- 1、[LG] Regularizing Generative Adversarial Networks under Limited Data
- 2、[LG] Modern Hopfield Networks for Few- and Zero-Shot Reaction Prediction
- 3、[SI] PageRank centrality and algorithms for weighted, directed networks with applications to World Input-Output Tables
- 4、[CV] Passive Inter-Photon Imaging
- 5、[LG] Scaling Scaling Laws with Board Games
- [CL] GrammarTagger: A Multilingual, Minimally-Supervised Grammar Profiler for Language Education
- [CV] Neural Articulated Radiance Field
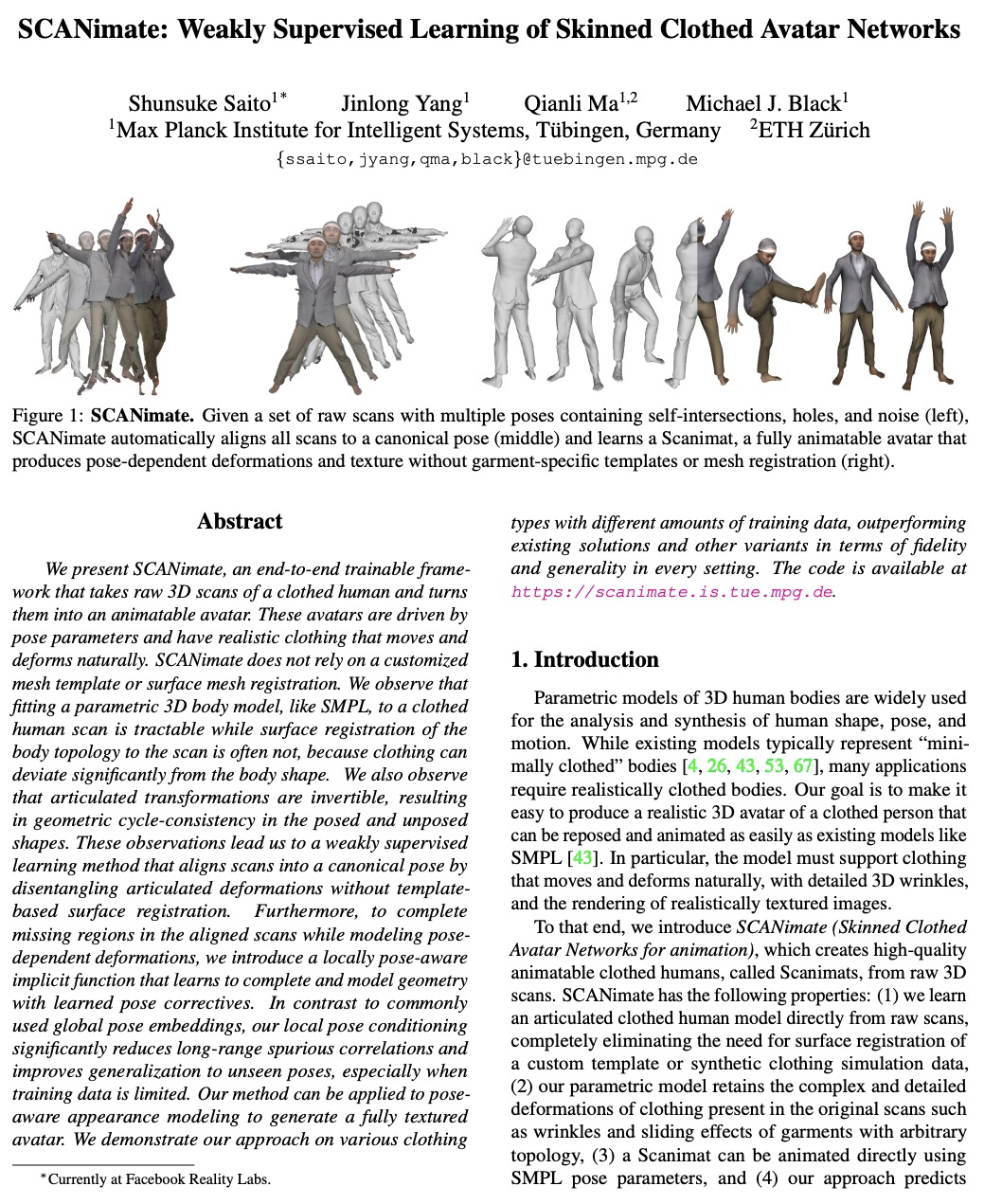
- [CV] On Self-Contact and Human Pose
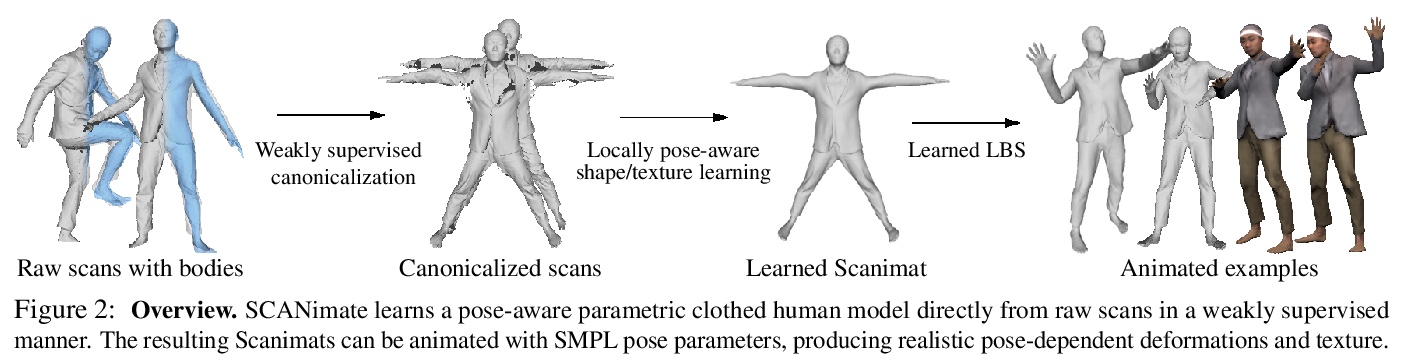
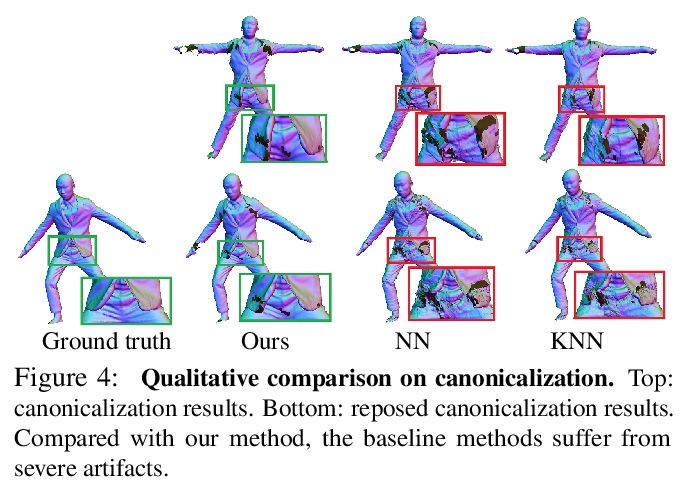
- [CV] SCANimate: Weakly Supervised Learning of Skinned Clothed Avatar Networks
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
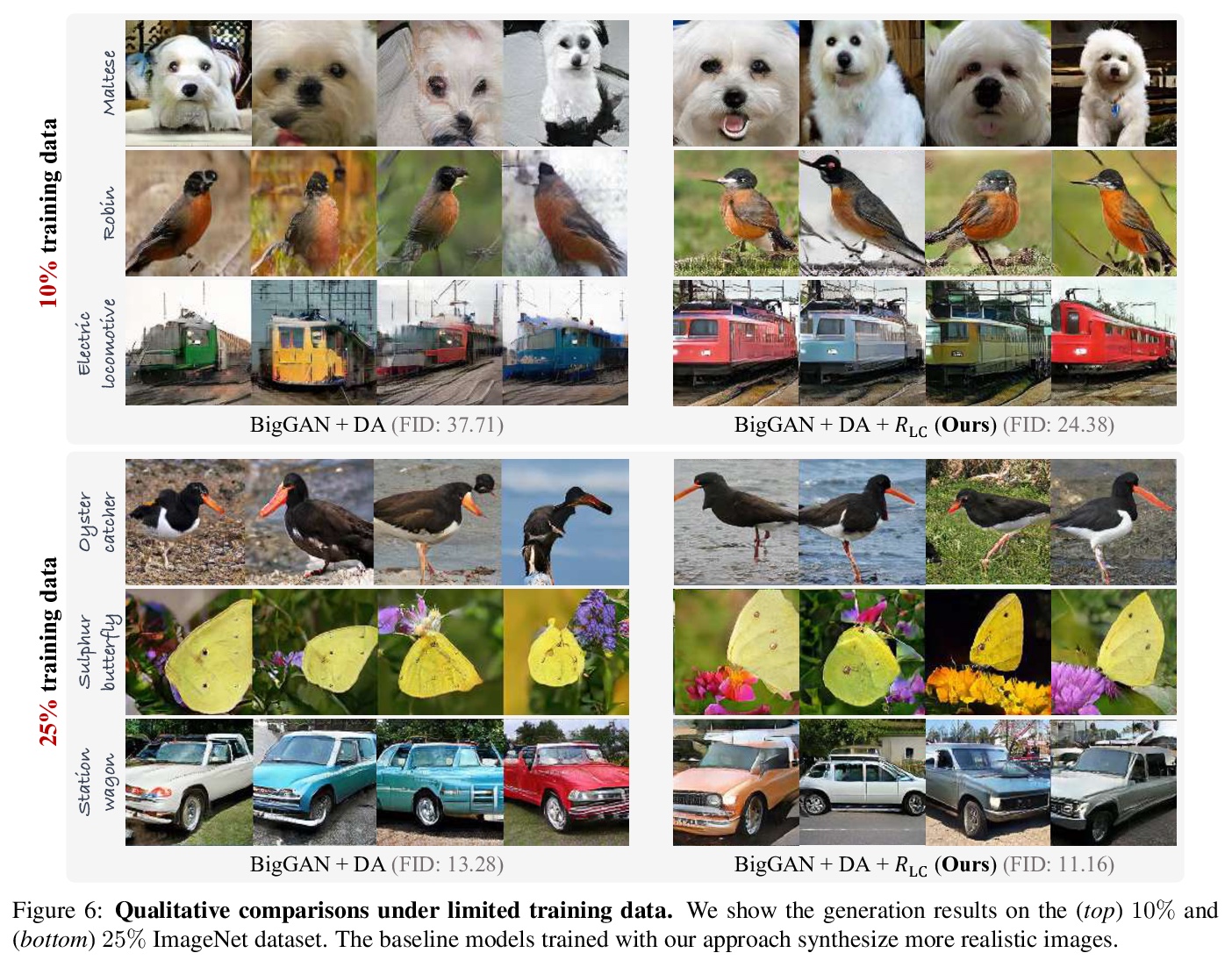
1、[LG] Regularizing Generative Adversarial Networks under Limited Data
有限数据下生成式对抗网络正则化。提出一种在有限数据上训练鲁棒GAN模型的正则化方法。在理论上展示了正则化损失和一种称为LeCam-divergence的f-divergence之间的联系,发现在有限训练数据下,LeCam-divergence更加鲁棒。在几个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,所提出的正则化方案,不仅提高了GAN模型在有限训练数据下的泛化性能并稳定了学习动态过程,也是对最近数据增强方法的很好补充。
Recent years have witnessed the rapid progress of generative adversarial networks (GANs). However, the success of the GAN models hinges on a large amount of training data. This work proposes a regularization approach for training robust GAN models on limited data. We theoretically show a connection between the regularized loss and an f-divergence called LeCam-divergence, which we find is more robust under limited training data. Extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed regularization scheme 1) improves the generalization performance and stabilizes the learning dynamics of GAN models under limited training data, and 2) complements the recent data augmentation methods. These properties facilitate training GAN models to achieve state-of-the-art performance when only limited training data of the ImageNet benchmark is available.
H Tseng, L Jiang, C Liu, M Yang, W Yang
[Google Research & University of California, Merced & Waymo]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ka2HzgKZj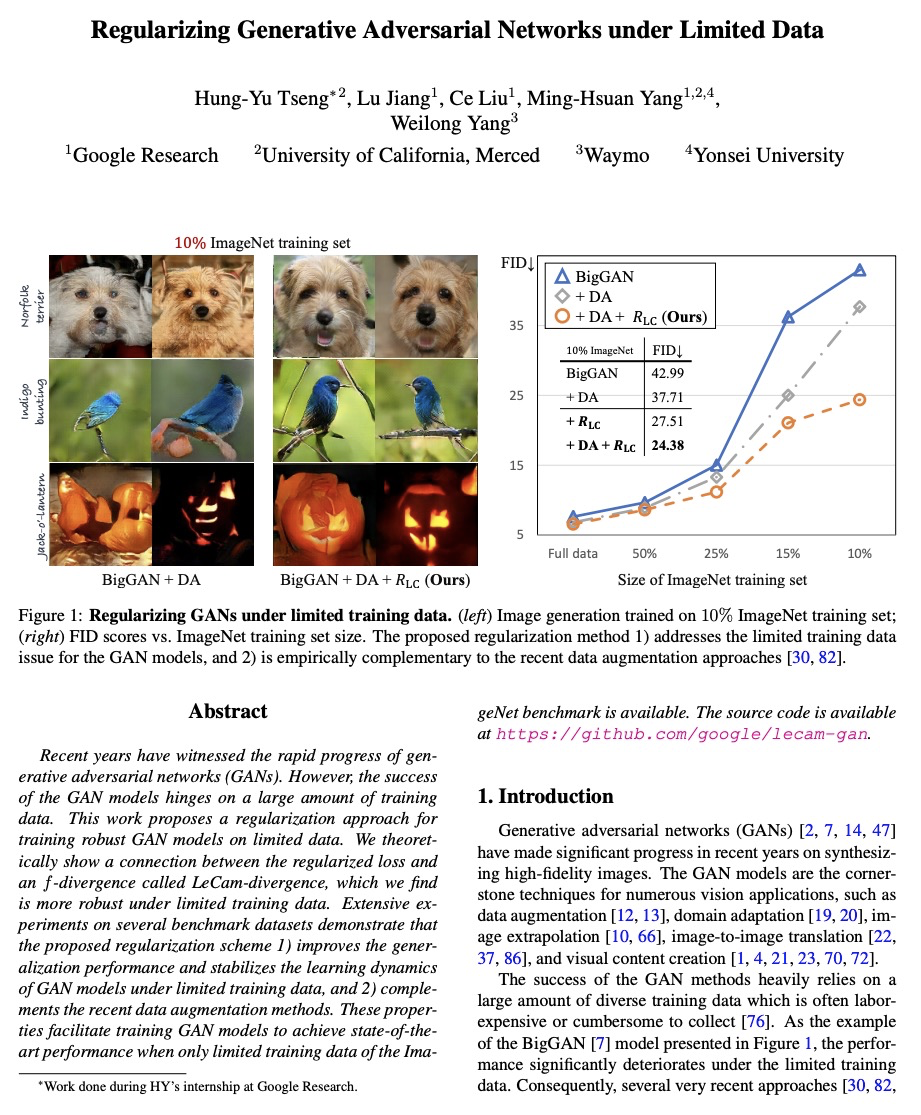
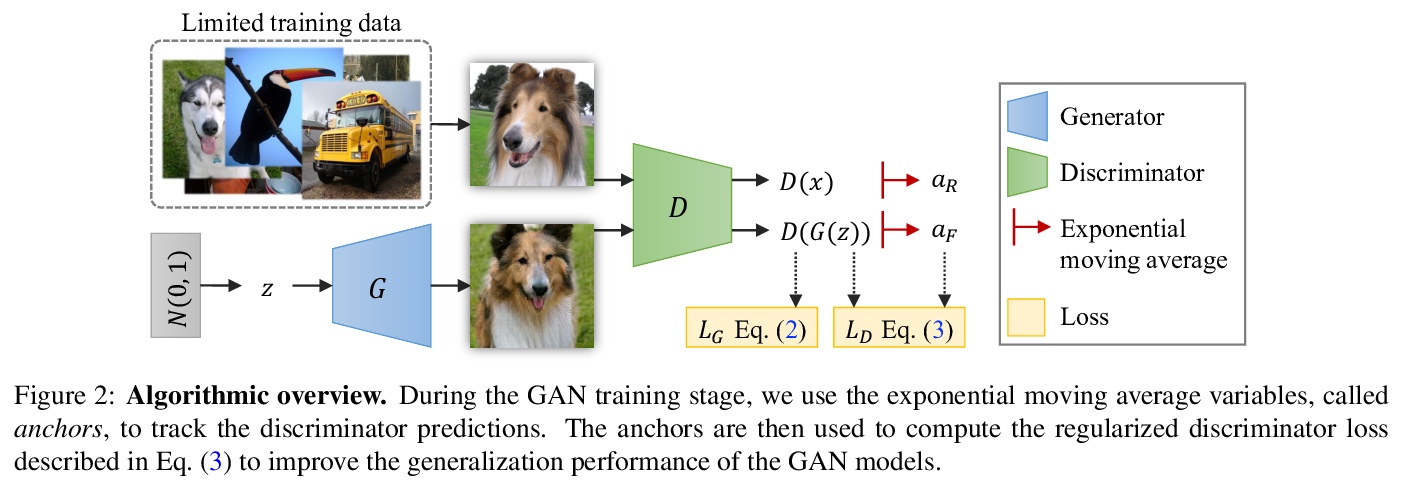


2、[LG] Modern Hopfield Networks for Few- and Zero-Shot Reaction Prediction
P Seidl, P Renz, N Dyubankova, P Neves, J Verhoeven, J K. Wegner, S Hochreiter, G Klambauer
[Johannes Kepler University & Janssen Pharmaceutica]
基于现代Hopfield网络的少样本和零样本反应预测。提出一种新的反应预测方法,采用现代Hopfield网络(MHN)深度学习架构,通过对比学习进行优化,MHN包括分子和反应模板编码器网络,可实现跨模板的泛化,从而实现零样本学习,并改进少样本学习。MHN是一种关联记忆,可以在深度学习架构的每一层中存储和检索化学反应。MHN对比学习方法可实现反应预测的少样本和零样本学习,与之前方法相比,可处理罕见的,单一的,甚至没有反应的训练样本。
An essential step in the discovery of new drugs and materials is the synthesis of a molecule that exists so far only as an idea to test its biological and physical properties. While computer-aided design of virtual molecules has made large progress, computer-assisted synthesis planning (CASP) to realize physical molecules is still in its infancy and lacks a performance level that would enable large-scale molecule discovery. CASP supports the search for multi-step synthesis routes, which is very challenging due to high branching factors in each synthesis step and the hidden rules that govern the reactions. The central and repeatedly applied step in CASP is reaction prediction, for which machine learning methods yield the best performance. We propose a novel reaction prediction approach that uses a deep learning architecture with modern Hopfield networks (MHNs) that is optimized by contrastive learning. An MHN is an associative memory that can store and retrieve chemical reactions in each layer of a deep learning architecture. We show that our MHN contrastive learning approach enables few- and zero-shot learning for reaction prediction which, in contrast to previous methods, can deal with rare, single, or even no training example(s) for a reaction. On a well established benchmark, our MHN approach pushes the state-of-the-art performance up by a large margin as it improves the predictive top-100 accuracy from > 0.858±0.004 to > 0.959±0.004. This advance might pave the way to large-scale molecule discovery.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ka2MNpYut
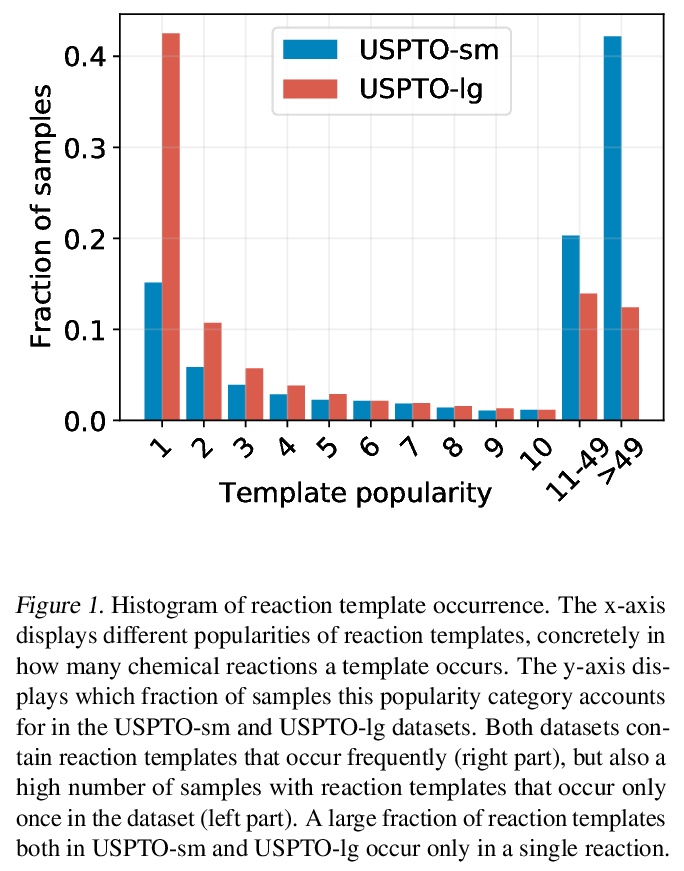
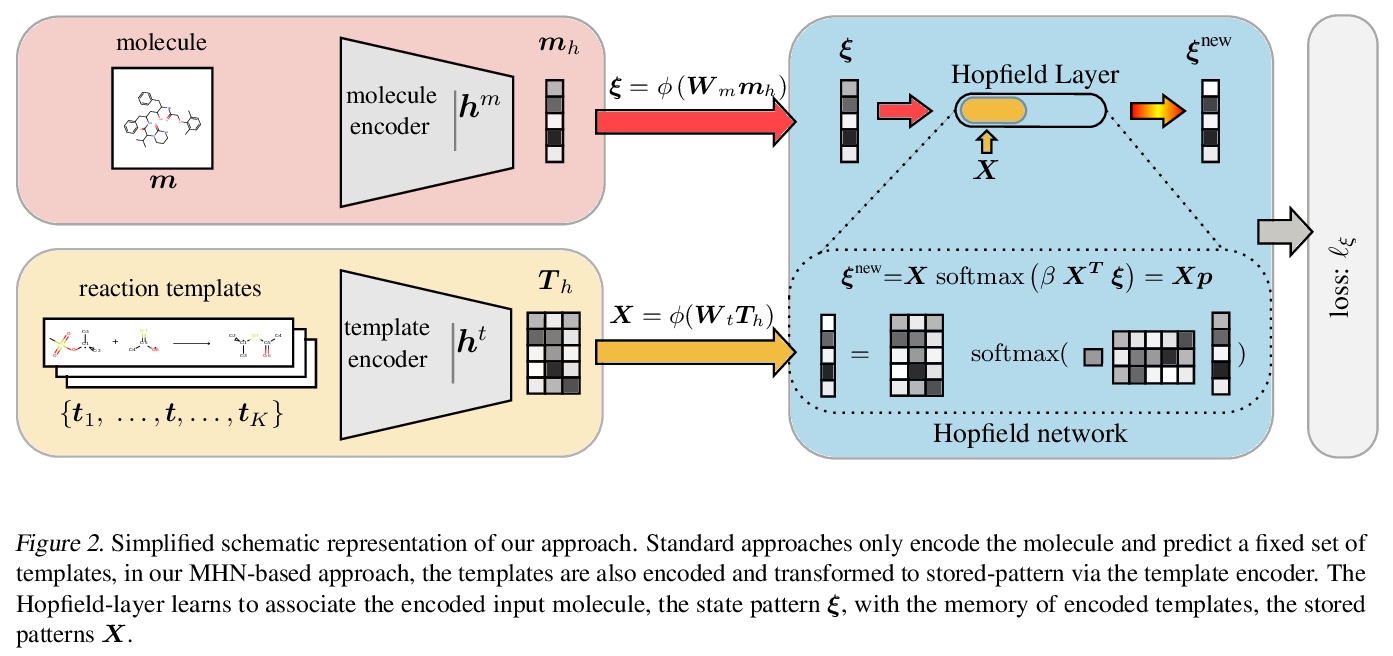
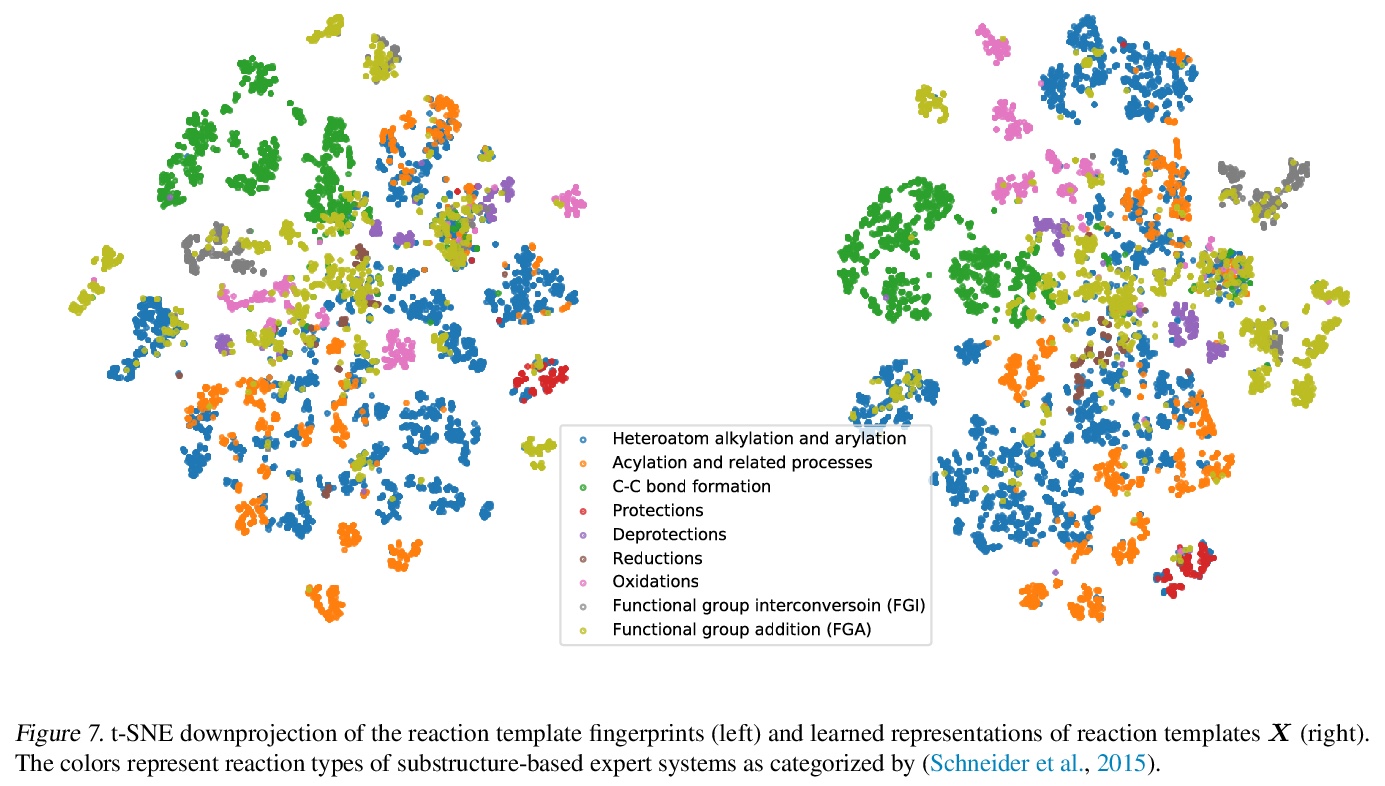
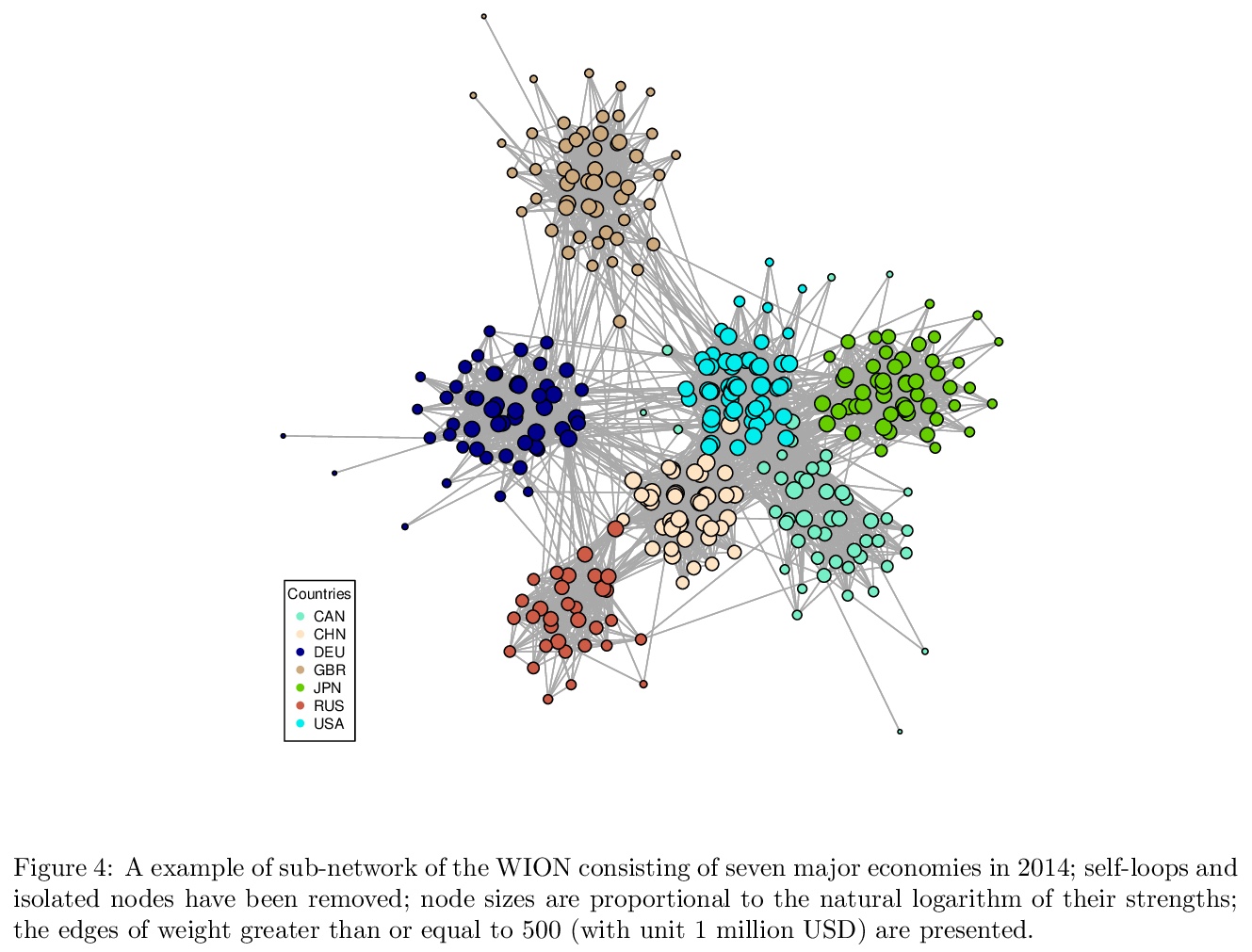
3、[SI] PageRank centrality and algorithms for weighted, directed networks with applications to World Input-Output Tables
P Zhang, T Wang, J Yan
[University of Pennsylvania & Texas A&M University & University of Connecticut]
加权定向网络的PageRank中心性和算法。提出一种加权PageRank的衡量方法(WPR),同时考虑了边缘权重和加权定向网络中节点相对重要性先验信息。节点强度和边缘权重的相对重要性由一个调整参数控制,以实现灵活性。在广泛使用的模拟网络模型上测试了WPR,发现其性能优于其他文献中的竞争方法。通过将WPR应用于由世界输入输出表产生的真实网络数据,看到了与全球经济趋势相一致的结果,使其成为分析中的首选指标。
PageRank (PR) is a fundamental tool for assessing the relative importance of the nodes in a network. In this paper, we propose a measure, weighted PageRank (WPR), extended from the classical PR for weighted, directed networks with possible non-uniform node-specific information that is dependent or independent of network structure. A tuning parameter leveraging node degree and strength is introduced. An efficient algorithm based on R program has been developed for computing WPR in large-scale networks. We have tested the proposed WPR on widely used simulated network models, and found it outperformed other competing measures in the literature. By applying the proposed WPR to the real network data generated from World Input-Output Tables, we have seen the results that are consistent with the global economic trends, which renders it a preferred measure in the analysis.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ka2QD567s

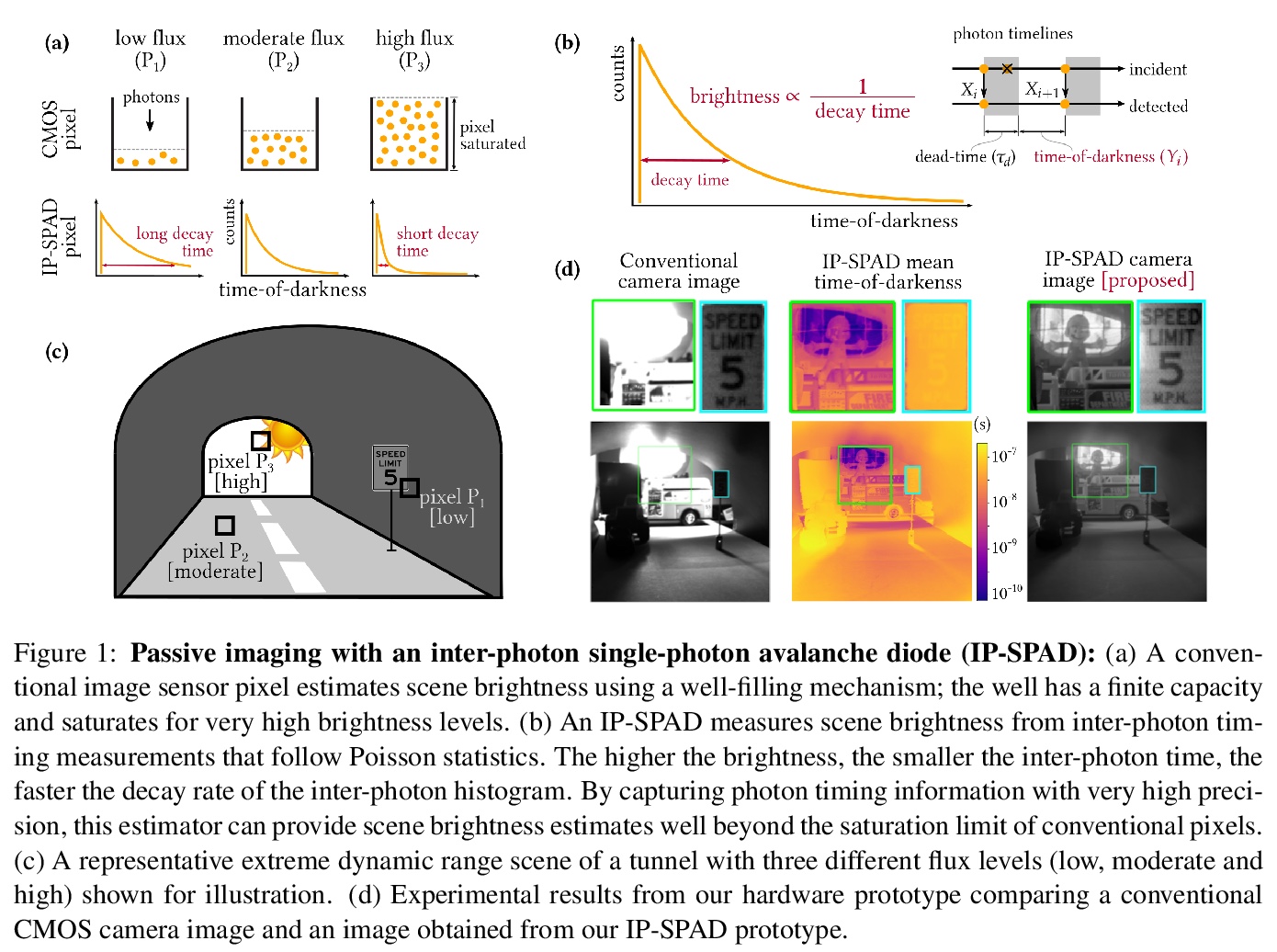
4、[CV] Passive Inter-Photon Imaging
A Ingle, T Seets, M Buttafava, S Gupta, A Tosi, M Gupta, A Velten
[University of Wisconsin-Madison & Politecnico di Milano]
无源光子间成像。数码相机的像素,是通过将入射光能转换为模拟电流,再将其数字化为固定宽度的二进制表示来测量图像强度。这种直接测量方法虽然在概念上简单,但存在动态范围有限和极端照度下性能差的问题—在低照度下电子噪声占主导,在明亮的照度下像素全孔容量导致饱和。本文提出一种基于测量光子间时序的新型强度线索,定义为检测连续光子间的时间延迟。基于时间分辨的单光子传感器测量的光子间时间的统计,开发了一种在极端动态范围内工作的场景亮度估计器的理论和算法;通过实验演示了动态范围超过千万分之一的成像场景。所提出的技术在皮秒级时序分辨率的单光子传感器(如单光子雪崩二极管(SPAD))的帮助下,将对广泛的成像应用产生影响:机器人、消费级摄影、天文学、显微镜和生物医学成像。
Digital camera pixels measure image intensities by converting incident light energy into an analog electrical current, and then digitizing it into a fixed-width binary representation. This direct measurement method, while conceptually simple, suffers from limited dynamic range and poor performance under extreme illumination — electronic noise dominates under low illumination, and pixel full-well capacity results in saturation under bright illumination. We propose a novel intensity cue based on measuring inter-photon timing, defined as the time delay between detection of successive photons. Based on the statistics of inter-photon times measured by a time-resolved single-photon sensor, we develop theory and algorithms for a scene brightness estimator which works over extreme dynamic range; we experimentally demonstrate imaging scenes with a dynamic range of over ten million to one. The proposed techniques, aided by the emergence of single-photon sensors such as single-photon avalanche diodes (SPADs) with picosecond timing resolution, will have implications for a wide range of imaging applications: robotics, consumer photography, astronomy, microscopy and biomedical imaging.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ka2UAzT54

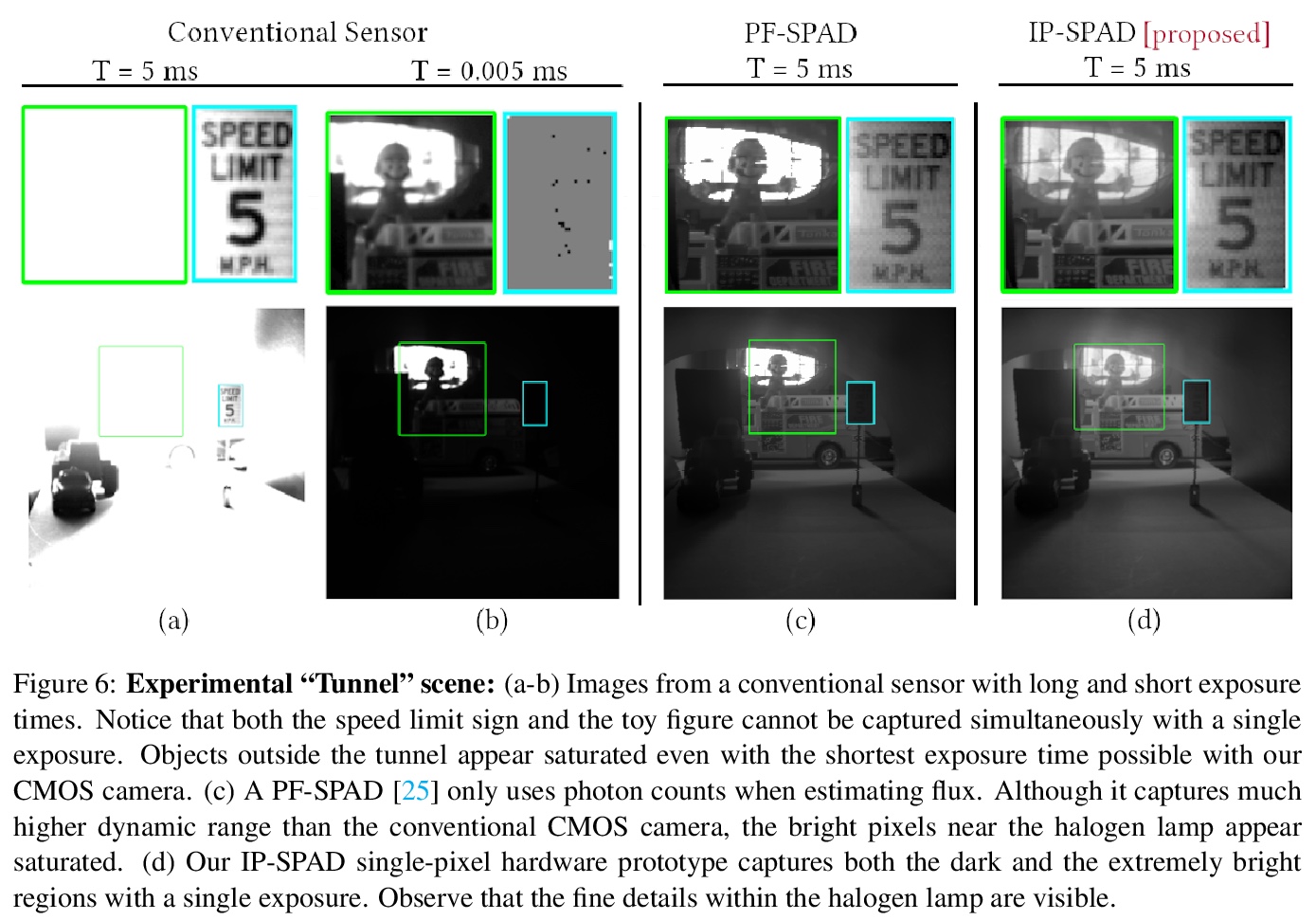
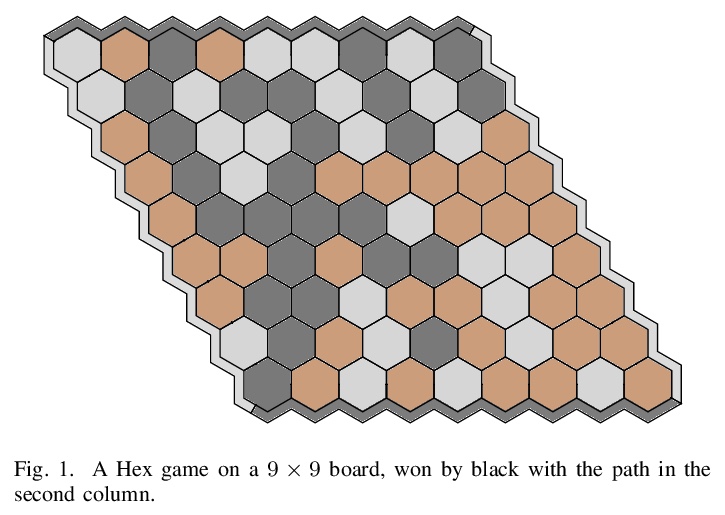
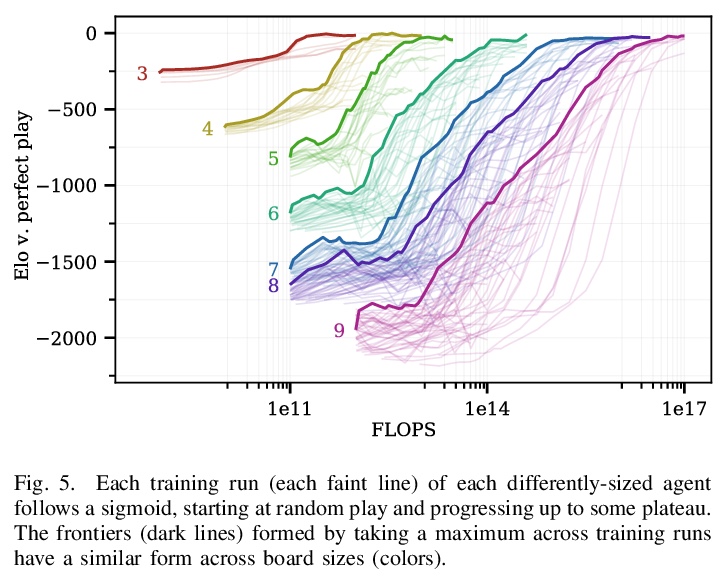
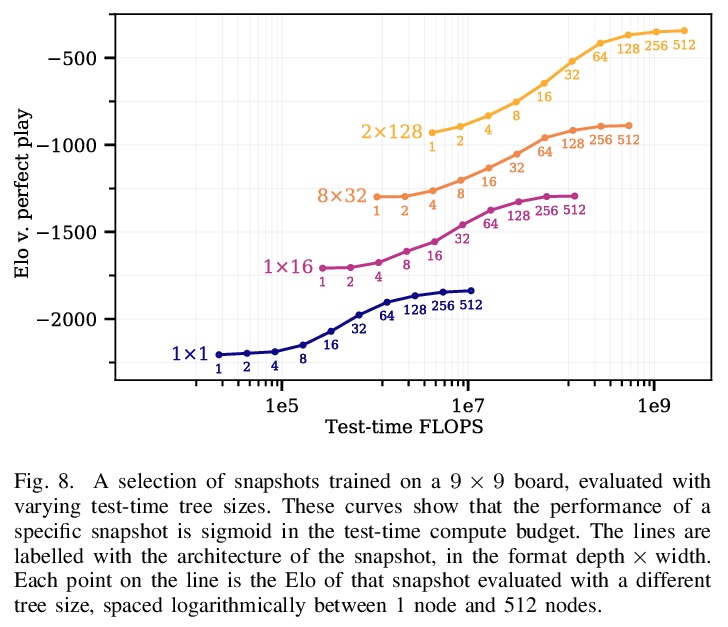
5、[LG] Scaling Scaling Laws with Board Games
A L. Jones
棋牌游戏缩放律的缩放。现在,机器学习中最大规模的实验所需要的资源,远远超出了除少数机构之外的其他所有机构的预算。幸运的是,最近已经证明,这些巨大实验的结果往往可以从一系列小得多、也便宜得多的实验结果中推断出来。本文表明,不仅可以根据模型的大小进行外推,还可以根据问题的大小进行外推。通过用AlphaZero和Hex进行一系列的实验表明,随着游戏的规模和难度的增加,在固定的计算量下可以达到的性能会出现可预见的下降;训练AlphaZero玩Hex游戏时,所需的计算量可直接从棋盘大小和期望的性能中计算出来。除主要结果之外,还进一步表明,增加智能体的测试时计算量可替代减少的训练时计算量,反之亦然,训练时的计算量和测试时的计算量可以根据简单关系进行权衡。本文证明了在小型廉价问题中发现的计算和性能之间的关系,是如何直接传递到更昂贵的更高数量级问题上的。
The largest experiments in machine learning now require resources far beyond the budget of all but a few institutions. Fortunately, it has recently been shown that the results of these huge experiments can often be extrapolated from the results of a sequence of far smaller, cheaper experiments. In this work, we show that not only can the extrapolation be done based on the size of the model, but on the size of the problem as well. By conducting a sequence of experiments using AlphaZero and Hex, we show that the performance achievable with a fixed amount of compute degrades predictably as the game gets larger and harder. Along with our main result, we further show that increasing the test-time compute available to an agent can substitute for reduced train-time compute, and vice versa.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ka303xSGq
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
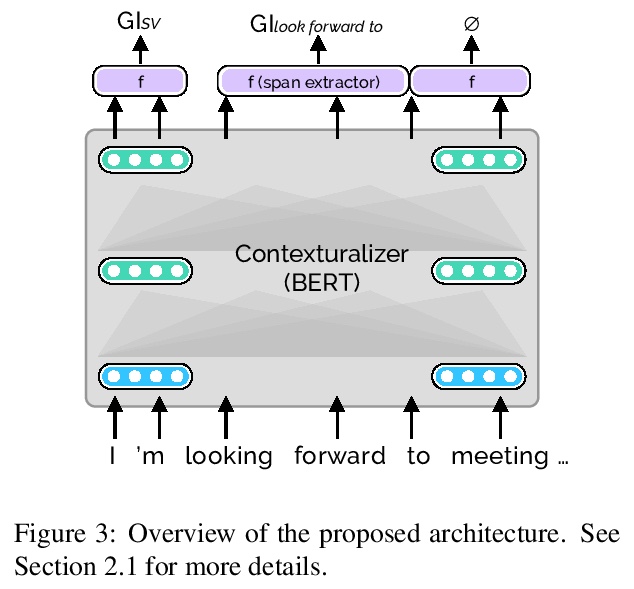
[CL] GrammarTagger: A Multilingual, Minimally-Supervised Grammar Profiler for Language Education
GrammarTagger:面向语言教育的多语言、最小监督语法分析器
M Hagiwara, J Tanner, K Sakaguchi
[Octanove Labs & University of Washington & Allen Institute for AI]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ka346FHxk


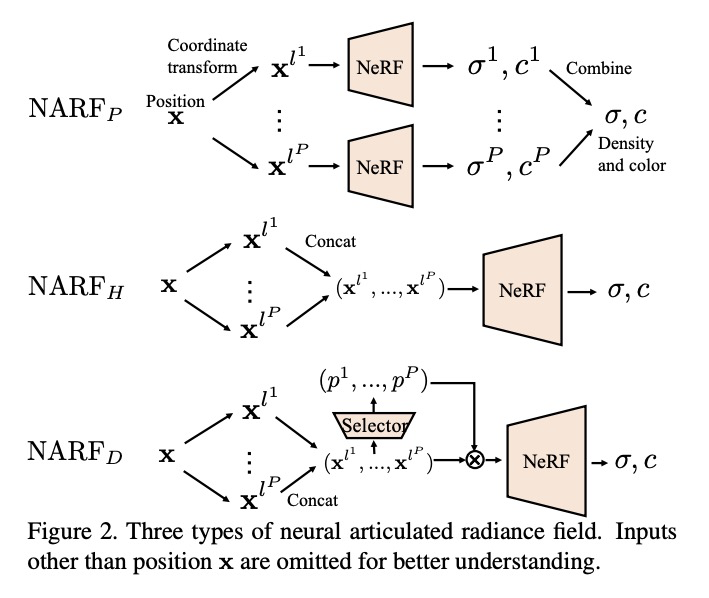
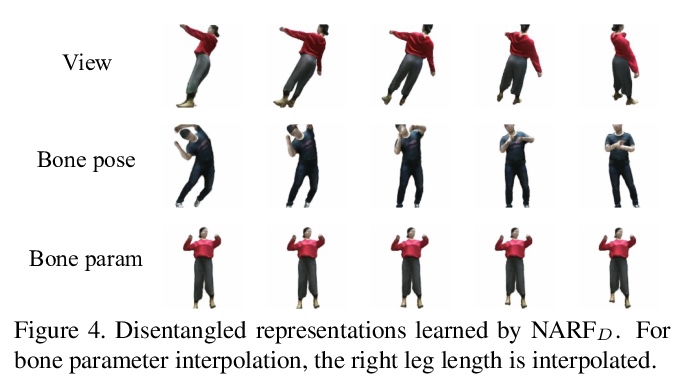
[CV] Neural Articulated Radiance Field
神经关节辐射场
A Noguchi, X Sun, S Lin, T Harada
[The University of Tokyo & Microsoft Research Asia]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ka35pFOaZ

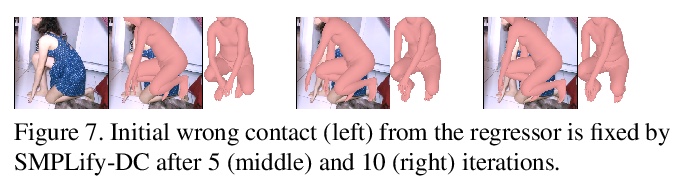
[CV] On Self-Contact and Human Pose
自触碰与人体姿态
L Müller, A A. A. Osman, S Tang, C P. Huang, M J. Black
[Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems & ETH Zurich]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ka37i5idm


[CV] SCANimate: Weakly Supervised Learning of Skinned Clothed Avatar Networks
SCANimate:皮肤化着装虚拟化身网络弱监督学习
S Saito, J Yang, Q Ma, M J. Black
[Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ka38Xvxzw