- 1、[LG] Physics-informed neural networks for solving Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes equations
- 2、[LG] Data vs classifiers, who wins?
- 3、[LG] Interpretable SincNet-based Deep Learning for Emotion Recognition from EEG brain activity
- 4、[CL] FLEX: Unifying Evaluation for Few-Shot NLP
- 5、[AS] Digital Einstein Experience: Fast Text-to-Speech for Conversational AI
- [AS] VQMIVC: Vector Quantization and Mutual Information-Based Unsupervised Speech Representation Disentanglement for One-shot Voice Conversion
- [CV] Unsupervised Learning of Depth and Depth-of-Field Effect from Natural Images with Aperture Rendering Generative Adversarial Networks
- [RO] An End-to-End Differentiable Framework for Contact-Aware Robot Design
- [LG] Characterizing Generalization under Out-Of-Distribution Shifts in Deep Metric Learning
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] Physics-informed neural networks for solving Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes equations
H Eivazi, M Tahani, P Schlatter, R Vinuesa
[University of Tehran & KTH Royal Institute of Technology]
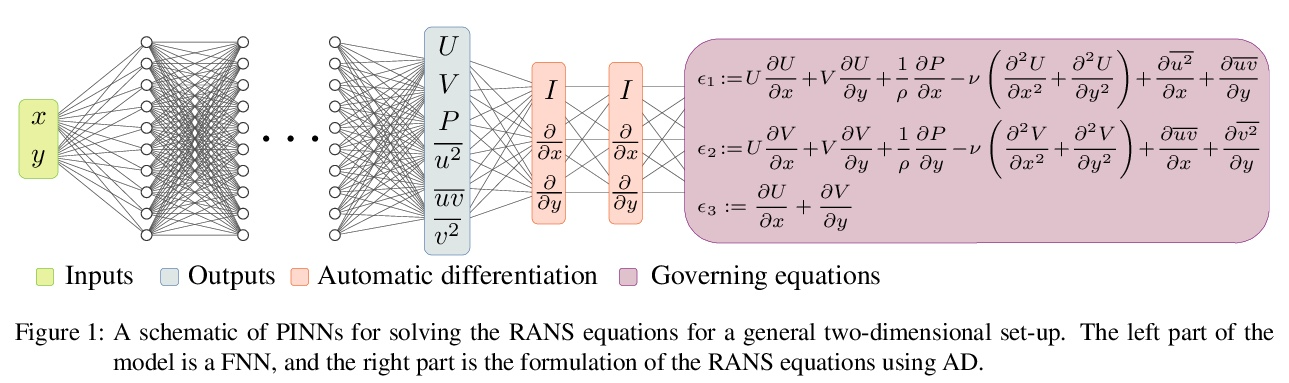
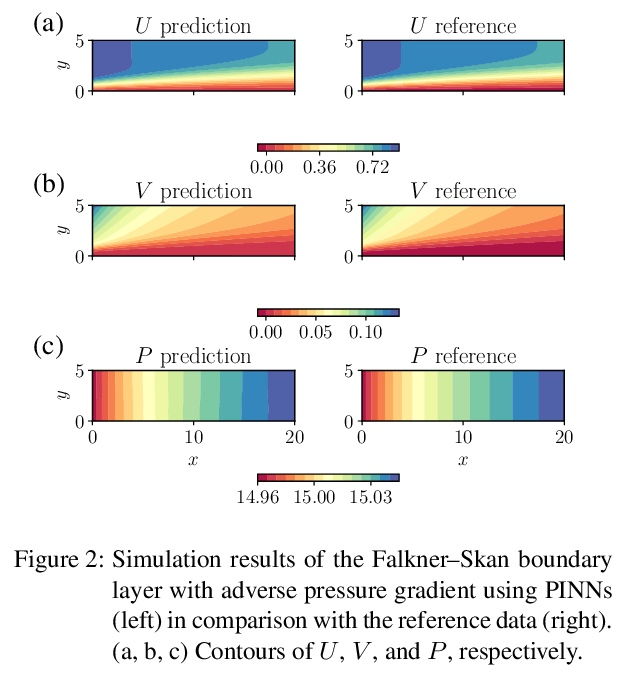
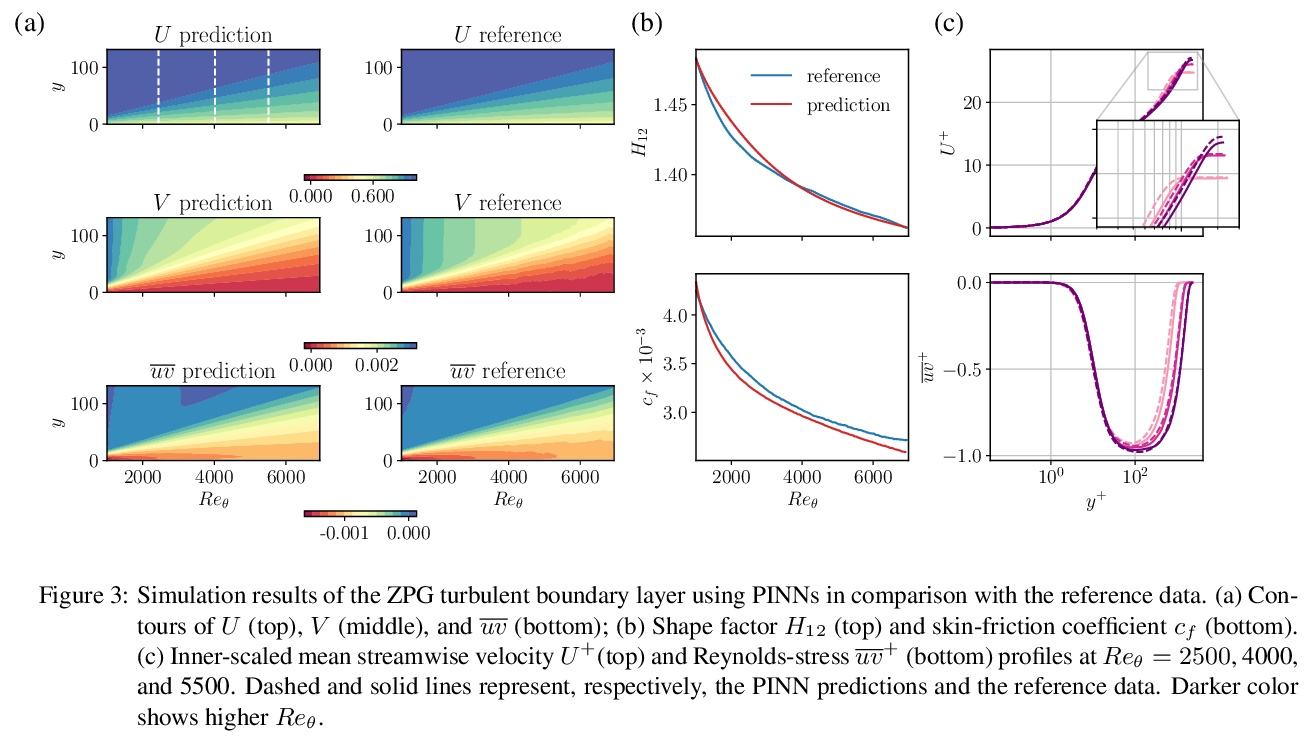
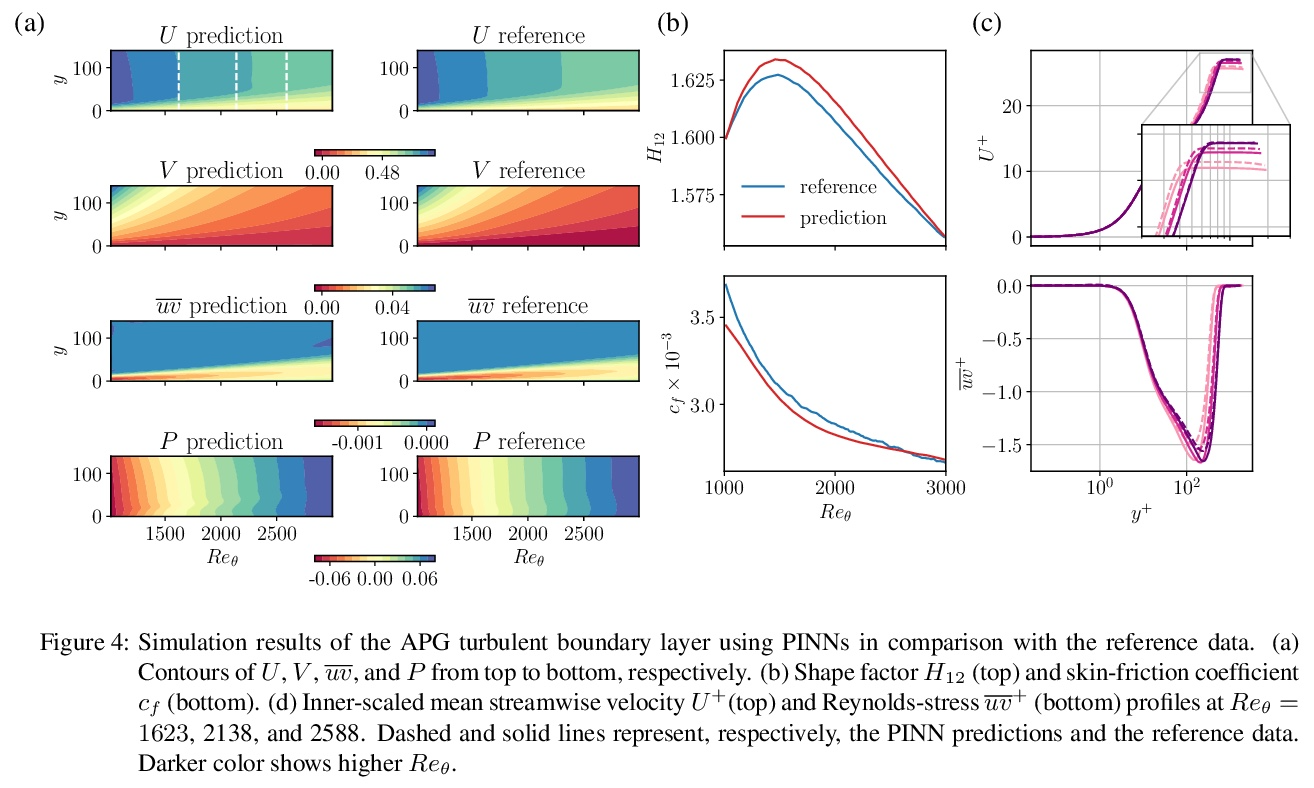
用物理信息神经网络求解RANS方程。物理信息神经网络(PINN)是解决和识别偏微分方程(PDE)的成功机器学习方法。本文采用PINN来解决不可压缩湍流的Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes(RANS)方程,不需要任何特定的湍流模型或假设,只需要获取域边界的数据。先通过求解Falkner-Skan边界层,展示了PINN在解决层流Navier–Stokes方程中的适用性。将PINN用于模拟四种湍流情况,即零压力梯度边界层、逆压力梯度边界层、NACA4412机翼湍流和周期性山丘。研究结果表明,PINN对具有强压力梯度的层流具有很好的适用性,可得到误差小于1%的预测结果。对于湍流,在模拟结果上也获得了非常好的准确性,甚至对于雷诺应力成分也是如此。
Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) are successful machine-learning methods for the solution and identification of partial differential equations (PDEs). We employ PINNs for solving the Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) equations for incompressible turbulent flows without any specific model or assumption for turbulence, and by taking only the data on the domain boundaries. We first show the applicability of PINNs for solving the Navier–Stokes equations for laminar flows by solving the Falkner–Skan boundary layer. We then apply PINNs for the simulation of four turbulent-flow cases, i.e., zero-pressure-gradient boundary layer, adversepressure-gradient boundary layer, and turbulent flows over a NACA4412 airfoil and the periodic hill. Our results show the excellent applicability of PINNs for laminar flows with strong pressure gradients, where predictions with less than 1% error can be obtained. For turbulent flows, we also obtain very good accuracy on simulation results even for the Reynolds-stress components.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kqjxd18AA 
2、[LG] Data vs classifiers, who wins?
L F. F. Cardoso, V C. A. Santos, R S. K Francês, R B. C. Prudêncio, R C. O. Alves
[Universidade Federal do Pará & Universidade Federal de Pernambuco & Instituto Tecnológico Vale]
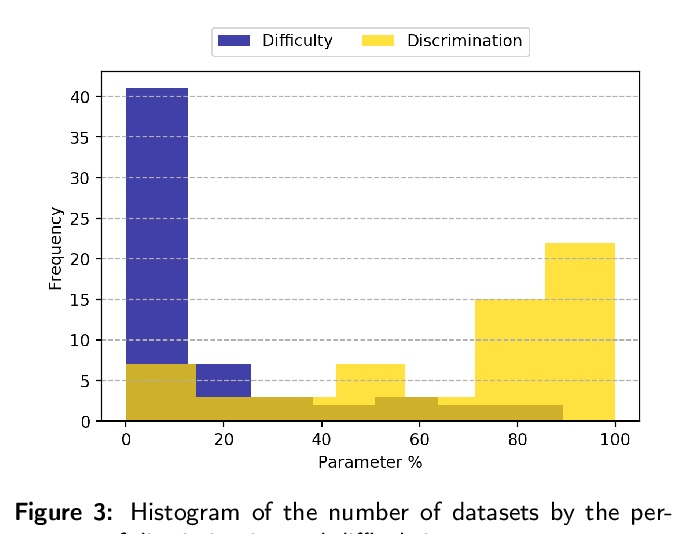
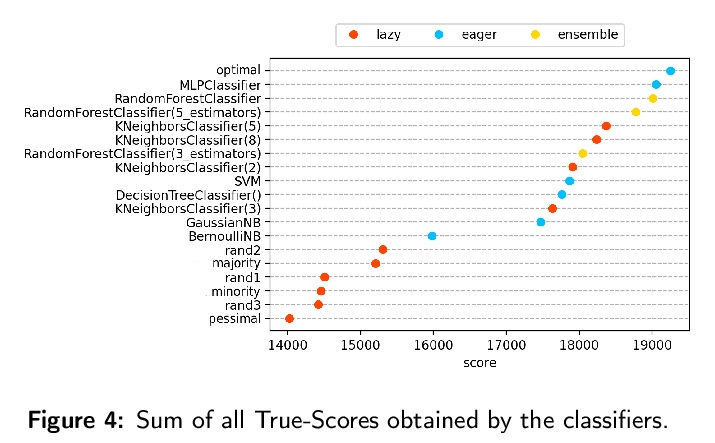
数据与分类器,谁是赢家?机器学习所涉及的分类实验有两个重要组成部分:数据和算法。由于它们是问题的基本部分,在根据基准评估模型的性能时,必须考虑这两个部分。最好的分类器需要强大的基准来进行正确的评估。为此,使用黄金标准的基准,如OpenMLCC18。然而,在性能评估期间,数据的复杂性通常不与模型一起考虑。最近的研究采用项反应理论(IRT)作为评估数据集和算法的新方法,能够同时评估两者。本文提出一种基于IRT和Glicko-2的新的评价方法,与为指导机器学习中的IRT估计而开发的decodIRT工具一起。探索了IRT作为工具来评估OpenML-CC18基准的算法评估能力,并检查是否有一个数据集的子集比原始基准更有效。几个分类器,从经典的到集成的,也使用IRT模型进行了评估。Glicko-2评级系统与IRT一起应用,以总结先天能力和分类器的性能。并不是所有的OpenML-CC18数据集都对评估算法真正有用,其中只有10%被评为真正困难。此外,还验证了一个更有效的子集的存在,它只包含原始规模的50%。而Randon Forest则被挑出作为具有最佳先天能力的算法。
The classification experiments covered by machine learning (ML) are composed by two important parts: the data and the algorithm. As they are a fundamental part of the problem, both must be considered when evaluating a model’s performance against a benchmark. The best classifiers need robust benchmarks to be properly evaluated. For this, gold standard benchmarks such as OpenMLCC18 are used. However, data complexity is commonly not considered along with the model during a performance evaluation. Recent studies employ Item Response Theory (IRT) as a new approach to evaluating datasets and algorithms, capable of evaluating both simultaneously. This work presents a new evaluation methodology based on IRT and Glicko-2, jointly with the decodIRT tool developed to guide the estimation of IRT in ML. It explores the IRT as a tool to evaluate the OpenML-CC18 benchmark for its algorithmic evaluation capability and checks if there is a subset of datasets more efficient than the original benchmark. Several classifiers, from classics to ensemble, are also evaluated using the IRT models. The Glicko-2 rating system was applied together with IRT to summarize the innate ability and classifiers performance. It was noted that not all OpenML-CC18 datasets are really useful for evaluating algorithms, where only 10% were rated as being really difficult. Furthermore, it was verified the existence of a more efficient subset containing only 50% of the original size. While Randon Forest was singled out as the algorithm with the best innate ability.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KqjBzahPz 

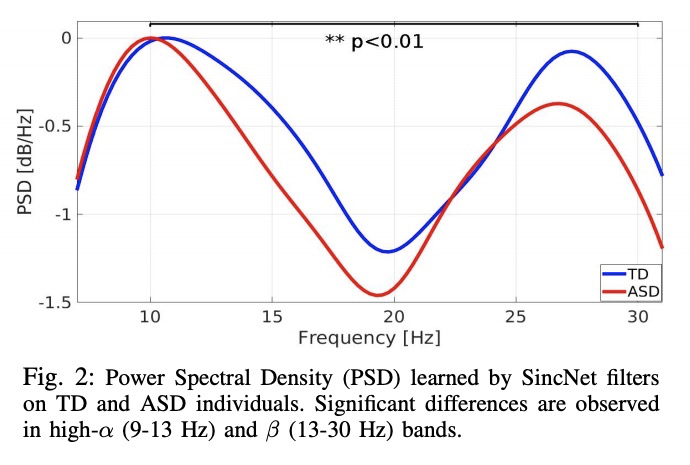
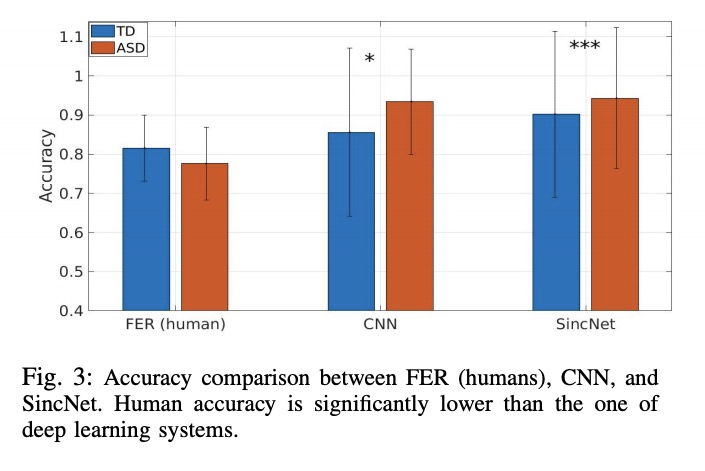
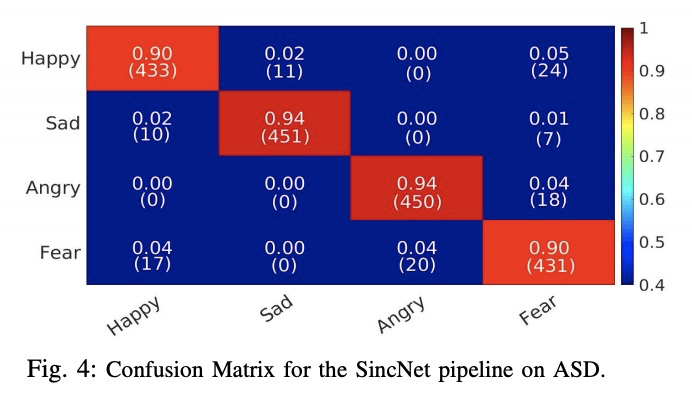
3、[LG] Interpretable SincNet-based Deep Learning for Emotion Recognition from EEG brain activity
J M Mayor-Torres, M Ravanelli, S E. Medina-DeVilliers, M D. Lerner, G Riccardi
[University of Trento & Mila & StonyBrook University]
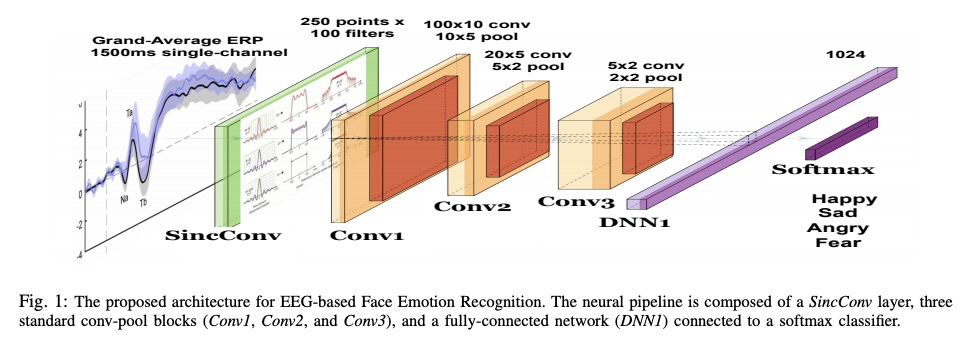
基于SincNet可解释深度学习的脑电活动情绪识别。机器学习方法,如深度学习,在医学领域显示出很好的效果。然而,这些算法缺乏可解释性,可能会阻碍它们对医疗决策支持系统的应用。本文研究了一种可解释的深度学习技术SincNet。SincNet是一种卷积神经网络,通过可训练的sinc-functions有效地学习定制的带通滤波器。用SincNet来分析自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)患者的神经活动,他们的神经振荡活动存在特征性差异。提出了一种新的基于SincNet的神经网络,用于用EEG信号检测ASD患者的情绪。习得的过滤器可以很容易检查出EEG频谱的哪一部分是用来预测情绪的。该系统自动学习了ASD个体中经常出现的高α(9-13赫兹)和β(13-30赫兹)频段抑制。这一结果与最近关于情绪识别的神经科学研究相一致,这些研究发现这些波段抑制与在ASD个体中观察到的行为缺陷之间存在关联。SincNet的可解释性的改善是在不牺牲情绪识别性能的情况下实现的。
Machine learning methods, such as deep learning, show promising results in the medical domain. However, the lack of interpretability of these algorithms may hinder their applicability to medical decision support systems. This paper studies an interpretable deep learning technique, called SincNet. SincNet is a convolutional neural network that efficiently learns customized band-pass filters through trainable sinc-functions. In this study, we use SincNet to analyze the neural activity of individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), who experience characteristic differences in neural oscillatory activity. In particular, we propose a novel SincNet-based neural network for detecting emotions in ASD patients using EEG signals. The learned filters can be easily inspected to detect which part of the EEG spectrum is used for predicting emotions. We found that our system automatically learns the high-α (9-13 Hz) and β (13-30 Hz) band suppression often present in individuals with ASD. This result is consistent with recent neuroscience studies on emotion recognition, which found an association between these band suppressions and the behavioral deficits observed in individuals with ASD. The improved interpretability of SincNet is achieved without sacrificing performance in emotion recognition.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KqjFIaxmc 
4、[CL] FLEX: Unifying Evaluation for Few-Shot NLP
J Bragg, A Cohan, K Lo, I Beltagy
[Allen Institute for AI]
FLEX:少样本NLP的统一评估。少样本NLP的研究非常活跃,但其评估组件缺乏具有挑战性的现实测试设置,也没有采用细致的实验设计,因此,社区不知道哪些技术表现最好,甚至不知道它们是否优于简单的基线。本文提出理想的少样本NLP基准的要求,并提出了FLEX2,第一个为少样本NLP技术提供统一、全面测量的基准、公共排行榜和框架。FLEX结合并引入了新的几率评估的最佳实践,包括对四种迁移设置的测量,零样本评估的文本标签,以及一种有原则的基准设计方法,在优化统计准确性的同时,使没有大量计算资源的研究人员也能接受评估的开销。提出了UniFew,一种简单而强大的基于提示的少样本学习模型,统一了预训练和微调提示格式,避免了最近基于提示的方法在适应下游任务格式和语言模型预训练目标时的复杂机制。尽管UniFew很简单,但它所取得的结果与流行的元学习和基于提示的方法相比都具有竞争力。
Few-shot NLP research is highly active, yet conducted in disjoint research threads with evaluation suites that lack challenging-yet-realistic testing setups and fail to employ careful experimental design. Consequently, the community does not know which techniques perform best or even if they outperform simple baselines. We formulate desiderata for an ideal few-shot NLP benchmark and present FLEX,2 the first benchmark, public leaderboard, and framework that provides unified, comprehensive measurement for few-shot NLP techniques. FLEX incorporates and introduces new best practices for few-shot evaluation, including measurement of four transfer settings, textual labels for zero-shot evaluation, and a principled approach to benchmark design that optimizes statistical accuracy while keeping evaluation costs accessible to researchers without large compute resources. In addition, we present UniFew, a simple yet strong prompt-based model for few-shot learning which unifies the pretraining and finetuning prompt formats, eschewing complex machinery of recent prompt-based approaches in adapting downstream task formats to language model pretraining objectives. We demonstrate that despite simplicity UniFew achieves results competitive with both popular meta-learning and prompt-based approaches.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KqjKzkaRN 
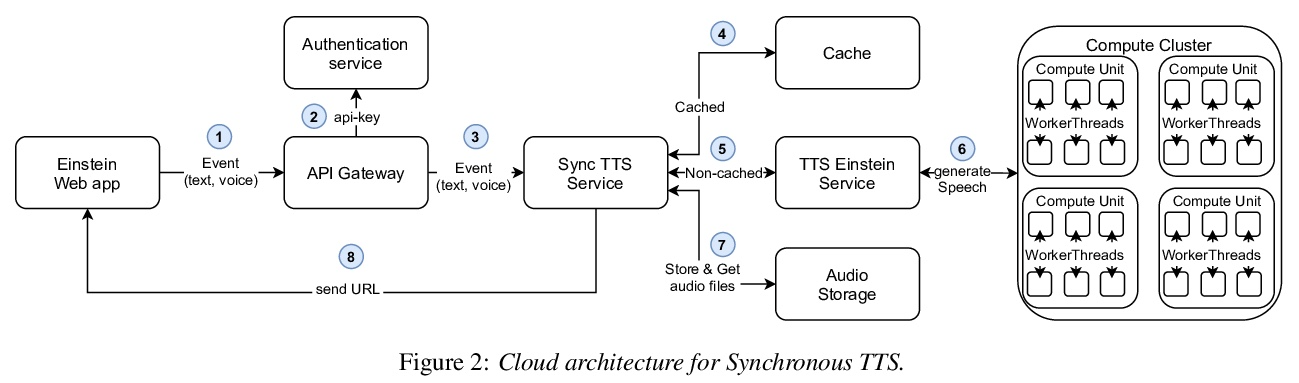
5、[AS] Digital Einstein Experience: Fast Text-to-Speech for Conversational AI
J Rownicka, K Sprenkamp, A Tripiana, V Gromoglasov, T P Kunz
[Aflorithmic Labs Ltd]
Digital Einstein Experience:面向对话式AI的快速文本到语音合成方法。本文描述了为对话式AI用例创建和提供自定义语音的方法,为数字化爱因斯坦的角色提供声音,以便在数字对话体验中实现人机互动。为了创造出适合语境的声音,首先设计了一个语音角色,并制作了对应于所需语音属性的录音。对语音进行建模,解决方案利用Fastspeech 2从音素中预测对数尺度梅尔谱图,并利用Parallel WaveGAN生成波形。该系统支持字符输入,在输出端给出一个语音波形。对选定的单词使用自定义字典,以确保其正确的发音。所提出的云架构能够实现快速的语音传递,使得有可能与数字化爱因斯坦实时对话。
We describe our approach to create and deliver a custom voice for a conversational AI use-case. More specifically, we provide a voice for a Digital Einstein character, to enable human-computer interaction within the digital conversation experience. To create the voice which fits the context well, we first design a voice character and we produce the recordings which correspond to the desired speech attributes. We then model the voice. Our solution utilizes Fastspeech 2 for log-scaled mel-spectrogram prediction from phonemes and Parallel WaveGAN to generate the waveforms. The system supports a character input and gives a speech waveform at the output. We use a custom dictionary for selected words to ensure their proper pronunciation. Our proposed cloud architecture enables for fast voice delivery, making it possible to talk to the digital version of Albert Einstein in real-time.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KqjOKcoWD 

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
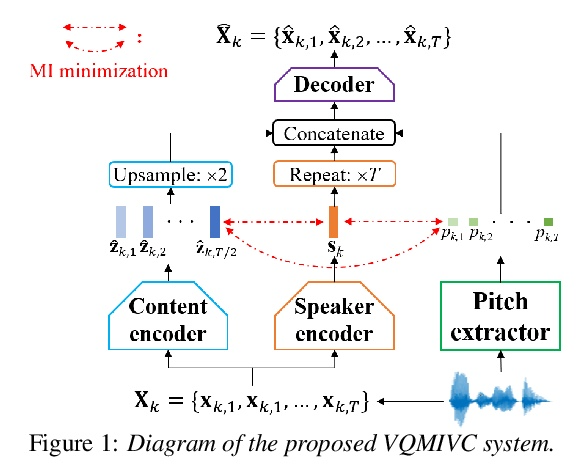
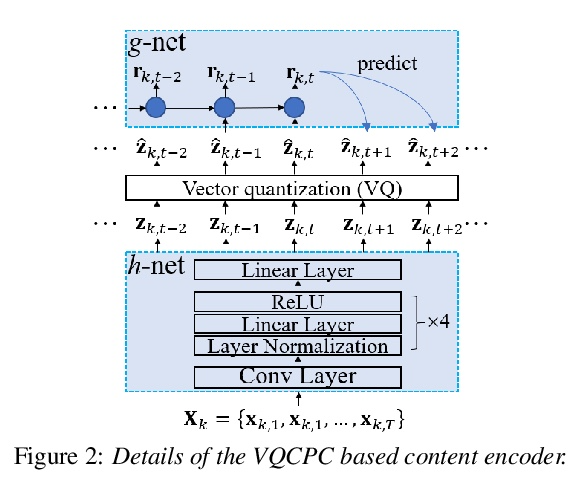
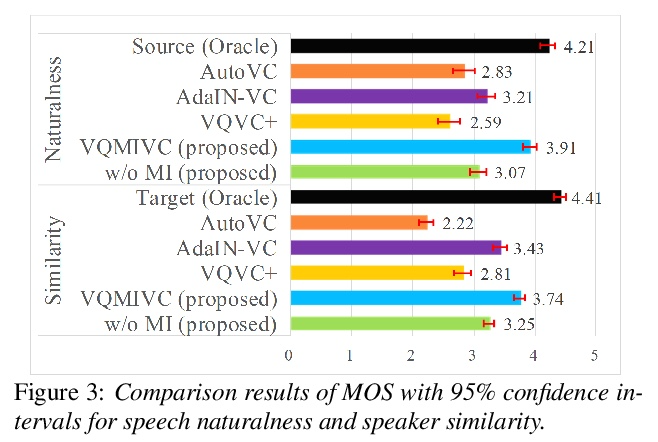
[AS] VQMIVC: Vector Quantization and Mutual Information-Based Unsupervised Speech Representation Disentanglement for One-shot Voice Conversion
VQMIVC:面向单样本语音转换的矢量量化和基于互信息的无监督语音表示解缠
D Wang, L Deng, Y T Yeung, X Chen, X Liu, H Meng
[The Chinese University of Hong Kong & Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KqjSNj7Ff 
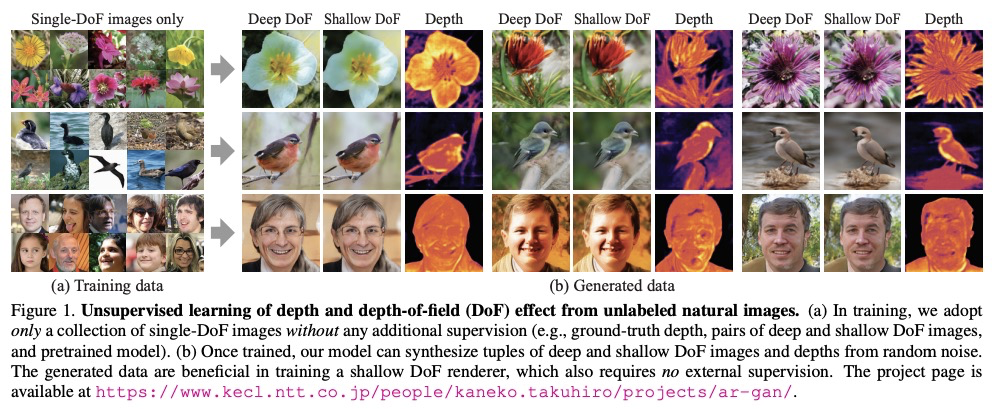
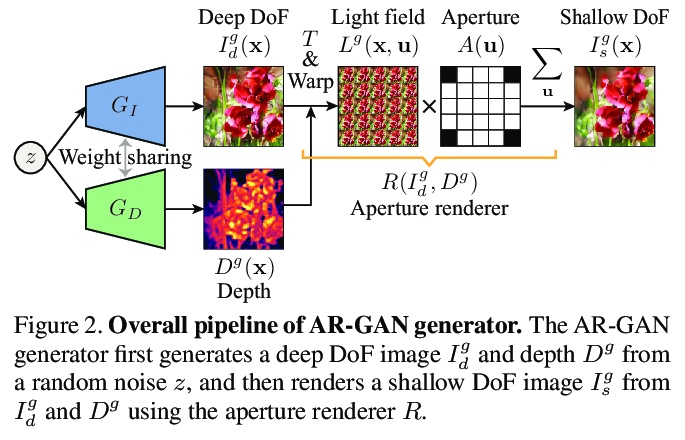
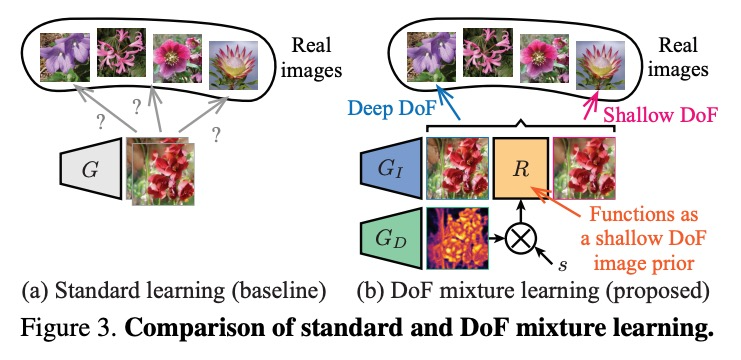
[CV] Unsupervised Learning of Depth and Depth-of-Field Effect from Natural Images with Aperture Rendering Generative Adversarial Networks
基于孔径渲染生成对抗网络的自然图像深度和景深效果的无监督学习
T Kaneko
[NTT Corporation]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KqjVv8sPf 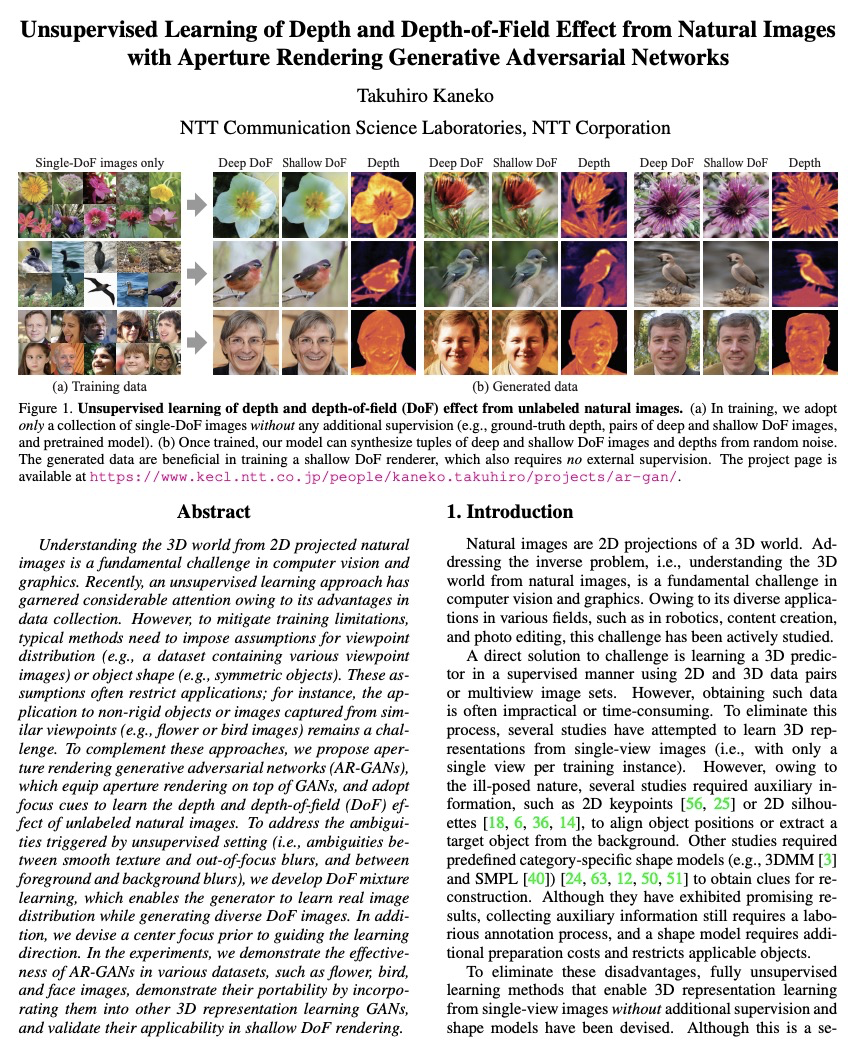

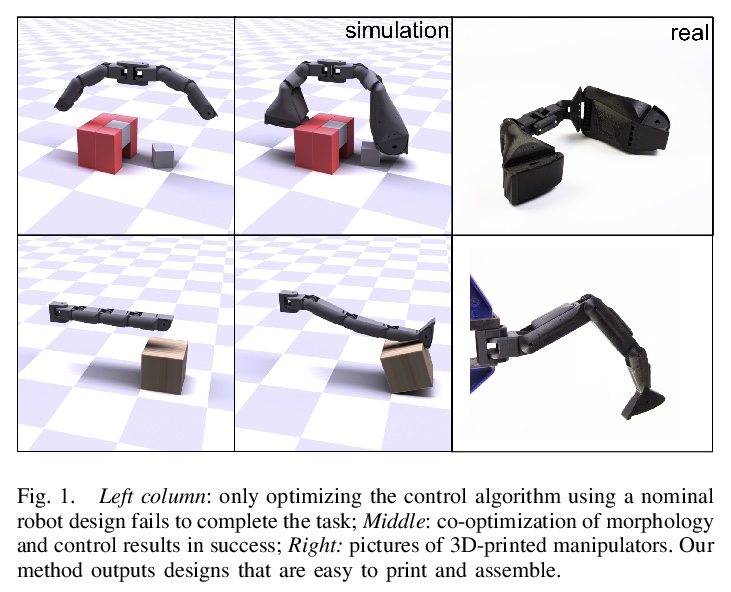
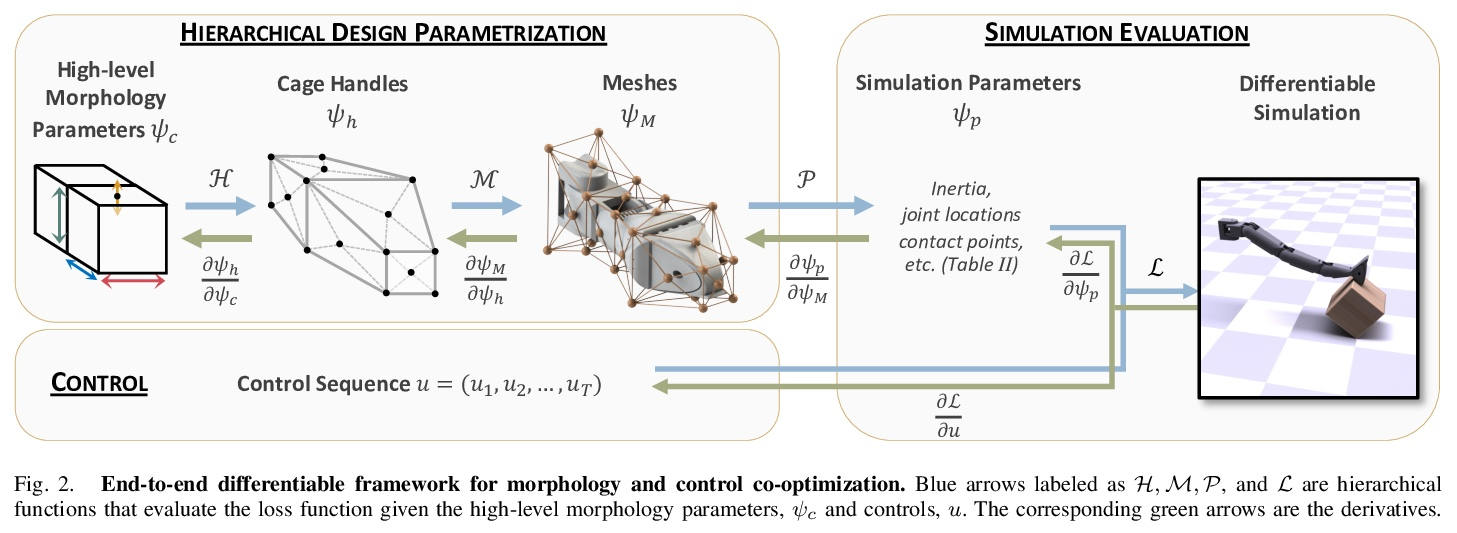
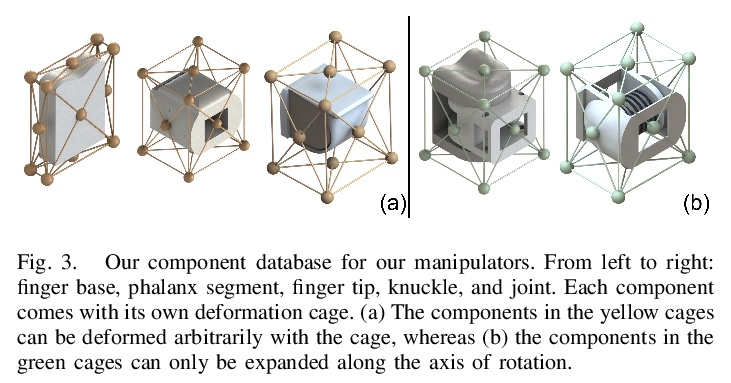
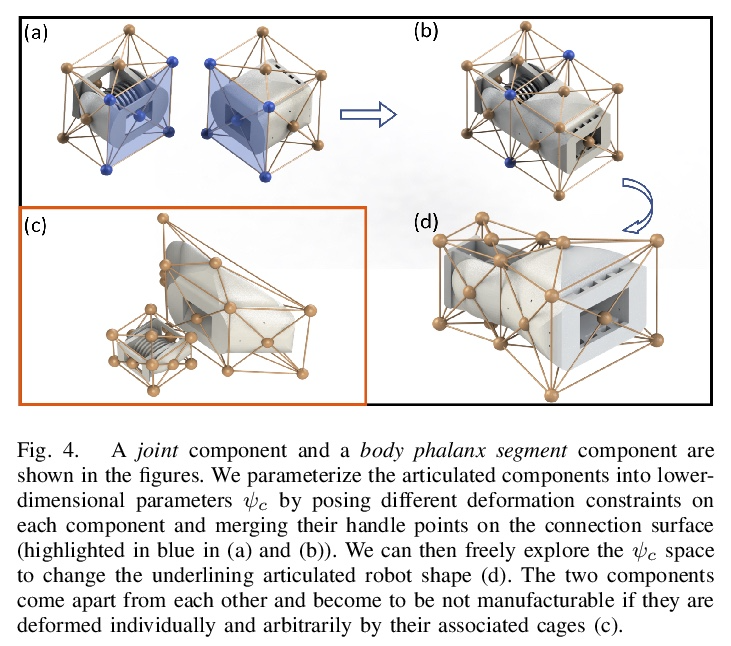
[RO] An End-to-End Differentiable Framework for Contact-Aware Robot Design
接触感知机器人设计的端到端可微框架
J Xu, T Chen, L Zlokapa, M Foshey, W Matusik, S Sueda, P Agrawal
[MIT & Texas A&M University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KqjYppyOr 
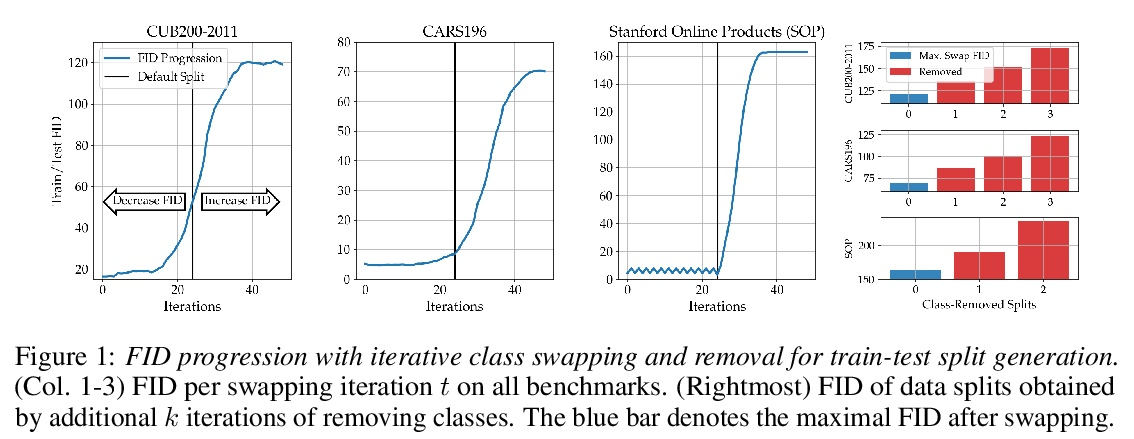
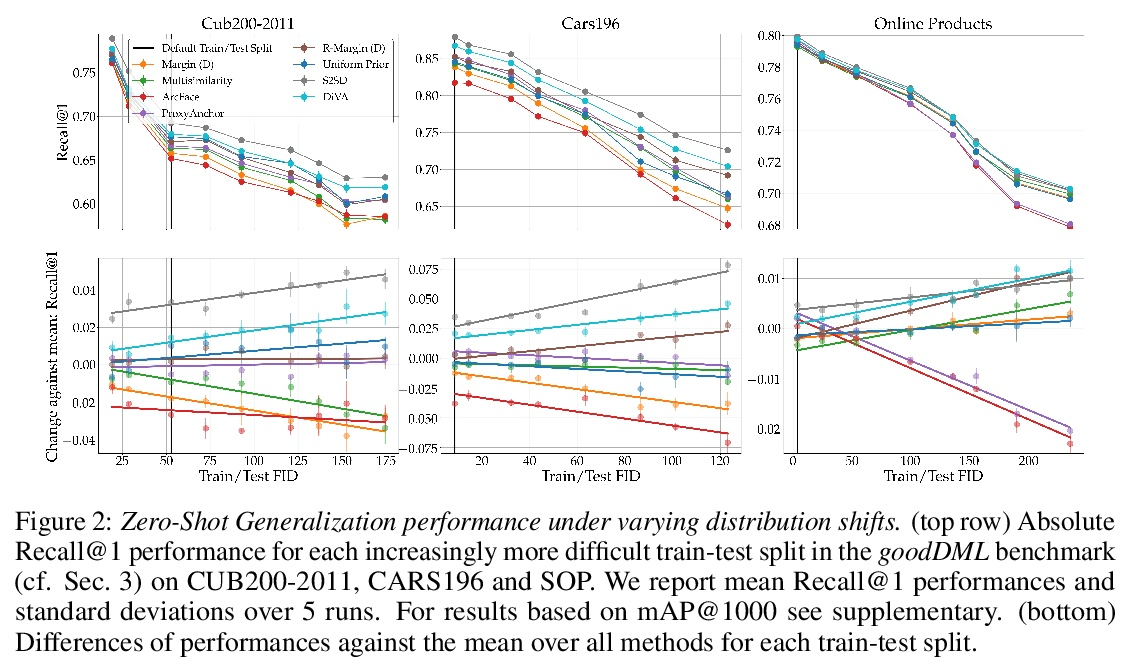
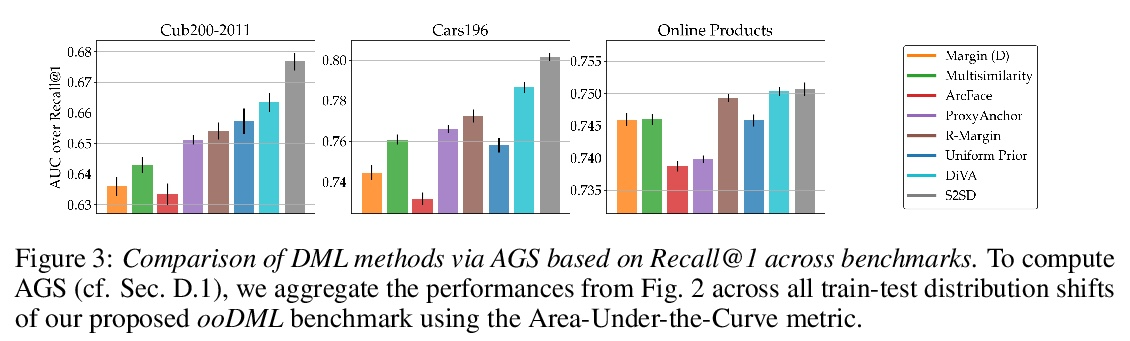
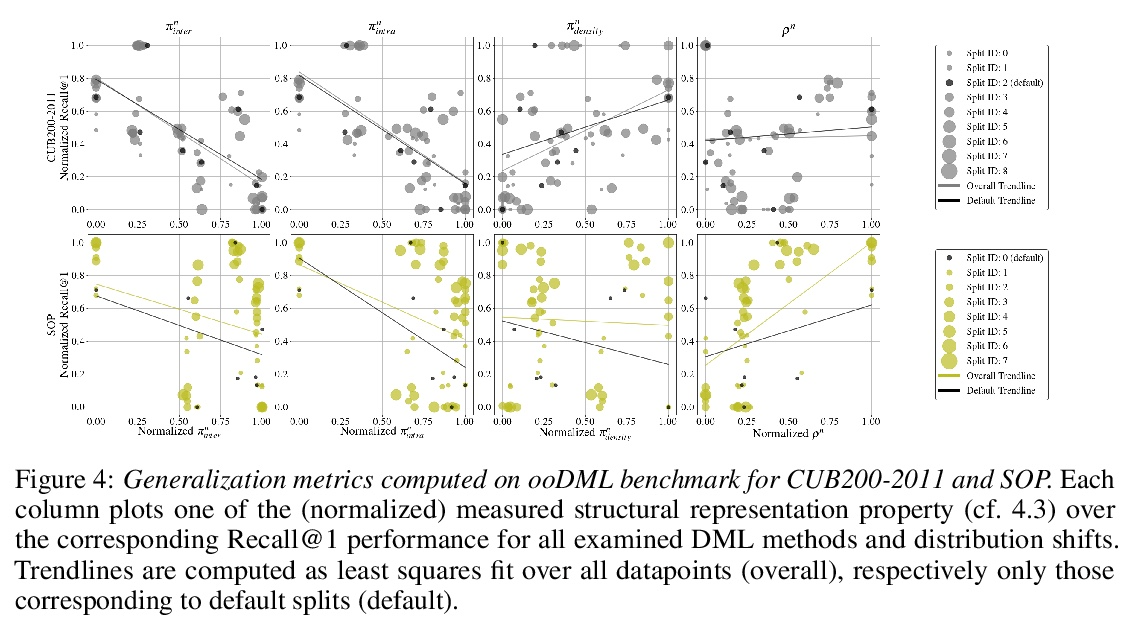
[LG] Characterizing Generalization under Out-Of-Distribution Shifts in Deep Metric Learning
深度度量学习分布外偏移下的泛化刻画
T Milbich, K Roth, S Sinha, L Schmidt, M Ghassemi, B Ommer
[University of Tübingen & University of Toronto & University of Washington & MIT]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kqk0xfdNL