- 1、[LG] AI Poincaré: Machine Learning Conservation Laws from Trajectories
- 2、[CL] Language Modelling as a Multi-Task Problem
- 3、[CV] PoseAug: A Differentiable Pose Augmentation Framework for 3D Human Pose Estimation
- 4、[LG] Neural Algorithmic Reasoning
- 5、[CV] Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning by Tracking Patches in Video
- [CV] Inverting Generative Adversarial Renderer for Face Reconstruction
- [CV] ACORN: Adaptive Coordinate Networks for Neural Scene Representation
- [IR] Rethinking Search: Making Experts out of Dilettantes
- [RO] Real-time Multi-Adaptive-Resolution-Surfel 6D LiDAR Odometry using Continuous-time Trajectory Optimization
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] AI Poincaré: Machine Learning Conservation Laws from Trajectories
Z Liu, M Tegmark (MIT)
[MIT]
AI Poincaré: 轨迹的守恒定律机器学习。机器学习已经为物理学的进步做出了许多贡献,如提高数值模拟、实验室实验和天文观测的速度或质量,但更宏伟的目标是设计智能机器,通过符号回归来实现新的科学发现,如物理对称性和物理公式的发现。本文的目标,是通过动力学系统轨迹,自动发现守恒定律。提出AI Poincaré,一种机器学习算法,用于利用未知动力学系统的轨迹数据自动发现守恒量。对五个哈密尔顿系统(包括引力三体问题)的测试表明,它不仅能自动发现守恒量的数量,还能发现周期性轨道、相变和近似守恒定律的崩溃时间尺度。AI Poincaré是通用的,因为它不需要任何领域知识,甚至不需要轨迹如何产生的物理模型。
We present AI Poincaré, a machine learning algorithm for auto-discovering conserved quantities using trajectory data from unknown dynamical systems. We test it on five Hamiltonian systems, including the gravitational 3-body problem, and find that it discovers not only all exactly conserved quantities, but also periodic orbits, phase transitions and breakdown timescales for approximate conservation laws.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kes935pQY
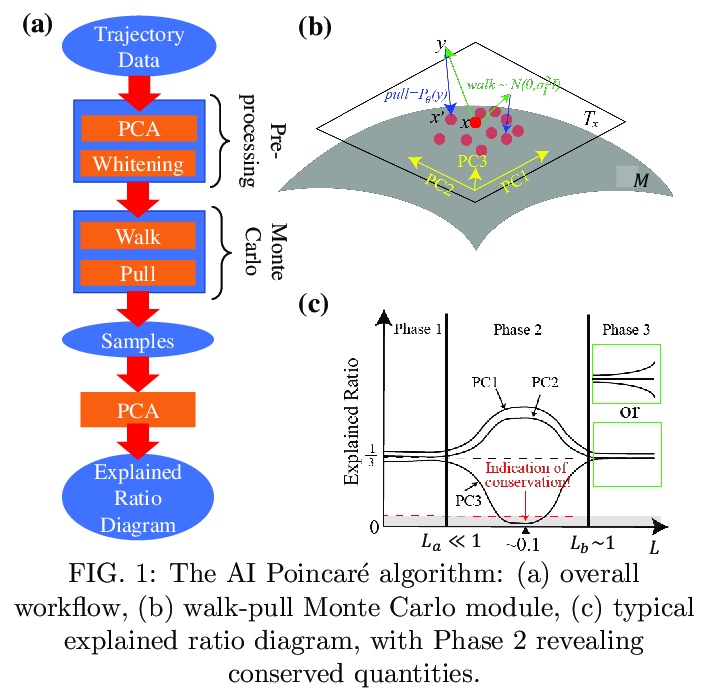
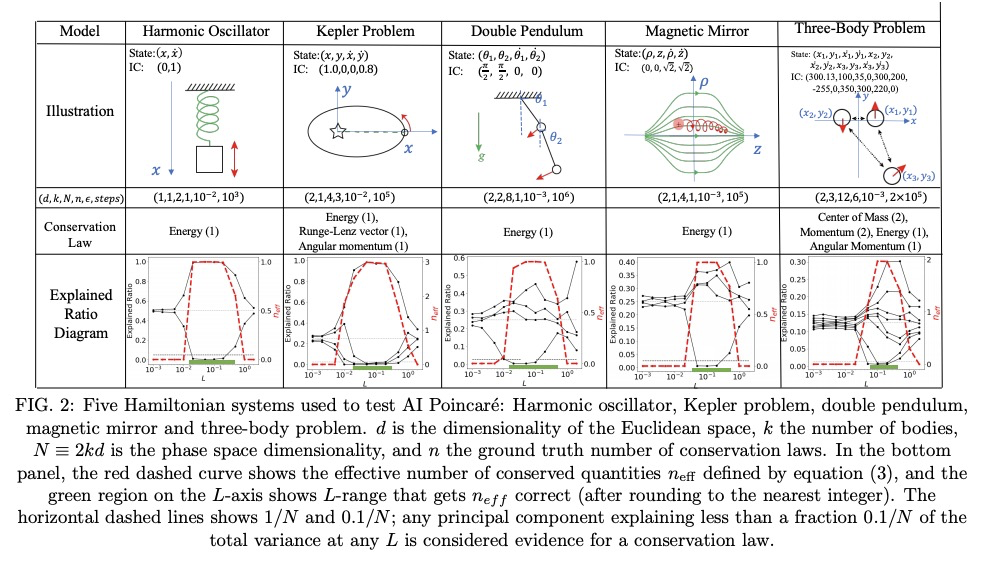
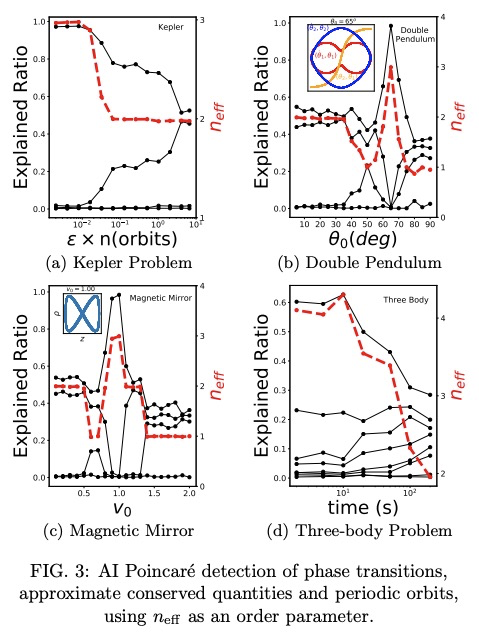
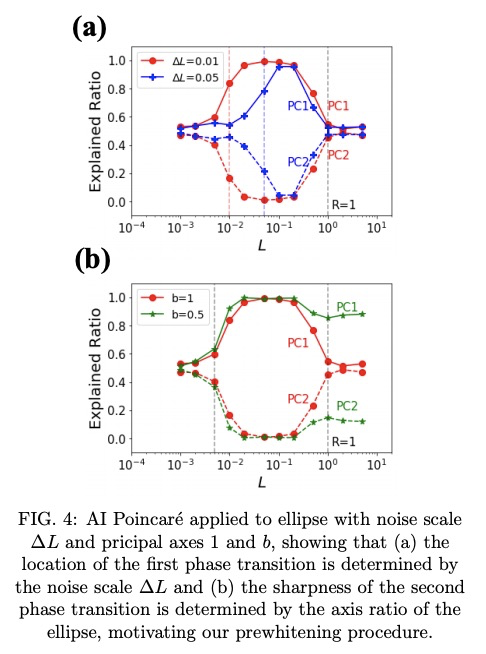
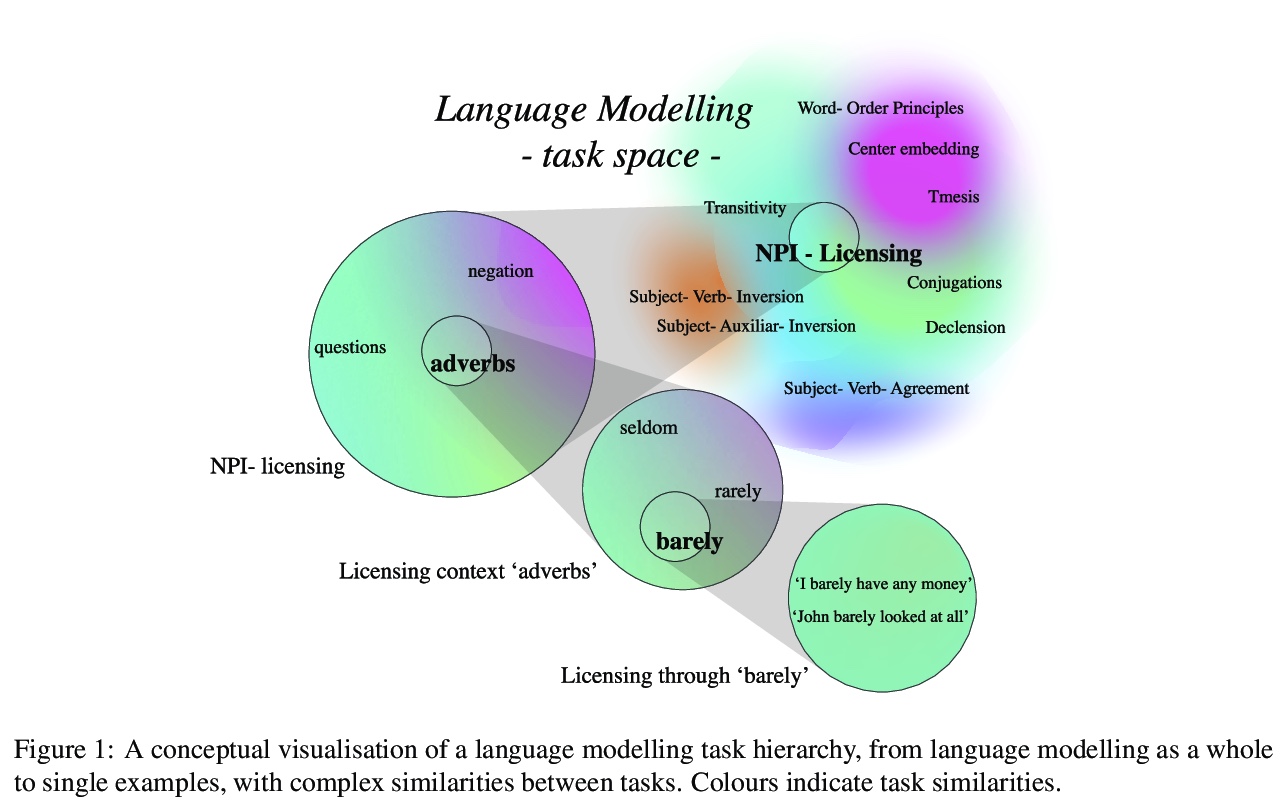
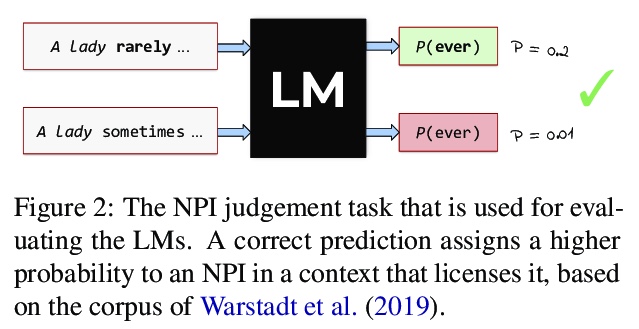
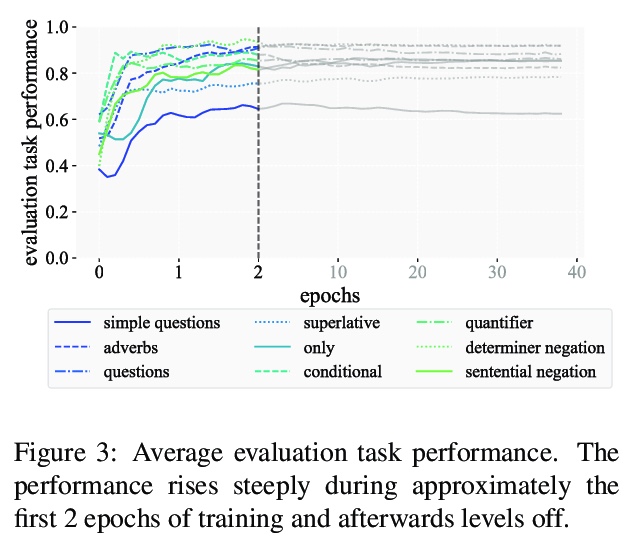
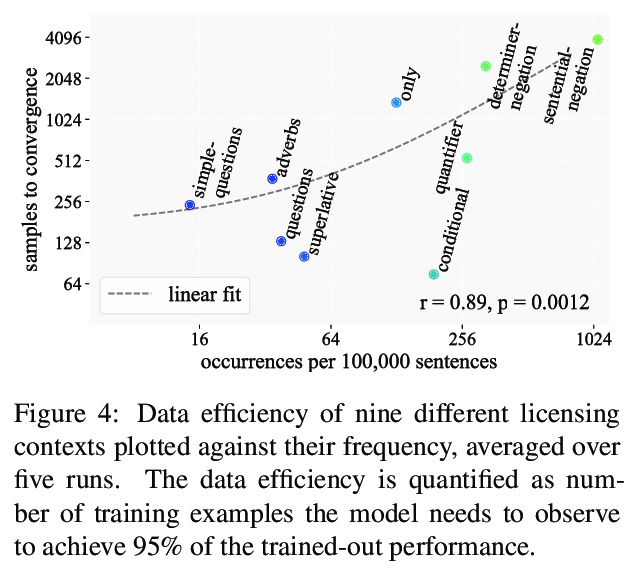
2、[CL] Language Modelling as a Multi-Task Problem
L Weber, J Jumelet, E Bruni, D Hupkes
[University Pompeu Fabra & University of Amsterdam & University of Osnabruck & Facebook AI Research]
将语言建模作为多任务问题。提出将语言建模作为多任务问题来研究,将多任务学习、语言学和可解释性三方面的研究结合起来。基于来自语言学理论的假设,研究了语言模型在训练过程中是否坚持了多任务学习的学习原则。神经语言模型会利用从语言学理论中假设的相似性,并利用这些相似性以较少的数据学习相似的语言结构,达到较高的精度。尤其是不太频繁的任务,会从这种效应中受益,其迁移行为也反映了传统构建的多任务学习环境中的泛化行为。为展示该想法,分析了语言模型在学习负面极性词(NPI)这一语言概念时的泛化行为。实验表明,在语言建模这一更普遍的任务目标中,自然会出现多任务设置。这种洞察对于多任务学习、语言学和可解释性研究是很有价值的,并且可以在这三个领域带来令人兴奋的新发现。
In this paper, we propose to study language modelling as a multi-task problem, bringing together three strands of research: multitask learning, linguistics, and interpretability. Based on hypotheses derived from linguistic theory, we investigate whether language models adhere to learning principles of multi-task learning during training. To showcase the idea, we analyse the generalisation behaviour of language models as they learn the linguistic concept of Negative Polarity Items (NPIs). Our experiments demonstrate that a multi-task setting naturally emerges within the objective of the more general task of language modelling. We argue that this insight is valuable for multitask learning, linguistics and interpretability research and can lead to exciting new findings in all three domains.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kesd6sDvp
3、[CV] PoseAug: A Differentiable Pose Augmentation Framework for 3D Human Pose Estimation
K Gong, J Zhang, J Feng
[National University of Singapore]
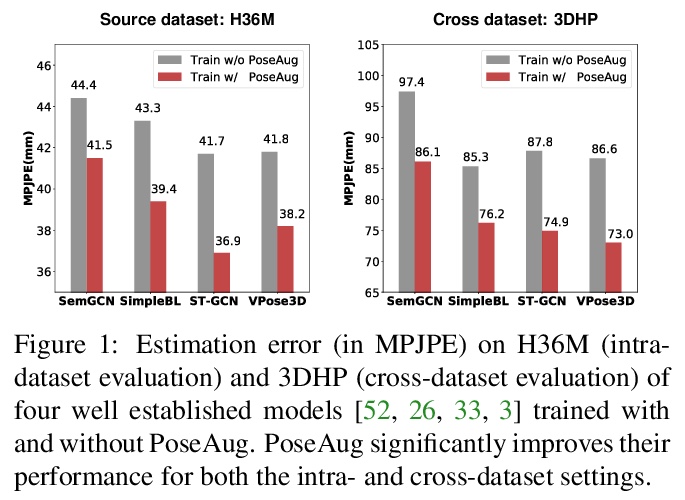
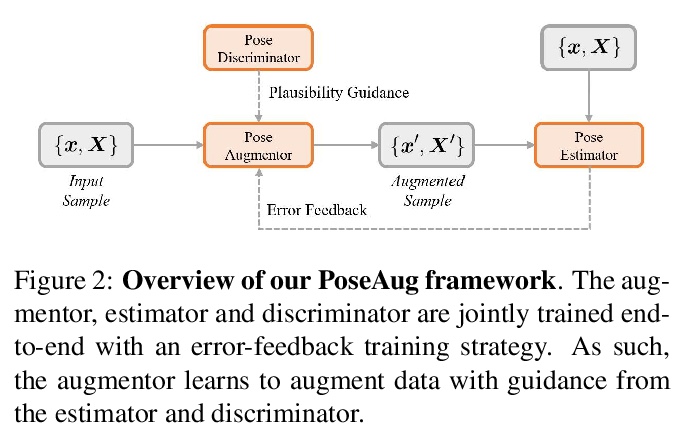
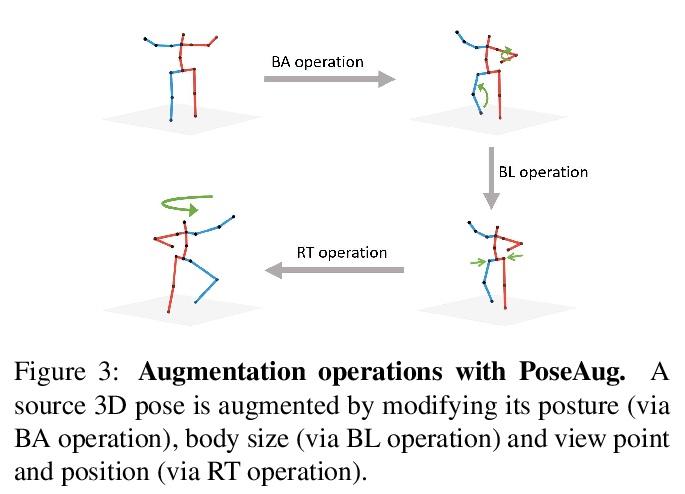
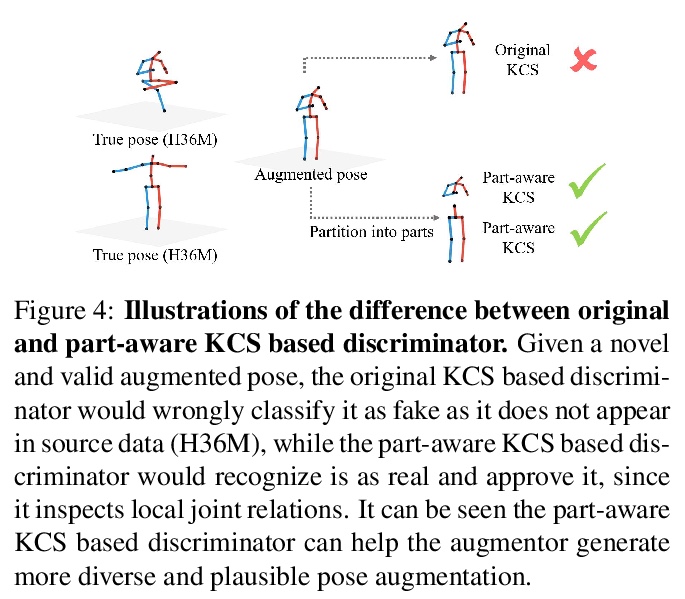
PoseAug: 面向3D人体姿态估计的可微姿态增强框架。现有的3D人体姿态估计器,对新数据集泛化性能很差,主要是由于训练数据中的2D-3D姿态对多样性有限。为解决该问题,提出新的自动增强框架PoseAug,可学习增强现有训练姿态的多样性,提高训练后的2D到3D姿态估计器的泛化能力。通过引入新的姿态增强器,学习通过可微操作来调整姿态的各种几何因素(例如,姿势、身体大小、视角和位置)。基于其可微性,增强器可以与3D姿态估计器联合优化,并将估计误差作为反馈,以在线方式生成更多样化和更复杂的姿态。PoseAug引入了新的部件感知运动链空间来评估局部关节角度的合理性,并相应开发了一个判别模块以确保增强姿态的合理性。这些设计使PoseAug能比现有的离线增强方法产生更多不同而又可信的姿态,改善姿态估计器的通用性。实验表明,PoseAug在场景内和跨场景的数据集上都带来了明显的改进,在跨数据集评估设置下,在MPI-INF-3DHP上实现了88.6%的3D PCK,比之前基于数据增强的最佳方法提高了9.1%
Existing 3D human pose estimators suffer poor generalization performance to new datasets, largely due to the limited diversity of 2D-3D pose pairs in the training data. To address this problem, we present PoseAug, a new autoaugmentation framework that learns to augment the available training poses towards a greater diversity and thus improve generalization of the trained 2D-to-3D pose estimator. Specifically, PoseAug introduces a novel pose augmentor that learns to adjust various geometry factors (e.g., posture, body size, view point and position) of a pose through differentiable operations. With such differentiable capacity, the augmentor can be jointly optimized with the 3D pose estimator and take the estimation error as feedback to generate more diverse and harder poses in an online manner. Moreover, PoseAug introduces a novel part-aware Kinematic Chain Space for evaluating local joint-angle plausibility and develops a discriminative module accordingly to ensure the plausibility of the augmented poses. These elaborate designs enable PoseAug to generate more diverse yet plausible poses than existing offline augmentation methods, and thus yield better generalization of the pose estimator. PoseAug is generic and easy to be applied to various 3D pose estimators. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PoseAug brings clear improvements on both intra-scenario and cross-scenario datasets. Notably, it achieves 88.6% 3D PCK on MPI-INF-3DHP under cross-dataset evaluation setup, improving upon the previous best data augmentation based method [22] by 9.1%.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KesicD98B
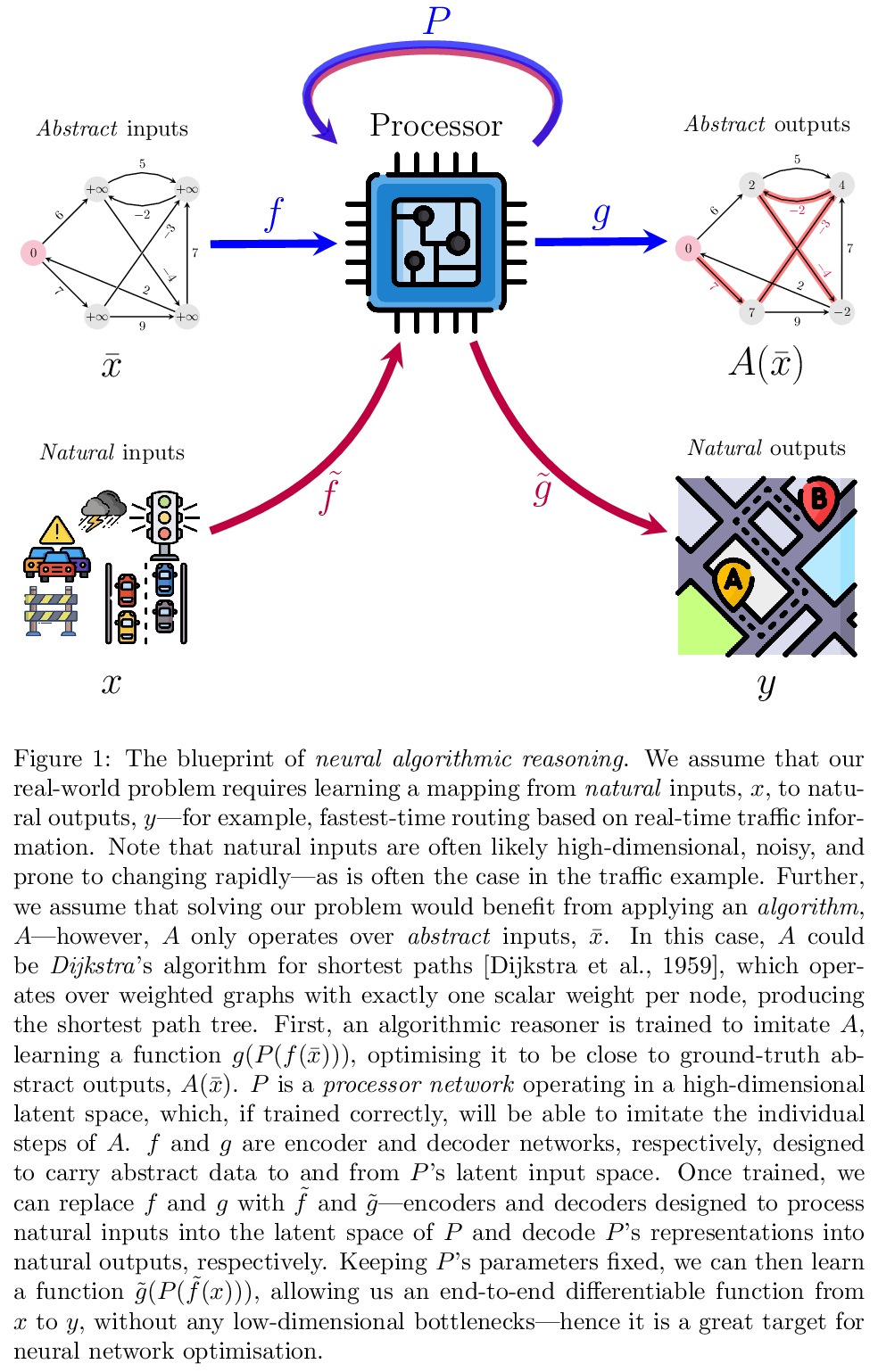
4、[LG] Neural Algorithmic Reasoning
P Veličković, C Blundell
[DeepMind]
神经算法推理。算法是最近全球技术进步的基础,也是一个领域技术进步迅速应用于另一个领域的基石。算法拥有与深度学习方法根本不同的品质,前者提供强有力的保证,但对所处理的问题不灵活,而后者提供很少的保证,但可以适应广泛的问题。如果深度学习方法能够更好地模仿算法,那么算法中具有的那种泛化能力将有可能在深度学习中实现——这是目前机器学习方法还无法达到的。此外,通过表示习得算法连续空间中的要素,神经网络能使已知的算法更贴近现实世界的问题,有可能找到比计算机科学家提出的还更有效、更务实的解决方案。本文提出了神经算法推理——构建能执行算法计算的神经网络,并就其在以前被认为是无法使用的输入上运行经典算法的变革潜力提出自己的看法。
Algorithms have been fundamental to recent global technological advances and, in particular, they have been the cornerstone of technical advances in one field rapidly being applied to another. We argue that algorithms possess fundamentally different qualities to deep learning methods, and this strongly suggests that, were deep learning methods better able to mimic algorithms, generalisation of the sort seen with algorithms would become possible with deep learning—something far out of the reach of current machine learning methods. Furthermore, by representing elements in a continuous space of learnt algorithms, neural networks are able to adapt known algorithms more closely to real-world problems, potentially finding more efficient and pragmatic solutions than those proposed by human computer scientists. Here we present neural algorithmic reasoning—the art of building neural networks that are able to execute algorithmic computation—and provide our opinion on its transformative potential for running classical algorithms on inputs previously considered inaccessible to them.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Keslt8wU0
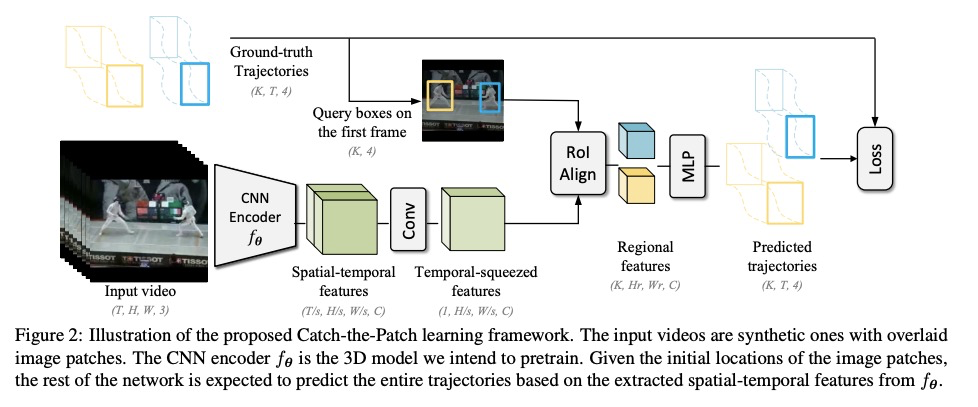
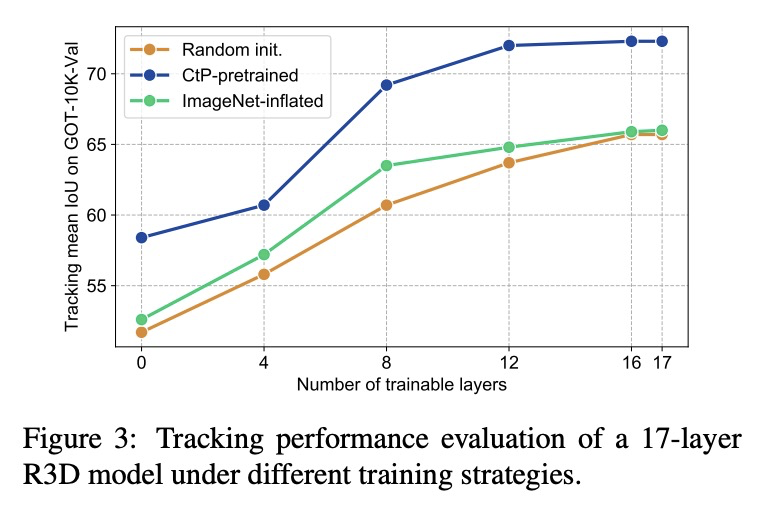
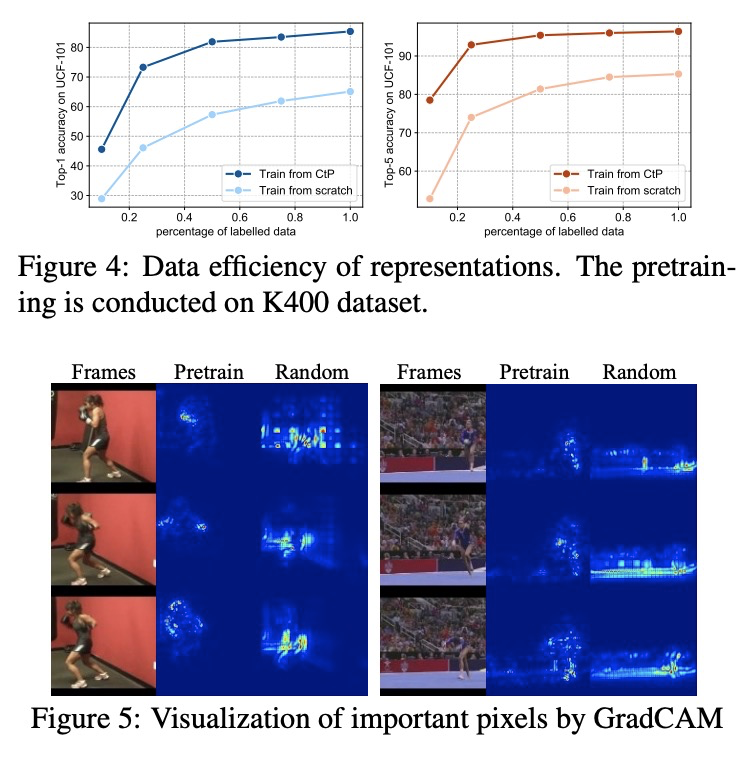
5、[CV] Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning by Tracking Patches in Video
G Wang, Y Zhou, C Luo, W Xie, W Zeng, Z Xiong
[University of Science and Technology of China & Microsoft Research Asia]
基于视频图块跟踪的无监督视觉表征学习。受人类眼睛在早期和中期持续发展跟踪能力的启发,本文建议将跟踪作为计算机视觉系统学习视觉表征的代理任务。以孩子们玩的”追捉”游戏为模型,为3D-CNN模型设计了一个”捕捉图块”(CtP)游戏,以学习有助于完成视频相关任务的视觉表征。所提出的预训练框架,从一个给定的视频中切割出图像块,让它按预先设定的轨迹缩放和移动。代理任务是在一连串的视频帧中估计图像块的位置和大小,只给定第一帧中的目标边框。同时用多个图块会带来明显的好处。通过随机使图块不可见来进一步增加游戏难度。对提出的方法进行了全面评估,CtP预训练不仅在标准的下游任务中取得了最先进的结果,还缩小了无监督和有监督的视频表示学习之间的性能差距。
Inspired by the fact that human eyes continue to develop tracking ability in early and middle childhood, we propose to use tracking as a proxy task for a computer vision system to learn the visual representations. Modelled on the Catch game played by the children, we design a Catch-thePatch (CtP) game for a 3D-CNN model to learn visual representations that would help with video-related tasks. In the proposed pretraining framework, we cut an image patch from a given video and let it scale and move according to a pre-set trajectory. The proxy task is to estimate the position and size of the image patch in a sequence of video frames, given only the target bounding box in the first frame. We discover that using multiple image patches simultaneously brings clear benefits. We further increase the difficulty of the game by randomly making patches invisible. Extensive experiments on mainstream benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance of CtP against other video pretraining methods. In addition, CtP-pretrained features are less sensitive to domain gaps than those trained by a supervised action recognition task. When both trained on Kinetics-400, we are pleasantly surprised to find that CtPpretrained representation achieves much higher action classification accuracy than its fully supervised counterpart on Something-Something dataset.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kesrk0rFd

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
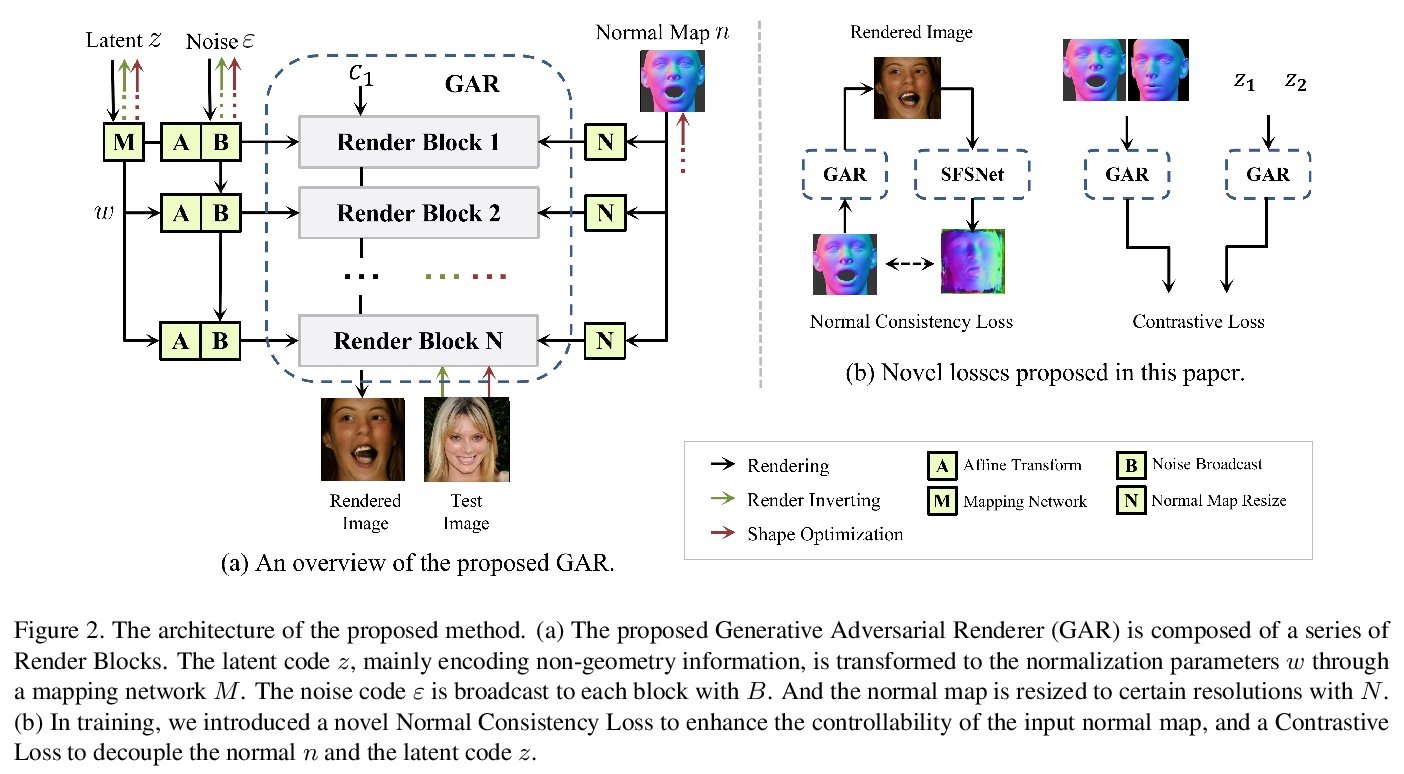
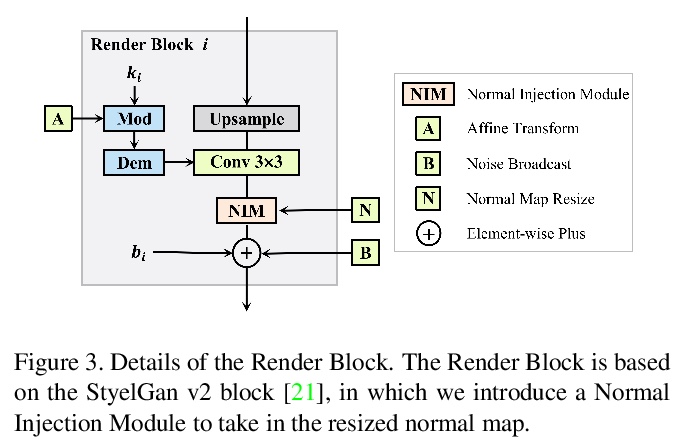
[CV] Inverting Generative Adversarial Renderer for Face Reconstruction
逆生成对抗渲染器人脸重建
J Piao, K Sun, K Lin, H Li
[The Chinese University of Hong Kong & SenseTime Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Keswb2nLw


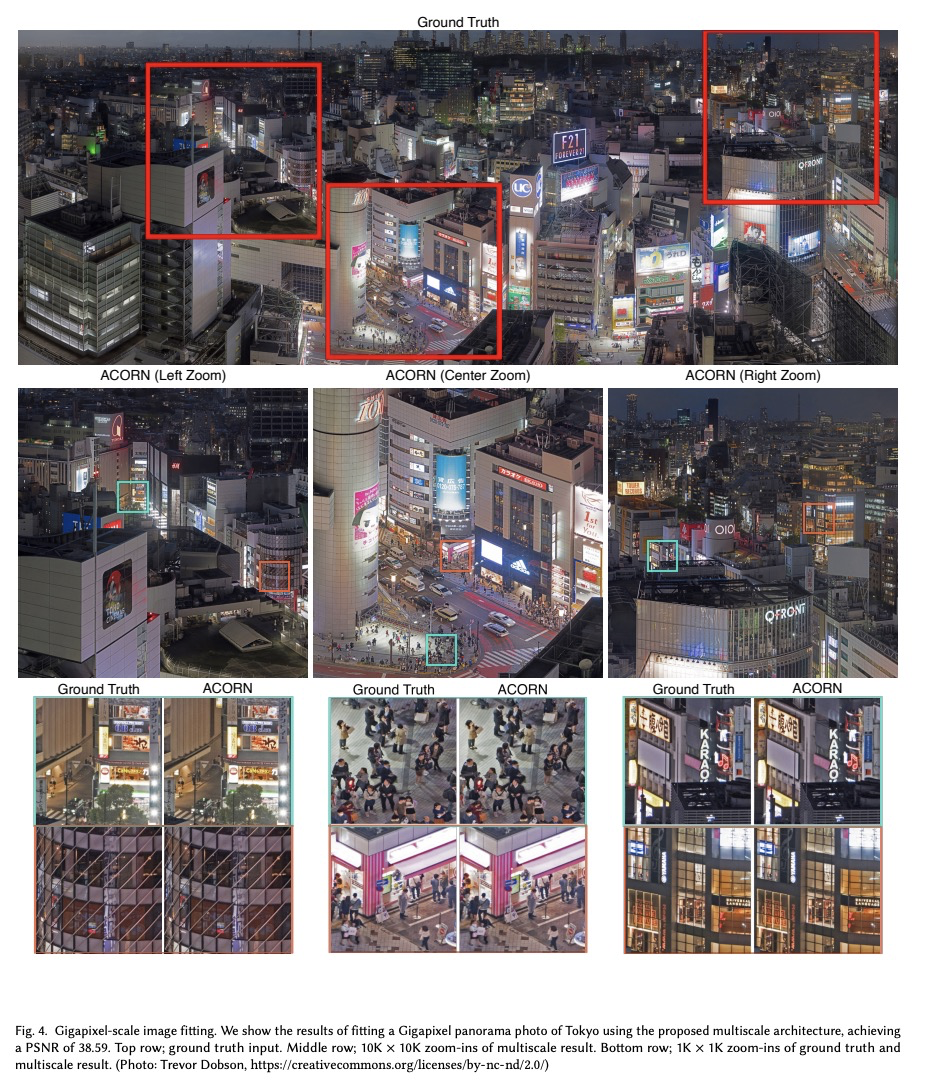
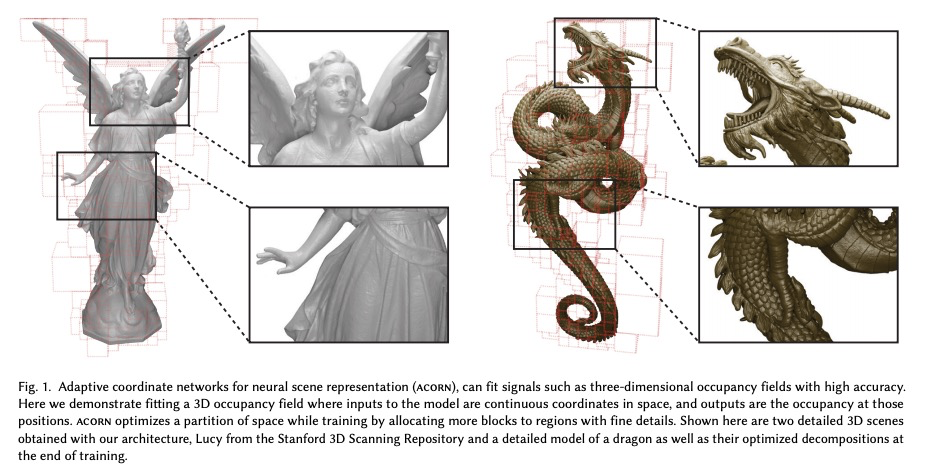
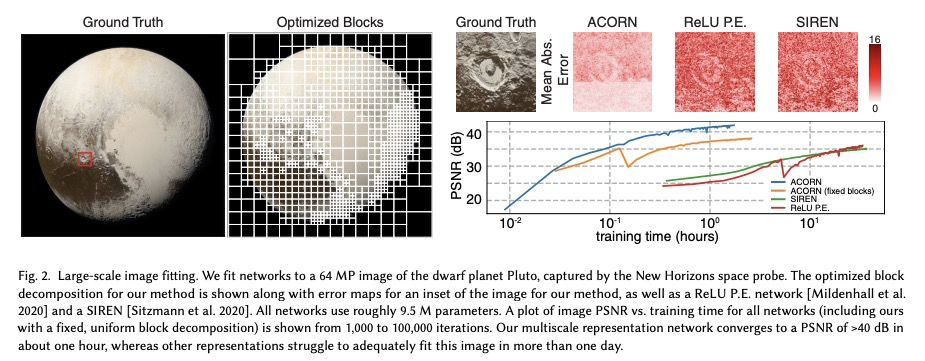
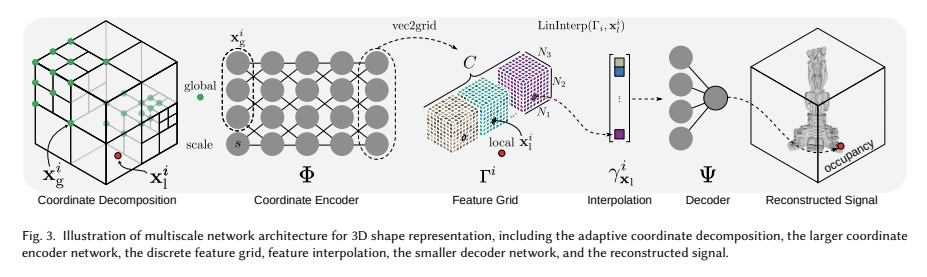
[CV] ACORN: Adaptive Coordinate Networks for Neural Scene Representation
ACORN:面向神经场景表示的自适应坐标网络
J N. P. Martel, D B. Lindell, C Z. Lin, E R. Chan, M Monteiro, G Wetzstein
[Stanford University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KesynfAXo

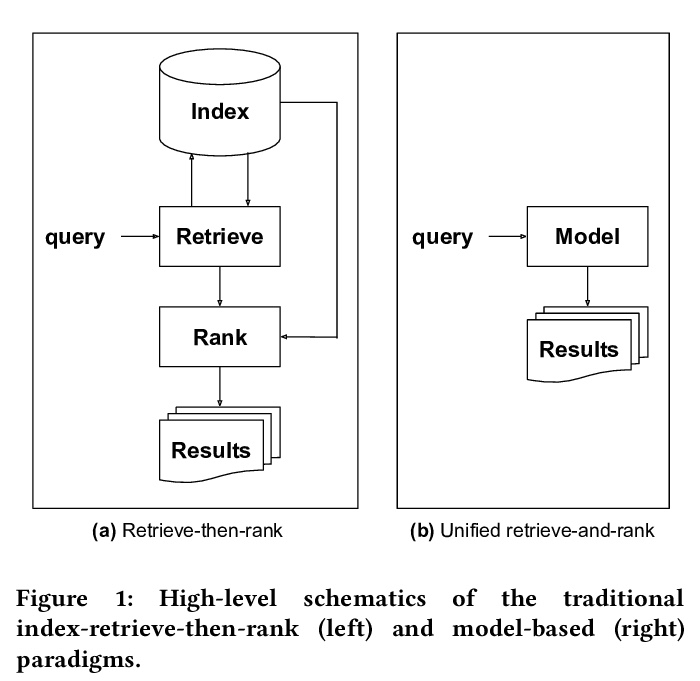
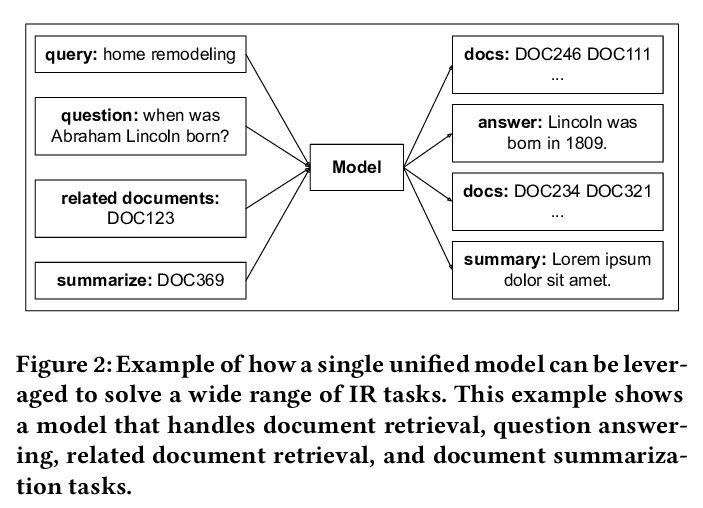
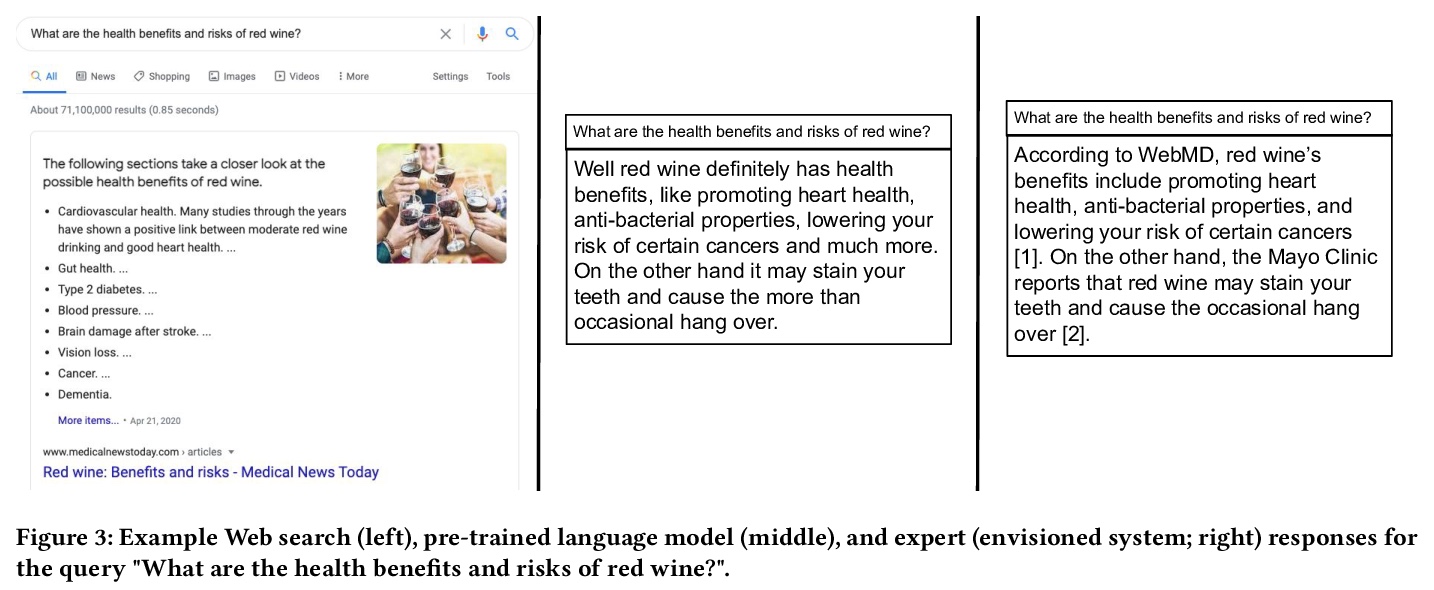
[IR] Rethinking Search: Making Experts out of Dilettantes
搜索的反思:IR与NLP进一步融合的下一代IR框架
D Metzler, Y Tay, D Bahri, M Najork
[Google Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KesBLoxNS
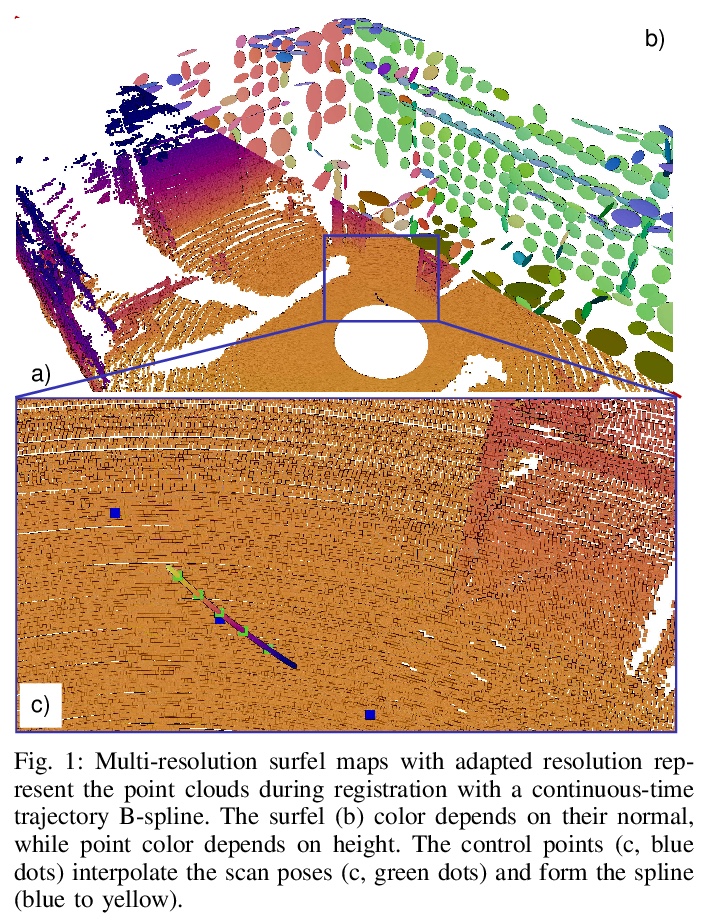
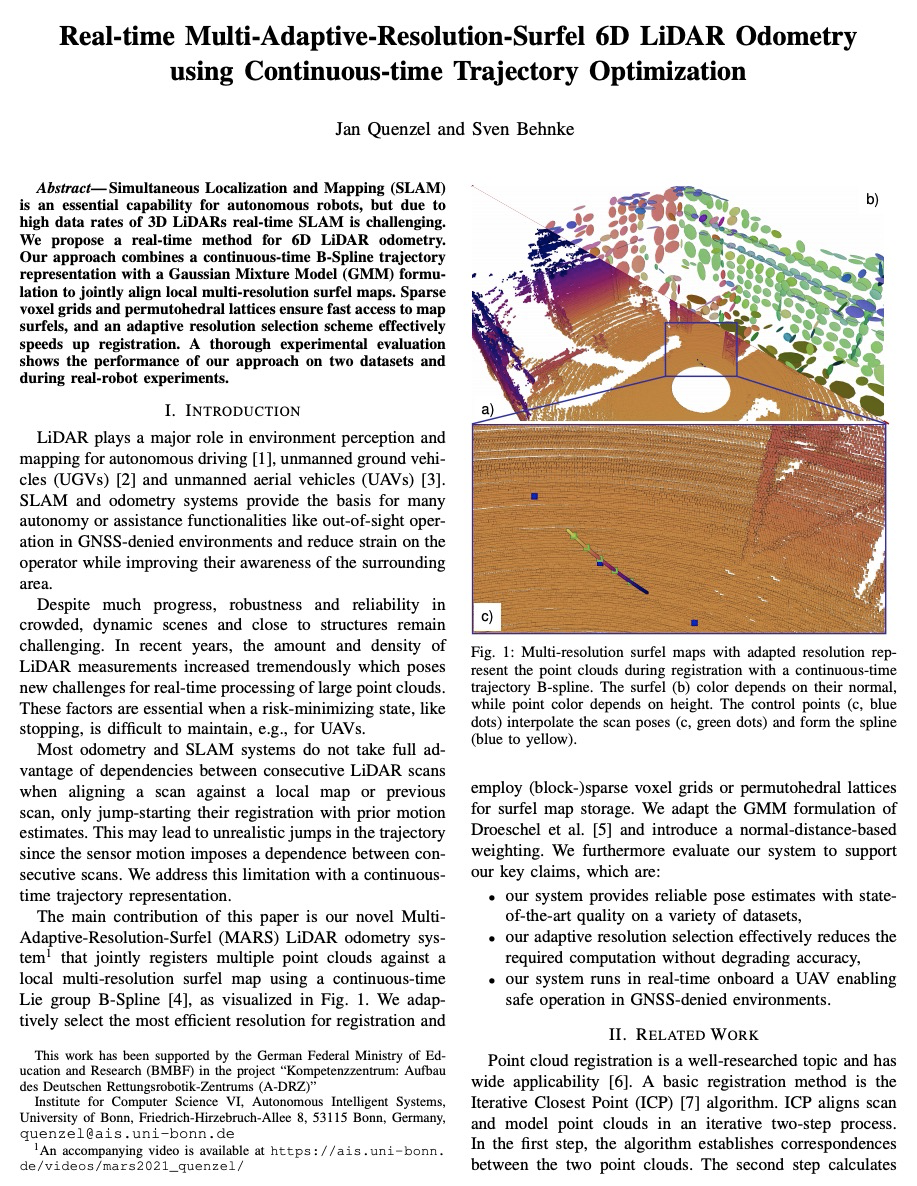
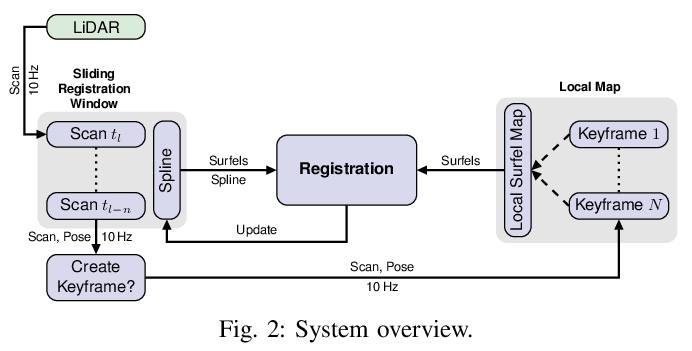
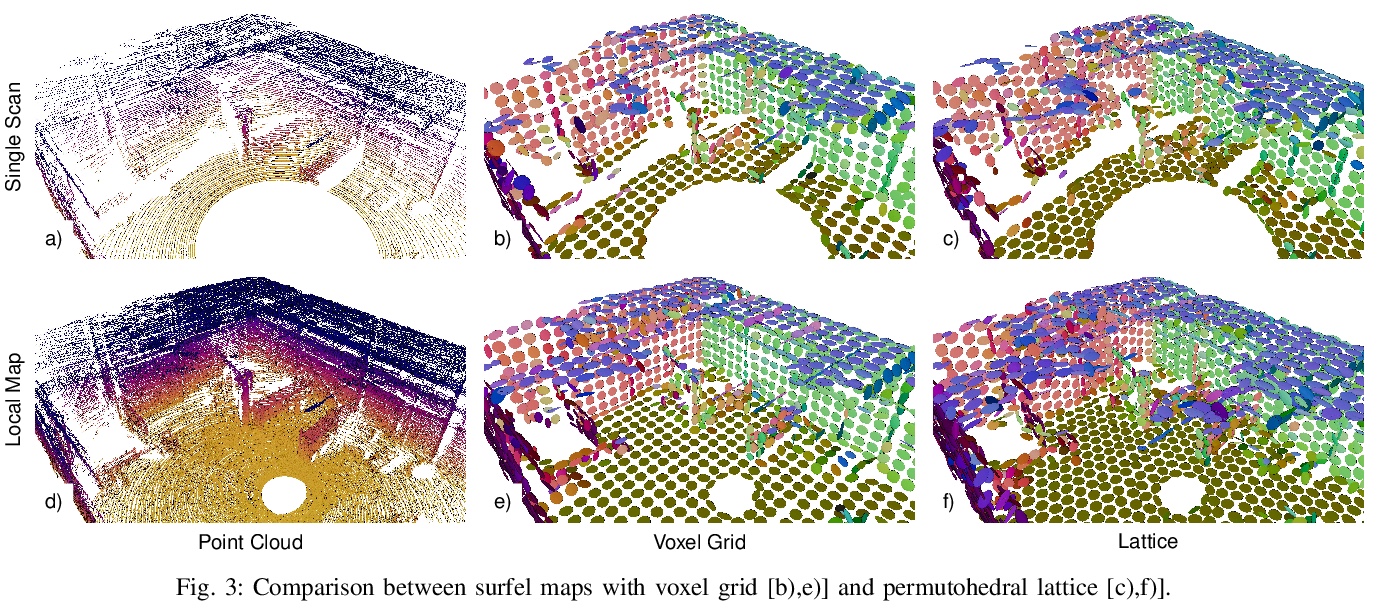
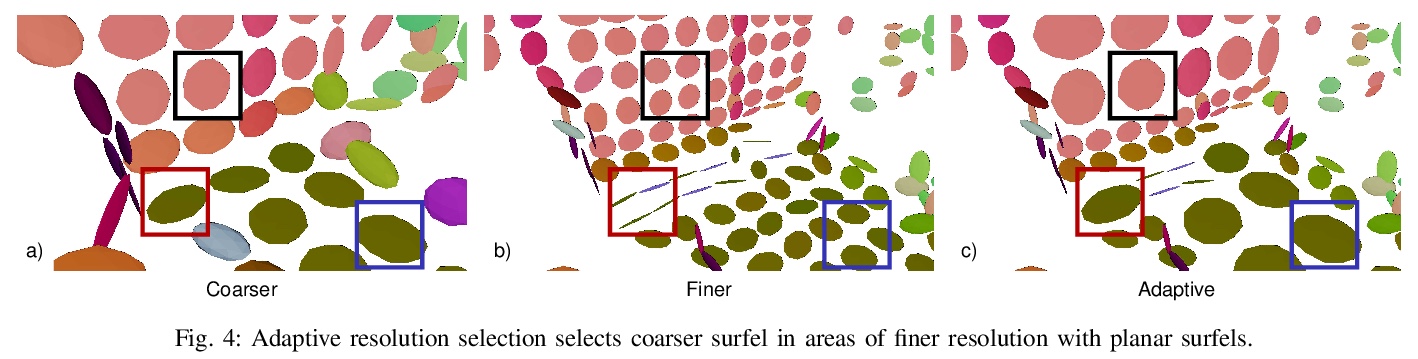
[RO] Real-time Multi-Adaptive-Resolution-Surfel 6D LiDAR Odometry using Continuous-time Trajectory Optimization
基于连续时间轨迹优化的实时多自适应分辨率表面6D激光雷达里程计
J Quenzel, S Behnke
[University of Bonn]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KesF8C3vu