- 1、[CV] NP-DRAW: A Non-Parametric Structured Latent Variable Model for Image Generation
- 2、[CV] Closed-Form Factorization of Latent Semantics in GANs
- 3、[CV] Towards Total Recall in Industrial Anomaly Detection
- 4、[CL] Scientific Credibility of Machine Translation Research: A Meta-Evaluation of 769 Papers
- 5、[CL] NodePiece: Compositional and Parameter-Efficient Representations of Large Knowledge Graphs
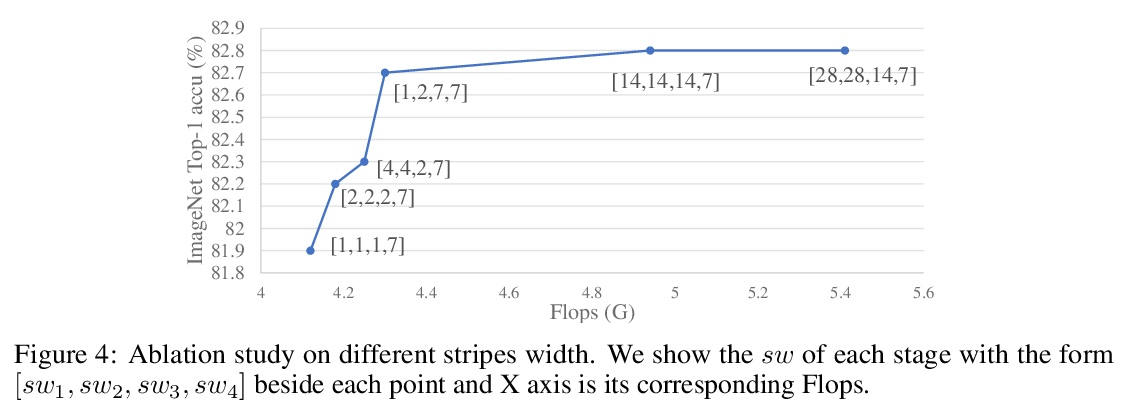
- [CV] CSWin Transformer: A General Vision Transformer Backbone with Cross-Shaped Windows
- [RO] Discovering Generalizable Skills via Automated Generation of Diverse Tasks
- [CV] Multi-Label Learning from Single Positive Labels
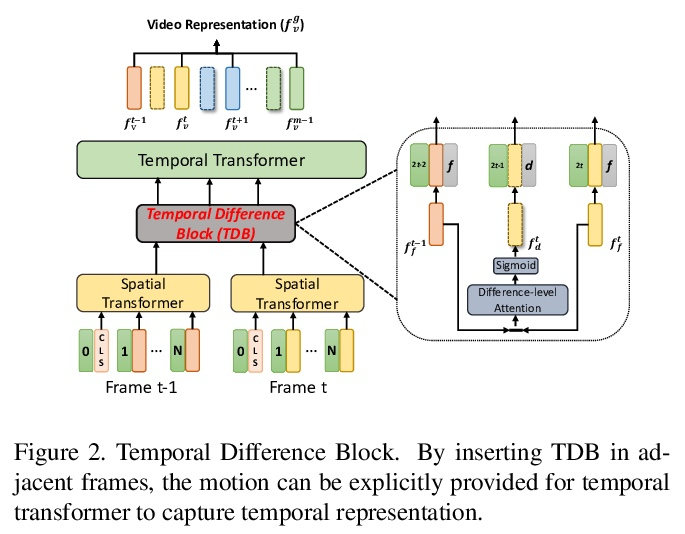
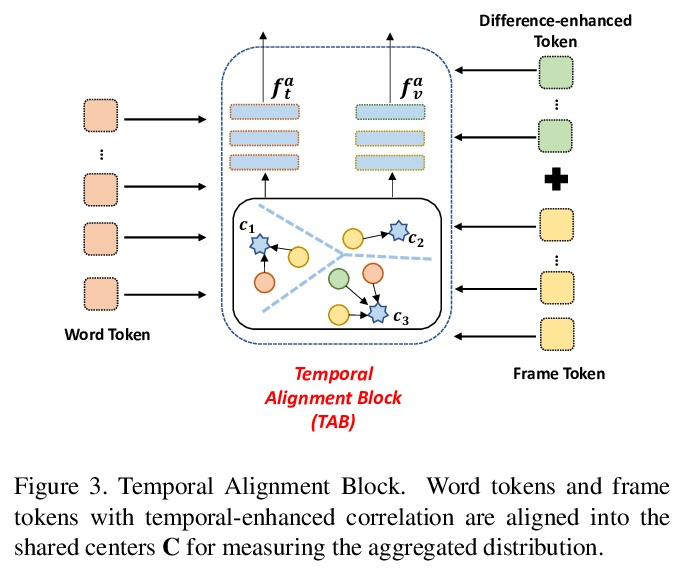
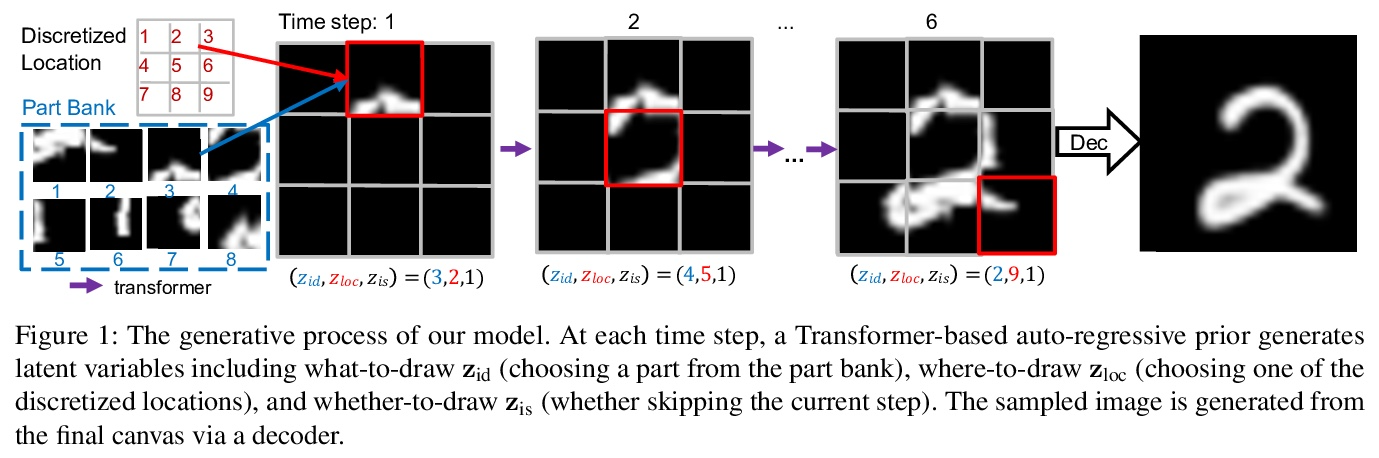
- [CV] CLIP2Video: Mastering Video-Text Retrieval via Image CLIP
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
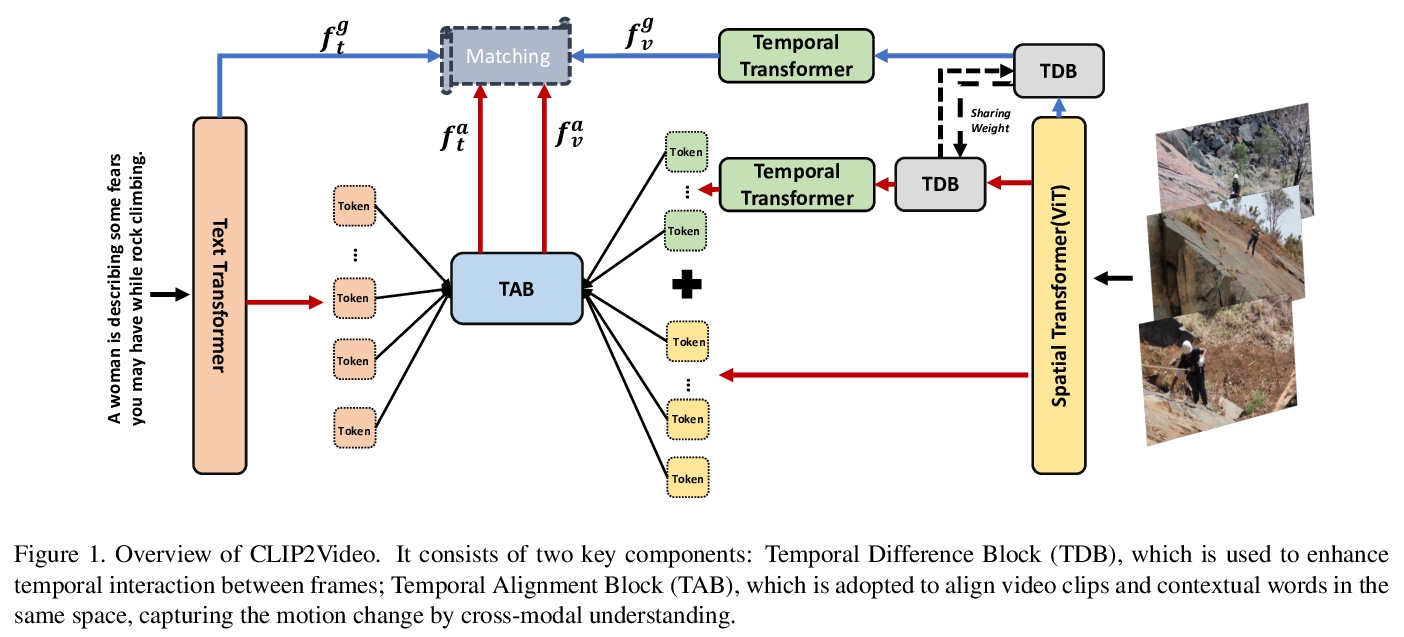
1、[CV] NP-DRAW: A Non-Parametric Structured Latent Variable Model for Image Generation
X Zeng, R Urtasun, R Zemel, S Fidler, R Liao
[University of Toronto]
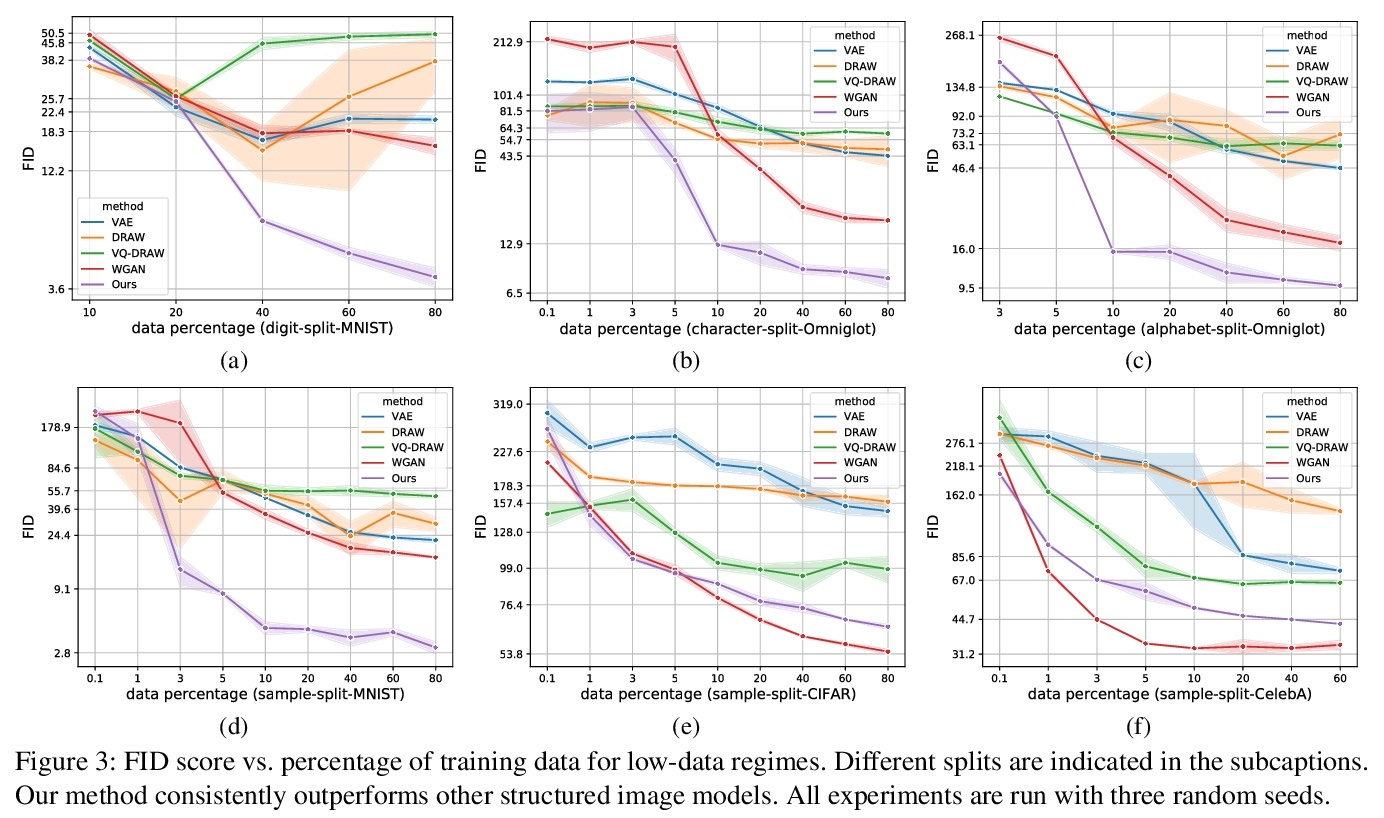
NP-DRAW:面向图像生成的非参数结构化潜变量模型。本文提出一种用于图像生成的非参数结构化潜变量模型NP-DRAW,以逐部分方式在潜画布上连续绘制,再从画布解码出图像。本文主要贡献如下:1) 提出一种关于图像部分外观的非参数先验分布,这样每一步的潜变量”画什么”就变成了分类的随机变量。与文献中使用的高斯分布相比,提高了表达能力并大大简化了学习。2)用Transformer对部件的顺序依赖结构进行建模,与文献中使用的RNN相比,更强大,更容易训练。3)提出一种有效的启发式解析算法来预训练先验。在MNIST、Omniglot、CIFAR-10和CelebA上的实验表明,该方法明显优于之前的结构化图像模型,如DRAW和AIR,并且对其他通用生成模型具有竞争力。此外,该模型的内在组成和可解释性在低数据学习场景和潜空间编辑中带来了显著的好处。
In this paper, we present a non-parametric structured latent variable model for image generation, called NP-DRAW, which sequentially draws on a latent canvas in a part-by-part fashion and then decodes the image from the canvas. Our key contributions are as follows. 1) We propose a nonparametric prior distribution over the appearance of image parts so that the latent variable “whatto-draw” per step becomes a categorical random variable. This improves the expressiveness and greatly eases the learning compared to Gaussians used in the literature. 2) We model the sequential dependency structure of parts via a Transformer, which is more powerful and easier to train compared to RNNs used in the literature. 3) We propose an effective heuristic parsing algorithm to pretrain the prior. Experiments on MNIST, Omniglot, CIFAR-10, and CelebA show that our method significantly outperforms previous structured image models like DRAW and AIR and is competitive to other generic generative models. Moreover, we show that our model’s inherent compositionality and interpretability bring significant benefits in the low-data learning regime and latent space editing.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kn7rSdzaq 
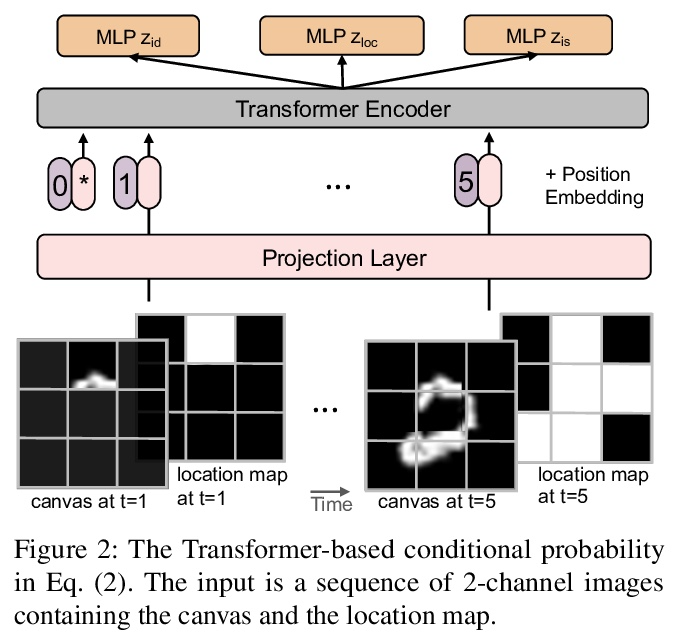

2、[CV] Closed-Form Factorization of Latent Semantics in GANs
Y Shen, B Zhou
[The Chinese University of Hong Kong]
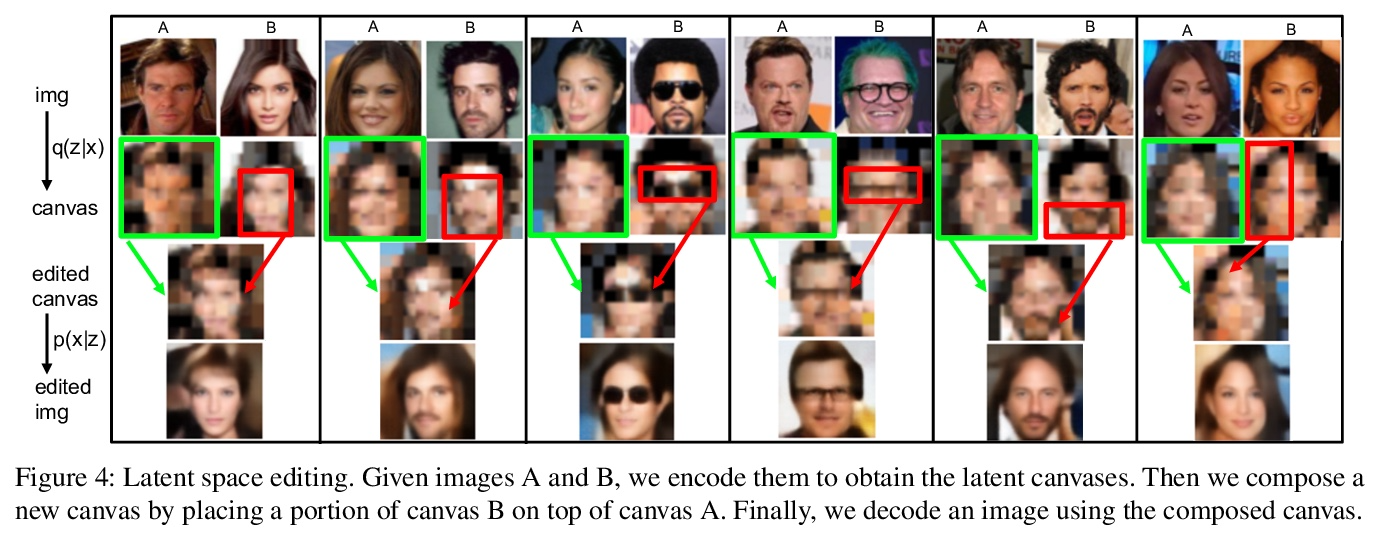
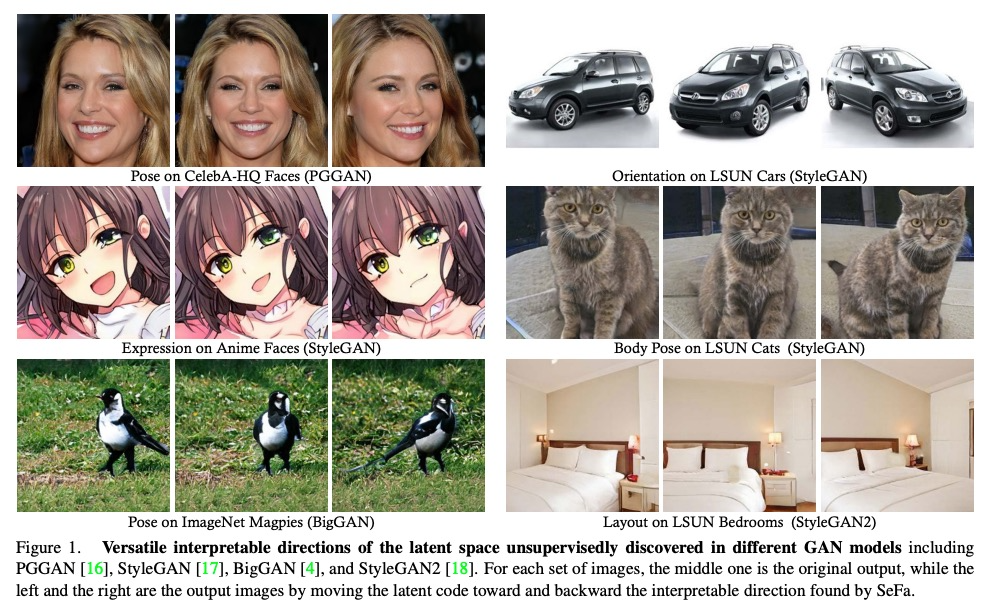
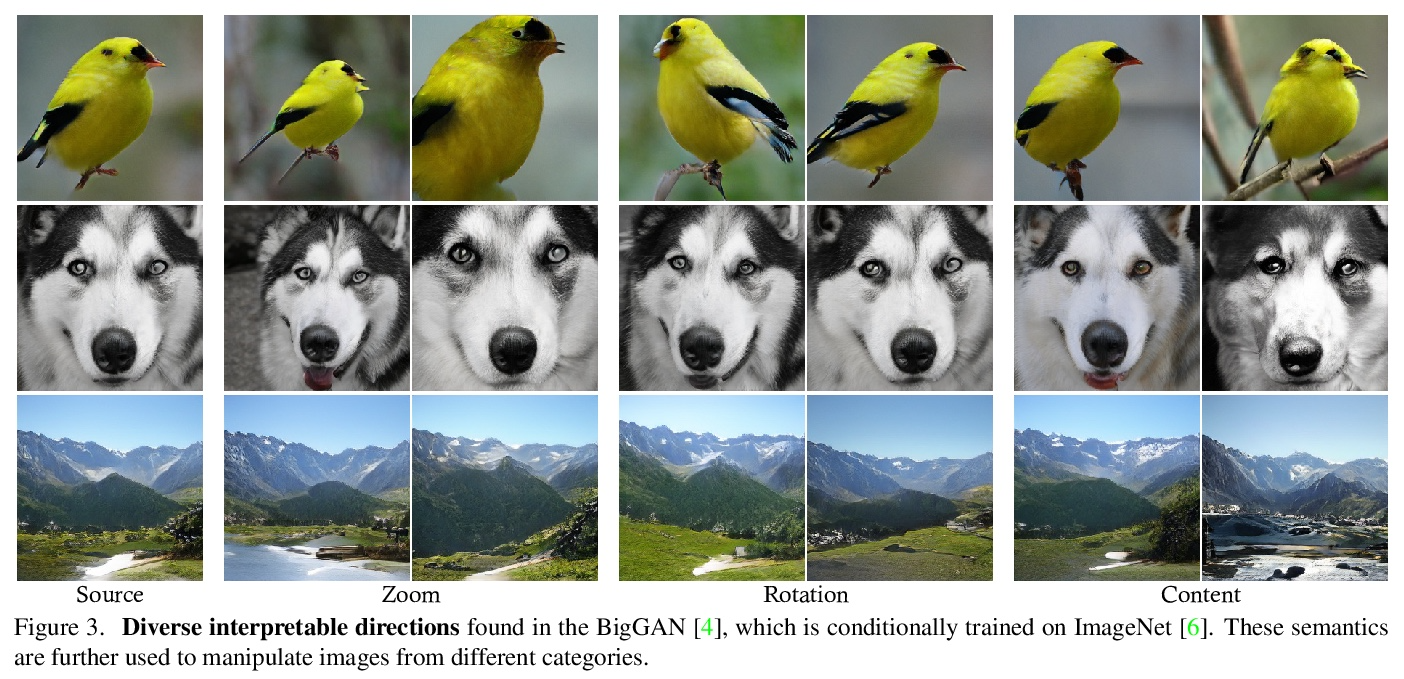
GAN潜语义闭式因子化。在为图像合成而训练的生成对抗网络(GAN)的潜空间中,已经出现了一组丰富的可解释维度。为了识别这种用于图像编辑的潜在维度,之前的方法通常会对合成的样本集进行标注,并在潜空间中训练线性分类器。然而,它们需要对目标属性的明确定义以及相应的人工标注,限制了在实践中的应用。本文研究了由GAN学习的内部表征,以无监督方式揭示了潜变化因素。通过直接分解预训练权重,进一步提出了一种用于潜语义发现的闭式因子化算法。通过超快的实现,该方法不仅能够找到与最先进的监督方法相媲美的带有语义的维度,而且在广泛的数据集上训练的多个GAN模型中产生了更为通用的概念。
A rich set of interpretable dimensions has been shown to emerge in the latent space of the Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) trained for synthesizing images. In order to identify such latent dimensions for image editing, previous methods typically annotate a collection of synthesized samples and train linear classifiers in the latent space. However, they require a clear definition of the target attribute as well as the corresponding manual annotations, limiting their applications in practice. In this work, we examine the internal representation learned by GANs to reveal the underlying variation factors in an unsupervised manner. In particular, we take a closer look into the generation mechanism of GANs and further propose a closedform factorization algorithm for latent semantic discovery by directly decomposing the pre-trained weights. With a lightning-fast implementation, our approach is capable of not only finding semantically meaningful dimensions comparably to the state-of-the-art supervised methods, but also resulting in far more versatile concepts across multiple GAN models trained on a wide range of datasets.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kn7xOrLTh 
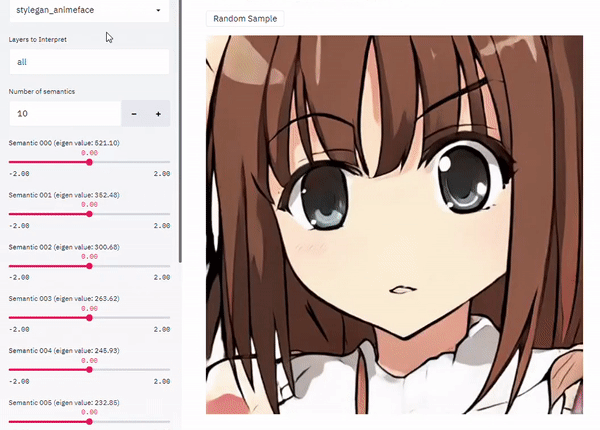



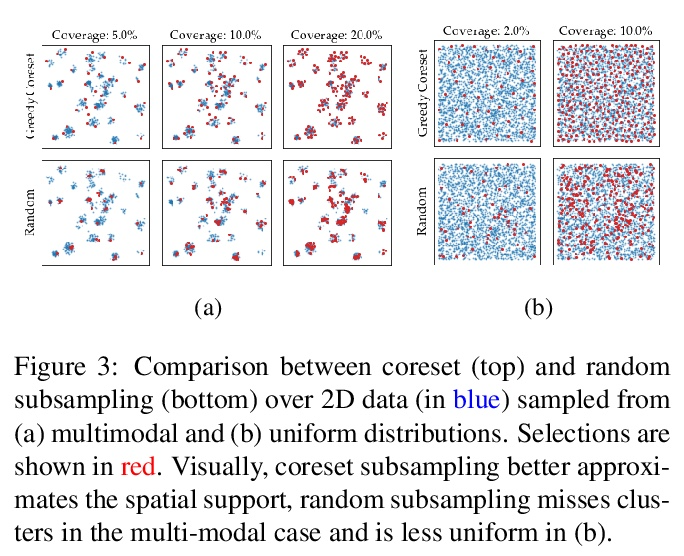
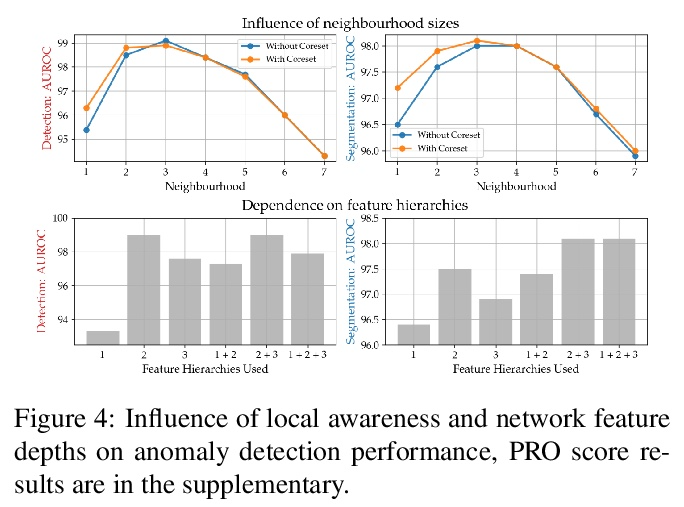
3、[CV] Towards Total Recall in Industrial Anomaly Detection
K Roth, L Pemula, J Zepeda, B Schölkopf, T Brox, P Gehler
[University of Tubingen & Amazon]
工业异常检测全召回研究。有缺陷部件的发现是大规模工业制造中一个重要组成部分。本文工作中解决的一个特殊挑战是冷启动问题:只用标称(非缺陷)样本图像来拟合模型。虽然每一类的手工解决方案是可能的,但本文的目标是建立同时在许多不同任务上自动工作的系统。最好的方法是将ImageNet模型的嵌入与离群点检测模型相结合。本文对这一工作思路进行了扩展,提出了PatchCore,用一个具有最大代表性的标称拼接特征的记忆库。PatchCore提供了有竞争力的推理时间,同时在检测和定位方面都达到了最先进的性能。在标准数据集MVTec AD上,PatchCore实现了99.1%的图像级异常检测AUROC得分,与下一个最佳竞争者相比,误差减少了一半以上。进一步报告了在另外两个数据集上的竞争结果,也发现了在少样本场景下的竞争结果。
Being able to spot defective parts is a critical component in large-scale industrial manufacturing. A particular challenge that we address in this work is the cold-start problem: fit a model using nominal (non-defective) example images only. While handcrafted solutions per class are possible, the goal is to build systems that work well simultaneously on many different tasks automatically. The best peforming approaches combine embeddings from ImageNet models with an outlier detection model. In this paper, we extend on this line of work and propose PatchCore, which uses a maximally representative memory bank of nominal patchfeatures. PatchCore offers competitive inference times while achieving state-of-the-art performance for both detection and localization. On the standard dataset MVTec AD PatchCore achieves an image-level anomaly detection AUROC score of 99.1%, more than halving the error compared to the next best competitor. We further report competitive results on two additional datasets and also find competitive results in the few samples regime.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kn7BipQKP 

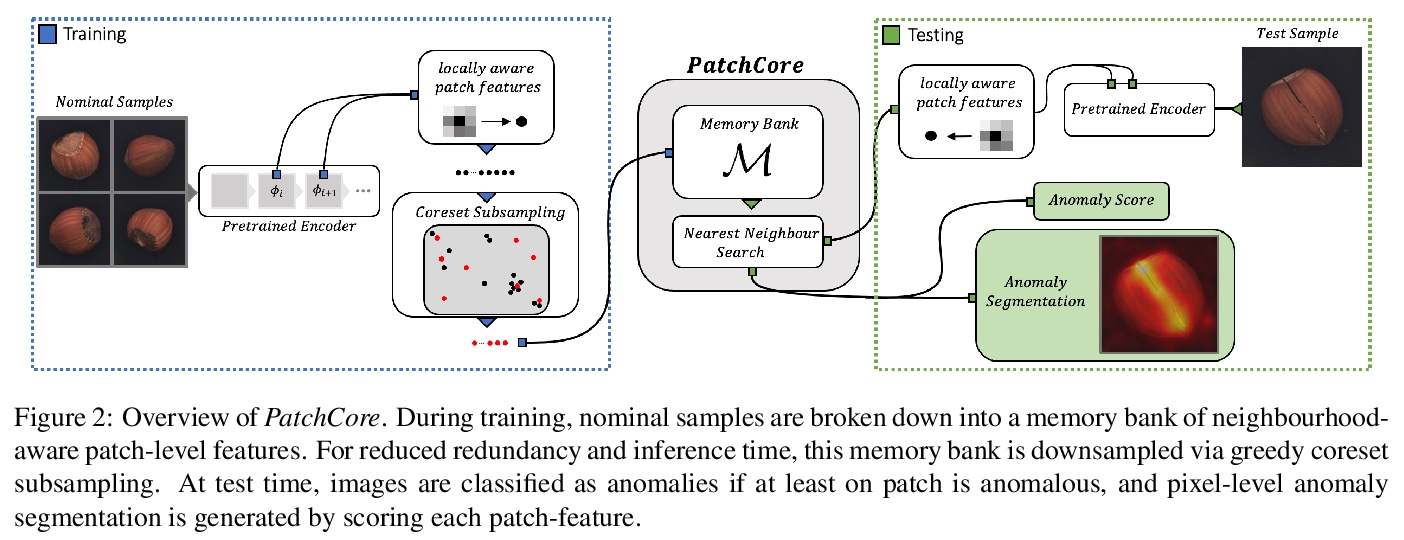
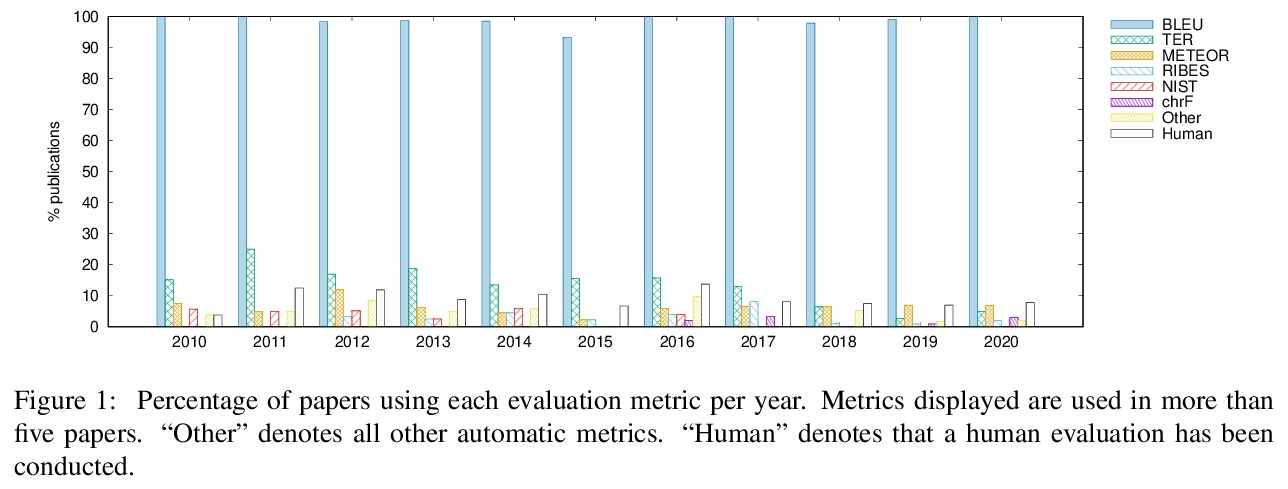
4、[CL] Scientific Credibility of Machine Translation Research: A Meta-Evaluation of 769 Papers
B Marie, A Fujita, R Rubino
[National Institute of Information and Communications Technology]
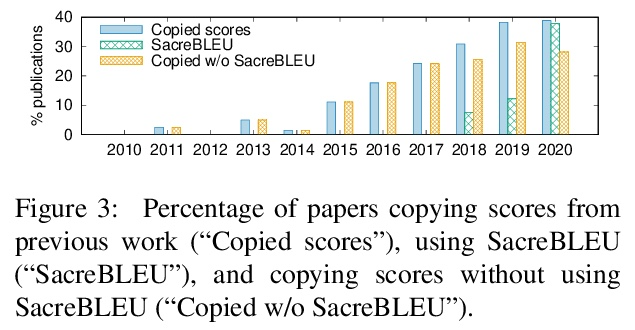
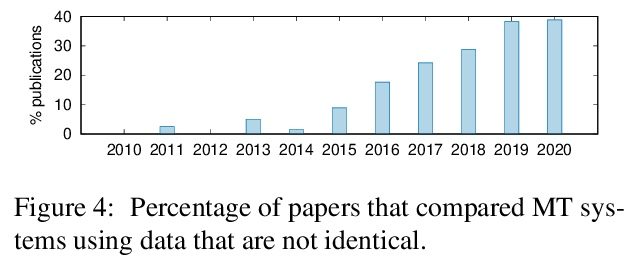
机器翻译研究的科学可信度:769篇论文的元评价。本文进行一个大规模的机器翻译(MT)元评价,对2010年至2020年发表的769篇研究论文中的机器翻译评估进行了标注。研究表明,在过去十年中,自动机器翻译评估的做法已经发生了巨大的变化,并遵循着令人担忧的趋势。越来越多的机器翻译评估完全依靠BLEU分数之间的差异来得出结论,而没有进行任何形式的统计学意义测试,也没有进行人工评估,同时至少提出了108个自称比BLEU更好的指标。最近的论文中的机器翻译评估倾向于从以前的工作中复制和比较自动指标得分,以宣称一种方法或算法的优越性,而没有确认是否使用了完全相同的训练、验证和测试数据,也没有确认指标得分的可比性。此外,报告标准化指标分数的工具仍然远远没有被机器翻译社区广泛采用。在展示了这些陷阱的积累如何导致可疑的评价之后,本文提出一个指导方针,以鼓励更好的自动机器翻译评价,以及一个简单的元评价评分方法来评估其可信度。
This paper presents the first large-scale metaevaluation of machine translation (MT). We annotated MT evaluations conducted in 769 research papers published from 2010 to 2020. Our study shows that practices for automatic MT evaluation have dramatically changed during the past decade and follow concerning trends. An increasing number of MT evaluations exclusively rely on differences between BLEU scores to draw conclusions, without performing any kind of statistical significance testing nor human evaluation, while at least 108 metrics claiming to be better than BLEU have been proposed. MT evaluations in recent papers tend to copy and compare automatic metric scores from previous work to claim the superiority of a method or an algorithm without confirming neither exactly the same training, validating, and testing data have been used nor the metric scores are comparable. Furthermore, tools for reporting standardized metric scores are still far from being widely adopted by the MT community. After showing how the accumulation of these pitfalls leads to dubious evaluation, we propose a guideline to encourage better automatic MT evaluation along with a simple meta-evaluation scoring method to assess its credibility.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kn7GfF7wC 
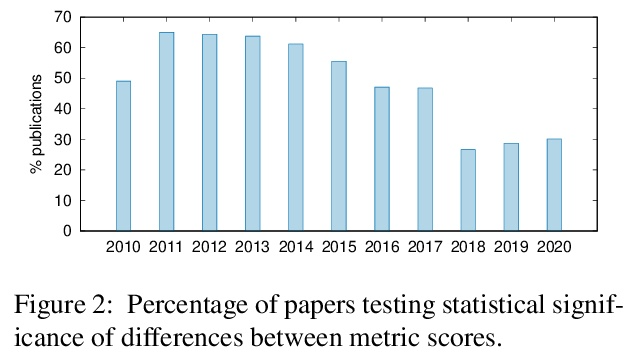
5、[CL] NodePiece: Compositional and Parameter-Efficient Representations of Large Knowledge Graphs
M Galkin, J Wu, E Denis, W L. Hamilton
[McGill University]
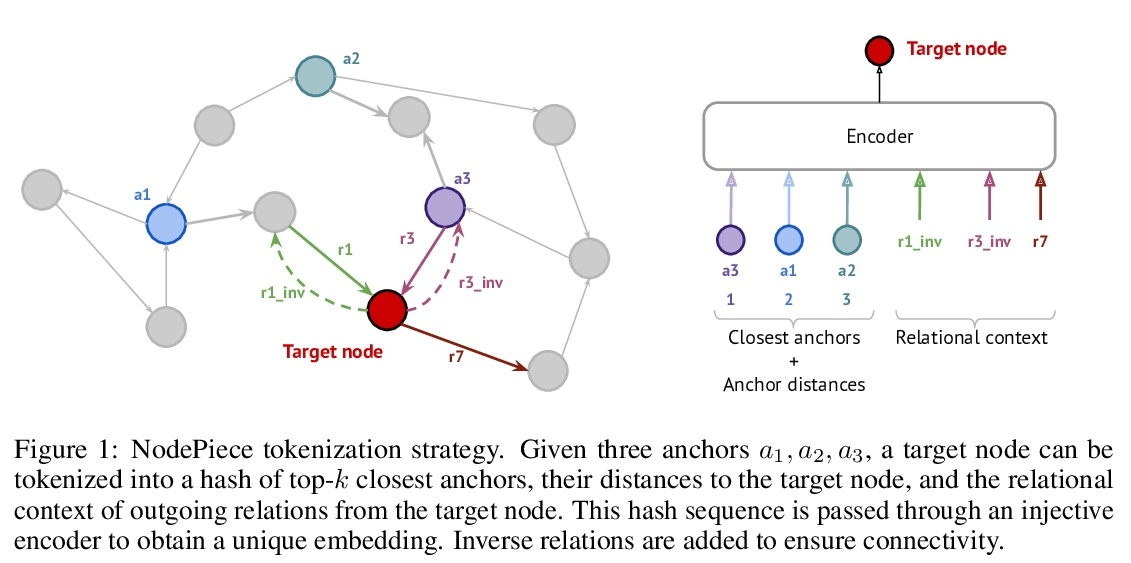
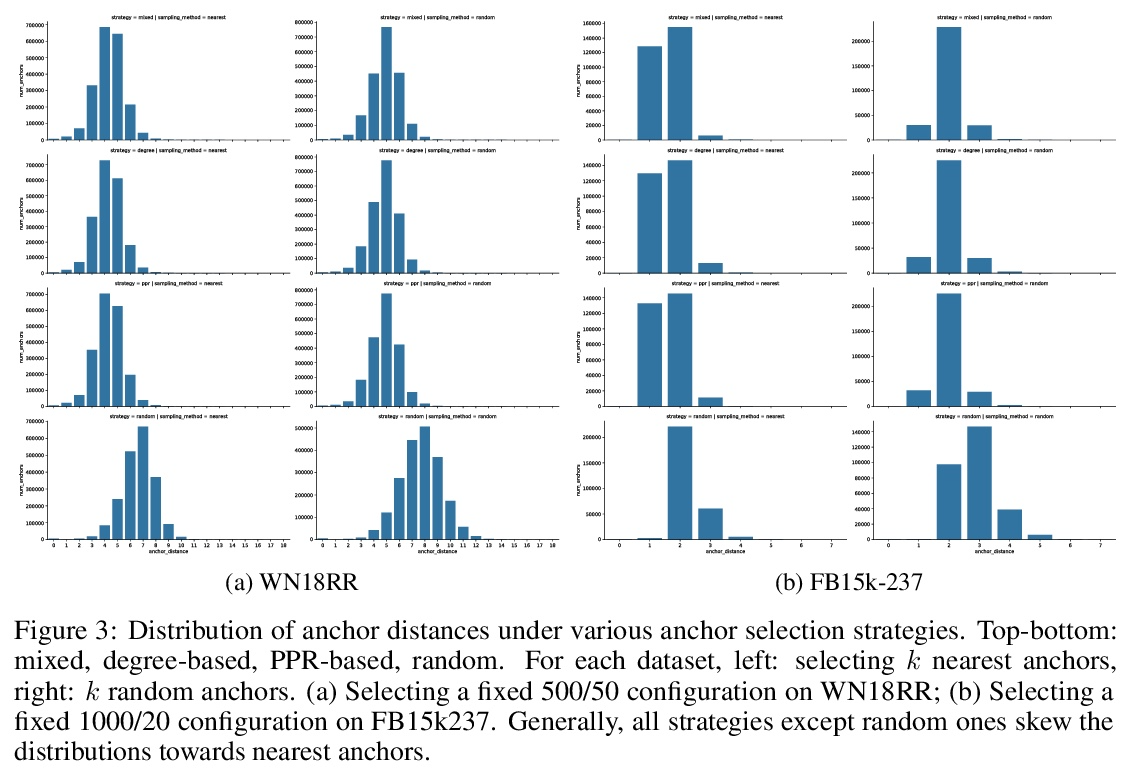
NodePiece: 大型知识图谱的组合式和参数高效的表示方法。传统的知识图谱(KG)表示学习算法将每个实体映射成一个唯一的嵌入向量。这样的浅层查找导致存储嵌入矩阵的内存消耗线性增长,并且在处理现实世界的知识图谱时产生了很高的计算成本。与NLP中常用的子词Token化相比较,本文探索了参数效率更高的节点嵌入策略的前景,其内存需求可能是亚线性的,提出NodePiece,一种基于锚的方法来学习一个固定大小的实体词表。在NodePiece中,一个子词/子实体单元的词表是由已知关系类型的图中的锚节点构建的。鉴于这样一个固定大小的词表,有可能对任何实体进行引导性编码和嵌入,包括那些在训练中未见过的实体。实验表明,NodePiece在节点分类、链接预测和关系预测任务中的表现很有竞争力,同时保留了图中不到10%的明确节点作为锚点,而且参数往往少了10倍。
Conventional representation learning algorithms for knowledge graphs (KG) map each entity to a unique embedding vector. Such a shallow lookup results in a linear growth of memory consumption for storing the embedding matrix and incurs high computational costs when working with real-world KGs. Drawing parallels with subword tokenization commonly used in NLP, we explore the landscape of more parameter-efficient node embedding strategies with possibly sublinear memory requirements. To this end, we propose NodePiece, an anchor-based approach to learn a fixed-size entity vocabulary. In NodePiece, a vocabulary of subword/subentity units is constructed from anchor nodes in a graph with known relation types. Given such a fixed-size vocabulary, it is possible to bootstrap an encoding and embedding for any entity, including those unseen during training. Experiments show that NodePiece performs competitively in node classification, link prediction, and relation prediction tasks while retaining less than 10% of explicit nodes in a graph as anchors and often having 10x fewer parameters.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kn7J1m71X 

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
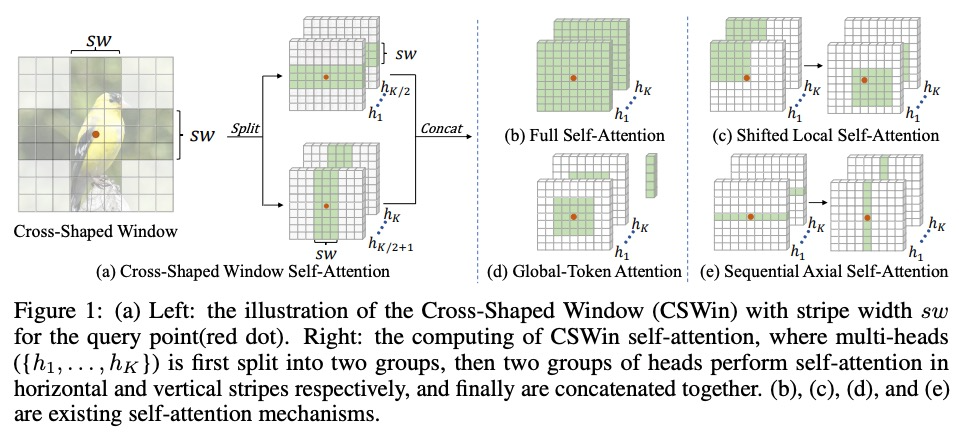
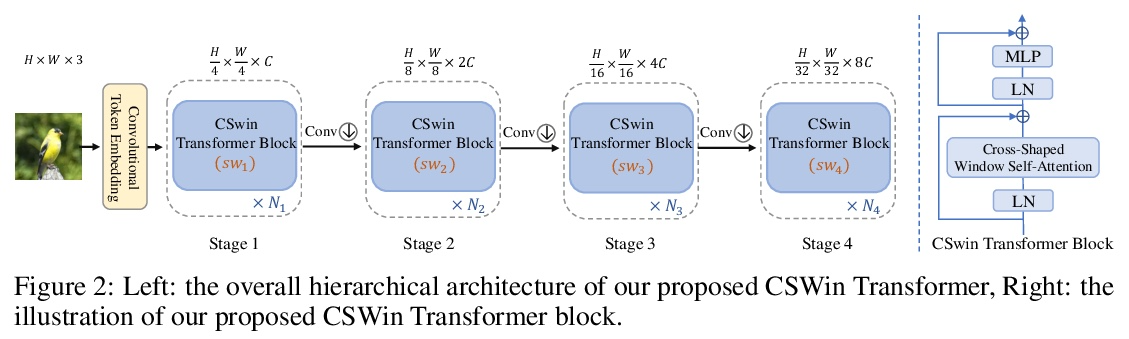
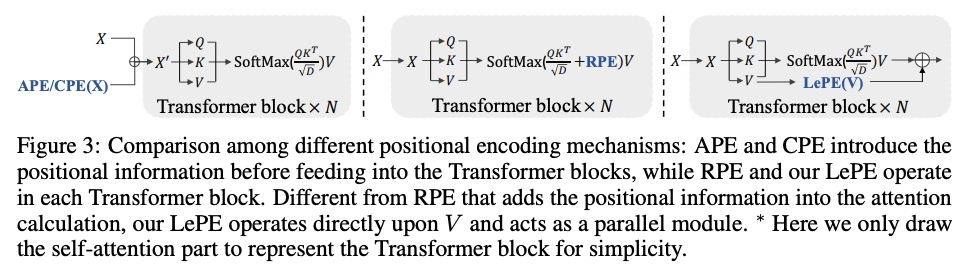
[CV] CSWin Transformer: A General Vision Transformer Backbone with Cross-Shaped Windows
CSWin Transformer:带十字形窗口的通用视觉Transformer骨干
X Dong, J Bao, D Chen, W Zhang, N Yu, L Yuan, D Chen, B Guo
[University of Science and Technology of China & Microsoft Research Asia & Microsoft Cloud + AI]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kn7LM9RJo 
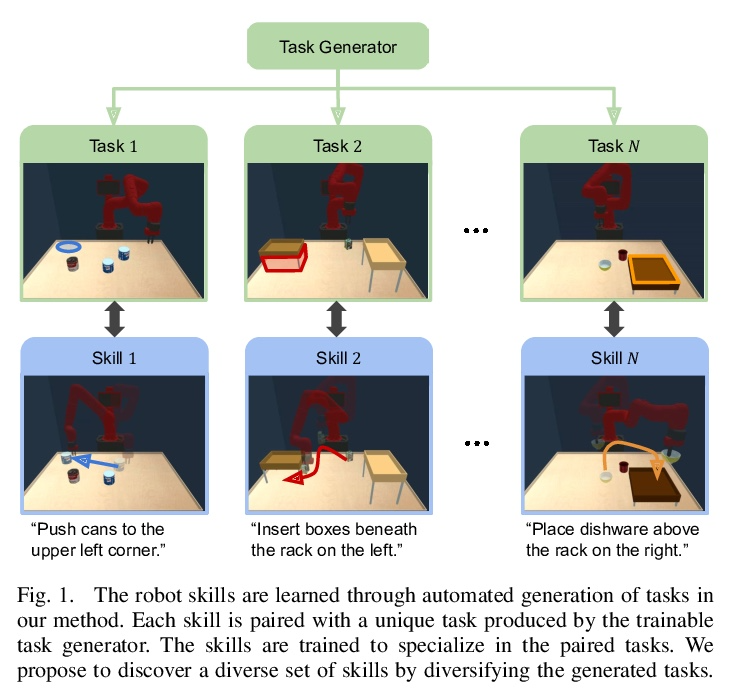
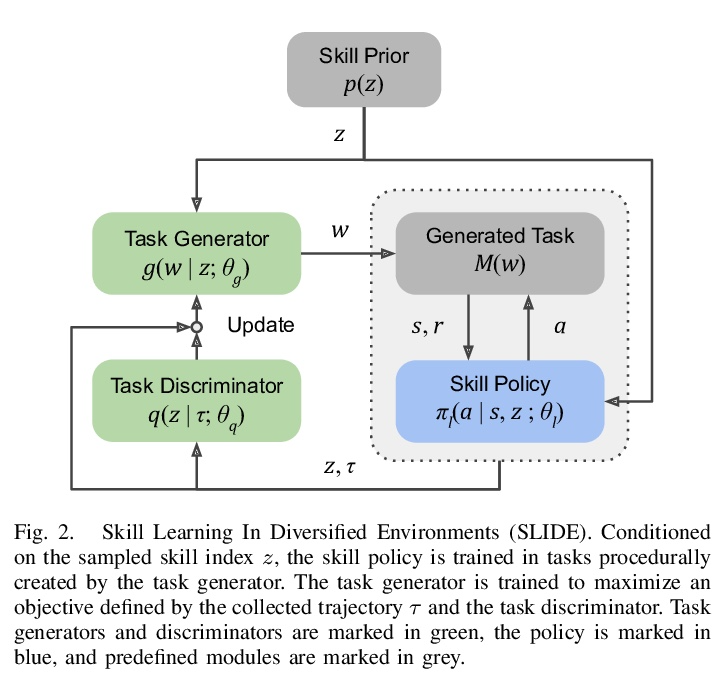
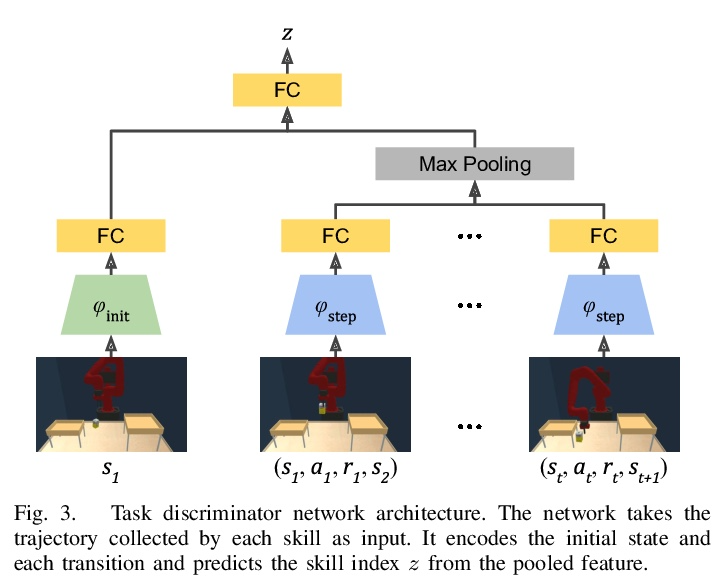
[RO] Discovering Generalizable Skills via Automated Generation of Diverse Tasks
基于多样任务自动生成的可泛化技能发现
K Fang, Y Zhu, S Savarese, L Fei-Fei
[Stanford University & UT Austin]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kn7NvqFsz 
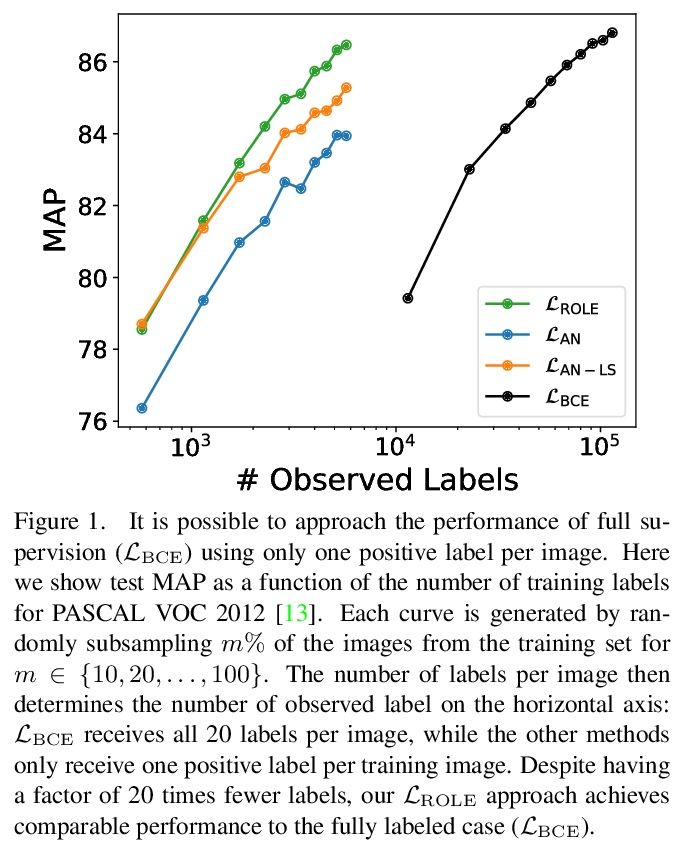
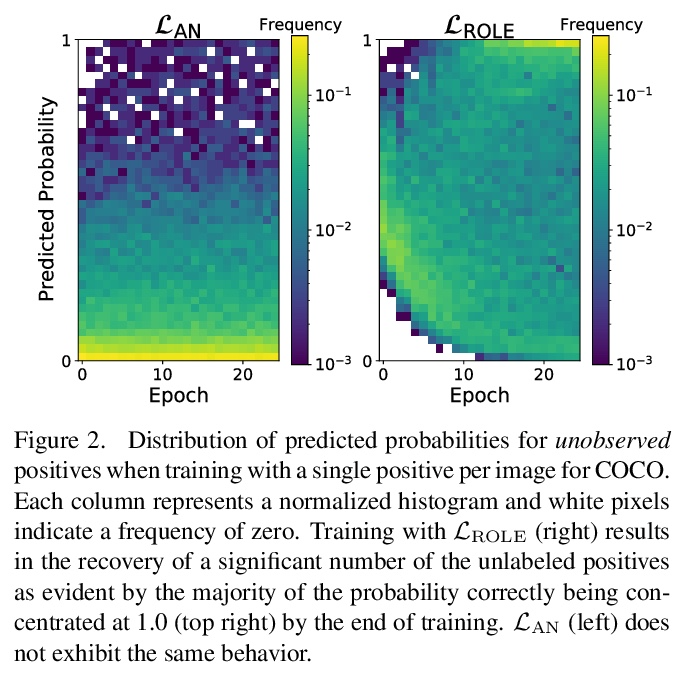
[CV] Multi-Label Learning from Single Positive Labels
从单个正标签学习多标签
E Cole, O M Aodha, T Lorieul, P Perona, D Morris, N Jojic
[Caltech & University of Edinburgh & Inria & Microsoft AI for Earth & Microsoft Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kn7Pm84JI 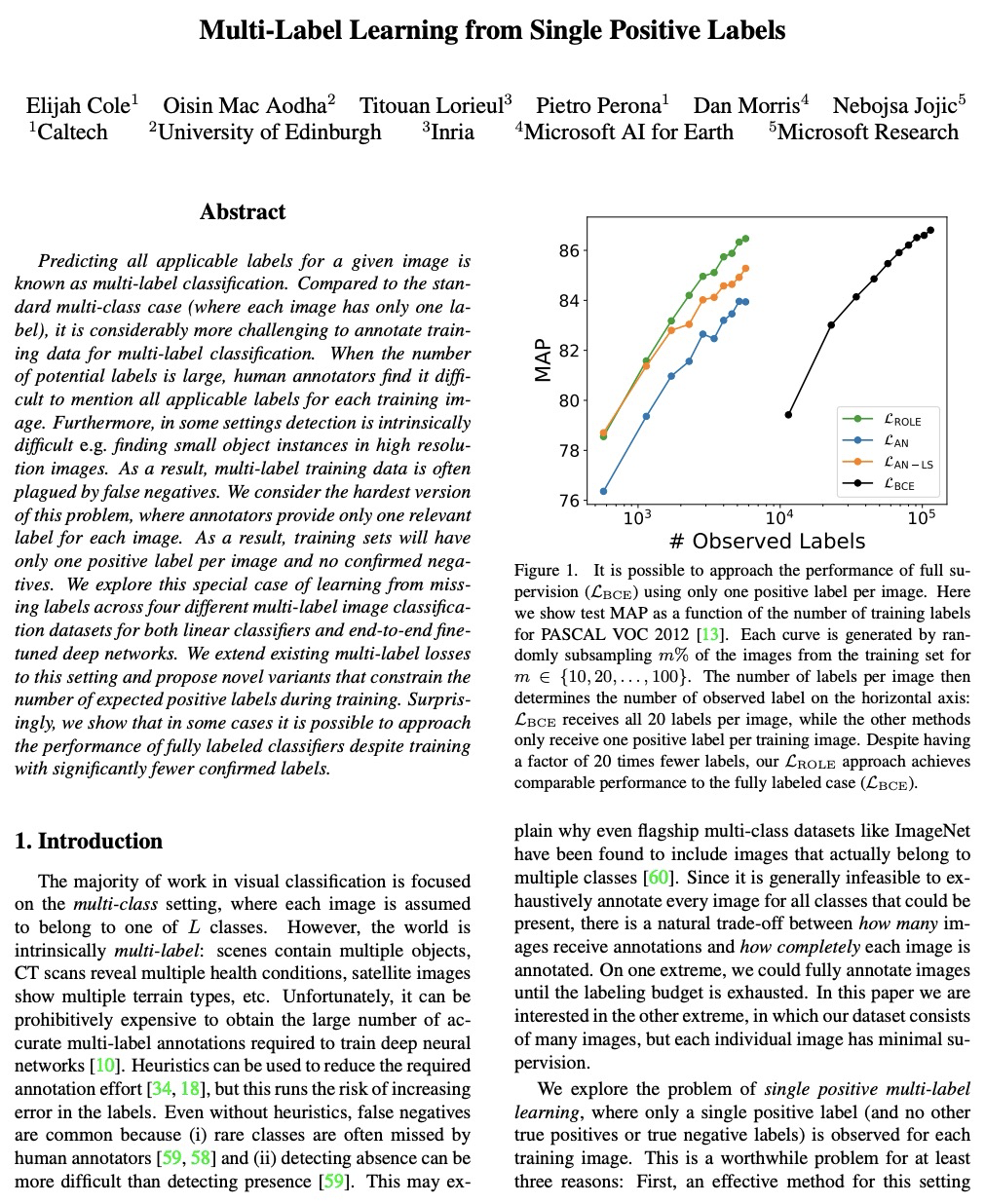
[CV] CLIP2Video: Mastering Video-Text Retrieval via Image CLIP
CLIP2Video:基于图像CLIP的视频-文本检索
H Fang, P Xiong, L Xu, Y Chen
[Tencent]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kn7Rd1Ahu