LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
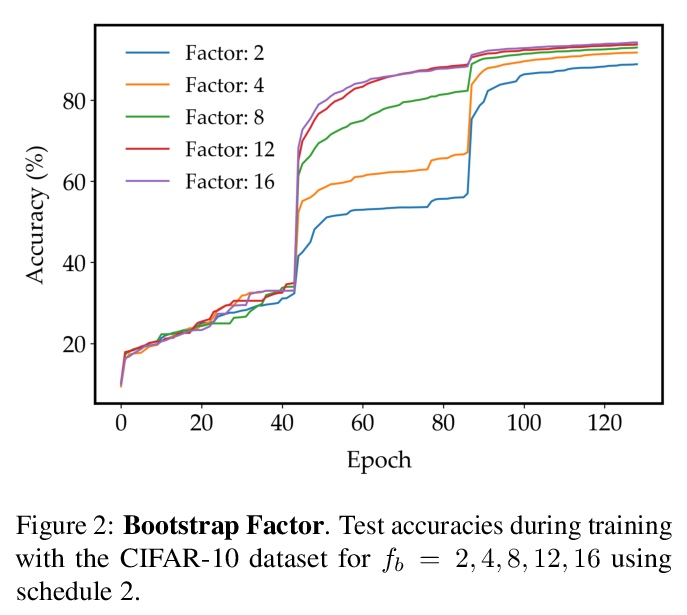
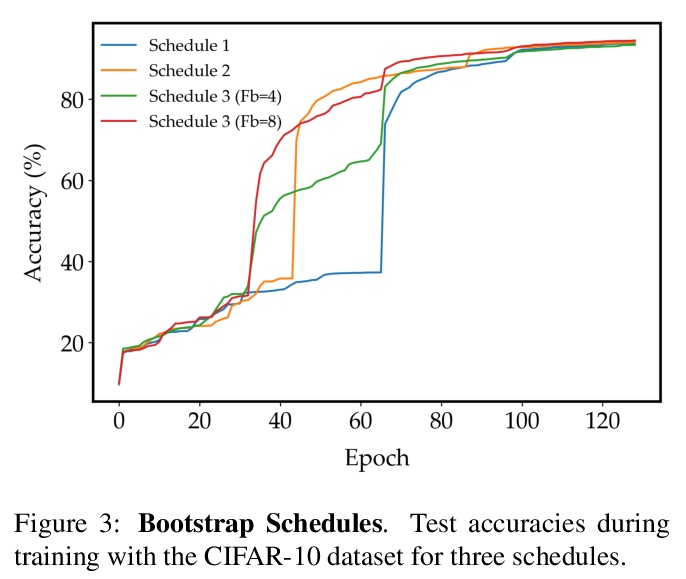
1、[LG] **FROST: Faster and more Robust One-shot Semi-supervised Training
H E. Liu, L N. Smith
[Thomas Jefferson HS for Science & Technology & US Naval Research Laboratory]
FROST:更快更鲁棒的单样本半监督训练。提出了单样本半监督学习方法FROST,将半监督学习与单阶段、单网络自训练相结合,比目前最先进方法快一个数量级,且更加鲁棒,对标记样本选择和超参数变化也更鲁棒。实验证明,FROST在未标记数据组成未知的情况下表现良好。
Recent advances in one-shot semi-supervised learning have lowered the barrier for deep learning of new applications. However, the state-of-the-art for semi-supervised learning is slow to train and the performance is sensitive to the choices of the labeled data and hyper-parameter values. In this paper, we present a one-shot semi-supervised learning method that trains up to an order of magnitude faster and is more robust than state-of-the-art methods. Specifically, we show that by combining semi-supervised learning with a one-stage, single network version of self-training, our FROST methodology trains faster and is more robust to choices for the labeled samples and changes in hyper-parameters. Our experiments demonstrate FROST’s capability to perform well when the composition of the unlabeled data is unknown; that is when the unlabeled data contain unequal numbers of each class and can contain out-of-distribution examples that don’t belong to any of the training classes. High performance, speed of training, and insensitivity to hyper-parameters make FROST the most practical method for one-shot semi-supervised training.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jv1vbAfcS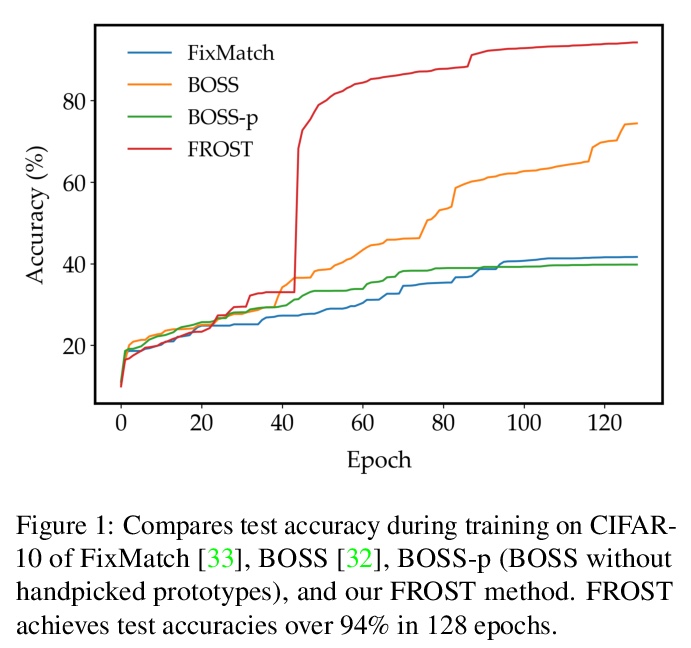
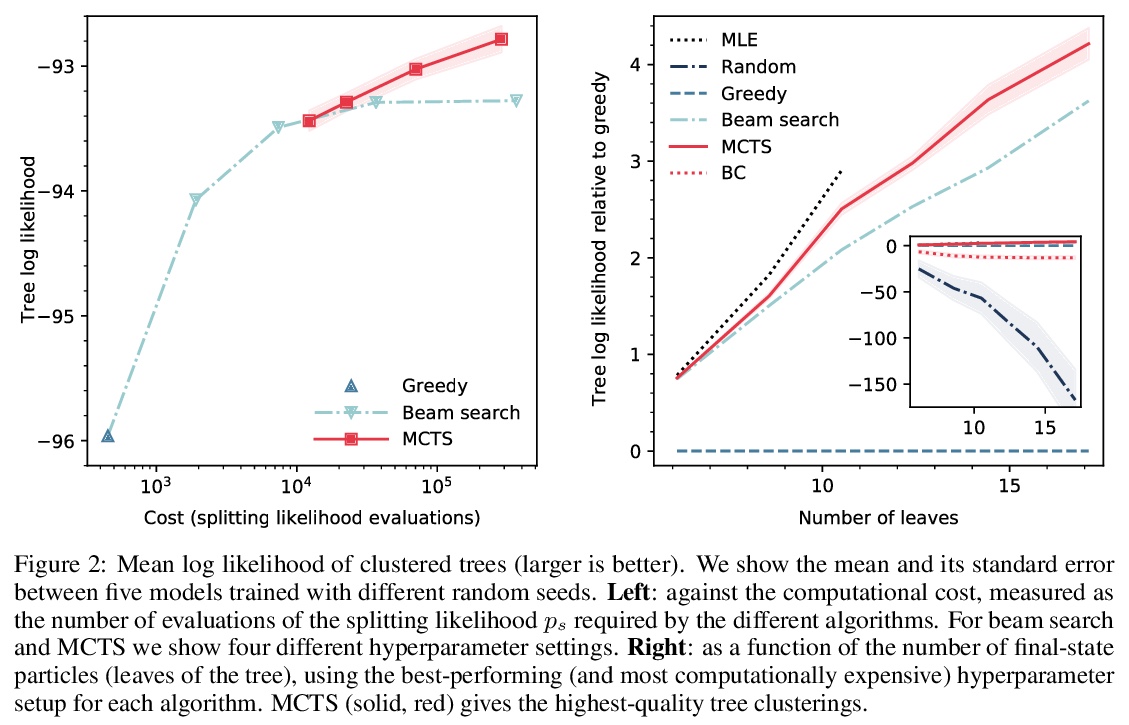
2、[LG] **Hierarchical clustering in particle physics through reinforcement learning
J Brehmer, S Macaluso, D Pappadopulo, K Cranmer
[New York University & Bloomberg L. P.]
粒子物理强化学习层次聚类。粒子物理实验通常需要通过对观察到的最终状态粒子进行层次聚类来重建衰变模式,该任务可描述为马尔可夫决策过程,用强化学习算法来解决。针对粒子物理中的层次聚类问题,提出了一种基于神经策略的蒙特卡罗树搜索和行为克隆的新算法。在使用GINKGO模拟器的简化场景中,相比贪婪和集束搜索,MCTS算法可生成更高质量的层次聚类。
Particle physics experiments often require the reconstruction of decay patterns through a hierarchical clustering of the observed final-state particles. We show that this task can be phrased as a Markov Decision Process and adapt reinforcement learning algorithms to solve it. In particular, we show that Monte-Carlo Tree Search guided by a neural policy can construct high-quality hierarchical clusterings and outperform established greedy and beam search baselines.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jv1A2q5dU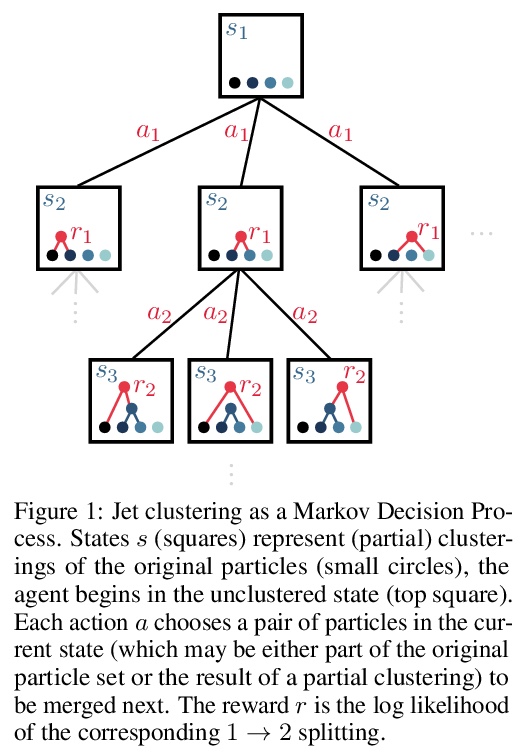
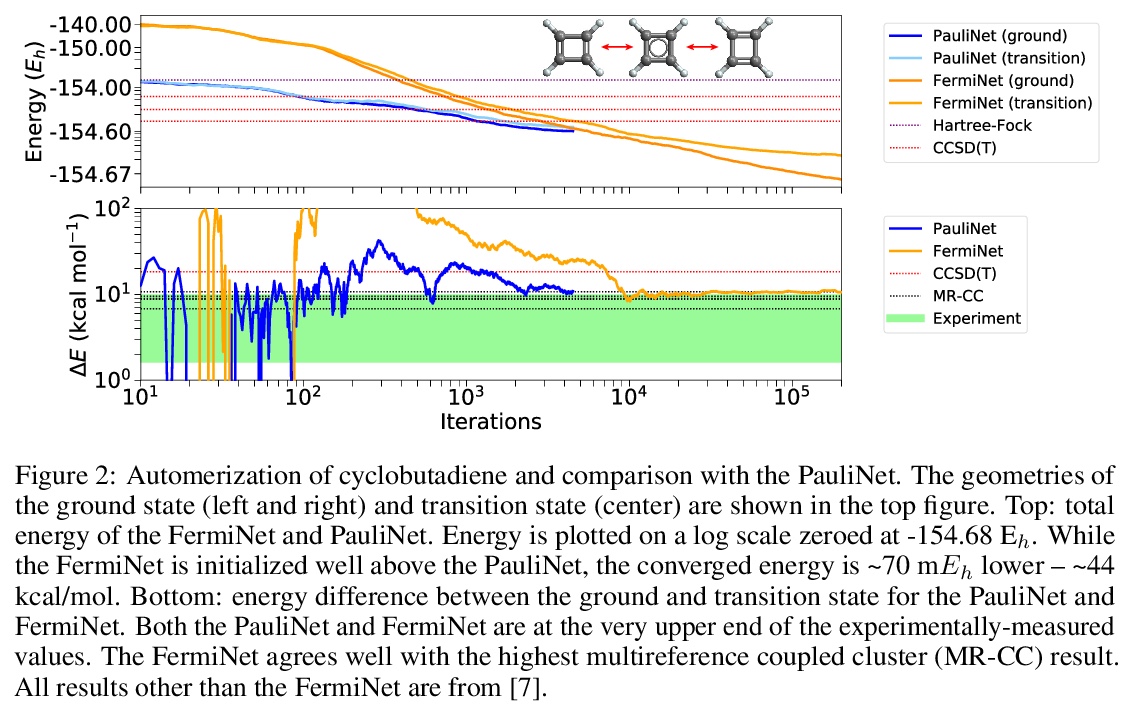
3、[LG] **Better, Faster Fermionic Neural Networks
J S. Spencer, D Pfau, A Botev, W. M. C. Foulkes
[DeepMind & Imperial College London]
更好更快的费米子神经网络(FermiNet)。提出了针对FermiNet的几点改进,在挑战性系统上创造了新的速度和精度记录。通过用JAX实现,并对网络组成部分进行简化,可将在大型系统上训练FermiNet所需的GPU时间减少一个数量级,还可通过简单增大网络来提高精度。
The Fermionic Neural Network (FermiNet) is a recently-developed neural network architecture that can be used as a wavefunction Ansatz for many-electron systems, and has already demonstrated high accuracy on small systems. Here we present several improvements to the FermiNet that allow us to set new records for speed and accuracy on challenging systems. We find that increasing the size of the network is sufficient to reach chemical accuracy on atoms as large as argon. Through a combination of implementing FermiNet in JAX and simplifying several parts of the network, we are able to reduce the number of GPU hours needed to train the FermiNet on large systems by an order of magnitude. This enables us to run the FermiNet on the challenging transition of bicyclobutane to butadiene and compare against the PauliNet on the automerization of cyclobutadiene, and we achieve results near the state of the art for both.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jv1EC14I9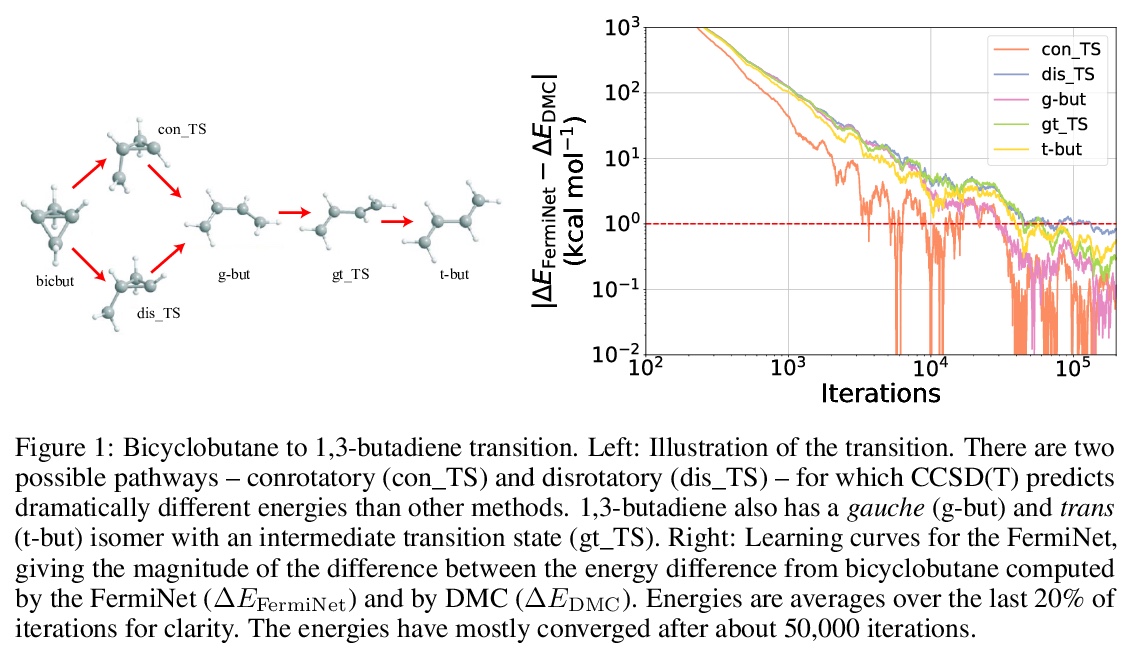
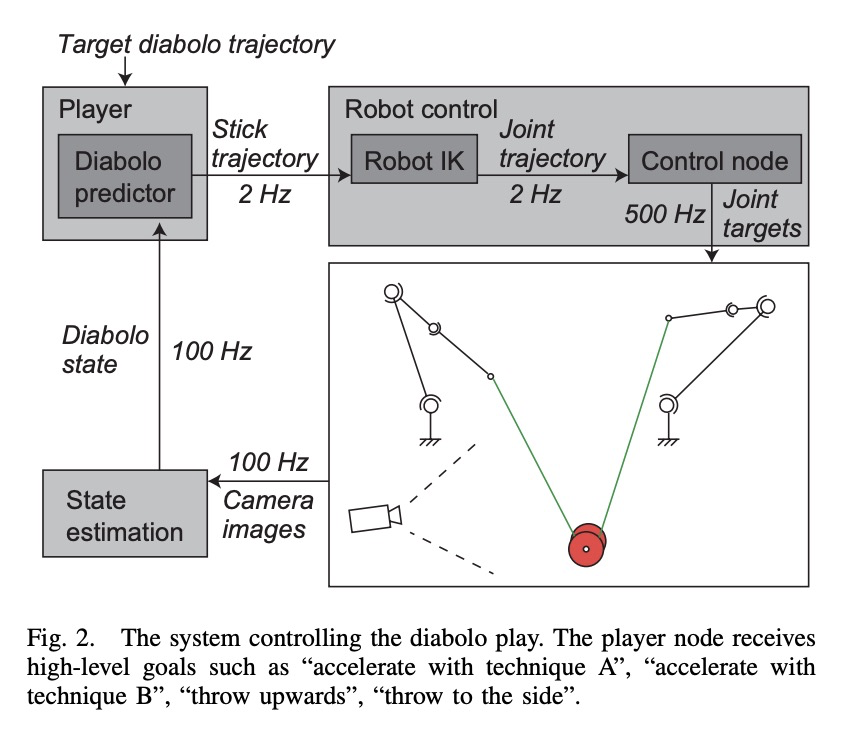
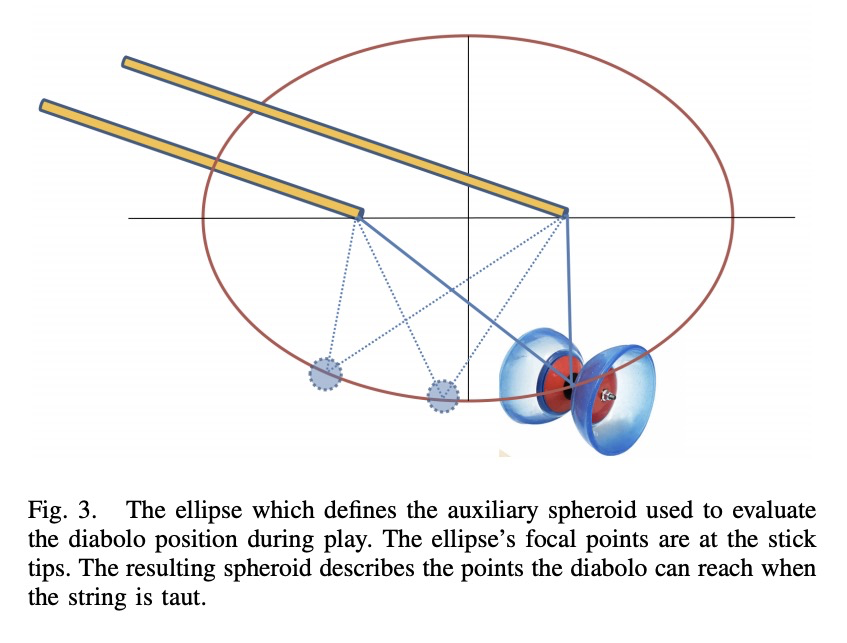
4、[RO] **An analytical diabolo model for robotic learning and control
F v Drigalski, D Joshi, T Murooka, K Tanaka, M Hamaya, Y Ijiri
[OMRON SINIC X Corporation]
机器人玩空竹的学习与控制分析模型。提出了用于机器人学习的空竹模型,以及用于产生和控制空竹机器人运动序列的系统,基于最优控制方法生成机器人轨迹,从而产生期望的空竹轨迹,模型在精确性和行为一致性方面都优于基于深度学习的预测器,可以产生稳定的运动,同时对空竹进行加速。
In this paper, we present a diabolo model that can be used for training agents in simulation to play diabolo, as well as running it on a real dual robot arm system. We first derive an analytical model of the diabolo-string system and compare its accuracy using data recorded via motion capture, which we release as a public dataset of skilled play with diabolos of different dynamics. We show that our model outperforms a deep-learning-based predictor, both in terms of precision and physically consistent behavior. Next, we describe a method based on optimal control to generate robot trajectories that produce the desired diabolo trajectory, as well as a system to transform higher-level actions into robot motions. Finally, we test our method on a real robot system by playing the diabolo, and throwing it to and catching it from a human player.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jv1Kk6xtk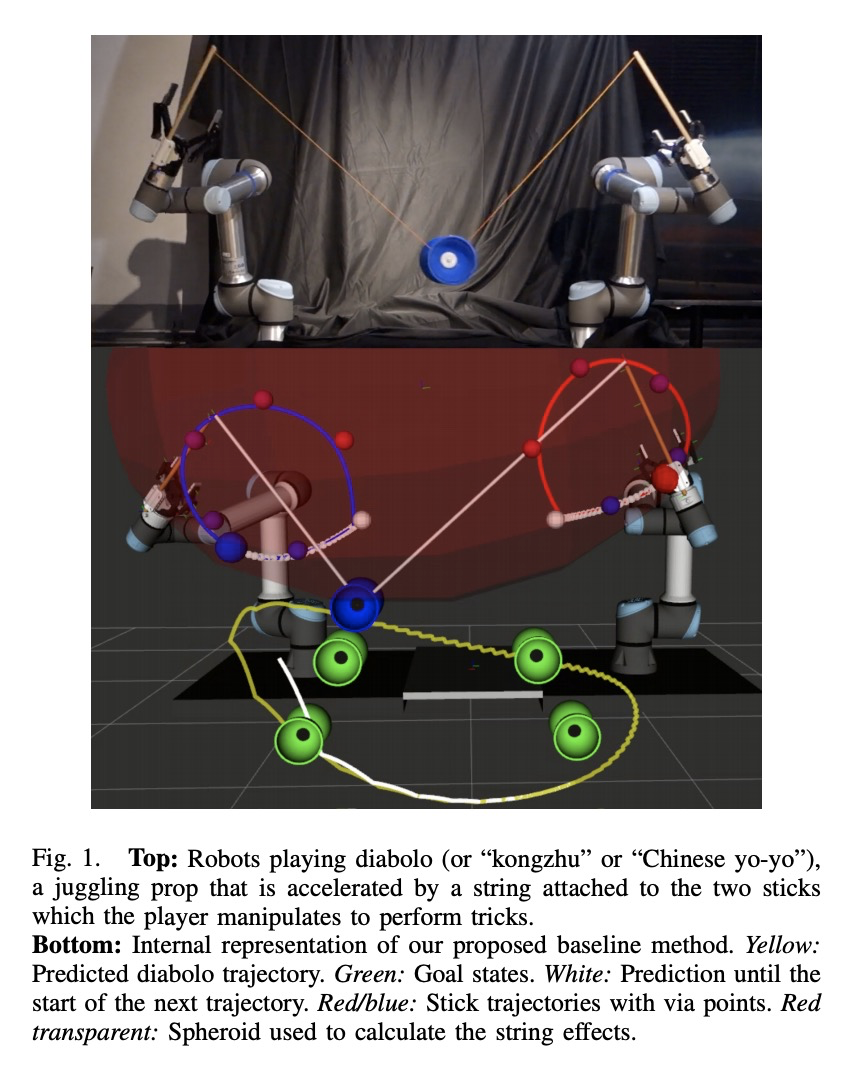
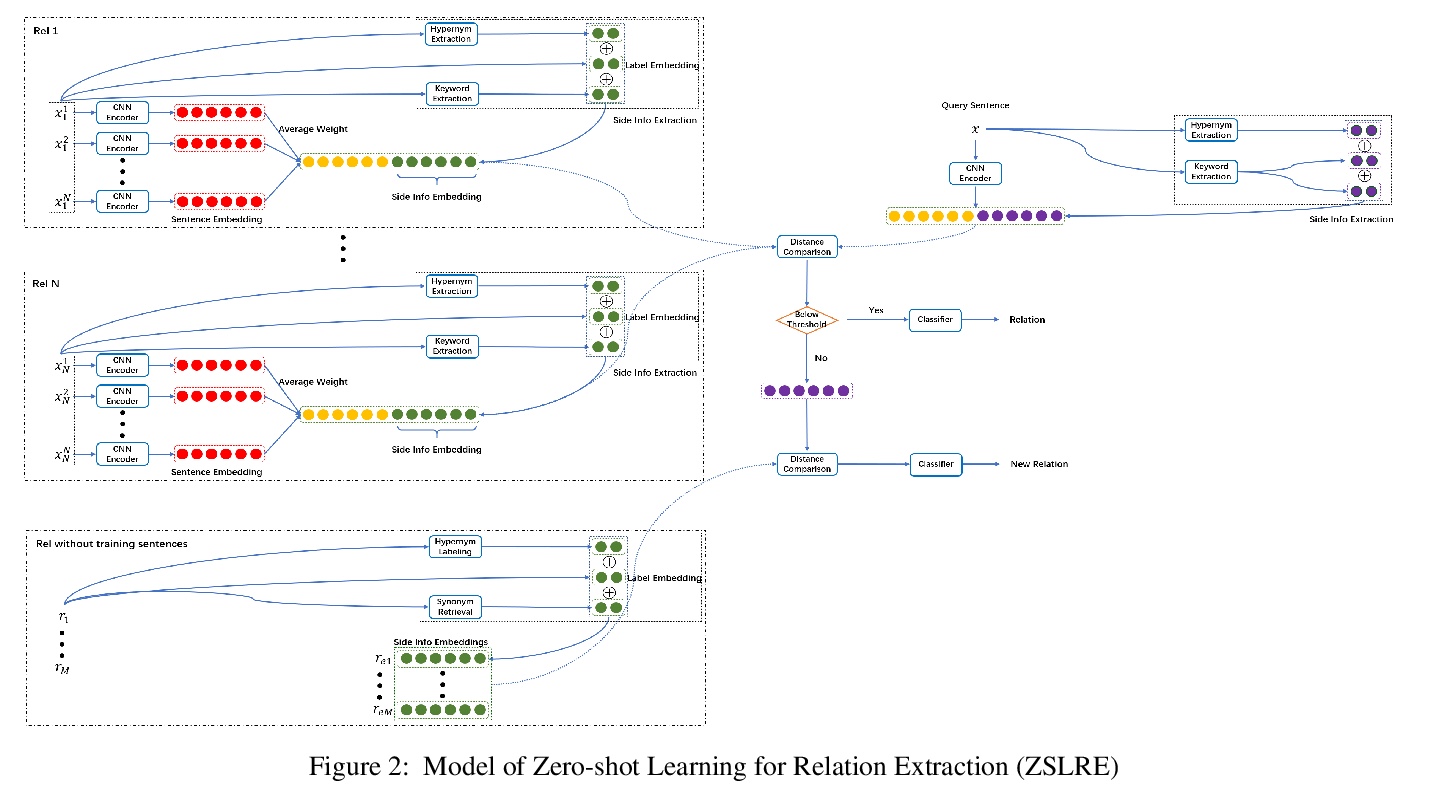
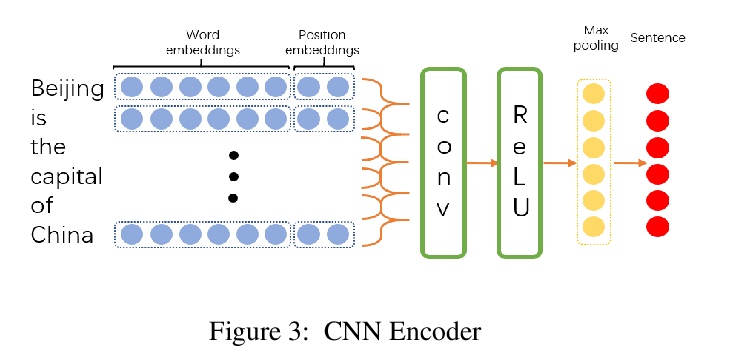
5、[CL] **Zero-shot Learning for Relation Extraction
J Gong, H Eldardiry
[Virginia Tech]
零样本学习关系抽取。提出一种基于改进原型网络的零样本学习关系抽取框架ZSLRE,利用自动上位词提取框架提取的实体的标签、关键词和上位词构造的边信息,在没有相应标记数据可用的情况下检测新关系。实验结果证明了模型的有效性和鲁棒性。
Most existing supervised and few-shot learning relation extraction methods have relied on labeled training data. However, in real-world scenarios, there exist many relations for which there is no available training data. We address this issue from the perspective of zero-shot learning (ZSL) which is similar to the way humans learn and recognize new concepts with no prior knowledge. We propose a zero-shot learning relation extraction (ZSLRE) framework, which focuses on recognizing novel relations that have no corresponding labeled data available for training. Our proposed ZSLRE model aims to recognize new relations based on prototypical networks that are modified to utilize side (auxiliary) information. The additional use of side information allows those modified prototype networks to recognize novel relations in addition to recognized previously known relations. We construct side information from labels and their synonyms, hypernyms of name entities, and keywords. We build an automatic hypernym extraction framework to help get hypernyms of various name entities directly from the web. We demonstrate using extensive experiments on two public datasets (NYT and FewRel) that our proposed model significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on supervised learning, few-shot learning, and zero-shot learning tasks. Our experimental results also demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed model in a combination scenario. Once accepted for publication, we will publish ZSLRE’s source code and datasets to enable reproducibility and encourage further research.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jv1PIvK9r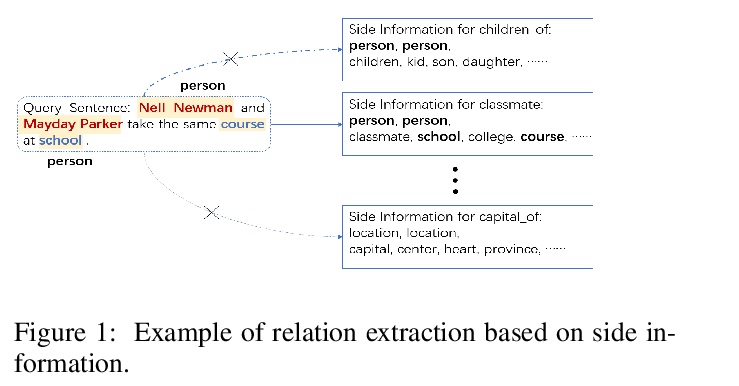
其他几篇值得关注的论文:
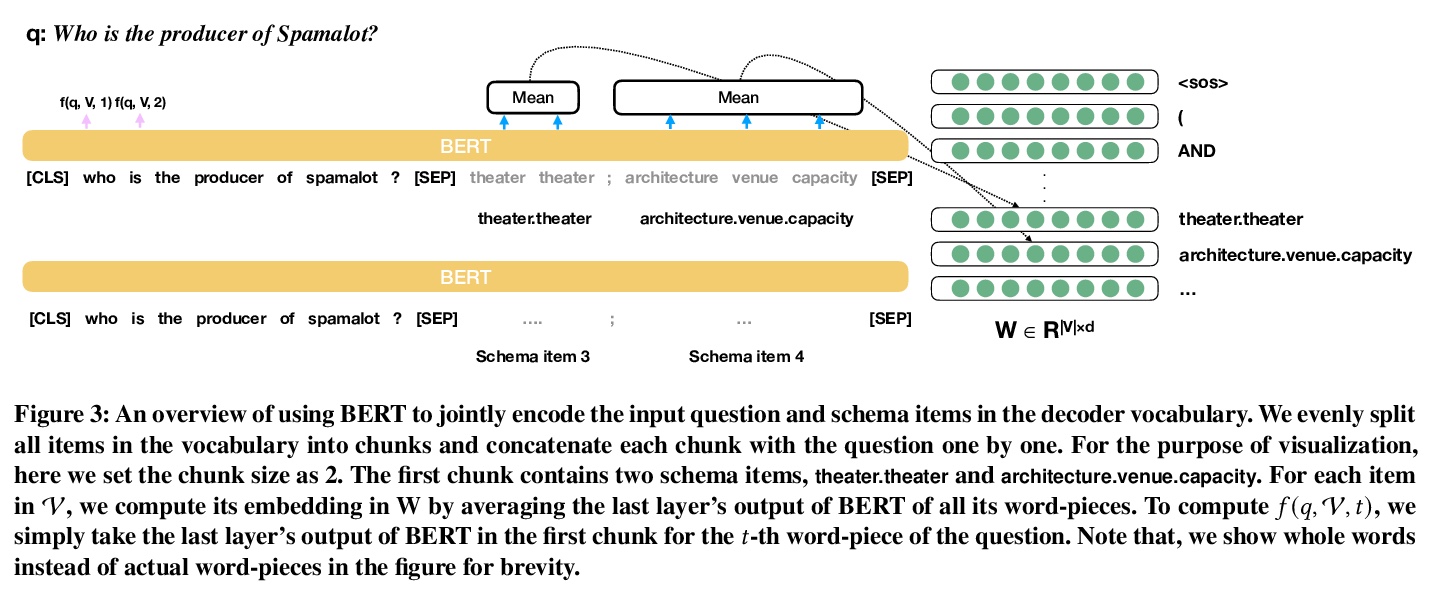
[CL] Beyond I.I.D.: Three Levels of Generalization for Question Answering on Knowledge Bases
知识库问答泛化的三个层次
Y Gu, S Kase, M Vanni, B Sadler, P Liang, X Yan, Y Su
[The Ohio State University & U.S. Army Research Laboratory & Stanford University & University of California, Santa]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jv1ZEmlU0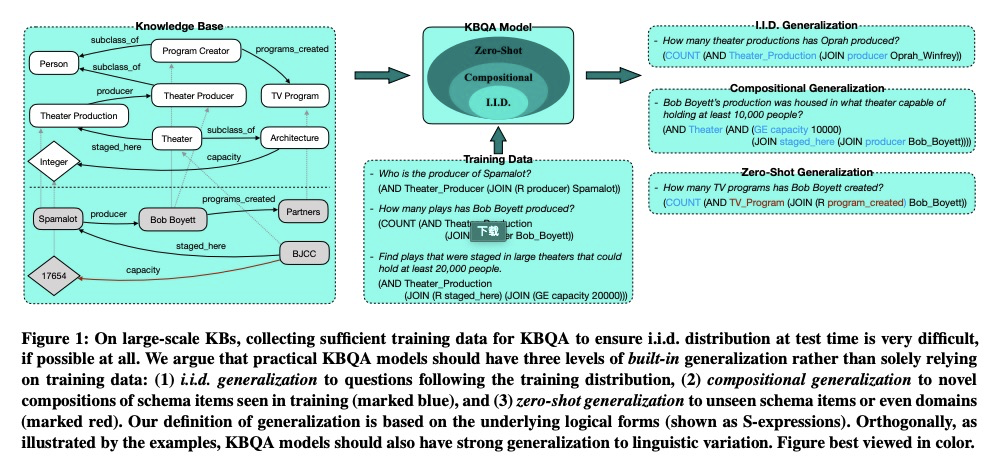
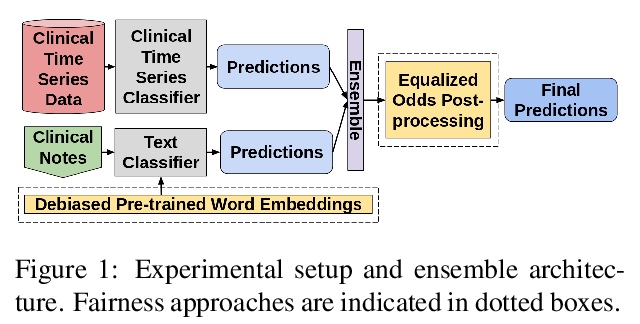
[CL] Exploring Text Specific and Blackbox Fairness Algorithms in Multimodal Clinical NLP
多模态临床自然语言处理中的文本特异性和黑盒公平性算法研究
J Chen, I Berlot-Atwell, S Hossain, X Wang, F Rudzicz
[University of Toronto & Vector Institute]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jv21A0LCo