- 1、[LG] Flow-based sampling for multimodal distributions in lattice field theory
- 2、[LG] Rapid Neural Architecture Search by Learning to Generate Graphs from Datasets
- 3、[LG] The Uncanny Similarity of Recurrence and Depth
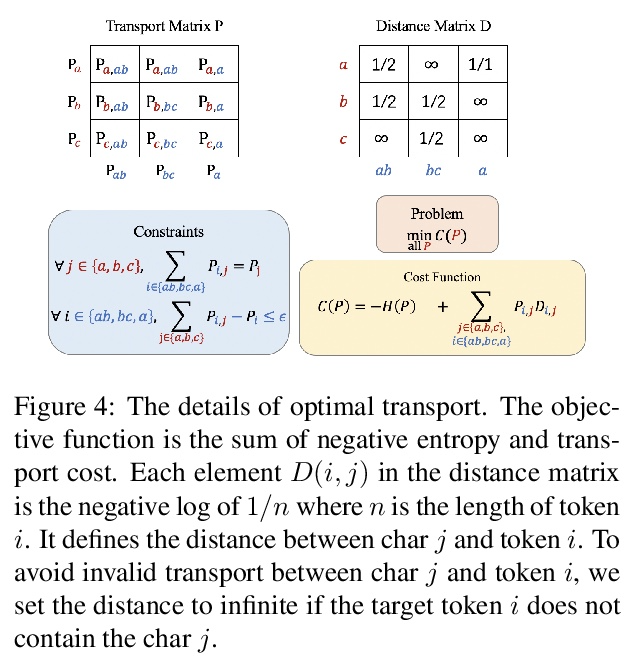
- 4、[CL] Vocabulary Learning via Optimal Transport for Machine Translation
- 5、[CL] All That’s ‘Human’ Is Not Gold: Evaluating Human Evaluation of Generated Text
- [CL] Neural Machine Translation with Monolingual Translation Memory
- [CL] UnNatural Language Inference
- [LG] Can You Learn an Algorithm? Generalizing from Easy to Hard Problems with Recurrent Networks
- [LG] Discrete-Valued Neural Communication
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] Flow-based sampling for multimodal distributions in lattice field theory
D C. Hackett, C Hsieh, M S. Albergo, D Boyda, J Chen, K Chen, K Cranmer, G Kanwar, P E. Shanahan
[MIT & National Taiwan University & New York University & Argonne National Laboratory]
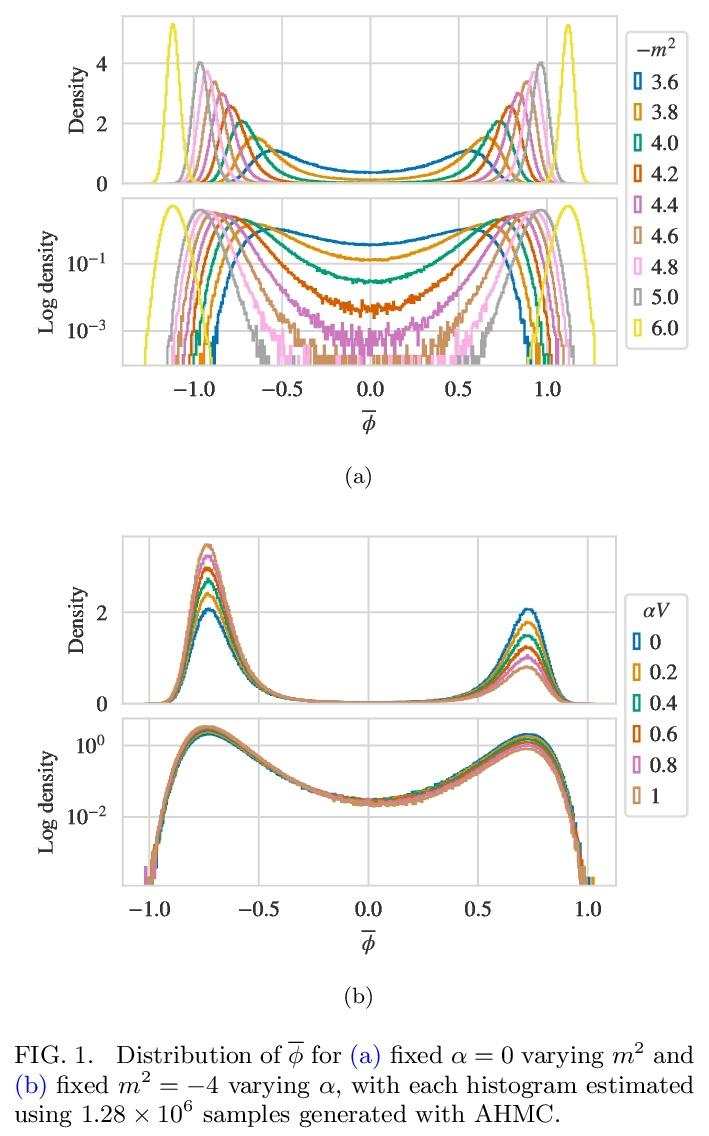
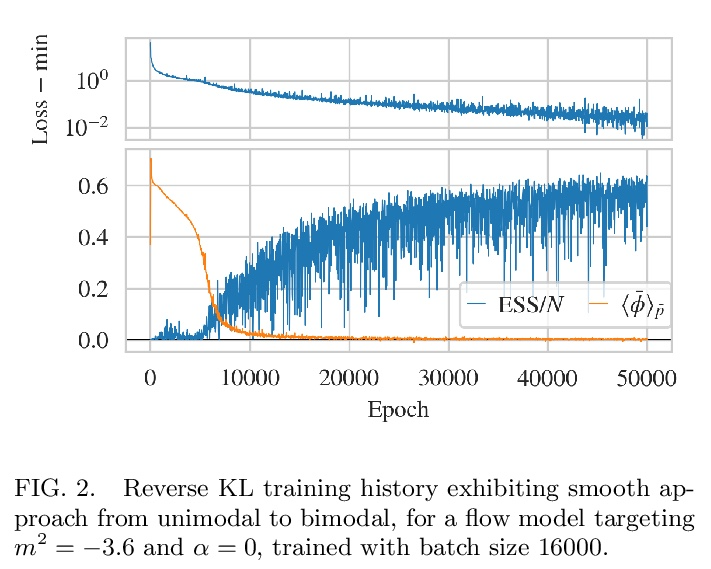
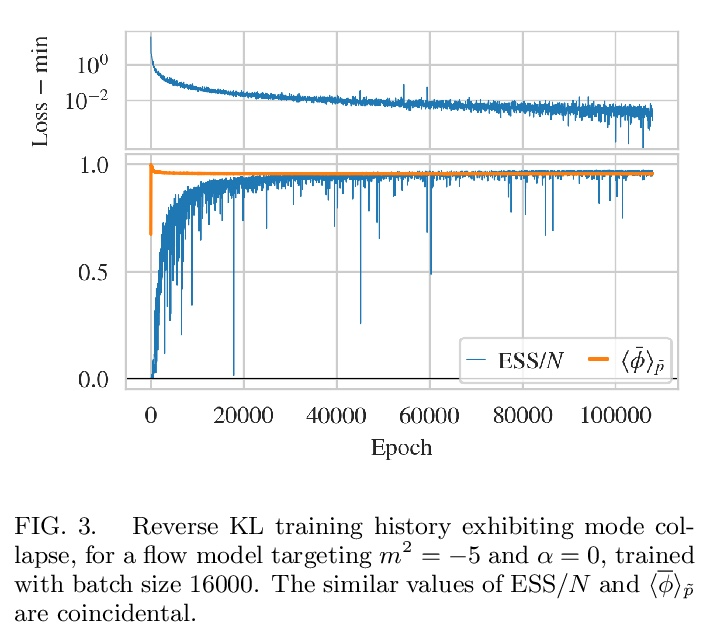
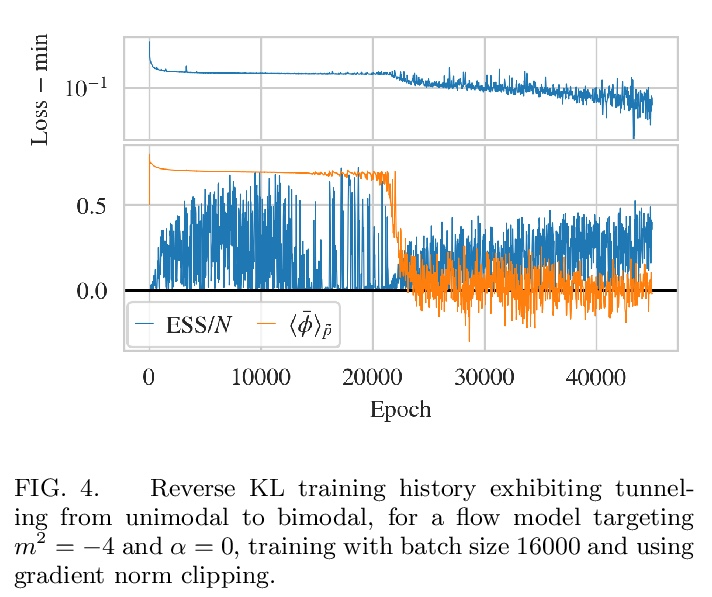
基于流的格点场论多峰分布采样。最近的研究结果表明,用基于流的生成模型构造的采样器,是格点场论配置生成的一种有希望的新方法。本文提出了一套为具有多种分离峰值的目标(即具有多个空间的理论)构建流模型的方法,展示了这些方法在建模二维实标量场理论的对称性破缺阶段的应用。研究了不同的基于流的采样算法的性能,包括一种复合采样算法,在这种算法中,基于流的方法偶尔会通过用HMC等传统算法的更新而得到增强。
Recent results have demonstrated that samplers constructed with flow-based generative models are a promising new approach for configuration generation in lattice field theory. In this paper, we present a set of methods to construct flow models for targets with multiple separated modes (i.e. theories with multiple vacua). We demonstrate the application of these methods to modeling two-dimensional real scalar field theory in its symmetry-broken phase. In this context we investigate the performance of different flow-based sampling algorithms, including a composite sampling algorithm where flow-based proposals are occasionally augmented by applying updates using traditional algorithms like HMC.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KokSh2M6Q 
2、[LG] Rapid Neural Architecture Search by Learning to Generate Graphs from Datasets
H Lee, E Hyung, S J Hwang
[KAIST]
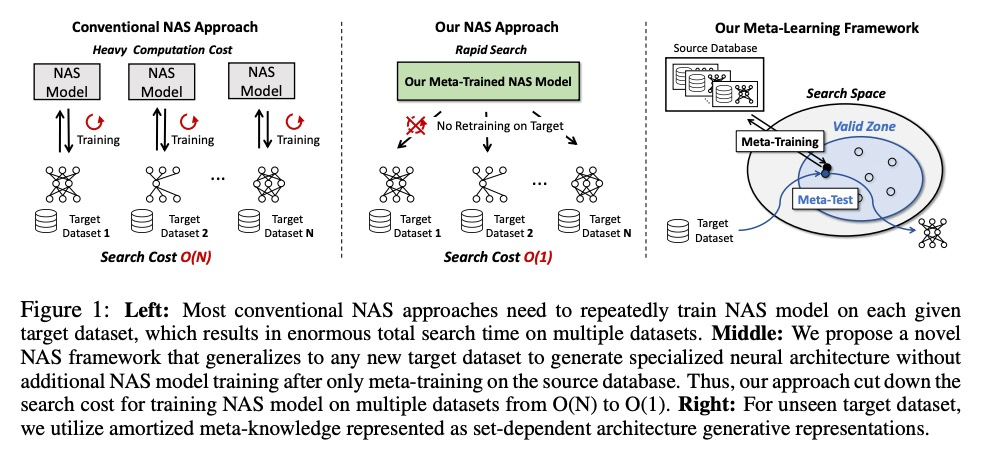
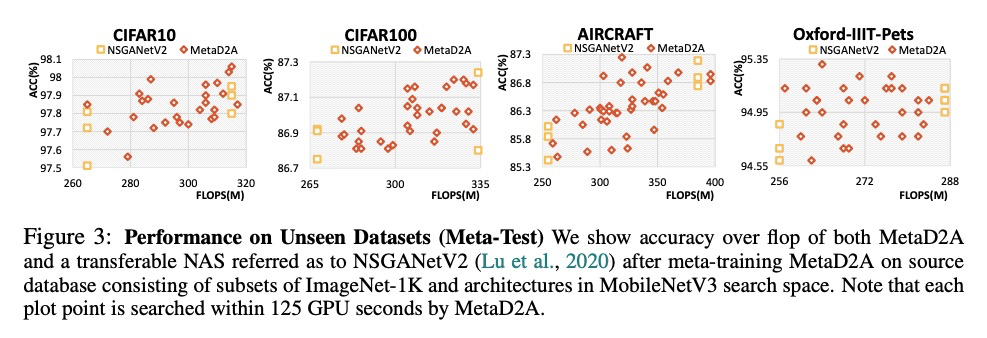
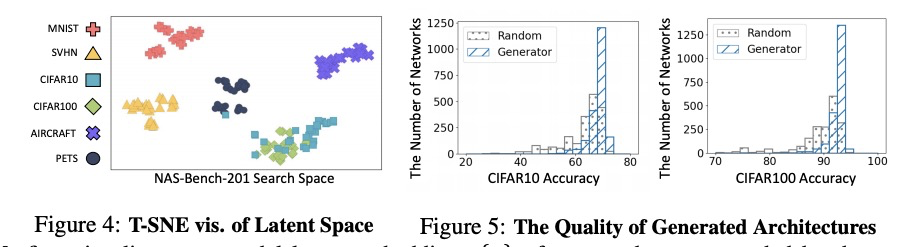
基于数据集图生成学习的快速神经网络架构搜索。尽管最近的神经网络架构搜索(NAS)方法在各种任务上取得了成功,显示出其输出的网络在很大程度上超过了人工设计的网络,但传统的NAS方法大多解决的是为单任务(数据集)搜索网络结构的优化问题,在多任务(数据集)中不能很好地推广。此外,由于这种特定任务的方法为每个给定任务从头开始搜索神经结构,会产生很大的计算成本,在时间和金钱预算有限的情况下是有问题的。本文提出一种高效的NAS框架,在由数据集和预训练网络组成的数据库上训练一次,能为新的数据集快速搜索神经网络架构。所提出的MetaD2A(Meta Dataset-to-Architecture)模型可通过一个用摊余元学习的跨模态潜空间从一个给定的集合(数据集)随机生成图(架构)。提出了一种元性能预测器,以估计和选择最佳架构,无需在目标数据集上直接训练。实验结果表明,在ImageNet-1K的子集和NAS-Bench 201搜索空间的架构上进行元学习的模型成功地推广到多个未见过的数据集,包括CIFAR-10和CIFAR-100,平均搜索时间为33GPU秒。即使在MobileNetV3搜索空间下,MetaD2A也比NSGANetV2这种可转移的NAS方法快5.5K倍,性能相当。MetaD2A为快速NAS提出了新的研究方向,以及利用过去几年积累的丰富的数据集和架构数据库的知识的方法。
Despite the success of recent Neural Architecture Search (NAS) methods on various tasks which have shown to output networks that largely outperform humandesigned networks, conventional NAS methods have mostly tackled the optimization of searching for the network architecture for a single task (dataset), which does not generalize well across multiple tasks (datasets). Moreover, since such task-specific methods search for a neural architecture from scratch for every given task, they incur a large computational cost, which is problematic when the time and monetary budget are limited. In this paper, we propose an efficient NAS framework that is trained once on a database consisting of datasets and pretrained networks and can rapidly search for a neural architecture for a novel dataset. The proposed MetaD2A (Meta Dataset-to-Architecture) model can stochastically generate graphs (architectures) from a given set (dataset) via a cross-modal latent space learned with amortized meta-learning. Moreover, we also propose a meta-performance predictor to estimate and select the best architecture without direct training on target datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that our model meta-learned on subsets of ImageNet-1K and architectures from NAS-Bench 201 search space successfully generalizes to multiple unseen datasets including CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100, with an average search time of 33 GPU seconds. Even under MobileNetV3 search space, MetaD2A is 5.5K times faster than NSGANetV2, a transferable NAS method, with comparable performance. We believe that the MetaD2A proposes a new research direction for rapid NAS as well as ways to utilize the knowledge from rich databases of datasets and architectures accumulated over the past years. Code is available at https://github.com/HayeonLee/MetaD2A.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KokWLoVDO 

3、[LG] The Uncanny Similarity of Recurrence and Depth
A Schwarzschild, A Gupta, A Ghiasi, M Goldblum, T Goldstein
[University of Maryland]
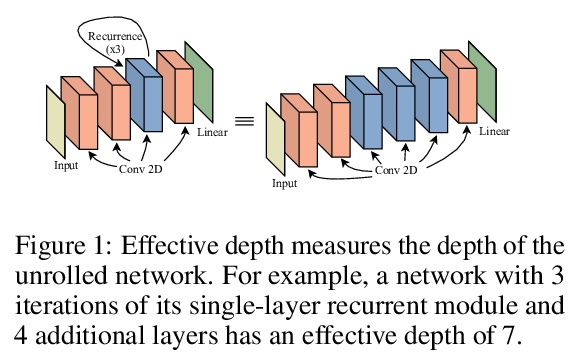
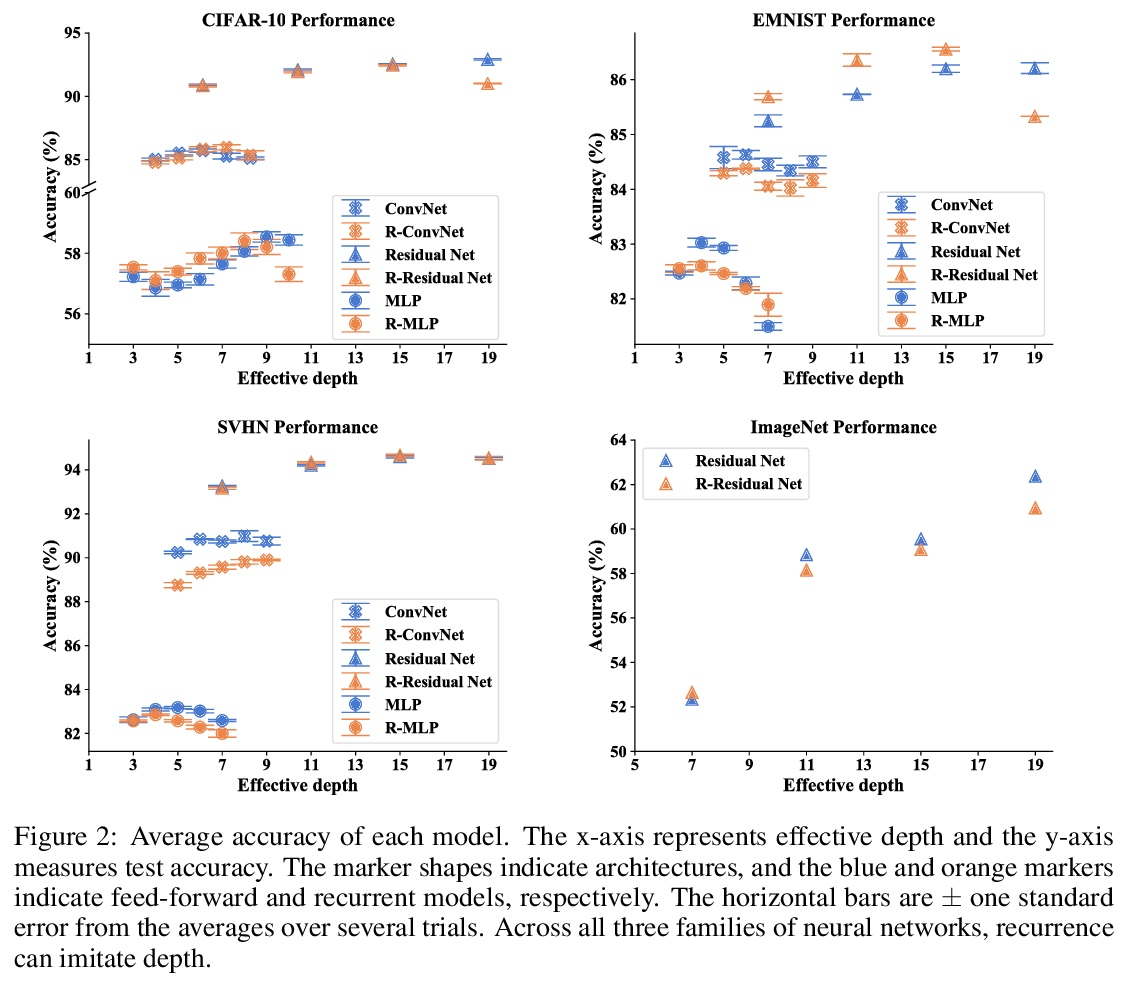
递归和深度不寻常的相似性。人们普遍认为,深度神经网络包含层的特化,在浅层提取代表边缘和模式的层次特征,在深层提取代表完整的对象。不同于普通的前馈模型在每一层都有不同的过滤器,递归网络在不同深度重复使用相同的参数。本文观察到,尽管在每次递归时重复使用相同的过滤器,但递归模型表现出相同的层次行为和类似的性能优势。通过在图像分类和迷宫求解的几个数据集上训练各种前馈和递归结构的模型,我们表明,递归网络有能力高度模仿非递归深度模型的行为,而且往往用更少的参数就能做到。
It is widely believed that deep neural networks contain layer specialization, wherein networks extract hierarchical features representing edges and patterns in shallow layers and complete objects in deeper layers. Unlike common feed-forward models that have distinct filters at each layer, recurrent networks reuse the same parameters at various depths. In this work, we observe that recurrent models exhibit the same hierarchical behaviors and the same performance benefits as depth despite reusing the same filters at every recurrence. By training models of various feed-forward and recurrent architectures on several datasets for image classification as well as maze solving, we show that recurrent networks have the ability to closely emulate the behavior of non-recurrent deep models, often doing so with far fewer parameters.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kol45uJvK 
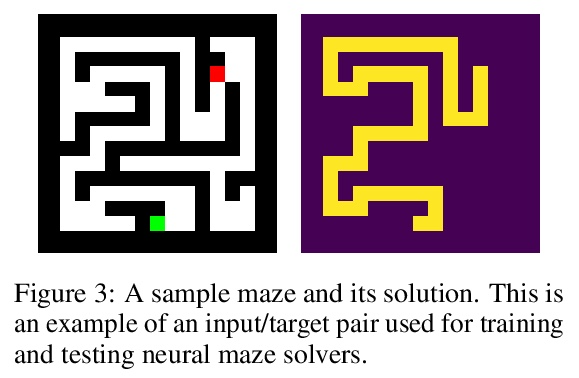
4、[CL] Vocabulary Learning via Optimal Transport for Machine Translation
J Xu, H Zhou, C Gan, Z Zheng, L Li
[ByteDance AI Lab]
面向神经网络机器翻译的最优传输词汇学习。Token词汇的选择会影响机器翻译的性能。本文旨在区分什么是好的词汇,以及是否可以在不进行测试训练的情况下找到最佳词汇。为回答这些问题,首先从信息论的角度对词汇的作用提供了另一种理解。受此启发,将词汇化的目标——寻找具有适当规模的最佳token词典——表述为一个最优传输(OT)问题。提出VOLT,一种简单有效的解决方案,不需要测试训练。经验结果表明,VOLT在不同场景下,包括WMT-14英德和TED多语言翻译中,优于广泛使用的词汇表。例如,VOLT在英德翻译中实现了近70%的词汇量减少和0.5的BLEU增益。此外,与BPE-搜索相比,VOLT将英德翻译的搜索时间从384个GPU小时减少到30个GPU小时。
The choice of token vocabulary affects the performance of machine translation. This paper aims to figure out what is a good vocabulary and whether one can find the optimal vocabulary without trial training. To answer these questions, we first provide an alternative understanding of the role of vocabulary from the perspective of information theory. Motivated by this, we formulate the quest of vocabularization – finding the best token dictionary with a proper size – as an optimal transport (OT) problem. We propose VOLT, a simple and efficient solution without trial training. Empirical results show that VOLT outperforms widely-used vocabularies in diverse scenarios, including WMT-14 English-German and TED multilingual translation. For example, VOLT achieves almost 70% vocabulary size reduction and 0.5 BLEU gain on English-German translation. Also, compared to BPE-search, VOLT reduces the search time from 384 GPU hours to 30 GPU hours on English-German translation.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kol7miOtD 

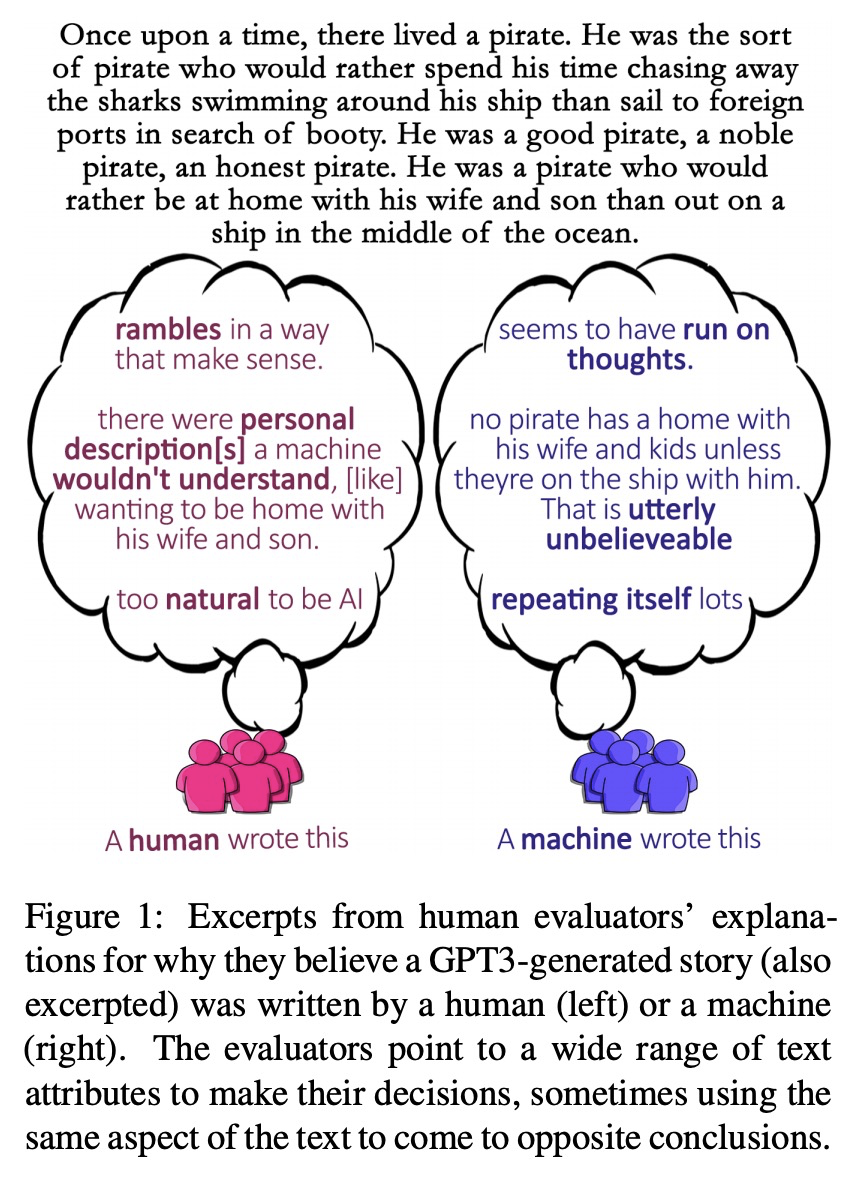
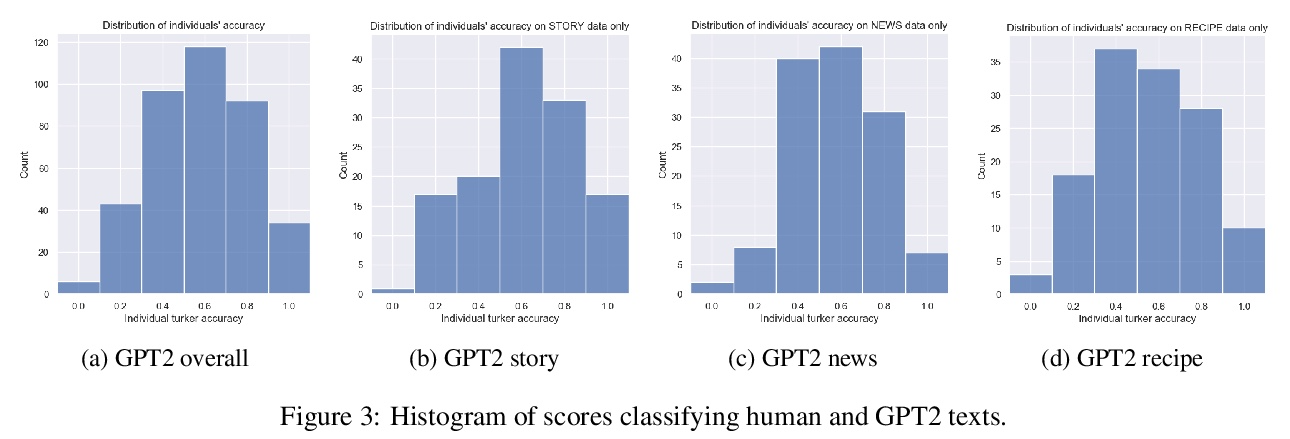
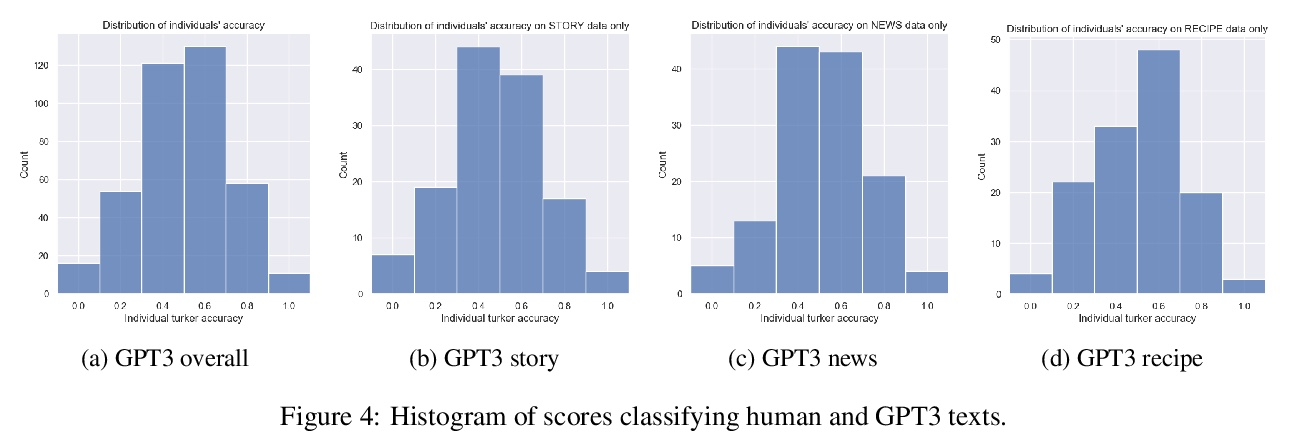
5、[CL] All That’s ‘Human’ Is Not Gold: Evaluating Human Evaluation of Generated Text
E Clark, T August, S Serrano, N Haduong, S Gururangan, N A. Smith
[University of Washington]
并非所有”人工”都绝对标准:对生成文本人工评价的评价。人工评价通常被认为是自然语言生成的绝对标准,但随着模型流畅性的提高,评价者能多大程度上检测和判断机器生成文本?本文进行了一项研究,评估非专家在三个领域(故事、新闻文章和菜谱)区分人工和机器撰写文本(GPT2和GPT3)的能力。在没有训练的情况下,评价者只能在随机水平上区分GPT3和人工撰写的文本。探讨了三种快速培训评估人员以更好地识别GPT3撰写文本的方法(详细说明、注释的样本和配对样本),发现虽然评价人员的准确率提高到55%,但在三个领域中并没有明显改善。鉴于不同文本领域的结果不一致,以及评估人员给出的判断理由往往相互矛盾,研究了未经训练的人工评价在NLG评价中发挥的作用,并向NLG研究人员提供建议,以改善人工对由最先进模型生成的文本的评价。
Human evaluations are typically considered the gold standard in natural language generation, but as models’ fluency improves, how well can evaluators detect and judge machinegenerated text? We run a study assessing nonexperts’ ability to distinguish between humanand machine-authored text (GPT2 and GPT3) in three domains (stories, news articles, and recipes). We find that, without training, evaluators distinguished between GPT3and humanauthored text at random chance level. We explore three approaches for quickly training evaluators to better identify GPT3-authored text (detailed instructions, annotated examples, and paired examples) and find that while evaluators’ accuracy improved up to 55%, it did not significantly improve across the three domains. Given the inconsistent results across text domains and the often contradictory reasons evaluators gave for their judgments, we examine the role untrained human evaluations play in NLG evaluation and provide recommendations to NLG researchers for improving human evaluations of text generated from state-of-the-art models.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KolafA4Dz 

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
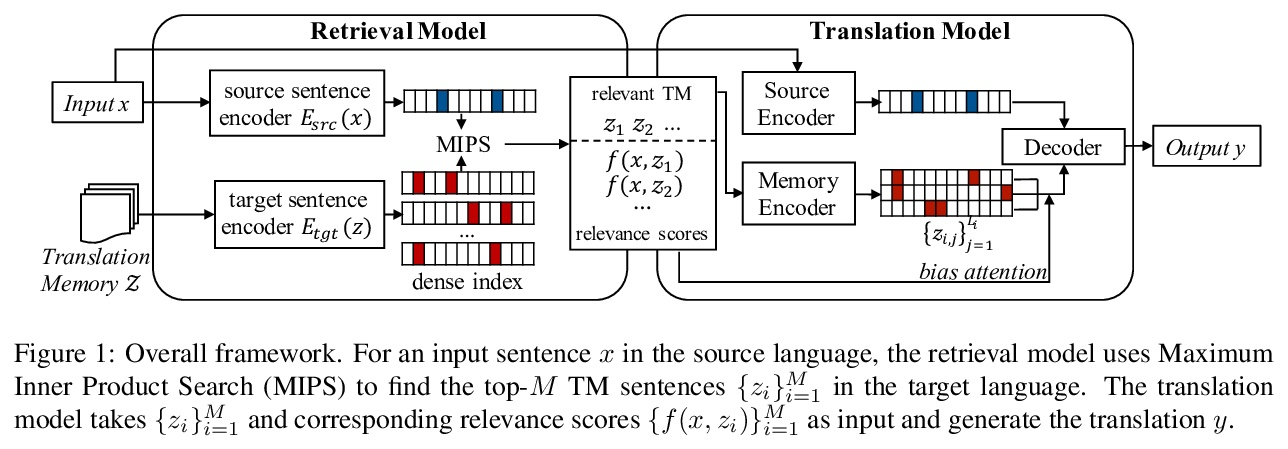
[CL] Neural Machine Translation with Monolingual Translation Memory
基于单语翻译记忆的神经网络机器翻译
D Cai, Y Wang, H Li, W Lam, L Liu
[Tencent AI Lab]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KolkDdmiF 
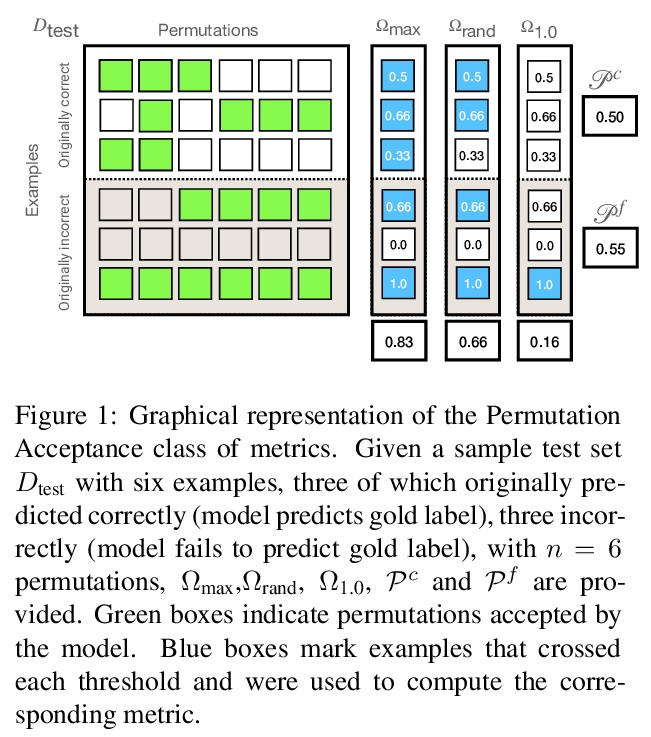
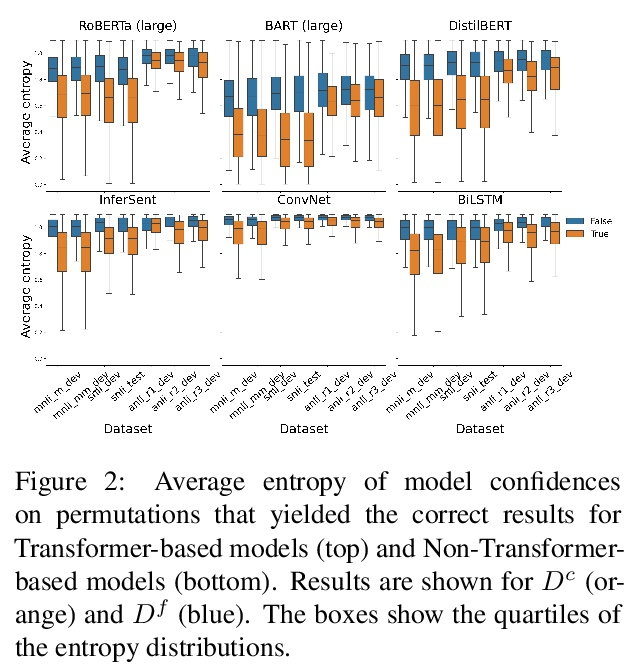
[CL] UnNatural Language Inference
“忽略”语法的非自然语言推理
K Sinha, P Parthasarathi, J Pineau, A Williams
[McGill University & Facebook AI Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kolom2pKg 
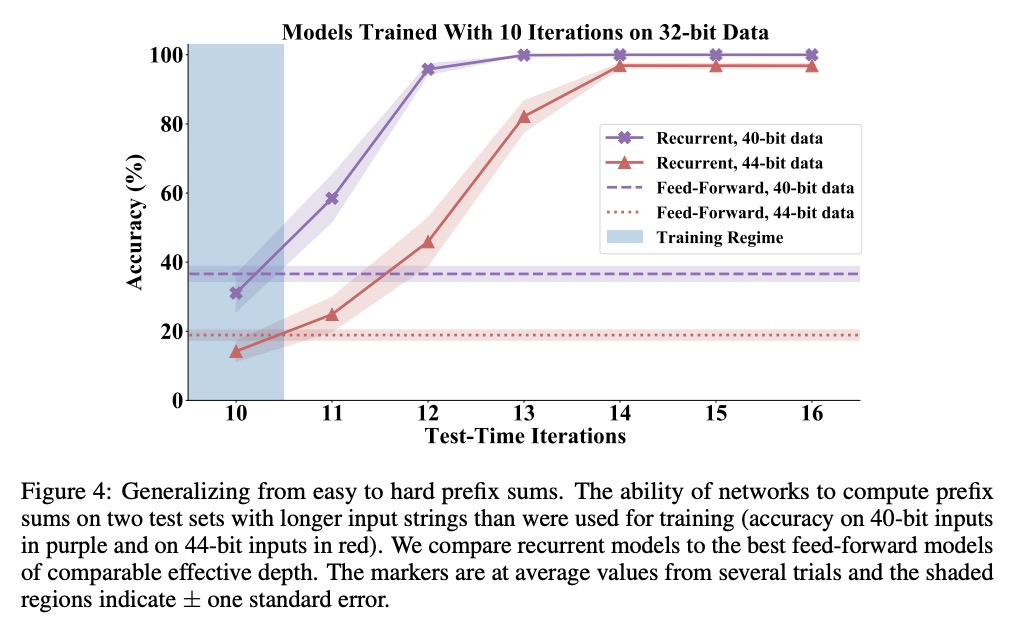
[LG] Can You Learn an Algorithm? Generalizing from Easy to Hard Problems with Recurrent Networks
你能学会某种算法吗?用递归网络从容易问题扩展到困难问题
A Schwarzschild, E Borgnia, A Gupta, F Huang, U Vishkin, M Goldblum, T Goldstein
[University of Maryland]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KolqA10cQ 

[LG] Discrete-Valued Neural Communication
离散值神经通信
D L Dianbo_Liu, A Lamb, K Kawaguchi, A Goyal, C Sun, M C Mozer, Y Bengio
[Mila & Harvard University & Google Brain ]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KolsDnn9k