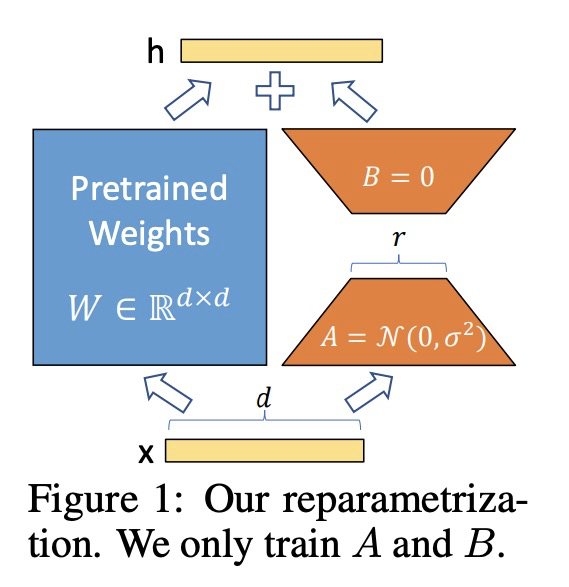
- 1、[CL] LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models
- 2、[CV] JOKR: Joint Keypoint Representation for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Motion Retargeting
- 3、[LG] Deep Learning Through the Lens of Example Difficulty
- 4、[CL] Multi-head or Single-head? An Empirical Comparison for Transformer Training
- 5、[RO] Cat-like Jumping and Landing of Legged Robots in Low-gravity Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
- [AS] WaveGrad 2: Iterative Refinement for Text-to-Speech Synthesis
- [LG] Algorithmic Bias and Data Bias: Understanding the Relation between Distributionally Robust Optimization and Data Curation
- [CV] XCiT: Cross-Covariance Image Transformers
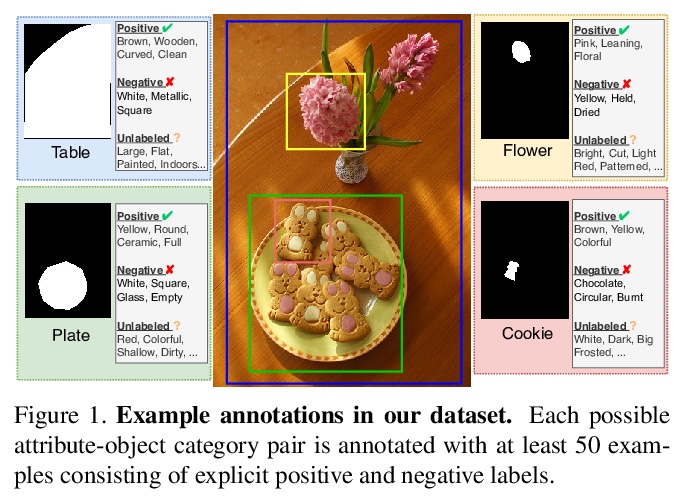
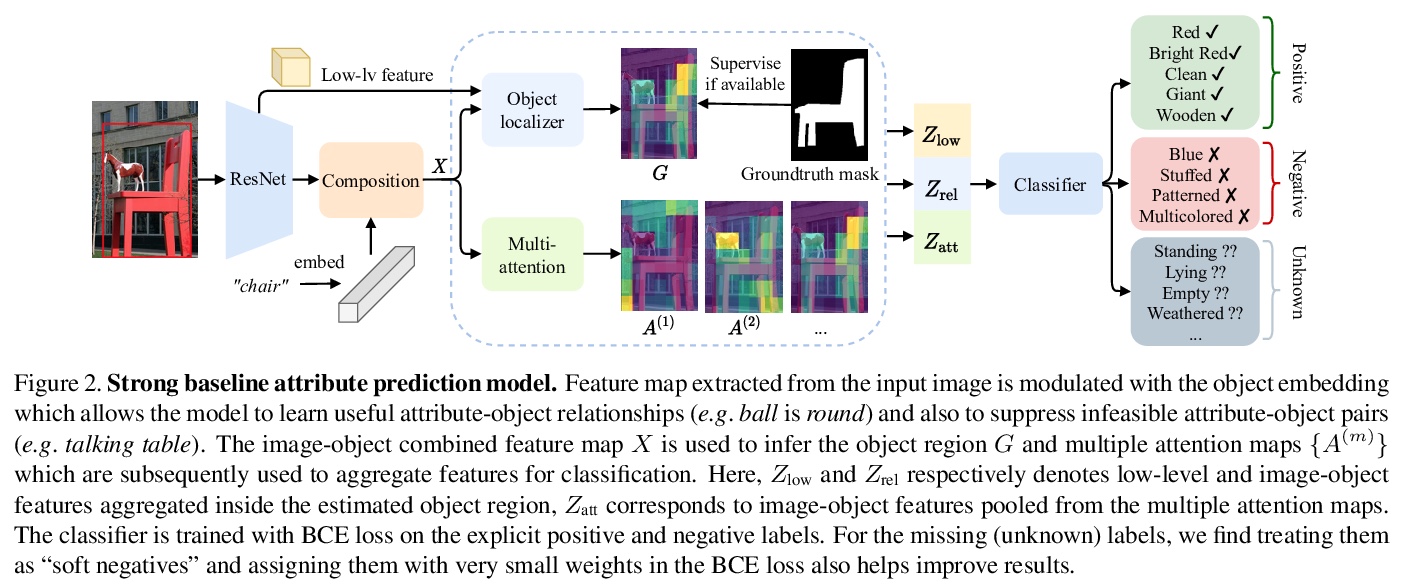
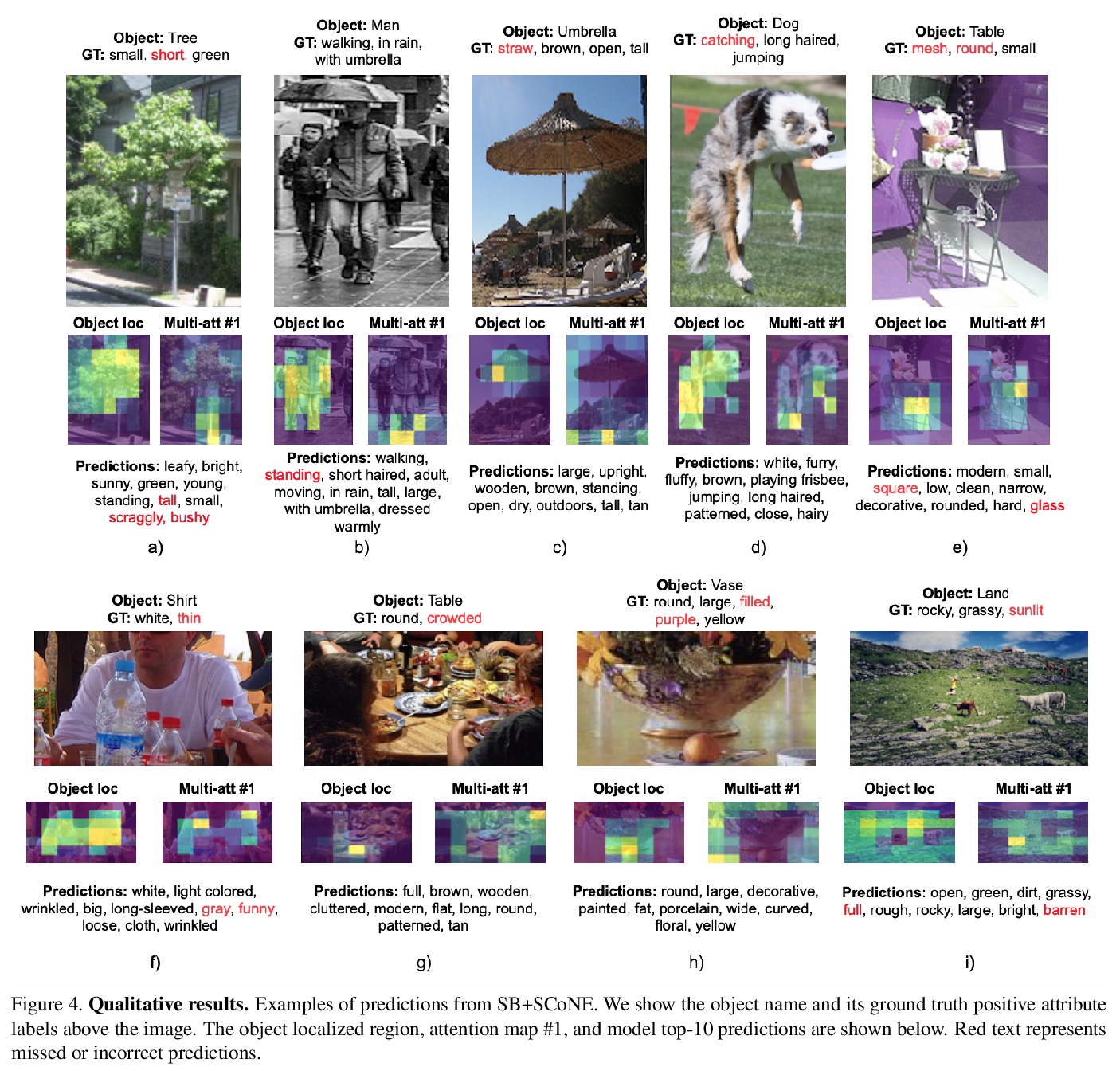
- [CV] Learning to Predict Visual Attributes in the Wild
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CL] LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models
E J. Hu, Y Shen, P Wallis, Z Allen-Zhu, Y Li, S Wang, W Chen
[Microsoft]
LoRA:大型语言模型低秩自适应。自然语言处理的主流范式,包括对通用领域的数据进行大规模预训练,以及对特定任务或域的自适应。随着对更大的模型进行预训练,传统的微调,即重新训练所有模型参数,变得不太可行。以GPT-3 175B为例,部署许多独立的微调模型实例,每个都有175B的参数,是非常昂贵的。本文提出低秩自适应LoRA,冻结预训练模型权重,将可训练的秩分解矩阵注入到Transformer架构每一层,大大减少了下游任务的可训练参数数量。对于GPT-3,与全微调相比,LoRA将可训练参数数量减少10,000倍,计算硬件需求减少3倍。LoRA在GPT-3和GPT-2上的模型质量表现与微调持平或更好,且可训练参数更少,训练吞吐量更高,没有额外的推理延时。
The dominant paradigm of natural language processing consists of large-scale pre-training on general domain data and adaptation to particular tasks or domains. As we pre-train larger models, conventional fine-tuning, which retrains all model parameters, becomes less feasible. Using GPT-3 175B as an example, deploying many independent instances of fine-tuned models, each with 175B parameters, is extremely expensive. We propose Low-Rank Adaptation, or LoRA, which freezes the pre-trained model weights and injects trainable rank decomposition matrices into each layer of the Transformer architecture, greatly reducing the number of trainable parameters for downstream tasks. For GPT-3, LoRA can reduce the number of trainable parameters by 10,000 times and the computation hardware requirement by 3 times compared to full fine-tuning. LoRA performs on-par or better than fine-tuning in model quality on both GPT-3 and GPT-2, despite having fewer trainable parameters, a higher training throughput, and no additional inference latency. We also provide an empirical investigation into rank-deficiency in language model adaptations, which sheds light on the efficacy of LoRA.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkQ47xEkm
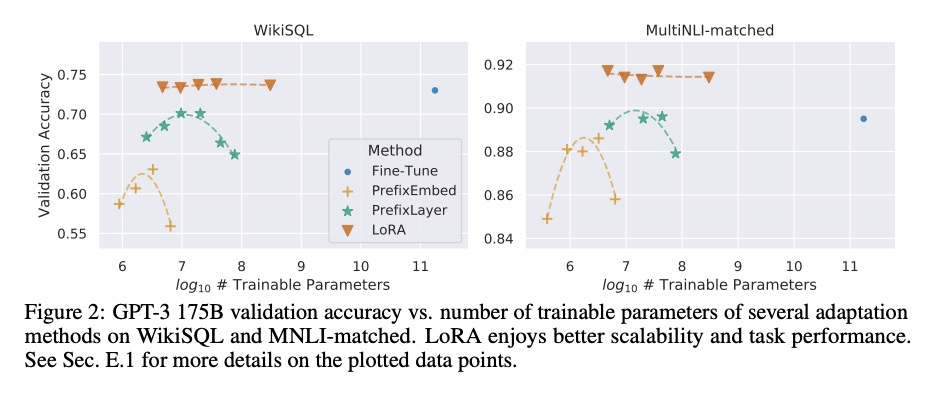
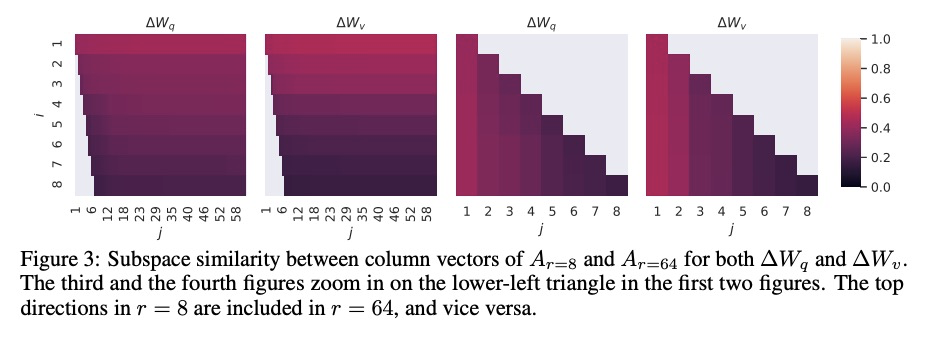
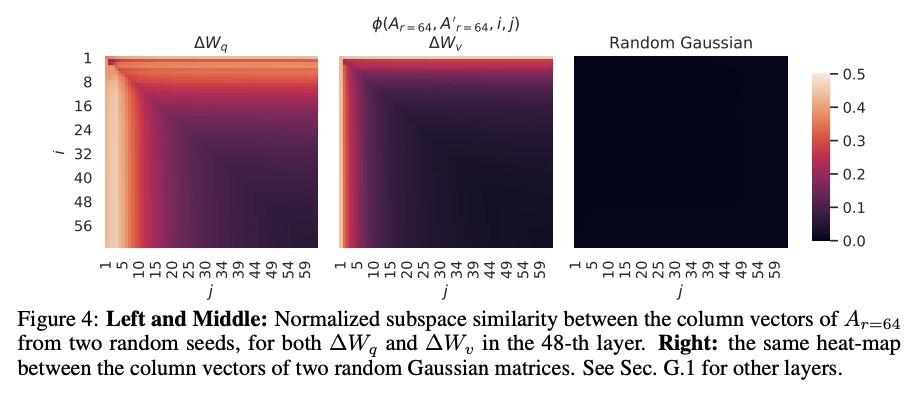
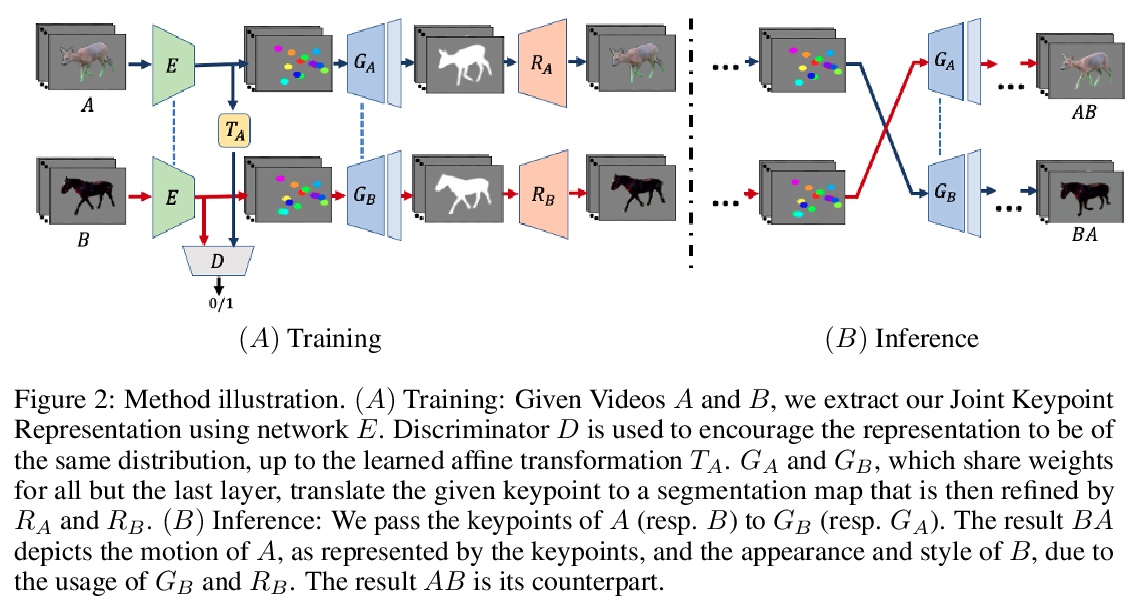
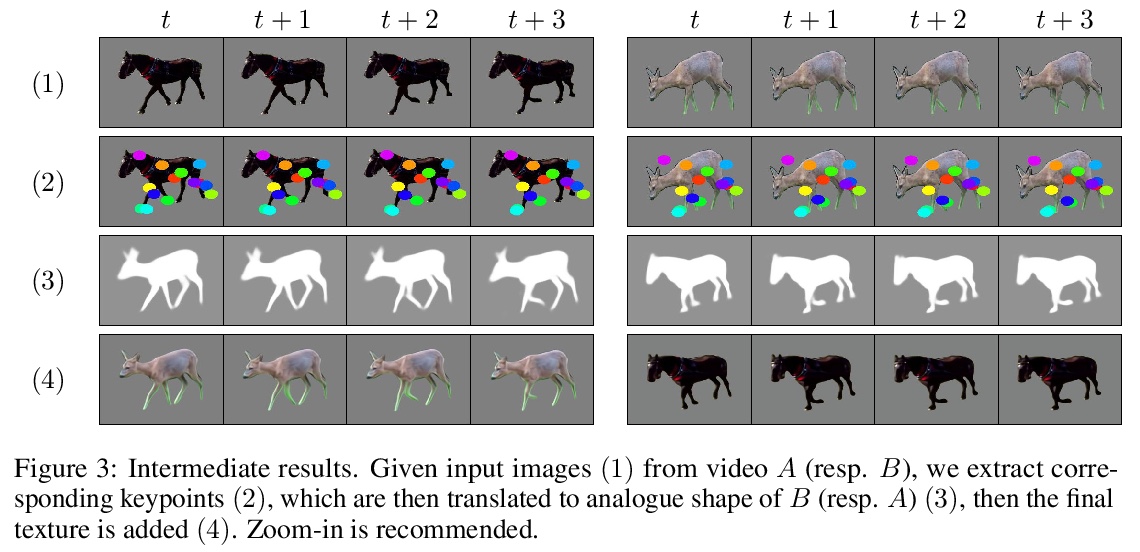
2、[CV] JOKR: Joint Keypoint Representation for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Motion Retargeting
R Mokady, R Tzaban, S Benaim, A H. Bermano, D Cohen-Or
[Tel Aviv University]
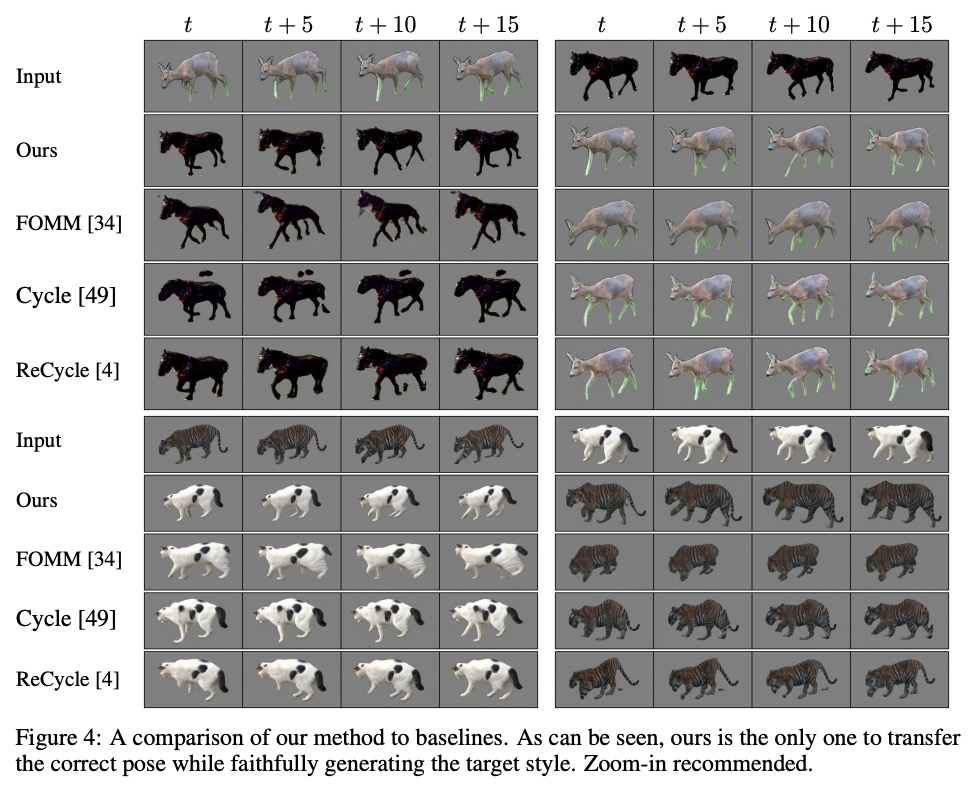
JOKR:面向无监督跨域运动重定位的联合关键点表示。通过使用深度神经网络,视频中的无监督运动重定向任务已经有了实质性的进展。早期的工作集中在特定的目标先验上,如人脸或身体,而最近的工作则考虑了无监督的情况。然而,当源视频和目标视频的形状不同时,目前方法就会失败。为缓解该问题,提出了联合关键点表示JOKR,可捕捉源视频和目标视频的共同运动,不需要任何目标先验或数据收集。通过领域混淆项,强制要求两视频无监督关键点表示不可区分,鼓励两个领域共同运动部分与它们独特的外观和运动之间进行解缠,使生成的视频能捕捉一个领域的运动,同时描述另一个领域的风格。为了使物体具有不同的比例或方向,在JOKR之间应用习得的仿射变换,这增强了表示的仿射不变性,并在实践中扩大了可能的重定位对的种类。这种几何驱动的表示,能进一步实现直观的控制,如时间上的一致性和手工编辑。通过全面的实验,证明了该方法对不同挑战的跨域视频对的适用性。对该方法进行了定性和定量的评估,证明其可以处理各种跨域情况,如不同的动物、不同的花和人。通过统计指标和用户研究,证明了与最先进的替代方法相比,该方法的时间一致性和视觉质量更出色。
The task of unsupervised motion retargeting in videos has seen substantial advancements through the use of deep neural networks. While early works concentrated on specific object priors such as a human face or body, recent work considered the unsupervised case. When the source and target videos, however, are of different shapes, current methods fail. To alleviate this problem, we introduce JOKR a JOint Keypoint Representation that captures the motion common to both the source and target videos, without requiring any object prior or data collection. By employing a domain confusion term, we enforce the unsupervised keypoint representations of both videos to be indistinguishable. This encourages disentanglement between the parts of the motion that are common to the two domains, and their distinctive appearance and motion, enabling the generation of videos that capture the motion of the one while depicting the style of the other. To enable cases where the objects are of different proportions or orientations, we apply a learned affine transformation between the JOKRs. This augments the representation to be affine invariant, and in practice broadens the variety of possible retargeting pairs. This geometry-driven representation enables further intuitive control, such as temporal coherence and manual editing. Through comprehensive experimentation, we demonstrate the applicability of our method to different challenging cross-domain video pairs. We evaluate our method both qualitatively and quantitatively, and demonstrate that our method handles various cross-domain scenarios, such as different animals, different flowers, and humans. We also demonstrate superior temporal coherency and visual quality compared to state-of-the-art alternatives, through statistical metrics and a user study.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkQ8WC6QN
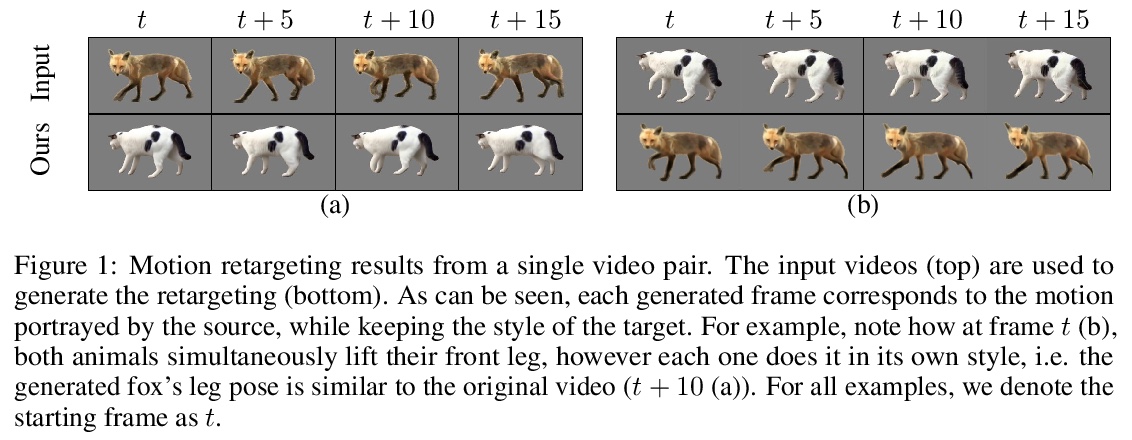

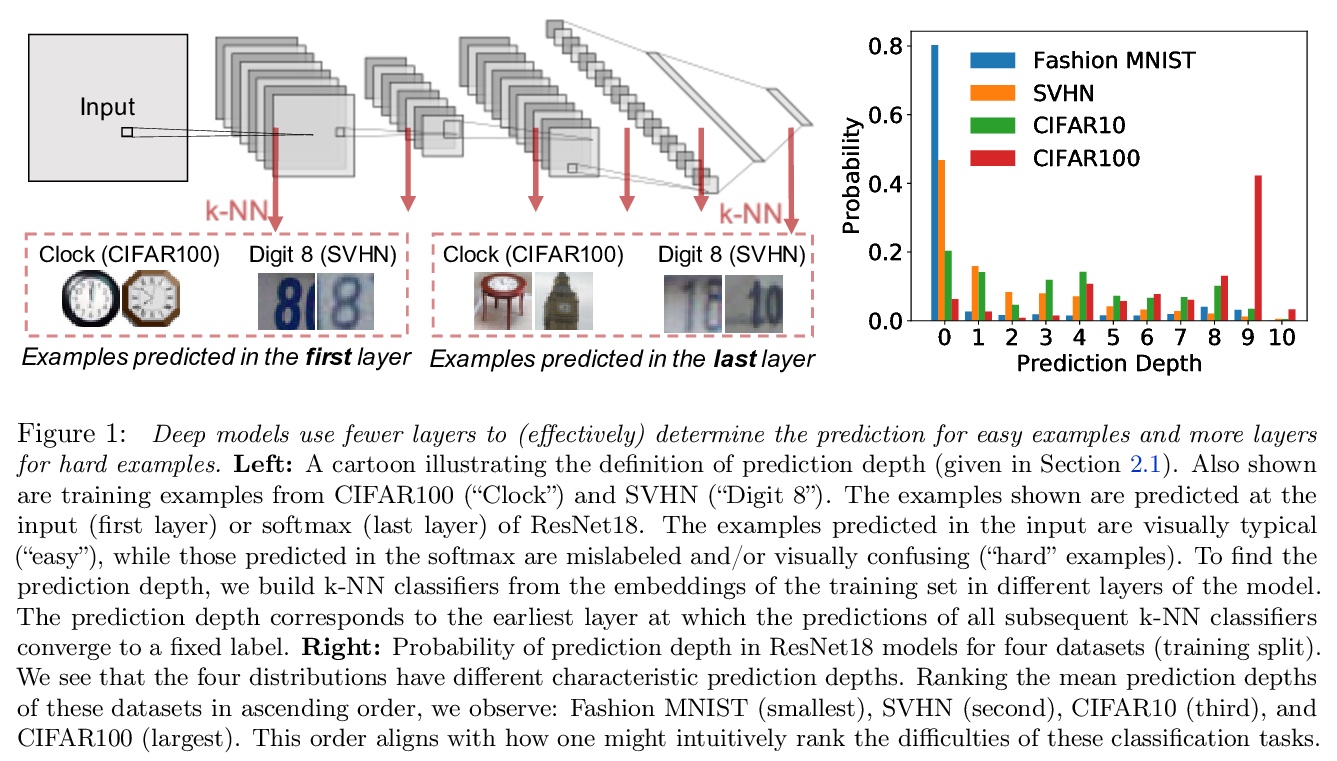
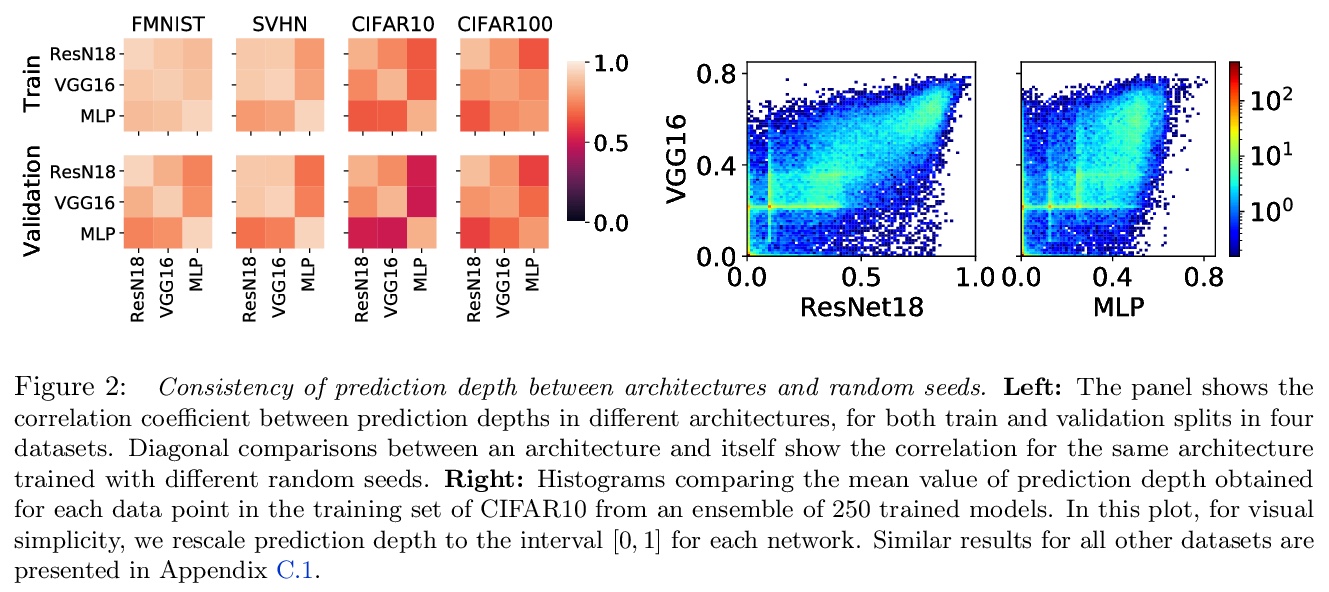
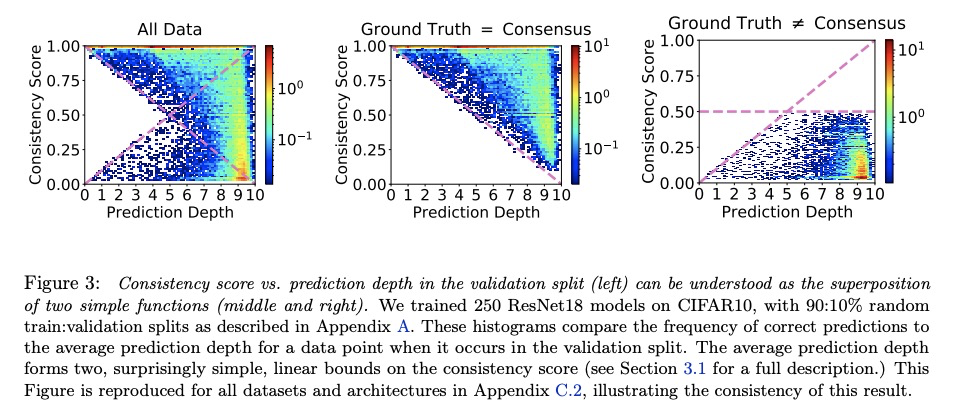
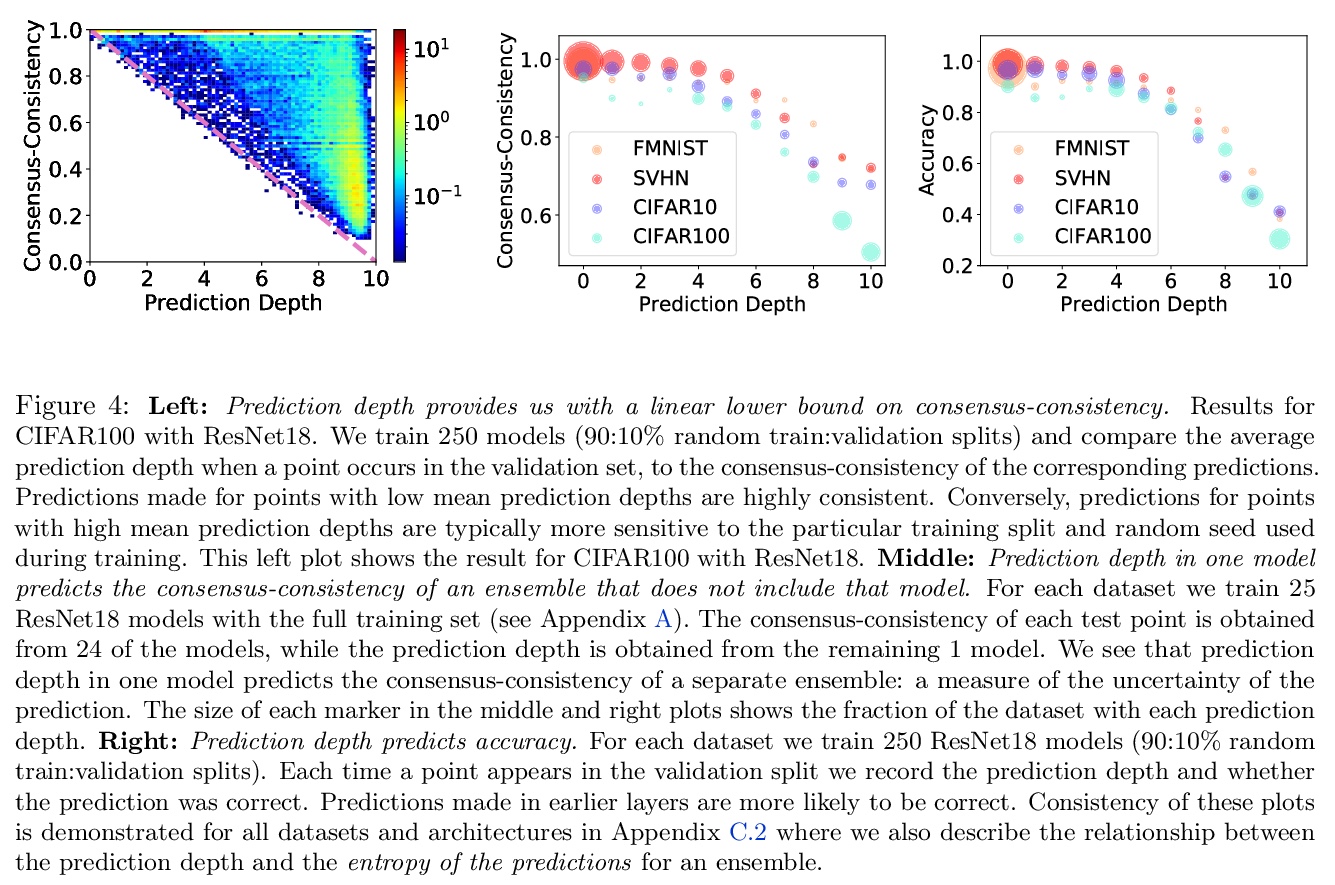
3、[LG] Deep Learning Through the Lens of Example Difficulty
R J. N. Baldock, H Maennel, B Neyshabur
[Google Research]
从样本难度的角度看深度学习。现有的关于理解深度学习的工作,往往是将所有与数据相关信息压缩成几个数字。本文采用一种基于单样本作用的观点。引入一个衡量对给定输入进行预测的计算难度的标准:(有效)预测深度,利用网络内部的数据处理,对一个样本的难度进行评分。通过广泛调查,揭示了一个给定输入的预测深度与模型的不确定性、置信、准确性和对该数据点的学习速度之间令人惊讶但又简单的关系。进一步将困难样本分为三个可解释的组,展示了这些组在深度模型内的不同处理方式,展示了这种理解会如何提高预测的准确性。从研究中得到的启示使得对文献中一些单独报道的现象有了一致的看法:前面的层泛化,而后面的层记忆;前面的层收敛更快,网络首先学习容易的数据和简单的函数。
Existing work on understanding deep learning often employs measures that compress all data-dependent information into a few numbers. In this work, we adopt a perspective based on the role of individual examples. We introduce a measure of the computational difficulty of making a prediction for a given input: the (effective) prediction depth. Our extensive investigation reveals surprising yet simple relationships between the prediction depth of a given input and the model’s uncertainty, confidence, accuracy and speed of learning for that data point. We further categorize difficult examples into three interpretable groups, demonstrate how these groups are processed differently inside deep models and showcase how this understanding allows us to improve prediction accuracy. Insights from our study lead to a coherent view of a number of separately reported phenomena in the literature: early layers generalize while later layers memorize; early layers converge faster and networks learn easy data and simple functions first.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkQeWEFue
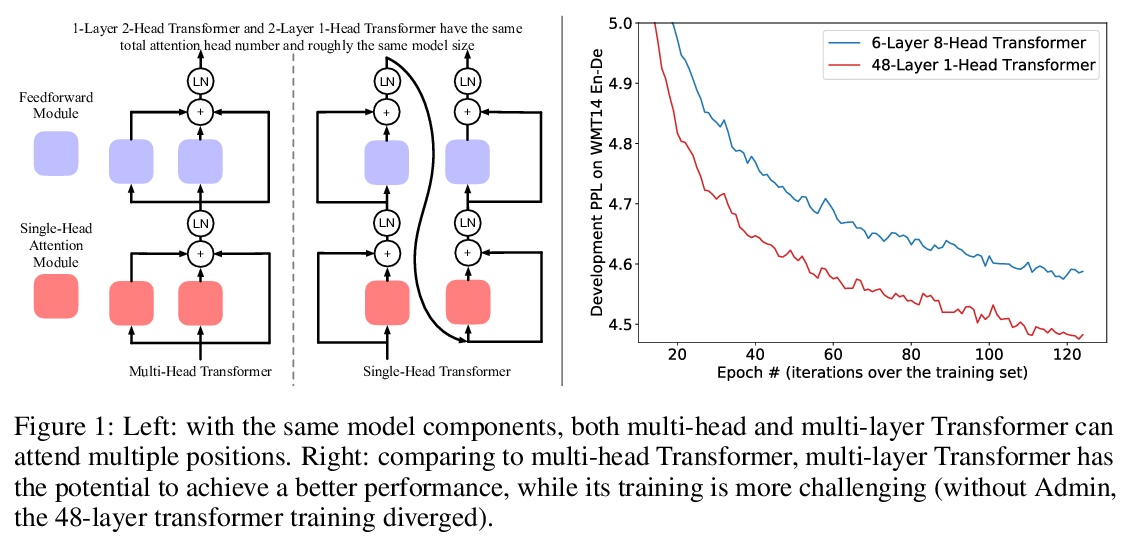
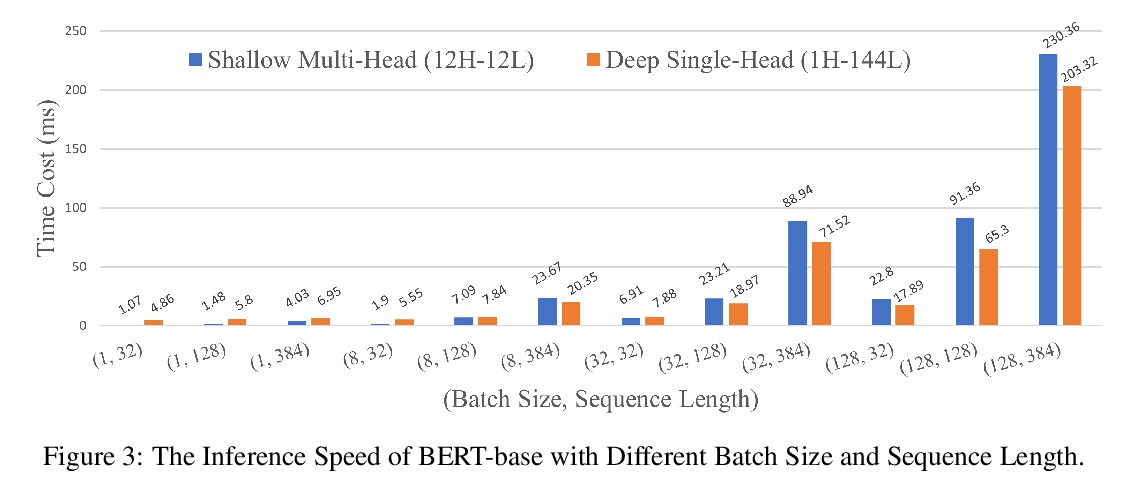
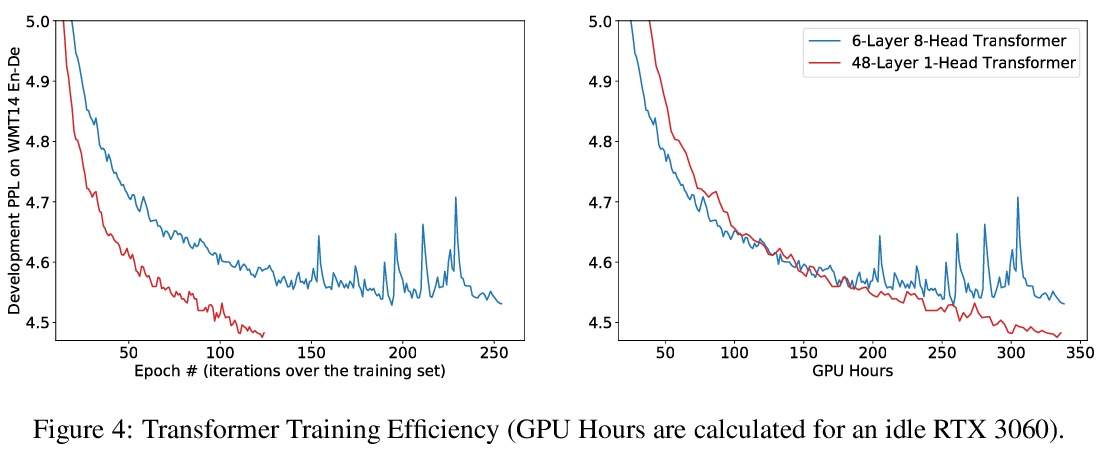
4、[CL] Multi-head or Single-head? An Empirical Comparison for Transformer Training
L Liu, J Liu, J Han
[University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign & Google Research]
多头还是单头?Transformer训练的实证比较。多头注意力在最近Transformer模型的成功中,起着至关重要的作用,在各种应用中比传统的注意力有持续的性能改进。流行的看法是,这种有效性源于联合关注多个位置的能力。本文首先证明了联合注意多个位置,并不是多头注意力的独特功能,多层单头注意力也会注意多个位置,而且更有效。多头注意力的主要优点是训练的稳定性,在注意相同数量位置时,层数比单头注意力少。例如,24层16头的Transformer(BERT-large)和384层的单头Transformer具有相同的总注意力头数和大致相同的模型大小,而多头的则明显更浅。随着深度学习的最新进展,已经可以成功地稳定384层Transformer的训练,由于训练难度不再是瓶颈,大幅加深的单头Transformer在不调整超参数的情况下实现了性能的持续改善。
Multi-head attention plays a crucial role in the recent success of Transformer models, which leads to consistent performance improvements over conventional attention in various applications. The popular belief is that this effectiveness stems from the ability of jointly attending multiple positions. In this paper, we first demonstrate that jointly attending multiple positions is not a unique feature of multi-head attention, as multi-layer single-head attention also attends multiple positions and is more effective. Then, we suggest the main advantage of the multi-head attention is the training stability, since it has less number of layers than the single-head attention, when attending the same number of positions. For example, 24-layer 16-head Transformer (BERT-large) and 384-layer single-head Transformer has the same total attention head number and roughly the same model size, while the multi-head one is significantly shallower. Meanwhile, we show that, with recent advances in deep learning, we can successfully stabilize the training of the 384-layer Transformer. As the training difficulty is no longer a bottleneck, substantially deeper single-head Transformer achieves consistent performance improvements without tuning hyper-parameters.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkQixa7qJ
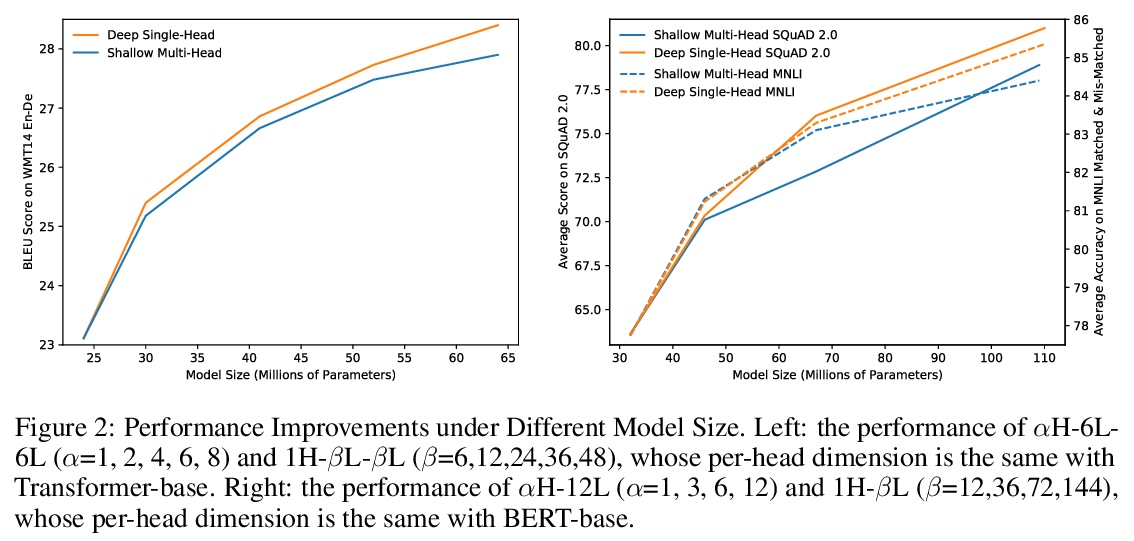
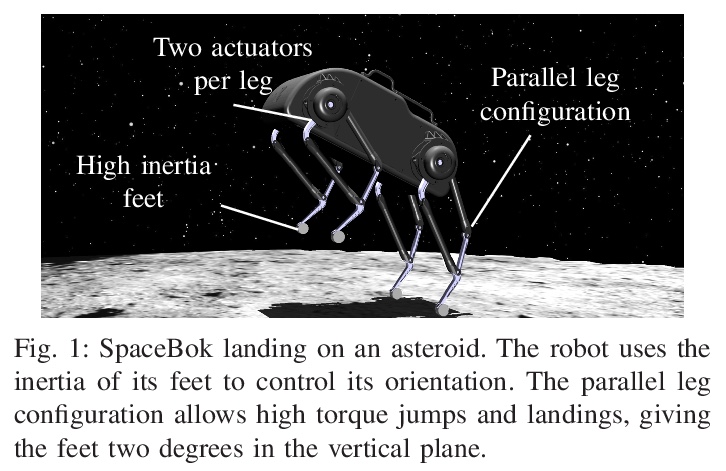
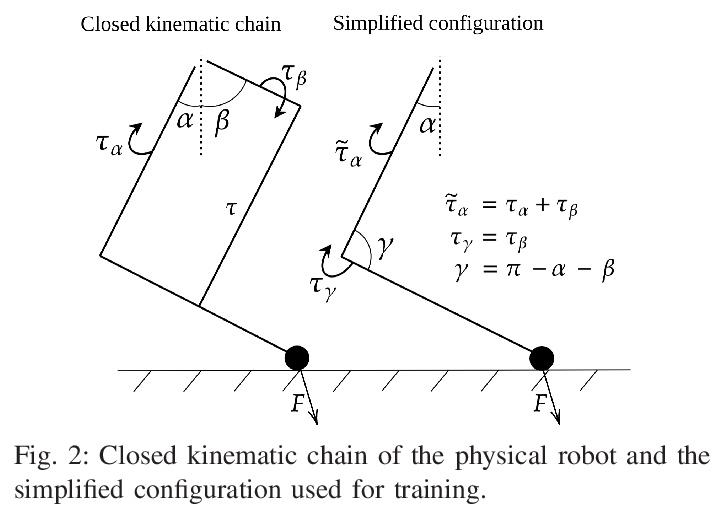
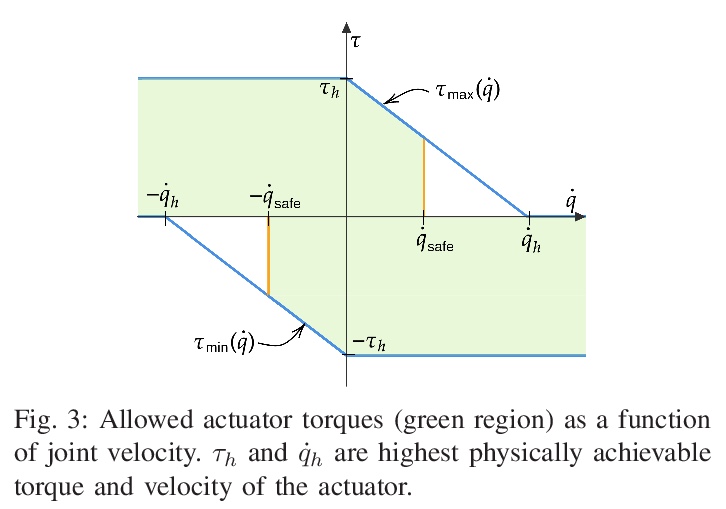
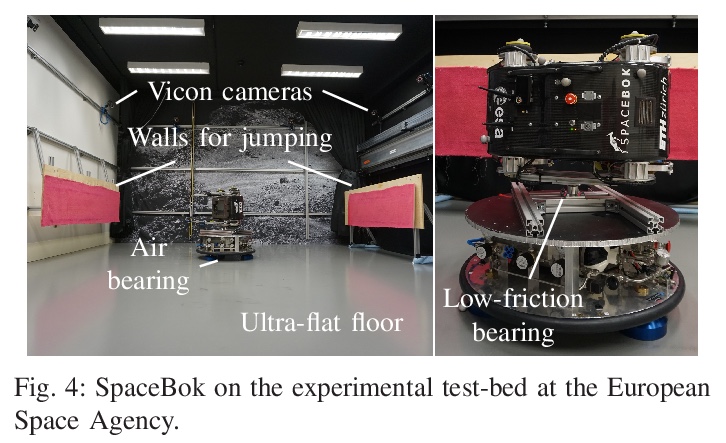
5、[RO] Cat-like Jumping and Landing of Legged Robots in Low-gravity Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
N Rudin, H Kolvenbach, V Tsounis, M Hutter
[ETH Zurich]
用深度强化学习实现低重力条件下四足机器人的猫式跳跃和着陆。本文表明,学习到的策略可用于解决具有扩展飞行阶段的腿部运动控制任务,例如在太空探索中遇到的那些任务。利用深度强化学习算法,训练神经网络来控制一个跳跃的四足机器人,只用四肢进行姿态控制。提出了逐步复杂化的任务,让四足机器人穿越模拟的低重力天体时实现3D(重)定位和着陆运动行为组合。该方法很容易在这些任务中得到推广,并为每种情况成功地训练了策略。利用模拟-现实迁移,在现实世界中把训练好的策略部署在SpaceBok机器人上,该机器人被放置在一个为2D微重力实验设计的实验台上。实验结果表明,重复的、可控的、具有自然敏捷性的跳跃和着陆是可能的。
We show that learned policies can be applied to solve legged locomotion control tasks with extensive flight phases, such as those encountered in space exploration. Using an offthe-shelf deep reinforcement learning algorithm, we trained a neural network to control a jumping quadruped robot while solely using its limbs for attitude control. We present tasks of increasing complexity leading to a combination of threedimensional (re-)orientation and landing locomotion behaviors of a quadruped robot traversing simulated low-gravity celestial bodies. We show that our approach easily generalizes across these tasks and successfully trains policies for each case. Using sim-toreal transfer, we deploy trained policies in the real world on the SpaceBok robot placed on an experimental testbed designed for two-dimensional micro-gravity experiments. The experimental results demonstrate that repetitive, controlled jumping and landing with natural agility is possible.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkQkUAX7p
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
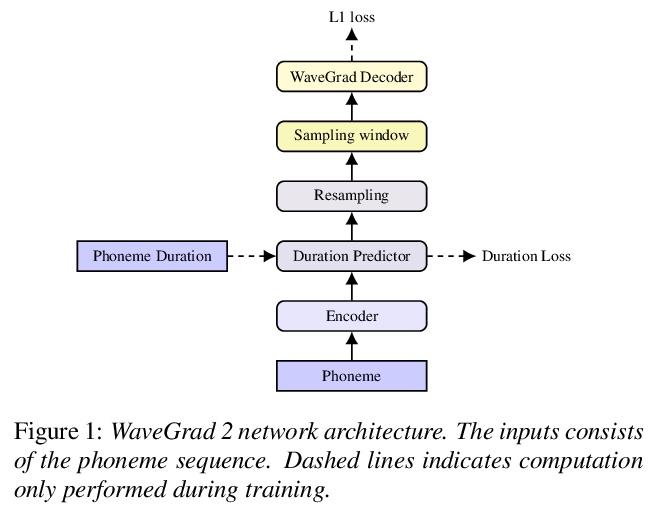
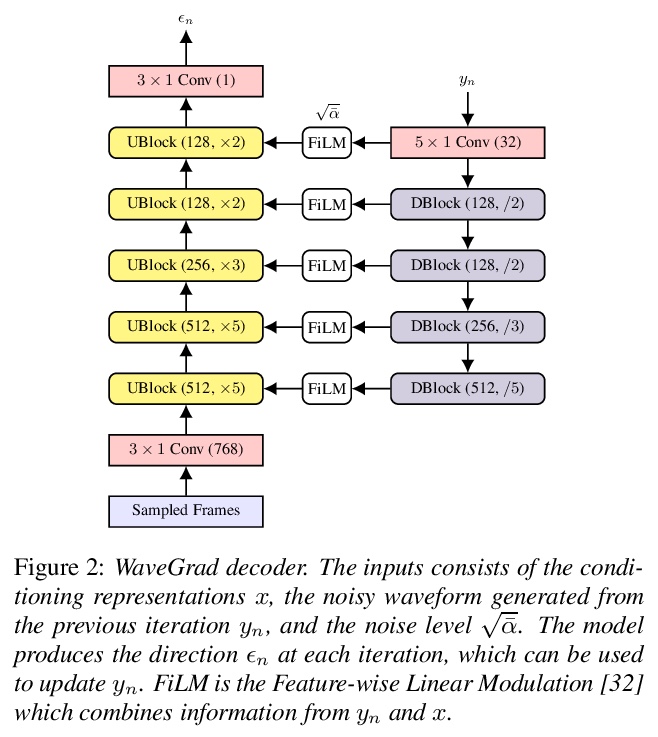
[AS] WaveGrad 2: Iterative Refinement for Text-to-Speech Synthesis
WaveGrad 2:文本-语音合成的迭代细化
N Chen, Y Zhang, H Zen, R J. Weiss, M Norouzi, N Dehak, W Chan
[Johns Hopkins University & Google Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkQnBuQVC
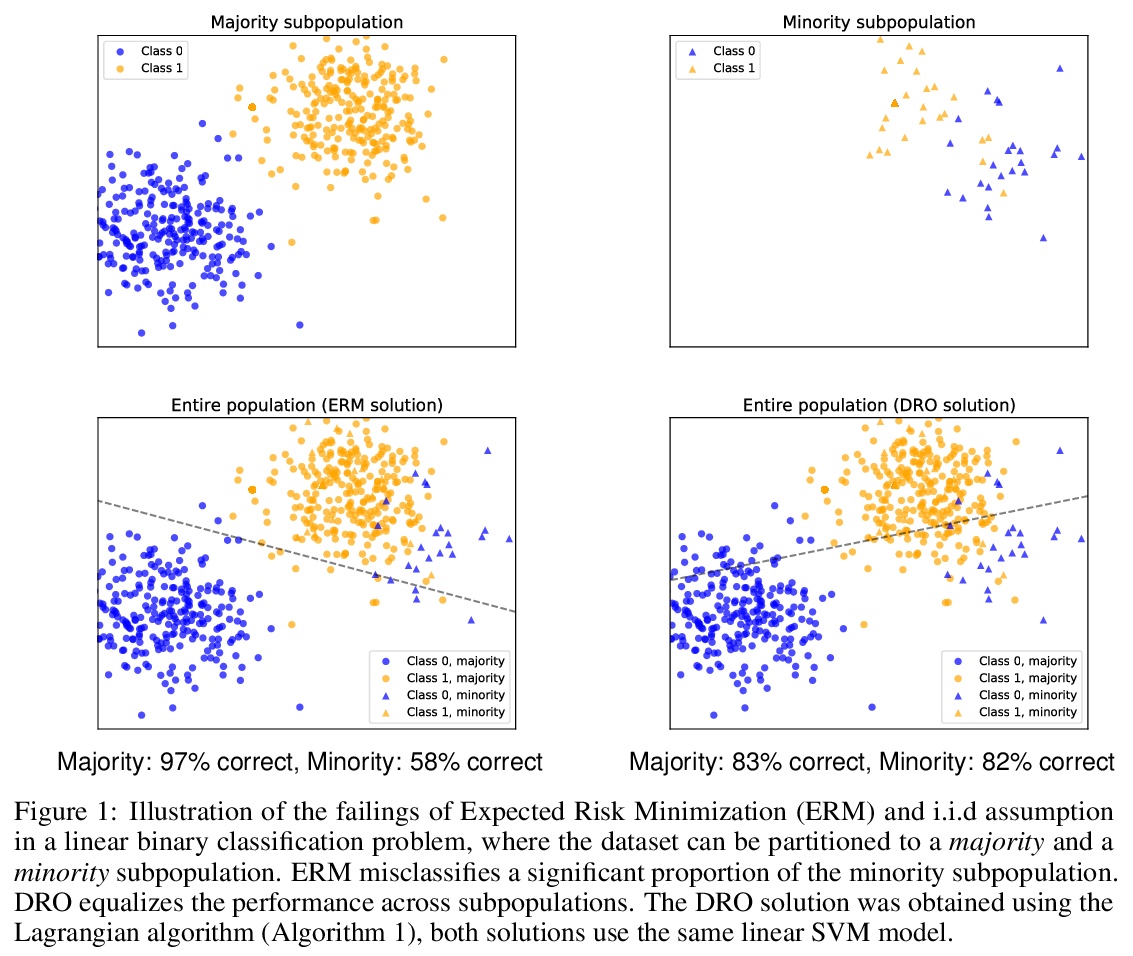
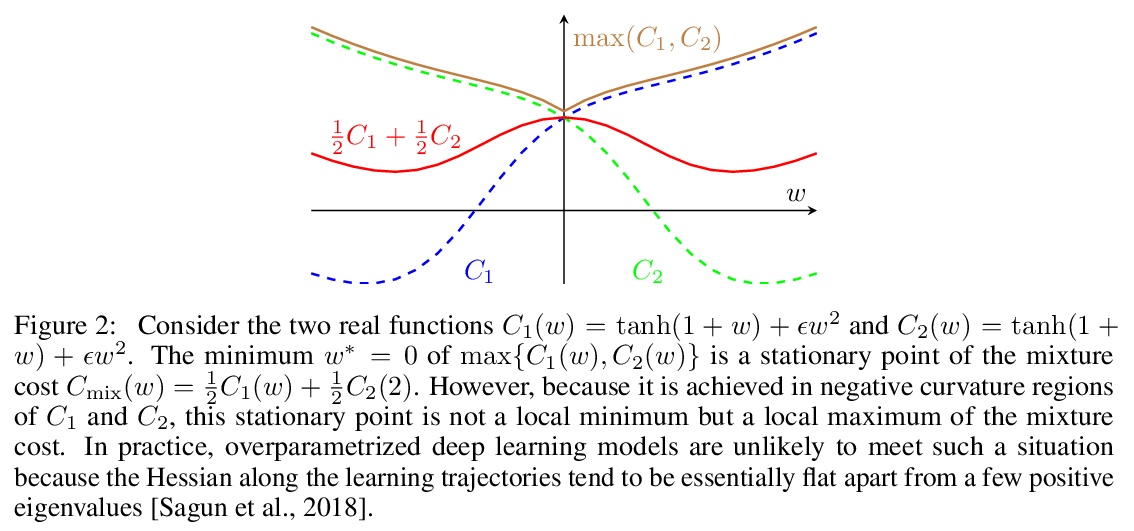
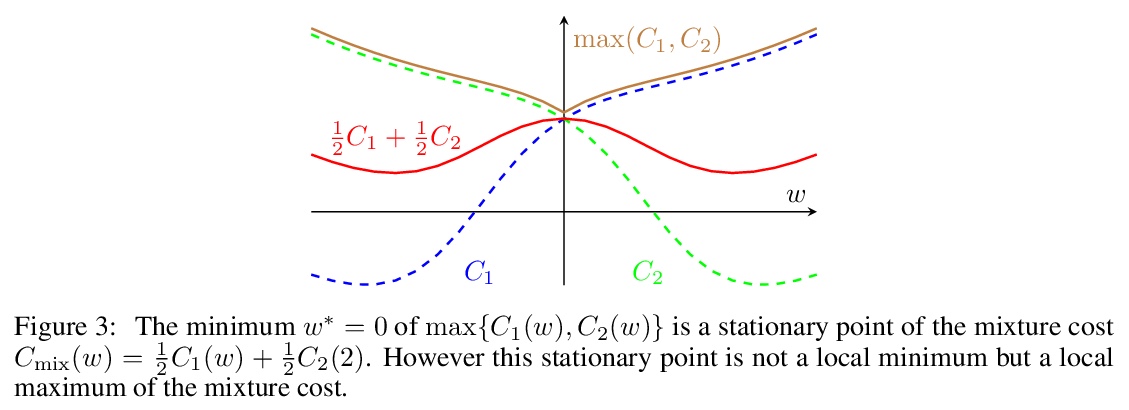
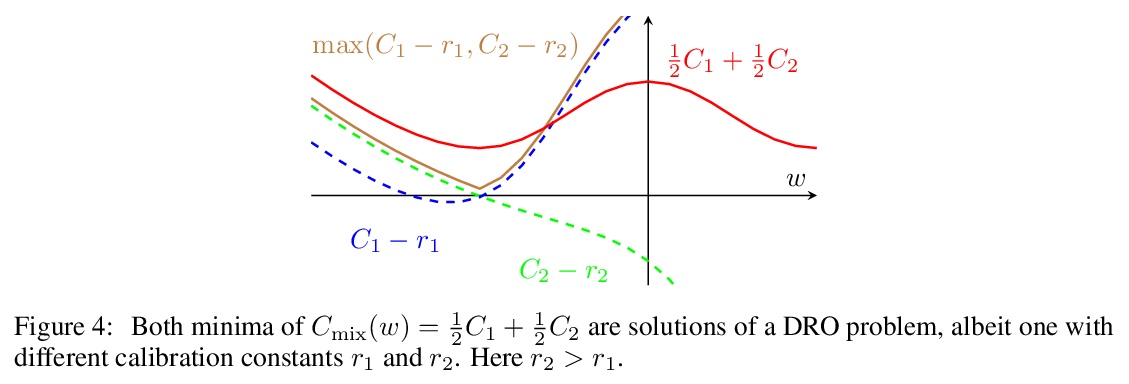
[LG] Algorithmic Bias and Data Bias: Understanding the Relation between Distributionally Robust Optimization and Data Curation
算法偏差和数据偏差:理解分布式鲁棒优化和数据监管之间的关系
A Słowik, L Bottou
[University of Cambridge & Facebook AI Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkQoVocbO
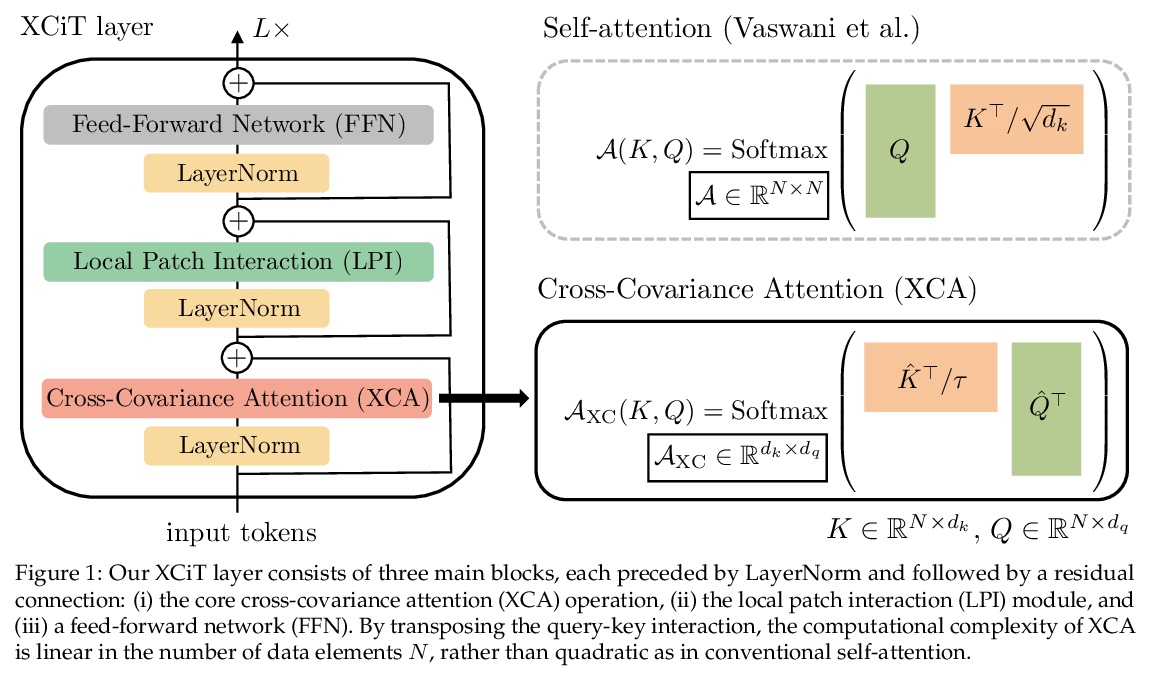
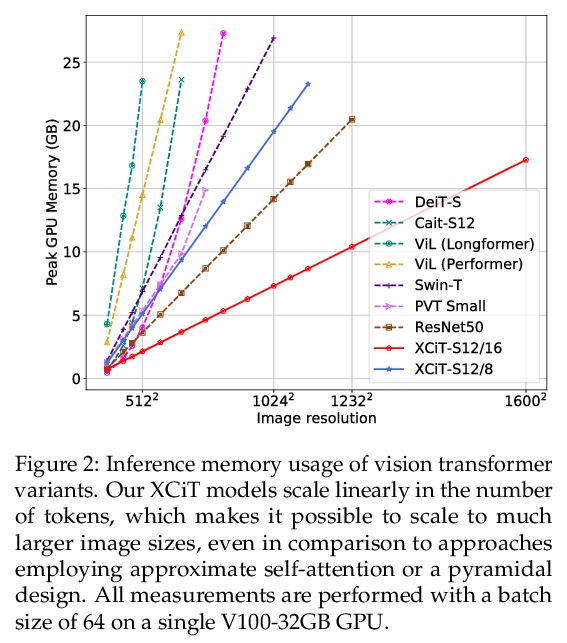
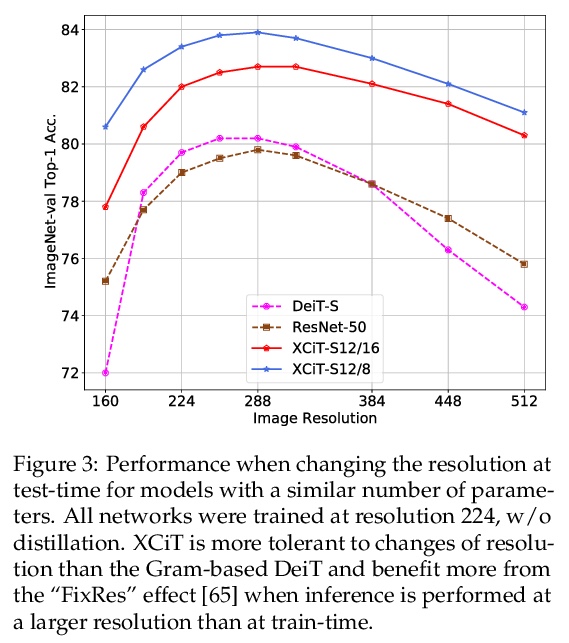
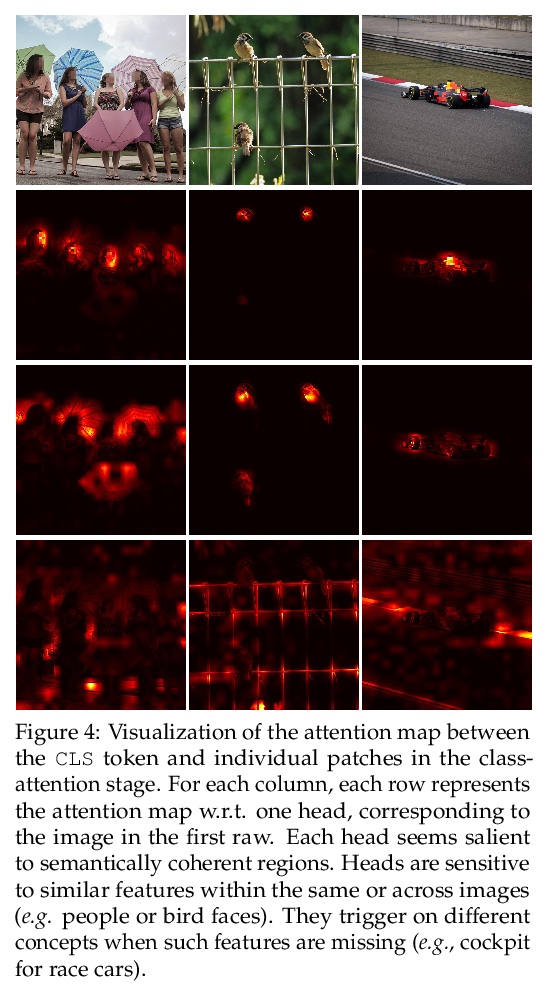
[CV] XCiT: Cross-Covariance Image Transformers
XCiT:交叉协方差图像Transformer
A El-Nouby, H Touvron, M Caron, P Bojanowski, M Douze, A Joulin, I Laptev, N Neverova, G Synnaeve, J Verbeek, H Jegou
[Facebook AI & Inria]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkQqqrRw2
[CV] Learning to Predict Visual Attributes in the Wild
真实场景视觉属性预测学习
K Pham, K Kafle, Z Lin, Z Ding, S Cohen, Q Tran, A Shrivastava
[University of Maryland & Adobe Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkQsgbDbe