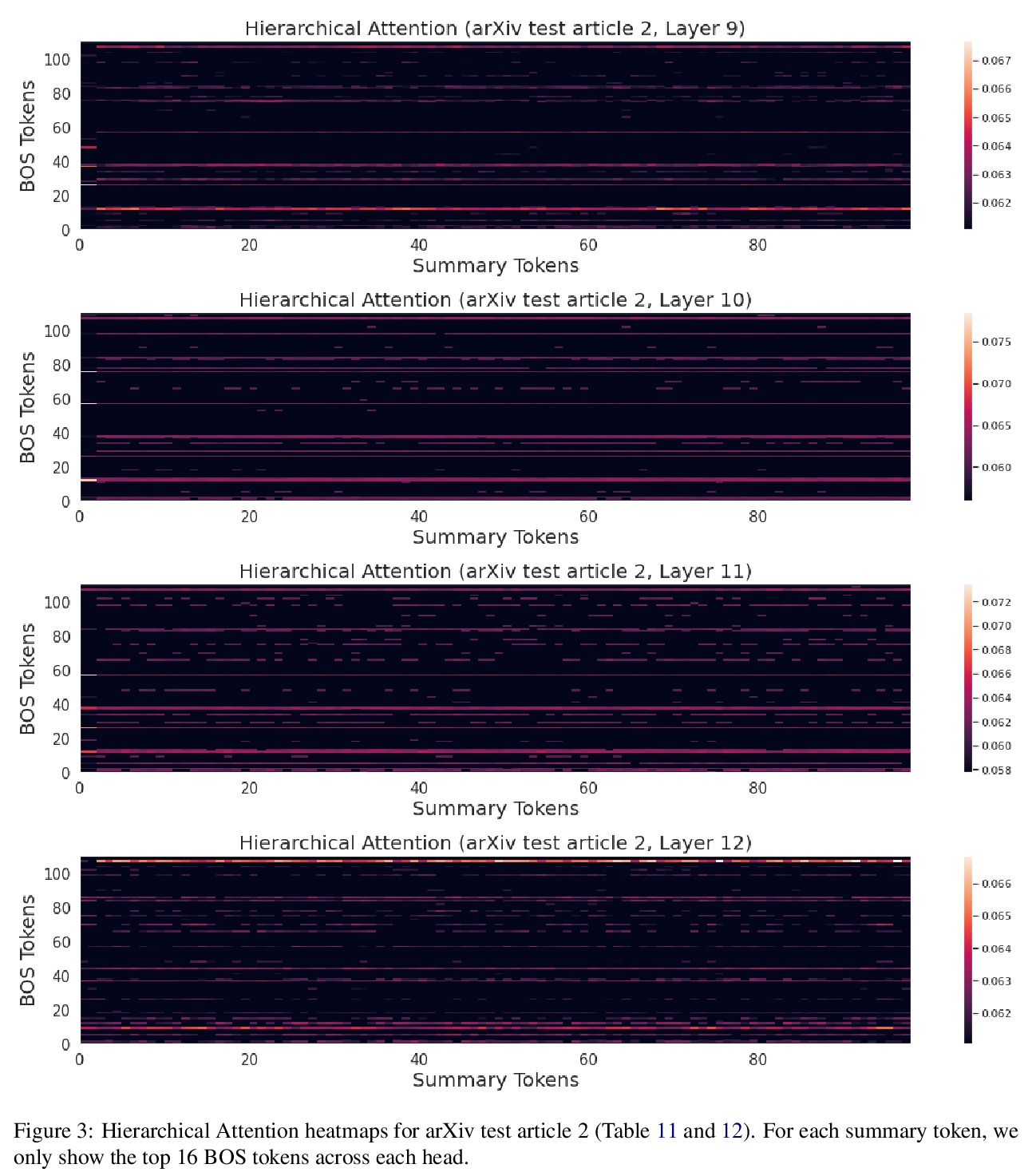
5、[CL] Hierarchical Learning for Generation with Long Source Sequences
T Rohde, X Wu, Y Liu
[Birch AI]
长源序列的层次生成学习。提出一种新的基于层次注意力Transformer的架构(HAT),在几个序列到序列任务特别是具有长源文档的摘要数据集上表现优于标准Transformer。该模型在ArXiv、CNN/DM、SAMSum和AMI等四个摘要任务上取得了最先进的结果,在WMT19 EN-DE文档翻译任务上的表现以28 BLEU明显优于文档级机器翻译基线。
One of the challenges for current sequence to sequence (seq2seq) models is processing long sequences, such as those in summarization and document level machine translation tasks. These tasks require the model to reason at the token level as well as the sentence and paragraph level. We design and study a new Hierarchical Attention Transformer-based architecture (HAT) that outperforms standard Transformers on several sequence to sequence tasks. In particular, our model achieves stateof-the-art results on four summarization tasks, including ArXiv, CNN/DM, SAMSum, and AMI, and we push PubMed R1 & R2 SOTA further. Our model significantly outperforms our document-level machine translation baseline by 28 BLEU on the WMT19 EN-DE document translation task. We also investigate what the hierarchical layers learn by visualizing the hierarchical encoder-decoder attention. Finally, we study hierarchical learning on encoder-only pre-training and analyze its performance on classification downstream tasks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbqdWmshZ

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
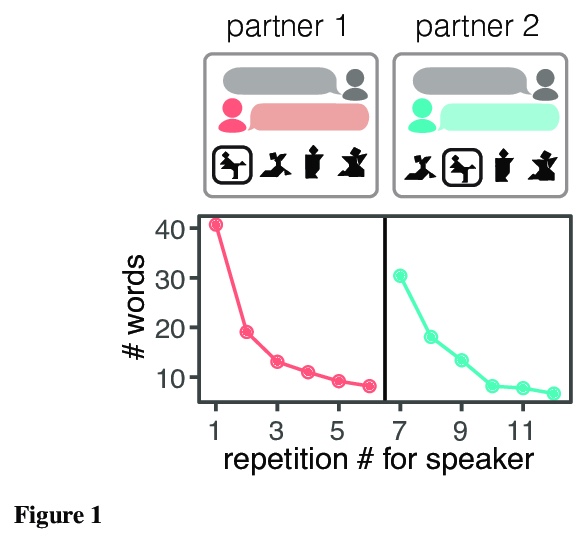
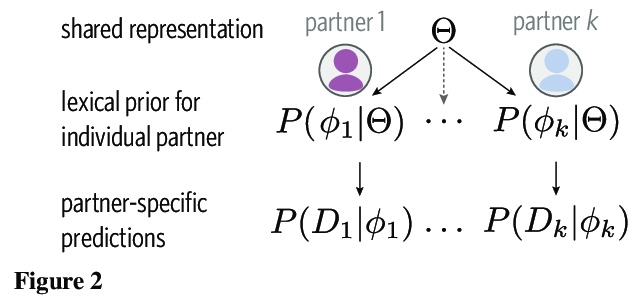
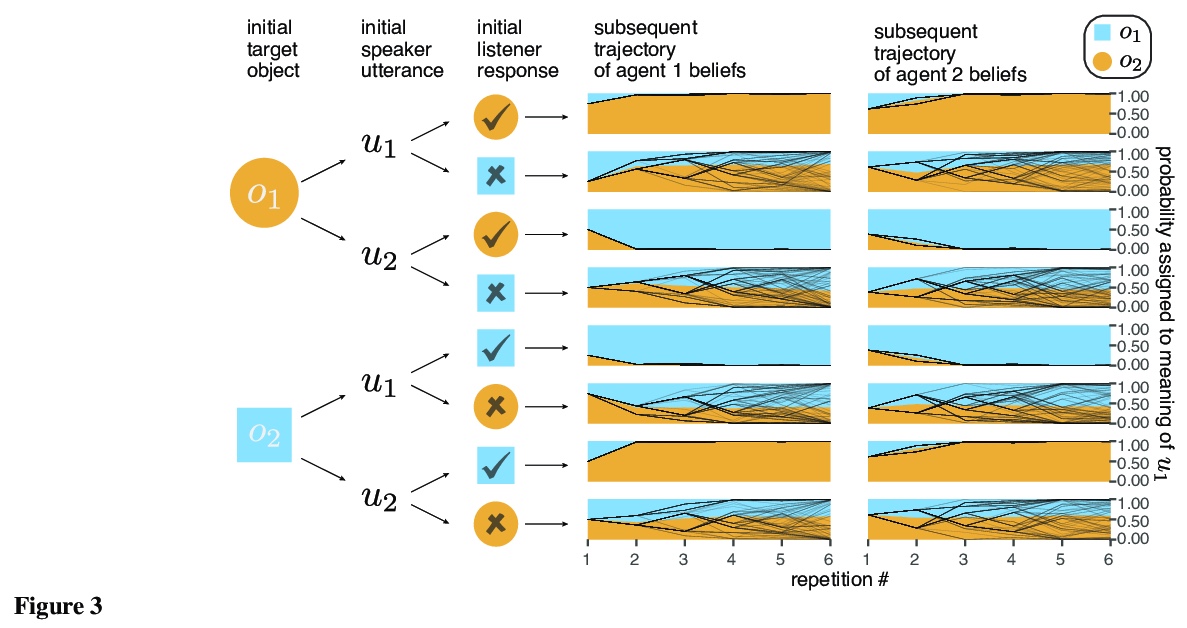
[CL] From partners to populations: A hierarchical Bayesian account of coordination and convention
从伙伴到大众:协调和公约的层次贝叶斯解释
R D. Hawkins, M Franke, M C. Frank, K Smith, T L. Griffiths, N D. Goodman
[Princeton University & University of Osnabrück & Stanford University & University of Edinburgh]
Languages are powerful solutions to coordination problems: they provide stable, shared expectations about how the words we say correspond to the beliefs and intentions in our heads. Yet language use in a variable and non-stationary social environment requires linguistic representations to be flexible: old words acquire new ad hoc or partner-specific meanings on the fly. In this paper, we introduce a hierarchical Bayesian theory of convention formation that aims to reconcile the long-standing tension between these two basic observations. More specifically, we argue that the central computational problem of communication is not simply transmission, as in classical formulations, but learning and adaptation over multiple timescales. Under our account, rapid learning within dyadic interactions allows for coordination on partner-specific common ground, while social conventions are stable priors that have been abstracted away from interactions with multiple partners. We present new empirical data alongside simulations showing how our model provides a cognitive foundation for explaining several phenomena that have posed a challenge for previous accounts: (1) the convergence to more efficient referring expressions across repeated interaction with the same partner, (2) the gradual transfer of partner-specific common ground to novel partners, and (3) the influence of communicative context on which conventions eventually form.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbpZOuYHS
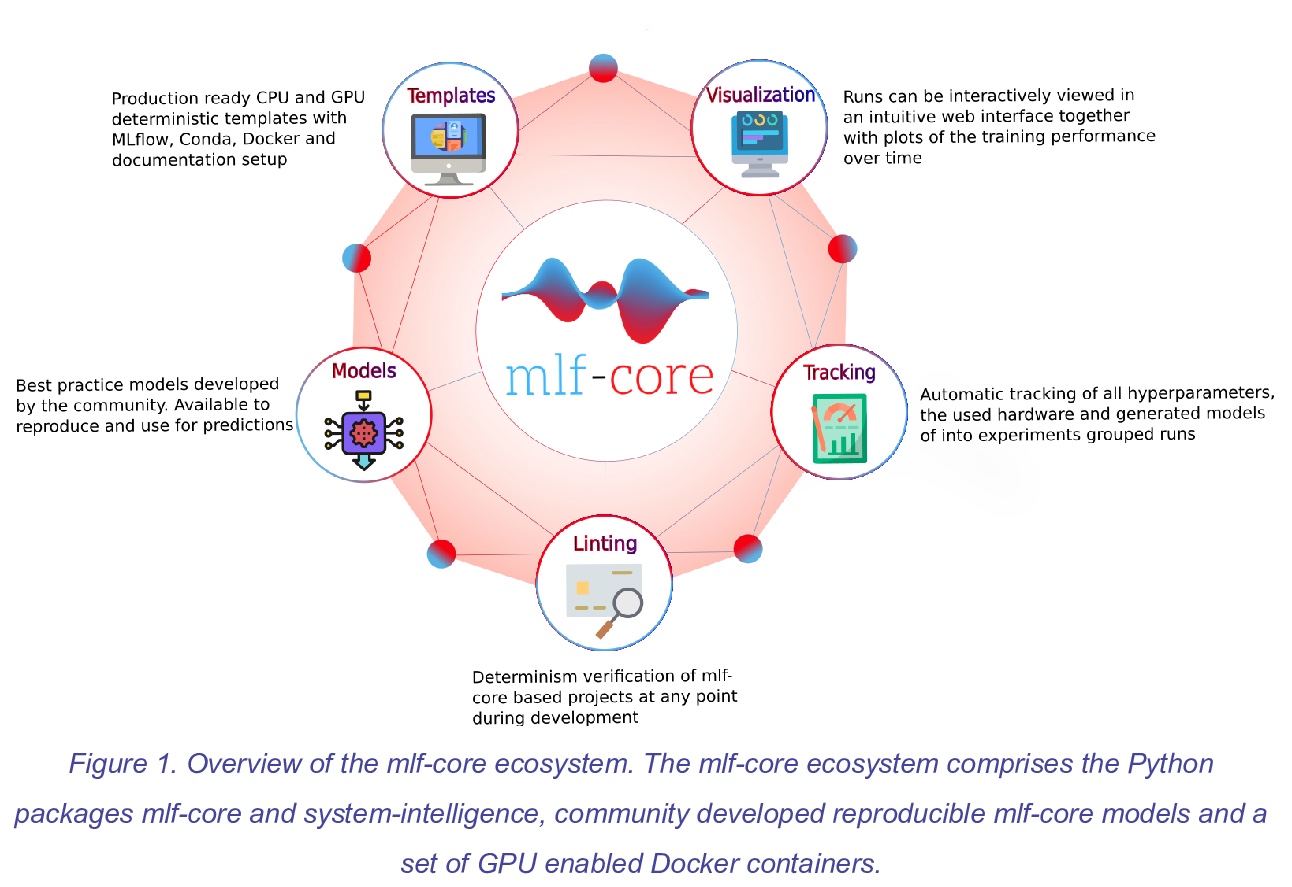
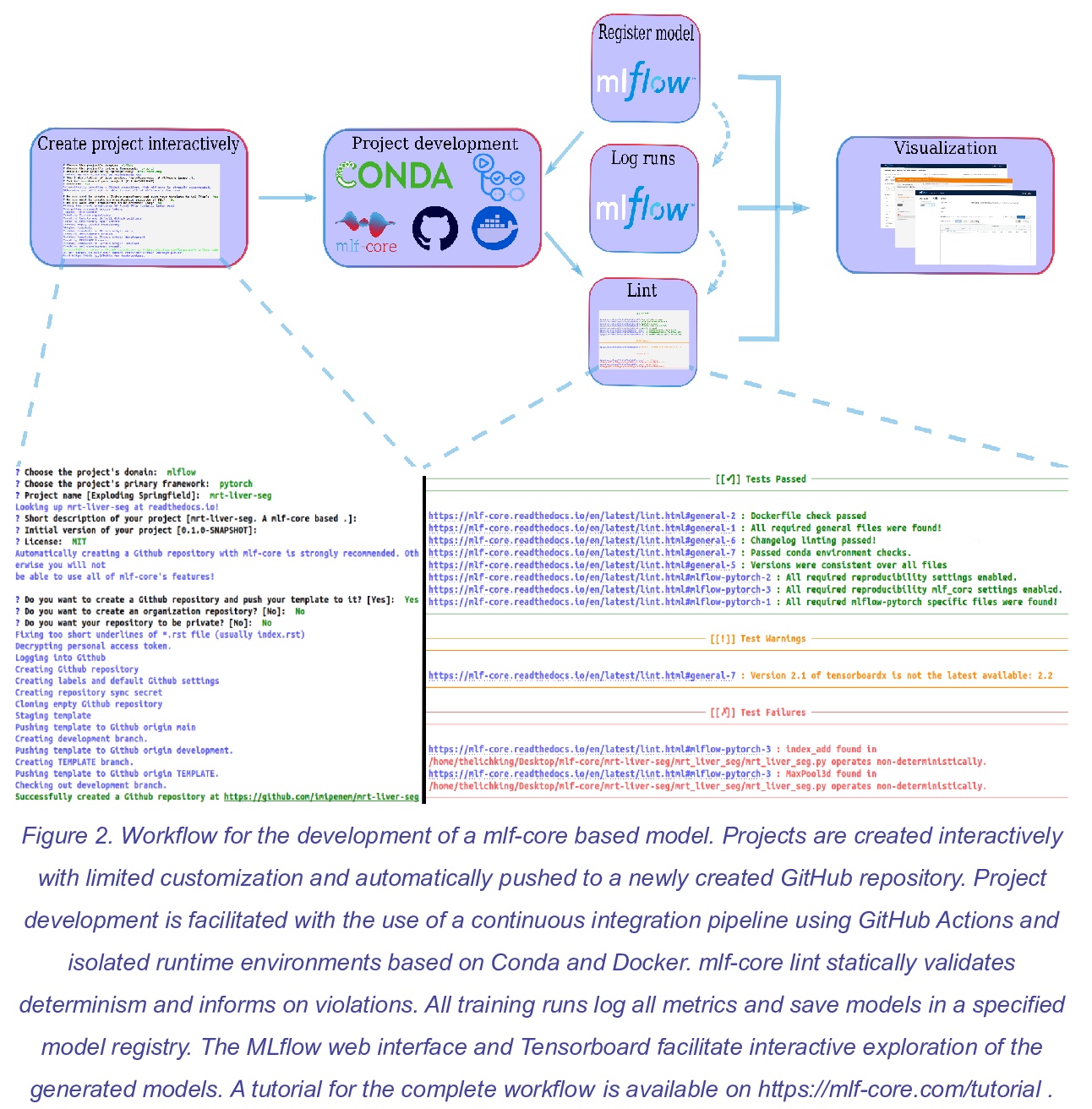
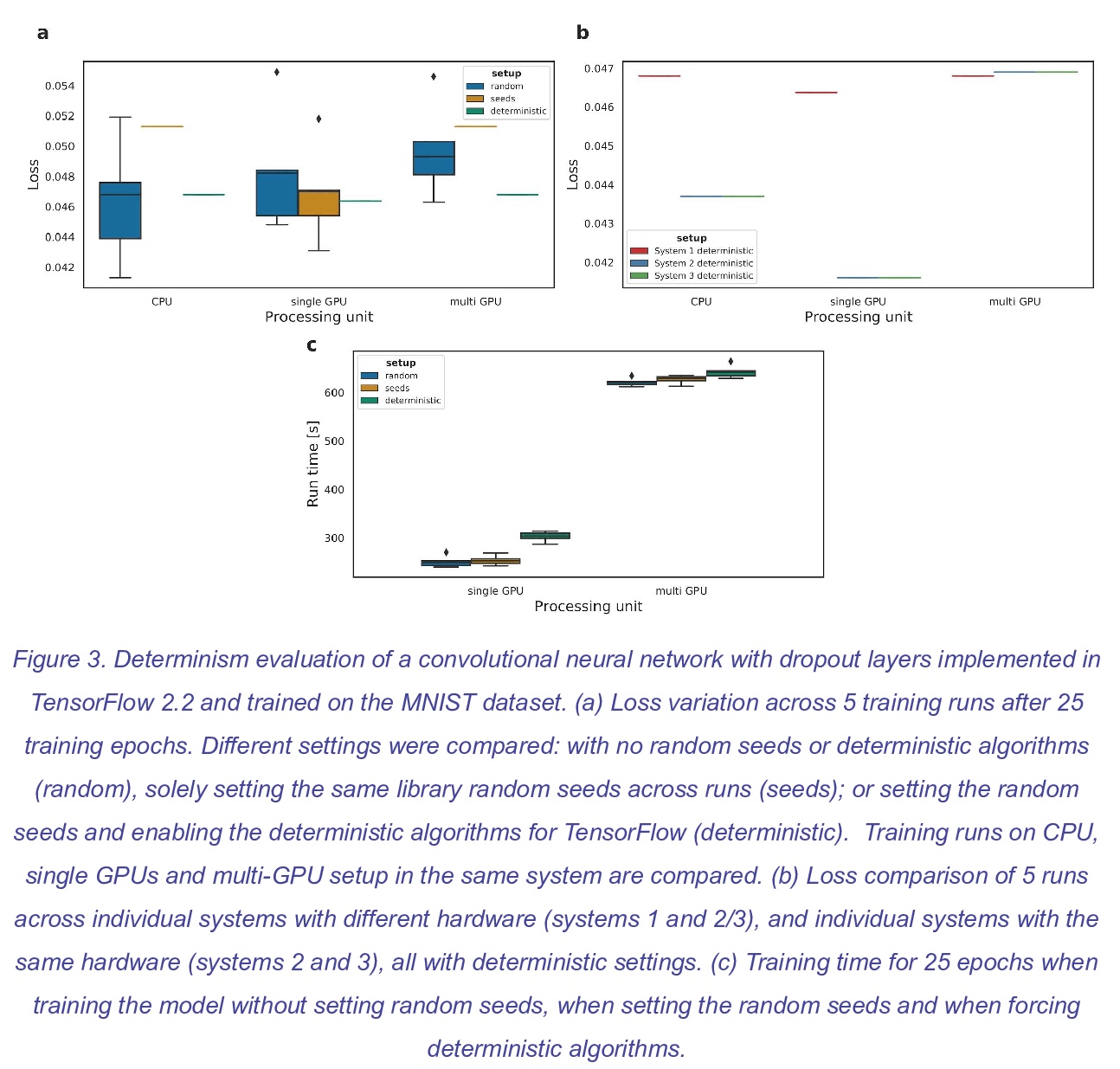
[LG] mlf-core: a framework for deterministic machine learning
mlf-core:确定性机器学习框架
L Heumos, P Ehmele, K Menden, L K Cuellar, E Miller, S Lemke, G Gabernet, S Nahnsen
[University of Tübingen & University of Hamburg]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbqhX8Bcd
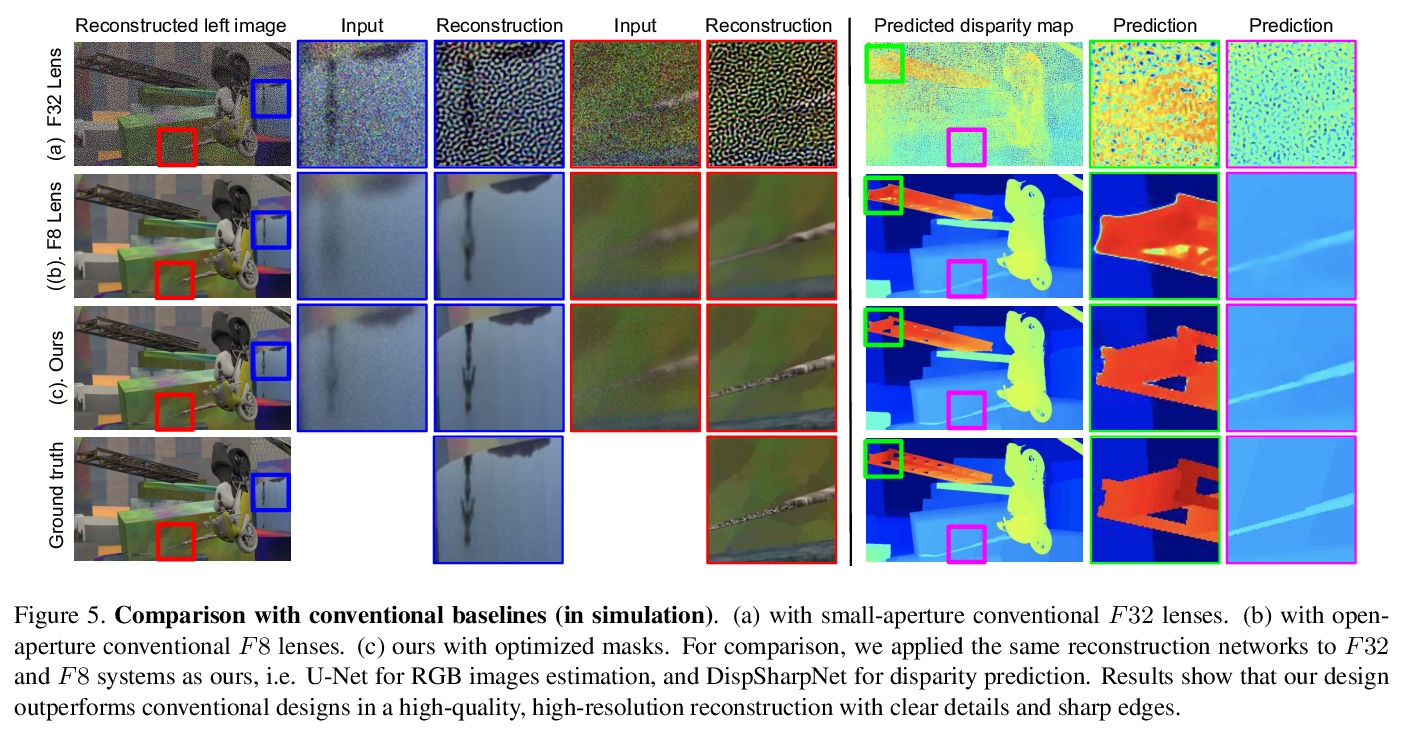
[CV] CodedStereo: Learned Phase Masks for Large Depth-of-field Stereo
CodedStereo:面向大景深立体的习得相位掩模
S Tan, Y Wu, S Yu, A Veeraraghavan
[Rice University & Facebook Reality Labs]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kbqj5qYVp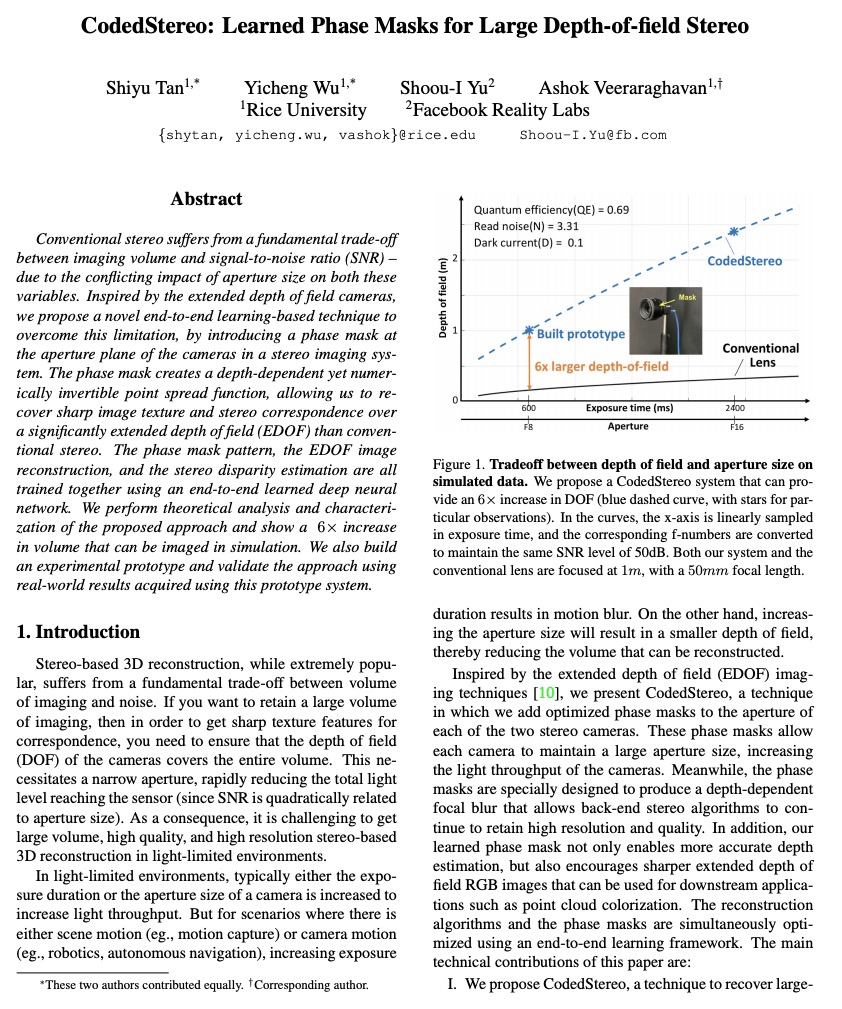

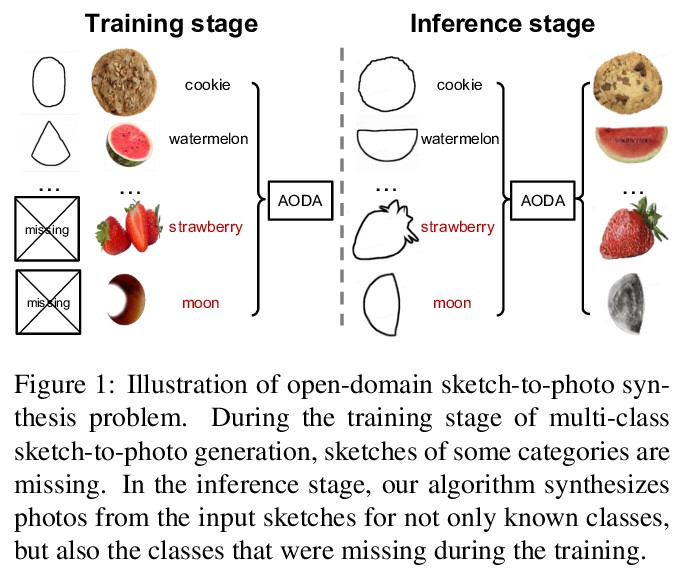
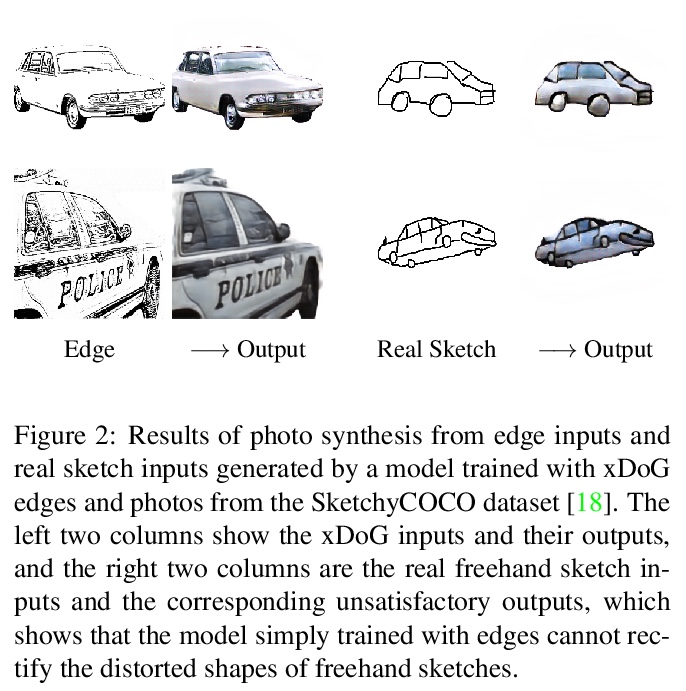
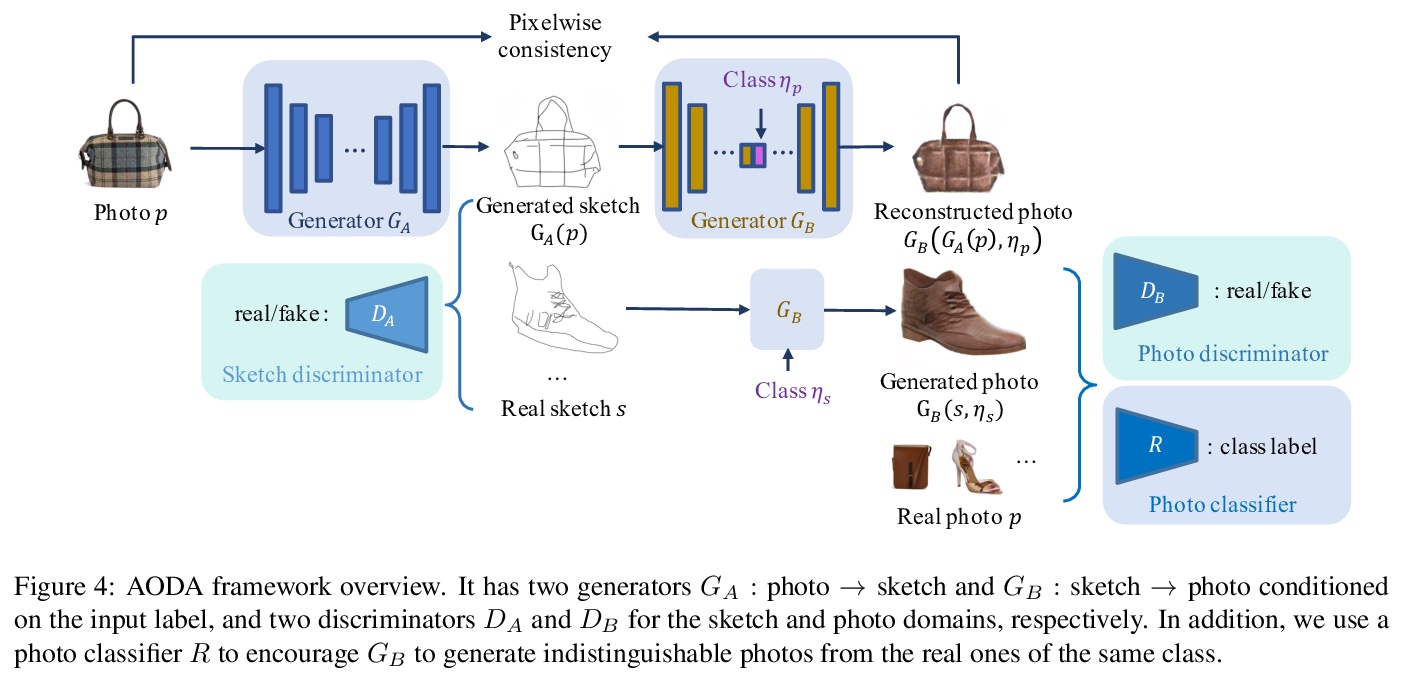
[CV] Adversarial Open Domain Adaption for Sketch-to-Photo Synthesis
基于对抗性开放域自适应的草图到照片合成
X Xiang, D Liu, X Yang, Y Zhu, X Shen, J P. Allebach
[Purdue University & ByteDance Inc]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kbqln0J0J