- 1、[CV] Animating Pictures with Eulerian Motion Fields
- 2、[CV] Taming Transformers for High-Resolution Image Synthesis
- 3、[LG] Descending through a Crowded Valley — Benchmarking Deep Learning Optimizers
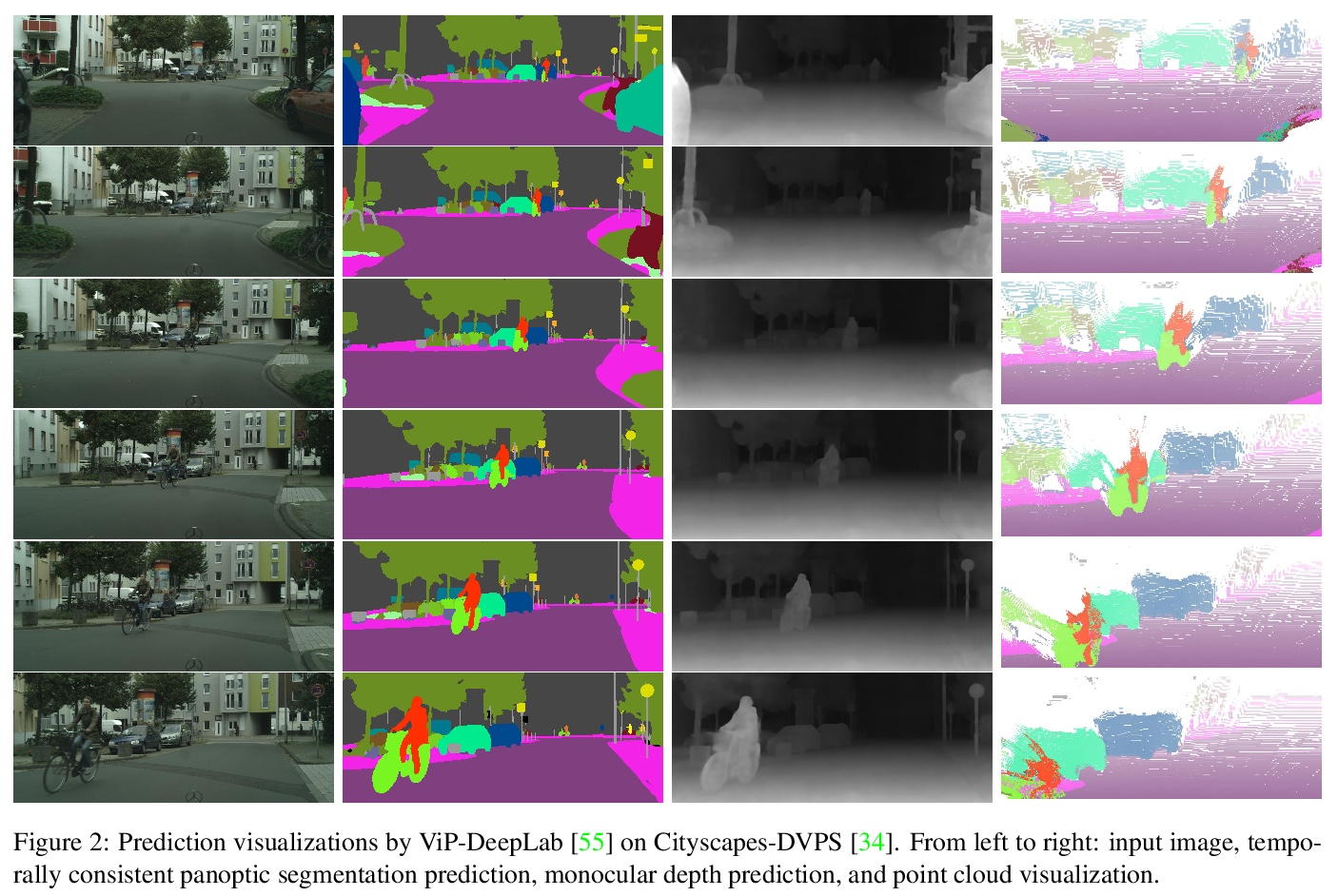
- 4、[CV] DeepLab2: A TensorFlow Library for Deep Labeling
- 5、[CV] Vision Permutator: A Permutable MLP-Like Architecture for Visual Recognition
- [LG] Multiplying Matrices Without Multiplying
- [LG] Active Offline Policy Selection
- [CL] GroupBERT: Enhanced Transformer Architecture with Efficient Grouped Structures
- [LG] Learning Knowledge Graph-based World Models of Textual Environments
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
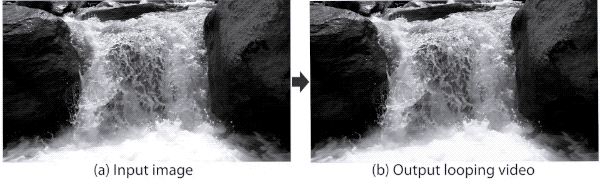
1、[CV] Animating Pictures with Eulerian Motion Fields
A Holynski, B Curless, S M. Seitz, R Szeliski
[University of Washington & Facebook]
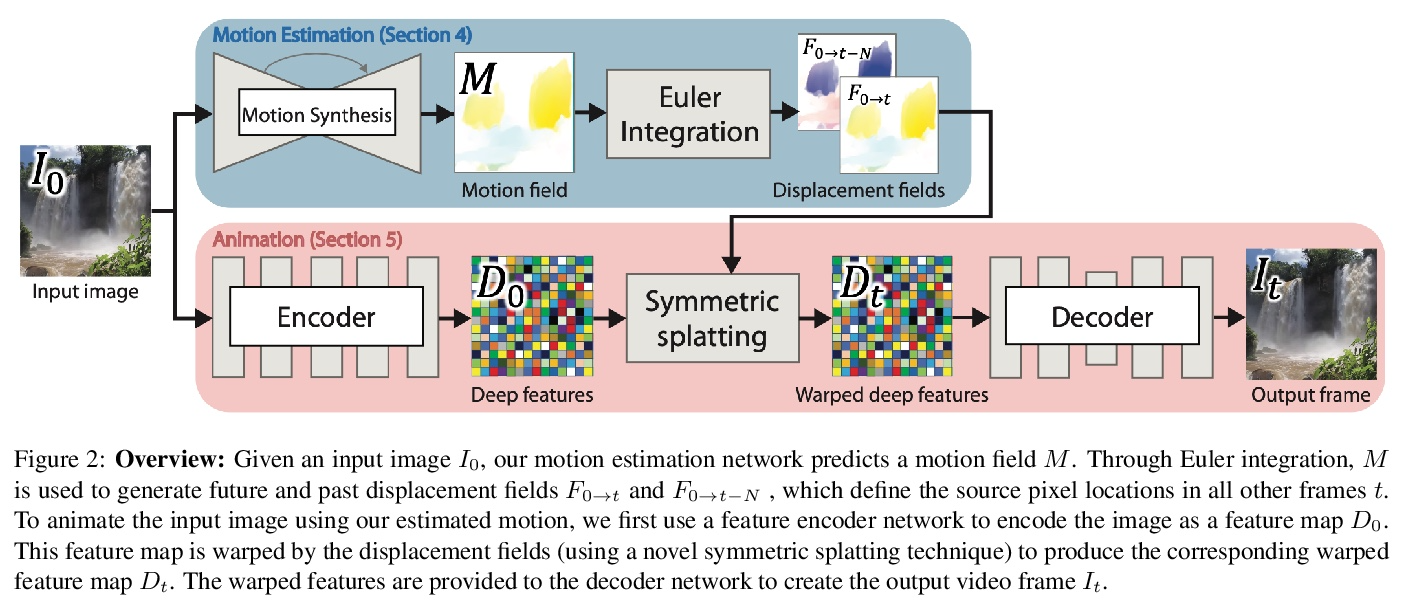
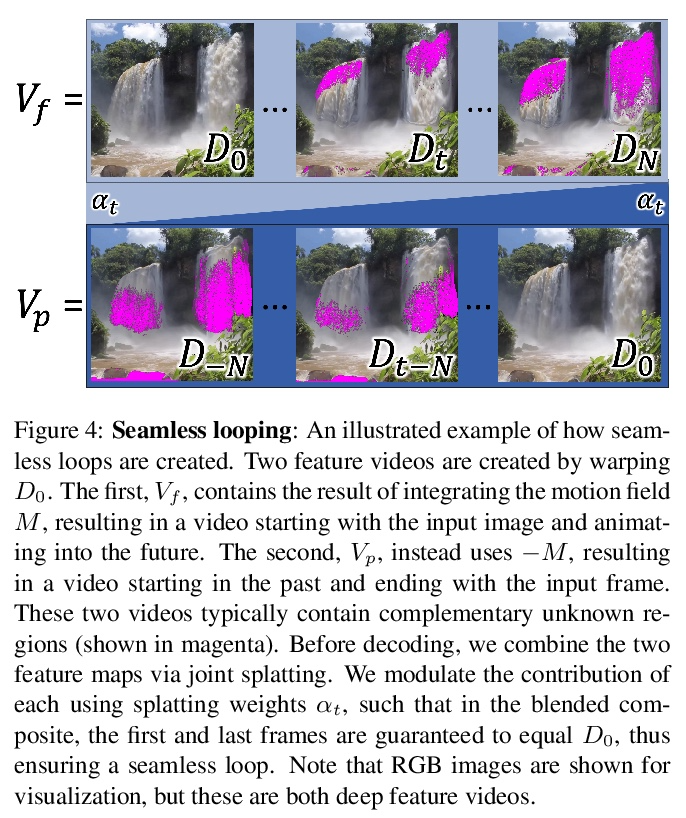
基于欧拉运动场的静态图片循环动画生成。本文展示了一种将静止图像转换为逼真的循环动画视频的全自动方法。针对具有连续流体运动的场景,例如流水和滚滚烟雾。该方法依赖于可以从静态欧拉运动描述中令人信服地再现这种类型自然运动的观察,即定义粒子在给定 2D 位置的即时运动的单个、时间恒定的流场。用图像到图像转换网络对从在线视频中收集的自然场景的运动先验进行编码,以便对于新照片,可以合成相应的运动场。通过深度变形技术使用生成的运动对图像进行动画处理:像素被编码为深度特征,这些特征通过欧拉运动变形,产生的变形特征图被解码为图像。为产生连续、无缝循环的视频纹理,提出一种新的视频循环技术,在时间上向前和向后流动特征,然后混合结果。通过将其应用于大量示例(包括海滩、瀑布和流动的河流)来证明该方法的有效性和鲁棒性。
In this paper, we demonstrate a fully automatic method for converting a still image into a realistic animated looping video. We target scenes with continuous fluid motion, such as flowing water and billowing smoke. Our method relies on the observation that this type of natural motion can be convincingly reproduced from a static Eulerian motion description, i.e. a single, temporally constant flow field that defines the immediate motion of a particle at a given 2D location. We use an image-to-image translation network to encode motion priors of natural scenes collected from online videos, so that for a new photo, we can synthesize a corresponding motion field. The image is then animated using the generated motion through a deep warping technique: pixels are encoded as deep features, those features are warped via Eulerian motion, and the resulting warped feature maps are decoded as images. In order to produce continuous, seamlessly looping video textures, we propose a novel video looping technique that flows features both forward and backward in time and then blends the results. We demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our method by applying it to a large collection of examples including beaches, waterfalls, and flowing rivers.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Km3vU6KPH 


2、[CV] Taming Transformers for High-Resolution Image Synthesis
P Esser, R Rombach, B Ommer
[Heidelberg University]
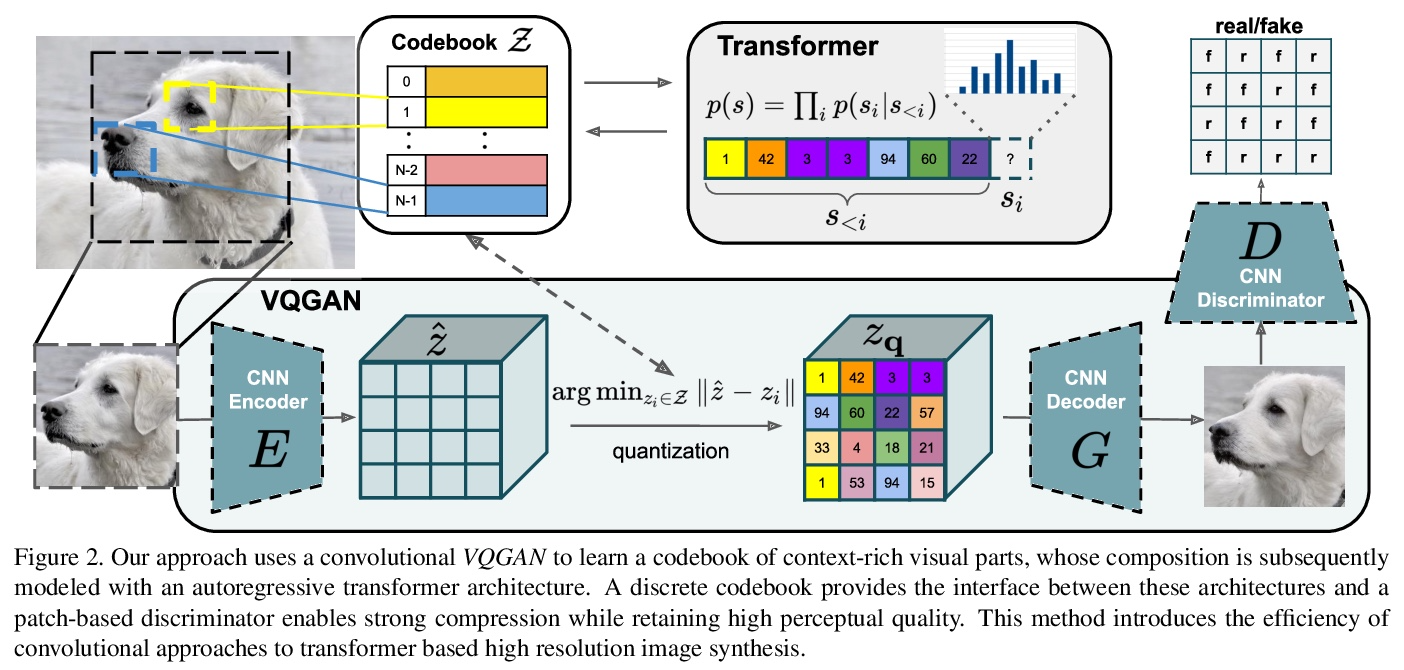
征服Transformer高分辨率图像合成。Transformer旨在学习序列数据上的长程交互,持续在各种任务上呈现出最先进的结果。与 CNN 相比,Transformer不包含优先考虑局部交互的归纳偏差。这使它们具有表现力,但对于长序列(如高分辨率图像)在计算上不可行。本文展示了如何将 CNN 归纳偏差的有效性与 Transformer 的表达能力相结合,使它们能够建模并合成高分辨率图像。本文展示了如何 (i) 用 CNN 来学习图像成分的上下文丰富的词汇表,并反过来 (ii) 用Transformer在高分辨率图像中有效地对其组成进行建模。该方法很容易应用于有条件的合成任务,其中非空间信息(如目标类)和空间信息(如分割)都可以控制生成图像。展示了带有Transformer的百万像素图像的语义引导合成的第一个结果,并在ImageNet 上的类条件 自回归模型中获得了最先进的结果。
Designed to learn long-range interactions on sequential data, transformers continue to show state-of-the-art results on a wide variety of tasks. In contrast to CNNs, they contain no inductive bias that prioritizes local interactions. This makes them expressive, but also computationally infeasible for long sequences, such as high-resolution images. We demonstrate how combining the effectiveness of the inductive bias of CNNs with the expressivity of transformers enables them to model and thereby synthesize high-resolution images. We show how to (i) use CNNs to learn a contextrich vocabulary of image constituents, and in turn (ii) utilize transformers to efficiently model their composition within high-resolution images. Our approach is readily applied to conditional synthesis tasks, where both non-spatial information, such as object classes, and spatial information, such as segmentations, can control the generated image. In particular, we present the first results on semanticallyguided synthesis of megapixel images with transformers and obtain the state of the art among autoregressive models on class-conditional ImageNet.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Km3BM6d1n 


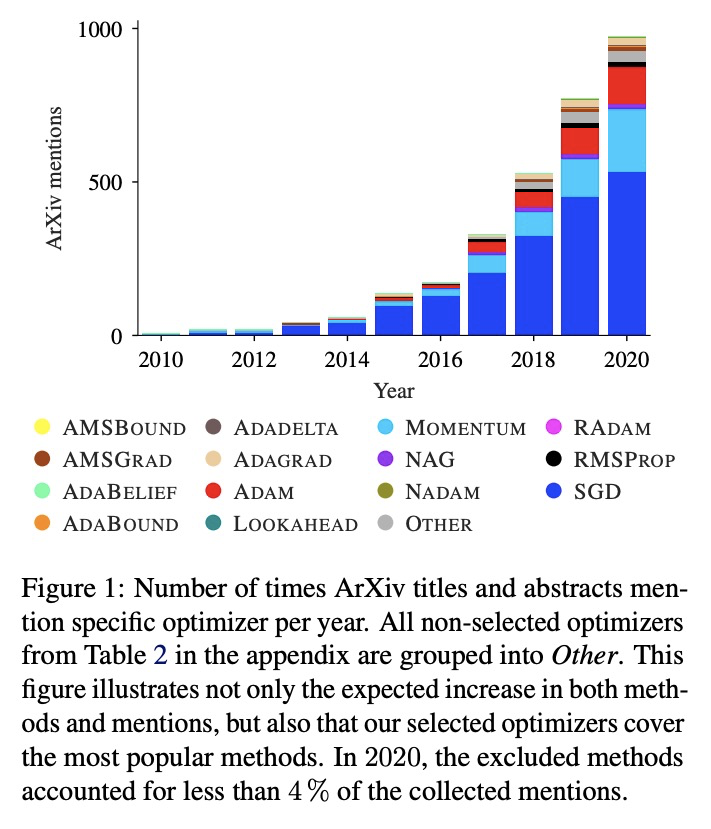
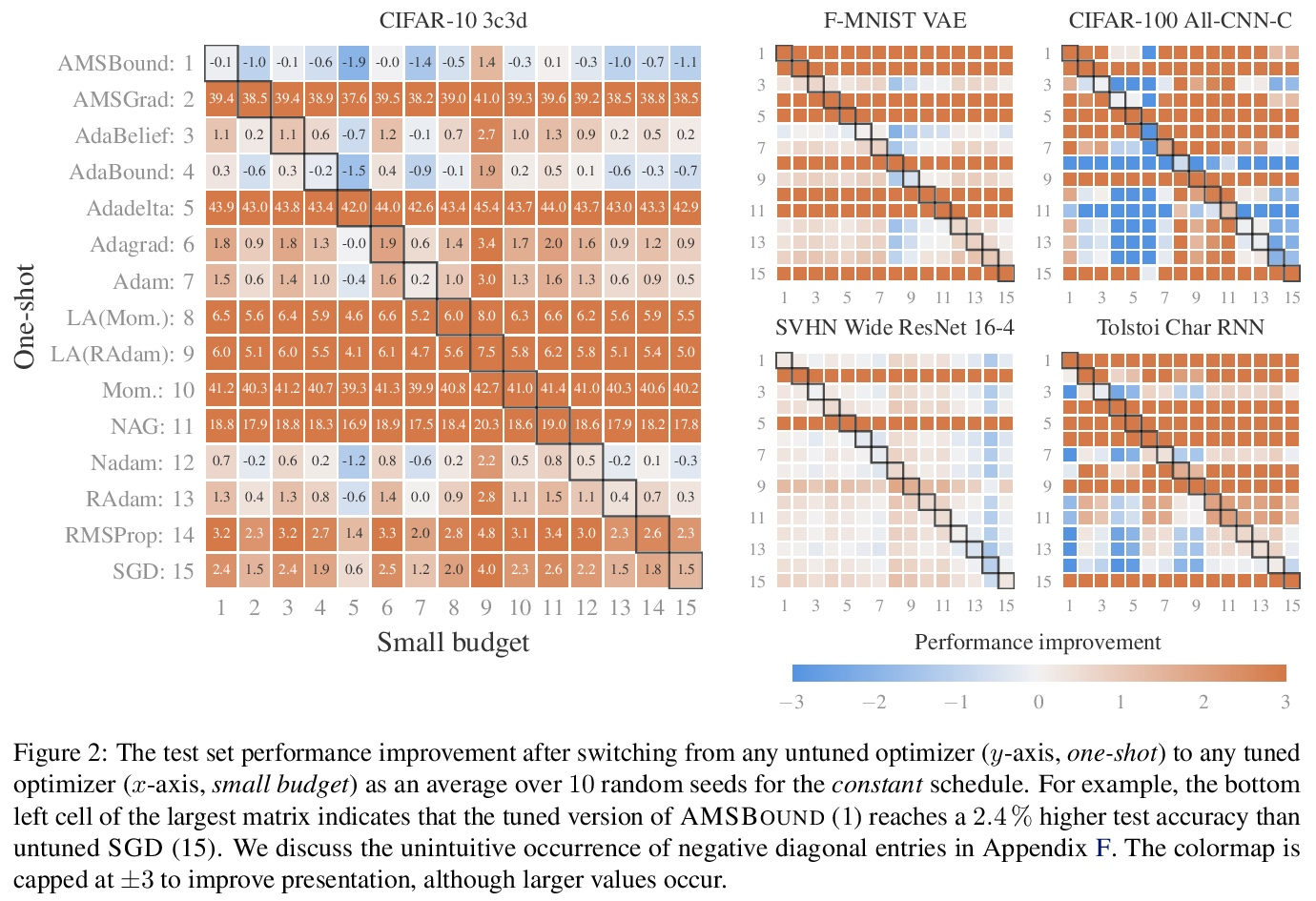
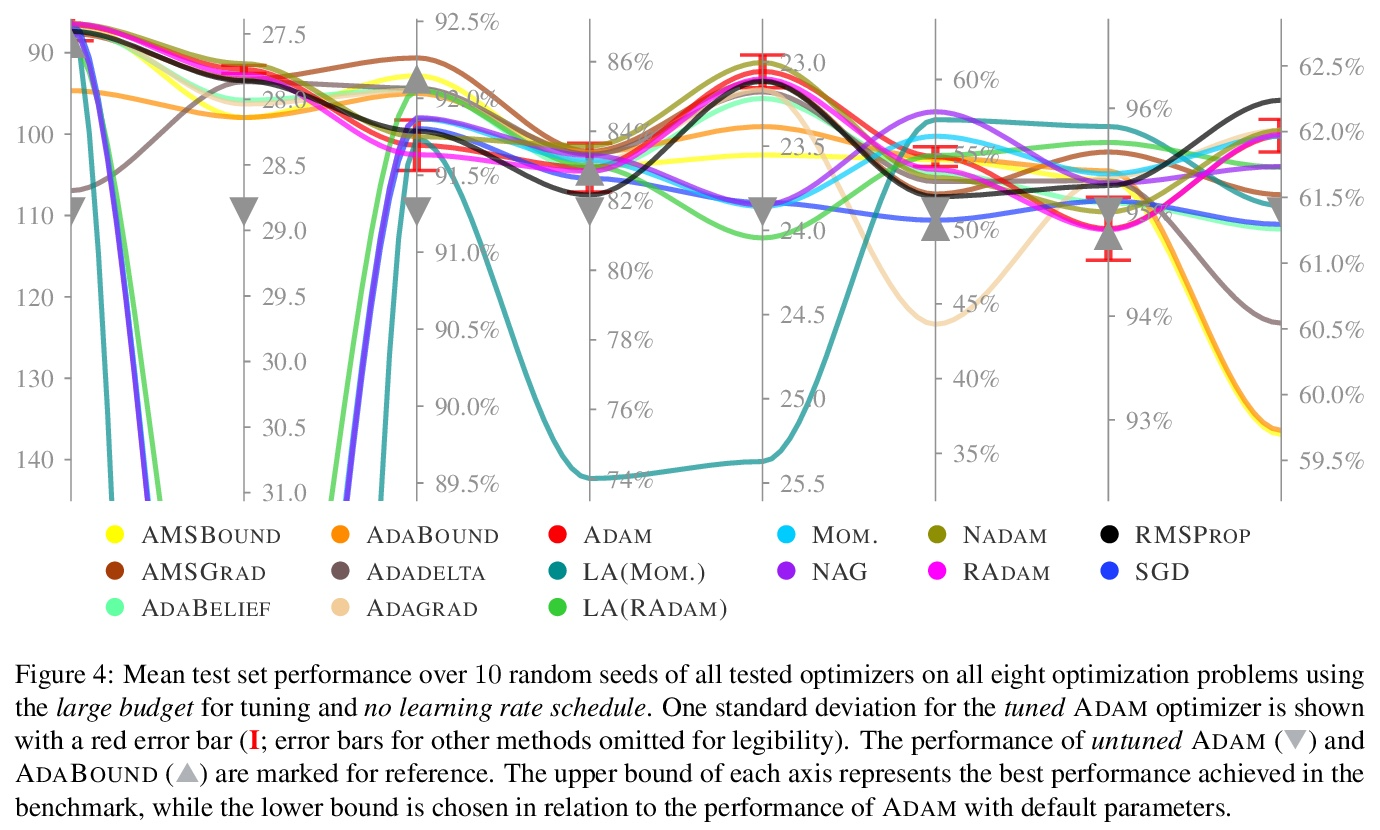
3、[LG] Descending through a Crowded Valley — Benchmarking Deep Learning Optimizers
R M. Schmidt, F Schneider, P Hennig
[University of Tübingen]
穿过拥挤的山谷——深度学习优化器基准测试。选择优化器被认为是深度学习中最关键的设计决策之一,这并不容易。还在不断增长中的文献已经提出了数百种优化方法。在缺乏明确理论指导和确凿经验证据的情况下,决策往往基于道听途说。本文的目标是取代这些口头经验,如果不是用结论性的排名,那么至少用有证据支持的启发式方法。为此,对 15 个最流行的深度学习优化器进行了广泛的标准化基准测试,同时简要概述了广泛的可能选择。分析了超过 50,000 次单独运行,得出三点结论:(i) 优化器性能因任务而异。 (ii) 使用默认参数评估多个优化器的效果与微调单个固定优化器超参数的效果大致相同。 (iii) 虽然无法清楚地辨别出在所有测试任务中占主导地位的优化方法,但确定了一个显著减少的特定优化器和参数选择的子集,这些子集通常会在实验中产生有竞争力的结果:ADAM 仍然是一个强有力的竞争者,而较新的方法未能显著并全面优于它。
Choosing the optimizer is considered to be among the most crucial design decisions in deep learning, and it is not an easy one. The growing literature now lists hundreds of optimization methods. In the absence of clear theoretical guidance and conclusive empirical evidence, the decision is often made based on anecdotes. In this work, we aim to replace these anecdotes, if not with a conclusive ranking, then at least with evidence-backed heuristics. To do so, we perform an extensive, standardized benchmark of fifteen particularly popular deep learning optimizers while giving a concise overview of the wide range of possible choices. Analyzing more than 50,000 individual runs, we contribute the following three points: (i) Optimizer performance varies greatly across tasks. (ii) We observe that evaluating multiple optimizers with default parameters works approximately as well as tuning the hyperparameters of a single, fixed optimizer. (iii) While we cannot discern an optimization method clearly dominating across all tested tasks, we identify a significantly reduced subset of specific optimizers and parameter choices that generally lead to competitive results in our experiments: ADAM remains a strong contender, with newer methods failing to significantly and consistently outperform it. Our open-sourced results1 are available as challenging and well-tuned baselines for more meaningful evaluations of novel optimization methods without requiring any further computational efforts.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Km3IpEXAD 

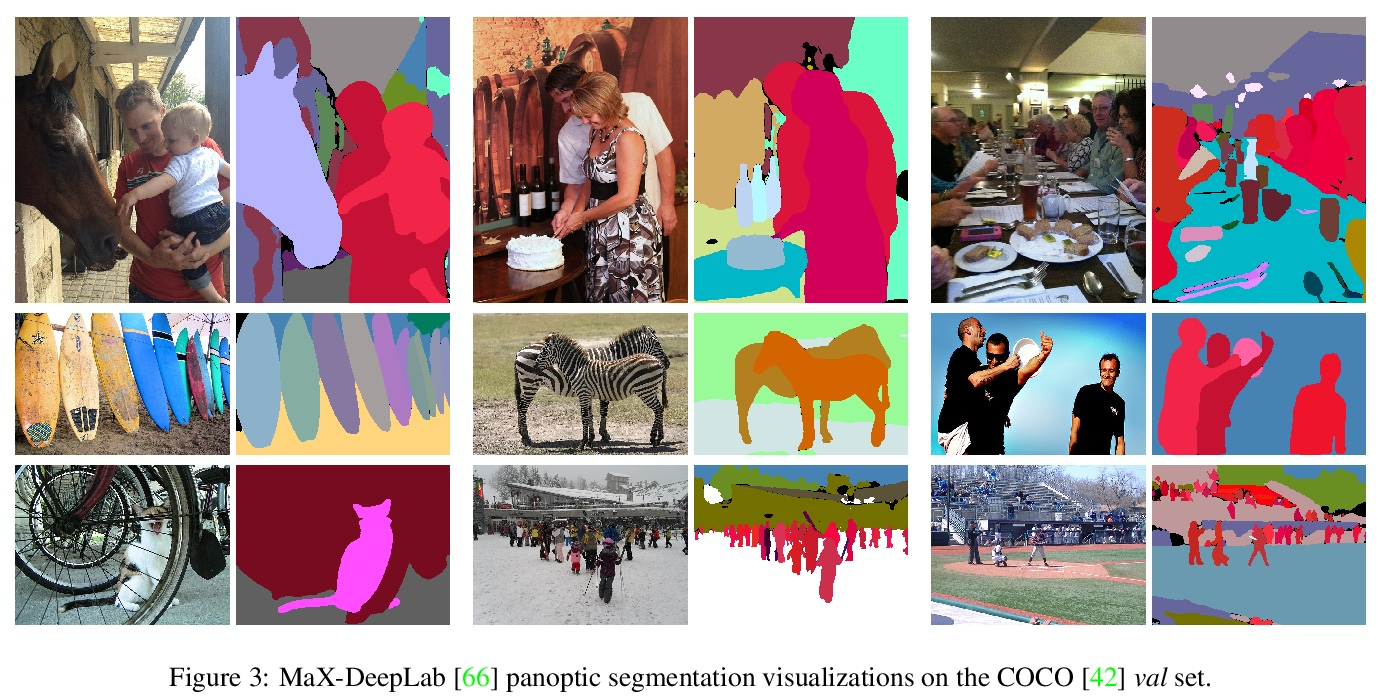
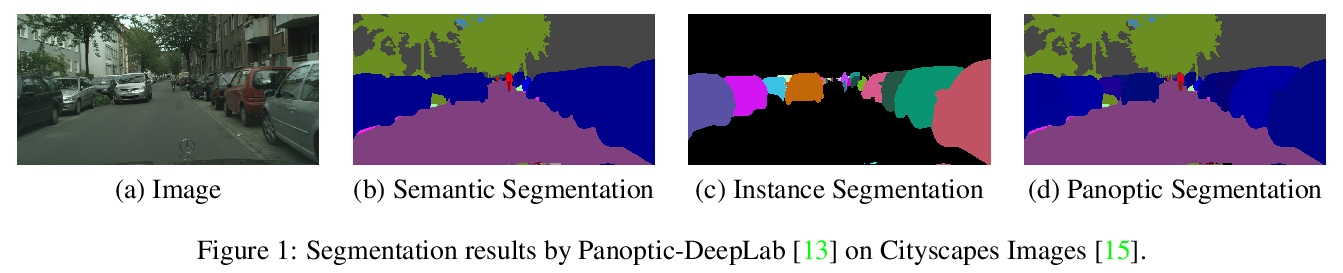
4、[CV] DeepLab2: A TensorFlow Library for Deep Labeling
M Weber, H Wang, S Qiao, J Xie, M D. Collins, Y Zhu, L Yuan, D Kim, Q Yu, D Cremers, L Leal-Taixe, A L. Yuille, F Schroff, H Adam, L Chen
[Technical University Munich & Johns Hopkins University & KAIST & Google Research]
DeepLab2:TensorFlow深度标记库。DeepLab2 是用于深度标记的 TensorFlow 库,旨在为计算机视觉中的一般密集像素预测问题提供最先进且易于使用的 TensorFlow 代码库。 DeepLab2 包括最近开发的所有带有预训练检查点的 DeepLab 模型变体及模型训练和评估代码,允许社区复制和进一步改进最先进系统。为展示 DeepLab2 的有效性,采用 AxialSWideRNet 作为网络主干的 Panoptic-DeepLab 在 Cityscaspes 验证集上实现了 68.0% PQ 或 83.5% mIoU,仅使用单尺度推理和 ImageNet-1K 预训练检查点。希望公开共享代码库可以促进未来对密集像素标记任务的研究,并设想该技术的新应用。
DeepLab2 is a TensorFlow library for deep labeling, aiming to provide a state-of-the-art and easy-to-use TensorFlow codebase for general dense pixel prediction problems in computer vision. DeepLab2 includes all our recently developed DeepLab model variants with pretrained checkpoints as well as model training and evaluation code, allowing the community to reproduce and further improve upon the state-of-art systems. To showcase the effectiveness of DeepLab2, our Panoptic-DeepLab employing AxialSWideRNet as network backbone achieves 68.0% PQ or 83.5% mIoU on Cityscaspes validation set, with only singlescale inference and ImageNet-1K pretrained checkpoints. We hope that publicly sharing our library could facilitate future research on dense pixel labeling tasks and envision new applications of this technology.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Km3MSD4L6 

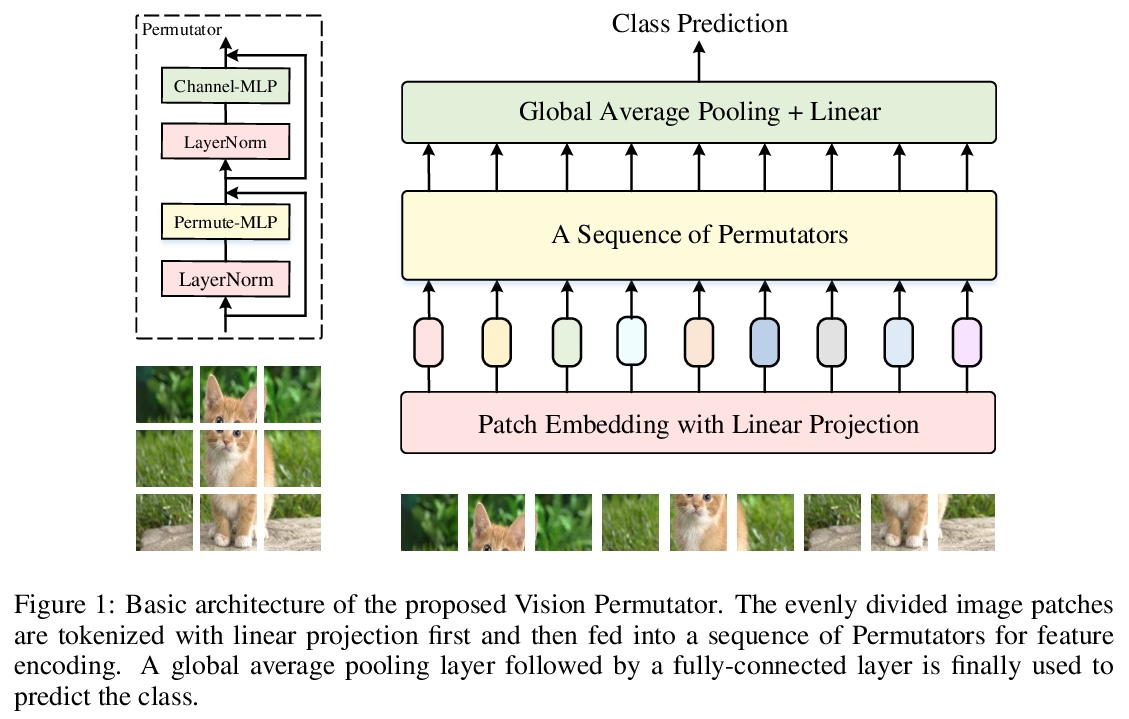
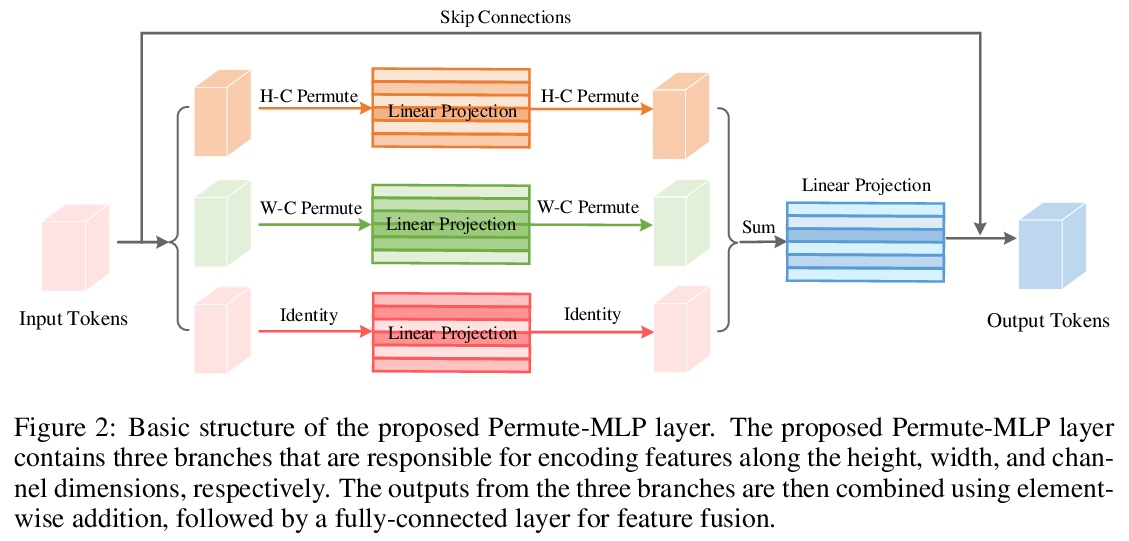
5、[CV] Vision Permutator: A Permutable MLP-Like Architecture for Visual Recognition
Q Hou, Z Jiang, L Yuan, M Cheng, S Yan, J Feng
[National University of Singapore & Nankai University & Sea AI Labs]
Vision Permutator:面向视觉识别的可置换类MLP架构。本文提出 Vision Permutator,一种概念上简单且数据高效的类 MLP 视觉识别架构。体现了 2D 特征表示所携带的位置信息的重要性,与最近的类 MLP 的模型沿展平的空间维度编码空间信息不同,Vision Permutator 用线性投影分别沿高和宽两个维度对特征表示进行编码。这允许 Vision Permutator 沿一个空间方向捕获长程依赖关系,同时沿另一个方向保留精确的位置信息。然后以互补的方式聚合所得到的位置敏感输出,以形成感兴趣目标的表达性表示。Vision Permutator 是卷积神经网络 (CNN) 和视觉 Transformer 的有力竞争对手。在不依赖空间卷积或注意力机制的情况下,Vision Permutator 在没有额外大规模训练数据(如 ImageNet-22k)的情况下,仅使用 25M 的可学习参数在 ImageNet 上实现了 81.5% 的 top-1 准确率,这比相同模型尺寸约束下的大多数 CNN 和视觉Transformer要好得多。当扩展到 88M 时,可以达到 83.2% 的 top-1 准确率。
In this paper, we present Vision Permutator, a conceptually simple and data efficient MLP-like architecture for visual recognition. By realizing the importance of the positional information carried by 2D feature representations, unlike recent MLP-like models that encode the spatial information along the flattened spatial dimensions, Vision Permutator separately encodes the feature representations along the height and width dimensions with linear projections. This allows Vision Permutator to capture long-range dependencies along one spatial direction and meanwhile preserve precise positional information along the other direction. The resulting position-sensitive outputs are then aggregated in a mutually complementing manner to form expressive representations of the objects of interest. We show that our Vision Permutators are formidable competitors to convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers. Without the dependence on spatial convolutions or attention mechanisms, Vision Permutator achieves 81.5% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet without extra large-scale training data (e.g., ImageNet-22k) using only 25M learnable parameters, which is much better than most CNNs and vision transformers under the same model size constraint. When scaling up to 88M, it attains 83.2% top-1 accuracy. We hope this work could encourage research on rethinking the way of encoding spatial information and facilitate the development of MLP-like models.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Km3PcdBcX 
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
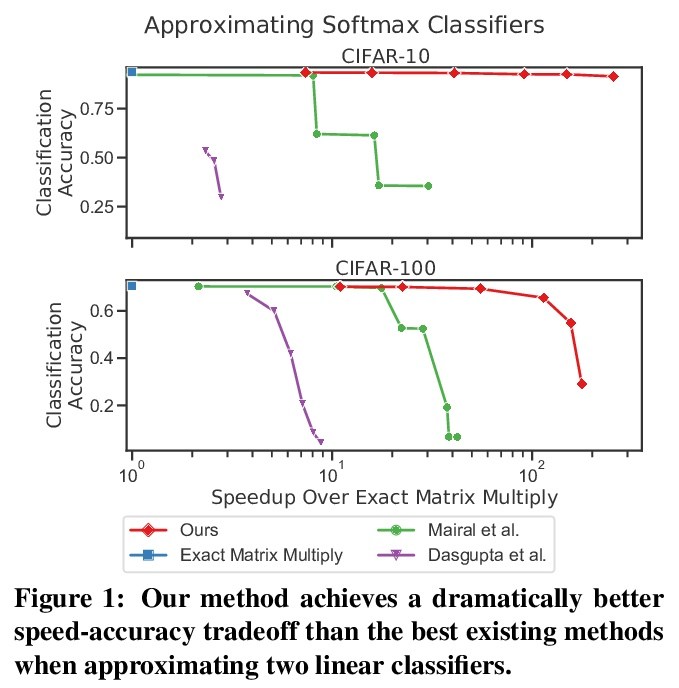
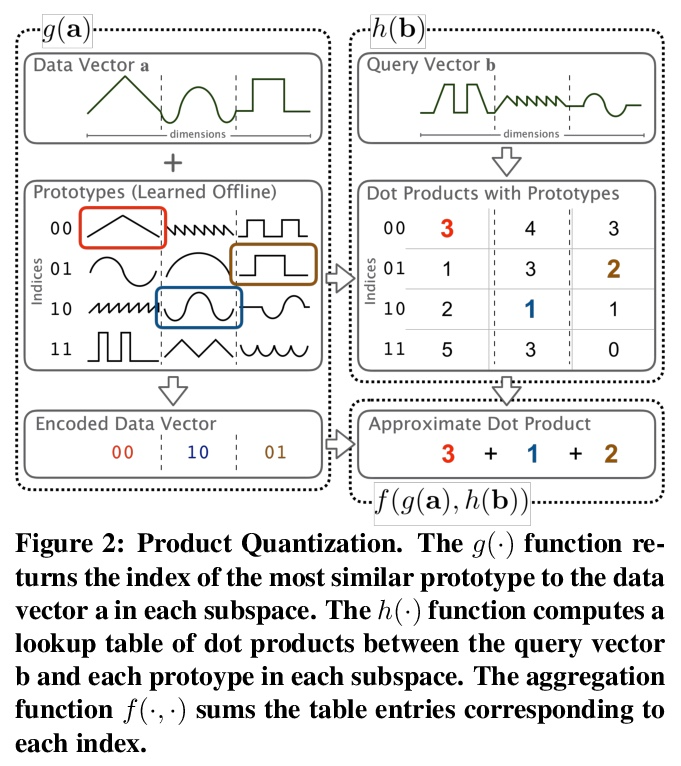
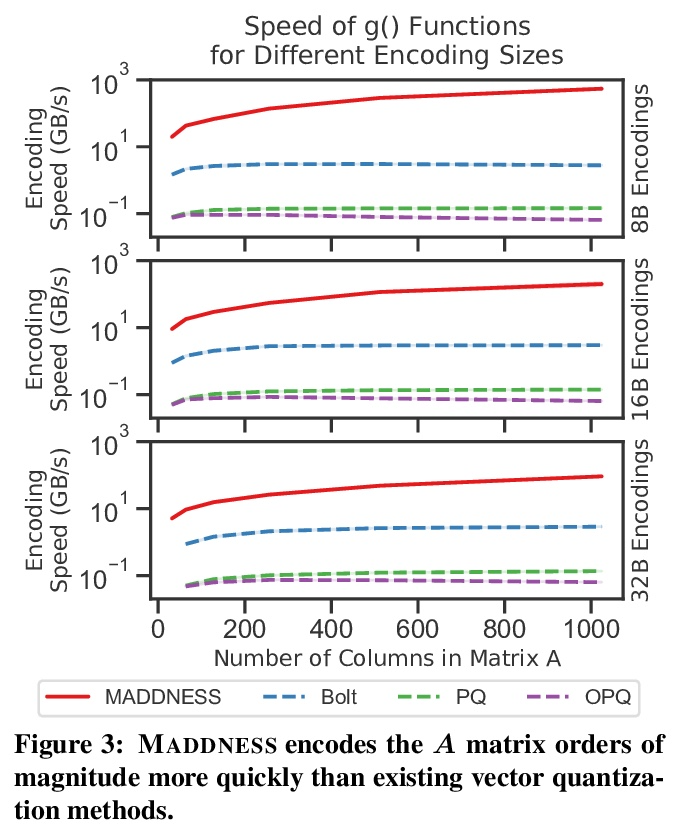
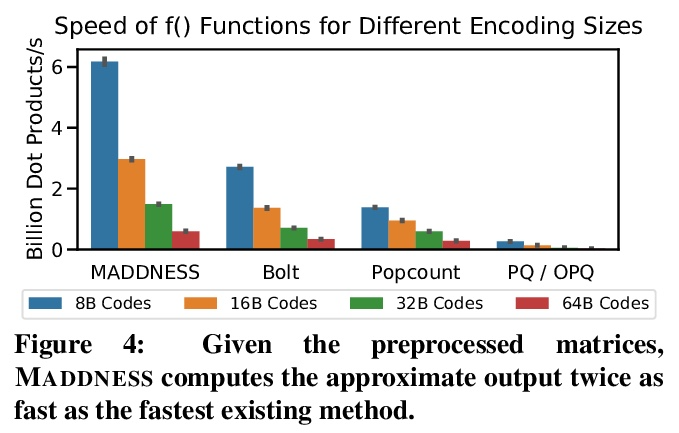
[LG] Multiplying Matrices Without Multiplying
无需相乘的高效矩阵乘法
D Blalock, J Guttag
[MosaicML & MIT CSAIL]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Km3UnmcAt 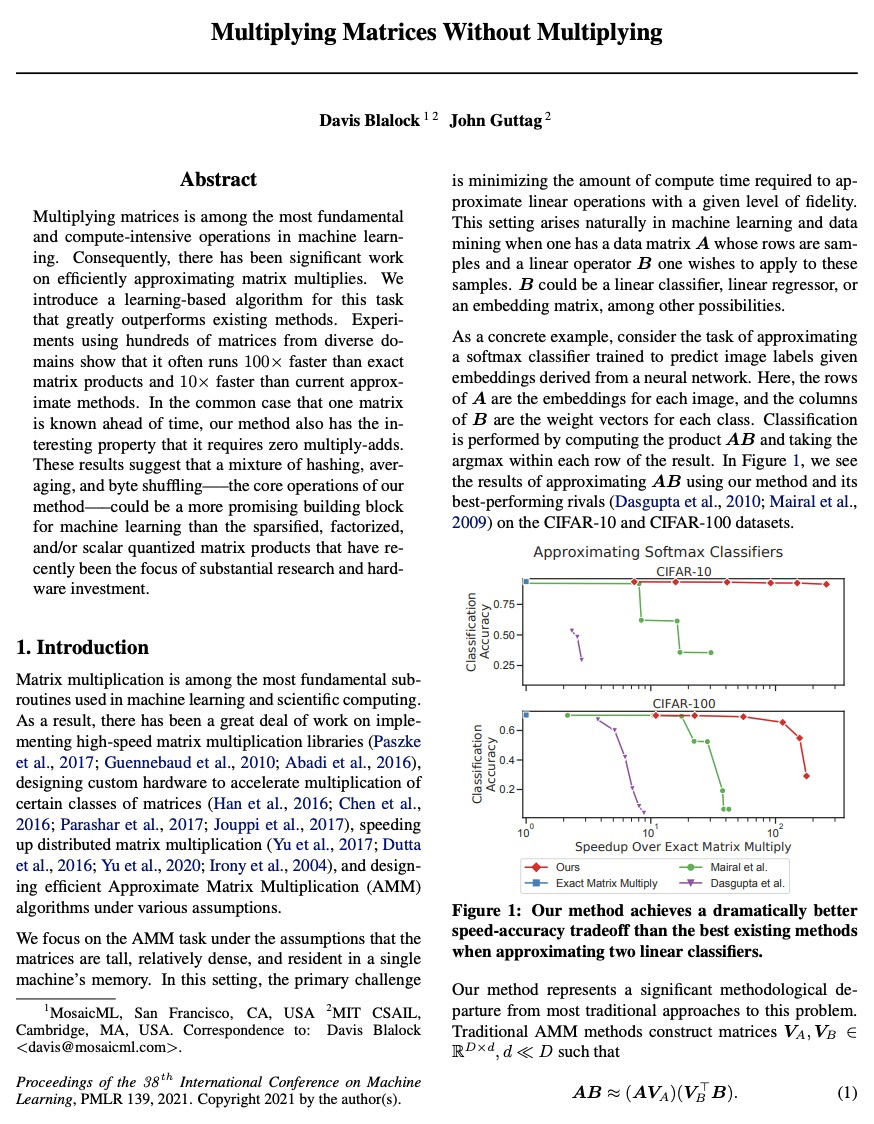
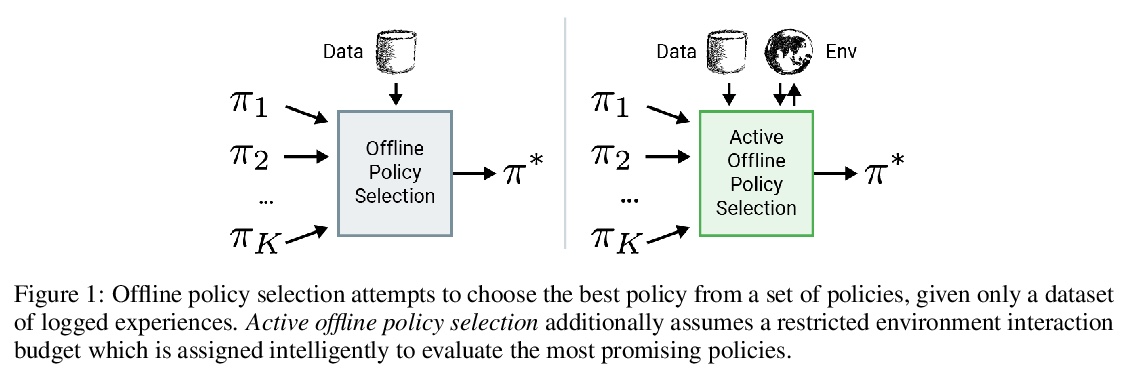
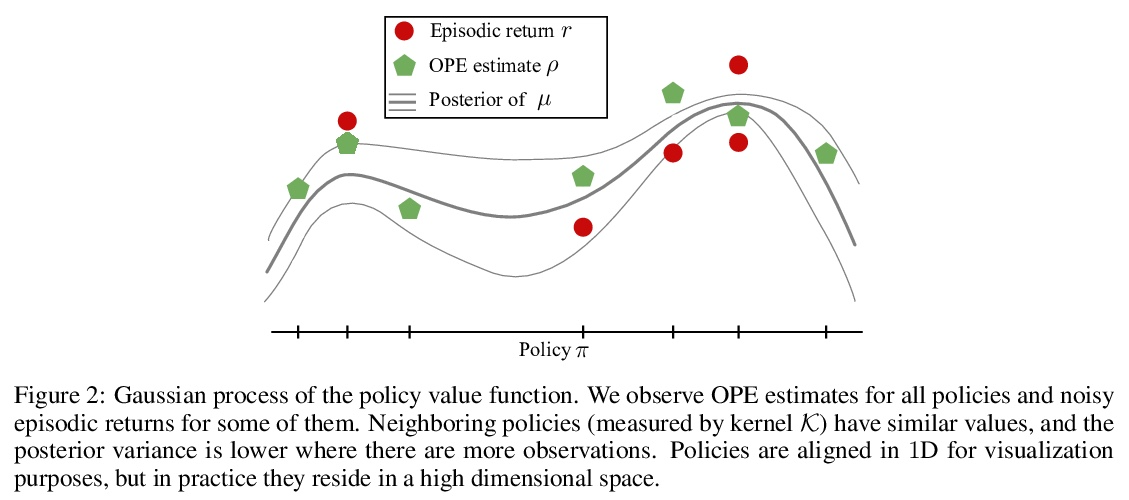
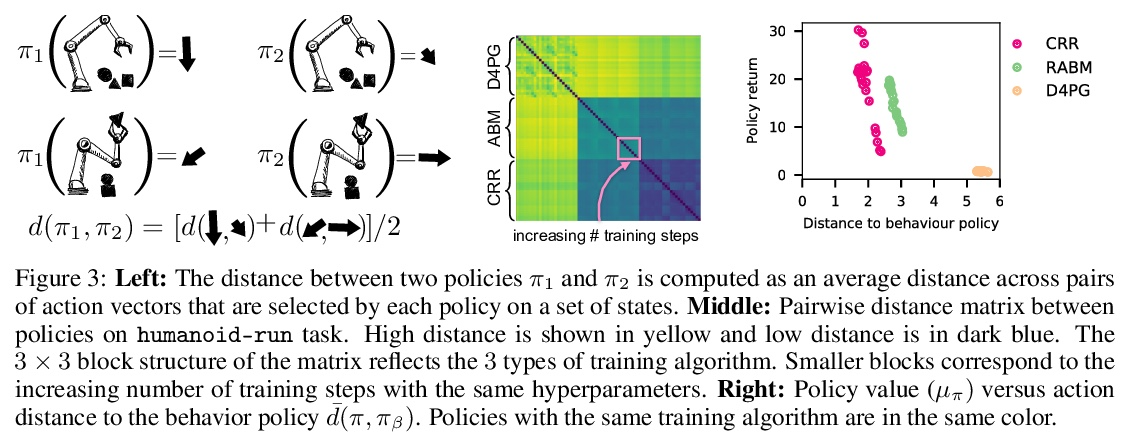
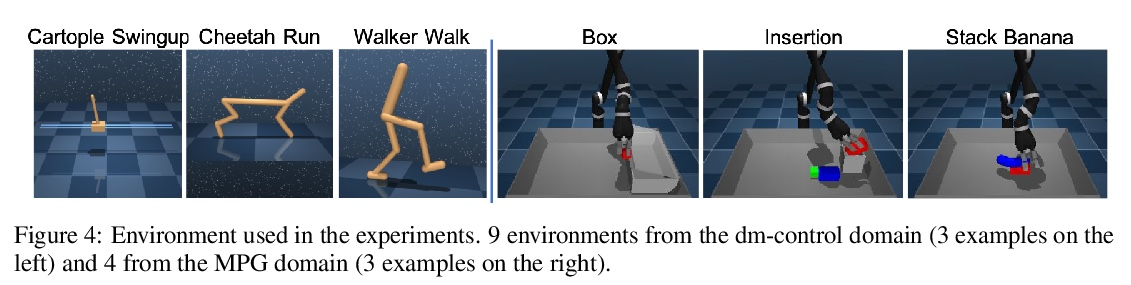
[LG] Active Offline Policy Selection
主动离线策略选择
K Konyushkova, Y Chen, T Paine, C Gulcehre, C Paduraru, D J Mankowitz, M Denil, N d Freitas
[DeepMind]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Km3WrBO4l 
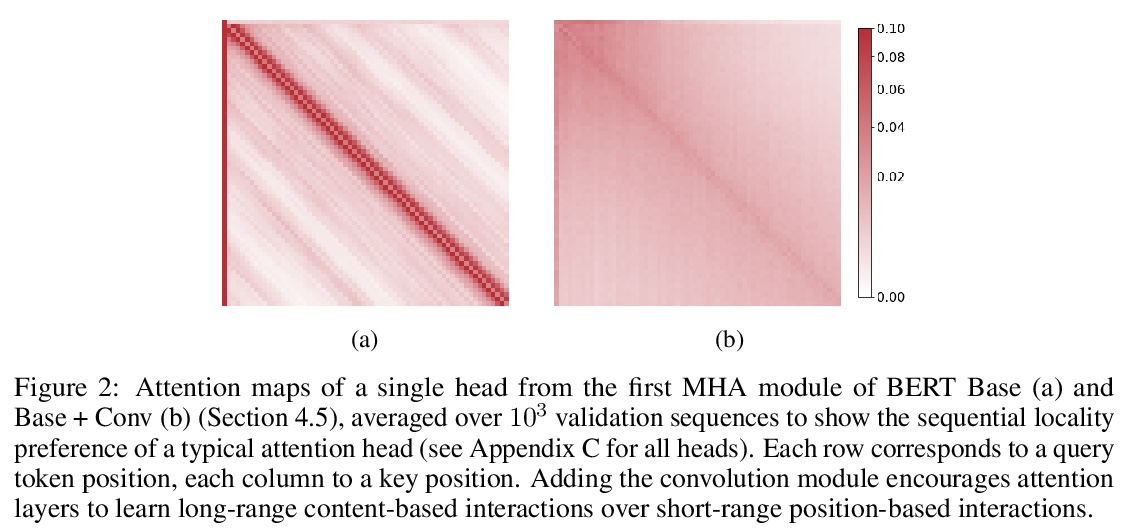
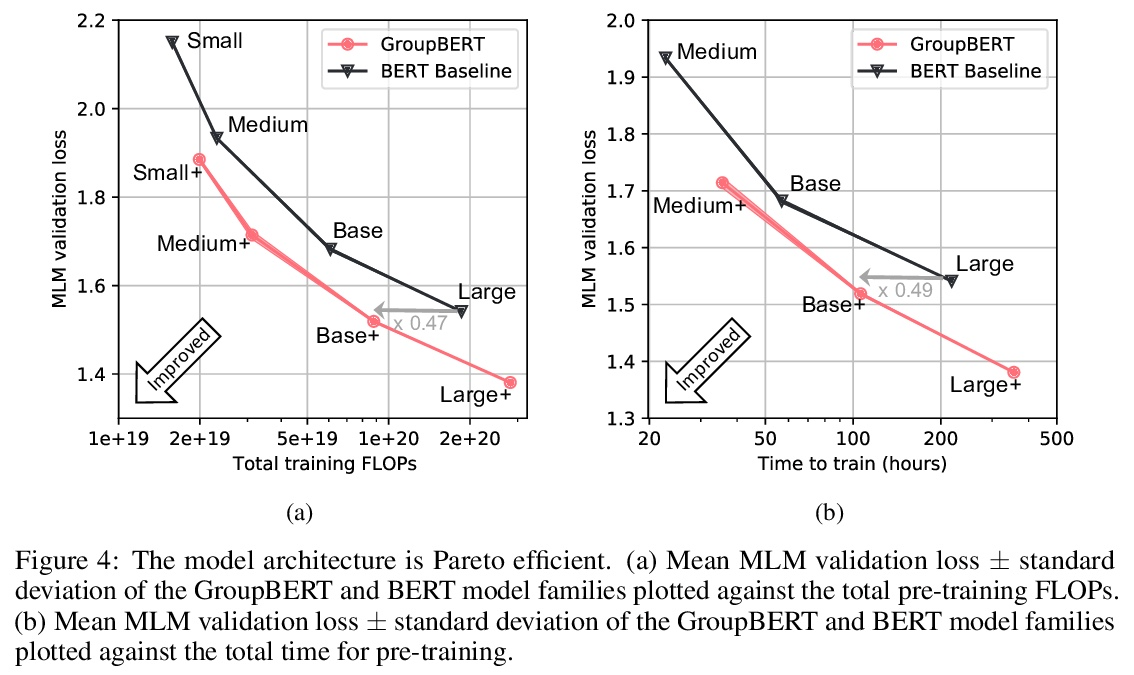
[CL] GroupBERT: Enhanced Transformer Architecture with Efficient Grouped Structures
GroupBERT:具有高效分组结构的增强型Transformer架构
I Chelombiev, D Justus, D Orr, A Dietrich, F Gressmann, A Koliousis, C Luschi
[Graphcore Research & New College of the Humanities]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Km3XPFvdF 


[LG] Learning Knowledge Graph-based World Models of Textual Environments
文本环境基于知识图谱世界模型学习
P Ammanabrolu, M O. Riedl
[Georgia Institute of Technology]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Km3ZbgVpu