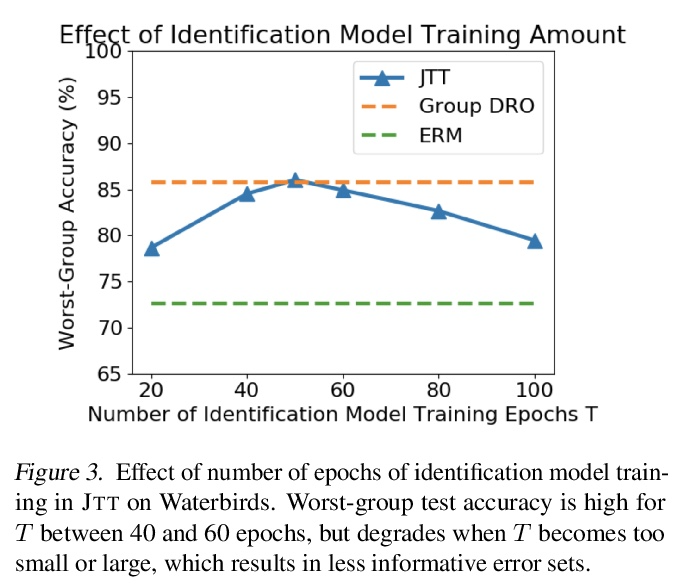
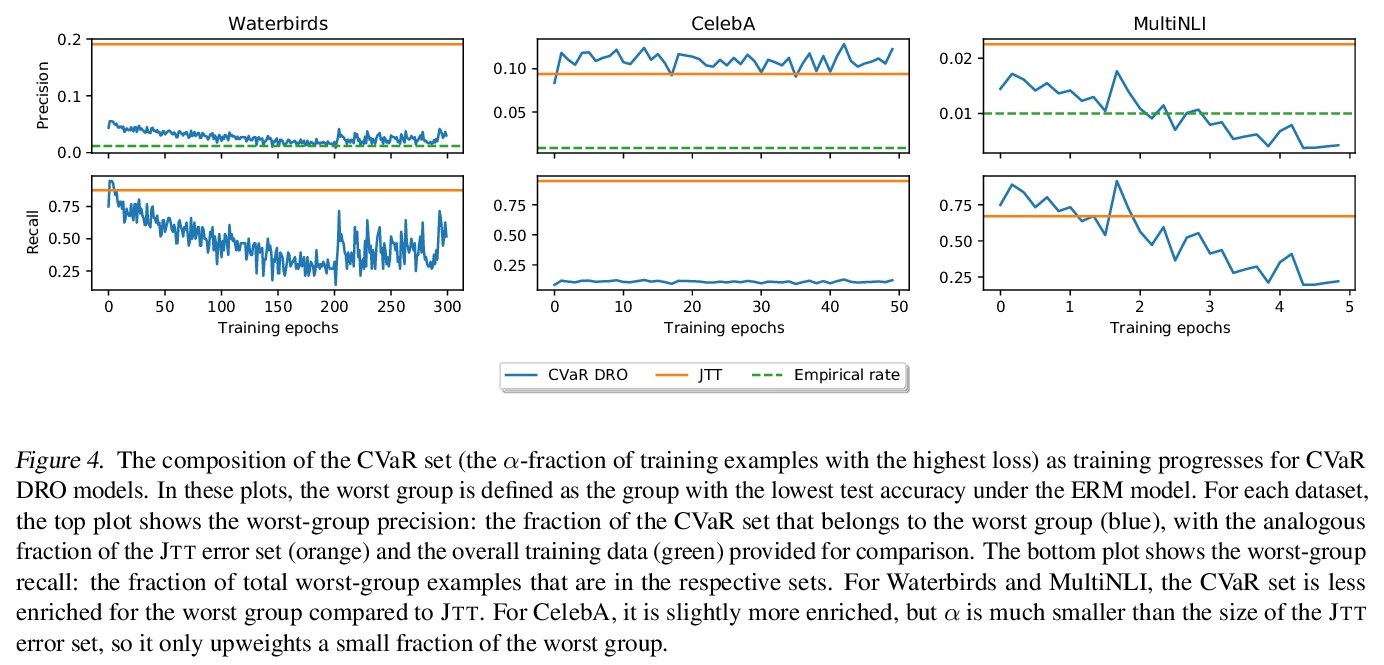
- 1、[LG] Just Train Twice: Improving Group Robustness without Training Group Information
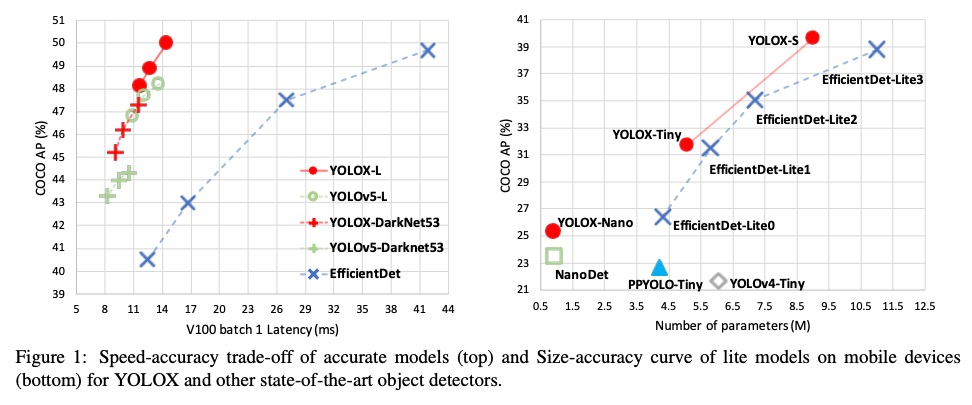
- 2、[CV] YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO Series in 2021
- 3、[LG] Epistemic Neural Networks
- 4、[LG] Reasoning-Modulated Representations
- 5、[LG] Unbiased Gradient Estimation in Unrolled Computation Graphs with Persistent Evolution Strategies
- [RO] Autonomy 2.0: Why is self-driving always 5 years away?
- [CV] CodeMapping: Real-Time Dense Mapping for Sparse SLAM using Compact Scene Representations
- [CL] Learning De-identified Representations of Prosody from Raw Audio
- [LG] Hierarchical Few-Shot Imitation with Skill Transition Models
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
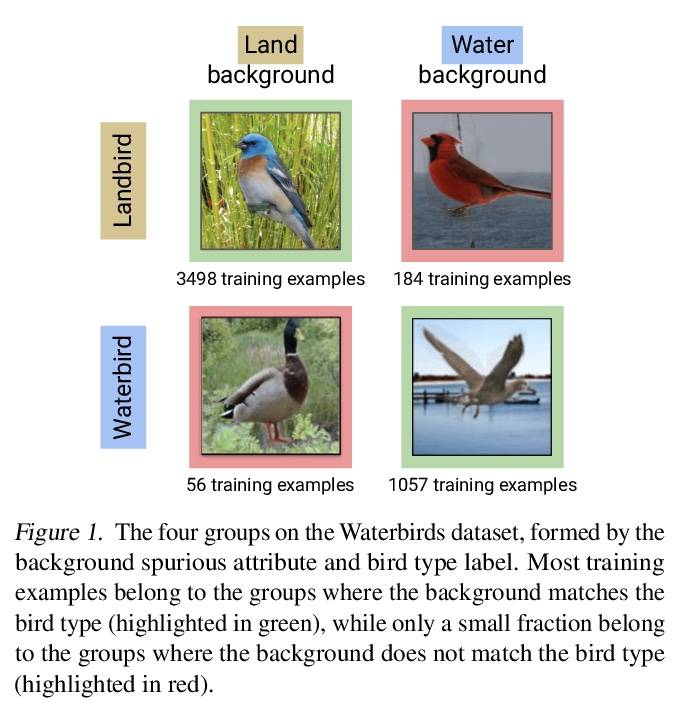
1、[LG] Just Train Twice: Improving Group Robustness without Training Group Information
E Z Liu, B Haghgoo, A S. Chen, A Raghunathan, P W Koh, S Sagawa, P Liang, C Finn
[Stanford University]
Just Train Twice:在不训练群组信息的情况下提高群组鲁棒性。通过经验风险最小化(ERM)的标准训练,可产生平均精度高但在某些群组上精度低的模型,特别是在输入和标记之间存在虚假关联的情况下。之前实现高的最差组准确率的方法,如组分布性鲁棒优化(group DRO),需要对每个训练点进行昂贵的组标记,而不使用这种组标记的方法通常得不到满意的最差组准确率。本文提出一种简单的两阶段方法——Just Train Twice(JTT),首先通过多轮训练一个标准的ERM模型,再训练第二个模型,对第一个模型错误分类的训练样本进行升权,在训练过程中不需要昂贵的群组标记就能大幅提高最差群组性能。直观地讲,就是提高了标准ERM模型表现不佳的群组样本的权重,从而提高了最差组的表现。对四项具有虚假关联的图像分类和自然语言处理任务进行平均,JTT缩小了标准ERM和群体DRO之间最差群体准确性的75%的差距,同时只需要在小型验证集上进行群体标注,以调整超参数。
Standard training via empirical risk minimization (ERM) can produce models that achieve high accuracy on average but low accuracy on certain groups, especially in the presence of spurious correlations between the input and label. Prior approaches that achieve high worst-group accuracy, like group distributionally robust optimization (group DRO) require expensive group annotations for each training point, whereas approaches that do not use such group annotations typically achieve unsatisfactory worst-group accuracy. In this paper, we propose a simple two-stage approach, JTT, that first trains a standard ERM model for several epochs, and then trains a second model that upweights the training examples that the first model misclassified. Intuitively, this upweights examples from groups on which standard ERM models perform poorly, leading to improved worst-group performance. Averaged over four image classification and natural language processing tasks with spurious correlations, JTT closes 75% of the gap in worst-group accuracy between standard ERM and group DRO, while only requiring group annotations on a small validation set in order to tune hyperparameters.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KpHLDa9AY 

2、[CV] YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO Series in 2021
Z Ge, S Liu, F Wang, Z Li, J Sun
[Megvii Technology]
YOLOX:2021超越YOLO系列。本文提出对YOLO系列的一些经验性的改进,形成了一个新的高性能检测器——YOLOX。将YOLO检测器切换到无锚方式,并采用其他先进的检测技术,即解耦头和先进的标签分配策略SimOTA,在所有模型大小上,YOLOX在速度和精度之间实现了比其他同类模型更好的权衡,在大规模模型上实现了最先进的结果。对于只有0.91M参数和1.08G FLOPs的YOLONano,在COCO上得到25.3%的AP,超过NanoDet 1.8%的AP;对于YOLOv3,工业界最广泛使用的检测器之一,我们将其在COCO上提升到47.3% AP,比目前的最佳结果高出3.0% AP;而YOLOX-L,其参数数量与YOLOv4CSP、YOLOv5-L大致相同,在Tesla V100上以68.9 FPS的速度在COCO上实现了50.0%的AP,比YOLOv5-L超出1.8%的AP。此外,用单个YOLOX-L模型赢得了流感知挑战赛(CVPR 2021自动驾驶Workshop)的第一名。
In this report, we present some experienced improvements to YOLO series, forming a new high-performance detector — YOLOX. We switch the YOLO detector to an anchor-free manner and conduct other advanced detection techniques, i.e., a decoupled head and the leading label assignment strategy SimOTA to achieve state-of-the-art results across a large scale range of models: For YOLONano with only 0.91M parameters and 1.08G FLOPs, we get 25.3% AP on COCO, surpassing NanoDet by 1.8% AP; for YOLOv3, one of the most widely used detectors in industry, we boost it to 47.3% AP on COCO, outperforming the current best practice by 3.0% AP; for YOLOX-L with roughly the same amount of parameters as YOLOv4CSP, YOLOv5-L, we achieve 50.0% AP on COCO at a speed of 68.9 FPS on Tesla V100, exceeding YOLOv5-L by 1.8% AP. Further, we won the 1st Place on Streaming Perception Challenge (Workshop on Autonomous Driving at CVPR 2021) using a single YOLOX-L model. We hope this report can provide useful experience for developers and * Equal contribution. † Corresponding author. researchers in practical scenes, and we also provide deploy versions with ONNX, TensorRT, NCNN, and Openvino supported.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KpHSk3yNx 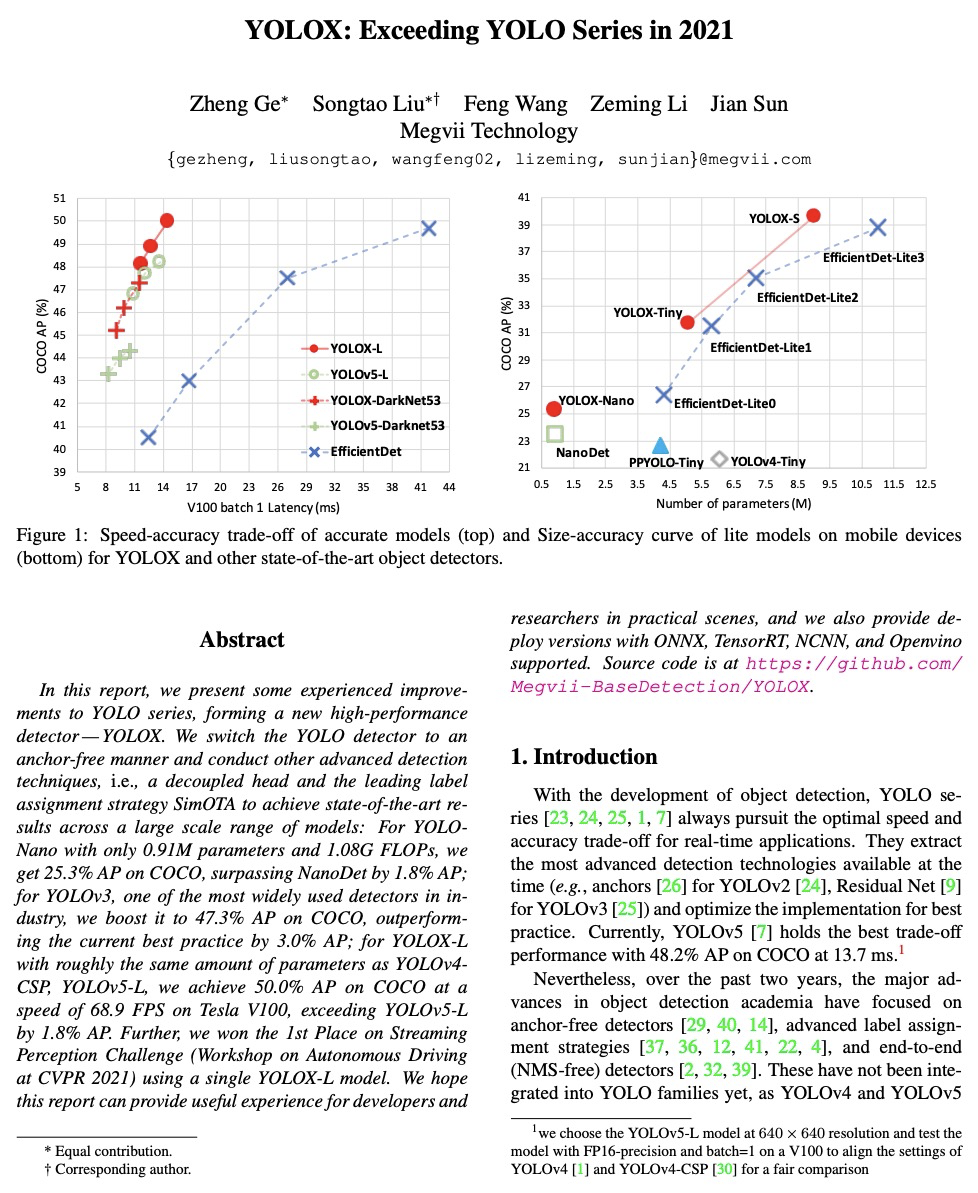

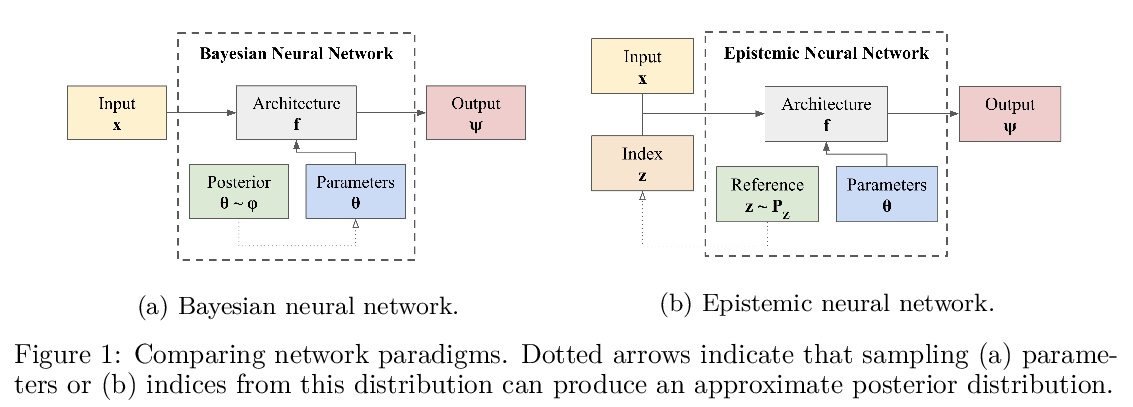
3、[LG] Epistemic Neural Networks
I Osband, Z Wen, M Asghari, M Ibrahimi, X Lu, B V Roy
[DeepMind]
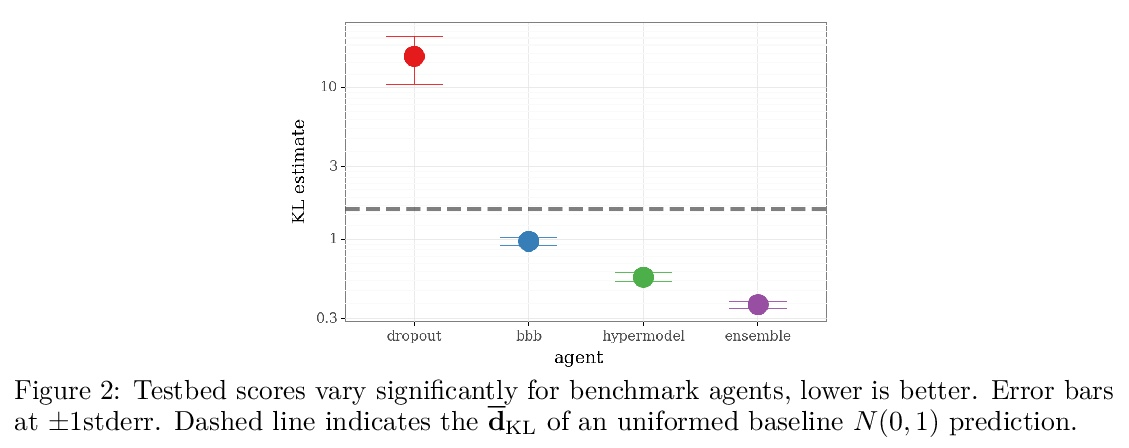
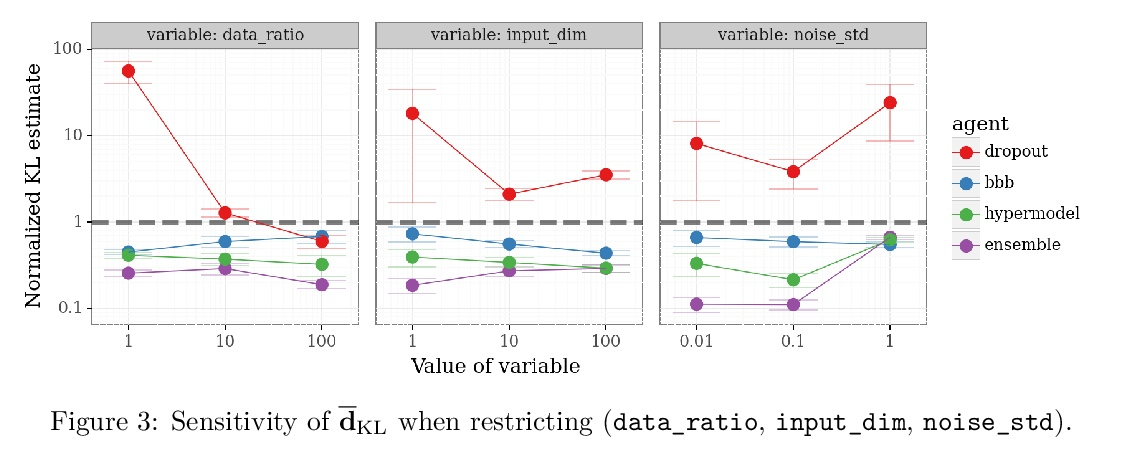
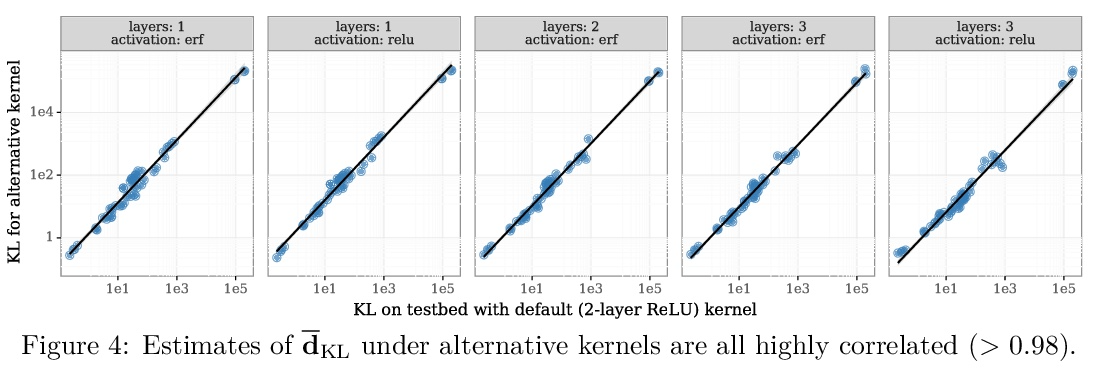
认知神经网络。本文提出认识神经网络(ENN),作为深度学习不确定性建模的接口。所有现有的不确定性建模方法都可表示为ENN,任何ENN都可与与贝叶斯神经网络一致。这个新视角为未来的研究提供了几个有希望的方向。之前的工作为神经网络开发了概率推理工具;但“哪些神经网络适合作为概率推理工具?”本文提出一种明确而简单的衡量ENN进展的标准:相对目标分布的KL散度。开发了基于神经网络高斯过程推理的计算测试平台,评估了深度学习中不确定性建模的几种典型方法,发现它们的性能差异很大,dropout作为一种ENN表现很差,适当提升(bootstrapped)的集成可以表现得非常好,而线性超模型和BBB则介于两者之间。深入了解了这些结果的敏感性,并表明本文提出的衡量标准与顺序决策问题的性能高度相关。”蒸馏”ENN同时也提供了一个简单的”概念证明”,即ENN设计中的创新可以在统计质量和/或计算成本方面提供数量级的改进。
We introduce the epistemic neural network (ENN) as an interface for uncertainty modeling in deep learning. All existing approaches to uncertainty modeling can be expressed as ENNs, and any ENN can be identified with a Bayesian neural network. However, this new perspective provides several promising directions for future research. Where prior work has developed probabilistic inference tools for neural networks; we ask instead, ‘which neural networks are suitable as tools for probabilistic inference?’. We propose a clear and simple metric for progress in ENNs: the KL-divergence with respect to a target distribution. We develop a computational testbed based on inference in a neural network Gaussian process and release our code as a benchmark at https://github.com/deepmind/enn. We evaluate several canonical approaches to uncertainty modeling in deep learning, and find they vary greatly in their performance. We provide insight to the sensitivity of these results and show that our metric is highly correlated with performance in sequential decision problems. Finally, we provide indications that new ENN architectures can improve performance in both the statistical quality and computational cost.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KpHXe2OF9 
4、[LG] Reasoning-Modulated Representations
P Veličković, M Bošnjak, T Kipf, A Lerchner, R Hadsell, R Pascanu, C Blundell
[DeepMind & Google Research]
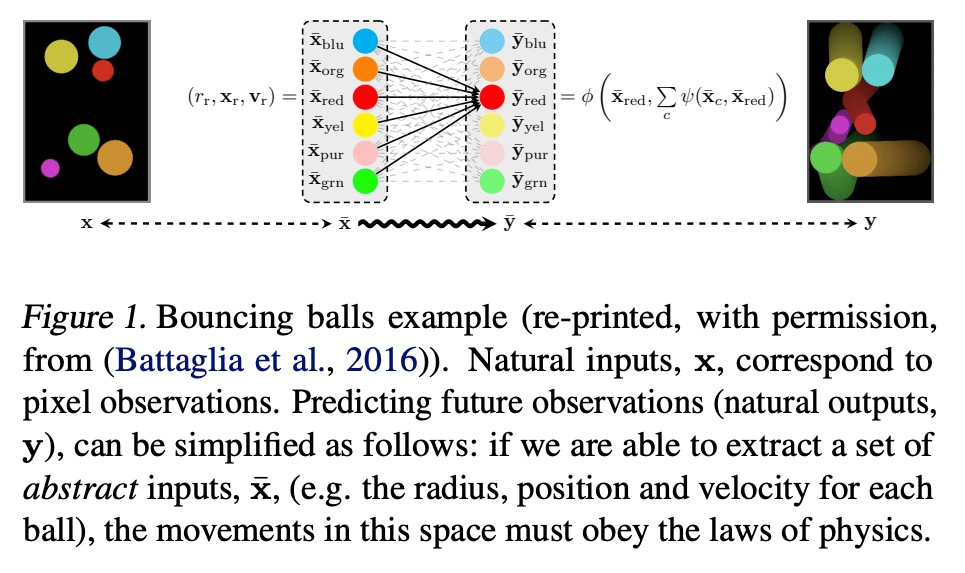
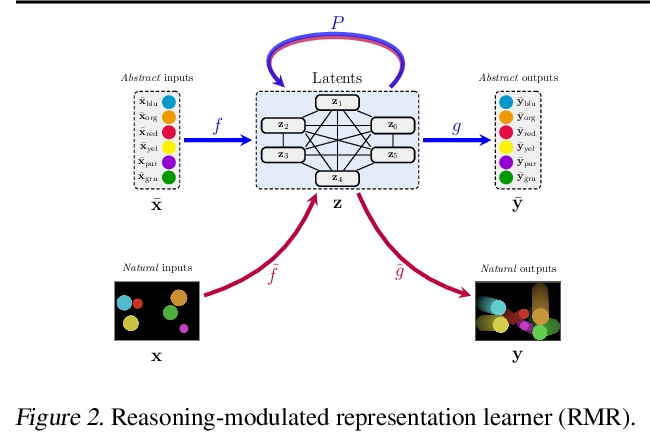
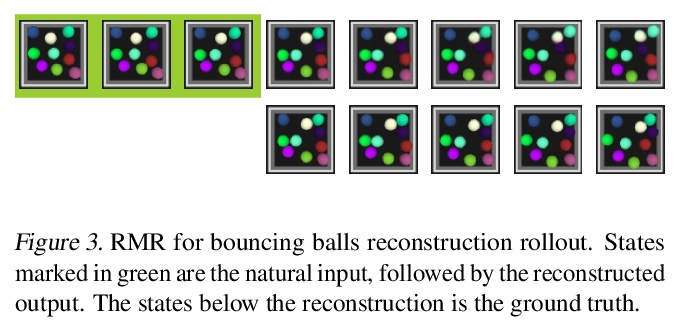
推理调控表示。神经网络利用强大的内部表示来实现泛化。学习它们是很困难的,通常需要一个大型的训练集,密集地覆盖数据分布。本文针对一种常见场景开展研究,其中的任务并不是完全不透明的。事实上,很多时候我们可以获得关于底层系统的信息(例如,观察结果必须遵守某些物理定律),而所有”像白纸一块”的神经网络都需要从头开始重新学习,这对数据效率是不利的。本文将这些信息纳入一个预训练好的推理模块,并研究其在不同的自监督学习环境下从像素中塑造所发现的表示的作用。所提出方法为一类新的高数据效率的表示学习铺平了道路。
Neural networks leverage robust internal representations in order to generalise. Learning them is difficult, and often requires a large training set that covers the data distribution densely. We study a common setting where our task is not purely opaque. Indeed, very often we may have access to information about the underlying system (e.g. that observations must obey certain laws of physics) that any “tabula rasa” neural network would need to re-learn from scratch, penalising data efficiency. We incorporate this information into a pre-trained reasoning module, and investigate its role in shaping the discovered representations in diverse self-supervised learning settings from pixels. Our approach paves the way for a new class of data-efficient representation learning.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KpI1E3ClA 
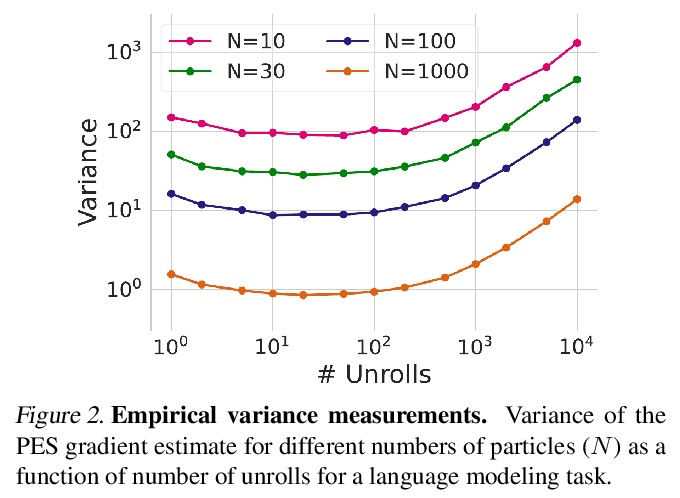
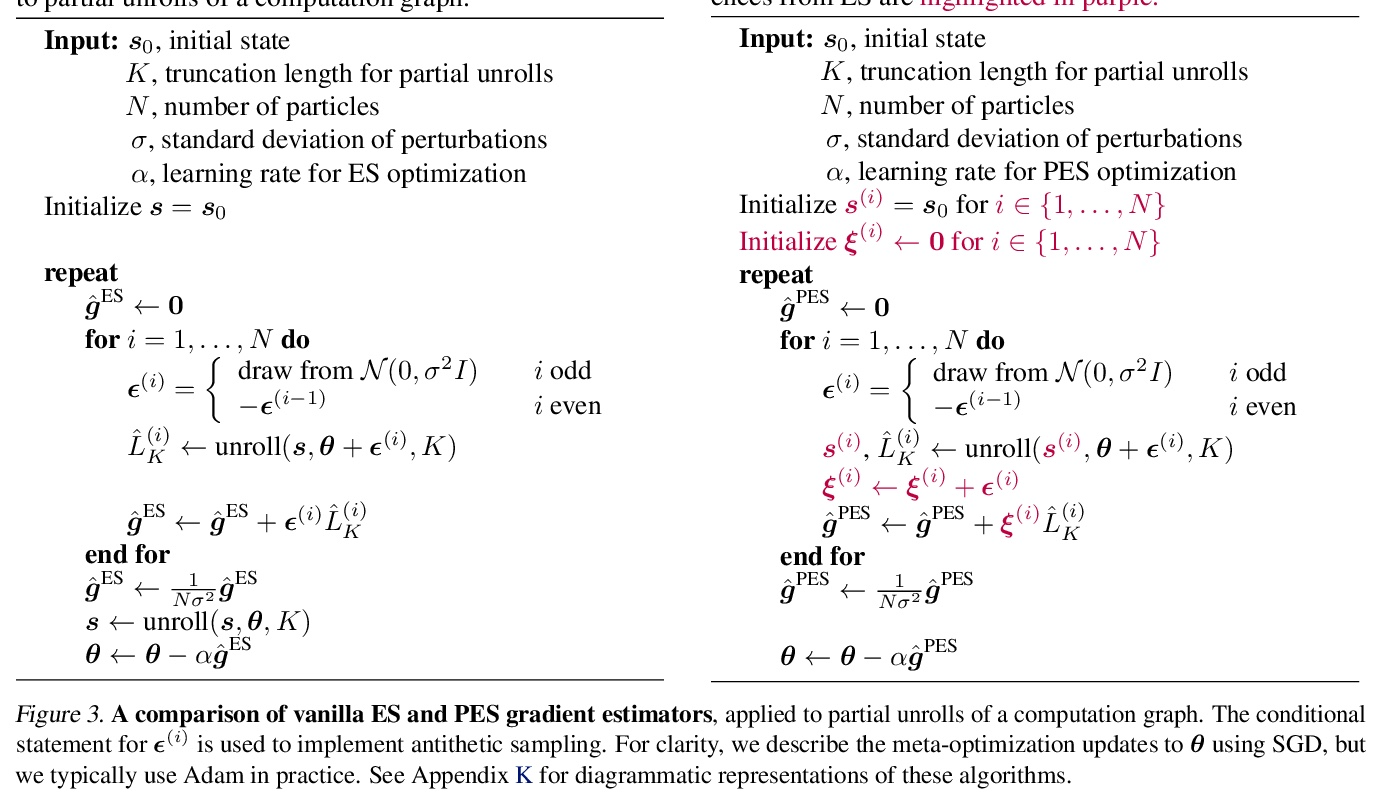
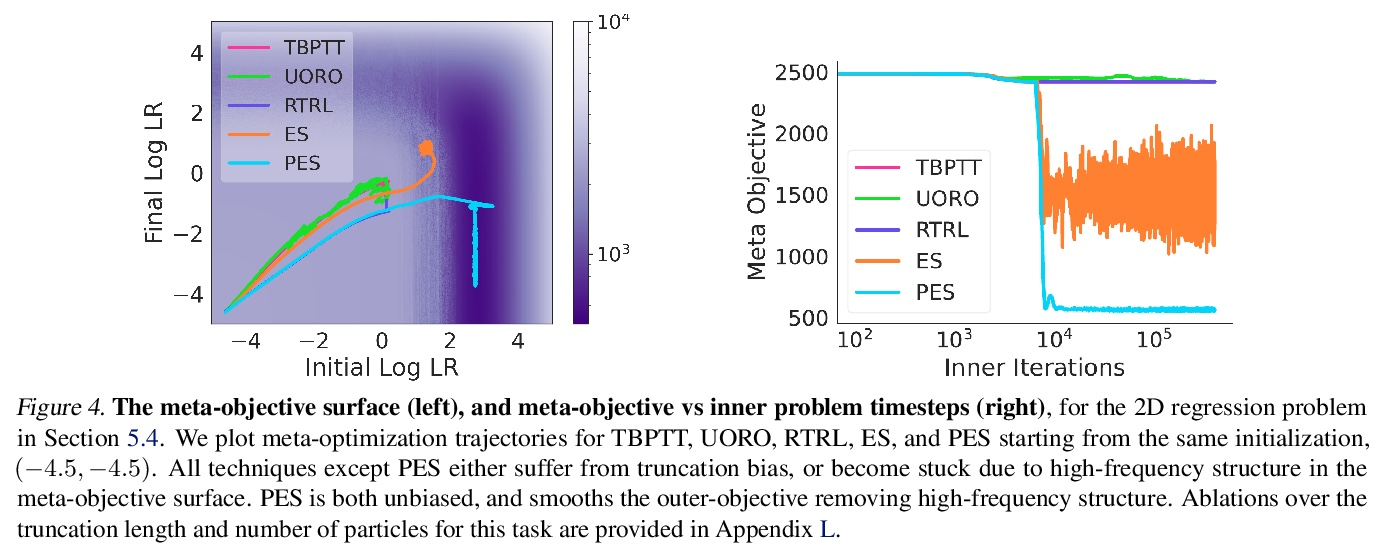
5、[LG] Unbiased Gradient Estimation in Unrolled Computation Graphs with Persistent Evolution Strategies
P Vicol, L Metz, J Sohl-Dickstein
[University of Toronto & Google Brain]
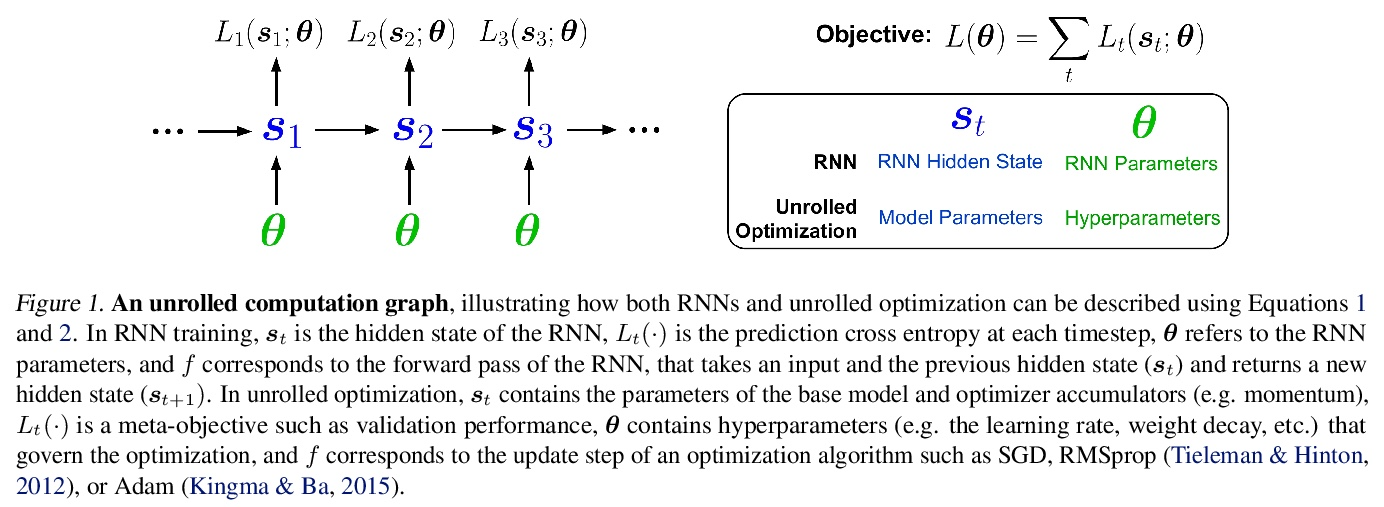
基于持续进化策略的展开计算图无偏梯度估计。展开计算图出现在许多场景中,包括训练RNN,通过展开优化调试超参数,以及训练习得优化器。目前在这种计算图中优化参数的方法存在高方差梯度、偏差、缓慢更新或大内存使用的问题。本文提出一种叫做持续进化策略(PES)的方法,将计算图划分为一系列截断展开,在每次展开后执行基于进化策略的更新步骤,通过在整个展开序列中积累修正项来消除这些截断的偏差。PES允许快速的参数更新,内存使用率低,无偏差,且具有合理的方差特性。通过实验证明了PES与其他几种合成任务的梯度估计方法相比的优势,并展示了它在类似RNN任务、超参数优化、强化学习和习得优化器的元训练中的适用性。
Unrolled computation graphs arise in many scenarios, including training RNNs, tuning hyperparameters through unrolled optimization, and training learned optimizers. Current approaches to optimizing parameters in such computation graphs suffer from high variance gradients, bias, slow updates, or large memory usage. We introduce a method called Persistent Evolution Strategies (PES), which divides the computation graph into a series of truncated unrolls, and performs an evolution strategies-based update step after each unroll. PES eliminates bias from these truncations by accumulating correction terms over the entire sequence of unrolls. PES allows for rapid parameter updates, has low memory usage, is unbiased, and has reasonable variance characteristics. We experimentally demonstrate the advantages of PES compared to several other methods for gradient estimation on synthetic tasks, and show its applicability to training learned optimizers and tuning hyperparameters.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KpI547QgL 
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
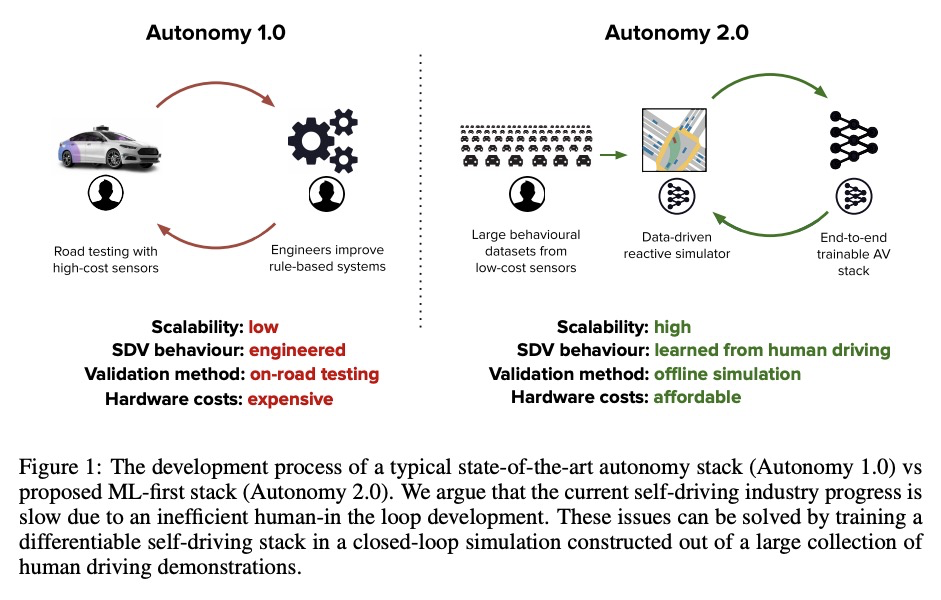
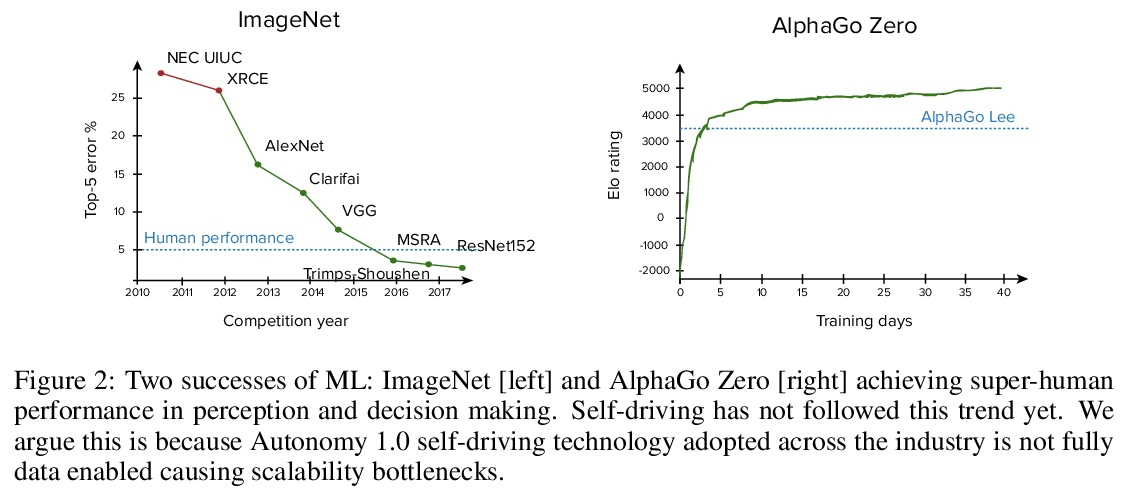
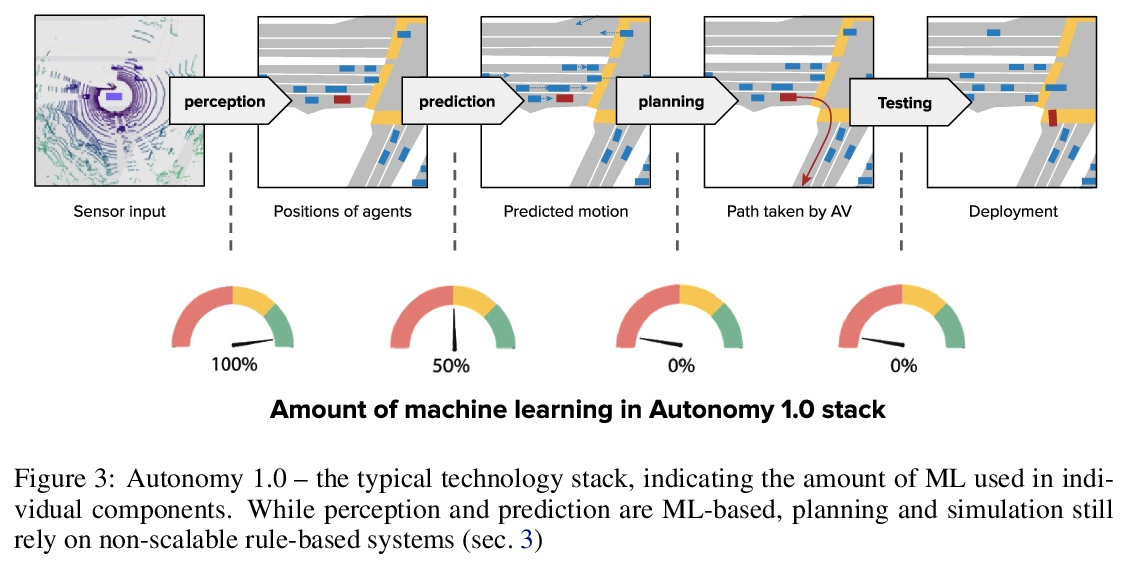
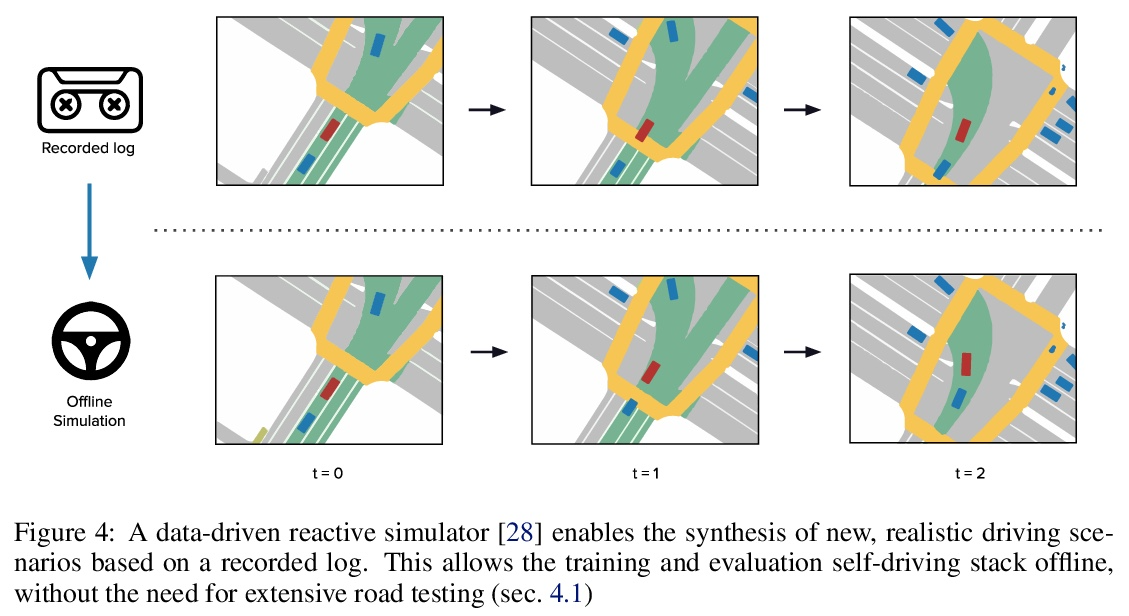
[RO] Autonomy 2.0: Why is self-driving always 5 years away?
自治2.0:为什么无人驾驶总是要再等五年?
A Jain, L D Pero, H Grimmett, P Ondruska
[Lyft Level 5 self-driving]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KpIb3ksIg 
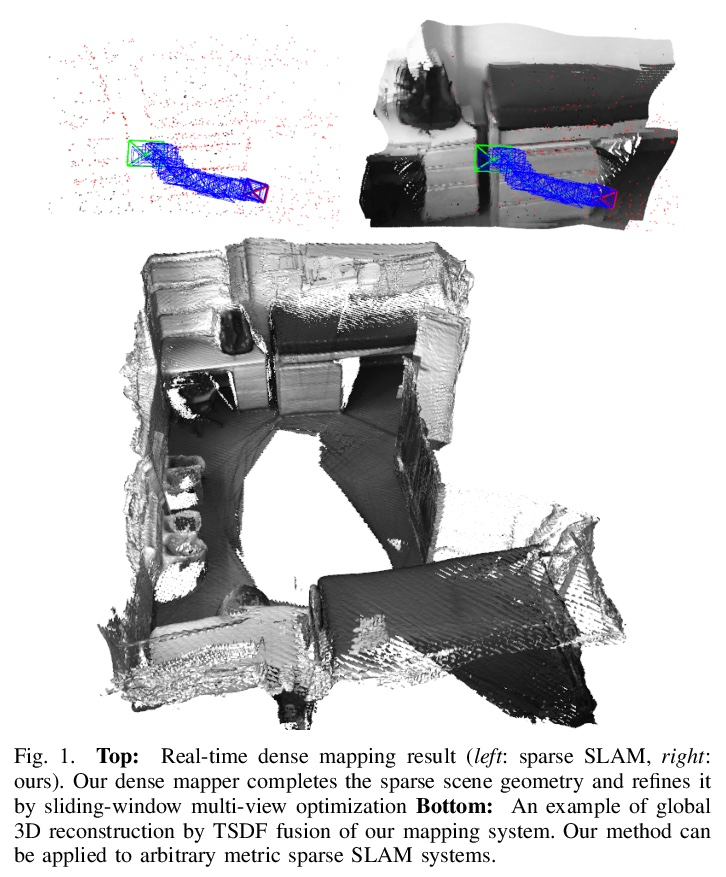
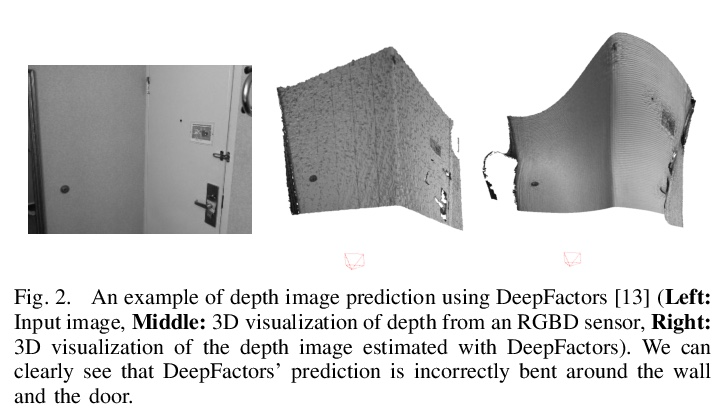
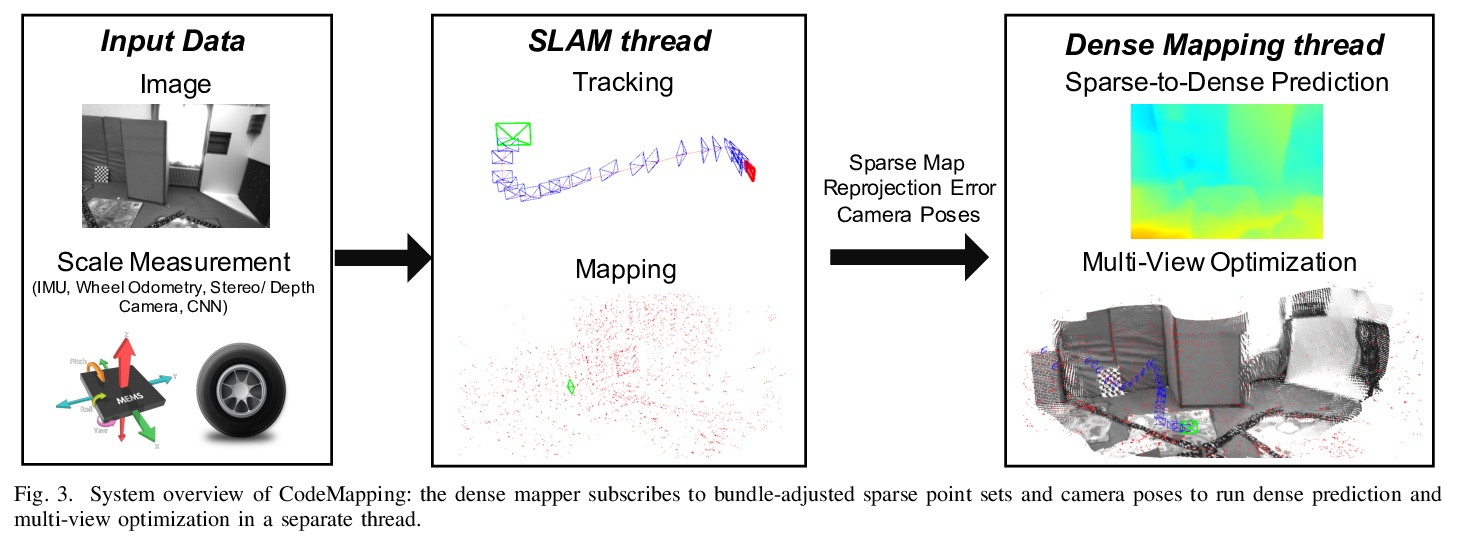
[CV] CodeMapping: Real-Time Dense Mapping for Sparse SLAM using Compact Scene Representations
CodeMapping:基于紧凑场景表示的稀疏SLAM实时密集映射
H Matsuki, R Scona, J Czarnowski, A J. Davison
[Imperial College London]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KpIftbmwJ 

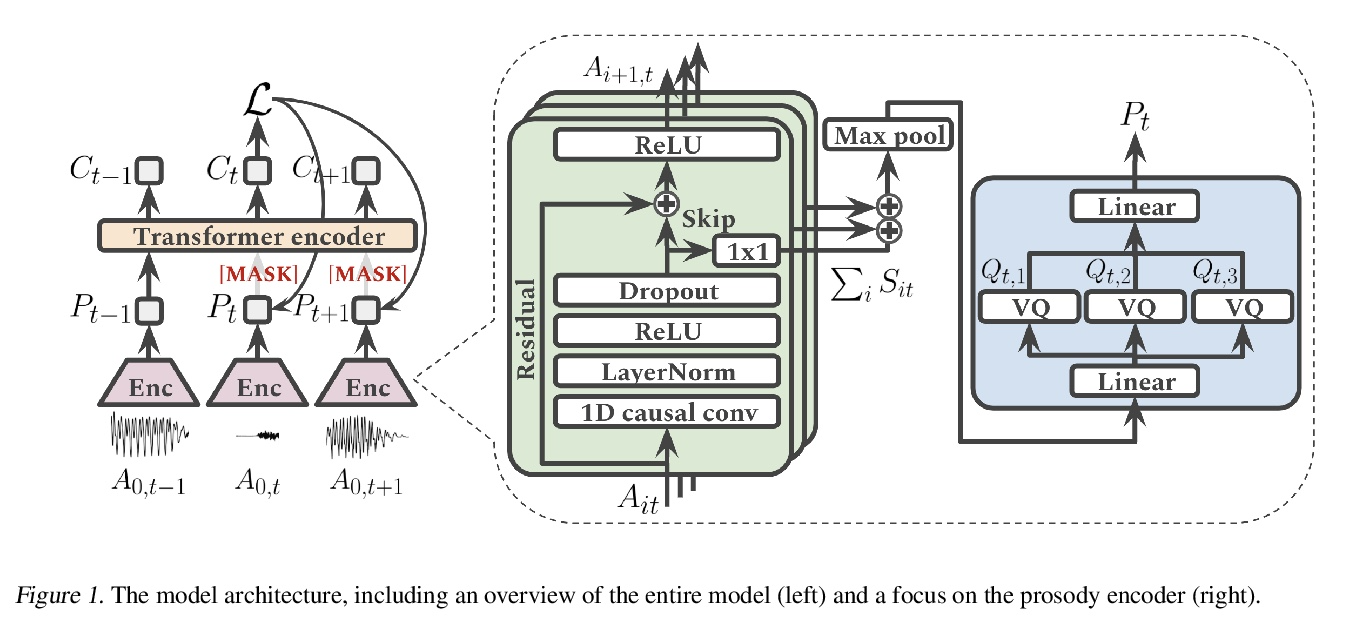
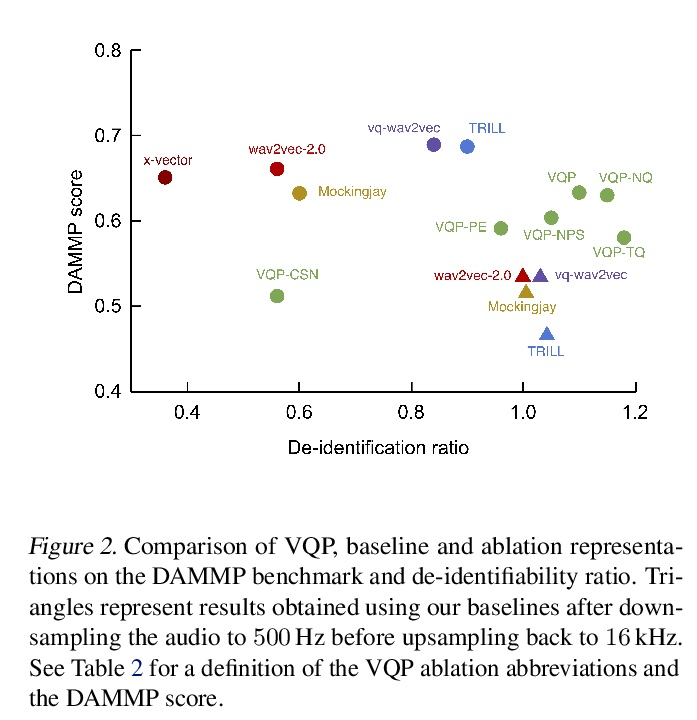
[CL] Learning De-identified Representations of Prosody from Raw Audio
从原始音频中学习韵律的去识别表示
J Weston, R Lenain, U Meepegama, E Fristed
[Novoic]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KpIgRvyMY 
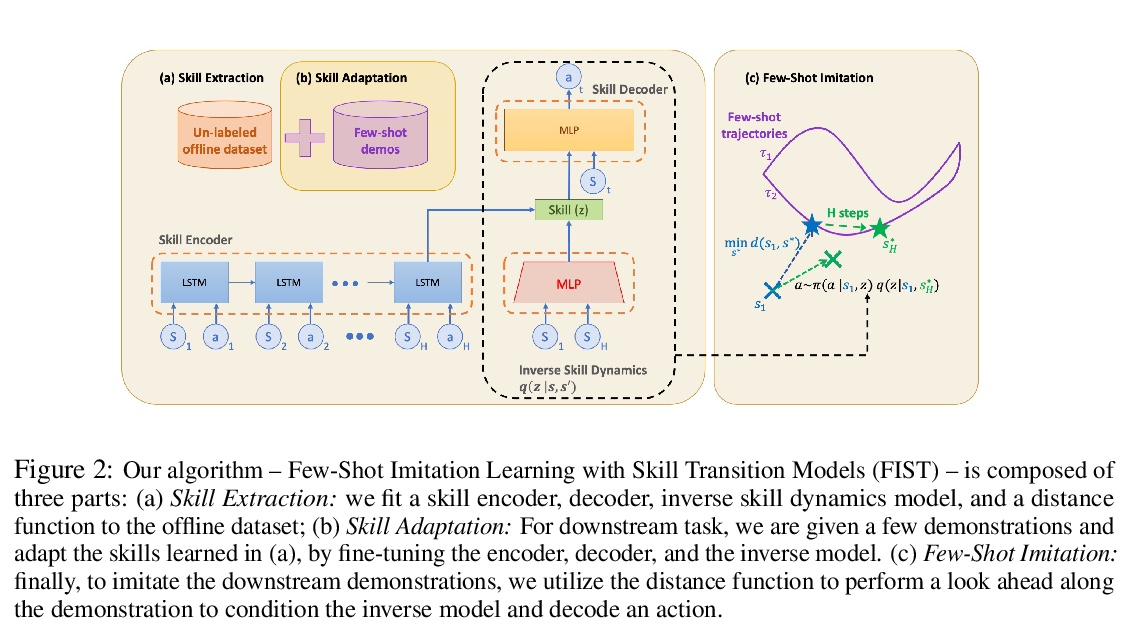
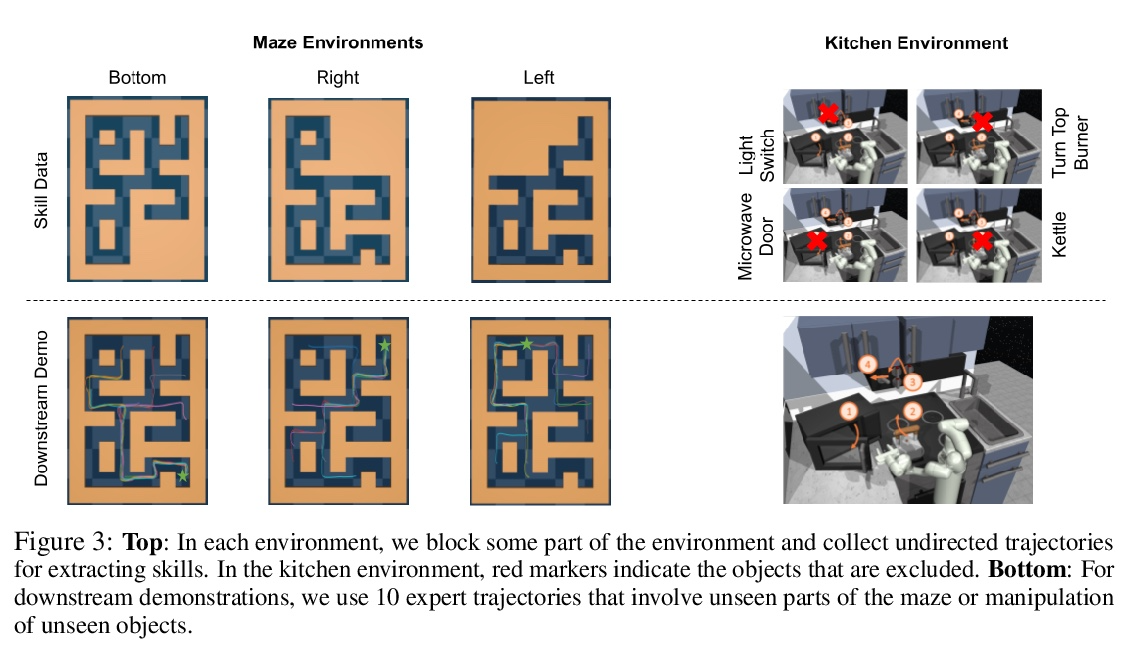
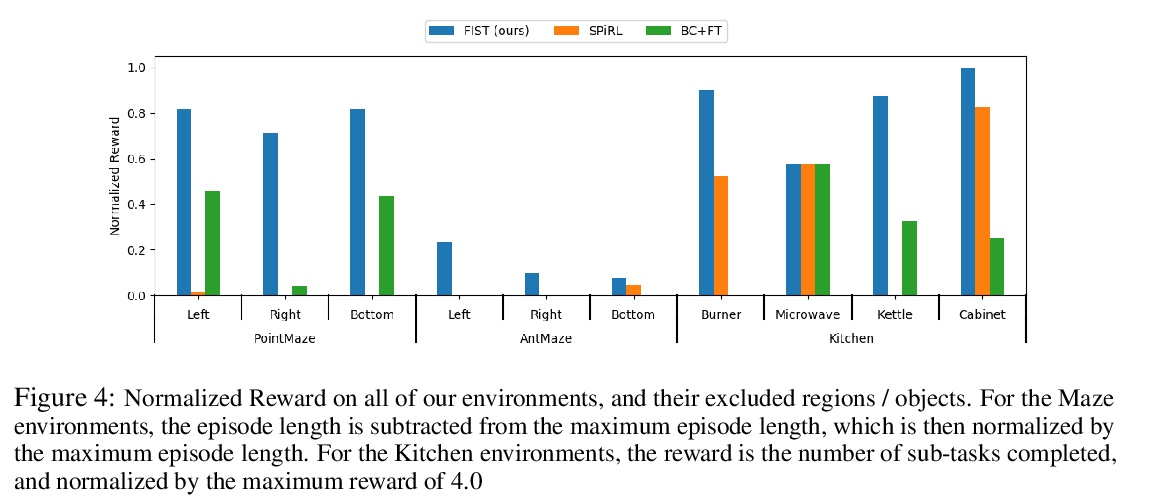
[LG] Hierarchical Few-Shot Imitation with Skill Transition Models
基于技能转换模型的分层少样本模仿
K Hakhamaneshi, R Zhao, A Zhan, P Abbeel, M Laskin
[UC Berkeley]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KpIiJ56zv