- 1、[LG] A Practical Method for Constructing Equivariant Multilayer Perceptrons for Arbitrary Matrix Groups
- 2、[AI] Cetacean Translation Initiative: a roadmap to deciphering the communication of sperm whales
- 3、[CV] Multi-Modal Fusion Transformer for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
- 4、[LG] Agent-Centric Representations for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
- 5、[IR] The Simpson’s Paradox in the Offline Evaluation of Recommendation Systems
- [AS] TalkNet 2: Non-Autoregressive Depth-Wise Separable Convolutional Model for Speech Synthesis with Explicit Pitch and Duration Prediction
- [IR] BEIR: A Heterogenous Benchmark for Zero-shot Evaluation of Information Retrieval Models
- [CV] Temporal Query Networks for Fine-grained Video Understanding
- [LG] Using Machine Learning at Scale in HPC Simulations with SmartSim: An Application to Ocean Climate Modeling
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] A Practical Method for Constructing Equivariant Multilayer Perceptrons for Arbitrary Matrix Groups
M Finzi, M Welling, A G Wilson
[New York University & University of Amsterdam]
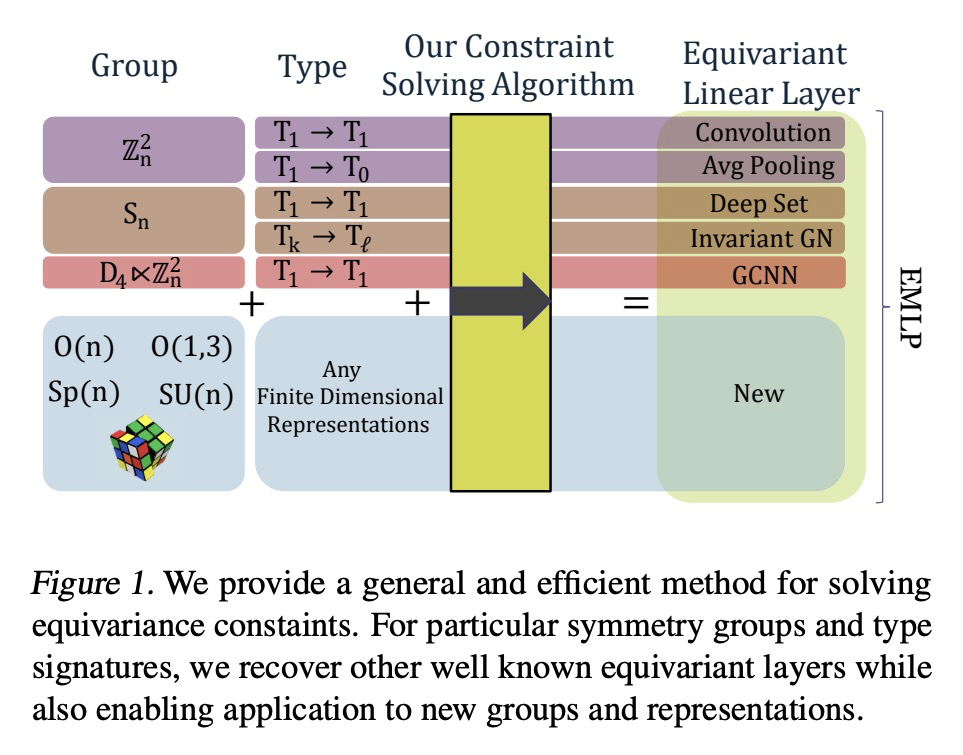
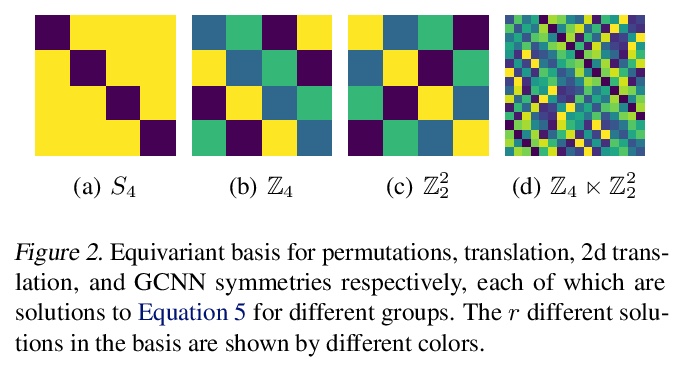
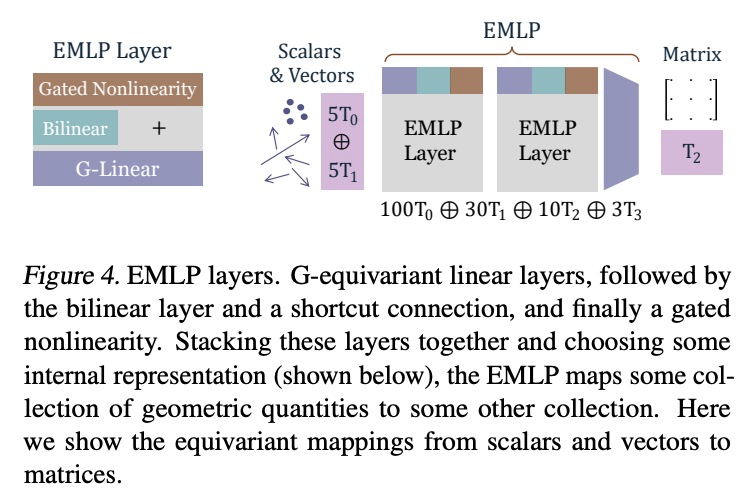
为任意矩阵群构造等变多层感知器的实用方法。对称性和等变性是神经网络在图像、图和点云等领域泛化的基础。现有工作主要集中在少数群上,如平移、旋转和置换群。本文提供了一种完全通用的算法,来解决矩阵群的等变层。提出了一种等变多层感知器(EMLP)的一般表述,给定一组输入和输出,根据对称群的有限维表示进行变换,描述了从一个空间映射到另一个空间的所有线性层,提供了计算它们的多项式时间算法,利用结构将其重塑为一个优化问题,可加速该方法。将网络应用于以前不可行的多个群,如五维正交群O(5),完整的洛伦兹群O(1, 3),对称群Sp(n),魔方群,采用相同的基础架构,表现优于非等价基线。
Symmetries and equivariance are fundamental to the generalization of neural networks on domains such as images, graphs, and point clouds. Existing work has primarily focused on a small number of groups, such as the translation, rotation, and permutation groups. In this work we provide a completely general algorithm for solving for the equivariant layers of matrix groups. In addition to recovering solutions from other works as special cases, we construct multilayer perceptrons equivariant to multiple groups that have never been tackled before, includingO(1,3),O(5),Sp(n), and the Rubik’s cube group. Our approach outperforms non-equivariant baselines, with applications to particle physics and dynamical systems. We release our software library to enable researchers to construct equivariant layers for arbitrary matrix groups.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbRUdDOOq

2、[AI] Cetacean Translation Initiative: a roadmap to deciphering the communication of sperm whales
J Andreas, G Beguš, M M. Bronstein, R Diamant, D Delaney, S Gero, S Goldwasser, D F. Gruber, S d Haas, P Malkin, R Payne, G Petri, D Rus, P Sharma, D Tchernov, P Tønnesen, A Torralba, D Vogt, R J. Wood
[MIT & UC Berkeley & Imperial College London & Haifa University…]
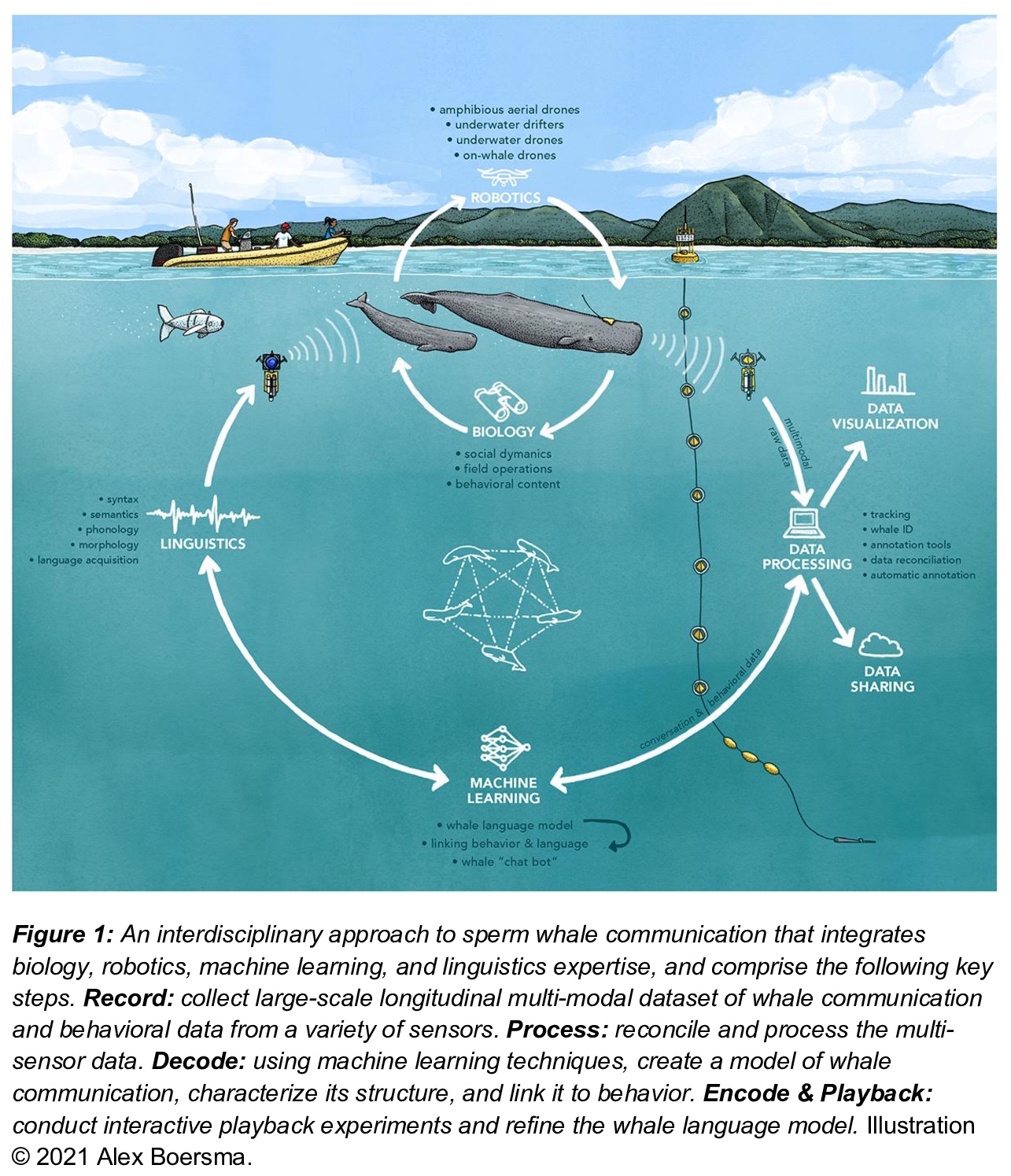
鲸类翻译计划:破译抹香鲸交流的路线图。过去十年见证了机器学习在人类语言分析方面的突破性崛起,目前的方法能够自动准确地从大规模数据集中恢复句法和语义的各个方面——包括句子结构和基础词义。最新研究表明,这类工具有望用于分析非人类物种的声音交流。机器学习将成为未来动物交流研究中收集、处理和分析多模态数据流的基石,包括生物声学、行为学、生物学和环境数据。鲸类是独特的非人类模式物种,因为它们拥有复杂的声学通信,但利用的是非常不同的编码系统,该系统是在水生而非陆生介质中进化的。特别是抹香鲸,其高度发达的神经解剖学特征、认知能力、社会结构和基于点的离散编码,是先进的机器学习工具的绝佳起点,未来可应用于其他动物。本文详细介绍了基于目前现有技术和多学科科学界努力实现这一目标的路线图。概述了收集和处理抹香鲸的大量生物声学数据所需的关键要素,检测它们的基本通信单元和类似语言的高层次结构,并通过互动播放实验验证这些模型。这项工作所开发的技术能力有可能在研究非人类交流和动物行为研究的更广泛的社区产生交叉应用和进步。
The past decade has witnessed a groundbreaking rise of machine learning for human language analysis, with current methods capable of automatically accurately recovering various aspects of syntax and semantics - including sentence structure and grounded word meaning - from large data collections. Recent research showed the promise of such tools for analyzing acoustic communication in nonhuman species. We posit that machine learning will be the cornerstone of future collection, processing, and analysis of multimodal streams of data in animal communication studies, including bioacoustic, behavioral, biological, and environmental data. Cetaceans are unique non-human model species as they possess sophisticated acoustic communications, but utilize a very different encoding system that evolved in an aquatic rather than terrestrial medium. Sperm whales, in particular, with their highly-developed neuroanatomical features, cognitive abilities, social structures, and discrete click-based encoding make for an excellent starting point for advanced machine learning tools that can be applied to other animals in the future. This paper details a roadmap toward this goal based on currently existing technology and multidisciplinary scientific community effort. We outline the key elements required for the collection and processing of massive bioacoustic data of sperm whales, detecting their basic communication units and language-like higher-level structures, and validating these models through interactive playback experiments. The technological capabilities developed by such an undertaking are likely to yield cross-applications and advancements in broader communities investigating non-human communication and animal behavioral research.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbS0XvDLA
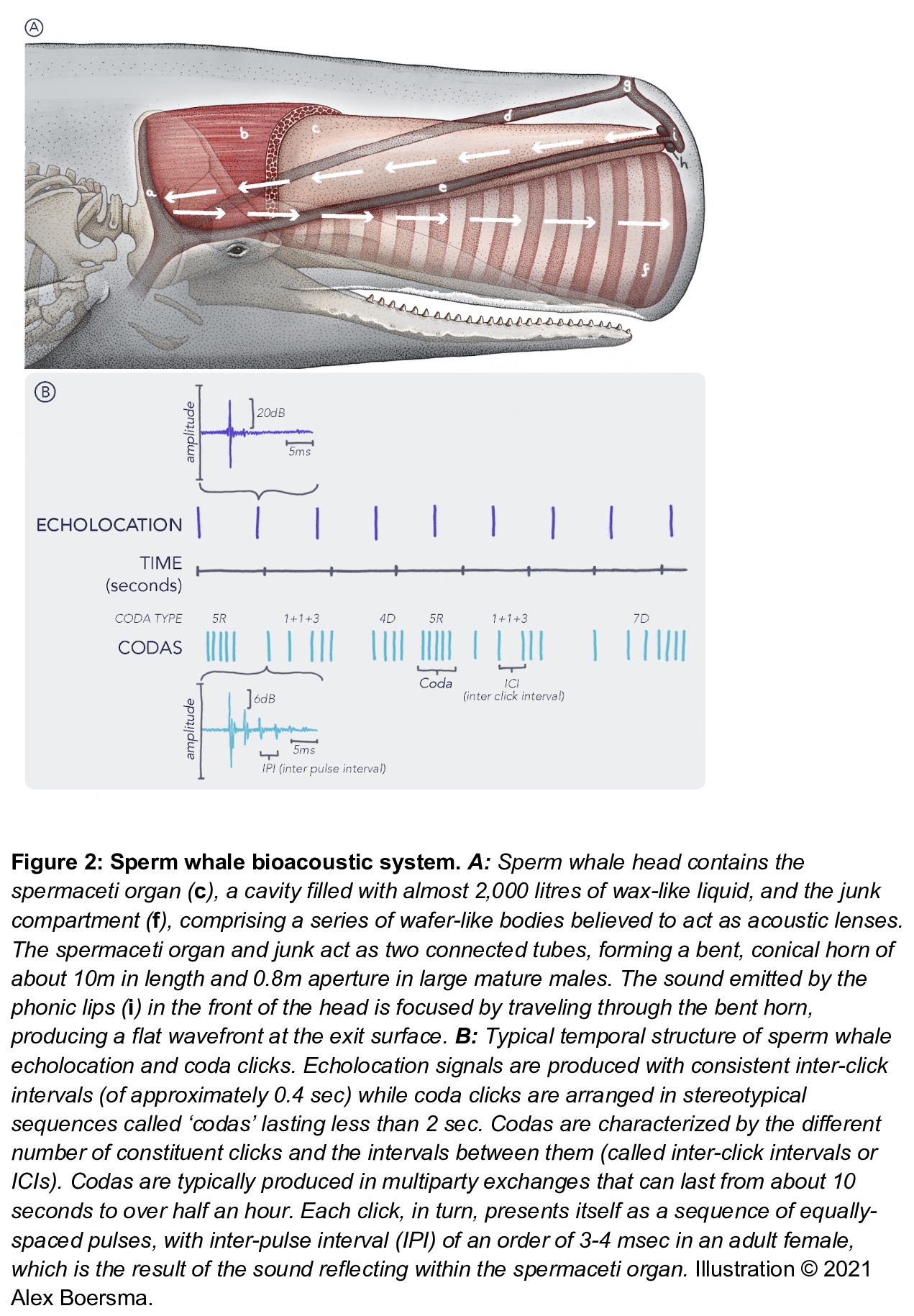
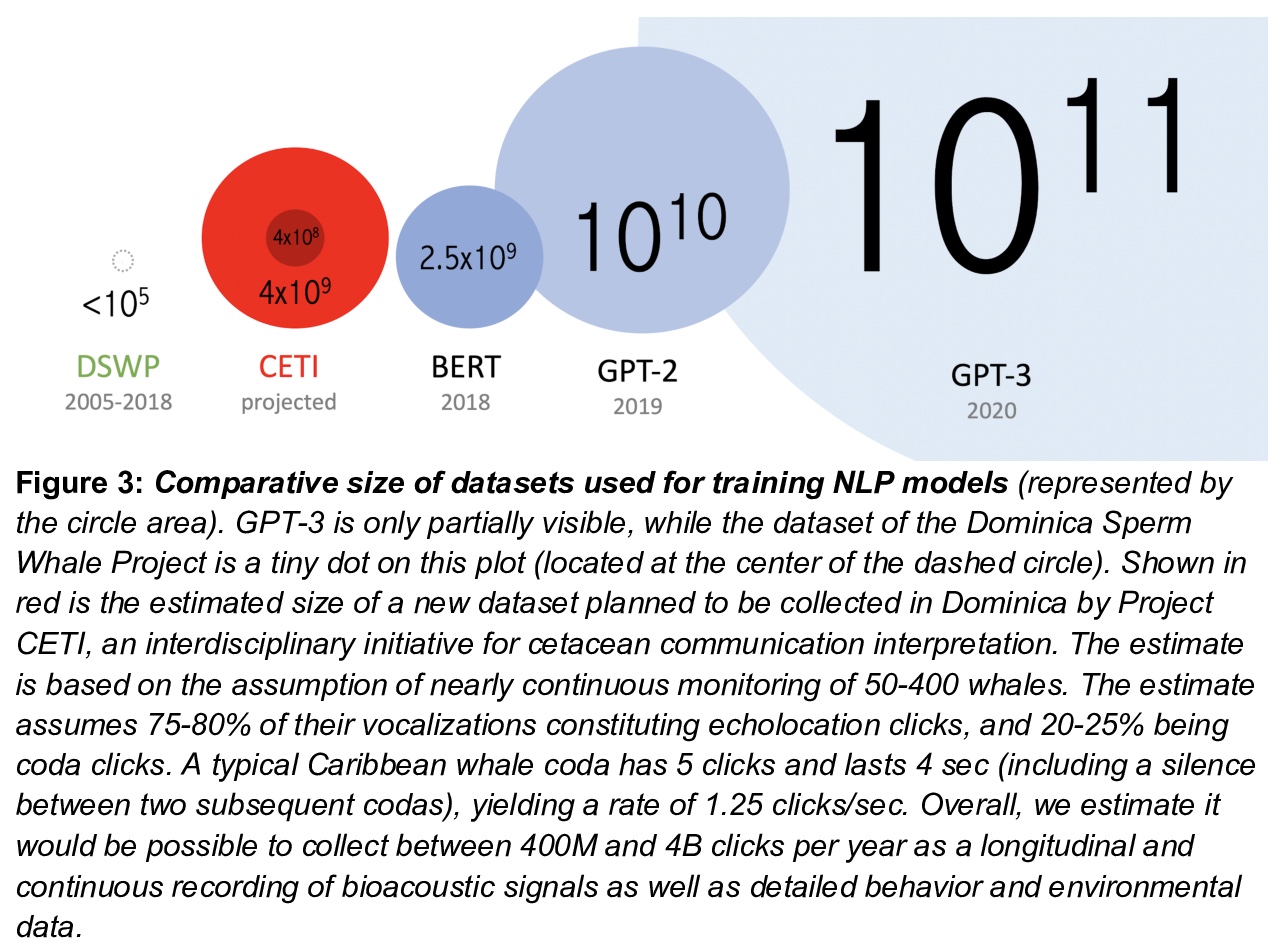
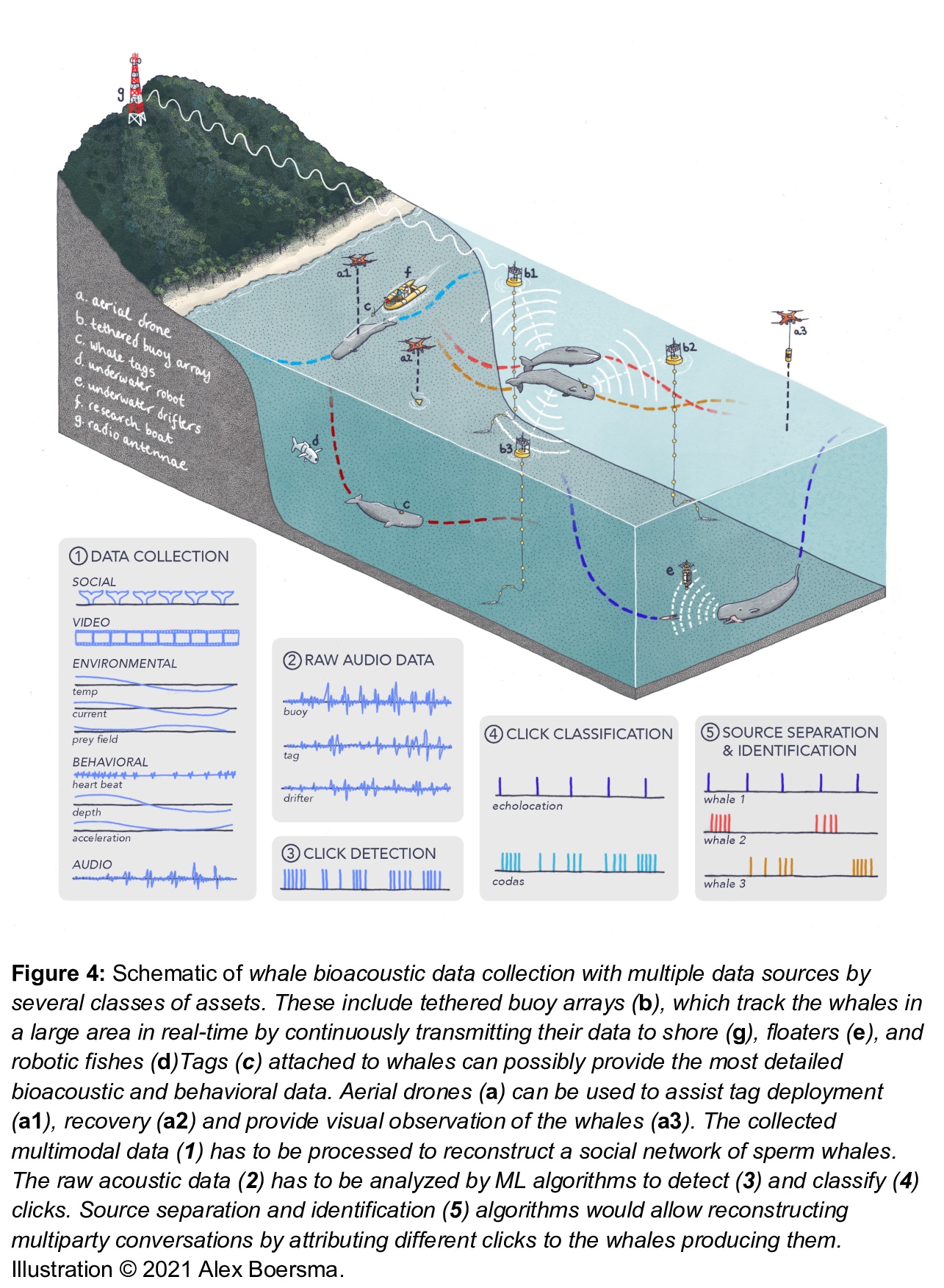
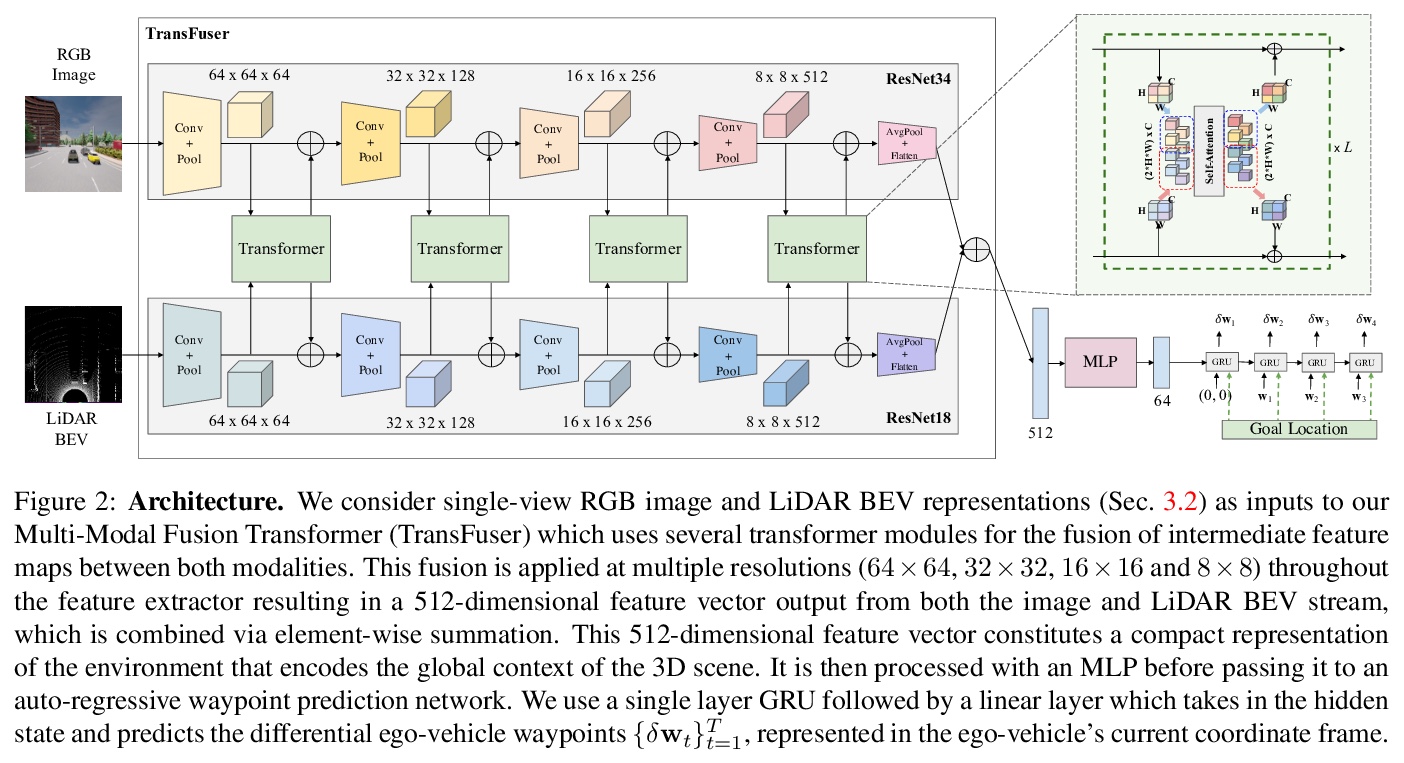
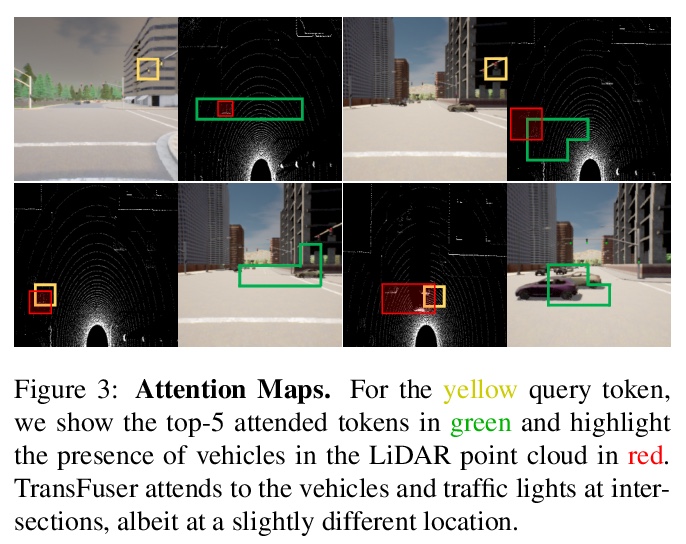
3、[CV] Multi-Modal Fusion Transformer for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
A Prakash, K Chitta, A Geiger
[Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems]
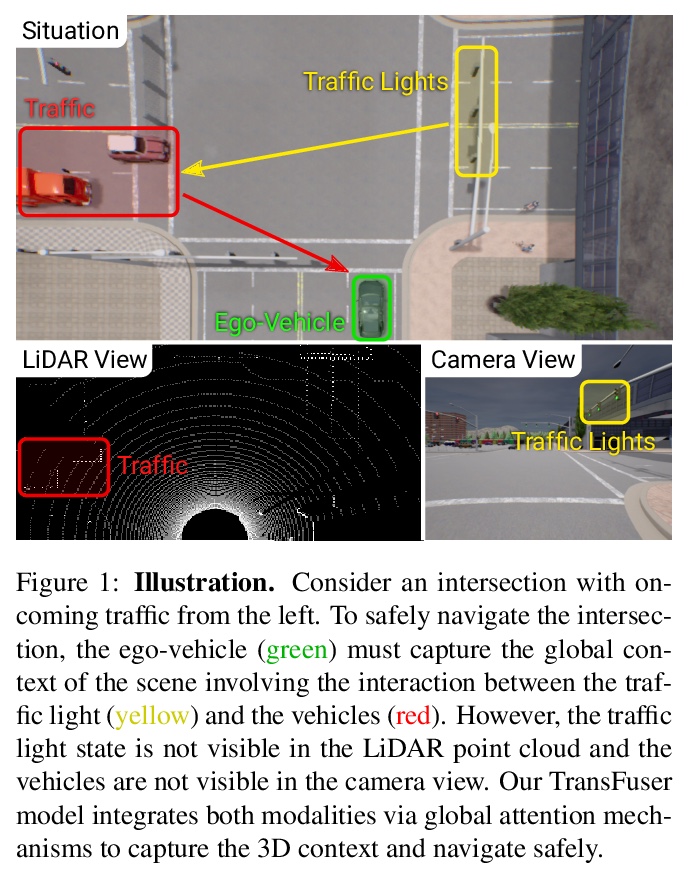
面向端到端无人驾驶的多模态融合Transformer。对无人驾驶来说,应该如何整合来自互补性传感器的表征?基于几何的传感器融合在感知任务中显示出巨大的前景,如目标检测和运动预测。然而,对于实际的驾驶任务,三维场景的全局上下文是关键,例如,交通灯状态的变化,会影响到在几何上远离该交通灯的车辆的行为。因此,仅靠几何学可能不足以有效地融合端到端驾驶模型中的表示。本文证明了基于现有传感器融合方法的模仿学习策略,在高密度的动态智能体和复杂场景中表现不佳,无法处理城市驾驶中的对抗性场景,这些场景需要全局性的推理,例如在不受控制的十字路口,处理从多个方向来的交通。提出了TransFuser,一种新的多模态融合Transformer,用注意力来整合图像和LiDAR的表示,捕捉全局的三维场景上下文,并专注于动态智能体和交通灯。利用CARLA城市驾驶模拟器,在涉及复杂场景的城市环境中实验验证了该方法的有效性,实现了最先进的驾驶性能,与基于几何的融合相比,减少了76%的碰撞。
How should representations from complementary sensors be integrated for autonomous driving? Geometry-based sensor fusion has shown great promise for perception tasks such as object detection and motion forecasting. However, for the actual driving task, the global context of the 3D scene is key, e.g. a change in traffic light state can affect the behavior of a vehicle geometrically distant from that traffic light. Geometry alone may therefore be insufficient for effectively fusing representations in end-to-end driving models. In this work, we demonstrate that imitation learning policies based on existing sensor fusion methods under-perform in the presence of a high density of dynamic agents and complex scenarios, which require global contextual reasoning, such as handling traffic oncoming from multiple directions at uncontrolled intersections. Therefore, we propose TransFuser, a novel Multi-Modal Fusion Transformer, to integrate image and LiDAR representations using attention. We experimentally validate the efficacy of our approach in urban settings involving complex scenarios using the CARLA urban driving simulator. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art driving performance while reducing collisions by 76% compared to geometry-based fusion.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbS54u132
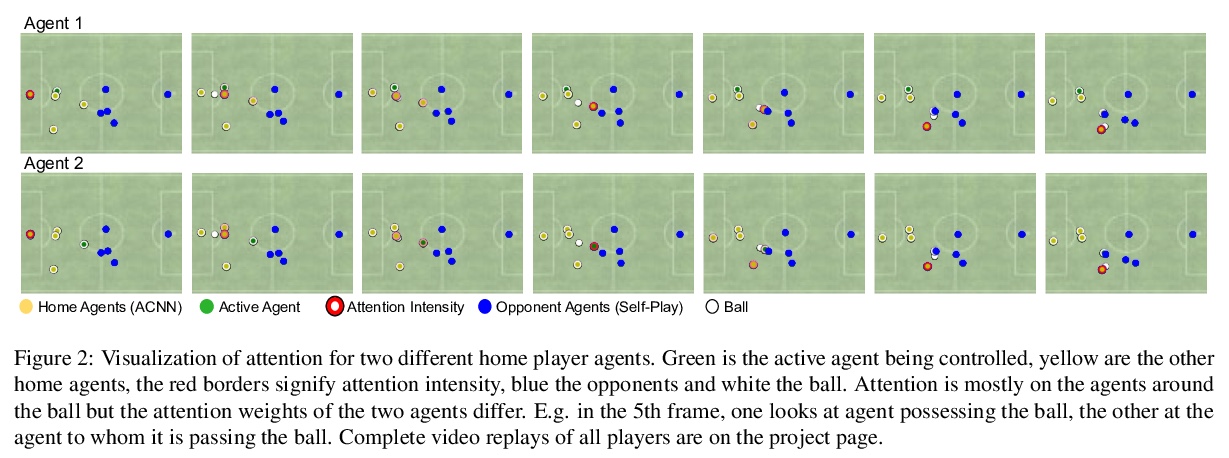
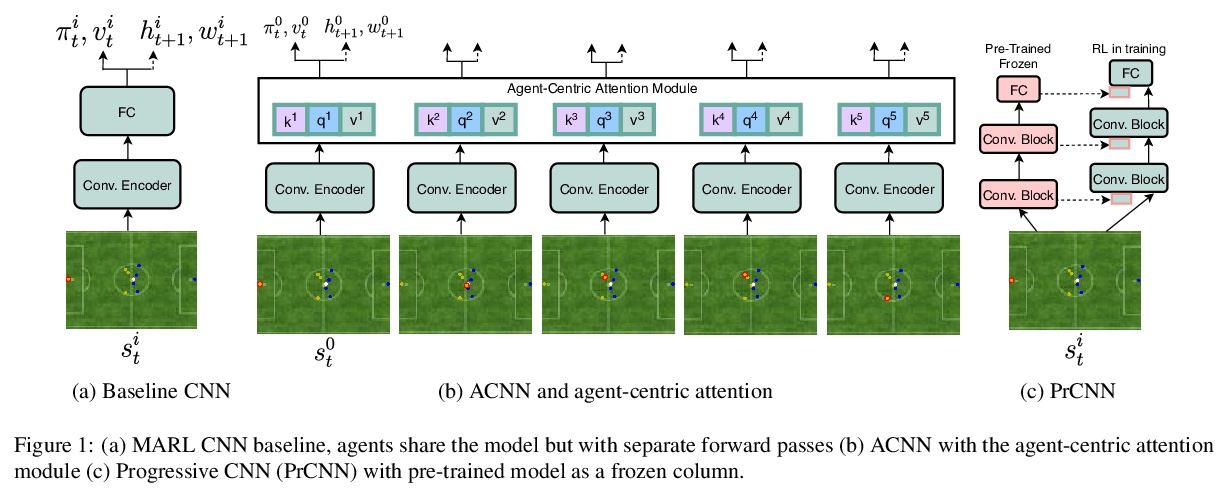
4、[LG] Agent-Centric Representations for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
W Shang, L Espeholt, A Raichuk, T Salimans
[DeepMind & Google]
多智能体强化学习的智能体中心表示。以对象为中心的表示最近在处理关系推理任务方面取得了重大进展。通过在神经架构中建立一个强大的以对象为中心的归纳偏见,最近的工作改善了这些问题的机器学习算法的泛化和数据效率。涉及关系推理的一类问题仍然没有得到充分探索,那就是多智能体强化学习(MARL)。本文为MARL引入了一个以智能体为中心的注意力模块,以鼓励复杂的合作策略和泛化。采用以智能体为中心的预测任务,作为MARL的辅助损失和/或预训练,以提高样本效率。在Google Research Football和DeepMind Lab 2D的挑战性任务上,用所提出的方法评价了在MARL上纳入以智能体为中心的归纳偏差。
Object-centric representations have recently enabled significant progress in tackling relational reasoning tasks. By building a strong object-centric inductive bias into neural architectures, recent efforts have improved generalization and data efficiency of machine learning algorithms for these problems. One problem class involving relational reasoning that still remains under-explored is multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). Here we investigate whether object-centric representations are also beneficial in the fully cooperative MARL setting. Specifically, we study two ways of incorporating an agent-centric inductive bias into our RL algorithm: 1. Introducing an agent-centric attention module with explicit connections across agents 2. Adding an agent-centric unsupervised predictive objective (i.e. not using action labels), to be used as an auxiliary loss for MARL, or as the basis of a pre-training step. We evaluate these approaches on the Google Research Football environment as well as DeepMind Lab 2D. Empirically, agent-centric representation learning leads to the emergence of more complex cooperation strategies between agents as well as enhanced sample efficiency and generalization.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbS91cpk3


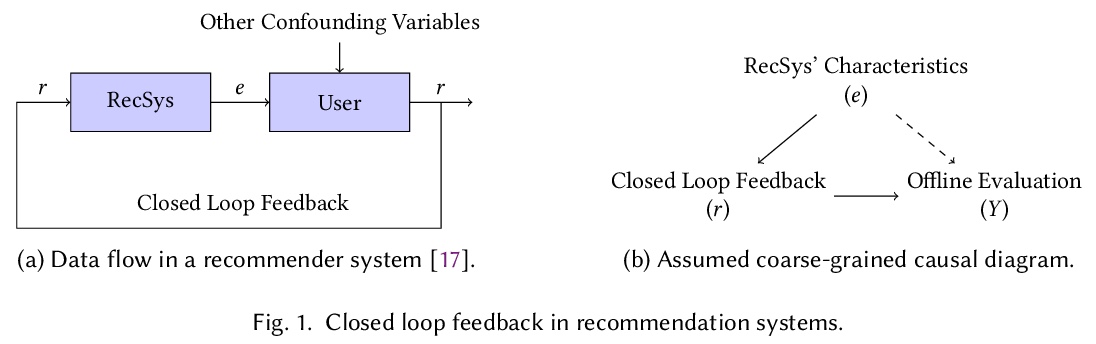
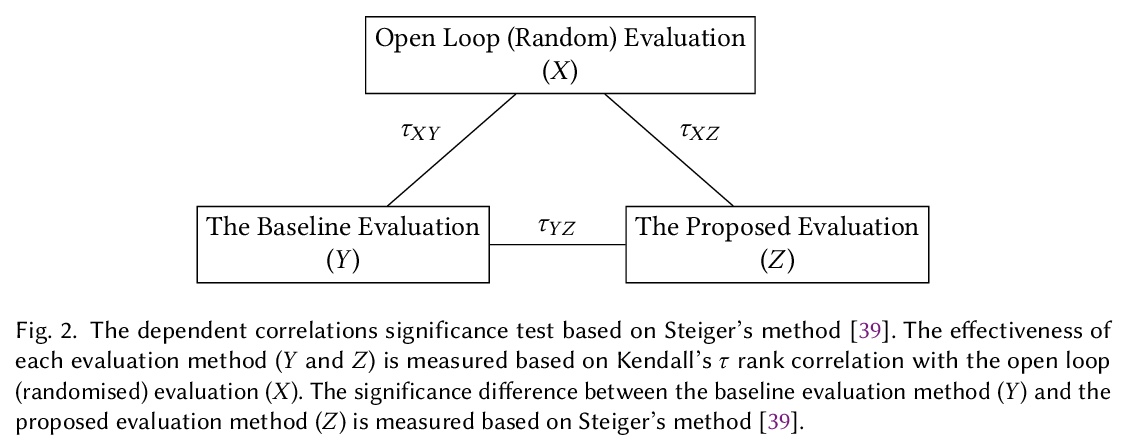
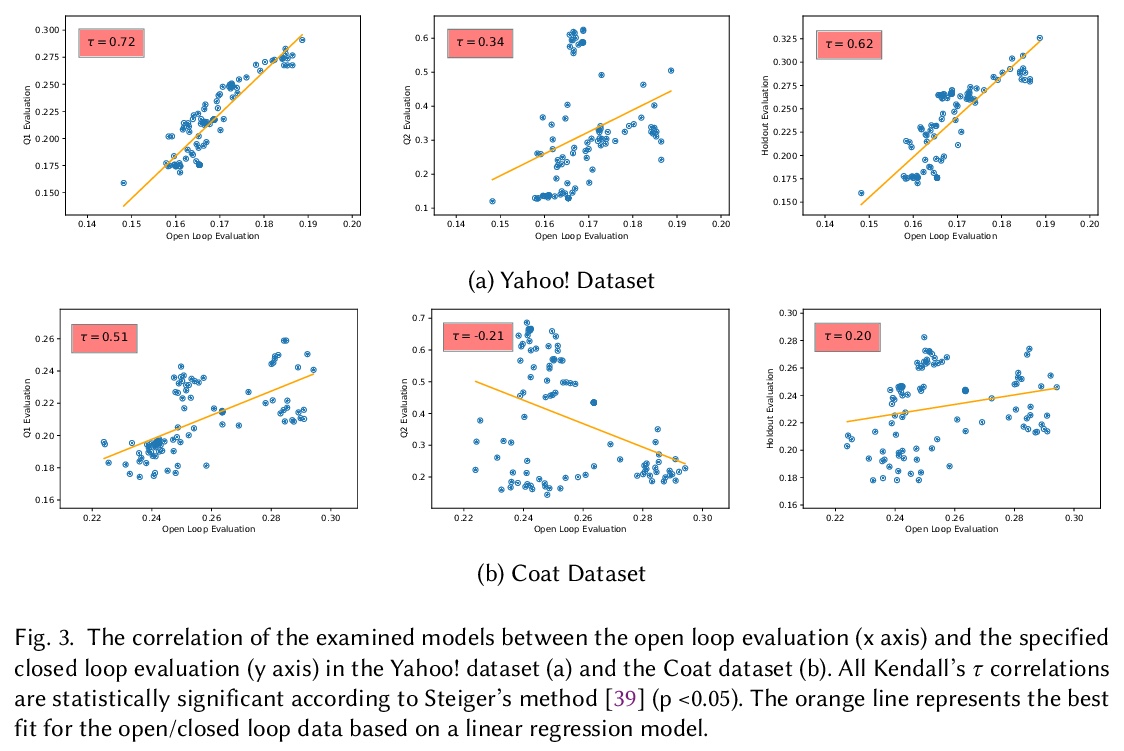
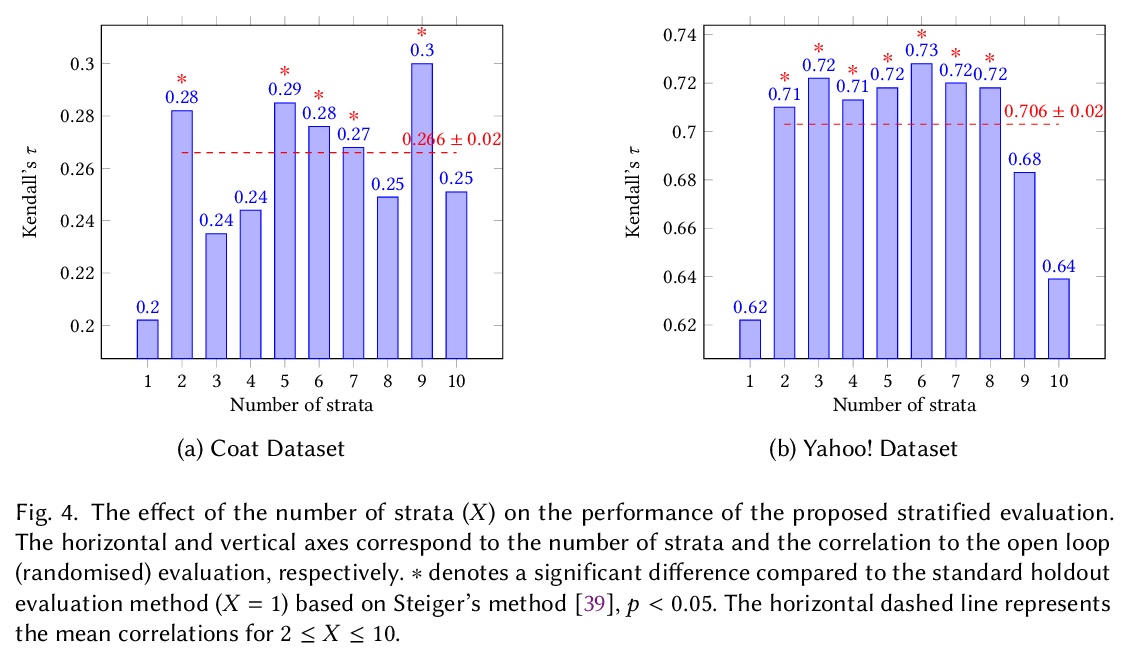
5、[IR] The Simpson’s Paradox in the Offline Evaluation of Recommendation Systems
A H. Jadidinejad, C Macdonald, I Ounis
[University of Glasgow]
推荐系统离线评价的”辛普森悖论”。推荐系统通常根据从现有的、已部署的推荐系统中收集到的用户互动进行评价。这种情况下,用户只对已曝光的项目提供反馈,他们可能不会对其他项目留下反馈,因为它们还没有被部署的系统曝光过。因此,收集到的用于评价新模型的反馈数据集,受到部署系统的影响,这是一种闭环反馈的形式。本文表明,典型的推荐系统离线评价,会受到所谓的辛普森悖论的影响。辛普森悖论是指,当一个重要的趋势出现在观察数据的几个不同的子群中,但当这些子群结合在一起时,就会消失甚至被逆转的现象。基于分层抽样的深入实验显示,在推荐系统的离线评价中,被部署的系统频繁曝光的极少数项目起到了干扰因素的作用。提出了一种新的基于倾向的分层评价方法,考虑到了干扰因素,即部署系统的特性。利用多种推荐模型的相对比较,就像在典型的推荐系统离线评价中一样,基于Kendall等级相关系数,所提出的评价方法在所考察的开环数据集(Yahoo和Coat)上表现出统计学上的明显改进,与标准评价相比,用开环(随机)评价反映系统的真实排名,分别提升了14%和40%。
Recommendation systems are often evaluated based on user’s interactions that were collected from an existing, already deployed recommendation system. In this situation, users only provide feedback on the exposed items and they may not leave feedback on other items since they have not been exposed to them by the deployed system. As a result, the collected feedback dataset that is used to evaluate a new model is influenced by the deployed system, as a form of closed loop feedback. In this paper, we show that the typical offline evaluation of recommender systems suffers from the so-called Simpson’s paradox. Simpson’s paradox is the name given to a phenomenon observed when a significant trend appears in several different sub-populations of observational data but disappears or is even reversed when these sub-populations are combined together. Our in-depth experiments based on stratified sampling reveal that a very small minority of items that are frequently exposed by the deployed system plays a confounding factor in the offline evaluation of recommendation systems. In addition, we propose a novel evaluation methodology that takes into account the confounder, i.e the deployed system’s characteristics. Using the relative comparison of many recommendation models as in the typical offline evaluation of recommender systems, and based on the Kendall rank correlation coefficient, we show that our proposed evaluation methodology exhibits statistically significant improvements of 14% and 40% on the examined open loop datasets (Yahoo! and Coat), respectively, in reflecting the true ranking of systems with an open loop (randomised) evaluation in comparison to the standard evaluation.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbScO8vYO
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
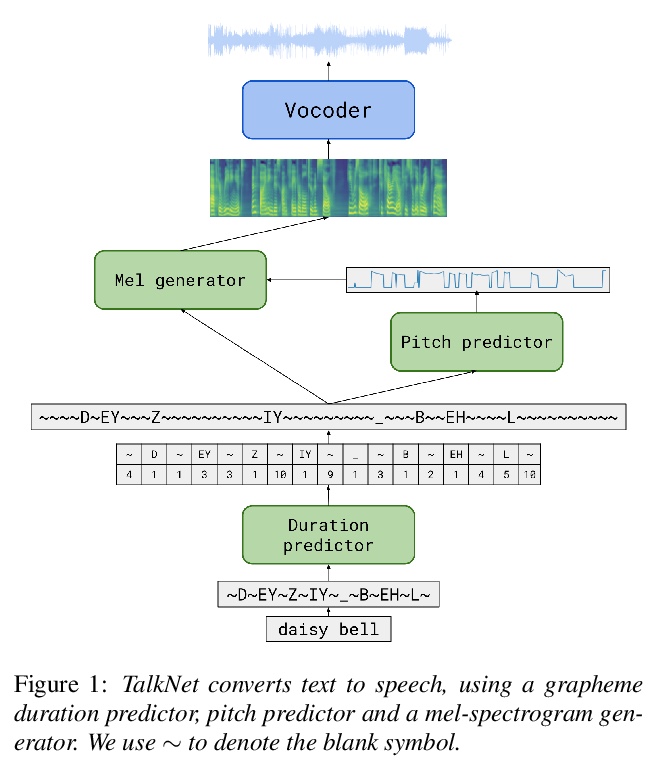
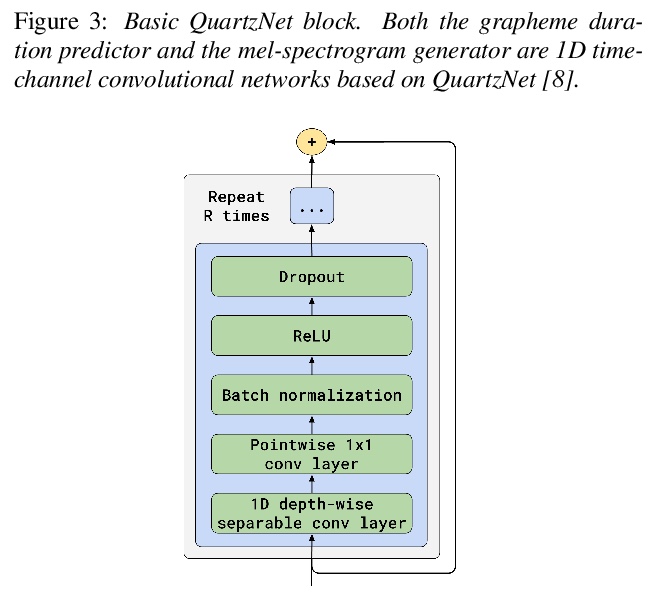
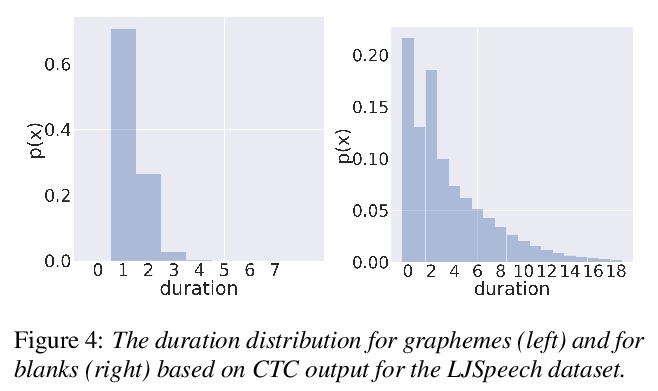
[AS] TalkNet 2: Non-Autoregressive Depth-Wise Separable Convolutional Model for Speech Synthesis with Explicit Pitch and Duration Prediction
TalkNet 2:面向语音合成基于显式基音与持续时间预测的非自回归深度分离卷积模型
S Beliaev, B Ginsburg
[NVIDIA]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbSgynObu

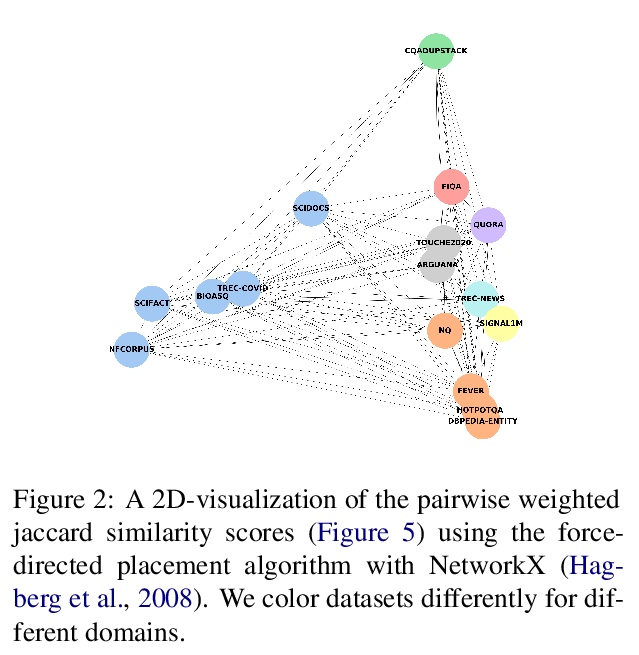
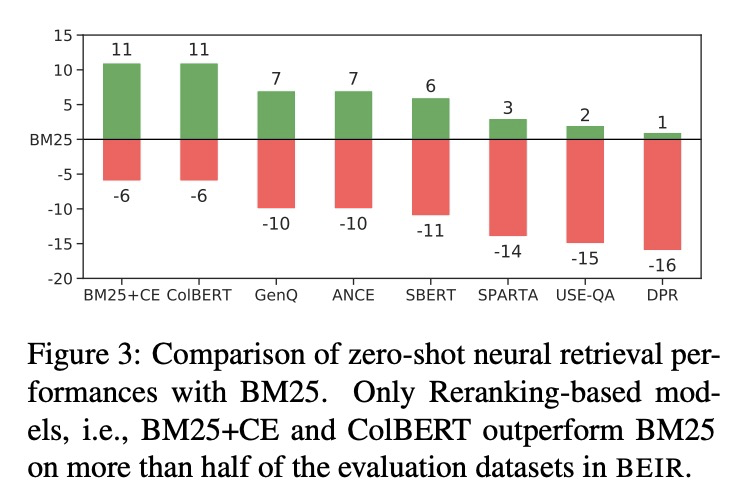
[IR] BEIR: A Heterogenous Benchmark for Zero-shot Evaluation of Information Retrieval Models
BEIR:信息检索模型零样本评价的异质基准
N Thakur, N Reimers, A Rücklé, A Srivastava, I Gurevych
[Technische Universität Darmstadt]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbSjqbwWQ

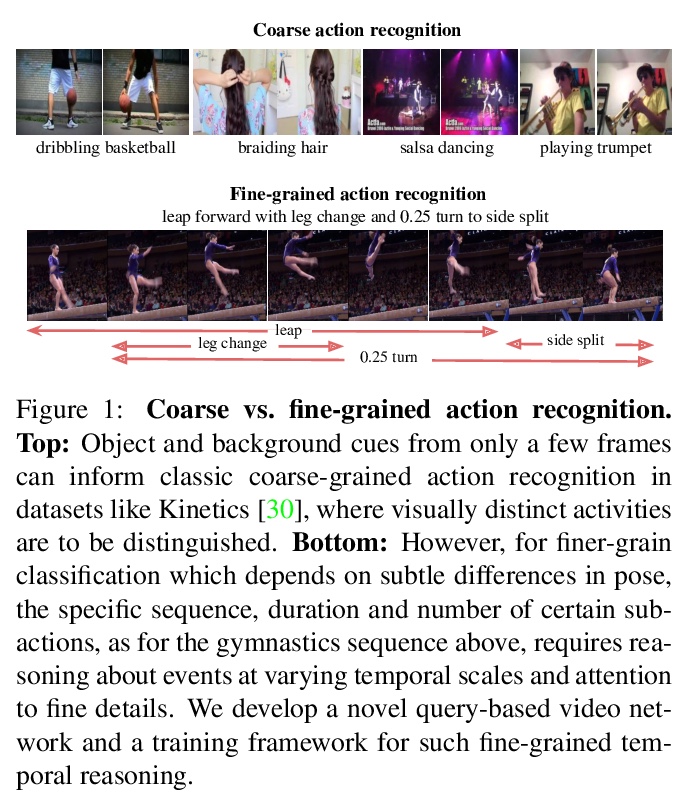
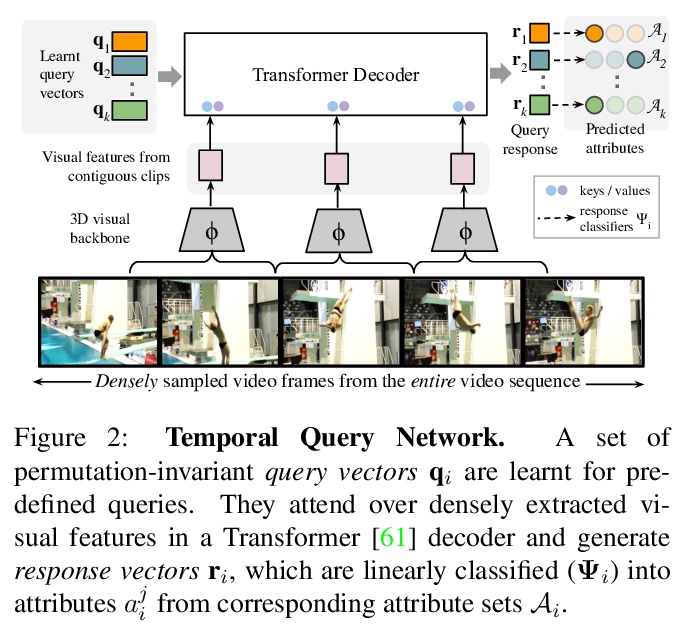
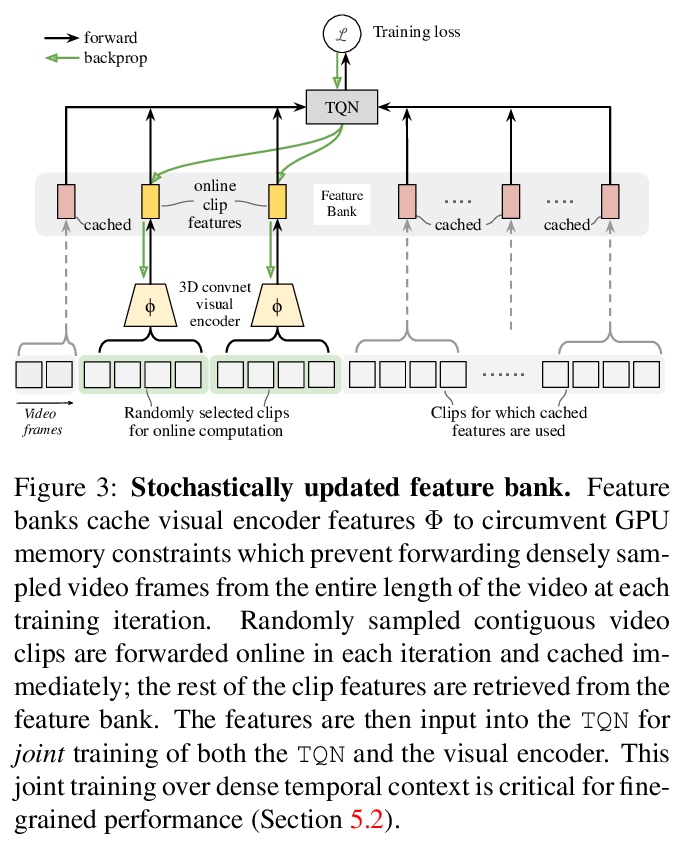
[CV] Temporal Query Networks for Fine-grained Video Understanding
面向细粒度视频理解的时间查询网络
C Zhang, A Gupta, A Zisserman
[University of Oxford & DeepMind]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbSliCYwE

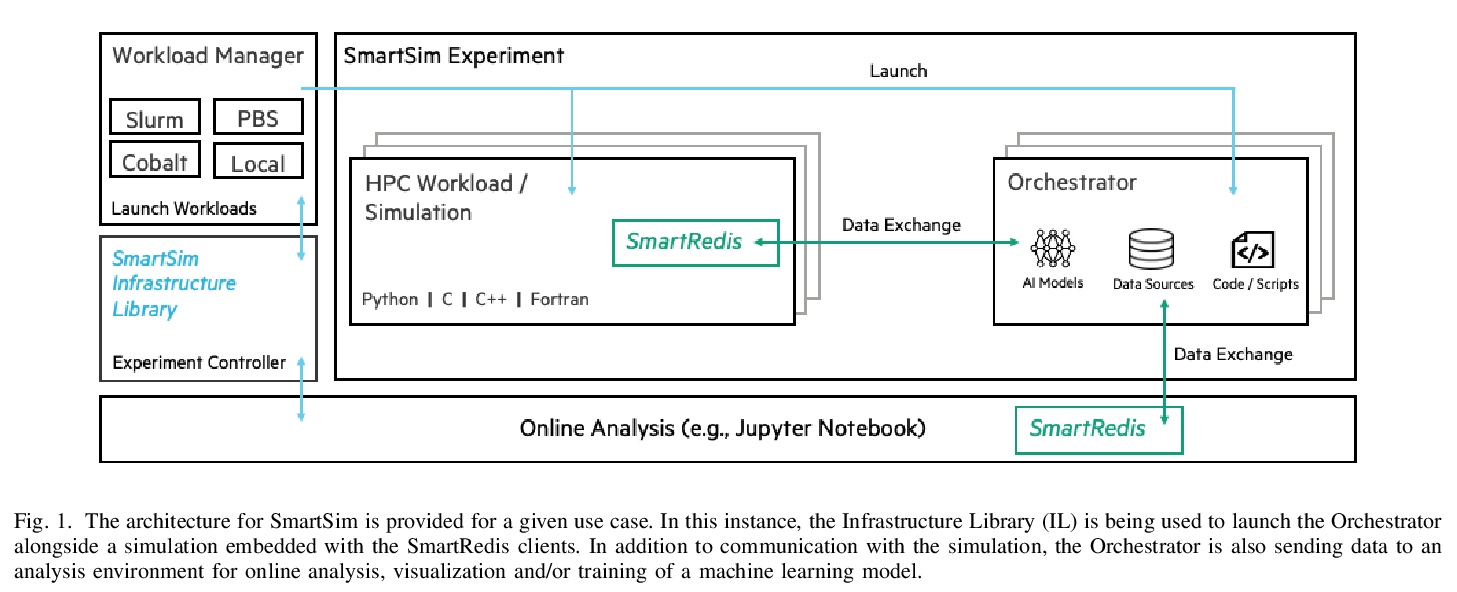
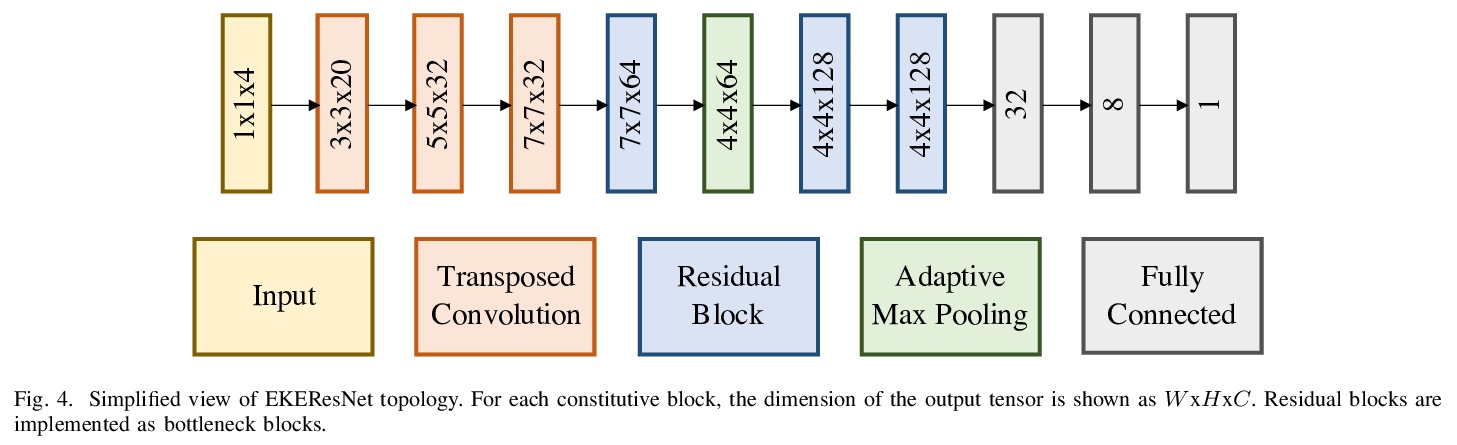
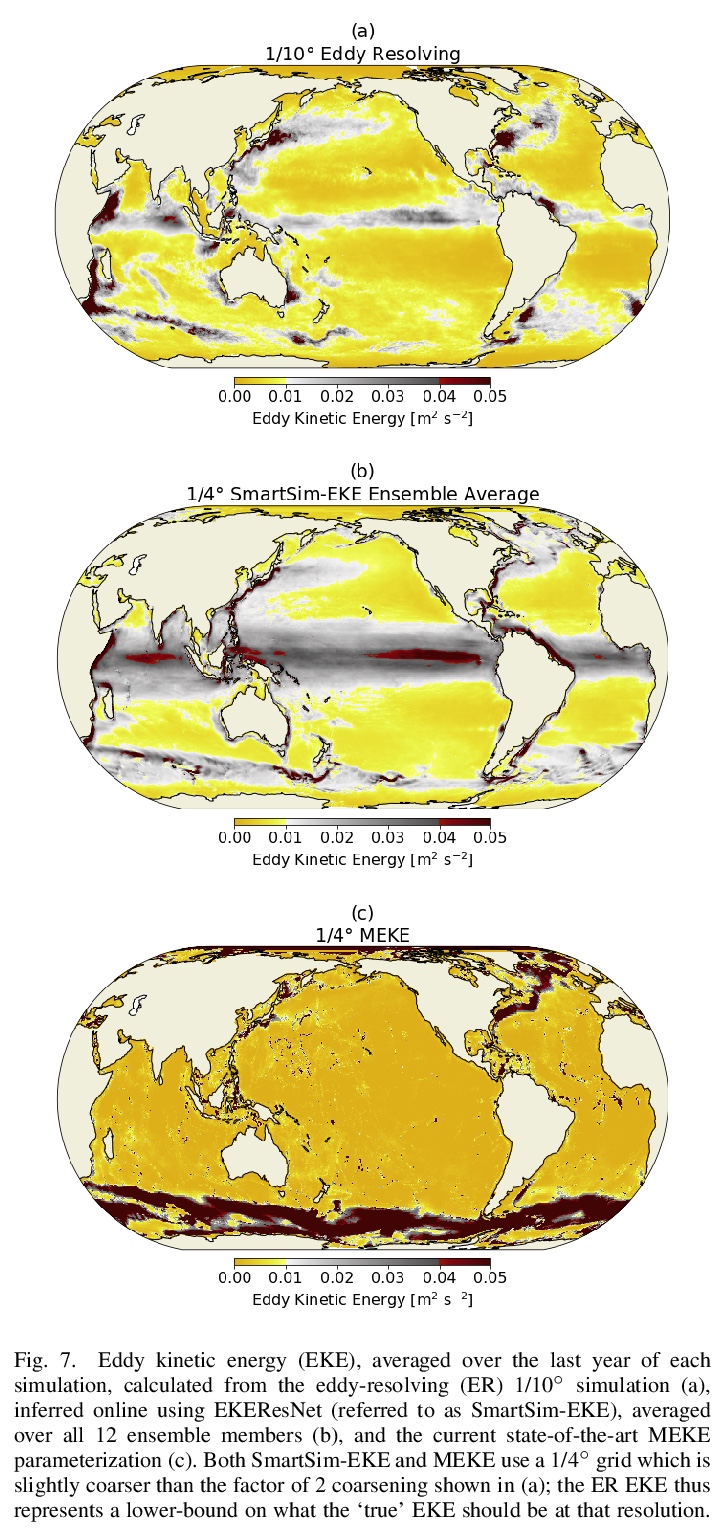
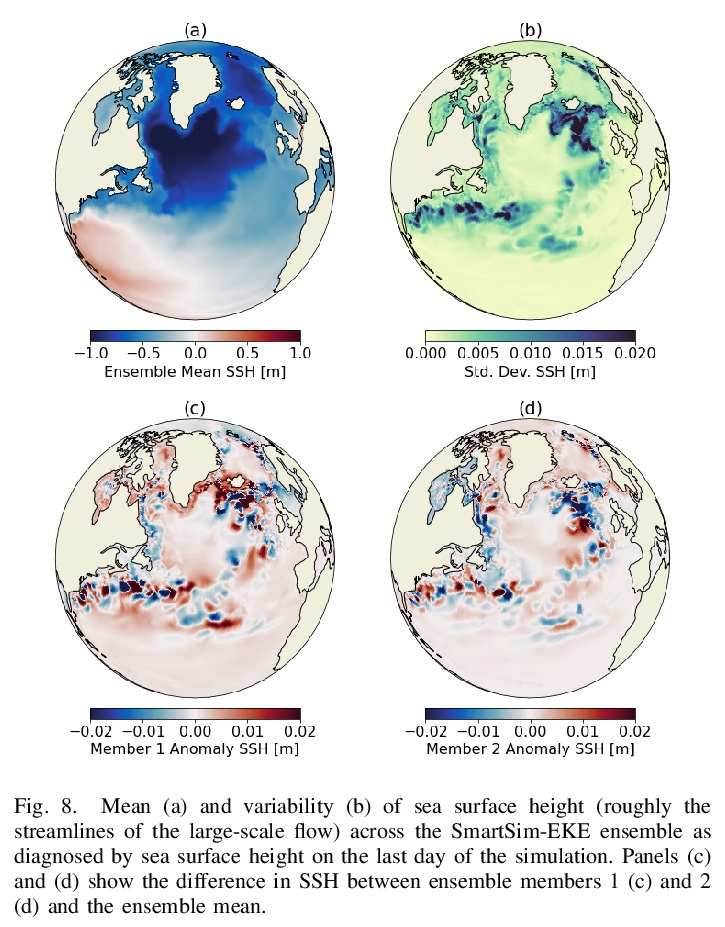
[LG] Using Machine Learning at Scale in HPC Simulations with SmartSim: An Application to Ocean Climate Modeling
高性能计算机仿真大规模机器学习:在海洋气候仿真中的应用
S Partee, M Ellis, A Rigazzi, S Bachman, G Marques, A Shao, B Robbins
[Hewlett Packard Enterprise & National Center for Atmospheric Research & University of Victoria]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KbSmMd6uS