- 1、[CV] Perceiver: General Perception with Iterative Attention
- 2、[LG] VidLanKD: Improving Language Understanding via Video-Distilled Knowledge Transfer
- 3、[LG] The Evolution of Out-of-Distribution Robustness Throughout Fine-Tuning
- 4、[LG] Learning Vision-Guided Quadrupedal Locomotion End-to-End with Cross-Modal Transformers
- 5、[CV] Collaboration of Experts: Achieving 80% Top-1 Accuracy on ImageNet with 100M FLOPs
- [LG] A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks
- [LG] Offline Meta-Reinforcement Learning with Online Self-Supervision
- [LG] Imitation by Predicting Observations
- [LG] Shared Data and Algorithms for Deep Learning in Fundamental Physics
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CV] Perceiver: General Perception with Iterative Attention
A Jaegle, F Gimeno, A Brock, A Zisserman, O Vinyals, J Carreira
[DeepMind]
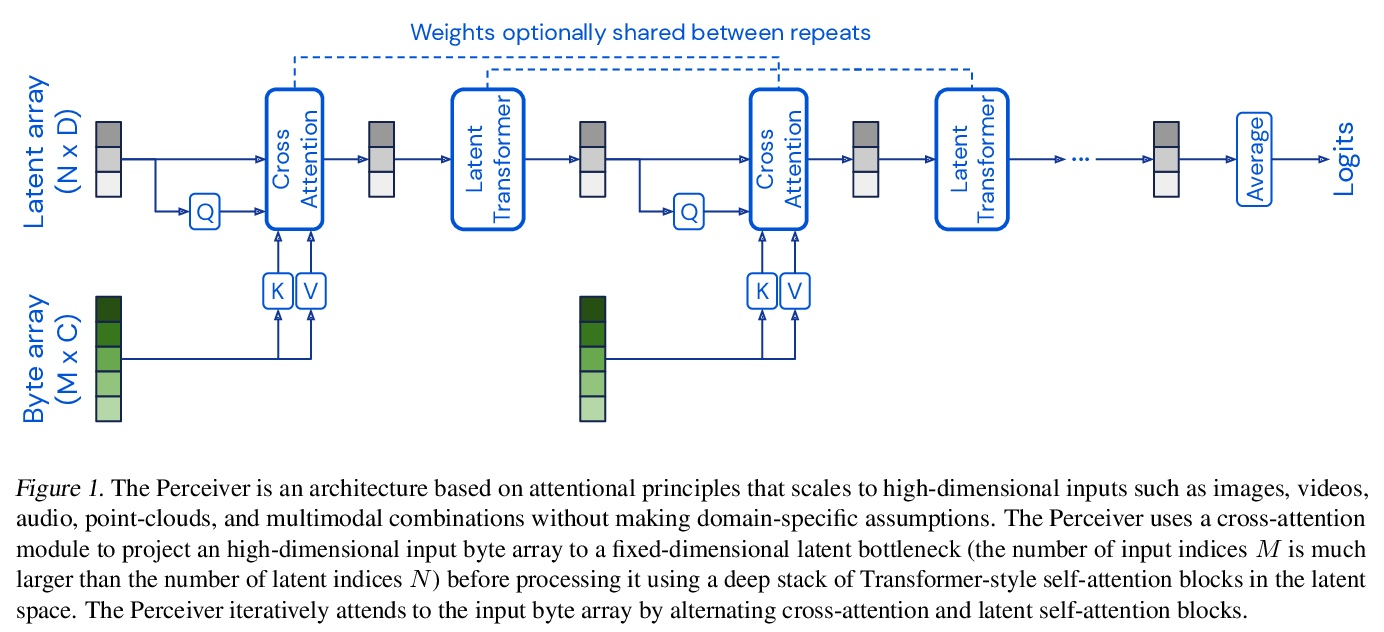
Perceiver:基于迭代注意力的一般感知。生物系统通过同时处理来自视觉、听觉、触觉、本体感觉等不同模态的高维输入来感知世界,而深度学习使用的感知模型是为单模态设计的,通常依赖于特定领域的假设,如几乎所有视觉模型所利用的局部网格结构。这些先验引入了有用的归纳偏差,但也将模型锁定在个别模态上。本文提出Perceiver——一种建立在Transformers基础上的模型,对其输入之间的关系没有什么架构上的假设,但也可以像ConvNets一样扩展到数十万个输入,可以处理任意的传感器配置,在所有层面上实现信息的融合。该模型利用非对称的注意力机制,将输入迭代提炼成一个紧密的潜在瓶颈,使其能够扩展到处理非常大的输入。实验表明,该架构在各种模式的分类任务上与强大的专门模型相竞争,甚至超过了它们:图像、点云、音频、视频和视频+音频。Perceiver通过直接处理50,000个像素,在ImageNet上获得了与ResNet-50和ViT相当的性能。它在AudioSet的所有模式中也有竞争力。
Biological systems perceive the world by simultaneously processing high-dimensional inputs from modalities as diverse as vision, audition, touch, proprioception, etc. The perception models used in deep learning on the other hand are designed for individual modalities, often relying on domainspecific assumptions such as the local grid structures exploited by virtually all existing vision models. These priors introduce helpful inductive biases, but also lock models to individual modalities. In this paper we introduce the Perceiver – a model that builds upon Transformers and hence makes few architectural assumptions about the relationship between its inputs, but that also scales to hundreds of thousands of inputs, like ConvNets. The model leverages an asymmetric attention mechanism to iteratively distill inputs into a tight latent bottleneck, allowing it to scale to handle very large inputs. We show that this architecture is competitive with or outperforms strong, specialized models on classification tasks across various modalities: images, point clouds, audio, video, and video+audio. The Perceiver obtains performance comparable to ResNet-50 and ViT on ImageNet without 2D convolutions by directly attending to 50,000 pixels. It is also competitive in all modalities in AudioSet.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ko22M6KH7 

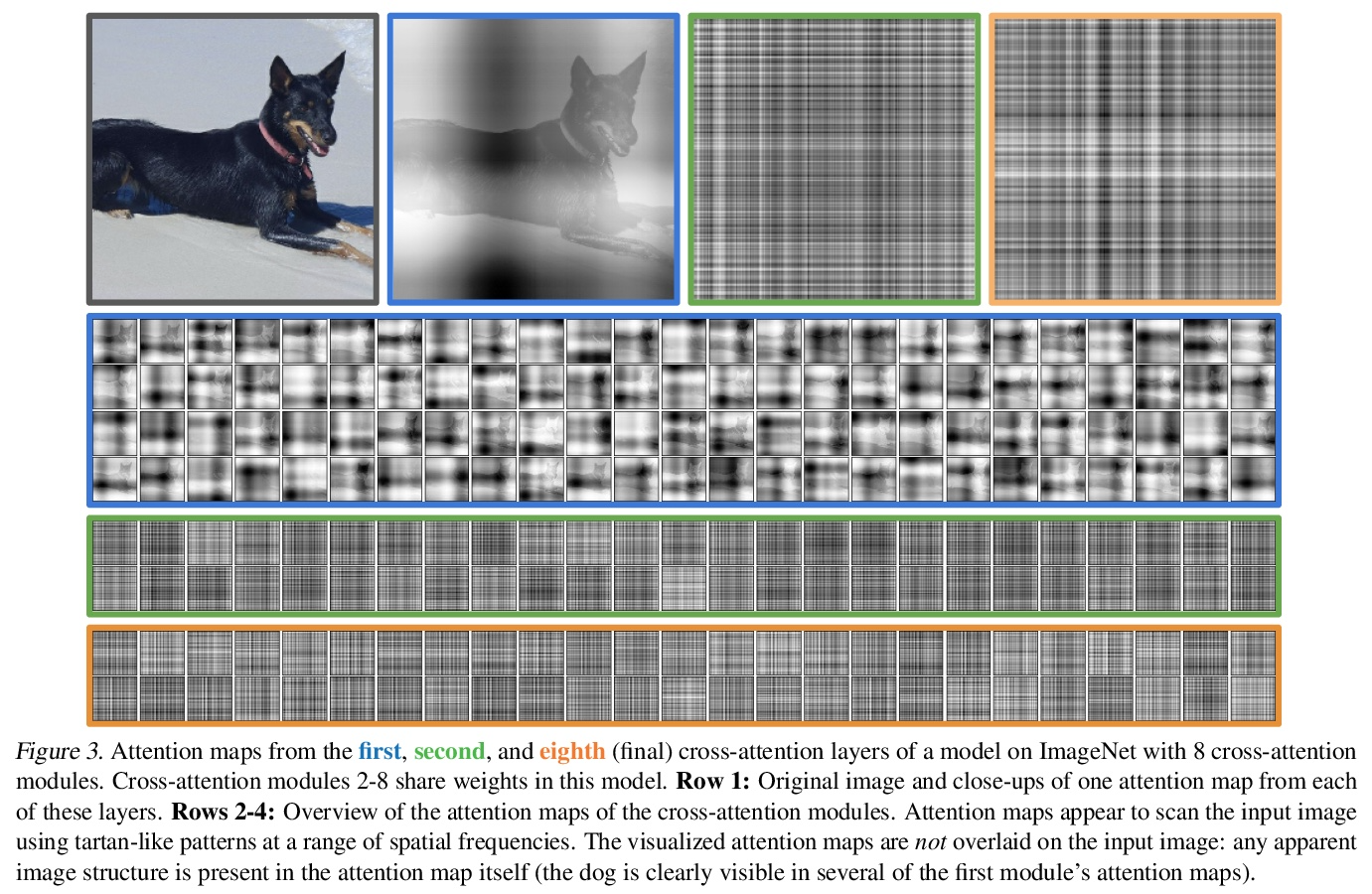

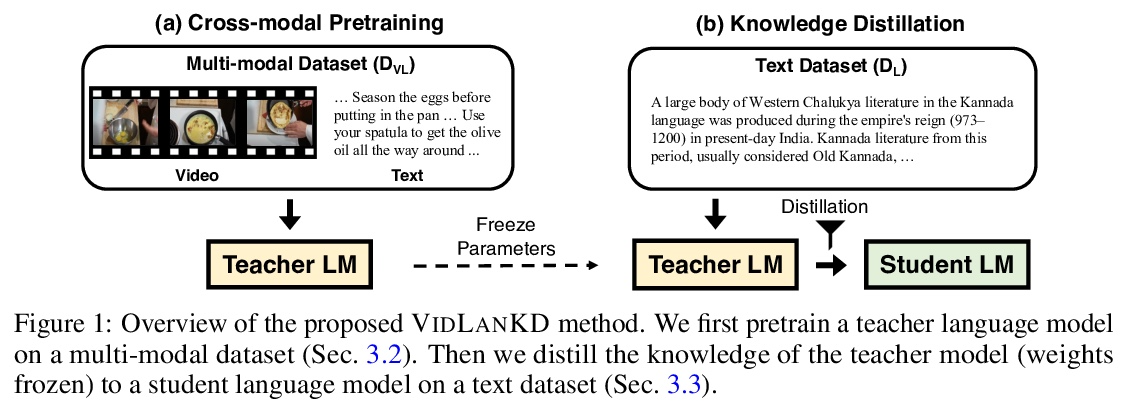
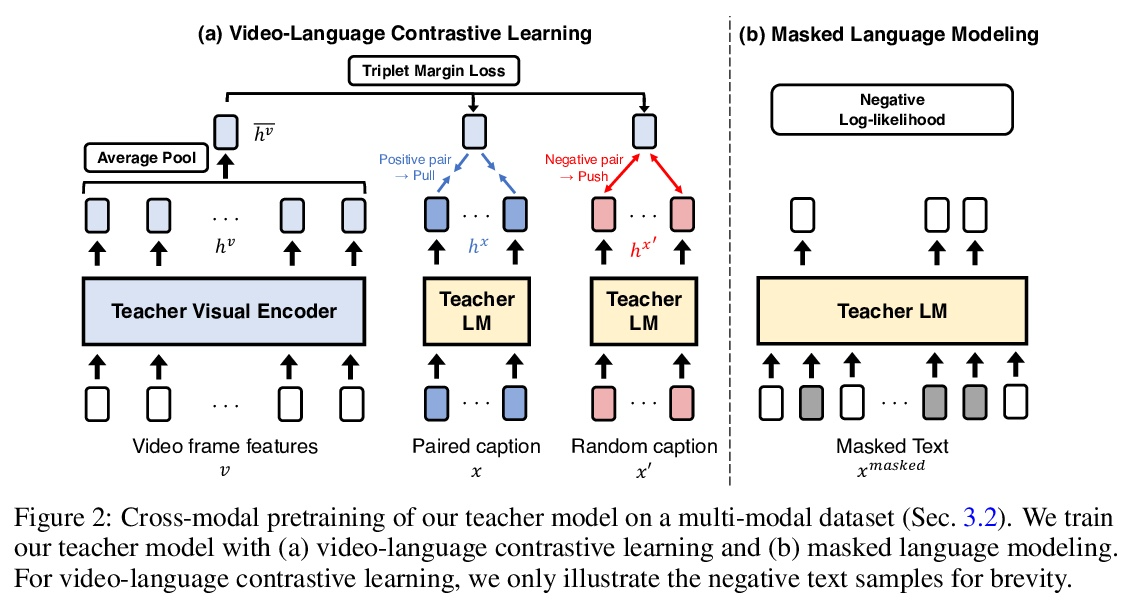
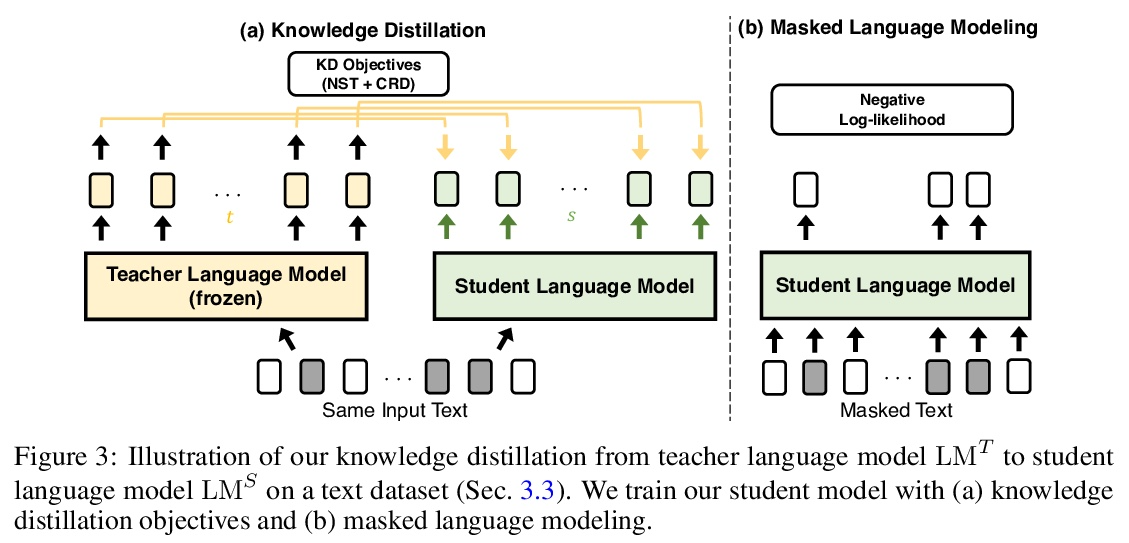
2、[LG] VidLanKD: Improving Language Understanding via Video-Distilled Knowledge Transfer
Z Tang, J Cho, H Tan, M Bansal
[UNC Chapel Hill]
VIDLANKD:基于视频蒸馏知识迁移提高语言理解能力。由于视觉感知可以为世界的理解提供超越文本描述的丰富信息,人们对利用视觉基础进行语言学习的兴趣越来越大。最近,vokenization通过用文本-图像检索模型的预测作为语言模型的监督标签,引起了人们的关注。尽管很成功,但该方法存在使用有限图像标签的近似误差和小型图像-文本数据集的词汇多样性不足的问题。为克服这些限制,本文提出VIDLANKD,一种用于改善语言理解的视频语言知识蒸馏方法。在视频-文本数据集上训练一个多模态的教师模型,然后用文本数据集将其知识迁移到学生语言模型上。为避免近似错误,建议使用不同的知识蒸馏目标。使用大规模的视频-文本数据集有助于学习多样化和更丰富的词汇。实验表明,VIDLANKD在包括GLUE、SQuAD和SWAG在内的几个下游语言理解任务中,取得了比纯文本语言模型和Token化模型更一致的改进。通过对GLUE-diagnostics、PIQA和TRACIE数据集的评估,证明了所提模型在世界知识、物理推理和时间推理方面的改进能力。进行了全面的消融研究,以及教师和学生语言模型的学习文本到视频的真实结果的可视化。
Since visual perception can give rich information beyond text descriptions for world understanding, there has been increasing interest in leveraging visual grounding for language learning. Recently, vokenization [69] has attracted attention by using the predictions of a text-to-image retrieval model as labels for language model supervision. Despite its success, the method suffers from approximation error of using finite image labels and the lack of vocabulary diversity of a small image-text dataset. To overcome these limitations, we present VIDLANKD, a video-language knowledge distillation method for improving language understanding. We train a multi-modal teacher model on a video-text dataset, and then transfer its knowledge to a student language model with a text dataset. To avoid approximation error, we propose to use different knowledge distillation objectives. In addition, the use of a large-scale video-text dataset helps learn diverse and richer vocabularies. In our experiments, VIDLANKD achieves consistent improvements over text-only language models and vokenization models, on several downstream language understanding tasks including GLUE, SQuAD, and SWAG. We also demonstrate the improved world knowledge, physical reasoning, and temporal reasoning capabilities of our model by evaluating on the GLUE-diagnostics, PIQA, and TRACIE datasets. Lastly, we present comprehensive ablation studies as well as visualizations of the learned text-to-video grounding results of our teacher and student language models.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ko26XAnuW 

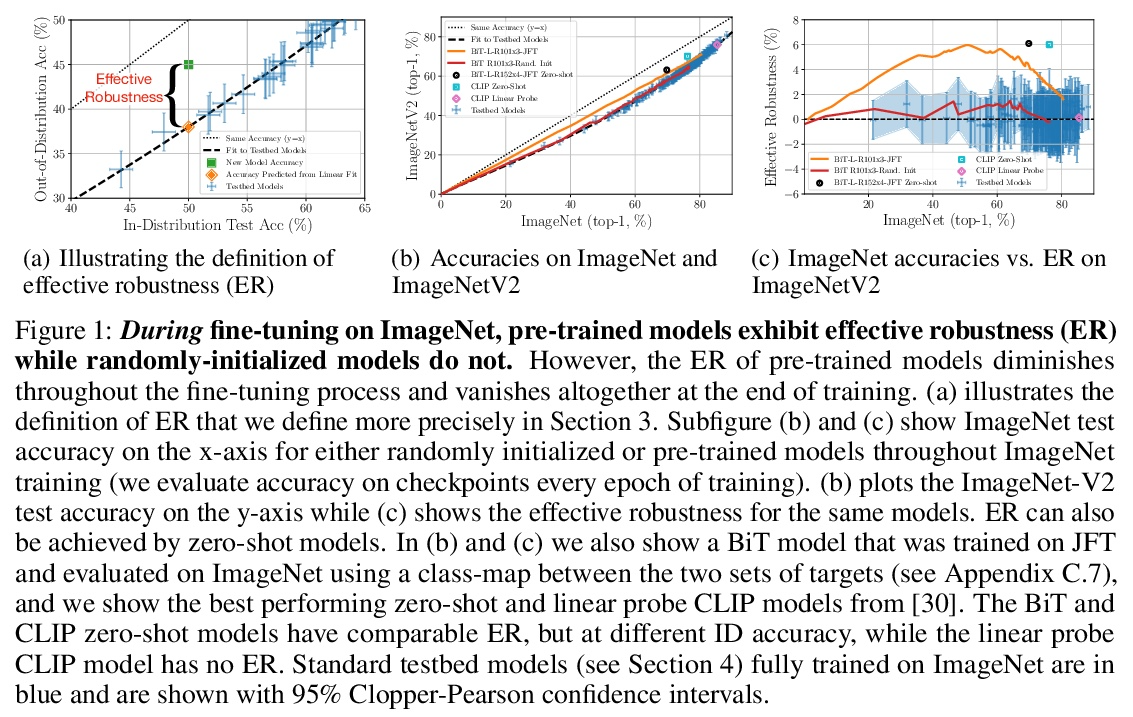
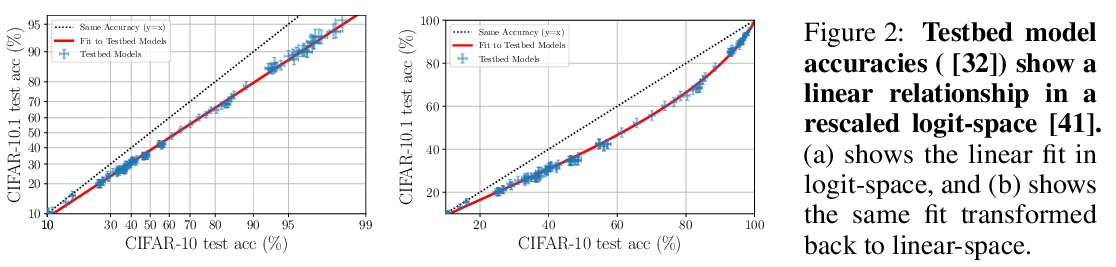
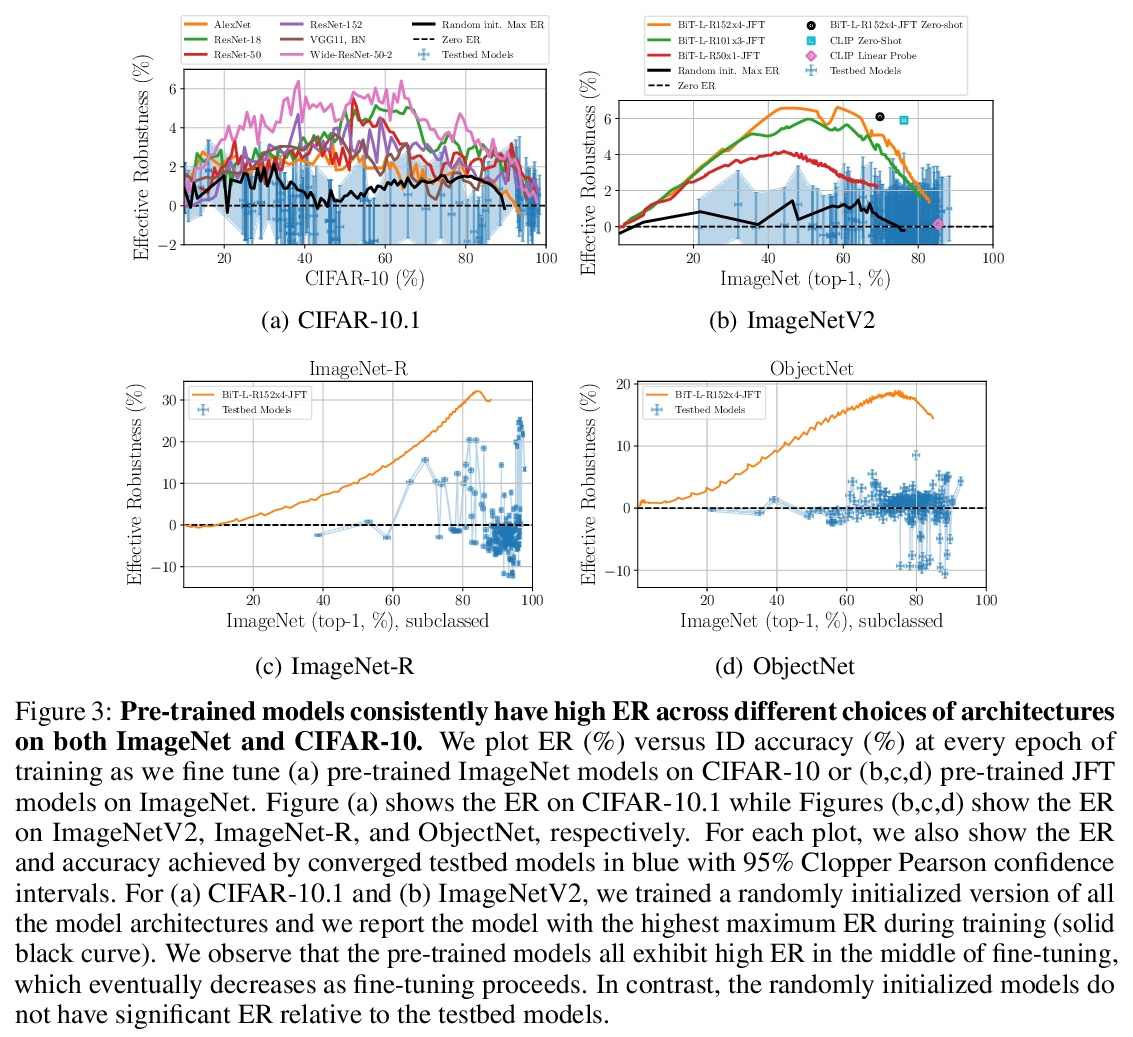
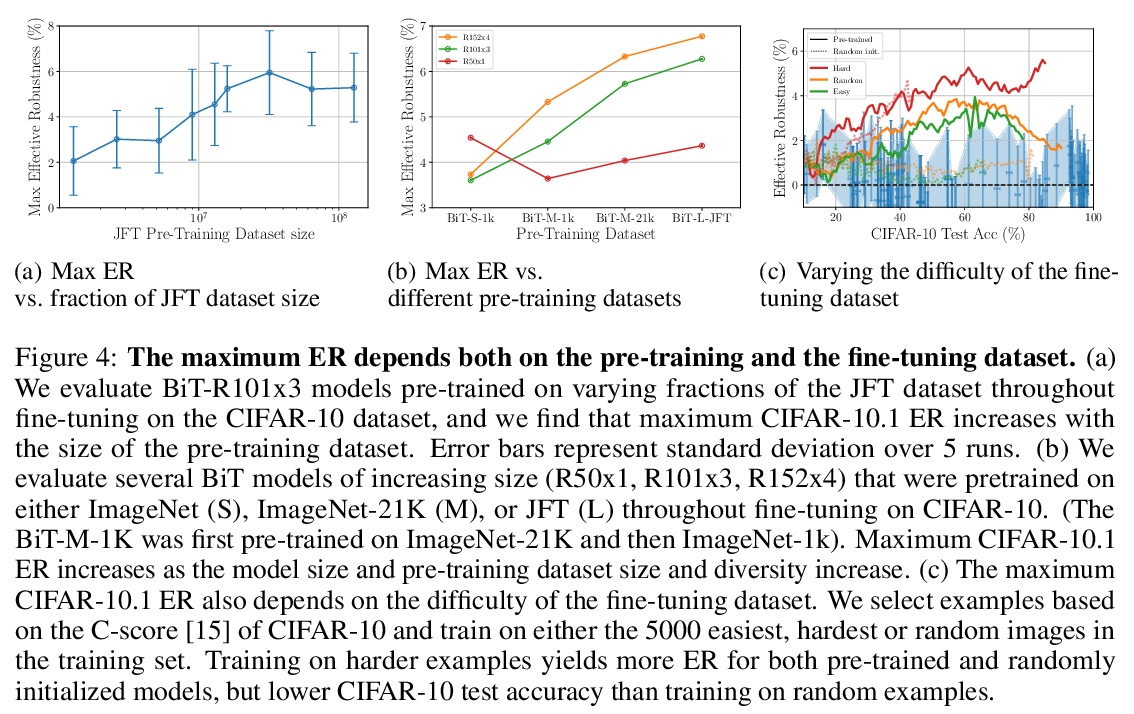
3、[LG] The Evolution of Out-of-Distribution Robustness Throughout Fine-Tuning
A Andreassen, Y Bahri, B Neyshabur, R Roelofs
[Google Research]
微调过程中分布外鲁棒性的演进。尽管机器学习模型在分布外数据上的性能通常会下降,但在对模型的测试平台进行评估时,普遍观察到分布外数据的准确性遵循某种单一的线性趋势。相对于这个基线,在分布外数据上更准确的模型表现出”有效的鲁棒性”,而且非常罕见。识别这样的模型,并了解它们的特性,是提高分布外性能的关键。本文对微调期间的有效鲁棒性进行了彻底的实证调查,发现在较大的数据集上预训练的模型在训练期间表现出有效的鲁棒性,但在收敛时却消失了。研究了数据的属性是如何影响有效鲁棒性的,表明它随着数据集的规模越大、多样性越强、样本难度越高而增加。显示出有效鲁棒性的模型能够正确分类10%的样本,而目前其他的测试平台模型都没有得到正确的分类。最后,讨论了几种将有效鲁棒性扩展到高准确率体系的策略,以提高最先进模型的分布外准确率。
Although machine learning models typically experience a drop in performance on out-of-distribution data, accuracies on inversus out-of-distribution data are widely observed to follow a single linear trend when evaluated across a testbed of models. Models that are more accurate on the out-of-distribution data relative to this baseline exhibit “effective robustness” and are exceedingly rare. Identifying such models, and understanding their properties, is key to improving out-of-distribution performance. We conduct a thorough empirical investigation of effective robustness during fine-tuning and surprisingly find that models pre-trained on larger datasets exhibit effective robustness during training that vanishes at convergence. We study how properties of the data influence effective robustness, and we show that it increases with the larger size, more diversity, and higher example difficulty of the dataset. We also find that models that display effective robustness are able to correctly classify 10% of the examples that no other current testbed model gets correct. Finally, we discuss several strategies for scaling effective robustness to the high-accuracy regime to improve the out-of-distribution accuracy of state-of-the-art models.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ko2b6hVEs 
4、[LG] Learning Vision-Guided Quadrupedal Locomotion End-to-End with Cross-Modal Transformers
R Yang, M Zhang, N Hansen, H Xu, X Wang
[UC San Diego & Tsinghua University & UC Berkeley]
用跨模态Transformer端到端学习视觉引导四足运动。本文建议采用强化学习和基于Transformer的模型解决四足运动任务,该模型可以学习结合本体信息和高维深度传感器输入。虽然基于学习的运动在使用强化学习方面取得了很大的进展,但大多数方法仍然依赖于领域随机化来训练盲目的智能体,以适应具有挑战性的地形。本文的关键见解是,本体感觉状态只为即时反应提供接触测量,而配备视觉感官观察的智能体可以通过提前许多步预测环境的变化,来学习在有障碍物和不平坦的地形环境中主动操纵。本文提出了LocoTransformer,一种用于四足运动的端到端强化学习方法,利用基于Transformer的模型来融合本体感觉状态和视觉观察。在具有不同障碍物和不平坦地形的挑战性模拟环境中评估了所提出方法。与仅有本体感觉状态输入的策略相比,获得了明显的改进,基于Transformer的模型进一步提高了跨环境的通用性。
We propose to address quadrupedal locomotion tasks using Reinforcement Learning (RL) with a Transformer-based model that learns to combine proprioceptive information and high-dimensional depth sensor inputs. While learning-based locomotion has made great advances using RL, most methods still rely on domain randomization for training blind agents that generalize to challenging terrains. Our key insight is that proprioceptive states only offer contact measurements for immediate reaction, whereas an agent equipped with visual sensory observations can learn to proactively maneuver environments with obstacles and uneven terrain by anticipating changes in the environment many steps ahead. In this paper, we introduce LocoTransformer, an end-to-end RL method for quadrupedal locomotion that leverages a Transformer-based model for fusing proprioceptive states and visual observations. We evaluate our method in challenging simulated environments with different obstacles and uneven terrain. We show that our method obtains significant improvements over policies with only proprioceptive state inputs, and that Transformer-based models further improve generalization across environments.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ko2fwhDcV 
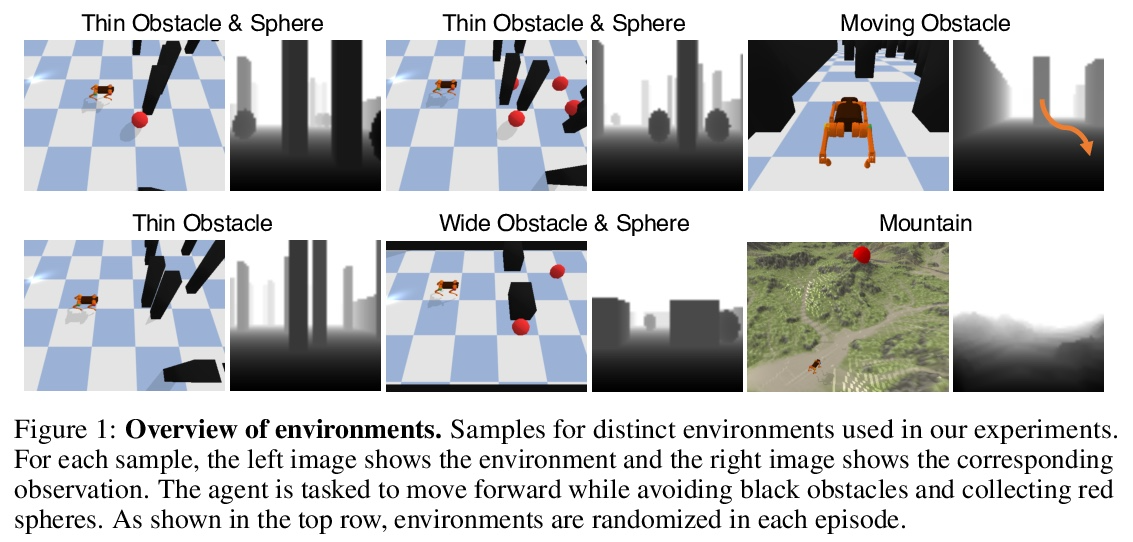
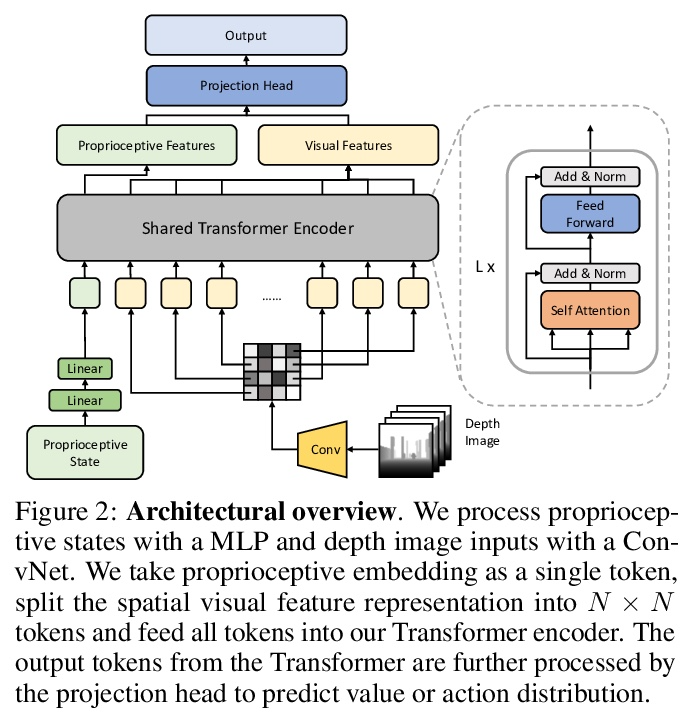
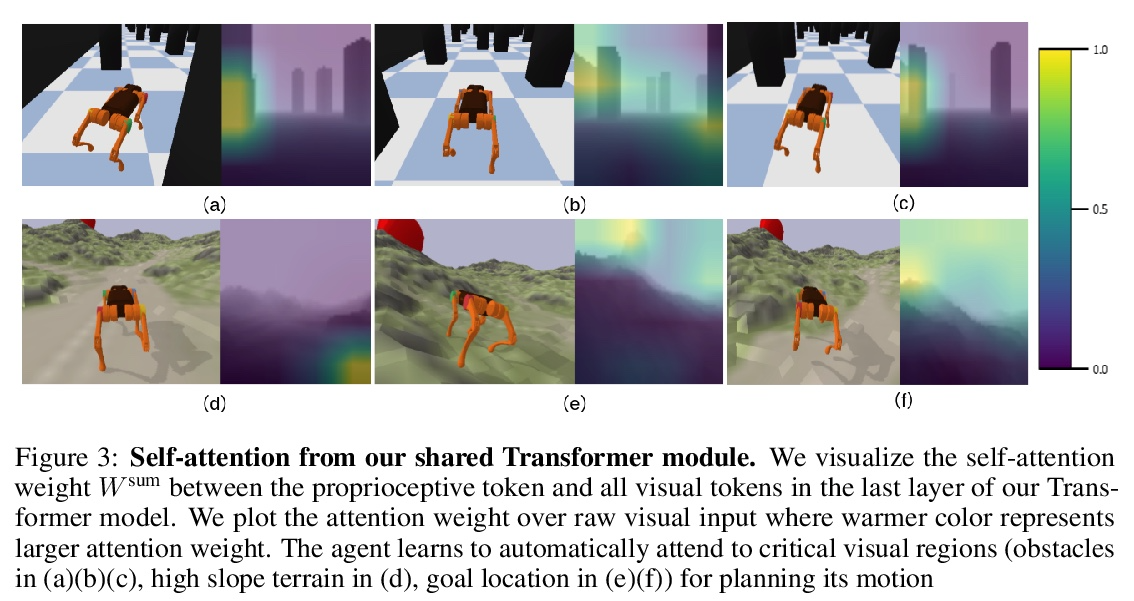
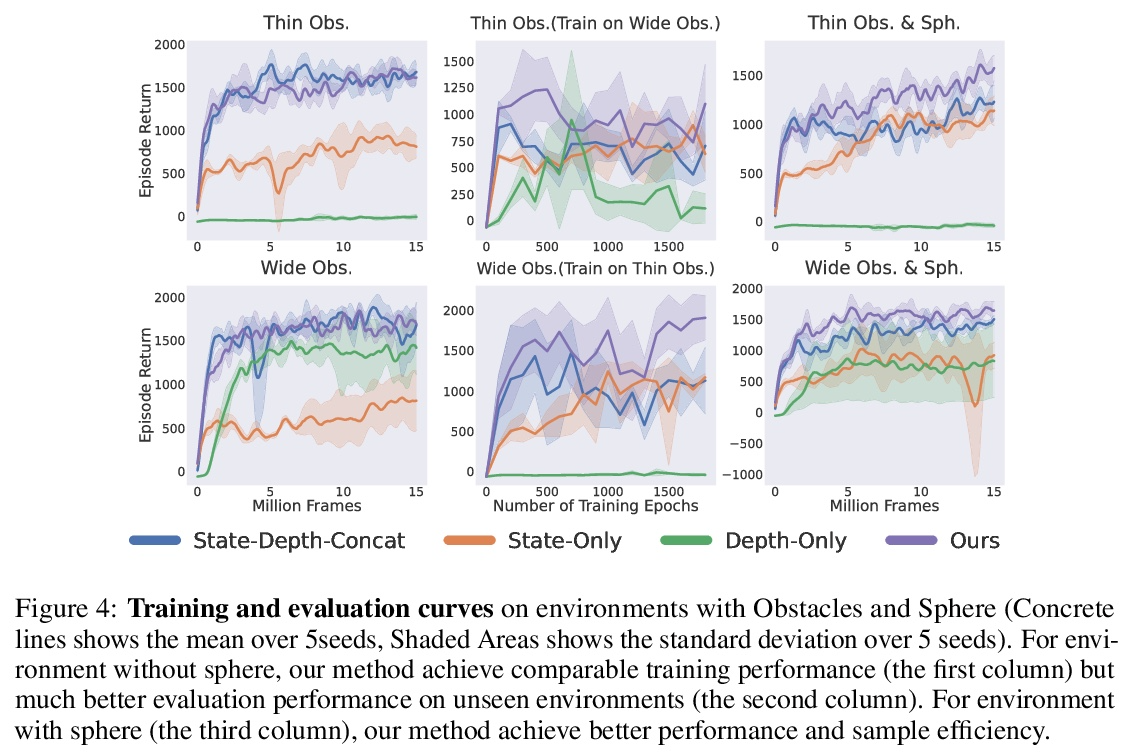
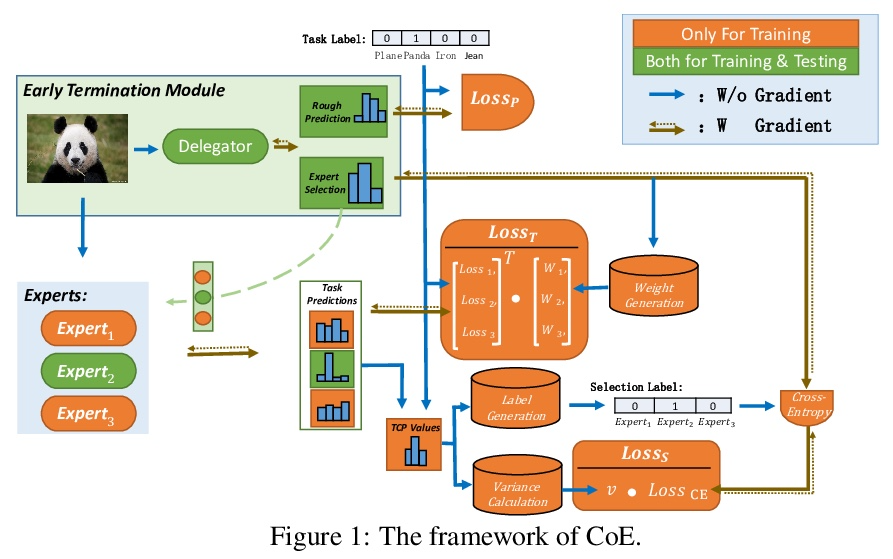
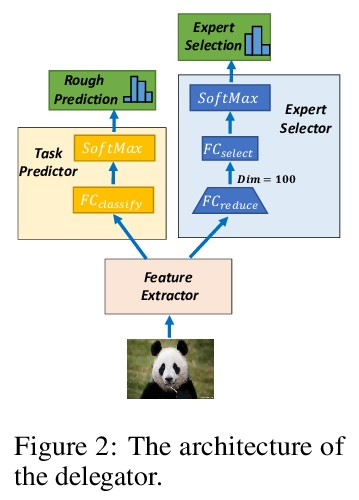
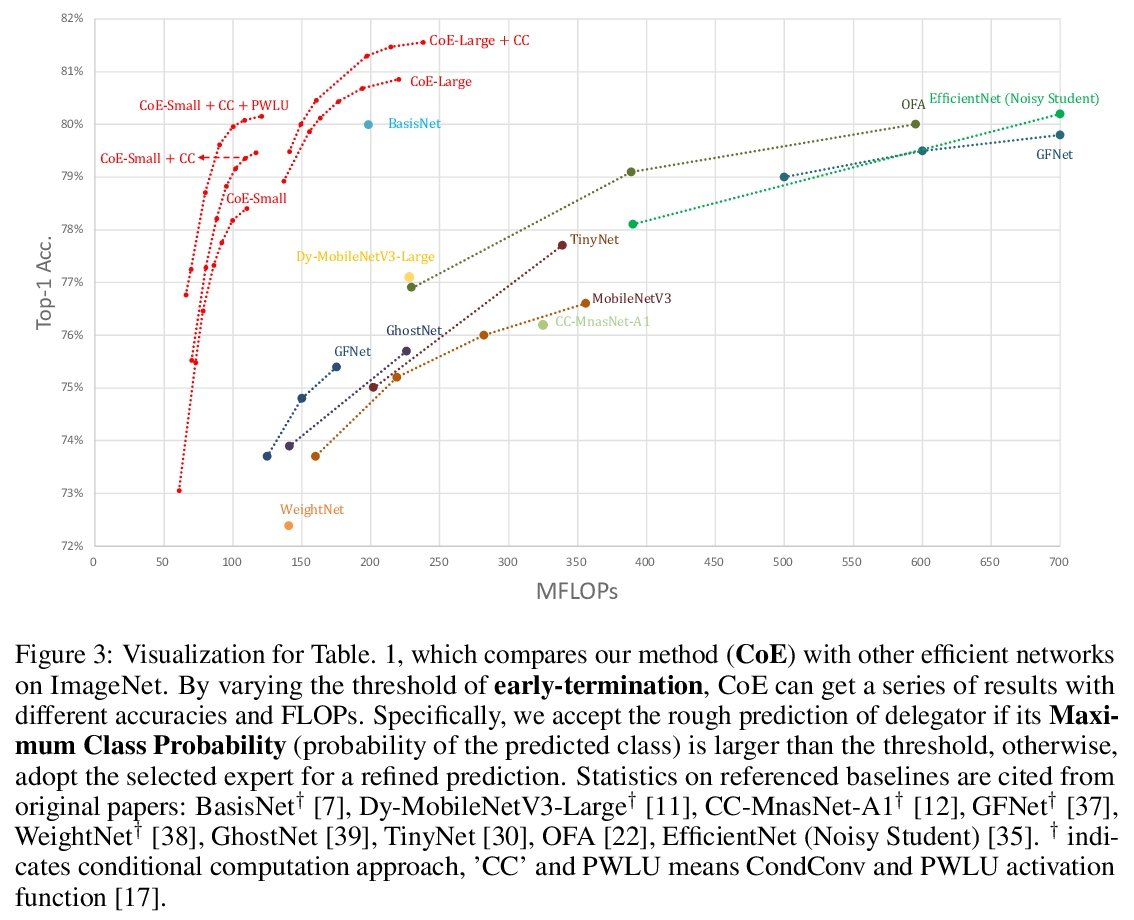
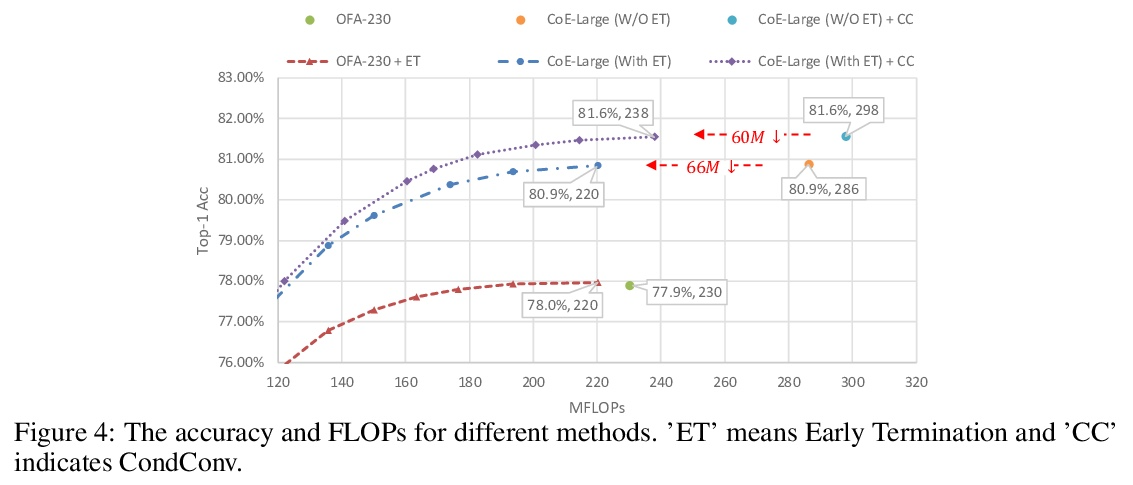
5、[CV] Collaboration of Experts: Achieving 80% Top-1 Accuracy on ImageNet with 100M FLOPs
Y Zhang, Z Chen, Z Zhong
[Huawei]
专家合作:用100M FLOPs在ImageNet上实现80%的Top-1准确率。本文提出一种专家协作(CoE)框架,将多个网络的专业知识汇集到一起,实现一个共同目标。每个专家都是一个单独的网络,在数据集的一个独特部分上有专长,这增强了协同能力。给定一个样本,由委托人选择一个专家,同时输出一个粗预测,以支持早期终止。为了实现这个框架,提出了三个模块来推动每个模型发挥其作用,即权重生成模块(WGM)、标签生成模块(LGM)和方差计算模块(VCM)。所提出方法在ImageNet上取得了最先进的性能,在194M FLOPs的情况下达到了80.7%的top-1精度。结合PWLU激活函数和CondConv,CoE首次在只有100M FLOPs的情况下进一步实现了80.0%的精度。该方法是硬件友好的,与现有的一些有条件计算方法相比,实现了3∼6倍的速度提升。
In this paper, we propose a Collaboration of Experts (CoE) framework to pool together the expertise of multiple networks towards a common aim. Each expert is an individual network with expertise on a unique portion of the dataset, which enhances the collective capacity. Given a sample, an expert is selected by the delegator, which simultaneously outputs a rough prediction to support early termination. To fulfill this framework, we propose three modules to impel each model to play its role, namely weight generation module (WGM), label generation module (LGM) and variance calculation module (VCM). Our method achieves the state-of-the-art performance on ImageNet, 80.7% top-1 accuracy with 194M FLOPs. Combined with PWLU activation function and CondConv, CoE further achieves the accuracy of 80.0% with only 100M FLOPs for the first time. More importantly, our method is hardware friendly and achieves a 3∼6x speedup compared with some existing conditional computation approaches.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ko2i6qXNG 
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
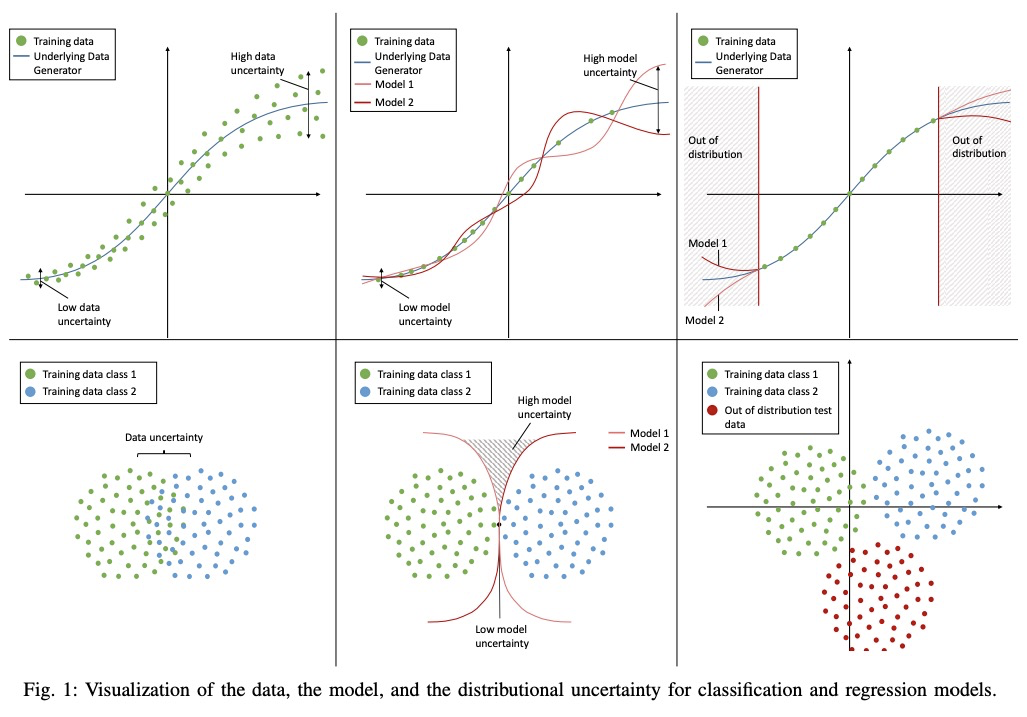
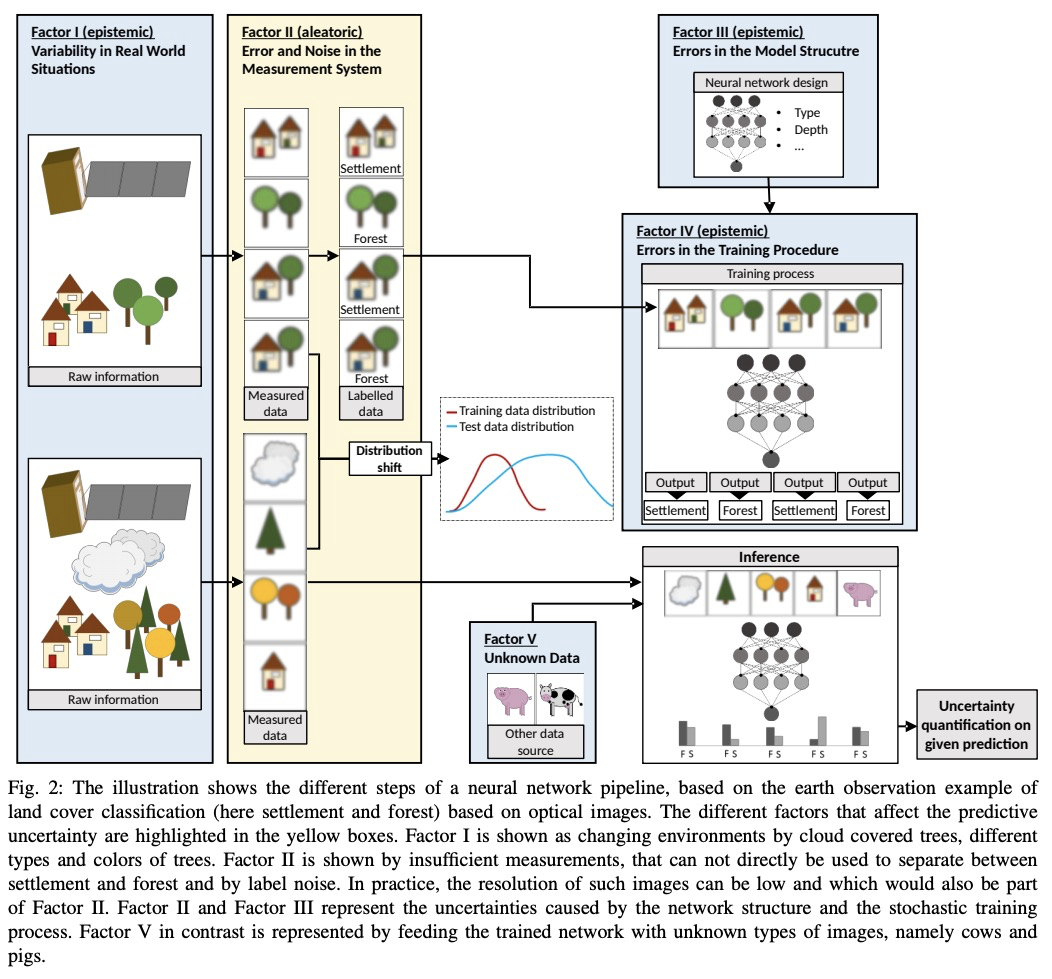
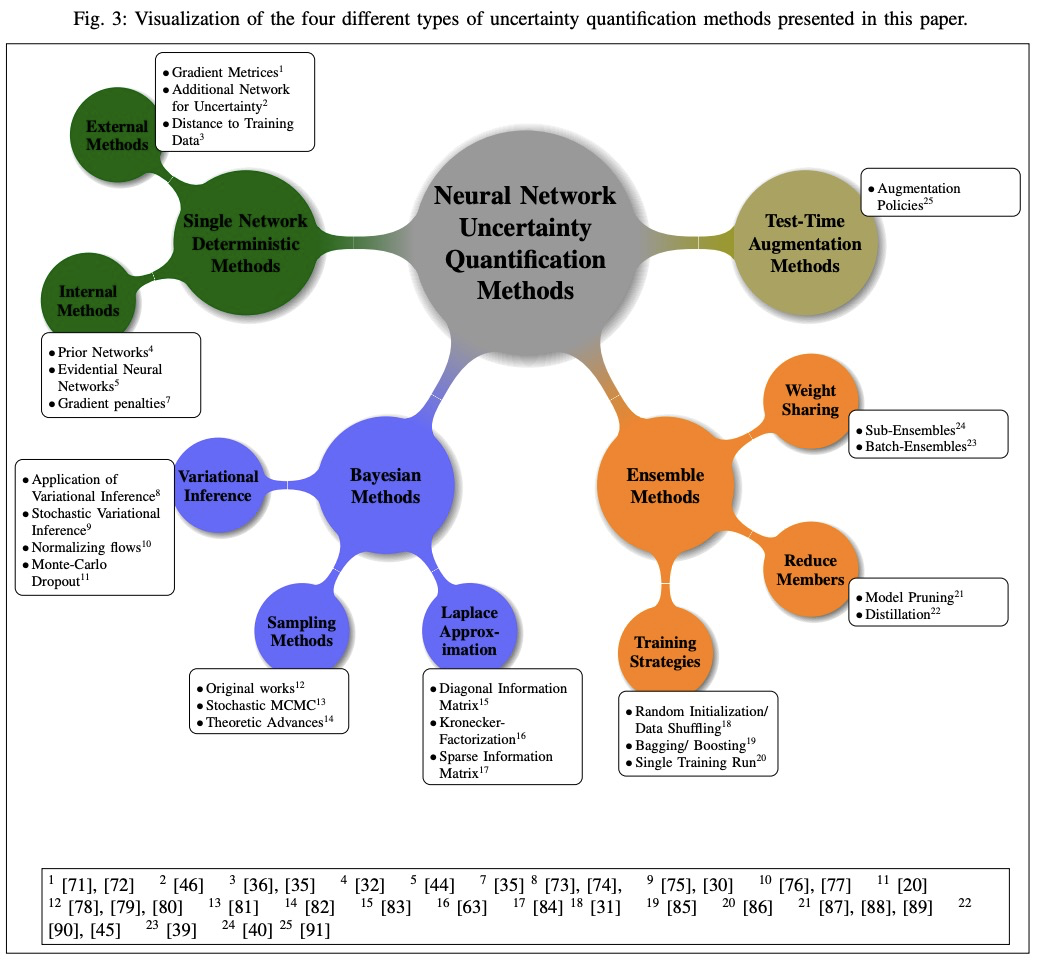
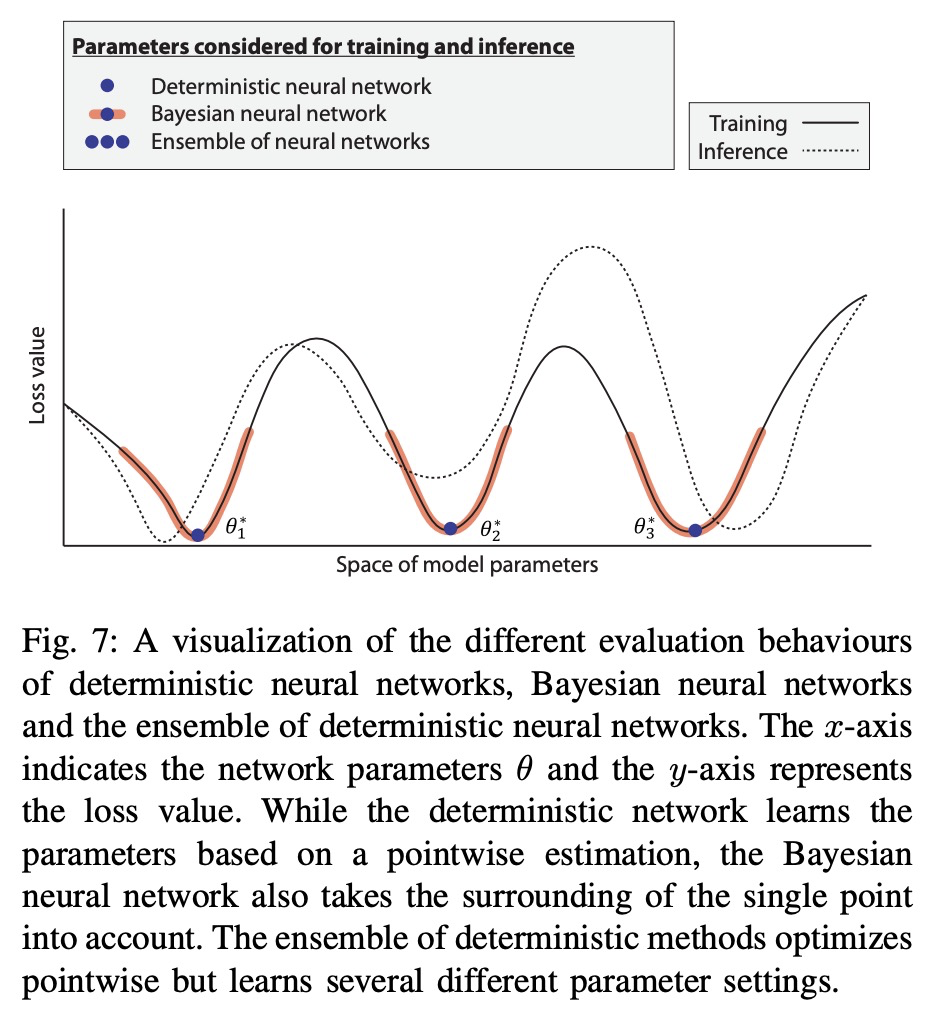
[LG] A Survey of Uncertainty in Deep Neural Networks
深度神经网络不确定性综述
J Gawlikowski, C R N Tassi, M Ali, J Lee, M Humt, J Feng, A Kruspe, R Triebel, P Jung, R Roscher, M Shahzad, W Yang, R Bamler, X X Zhu 
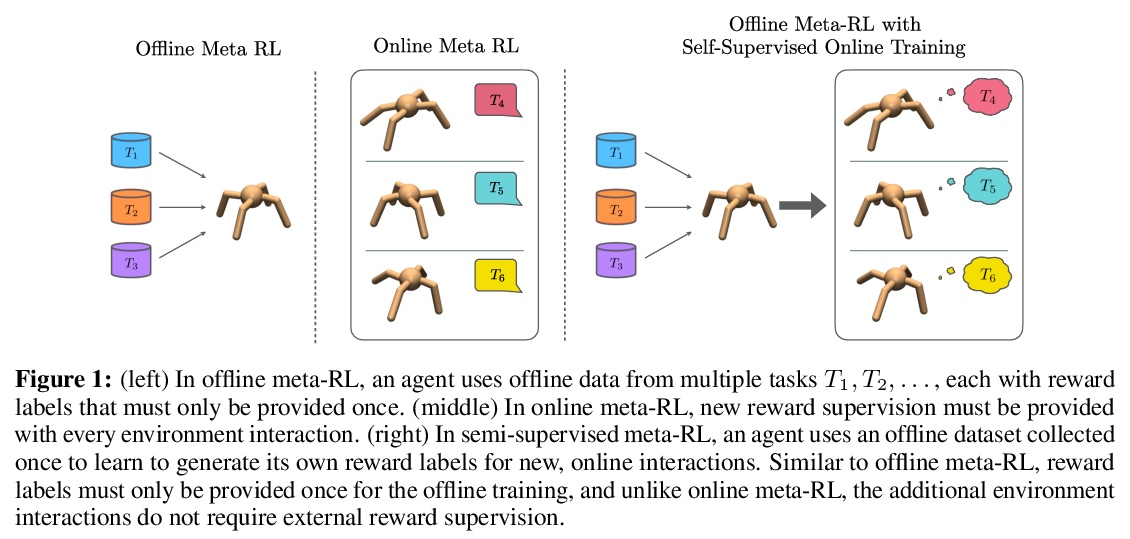
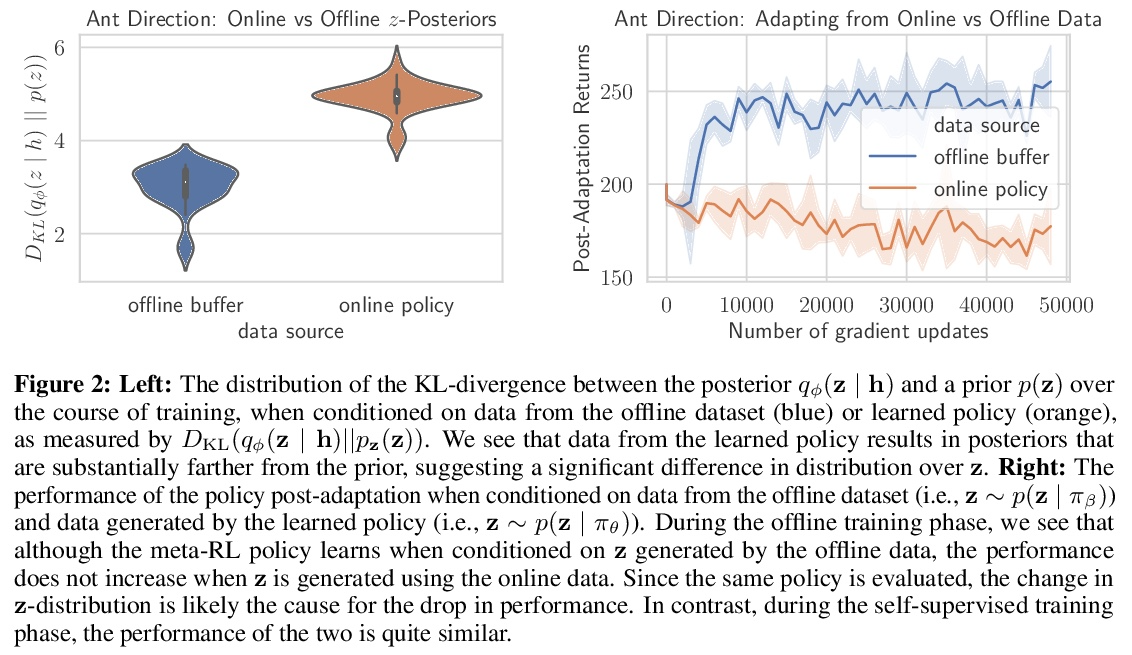
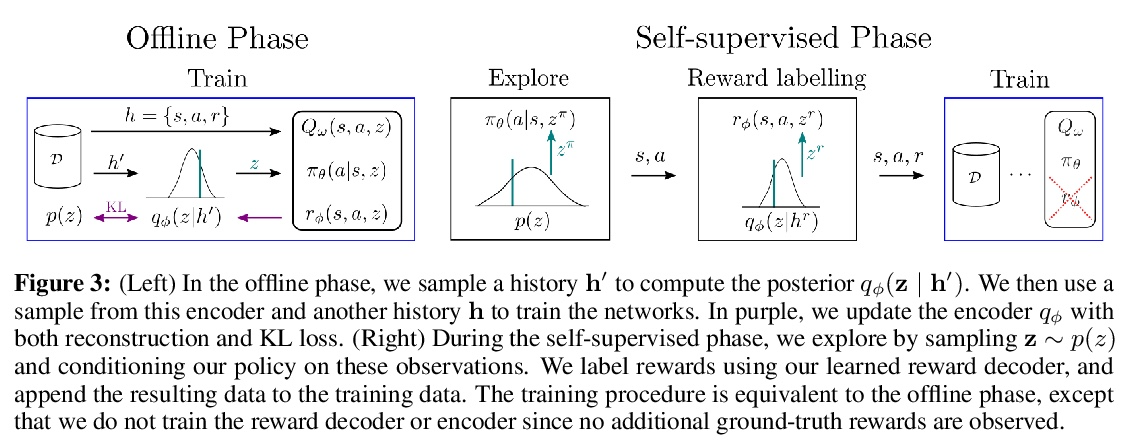
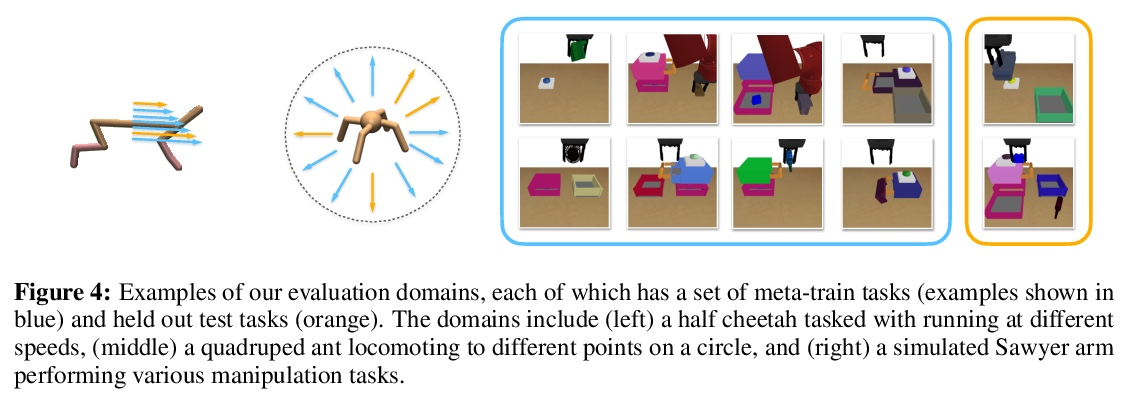
[LG] Offline Meta-Reinforcement Learning with Online Self-Supervision
在线自监督离线元强化学习
V H. Pong, A Nair, L Smith, C Huang, S Levine
[UC Berkeley]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ko2p23EaL 
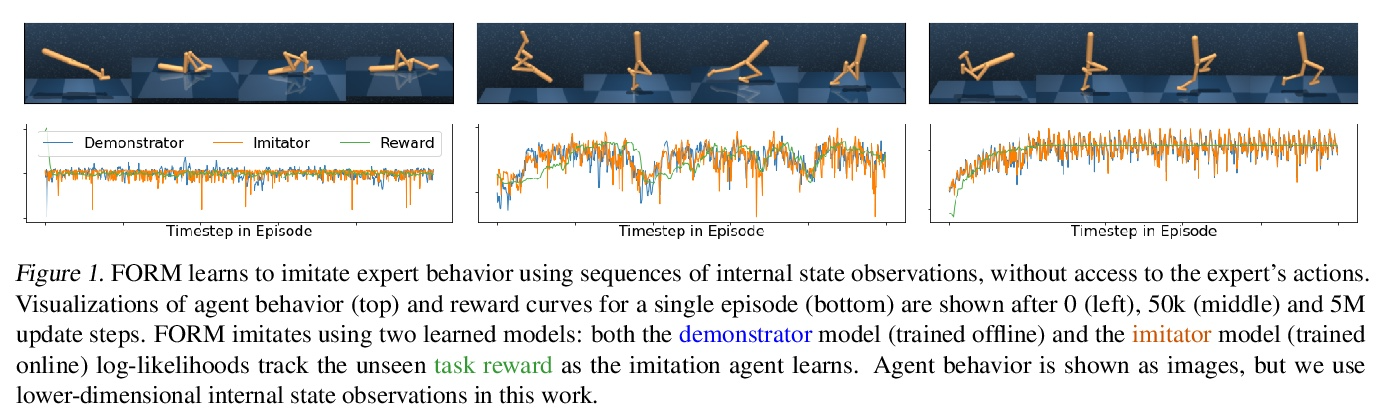
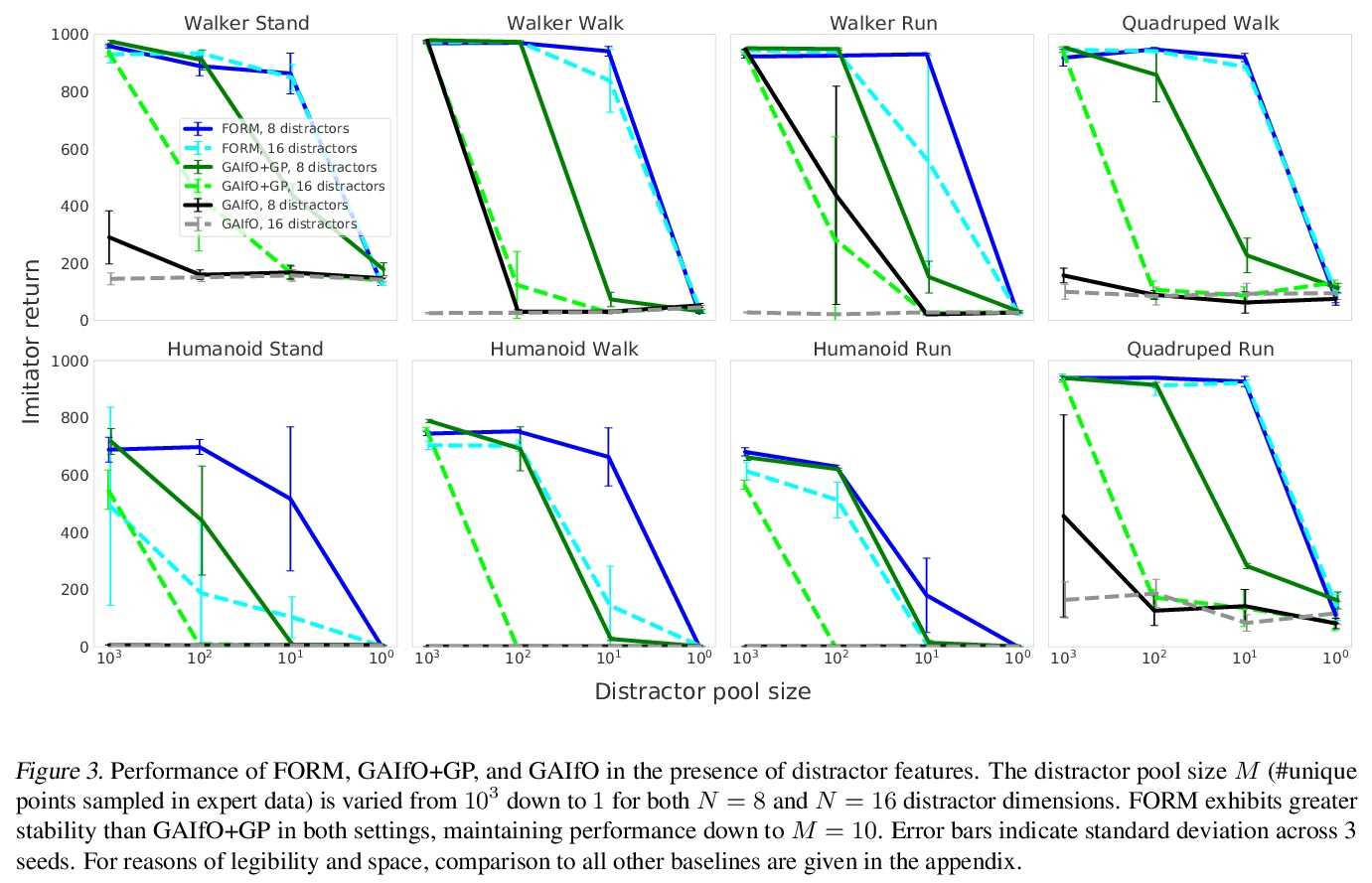
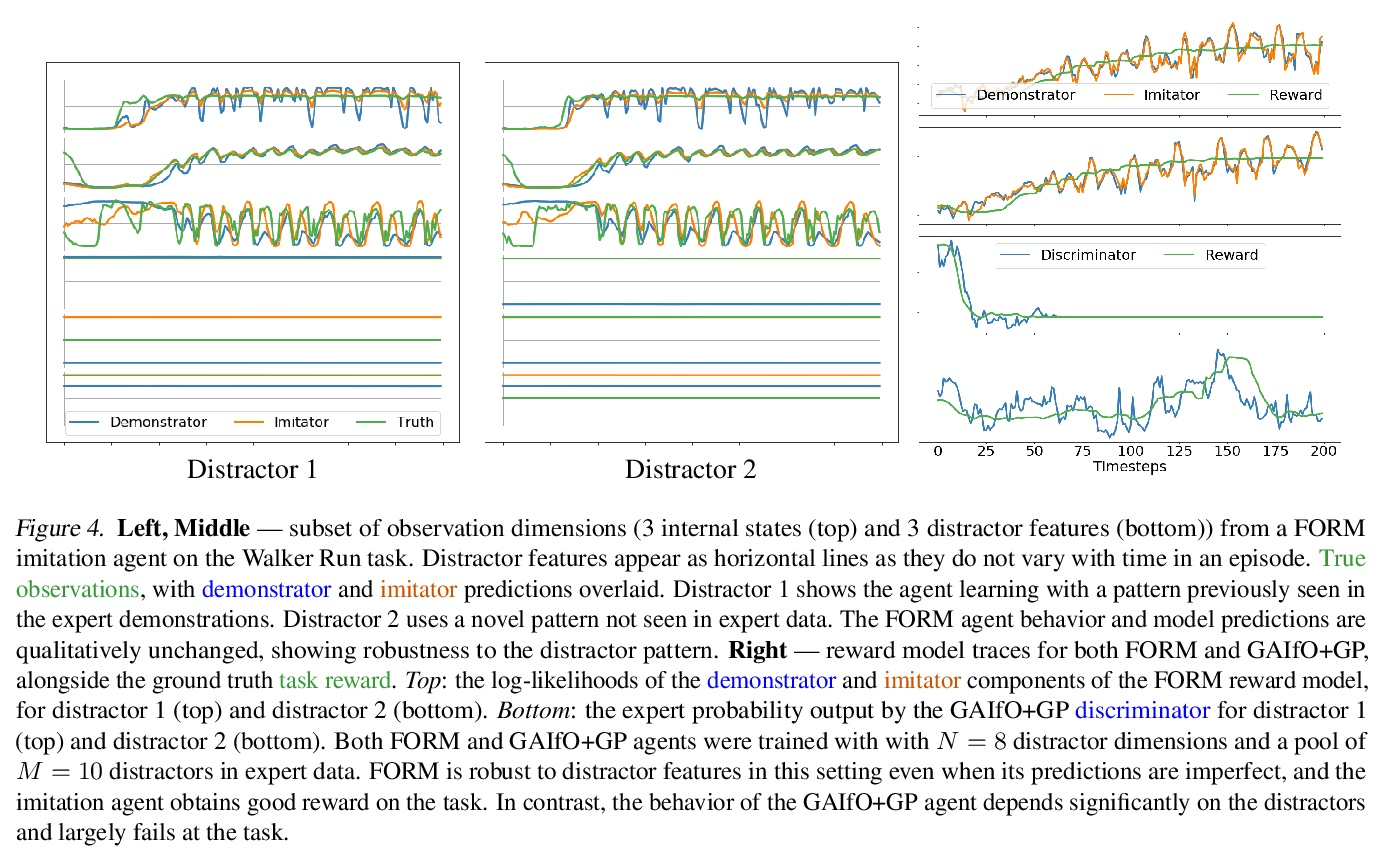
[LG] Imitation by Predicting Observations
通过预测观察进行模仿
A Jaegle, Y Sulsky, A Ahuja, J Bruce, R Fergus, G Wayne
[DeepMind]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ko2semeQF 

[LG] Shared Data and Algorithms for Deep Learning in Fundamental Physics
基础物理深度学习的共享数据和算法
L Benato, E Buhmann, M Erdmann, P Fackeldey, J Glombitza, N Hartmann, G Kasieczka, W Korcari, T Kuhr, J Steinheimer, H Stöcker, T Plehn, K Zhou
[Universitat Hamburg & RWTH Aachen University & Ludwig Maximilians University Munich]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ko2tIyRs8