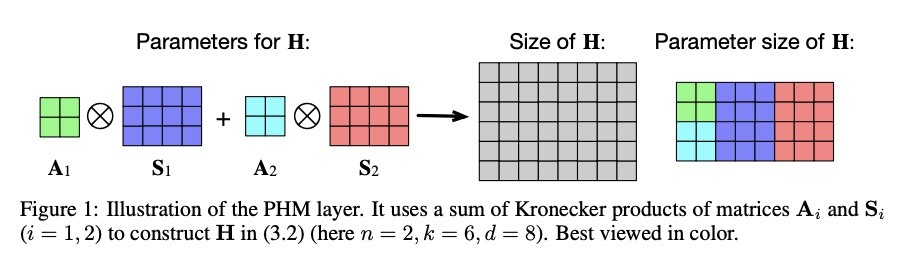
- 1、[LG] Beyond Fully-Connected Layers with Quaternions: Parameterization of Hypercomplex Multiplications with Parameters
- 2、[LG] Learning Mesh-Based Simulation with Graph Networks
- 3、[AS] Neural Synthesis of Binaural Speech From Mono Audio
- 4、[LG] Improving Adversarial Robustness Using Proxy Distributions
- 5、[CL] Demystify Optimization Challenges in Multilingual Transformers
- [CV] Dual Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation
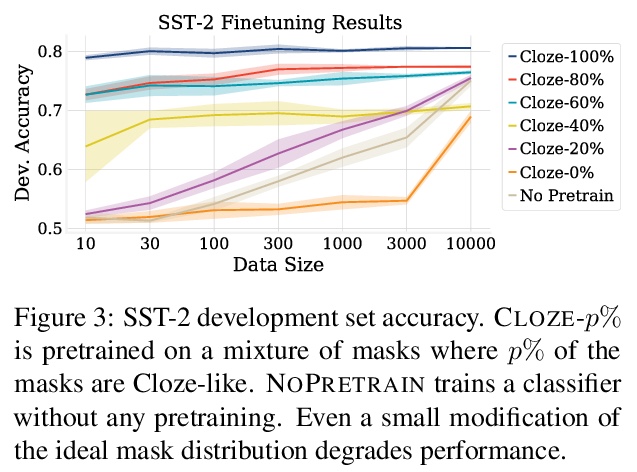
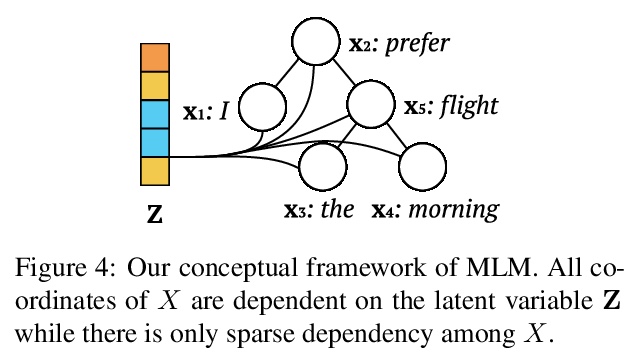
- [CL] On the Inductive Bias of Masked Language Modeling: From Statistical to Syntactic Dependencies
- [CV] Shape and Material Capture at Home
- [CV] UNISURF: Unifying Neural Implicit Surfaces and Radiance Fields for Multi-View Reconstruction
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[LG] Beyond Fully-Connected Layers with Quaternions: Parameterization of Hypercomplex Multiplications with Parameters
A Zhang, Y Tay, S Zhang, A Chan, A T Luu, S Hui, J Fu
[Amazon Web Services AI & Google Research & ETH Zurich & NTU]
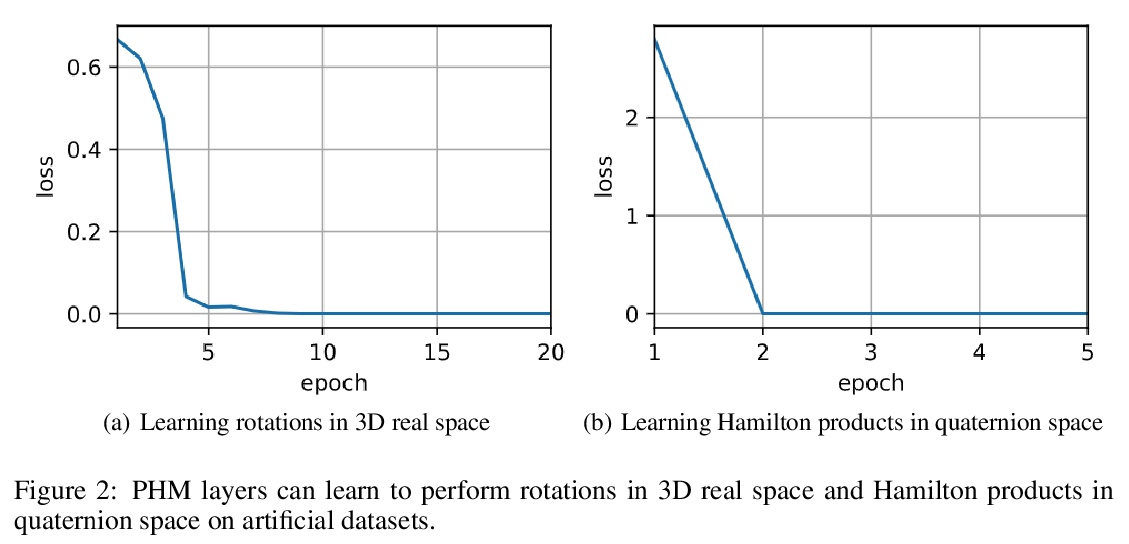
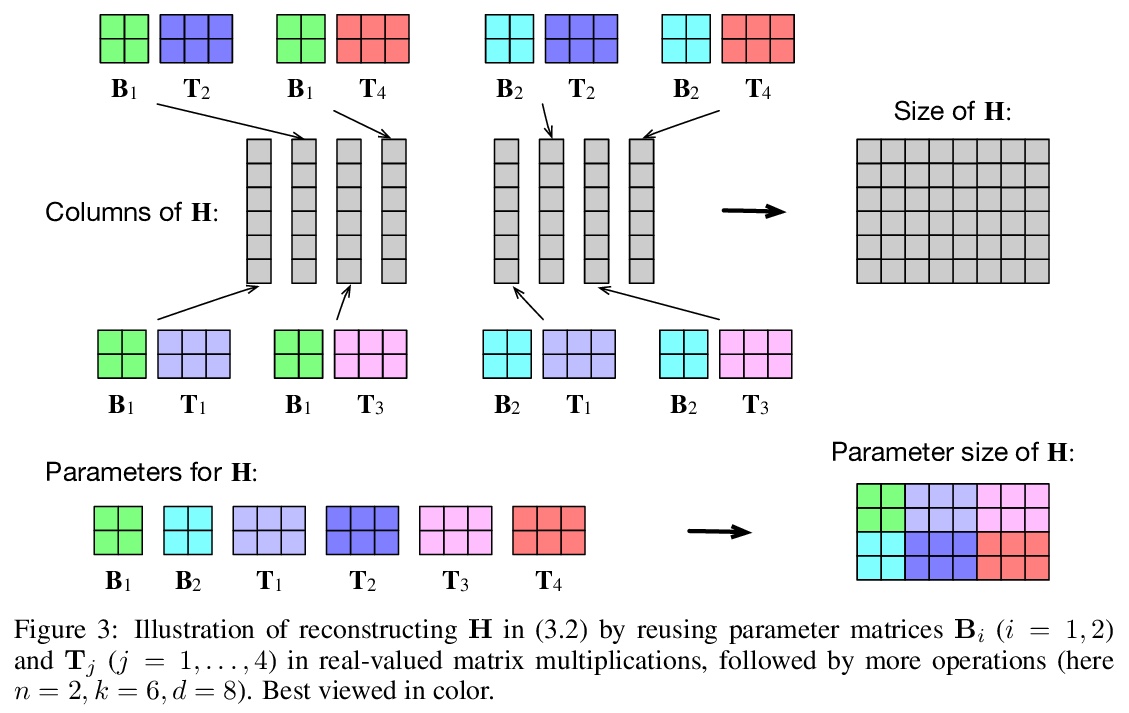
带参数的超复数乘法参数化。提出了一种新的超复数乘法的参数化:参数化超复数乘法(PHM)层。与全连接层对应的参数相比,该层有1/n的可学习参数,其中n可以由用户灵活指定。PHM层的关键思想是利用克朗克积之和从数据中学习实部和虚部之间的相互作用,即乘法规则。通过在两个主流的神经网络架构中用PHM层来证明其适用性:LSTM和转化器模型。通过对五个自然语言推理任务、七个机器翻译数据集以及文本风格转换和主语动词一致任务,进行广泛的实验,实证地展示了PHM层的架构灵活性和有效性。
Recent works have demonstrated reasonable success of representation learning in hypercomplex space. Specifically, “fully-connected layers with quaternions” (quaternions are 4D hypercomplex numbers), which replace real-valued matrix multiplications in fully-connected layers with Hamilton products of quaternions, both enjoy parameter savings with only 1/4 learnable parameters and achieve comparable performance in various applications. However, one key caveat is that hypercomplex space only exists at very few predefined dimensions (4D, 8D, and 16D). This restricts the flexibility of models that leverage hypercomplex multiplications. To this end, we propose parameterizing hypercomplex multiplications, allowing models to learn multiplication rules from data regardless of whether such rules are predefined. As a result, our method not only subsumes the Hamilton product, but also learns to operate on any arbitrary nD hypercomplex space, providing more architectural flexibility using arbitrarily 1/n learnable parameters compared with the fully-connected layer counterpart. Experiments of applications to the LSTM and transformer models on natural language inference, machine translation, text style transfer, and subject verb agreement demonstrate architectural flexibility and effectiveness of the proposed approach.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KctEzBAD1
2、[LG] Learning Mesh-Based Simulation with Graph Networks
T Pfaff, M Fortunato, A Sanchez-Gonzalez, P W. Battaglia
[Deepmind]
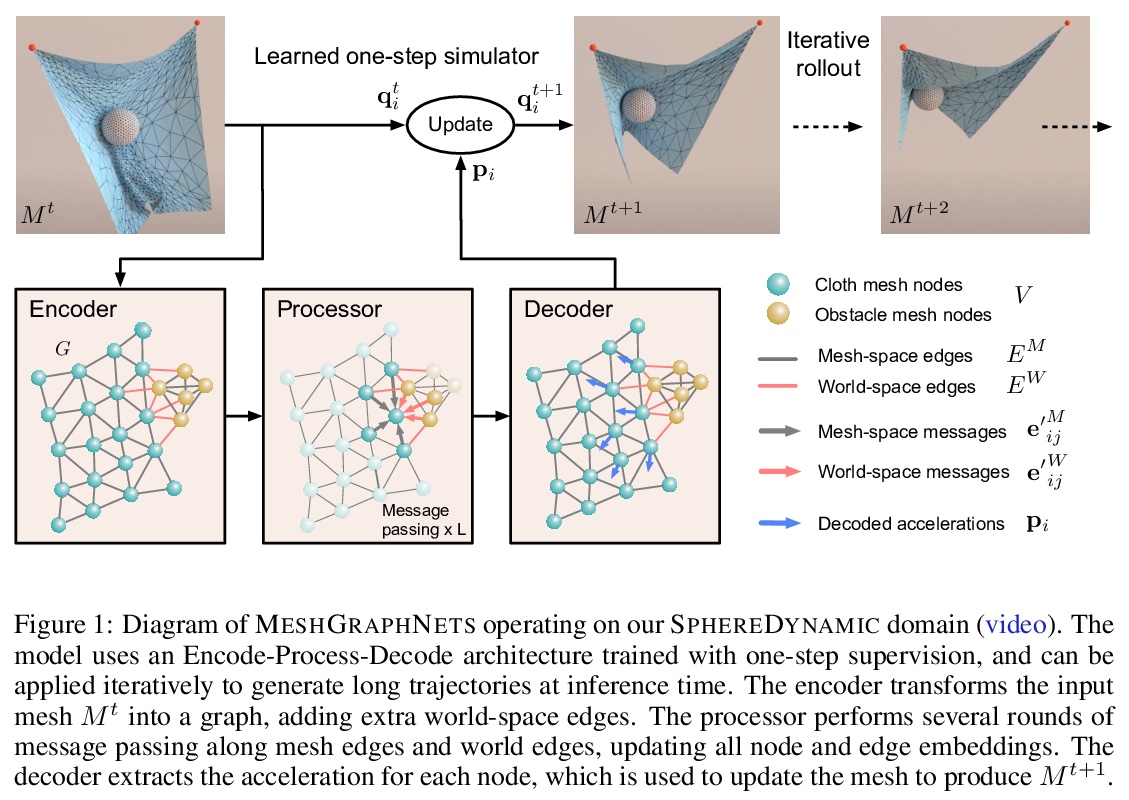
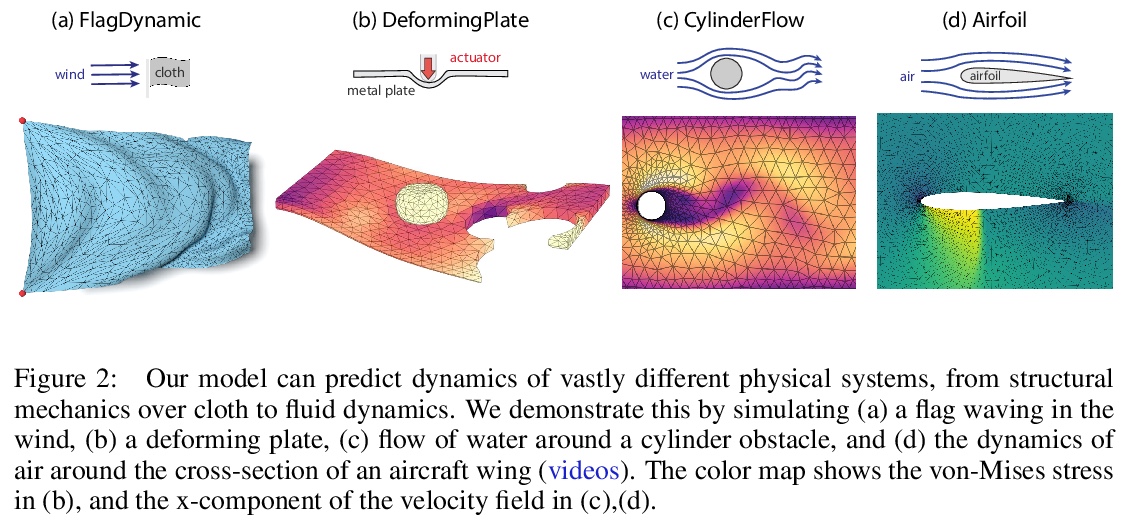
基于图网络的网格仿真学习。基于网格的仿真,在科学和工程许多学科中是复杂物理系统建模的核心。网格表示支持强大的数值集成方法,其分辨率可以调整,以便在精度和效率之间取得有效的权衡。然而,高维科学仿真的运行成本很高,而且求解器和参数往往必须根据所研究的每个系统单独进行调整。本文提出MESHGRAPHNETS,一种用图神经网络学习基于网格的仿真的框架,可以准确有效地对各种物理系统进行建模,泛化效果好,并可在推理时扩大规模。该模型可以训练成在网格图上传递信息,并在前向仿真中自适应网状离散化。实验结果表明,该模型可准确预测广泛的物理系统的动力学,包括空气动力学、结构力学和布。该模型的适应性支持学习与分辨率无关的动力学,并能在测试时扩展到更复杂的状态空间。同时该方法也是非常高效的,运行速度比用来训练的仿真快1-2个数量级。MESHGRAPHNETS的性能优于基于粒子和网格的基线,可推广到用来训练的更复杂的动力学。
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KctKW8VPG
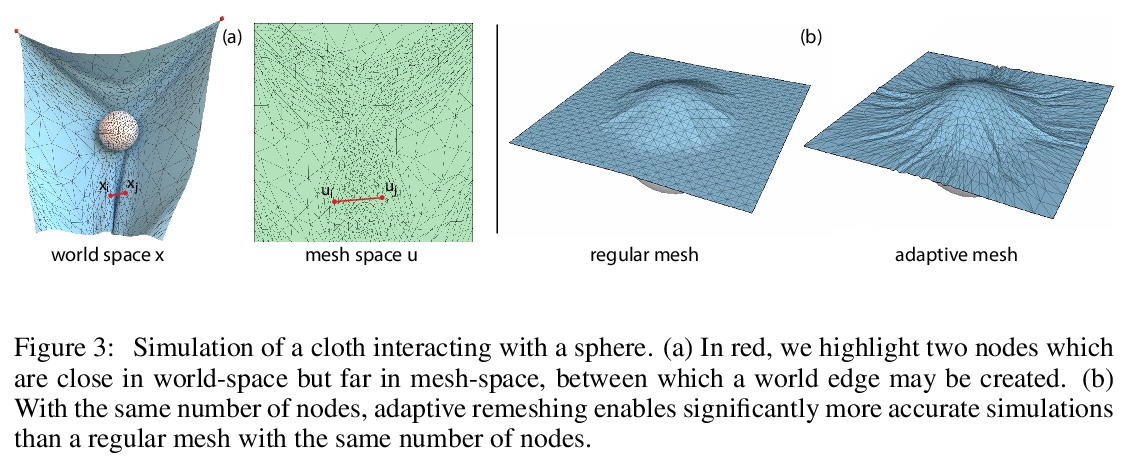
3、[AS] Neural Synthesis of Binaural Speech From Mono Audio
A Richard, D Markovic, I D. Gebru, S Krenn, G A Butler, F Torre, Y Sheikh
[Facebook Reality Labs]
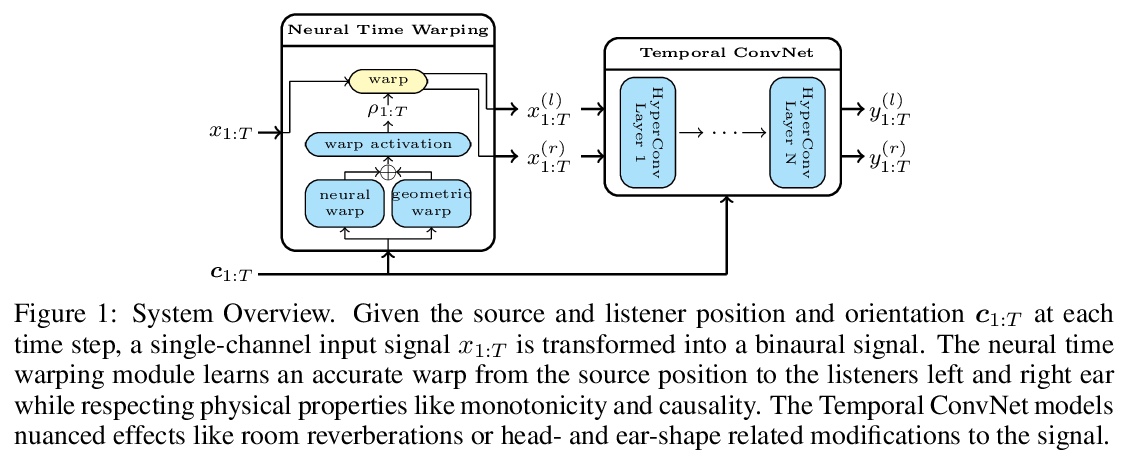
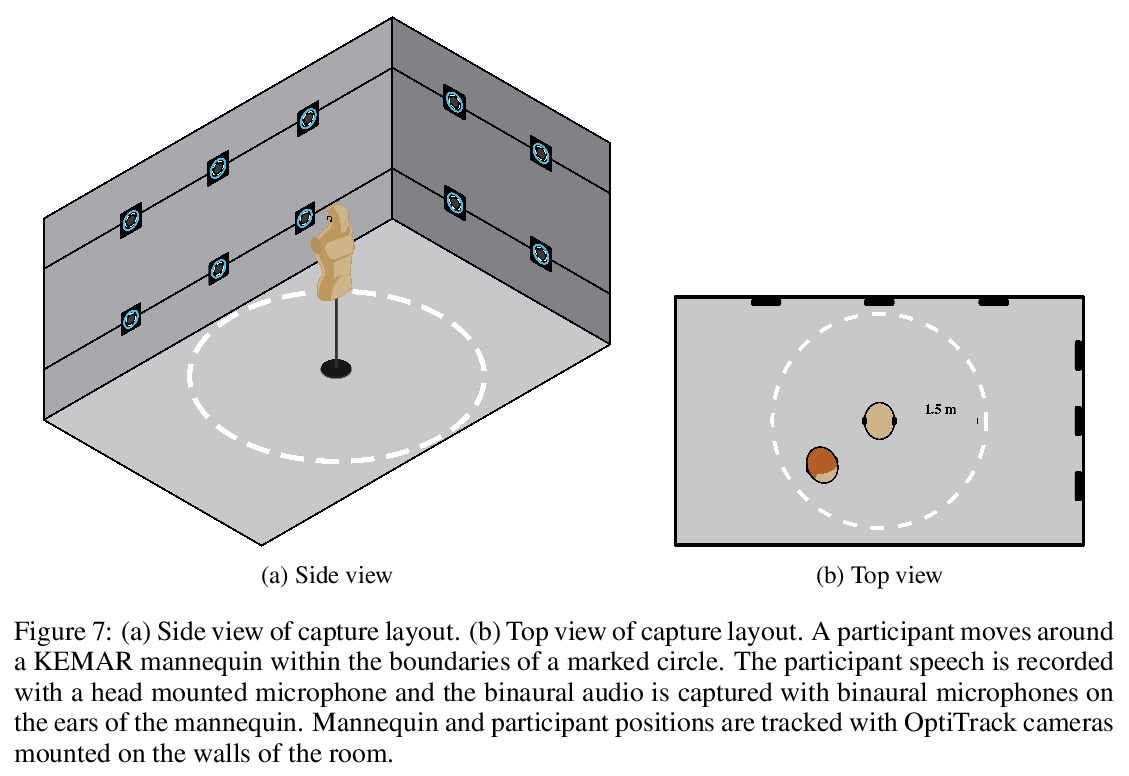
单声道音频的双声道神经合成。在增强现实和虚拟现实中,人工空间的兴起需要有效地生成准确的空间化音频。空间听觉(从双声道信号中解释空间线索的能力),不仅有助于在三维环境中定位,还可以通过向大脑提供一致的声音和视觉输入来建立沉浸式空间。本文提出一种用于双声道声音合成的神经渲染方法,可实时产生真实的、空间上准确的双声道声音。该网络将单声道音源作为输入,根据听众与音源的相对位置和方向,合成双声道双耳声音作为输出。在理论分析中研究了l2损失在原始波形上的缺陷,提出一种克服这些限制的改进的损失。该模型是第一个纯数据驱动的端到端模型,能自然捕捉到声波传播的线性和非线性效应,并且由于是全卷积,可在消费级硬件上高效执行,与传统的双声道化方法相比,显示出令人信服的性能。从数量上和用户的感知研究中,显示出该模型的有效性。
We present a neural rendering approach for binaural sound synthesis that can produce realistic and spatially accurate binaural sound in realtime. The network takes, as input, a single-channel audio source and synthesizes, as output, two-channel binaural sound, conditioned on the relative position and orientation of the listener with respect to the source. We investigate deficiencies of the l2-loss on raw waveforms in a theoretical analysis and introduce an improved loss that overcomes these limitations. In an empirical evaluation, we establish that our approach is the first to generate spatially accurate waveform outputs (as measured by real recordings) and outperforms existing approaches by a considerable margin, both quantitatively and in a perceptual study. Dataset and code are available online.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KctRObyVu


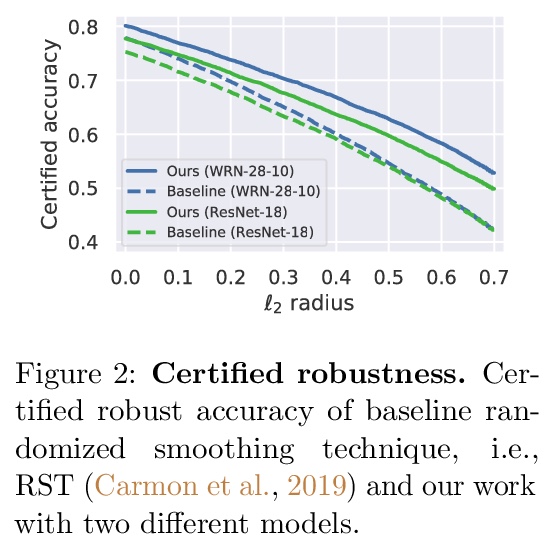
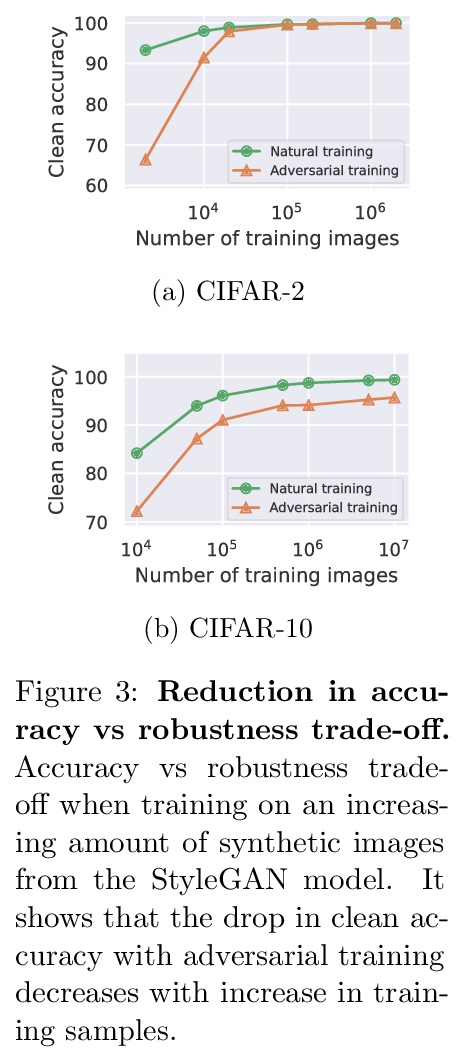
4、[LG] Improving Adversarial Robustness Using Proxy Distributions
V Sehwag, S Mahloujifar, T Handina, S Dai, C Xiang, M Chiang, P Mittal
[Princeton University & Purdue University]
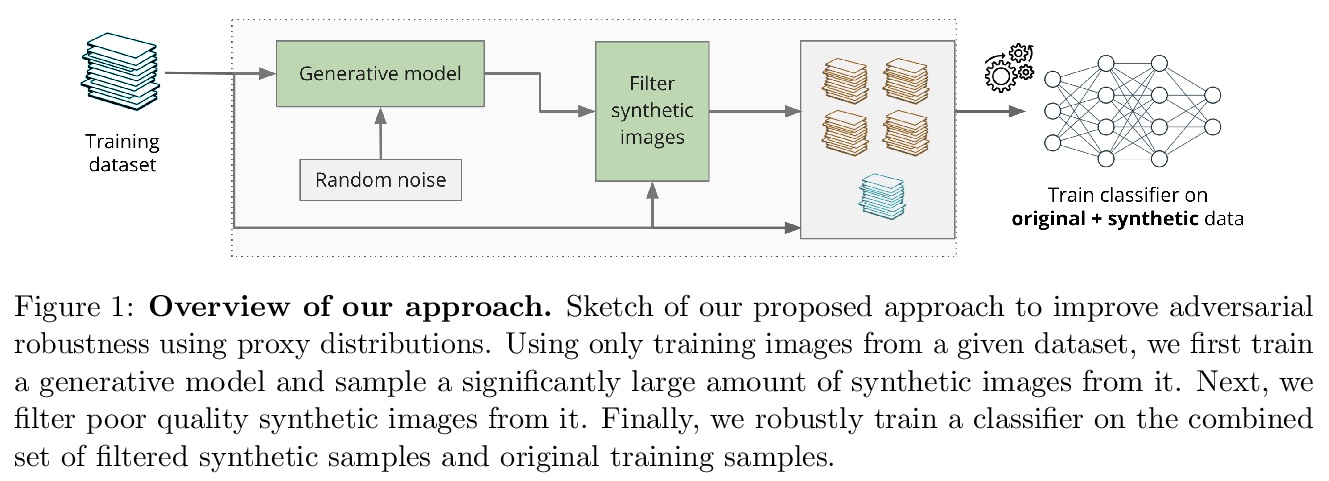
用代理分布改善对抗鲁棒性。专注于用代理分布,即训练数据集基本分布的近似值,来理解和改善图像分类中的对抗鲁棒性。虽然额外的训练数据有助于对抗性训练,但筹备大量的真实世界的图像是具有挑战性的。相比之下,代理分布能对潜在的无限数量的图像进行抽样,并利用这些样本提高对抗鲁棒性。本文对数据分布之间对抗鲁棒性的迁移提供了理论上的理解和经验上的验证,为两个数据分布上的分类器的鲁棒性之间的差异提供了一个严格的上界。提出将对抗性训练与代理分布相结合。通过利用从代理分布中取样的额外图像,可大幅提高鲁棒准确性。通过在2K到10M的图像上训练深度神经网络,首次对准确性与鲁棒性的权衡以及对抗性训练的样本复杂度进行了大规模的经验调查。
We focus on the use of proxy distributions, i.e., approximations of the underlying distribution of the training dataset, in both understanding and improving the adversarial robustness in image classification. While additional training data helps in adversarial training, curating a very large number of real-world images is challenging. In contrast, proxy distributions enable us to sample a potentially unlimited number of images and improve adversarial robustness using these samples. We first ask the question: when does adversarial robustness benefit from incorporating additional samples from the proxy distribution in the training stage? We prove that the difference between the robustness of a classifier on the proxy and original training dataset distribution is upper bounded by the conditional Wasserstein distance between them. Our result confirms the intuition that samples from a proxy distribution that closely approximates training dataset distribution should be able to boost adversarial robustness. Motivated by this finding, we leverage samples from state-of-the-art generative models, which can closely approximate training data distribution, to improve robustness. In particular, we improve robust accuracy by up to 6.1% and 5.7% inl∞andl2threat model, and certified robust accuracy by 6.7% over baselines not using proxy distributions on the CIFAR-10 dataset. Since we can sample an unlimited number of images from a proxy distribution, it also allows us to investigate the effect of an increasing number of training samples on adversarial robustness. Here we provide the first large scale empirical investigation of accuracy vs robustness trade-off and sample complexity of adversarial training by training deep neural networks on 2K to 10M images.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KctYyEMqy
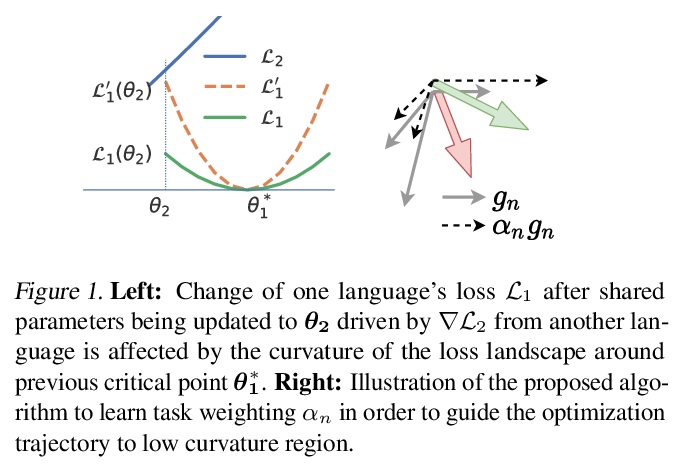
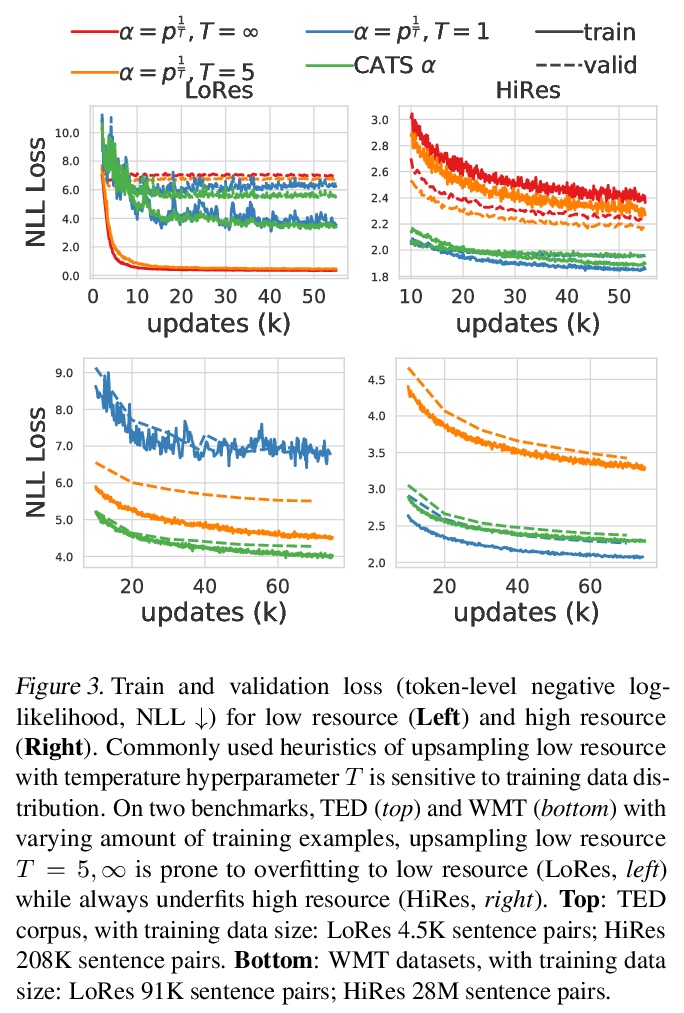
5、[CL] Demystify Optimization Challenges in Multilingual Transformers
X Li, H Gong
[Facebook AI]
多语言Transformer优化挑战解密。多语言Transformer改善了参数效率和跨语言的迁移。如何有效地训练多语言模型还未得到很好的研究。本文利用多语言机器翻译作为测试平台,从损失地貌和参数可塑性的角度研究优化挑战。不平衡的训练数据对高资源和低资源的语言构成了任务干扰,其特点是主要参数的梯度几乎是正交的,优化轨迹主要由高资源主导。损失表面的局部曲率会影响干扰的程度,现有的数据采样启发式方法隐含地降低了尖锐度,但仍然面临着高资源和低资源语言之间的权衡。本文提出一种原则性的多目标优化算法——曲率感知任务缩放(CATS),既改善了优化,又提高了通用性,特别是对低资源而言。在TED、WMT和OPUS-100基准上的实验表明,CATS推进了精度的Pareto前沿,同时有效地应用于100种语言规模的大规模多语言环境。
Multilingual Transformer improves parameter efficiency and crosslingual transfer. How to effectively train multilingual models has not been well studied. Using multilingual machine translation as a testbed, we study optimization challenges from loss landscape and parameter plasticity perspectives. We found that imbalanced training data poses task interference between high and low resource languages, characterized by nearly orthogonal gradients for major parameters and the optimization trajectory being mostly dominated by high resource. We show that local curvature of the loss surface affects the degree of interference, and existing heuristics of data subsampling implicitly reduces the sharpness, although still face a trade-off between high and low resource languages. We propose a principled multi-objective optimization algorithm, Curvature Aware Task Scaling (CATS), which improves both optimization and generalization especially for low resource. Experiments on TED, WMT and OPUS-100 benchmarks demonstrate that CATS advances the Pareto front of accuracy while being efficient to apply to massive multilingual settings at the scale of 100 languages.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kcu3a2fzO
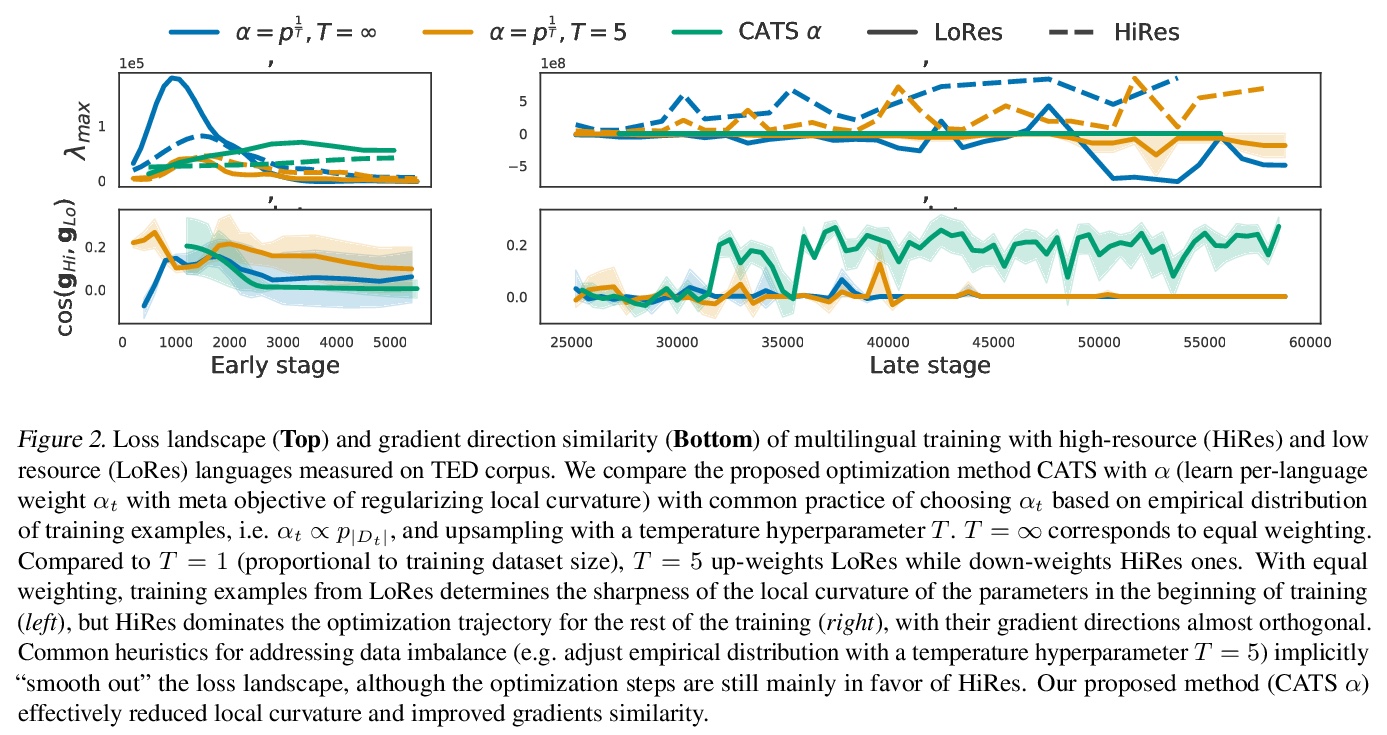
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
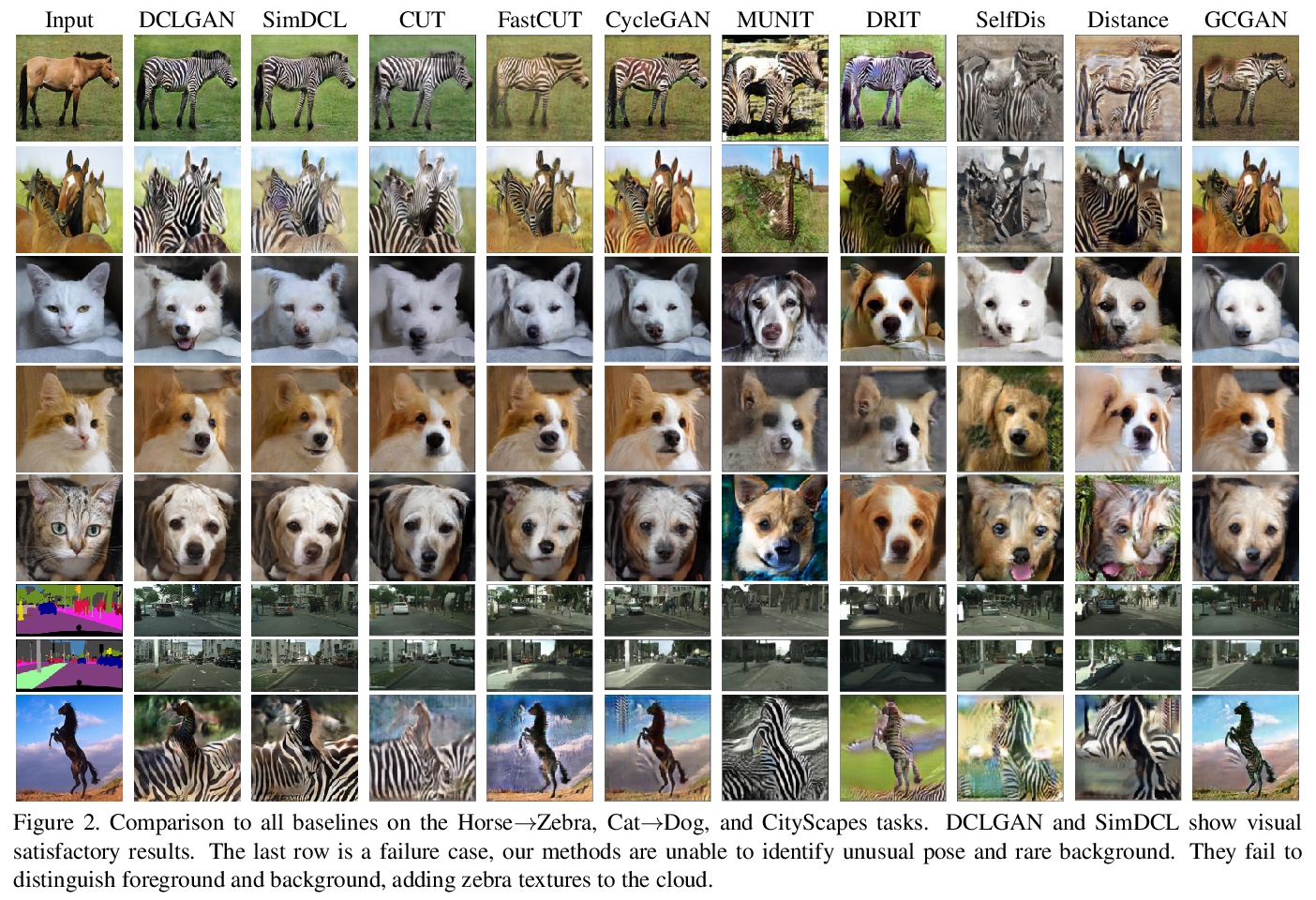
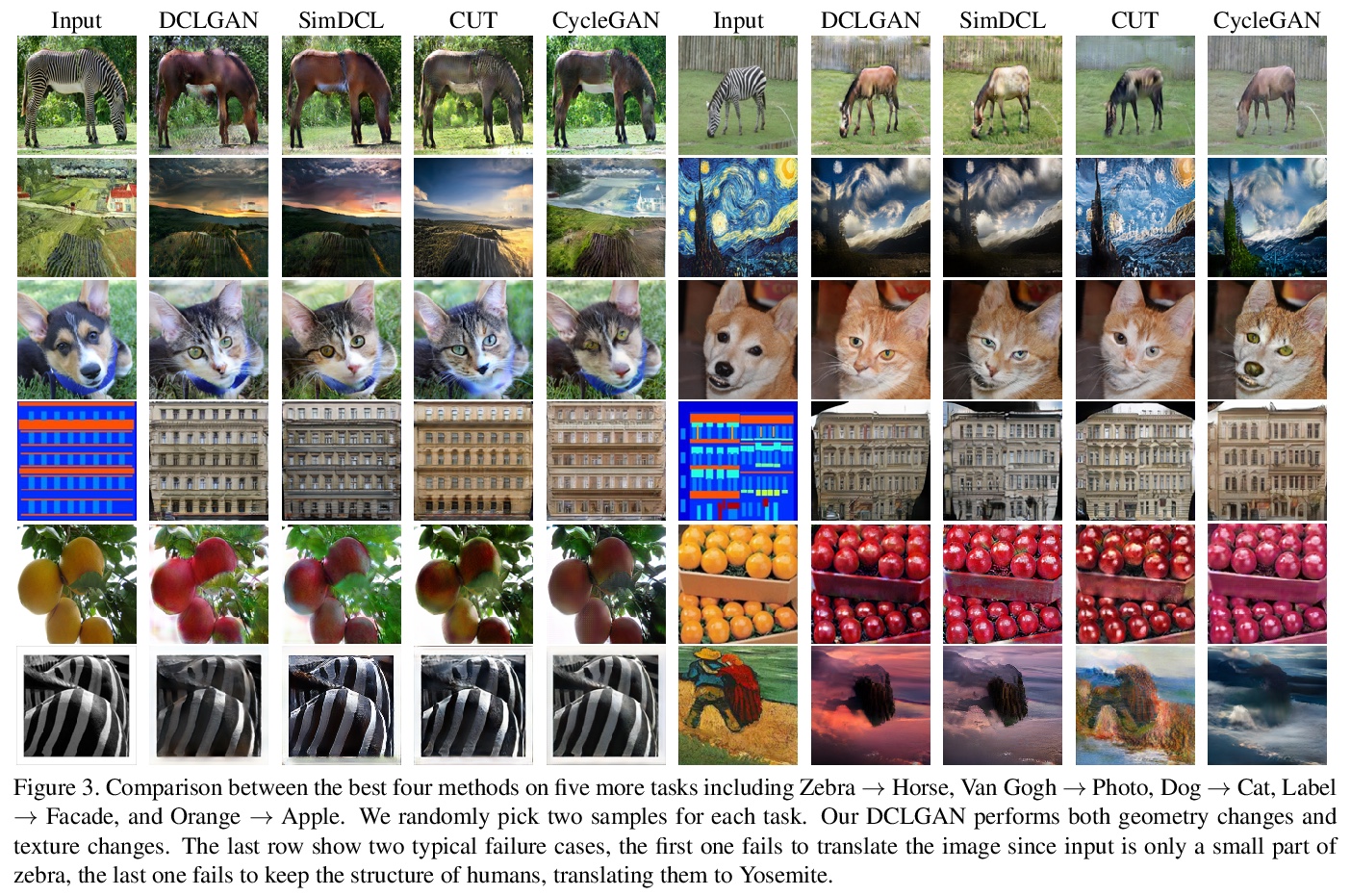
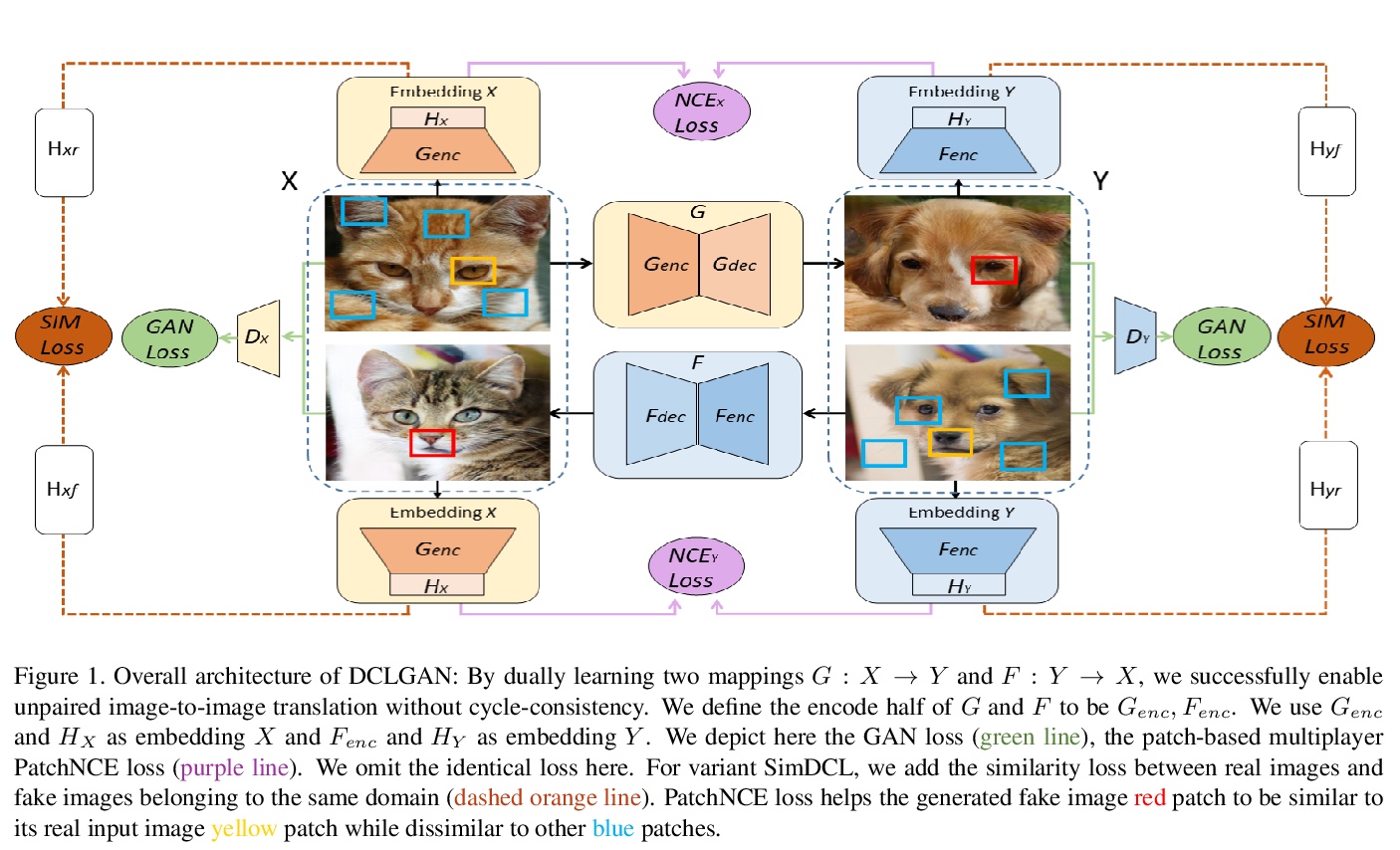
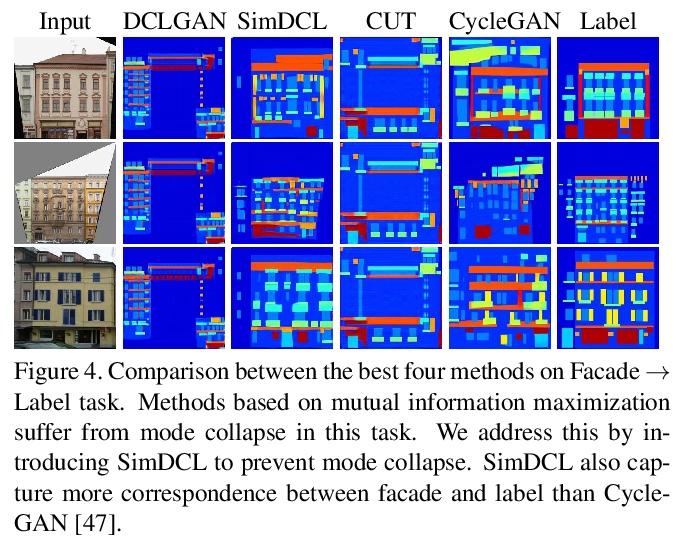
[CV] Dual Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation
双对比学习无监督图到图变换
J Han, M Shoeiby, L Petersson, M A Armin
[DATA61-CSIRO]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kcu6E2www


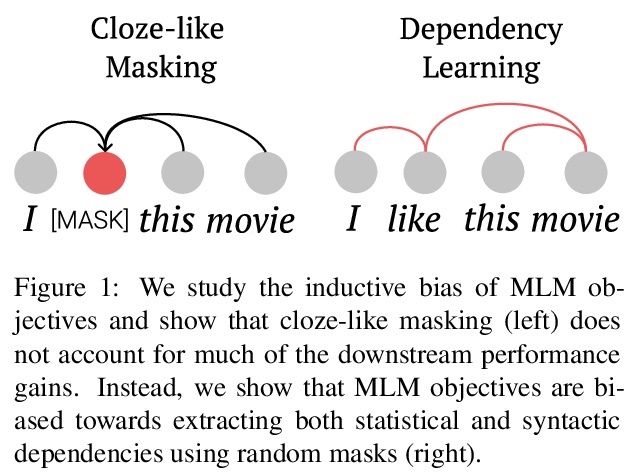
[CL] On the Inductive Bias of Masked Language Modeling: From Statistical to Syntactic Dependencies
掩码语言建模归纳偏差:从统计到句法依存
T Zhang, T Hashimoto
[Stanford University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kcu88jy6p

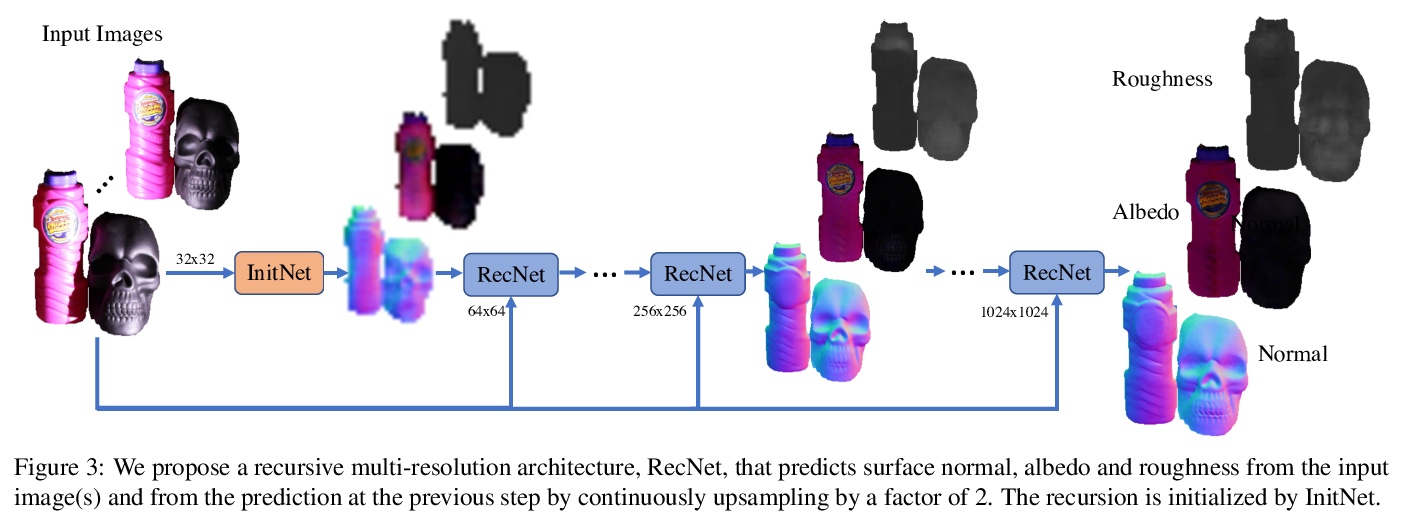
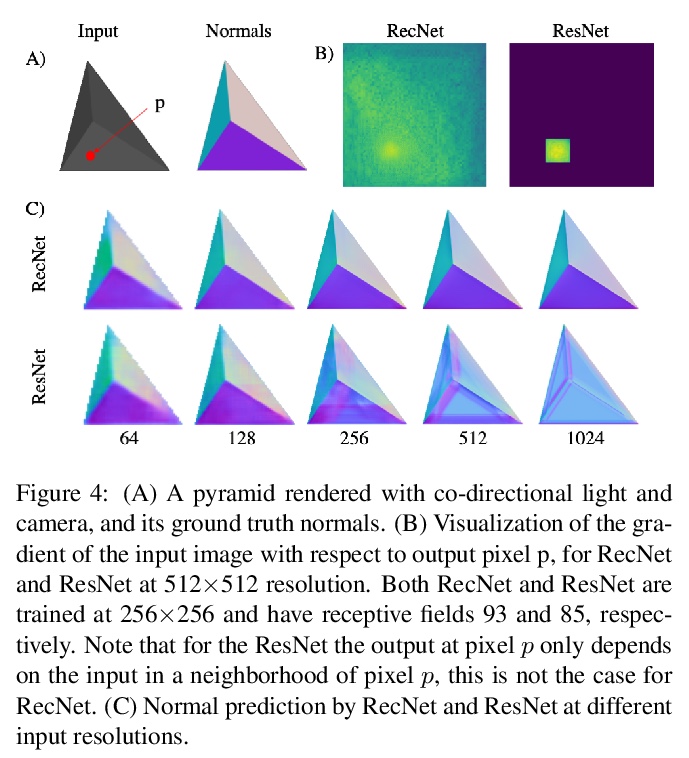
[CV] Shape and Material Capture at Home
简易形状/材质采集方法
D Lichy, J Wu, S Sengupta, D W. Jacobs
[University of Maryland & University of Washington]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kcubzh1ck


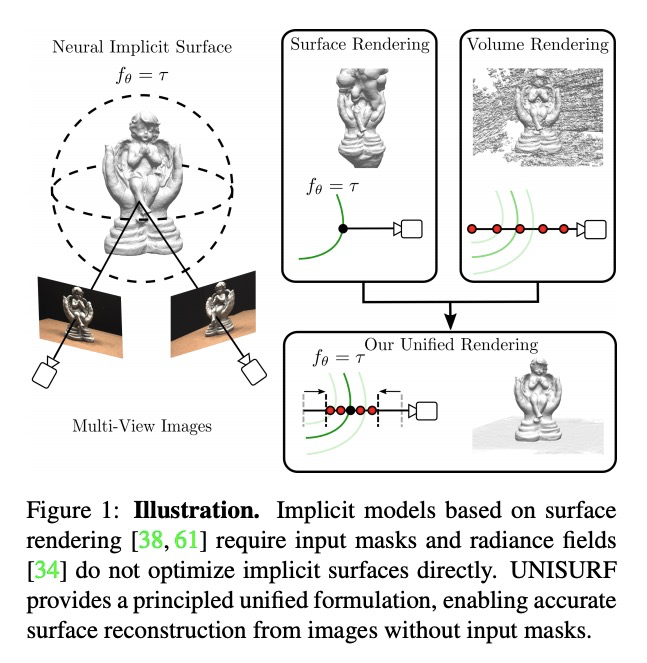
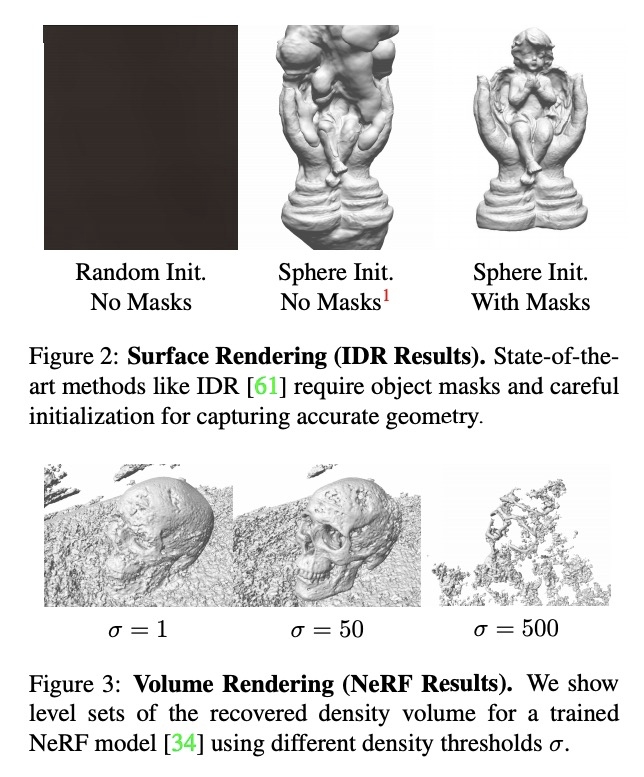
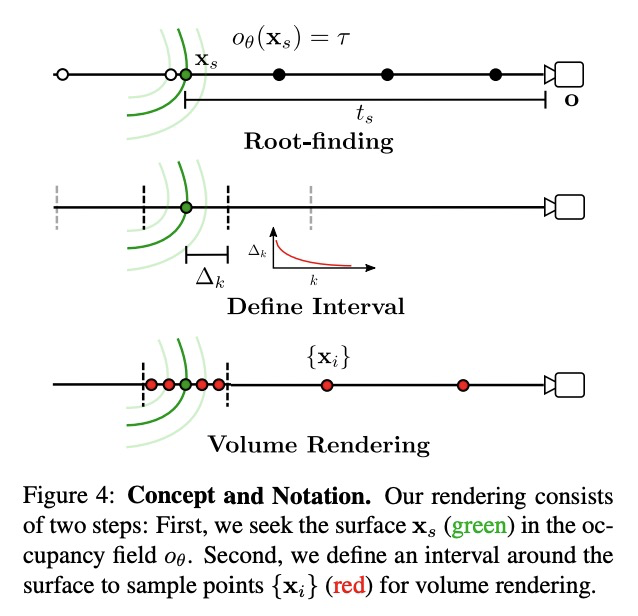
[CV] UNISURF: Unifying Neural Implicit Surfaces and Radiance Fields for Multi-View Reconstruction
UNISURF:多视角重建神经隐式曲面和辐射场的统一
M Oechsle, S Peng, A Geiger
[Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcuiQxcFe