- 1、[LG] E(n) Equivariant Normalizing Flows for Molecule Generation in 3D
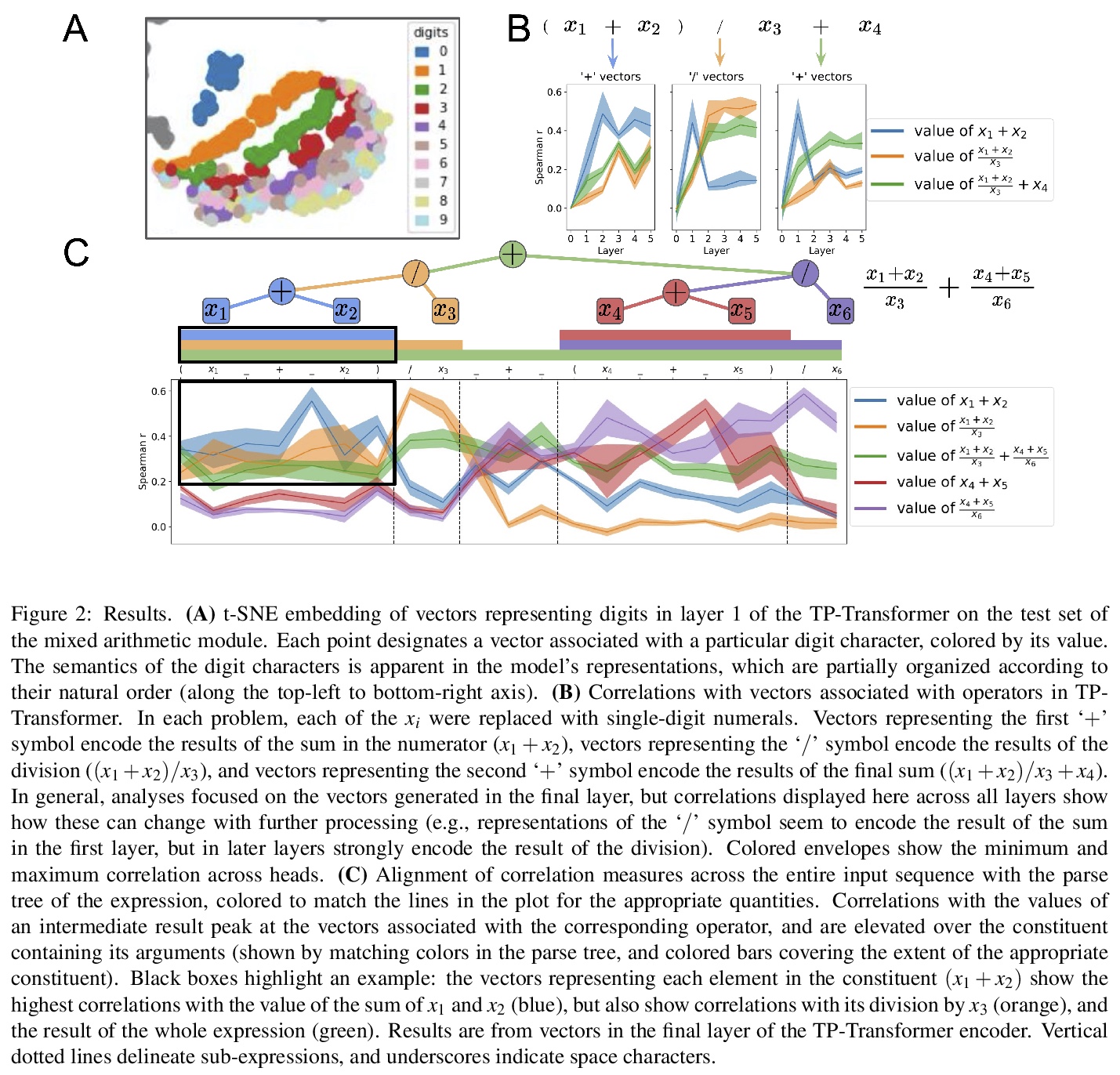
- 2、[LG] Compositional Processing Emerges in Neural Networks Solving Math Problems
- 3、[CV] Recursive-NeRF: An Efficient and Dynamically Growing NeRF
- 4、[CL] User Preference-aware Fake News Detection
- 5、[CV] High-Resolution Photorealistic Image Translation in Real-Time: A Laplacian Pyramid Translation Network
- [CV] Pathdreamer: A World Model for Indoor Navigation
- [CL] Effective Attention Sheds Light On Interpretability
- [CV] Large-scale Localization Datasets in Crowded Indoor Spaces
- [CV] Multi-Person Extreme Motion Prediction with Cross-Interaction Attention
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
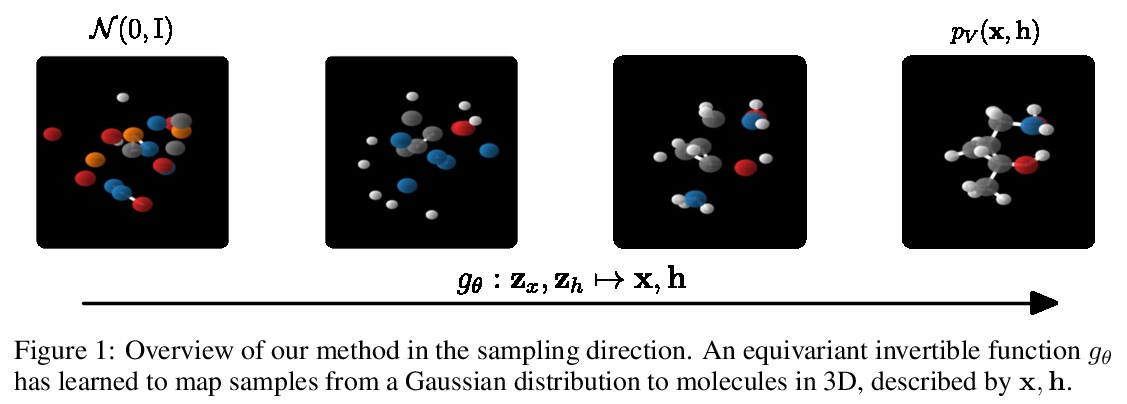
1、[LG] E(n) Equivariant Normalizing Flows for Molecule Generation in 3D
V G Satorras, E Hoogeboom, F B. Fuchs, I Posner, M Welling
[University of Amsterdam & University of Oxford]
E(n)等价归一化流3D分子生成。提出一种与欧几里得对称性等价的生成模型:E(n)等价归一化流(E-NF)。为构建E-NFs,将判别性E(n)图神经网络整合为一个微分方程,以获得可逆的等价函数:连续时间归一化流。证明了E-NF在DW4和LJ13等粒子系统以及QM9的分子上的对数可能性方面大大超过了基线和文献中的现有方法。这是第一个基于似然的深度生成模型,可生成3D分子。
This paper introduces a generative model equivariant to Euclidean symmetries: E(n) Equivariant Normalizing Flows (E-NFs). To construct E-NFs, we take the discriminative E(n) graph neural networks and integrate them as a differential equation to obtain an invertible equivariant function: a continuous-time normalizing flow. We demonstrate that E-NFs considerably outperform baselines and existing methods from the literature on particle systems such as DW4 and LJ13, and on molecules from QM9 in terms of log-likelihood. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first likelihood-based deep generative model that generates molecules in 3D.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KgqHb4U42
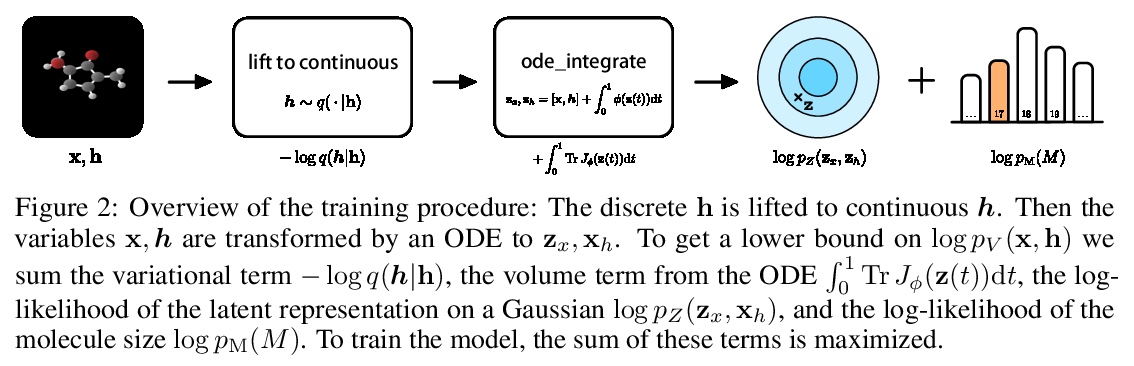
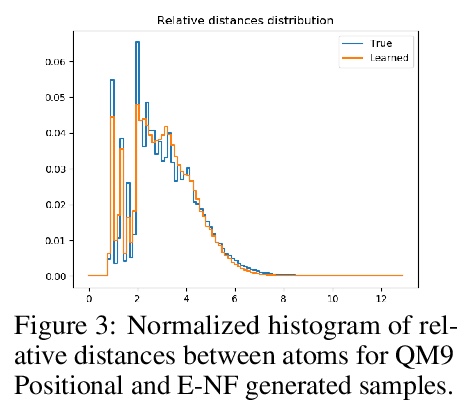
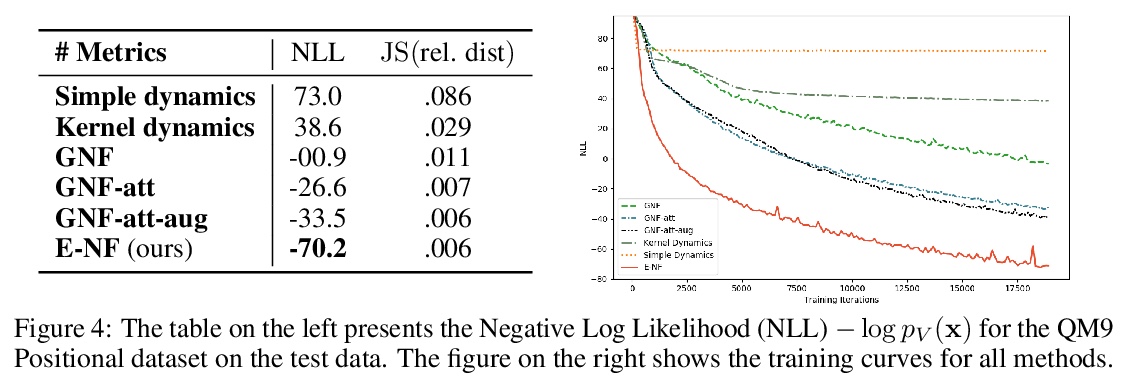
2、[LG] Compositional Processing Emerges in Neural Networks Solving Math Problems
J Russin, R Fernandez, H Palangi, E Rosen, N Jojic, P Smolensky, J Gao
[UC Davis & Microsoft Research & Johns Hopkins University]
神经网络求解数学问题中涌现的合成性语义。认知科学中一个长期存在的问题涉及人类认知中合成性的学习机制。人类可以推断出其感官观察(如听觉语言)中隐含的结构关系(如语法规则),并利用这些知识来指导将较简单的意义组成复杂的整体。人工神经网络的最新进展表明,当大型模型在足够多的语言数据上进行训练时,语法结构就会在其表征中涌现。将这项工作扩展到数学推理领域,在该领域,有可能制定关于如何根据结构化规则(如运算顺序)合成意义(如对应于数字的数量)的精确假设。本文工作表明,神经网络不仅能够推断出一些隐含在其训练数据中的结构性关系,还能运用这些知识来指导将单个意义组成合成整体。隐含在字符级数学问题中的合成性语义可在神经网络中涌现。
A longstanding question in cognitive science concerns the learning mechanisms underlying compositionality in human cognition. Humans can infer the structured relationships (e.g., grammatical rules) implicit in their sensory observations (e.g., auditory speech), and use this knowledge to guide the composition of simpler meanings into complex wholes. Recent progress in artificial neural networks has shown that when large models are trained on enough linguistic data, grammatical structure emerges in their representations. We extend this work to the domain of mathematical reasoning, where it is possible to formulate precise hypotheses about how meanings (e.g., the quantities corresponding to numerals) should be composed according to structured rules (e.g., order of operations). Our work shows that neural networks are not only able to infer something about the structured relationships implicit in their training data, but can also deploy this knowledge to guide the composition of individual meanings into composite wholes.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KgqJNzUpd
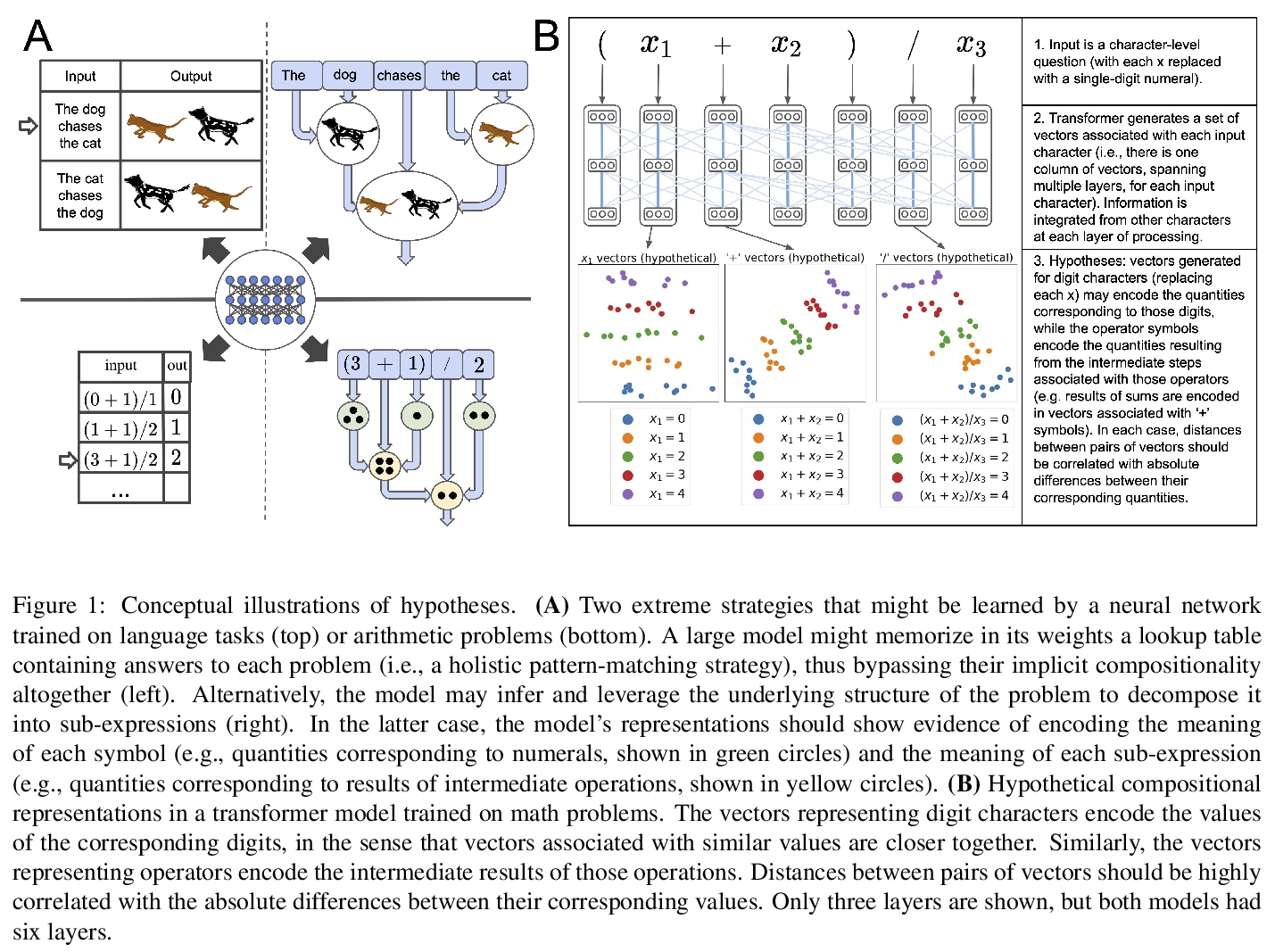
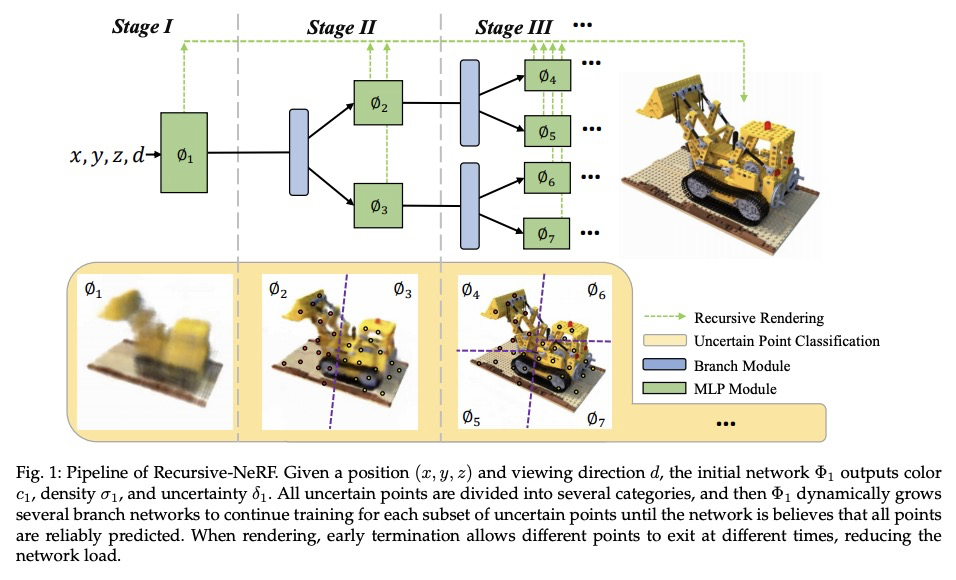
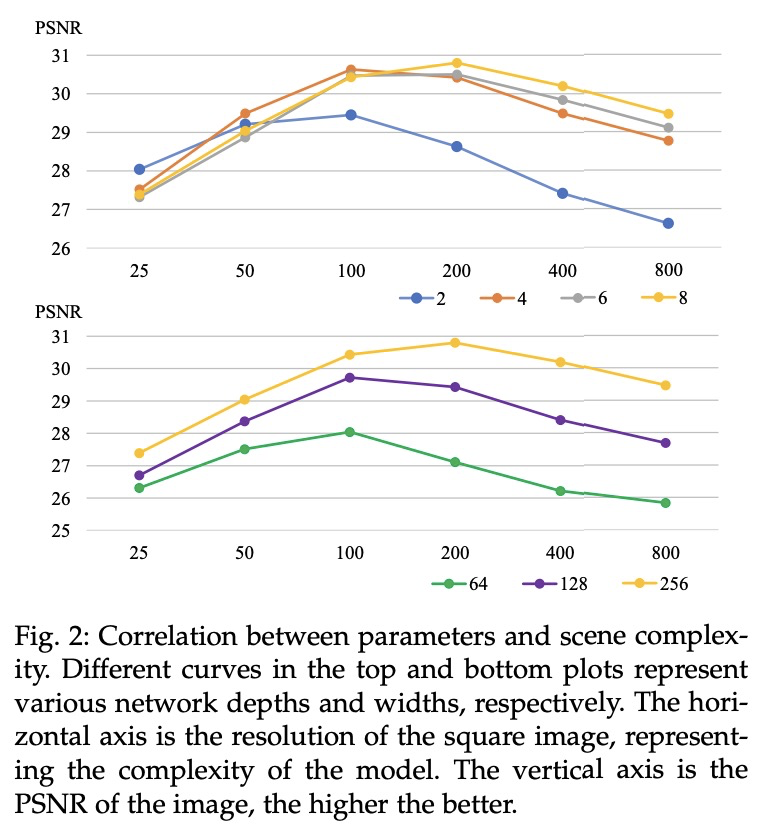
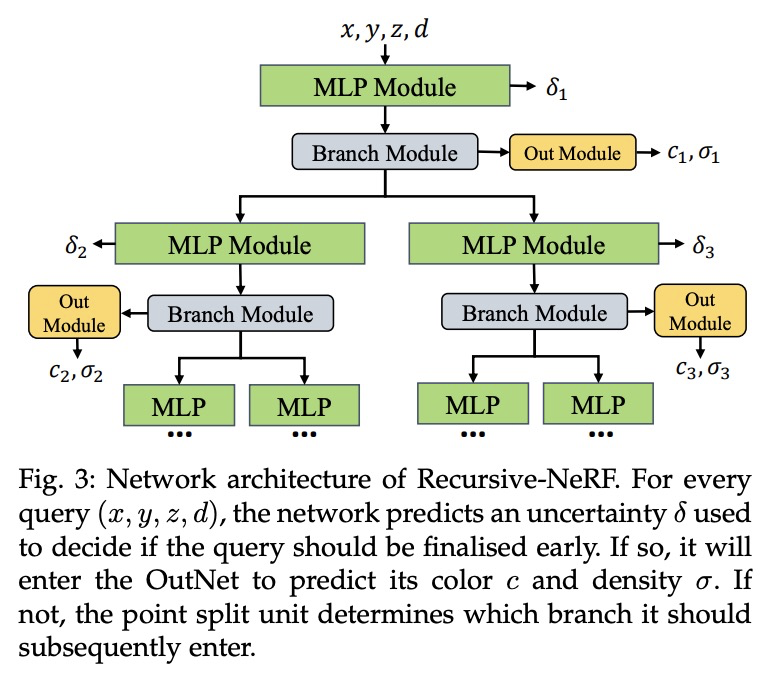
3、[CV] Recursive-NeRF: An Efficient and Dynamically Growing NeRF
G Yang, W Zhou, H Peng, D Liang, T Mu, S Hu
[Tsinghua University]
递归-神经辐射场:一种高效且动态生长的神经辐射场。使用从一组图像中学习到的隐连续形状表征的视图合成方法,如神经辐射场(NeRF)方法,由于高质量的图像和对高分辨率的可扩展性,已经获得了越来越多的关注。然而,方法所需的繁重计算,使NeRF在实践中无法发挥作用;渲染一张几百万像素的图像需要几分钟。现在,一个场景的图像可以按细节等级进行渲染,复杂场景区域应该由大的神经网络来表示,而小的神经网络能编码简单区域,从而实现效率和质量之间的平衡。递归神经辐射场是对这一思想的体现,为NeRF提供了一种高效和自适应的渲染和训练方法。递归-神经辐射场的核心,是学习查询坐标的不确定性,代表每一级预测的颜色和体强度的质量。只有具有高不确定性的查询坐标才会被转发到下一级具有更强大表示能力的大型神经网络。最终呈现的图像,是由所有级别的神经网络的结果组成的。对三个公共数据集的评估表明,递归-神经网络比神经网络更有效率,同时提供最先进的质量。
View synthesis methods using implicit continuous shape representations learned from a set of images, such as the Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) method, have gained increasing attention due to their high quality imagery and scalability to high resolution. However, the heavy computation required by its volumetric approach prevents NeRF from being useful in practice; minutes are taken to render a single image of a few megapixels. Now, an image of a scene can be rendered in a level-of-detail manner, so we posit that a complicated region of the scene should be represented by a large neural network while a small neural network is capable of encoding a simple region, enabling a balance between efficiency and quality. Recursive-NeRF is our embodiment of this idea, providing an efficient and adaptive rendering and training approach for NeRF. The core of Recursive-NeRF learns uncertainties for query coordinates, representing the quality of the predicted color and volumetric intensity at each level. Only query coordinates with high uncertainties are forwarded to the next level to a bigger neural network with a more powerful representational capability. The final rendered image is a composition of results from neural networks of all levels. Our evaluation on three public datasets shows that Recursive-NeRF is more efficient than NeRF while providing state-of-the-art quality.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KgqNJ8yZ0

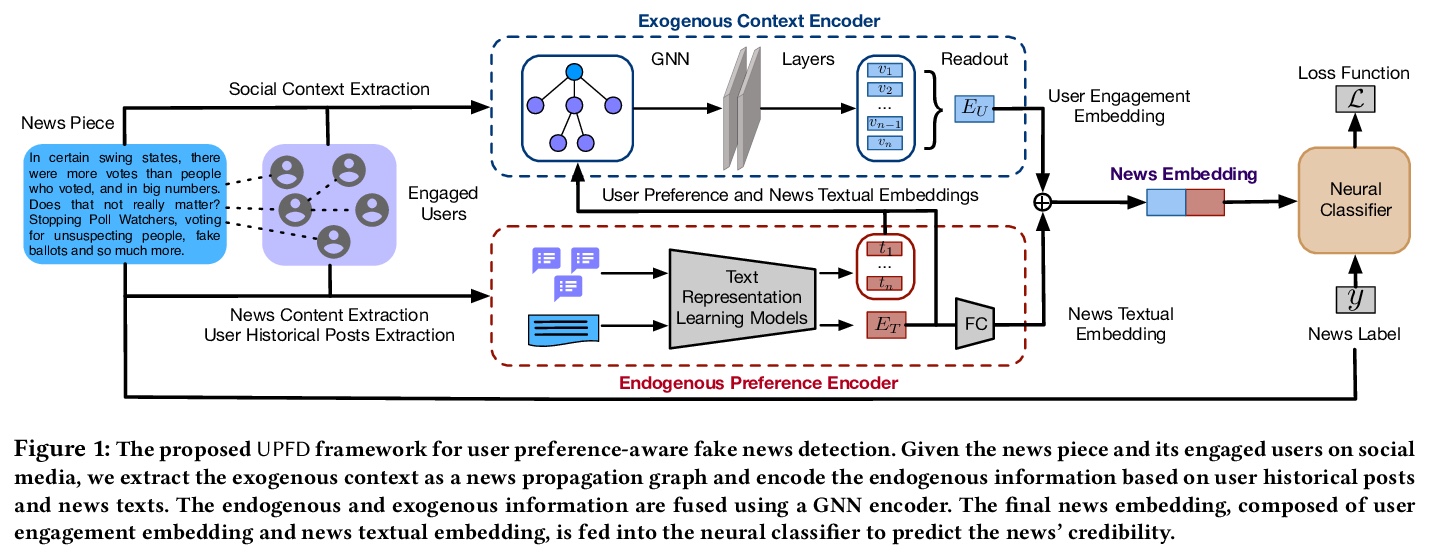
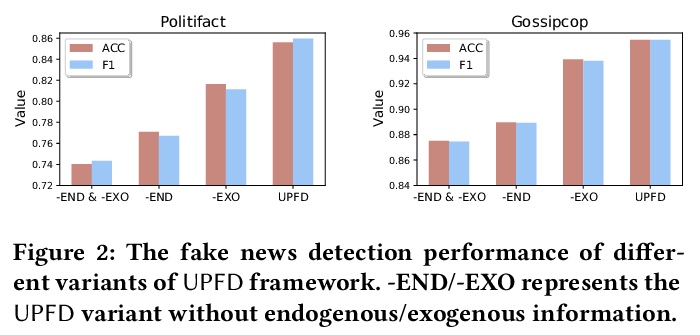
4、[CL] User Preference-aware Fake News Detection
Y Dou, K Shu, C Xia, P S. Yu, L Sun
[University of Illinois at Chicago & Illinois Institute of Technology & Lehigh University]
用户偏好感知的假新闻检测。近年来,假消息和假新闻对个人和社会造成了有害影响,引起了人们对假新闻检测的广泛关注。现有的假新闻检测算法大多集中在挖掘新闻内容和/或周围的外生环境以发现欺骗性信号;而用户在决定是否传播假新闻时的内生偏好却被忽略了。确认偏见理论指出,当假新闻证实了用户现有的信念/偏好时,其更有可能传播假新闻。用户的历史、社交活动(如帖子)提供了关于用户对新闻的偏好的丰富信息,对推进假新闻检测有很大的潜力。然而,探索用户对假新闻检测的偏好的工作,在某种程度上是有限的。本文研究了利用用户偏好进行假新闻检测的问题,提出一个新框架UPFD,通过内容和图联合建模,同时捕捉来自用户偏好的各种信号。在真实世界的数据集上的实验结果,证明了所提框架的有效性。
Disinformation and fake news have posed detrimental effects on individuals and society in recent years, attracting broad attention to fake news detection. The majority of existing fake news detection algorithms focus on mining news content and/or the surrounding exogenous context for discovering deceptive signals; while the endogenous preference of a user when he/she decides to spread a piece of fake news or not is ignored. The confirmation bias theory has indicated that a user is more likely to spread a piece of fake news when it confirms his/her existing beliefs/preferences. Users’ historical, social engagements such as posts provide rich information about users’ preferences toward news and have great potentials to advance fake news detection. However, the work on exploring user preference for fake news detection is somewhat limited. Therefore, in this paper, we study the novel problem of exploiting user preference for fake news detection. We propose a new framework, UPFD, which simultaneously captures various signals from user preferences by joint content and graph modeling. Experimental results on real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KgqQdl4la
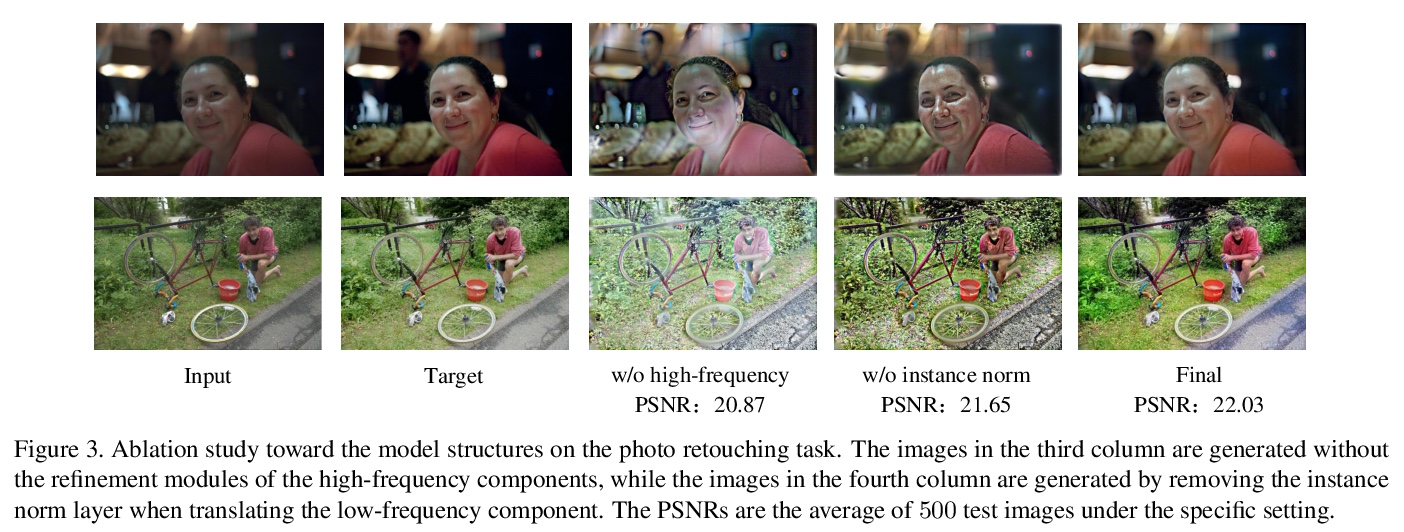
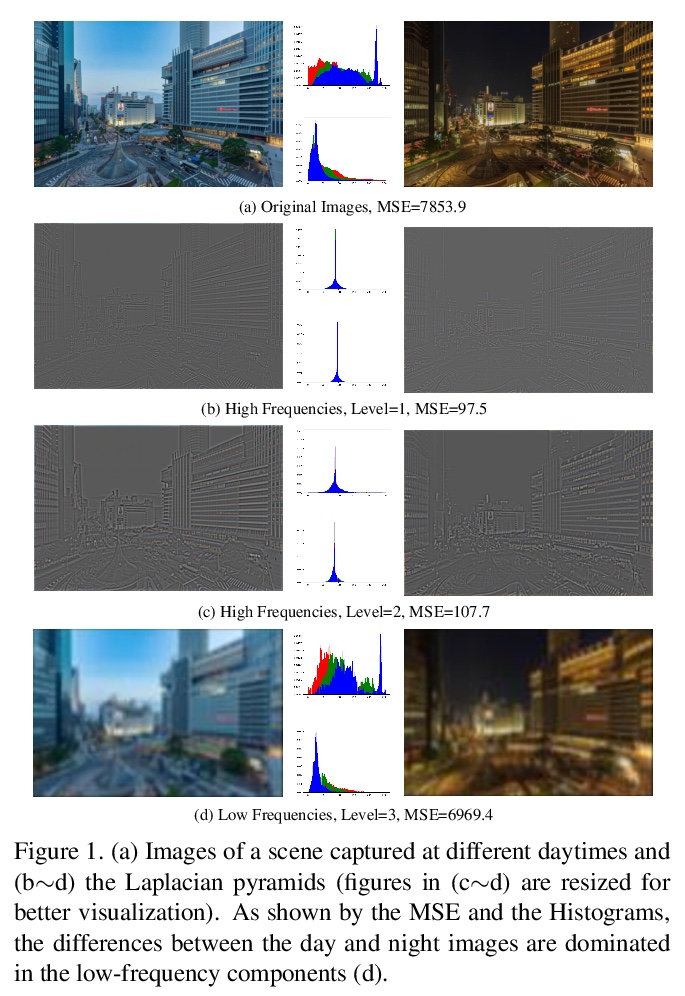
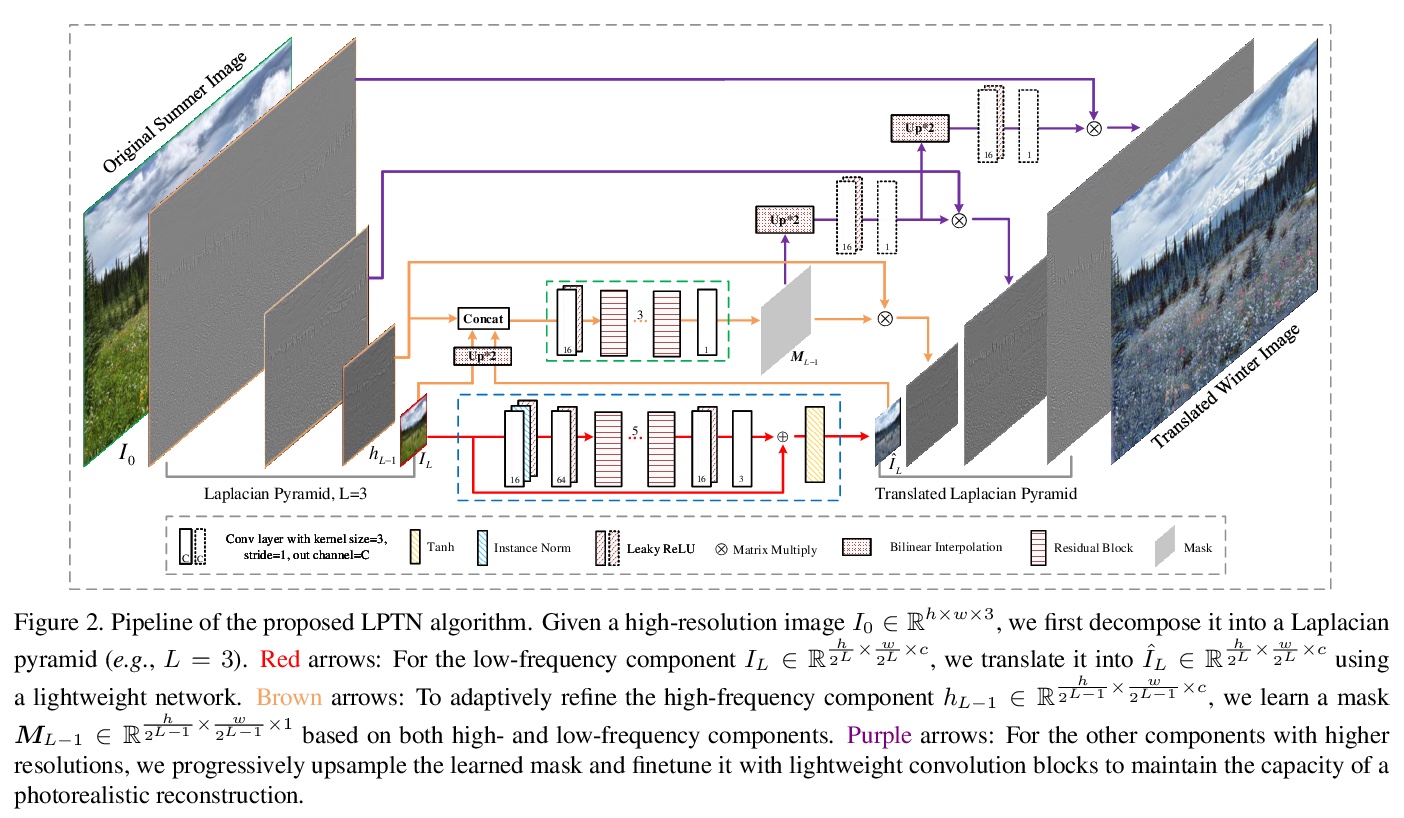
5、[CV] High-Resolution Photorealistic Image Translation in Real-Time: A Laplacian Pyramid Translation Network
J Liang, H Zeng, L Zhang
[The HongKong Polytechnic University]
高分辨率逼真图像实时转换:拉普拉斯金字塔转换网络。现有的图像到图像转换(I2IT)方法,要么受限于低分辨率图像,要么由于对高分辨率特征图的卷积有沉重的计算负担而导致推理时间长。本文专注于加快基于闭式拉普拉斯金字塔分解和重建的高分辨率逼真I2IT任务。揭示了属性转换,如光照和颜色处理,更多的是与低频分量有关,而内容细节可以在高频分量上自适应细化。提出一种拉普拉斯金字塔转换网络(LPTN),用来同时执行这两项任务,设计了一种轻量网络来转换分辨率降低的低频分量,以及渐进式的掩蔽策略,用来有效地完善高频分量。该模型避免了处理高分辨率特征图所消耗的大部分沉重计算,忠实地保留了图像的细节。在各种任务上的大量实验结果表明,所提出的方法可以使用一个普通的GPU实时4K图像转换,同时取得与现有方法相当的转换性能。
Existing image-to-image translation (I2IT) methods are either constrained to low-resolution images or long inference time due to their heavy computational burden on the convolution of high-resolution feature maps. In this paper, we focus on speeding-up the high-resolution photorealistic I2IT tasks based on closed-form Laplacian pyramid decomposition and reconstruction. Specifically, we reveal that the attribute transformations, such as illumination and color manipulation, relate more to the low-frequency component, while the content details can be adaptively refined on high-frequency components. We consequently propose a Laplacian Pyramid Translation Network (LPTN) to simultaneously perform these two tasks, where we design a lightweight network for translating the low-frequency component with reduced resolution and a progressive masking strategy to efficiently refine the high-frequency ones. Our model avoids most of the heavy computation consumed by processing high-resolution feature maps and faithfully preserves the image details. Extensive experimental results on various tasks demonstrate that the proposed method can translate 4K images in real-time using one normal GPU while achieving comparable transformation performance against existing methods.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KgqSB72sz


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
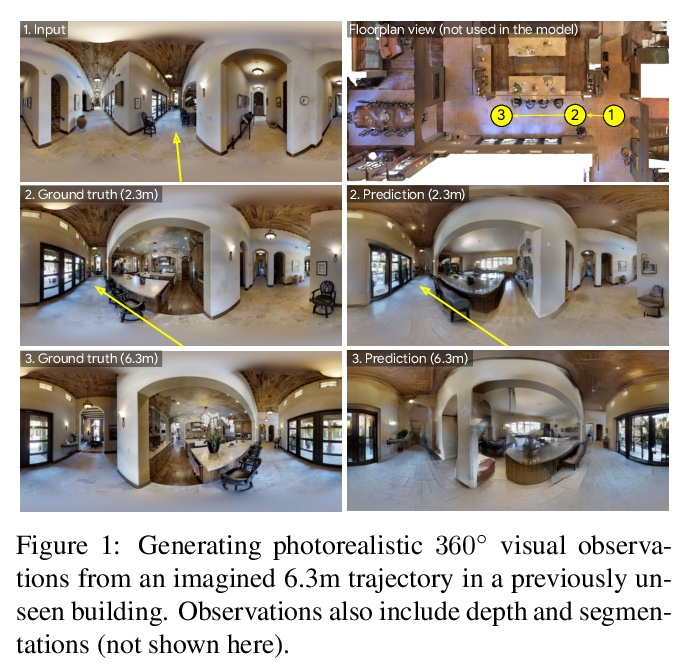
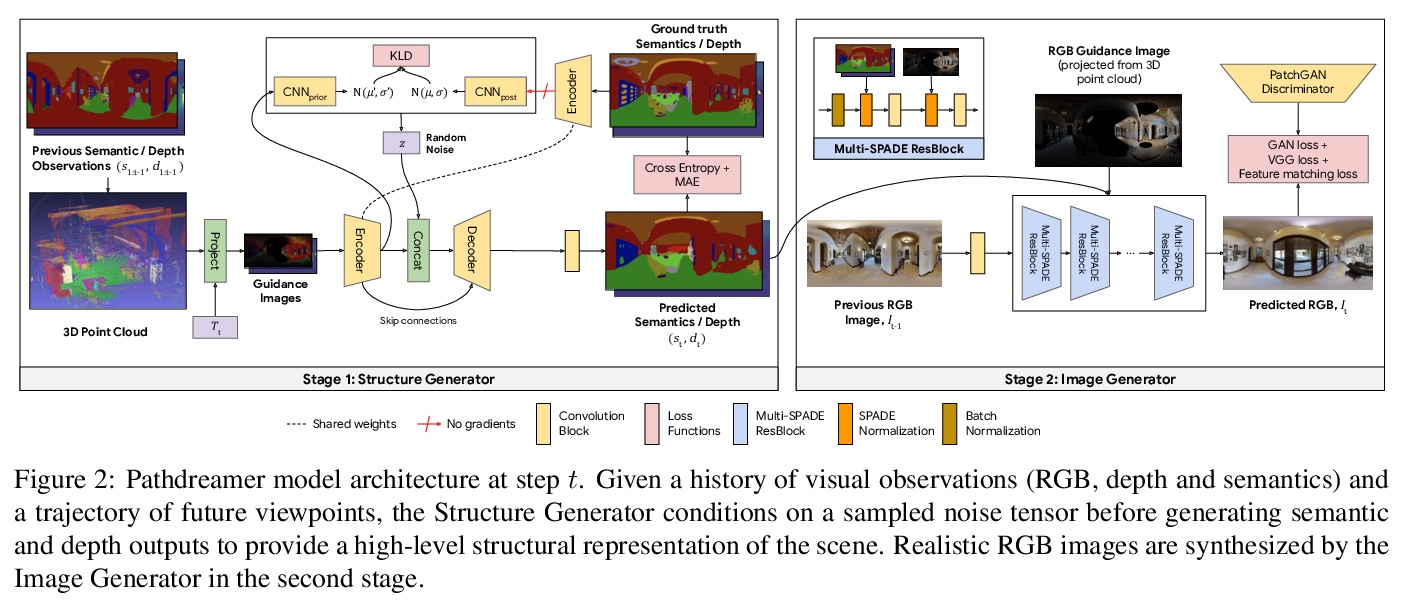
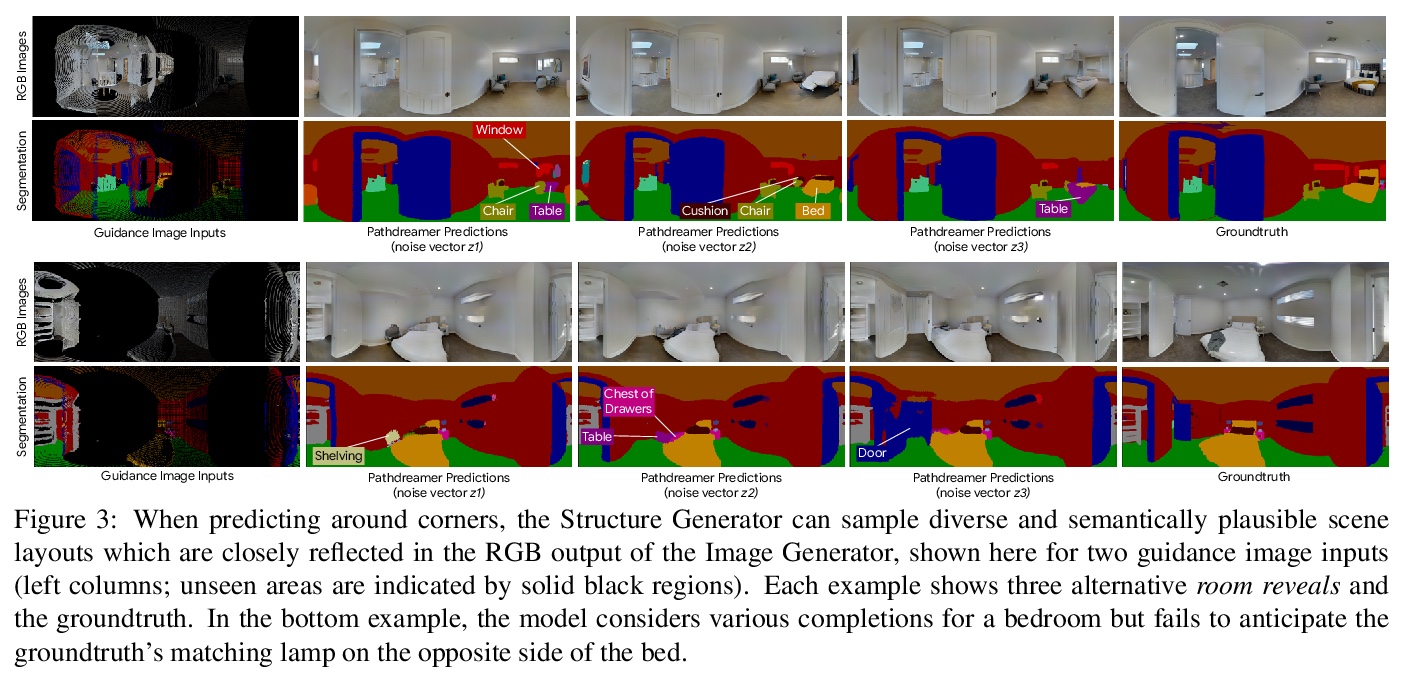
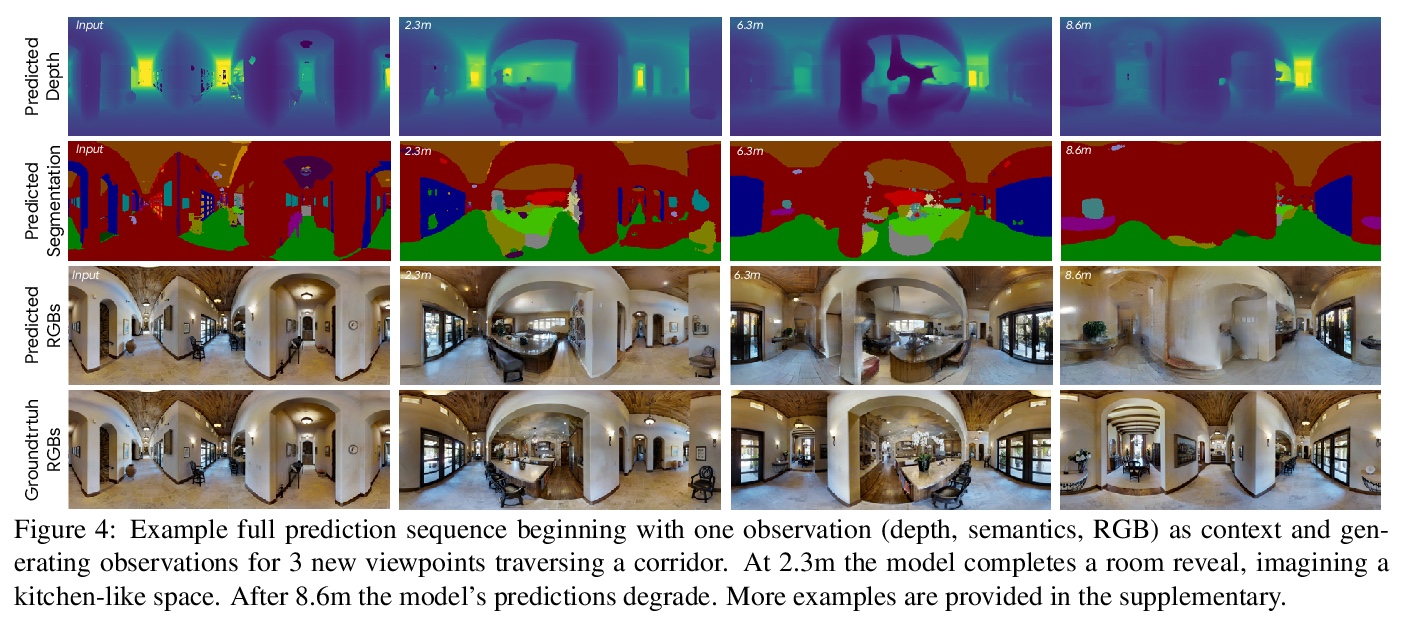
[CV] Pathdreamer: A World Model for Indoor Navigation
Pathdreamer: 室内导航的世界模型
J Y Koh, H Lee, Y Yang, J Baldridge, P Anderson
[Google Research & University of Michigan]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KgqVAqD73

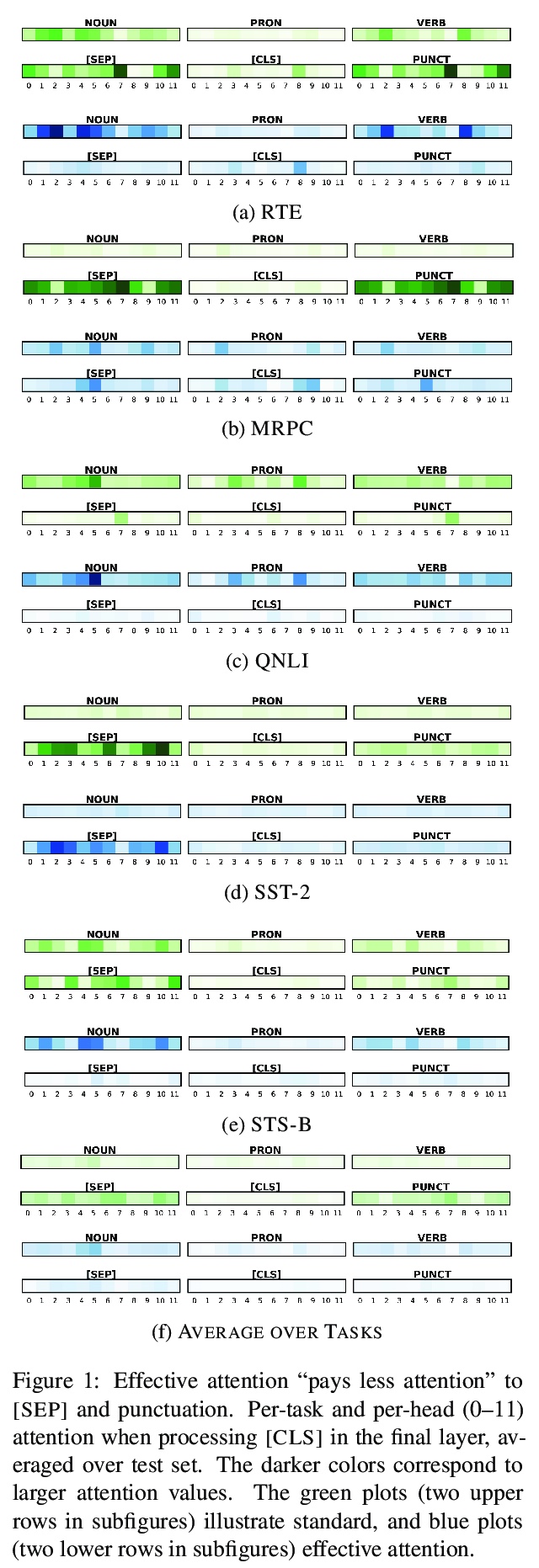
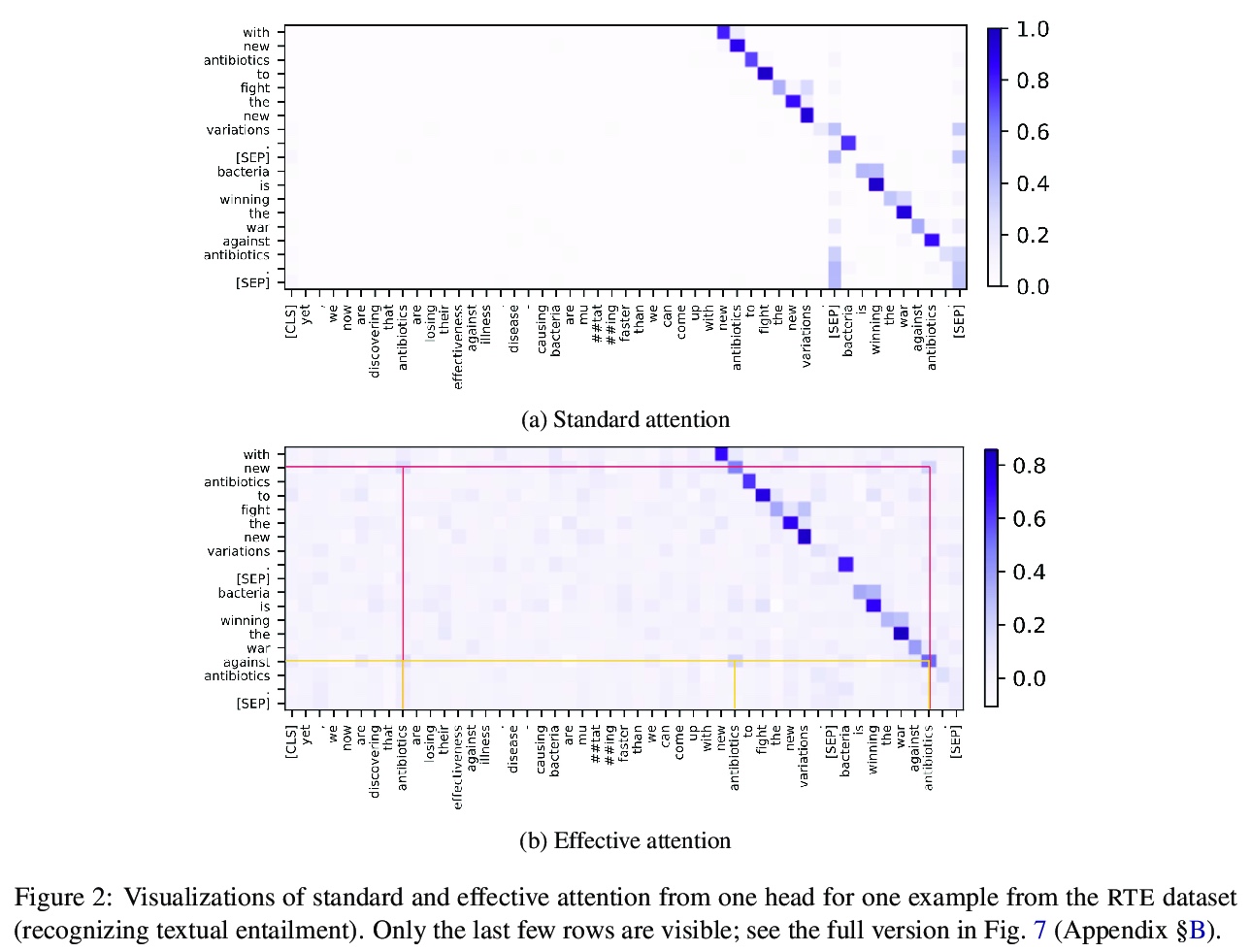
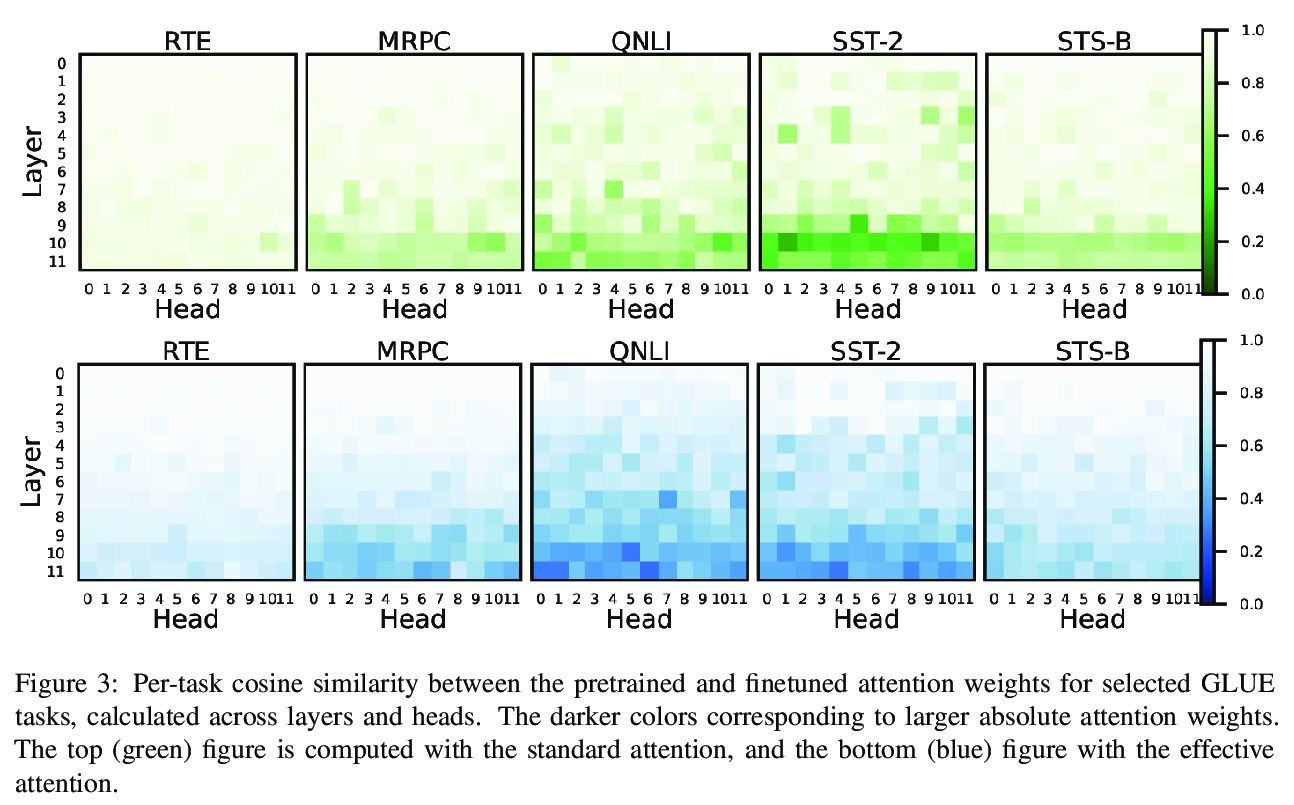
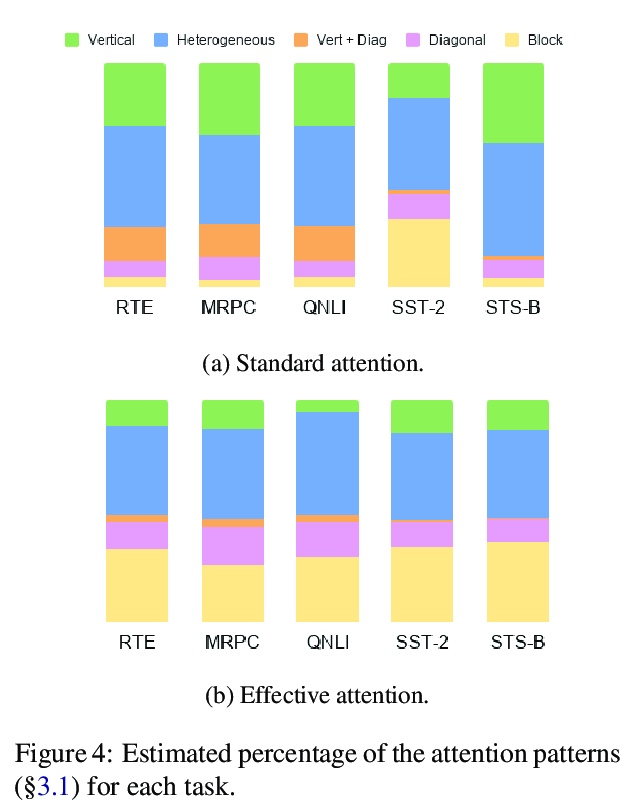
[CL] Effective Attention Sheds Light On Interpretability
用有效注意力揭示可解释性
K Sun, A Marasović
[University of Washington & Allen Institute for AI]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KgqX1096f
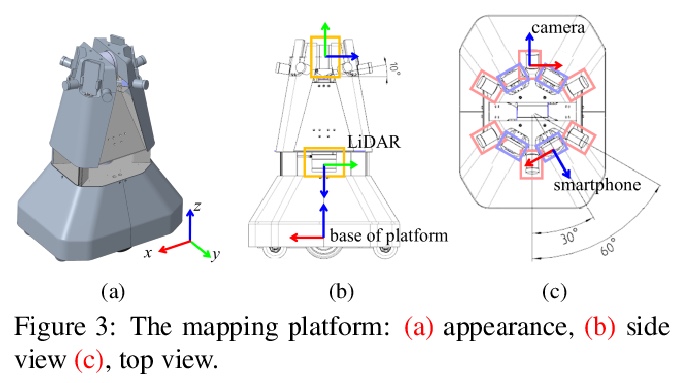
[CV] Large-scale Localization Datasets in Crowded Indoor Spaces
拥挤室内空间大规模定位数据集
D Lee, S Ryu, S Yeon, Y Lee, D Kim, C Han, Y Cabon, P Weinzaepfel, N Guérin, G Csurka, M Humenberger
[NAVER LABS]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KgqYPzW0c


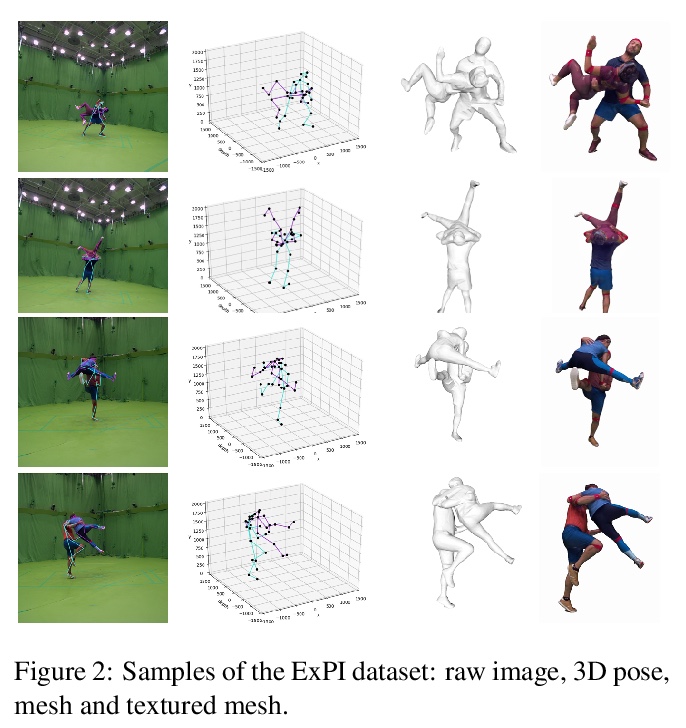
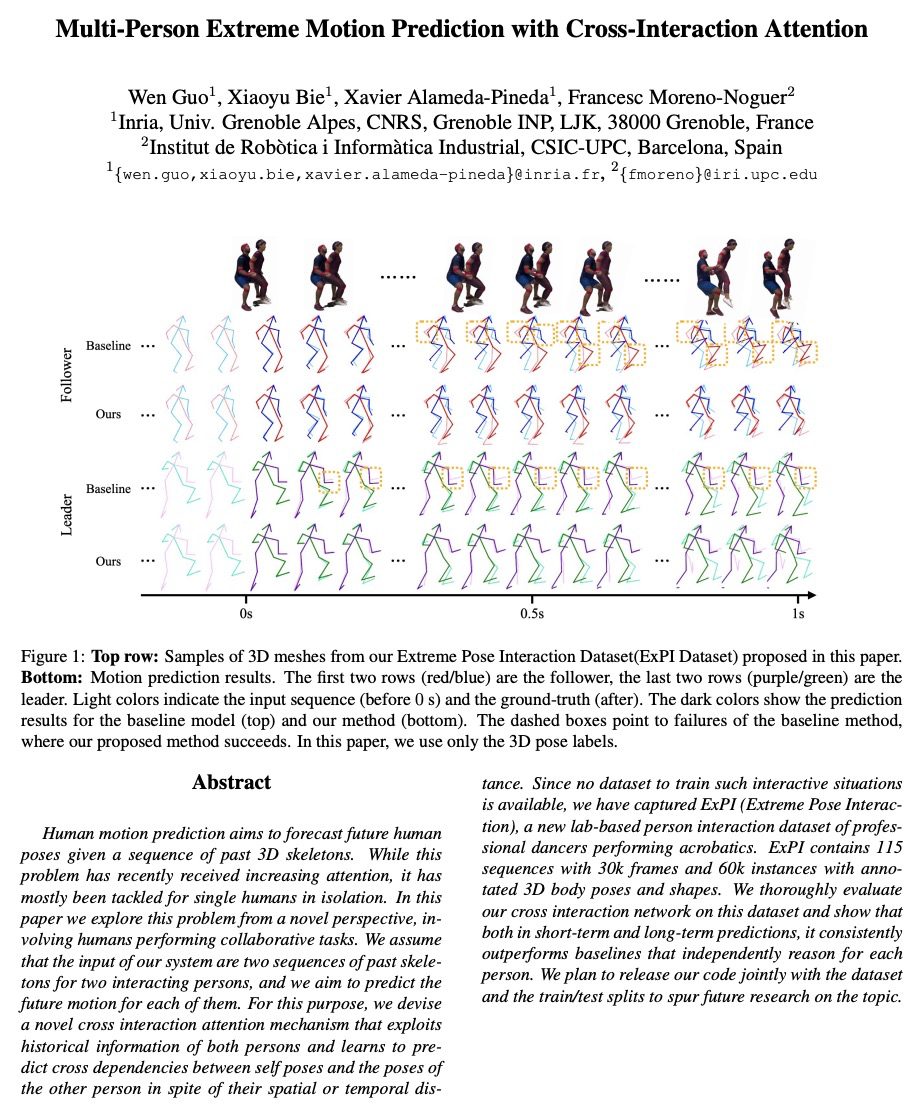
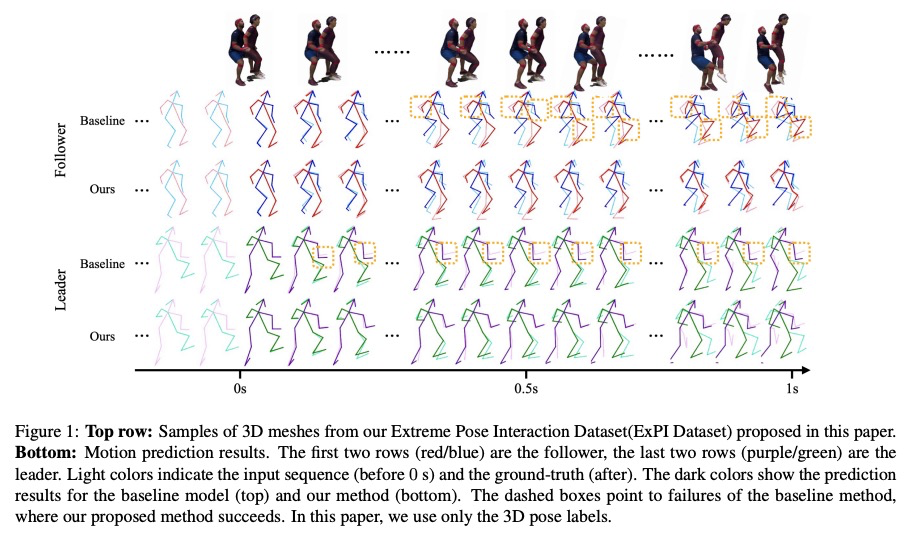
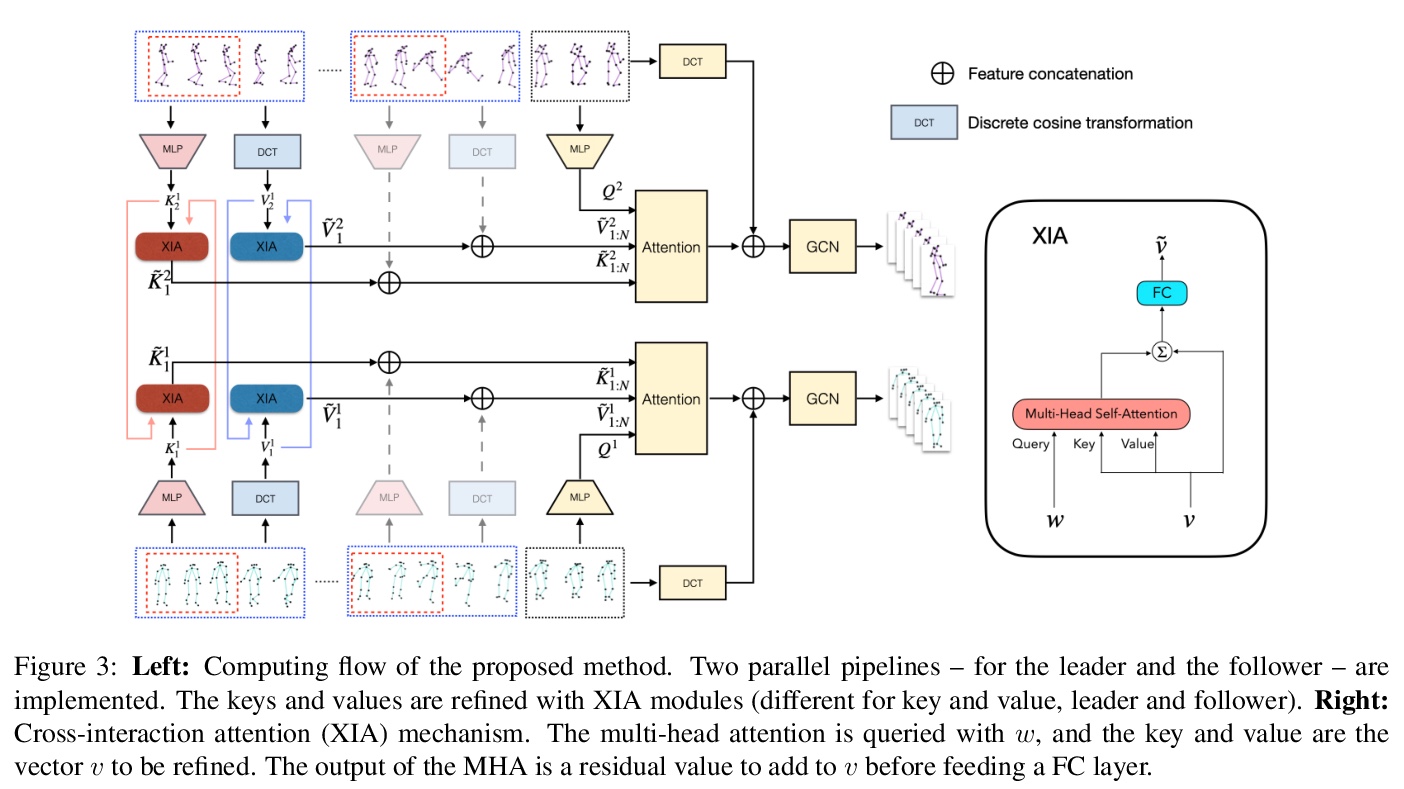
[CV] Multi-Person Extreme Motion Prediction with Cross-Interaction Attention
基于交叉交互注意力的多人极端运动预测
W Guo, X Bie, X Alameda-Pineda, F Moreno
[Univ. Grenoble Alpes & CSIC-UPC]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kgr022UGJ