- 1、[CV] MERLOT: Multimodal Neural Script Knowledge Models
- 2、[LG] Tabular Data: Deep Learning is Not All You Need
- 3、[RO] Motion Planning Transformers: One Model to Plan Them All
- 4、[LG] Learning to Efficiently Sample from Diffusion Probabilistic Models
- 5、[CV] 3DB: A Framework for Debugging Computer Vision Models
- [LG] The Inductive Bias of Quantum Kernels
- [CV] Refiner: Refining Self-attention for Vision Transformers
- [LG] BayesIMP: Uncertainty Quantification for Causal Data Fusion
- [CV] SIMONe: View-Invariant, Temporally-Abstracted Object Representations via Unsupervised Video Decomposition
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CV] MERLOT: Multimodal Neural Script Knowledge Models
R Zellers, X Lu, J Hessel, Y Yu, J S Park, J Cao, A Farhadi, Y Choi
[University of Washington & Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence]
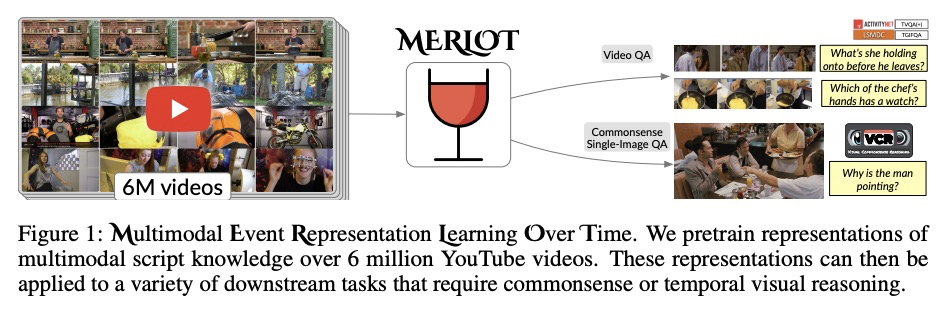
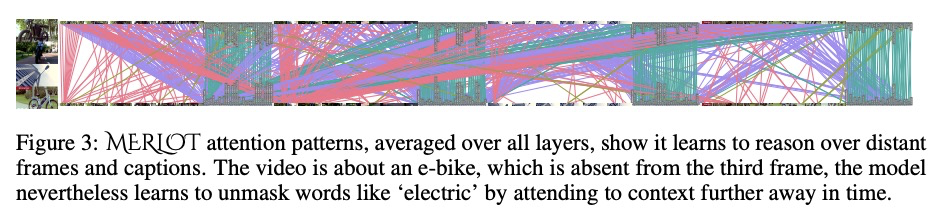
MERLOT:多模态神经脚本知识模型。人类观察事件的视觉上下文,进行跨时间的多模态推理,对过去、现在和未来做出推断,进而理解世界。本文提出MERLOT,通过观看数以百万计的YouTube视频和转录语音,来学习多模态脚本知识的模型——以一种完全无标记、自监督的方式。通过对帧级(空间)和视频级(时间)目标的混合预训练,模型不仅学会了将图像与时间上对应的词语相匹配,还学会了将全局发生的事件与时间相联系,表现出强大的开箱即用的时间常识表示,微调后在12个不同的视频问答保证数据集上实现了最先进的性能,能很好地迁移到静态图像世界,允许模型推理视觉场景背后的动态上下文。在视觉共感推理中,MERLOT以80.6%的准确率回答问题,比类似规模的先进模型高出3%以上,即使是那些大量使用辅助监督数据(如物体边框)的模型。消融分析显示了以下的互补重要性:1)在视频与静态图像上进行训练;2)扩大预训练视频语料库的规模和多样性;3)使用不同的目标,鼓励从识别到认知层面的全栈多模态推理。
As humans, we understand events in the visual world contextually, performing multimodal reasoning across time to make inferences about the past, present, and future. We introduce MERLOT, a model that learns multimodal script knowledge by watching millions of YouTube videos with transcribed speech – in an entirely label-free, self-supervised manner. By pretraining with a mix of both framelevel (spatial) and video-level (temporal) objectives, our model not only learns to match images to temporally corresponding words, but also to contextualize what is happening globally over time. As a result, MERLOT exhibits strong out-of-the-box representations of temporal commonsense, and achieves state-ofthe-art performance on 12 different video QA datasets when finetuned. It also transfers well to the world of static images, allowing models to reason about the dynamic context behind visual scenes. On Visual Commonsense Reasoning, MERLOT answers questions correctly with 80.6% accuracy, outperforming stateof-the-art models of similar size by over 3%, even those that make heavy use of auxiliary supervised data (like object bounding boxes). Ablation analyses demonstrate the complementary importance of: 1) training on videos versus static images; 2) scaling the magnitude and diversity of the pretraining video corpus; and 3) using diverse objectives that encourage full-stack multimodal reasoning, from the recognition to cognition level.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjjOkiGH3

2、[LG] Tabular Data: Deep Learning is Not All You Need
R Shwartz-Ziv, A Armon
[Intel]
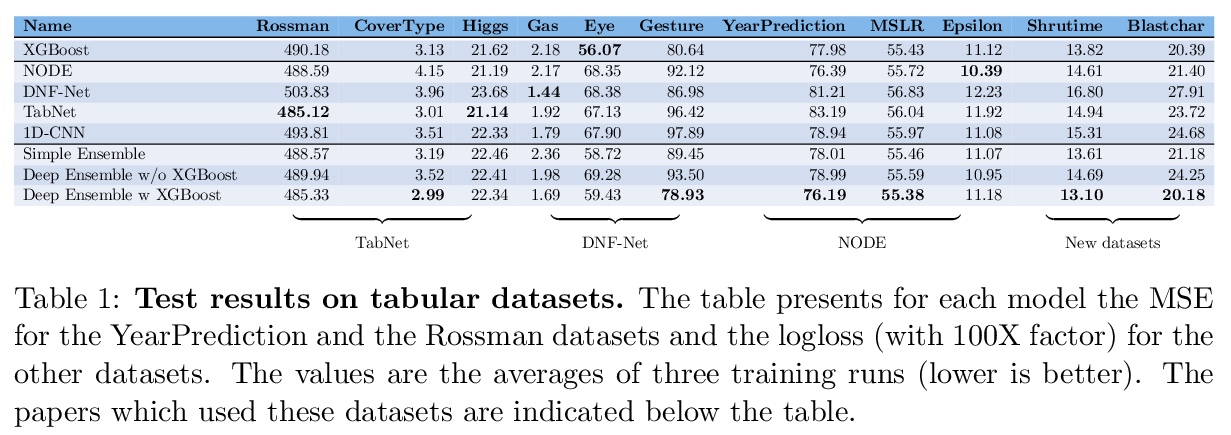
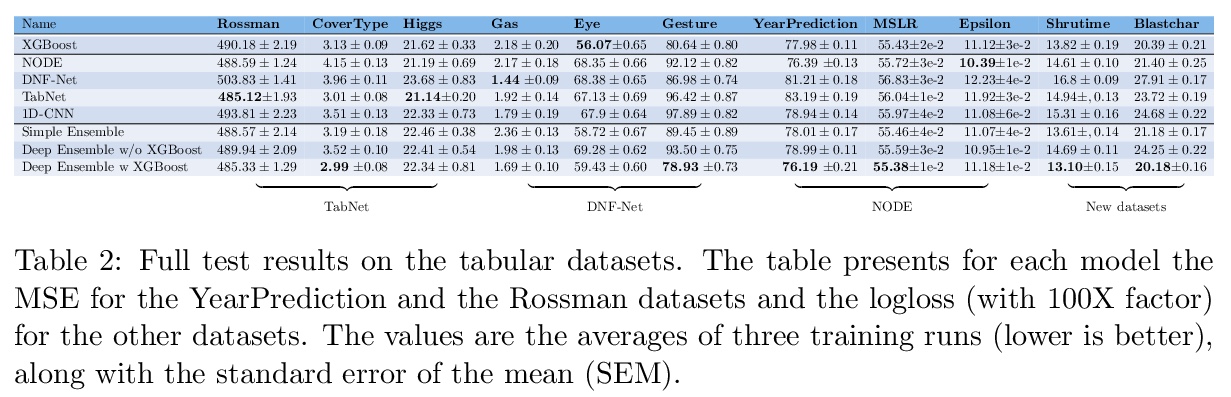
表格数据:未必要深度学习。AutoML系统的一个关键因素,是设置用于每种类型任务的模型类型。对于表格数据的分类和回归问题,通常建议使用树集成模型(如XGBoost)。最近有人提出了几种用于表格数据的深度学习模型,声称在某些使用情况下比XGBoost更出色。本文通过在各种数据集上严格比较新的深度模型和XGBoost,探讨这些深度模型是否应该成为表格数据的推荐选项。除了系统地比较它们的准确性外,还考虑了它们所需要的微调和计算。研究表明,XGBoost在各种数据集上的表现都优于这些深度模型,包括提出这些深度模型的论文中使用的数据集,XGBoost需要的微调要少得多。在积极的方面,深度模型和XGBoost的集成在这些数据集上的表现比XGBoost单独的表现更好。
A key element of AutoML systems is setting the types of models that will be used for each type of task. For classification and regression problems with tabular data, the use of tree ensemble models (like XGBoost) is usually recommended. However, several deep learning models for tabular data have recently been proposed, claiming to outperform XGBoost for some use-cases. In this paper, we explore whether these deep models should be a recommended option for tabular data, by rigorously comparing the new deep models to XGBoost on a variety of datasets. In addition to systematically comparing their accuracy, we consider the tuning and computation they require. Our study shows that XGBoost outperforms these deep models across the datasets, including datasets used in the papers that proposed the deep models. We also demonstrate that XGBoost requires much less tuning. On the positive side, we show that an ensemble of the deep models and XGBoost performs better on these datasets than XGBoost alone.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjjSBDE56
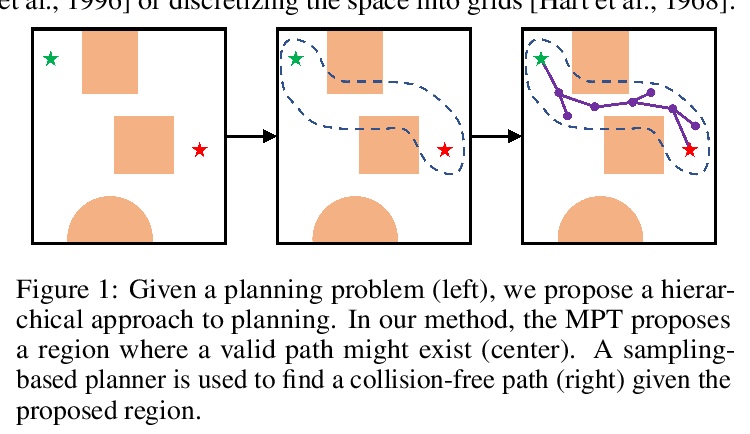
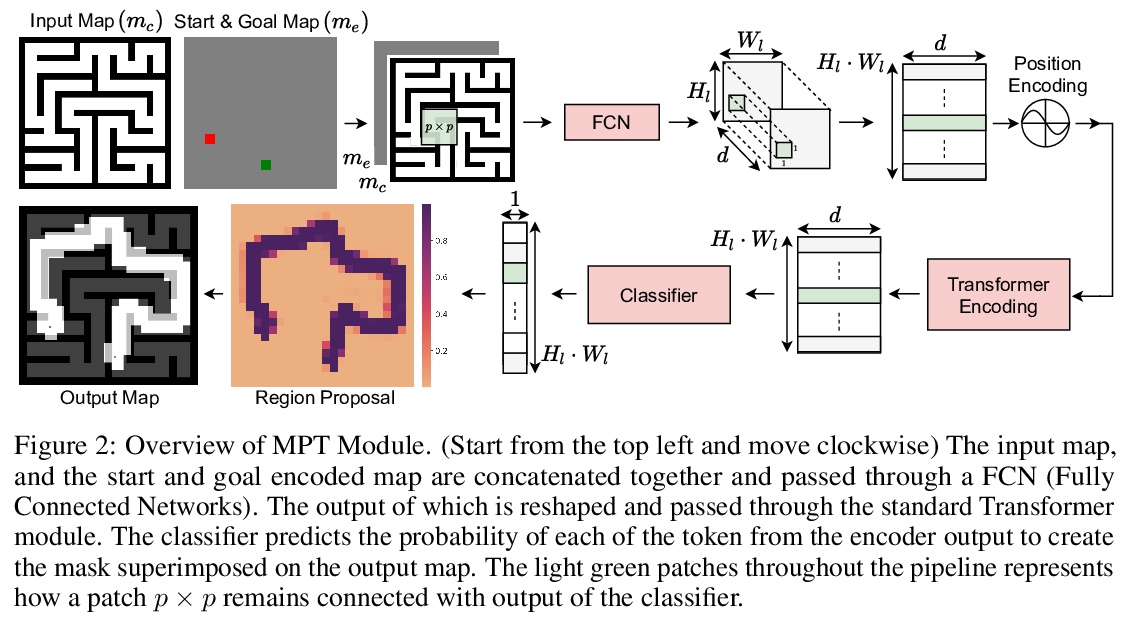
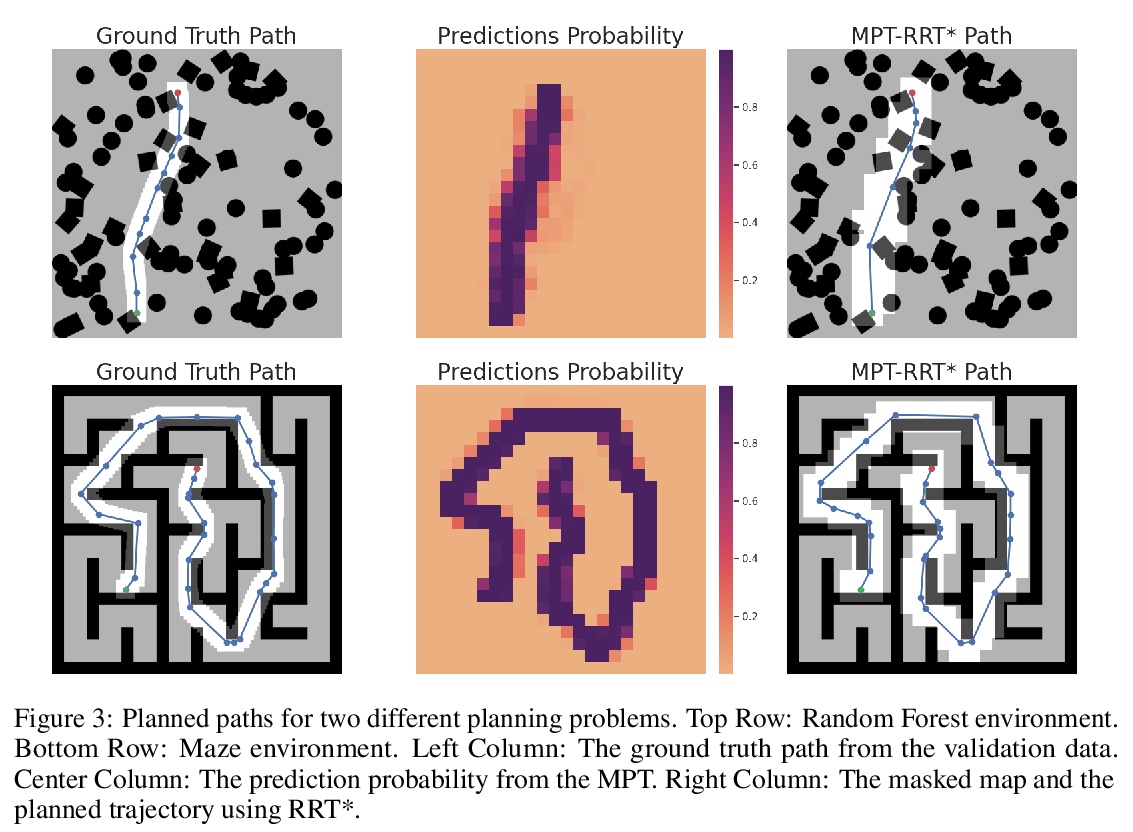
3、[RO] Motion Planning Transformers: One Model to Plan Them All
J J. Johnson, L Li, A H. Qureshi, M C. Yip
[University of California San Diego]
运动规划Transformer:单个模型全盘规划。Transformer已经成为自然语言处理的动力来源,最近在计算机视觉任务中也发现了它的用途,其对注意力的有效利用也适用于其他场景。本文提出一种基于Transformer的方法,用来有效解决复杂的运动规划问题。传统的基于神经网络的运动规划,用卷积网络对规划空间进行编码,但这些方法仅限于固定地图大小,在真实世界中往往是不现实的。本方法用Transformer识别地图上的区域,以提供对可能包括最佳路径的地图区域的关注,应用局部规划器来生成最终的无碰撞路径。在各种随机生成的具有不同地图大小的环境中验证了该方法,证明了规划复杂度的降低,并达到了与传统规划器相当的精度。
Transformers have become the powerhouse of natural language processing and recently found use in computer vision tasks. Their effective use of attention can be used in other contexts as well, and in this paper, we propose a transformer-based approach for efficiently solving the complex motion planning problems. Traditional neural network-based motion planning uses convolutional networks to encode the planning space, but these methods are limited to fixed map sizes, which is often not realistic in the real-world. Our approach first identifies regions on the map using transformers to provide attention to map areas likely to include the best path, and then applies local planners to generate the final collision-free path. We validate our method on a variety of randomly generated environments with different map sizes, demonstrating reduction in planning complexity and achieving comparable accuracy to traditional planners.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjjX7tzPm
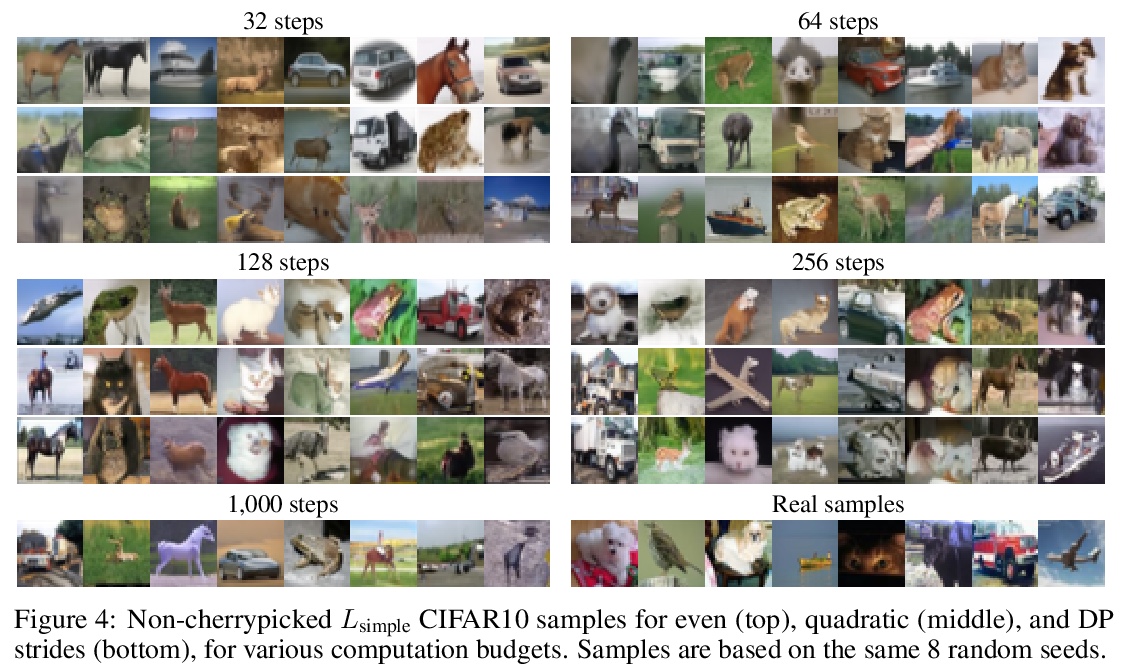
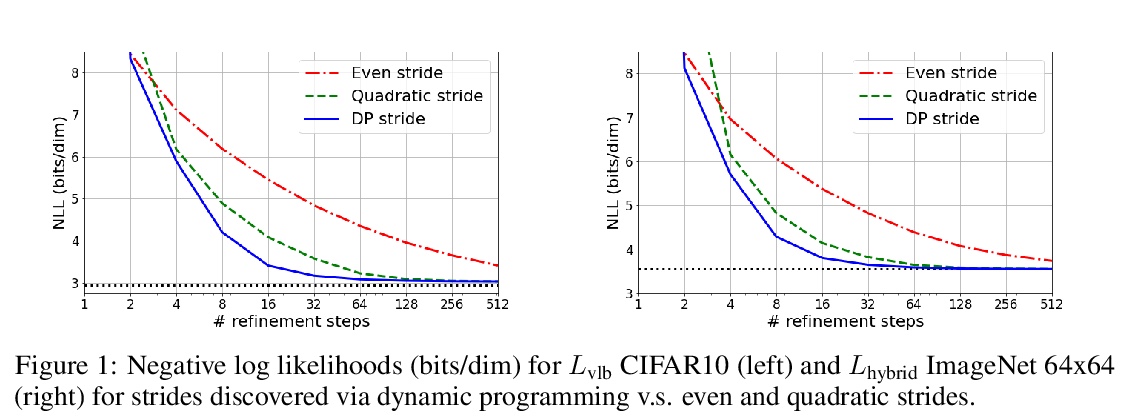
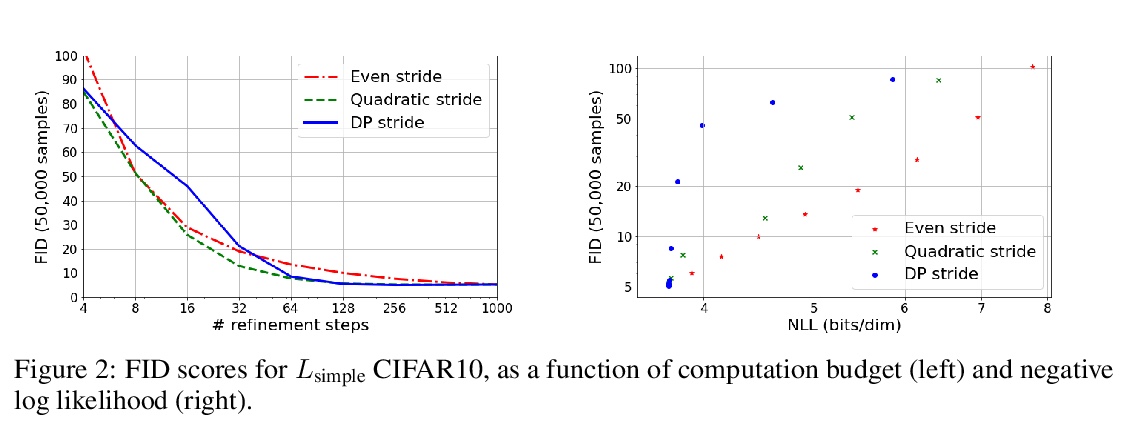
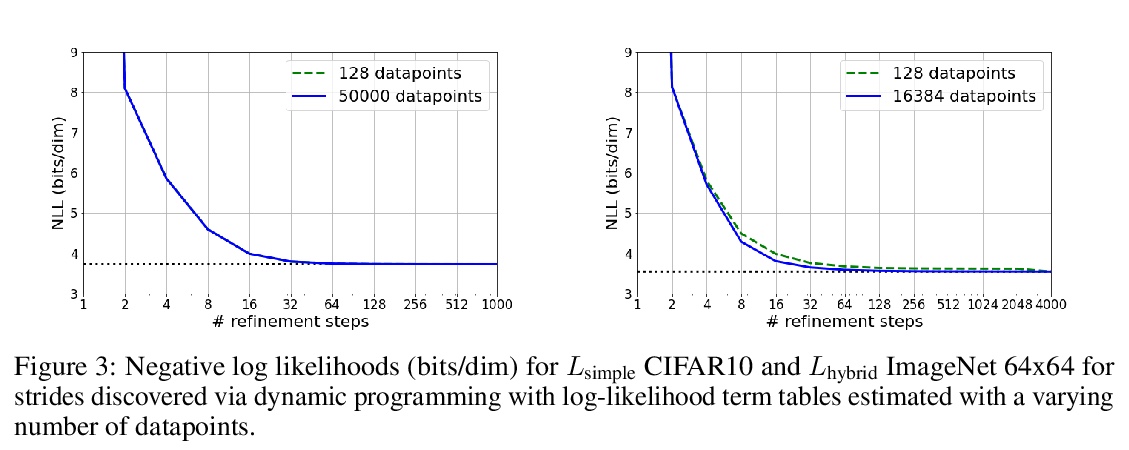
4、[LG] Learning to Efficiently Sample from Diffusion Probabilistic Models
D Watson, J Ho, M Norouzi, W Chan
[Google Research]
扩散概率模型高效采样学习。去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)已经成为一个强大的生成模型族,可以在图像和语音合成等领域产生高保真的样本和有竞争力的对数似然。DDPM的主要优势包括:与生成式对抗网络相比,更易于训练;与自回归模型相比,生成速度更快。然而,DDPM通常需要数百到数千个步骤来生成一个高保真样本,对高维问题成本过高。幸运的是,DDPM可通过调整细化步骤数量作为后处理,以样本质量换取生成速度。之前的工作已经成功地通过试错来手动安排时间表来提高生成速度。本文将推理时间表的选择视为优化问题,引入一个精确的动态规划算法,为任意预训练DDPM找到最佳离散时间表。本方法利用了ELBO可以被分解为独立的KL项的事实,在给定任何计算预算的情况下,可准确发现使训练ELBO最大化的时间表。该方法是高效的,没有自己的超参数,可应用于任何预训练DDPM,而不需要重新训练。推理时间表只需要32个细化步骤,与ImageNet 64x64上使用的默认4000个步骤相比,每一维牺牲了不到0.1个比特。
Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPMs) have emerged as a powerful family of generative models that can yield high-fidelity samples and competitive loglikelihoods across a range of domains, including image and speech synthesis. Key advantages of DDPMs include ease of training, in contrast to generative adversarial networks, and speed of generation, in contrast to autoregressive models. However, DDPMs typically require hundreds-to-thousands of steps to generate a high fidelity sample, making them prohibitively expensive for high dimensional problems. Fortunately, DDPMs allow trading generation speed for sample quality through adjusting the number of refinement steps as a post process. Prior work has been successful in improving generation speed through handcrafting the time schedule by trial and error. We instead view the selection of the inference time schedules as an optimization problem, and introduce an exact dynamic programming algorithm that finds the optimal discrete time schedules for any pre-trained DDPM. Our method exploits the fact that ELBO can be decomposed into separate KL terms, and given any computation budget, discovers the time schedule that maximizes the training ELBO exactly. Our method is efficient, has no hyper-parameters of its own, and can be applied to any pre-trained DDPM with no retraining. We discover inference time schedules requiring as few as 32 refinement steps, while sacrificing less than 0.1 bits per dimension compared to the default 4,000 steps used on ImageNet 64x64 [Ho et al., 2020, Nichol and Dhariwal, 2021].
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjjZaBE3i

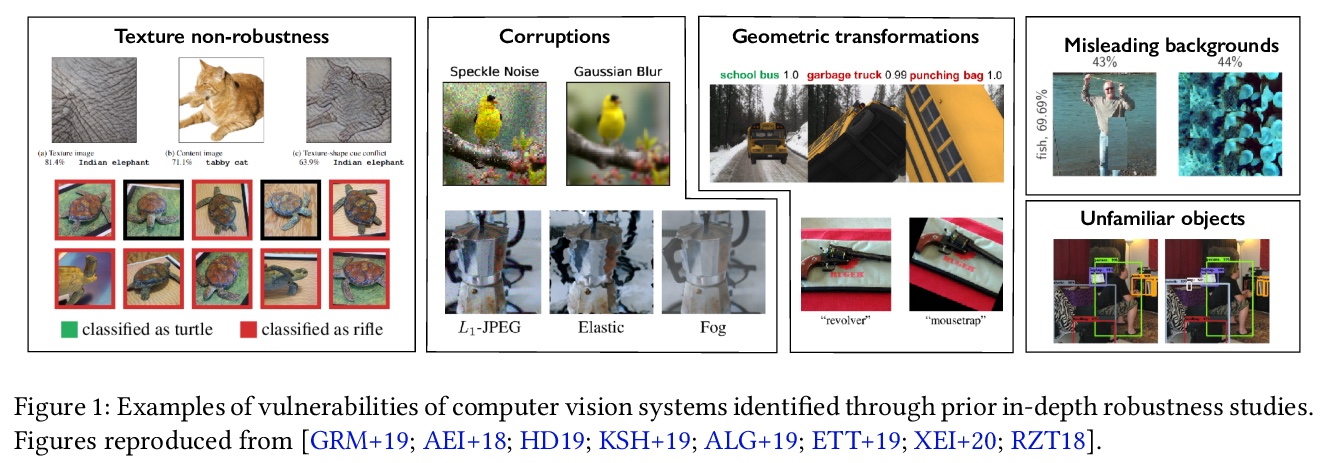
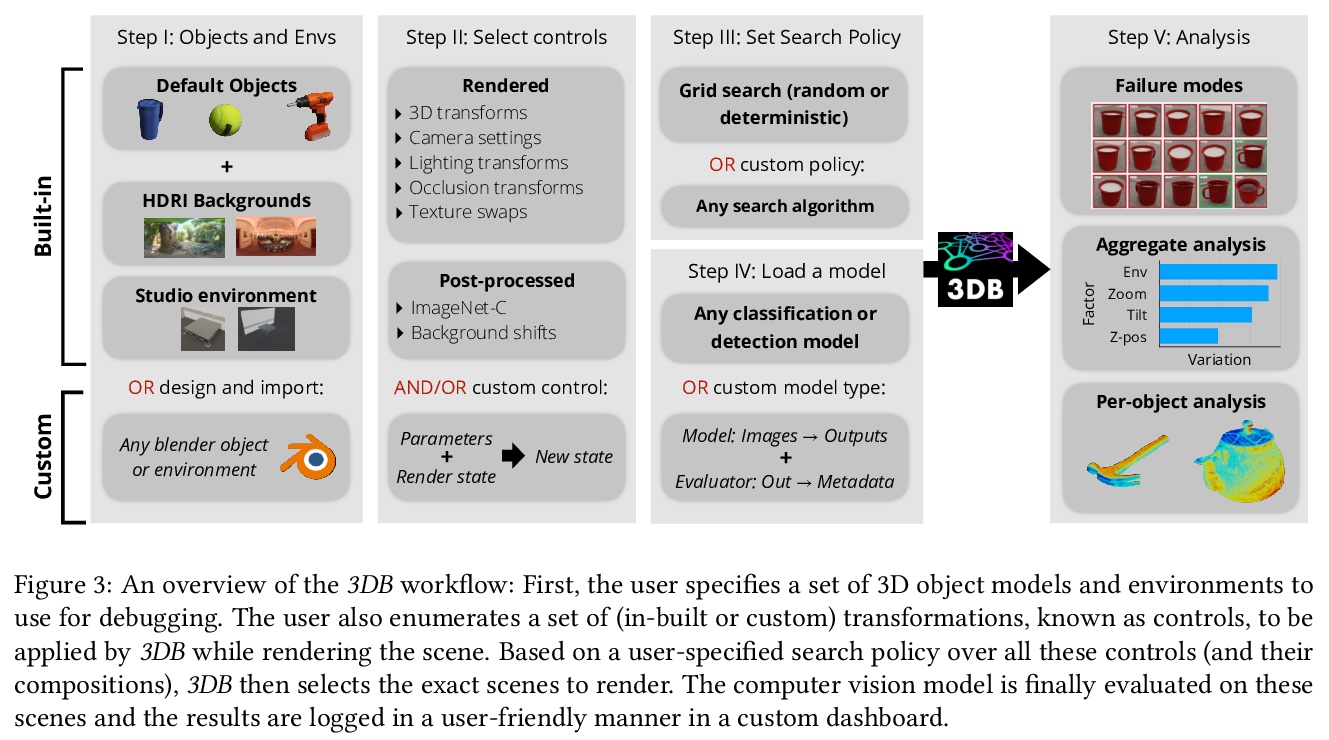
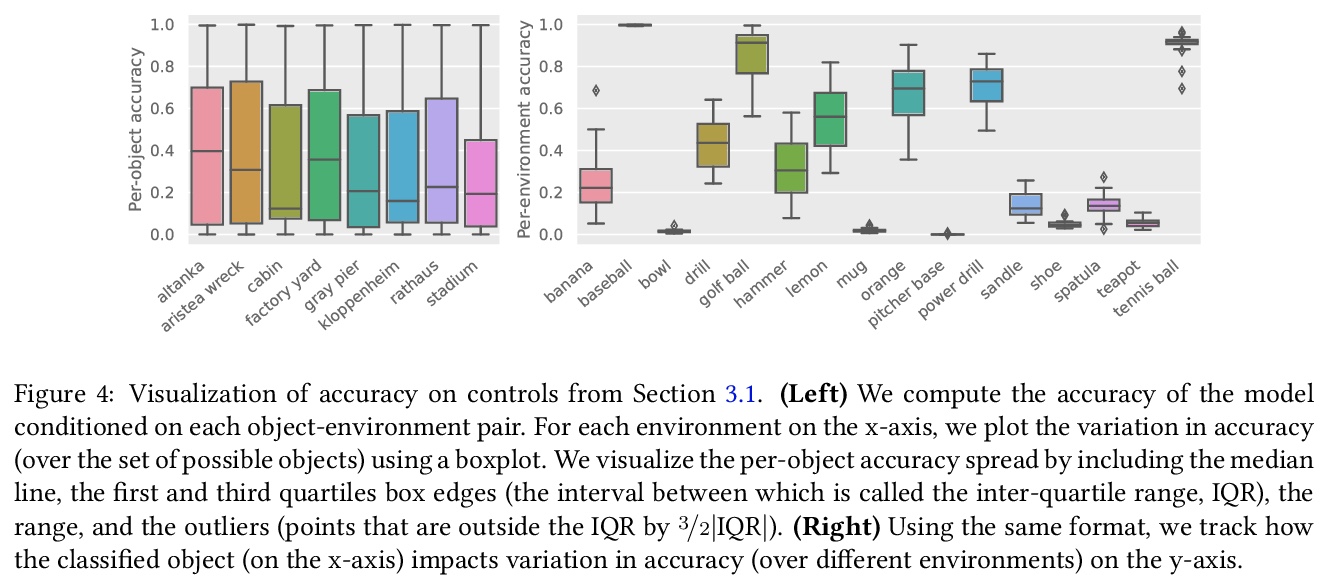
5、[CV] 3DB: A Framework for Debugging Computer Vision Models
G Leclerc, H Salman, A Ilyas, S Vemprala, L Engstrom, V Vineet, K Xiao, P Zhang, S Santurkar, G Yang, A Kapoor, A Madry
[MIT & Microsoft Research]
3DB:计算机视觉模型调试框架,一种可扩展的统一框架,可以用逼真的仿真测试和调试视觉模型。通过广泛的使用案例证明,3DB允许用户发现计算机视觉系统中的漏洞,并深入了解模型如何做出决策。3DB捕捉并概括了之前工作中的许多鲁棒性分析,使人们能研究它们的相互作用。该系统产生的洞察力可以迁移到物理世界。
We introduce 3DB: an extendable, uni ed framework for testing and debugging vision models using photorealistic simulation. We demonstrate, through a wide range of use cases, that 3DB allows users to discover vulnerabilities in computer vision systems and gain insights into how models make decisions. 3DB captures and generalizes many robustness analyses from prior work, and enables one to study their interplay. Finally, we nd that the insights generated by the system transfer to the physical world. We are releasing 3DB as a library alongside a set of example analyses, guides, and documentation.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kjk3IcXl9

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
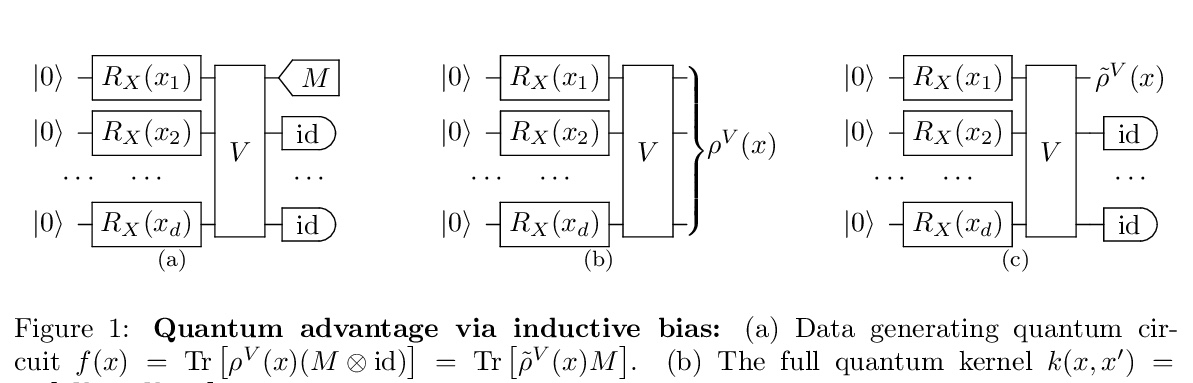
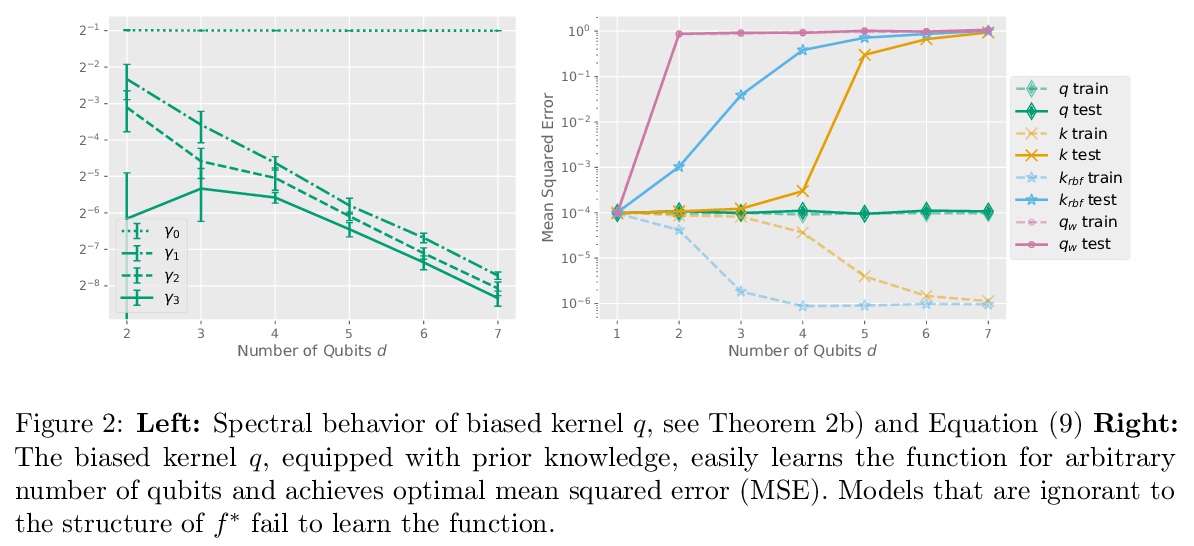
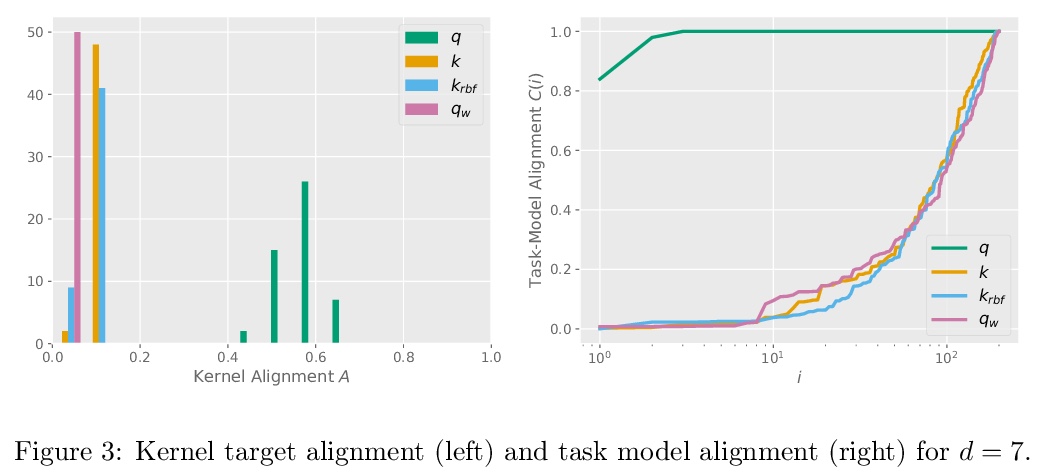
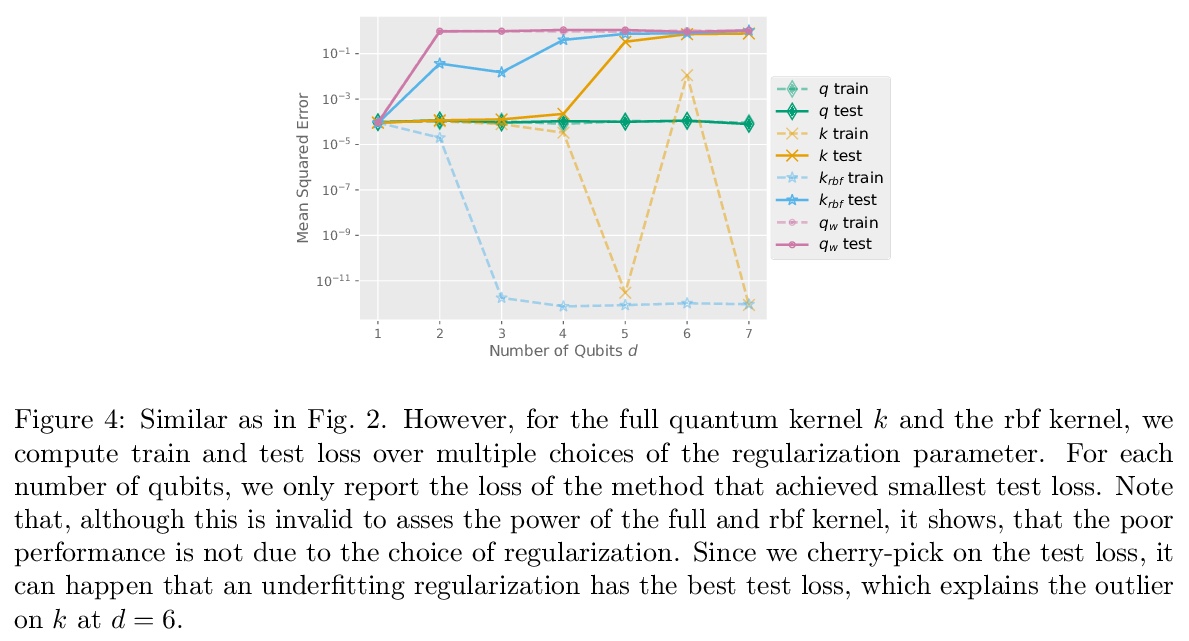
[LG] The Inductive Bias of Quantum Kernels
量子核的归纳偏差
J M. Kübler, S Buchholz, B Schölkopf
[Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KjjVHe6x4
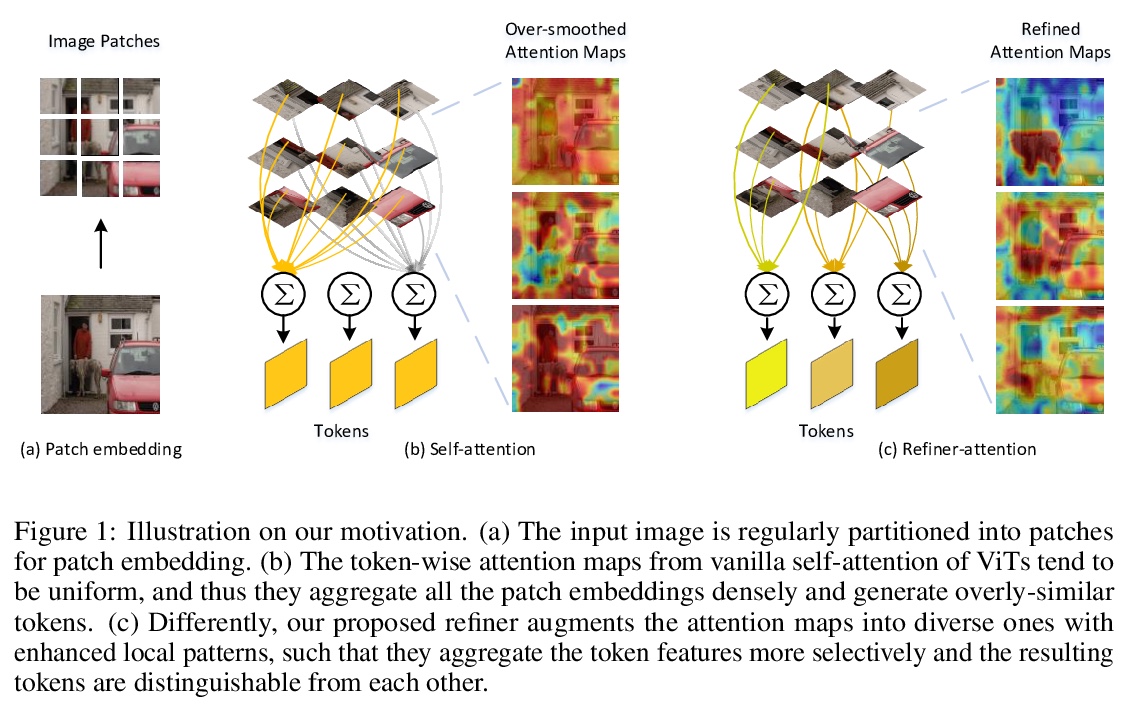
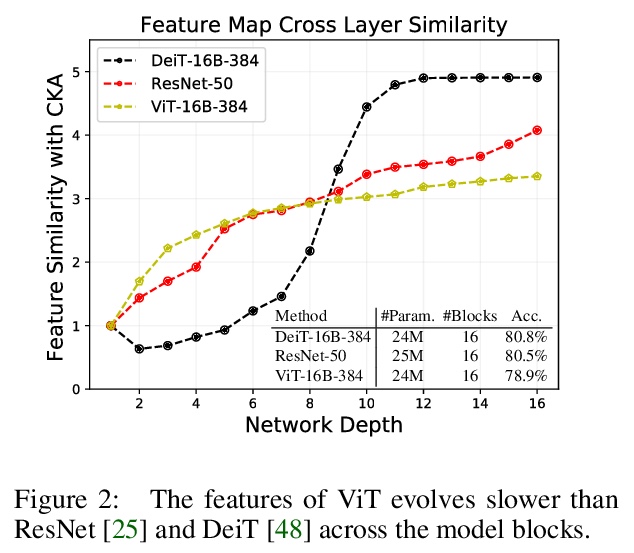
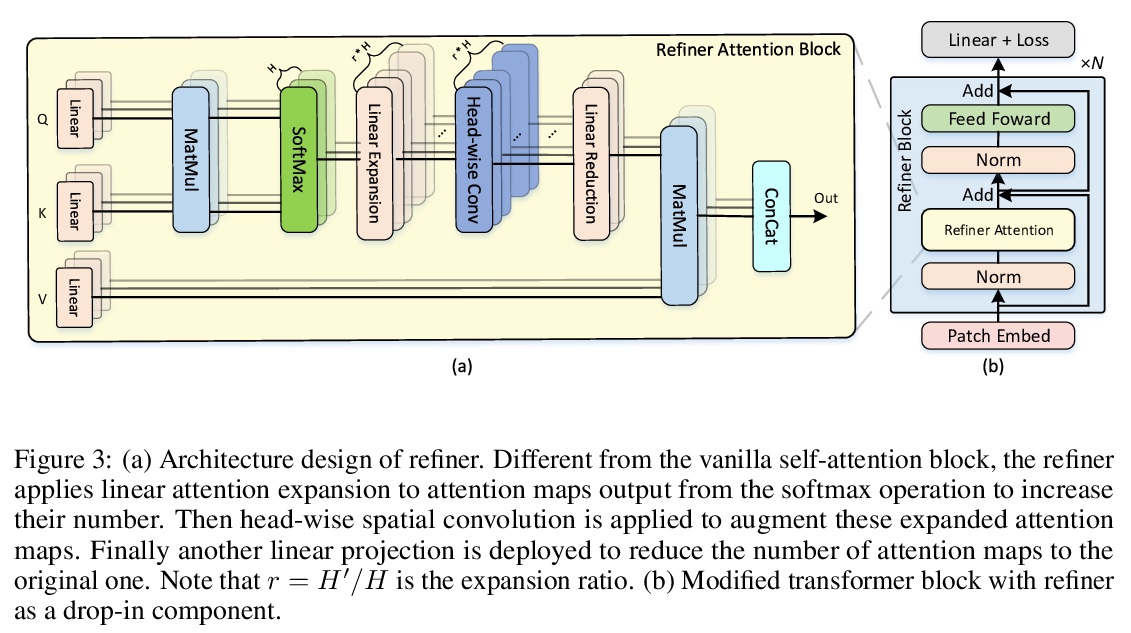
[CV] Refiner: Refining Self-attention for Vision Transformers
Refiner:提炼视觉Transformer的自注意力
D Zhou, Y Shi, B Kang, W Yu, Z Jiang, Y Li, X Jin, Q Hou, J Feng
[National University of Singapore]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kjk6ccg2G

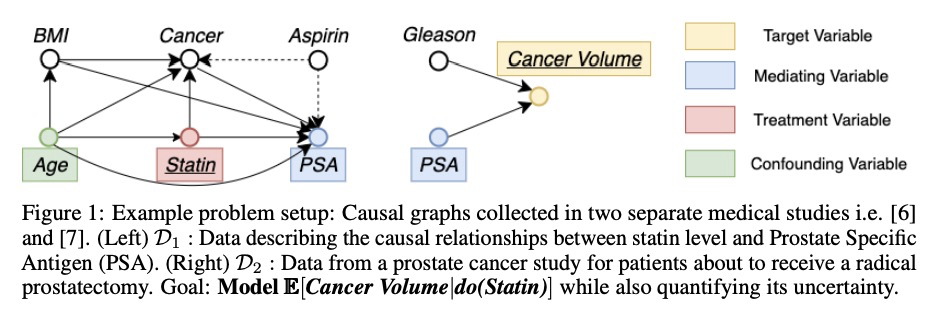
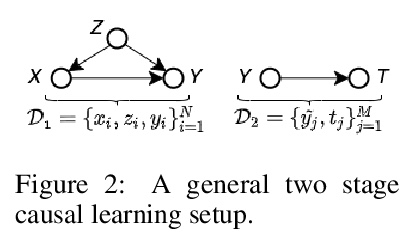
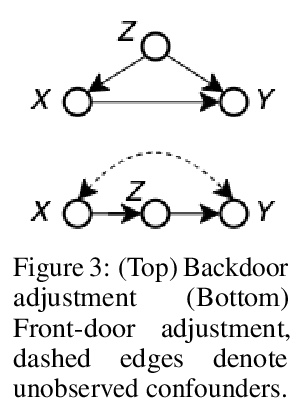
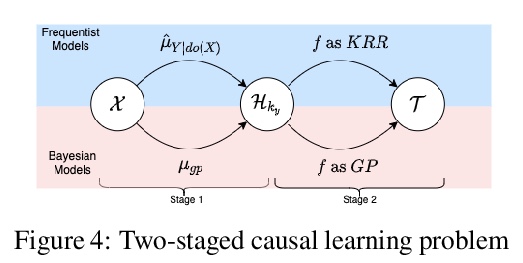
[LG] BayesIMP: Uncertainty Quantification for Causal Data Fusion
BayesIMP:因果数据融合不确定性量化
S L Chau, J Ton, J González, Y W Teh, D Sejdinovic
[University of Oxford & Microsoft Research Cambridge]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kjk7qFLKh
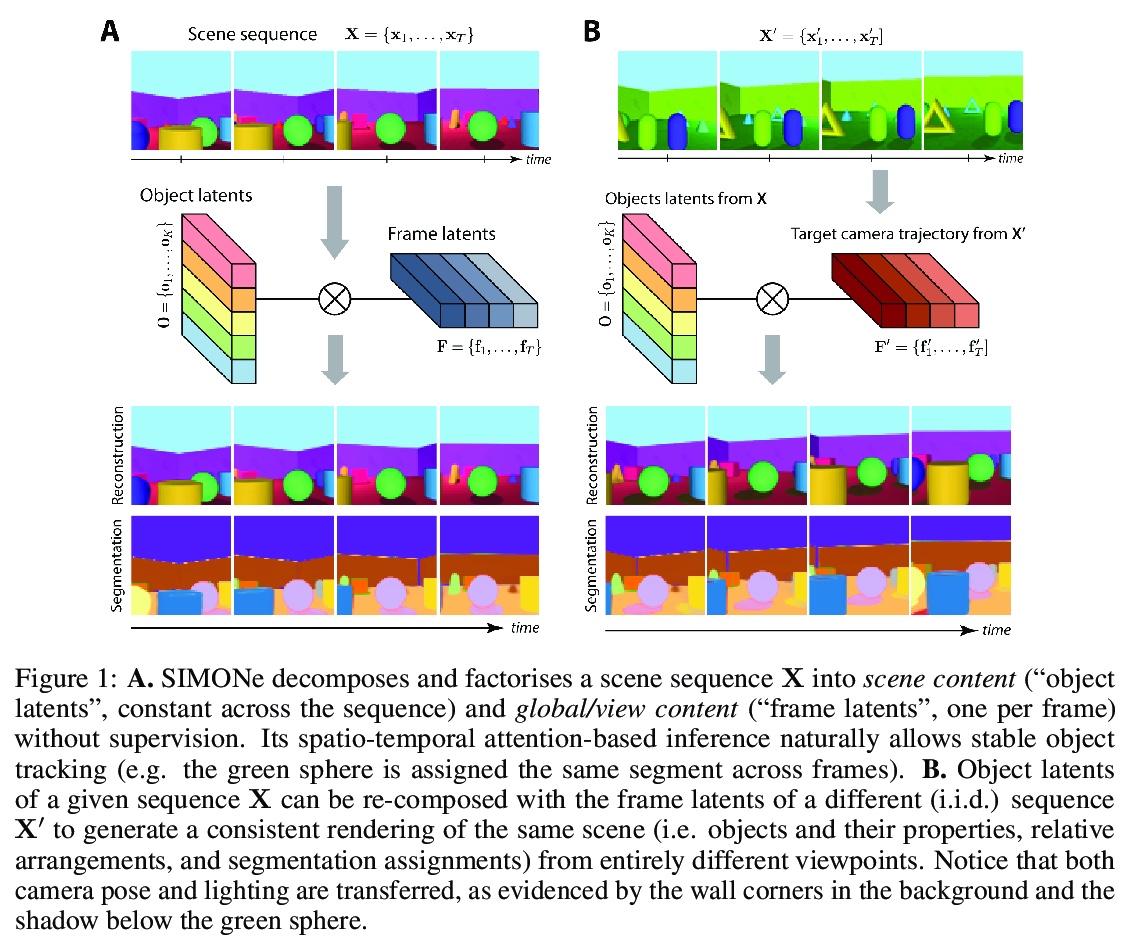
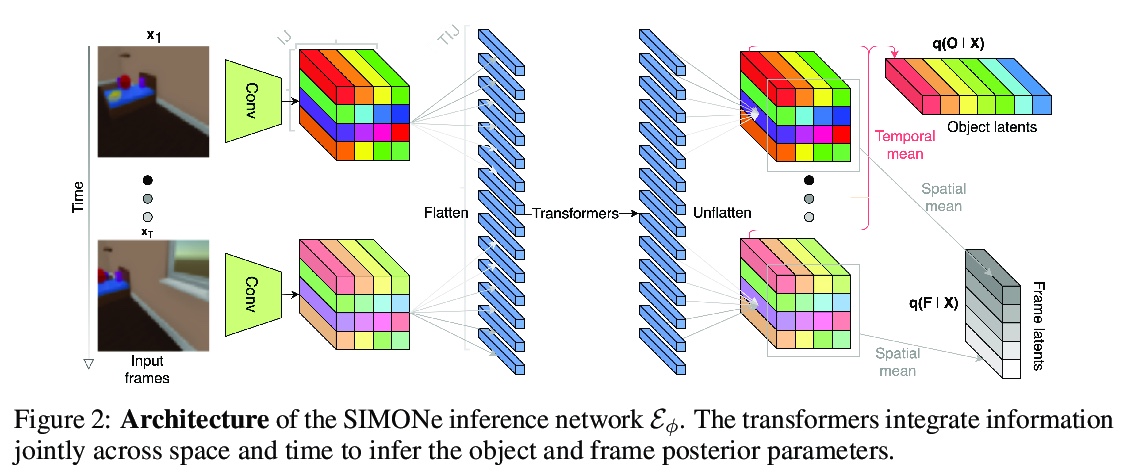
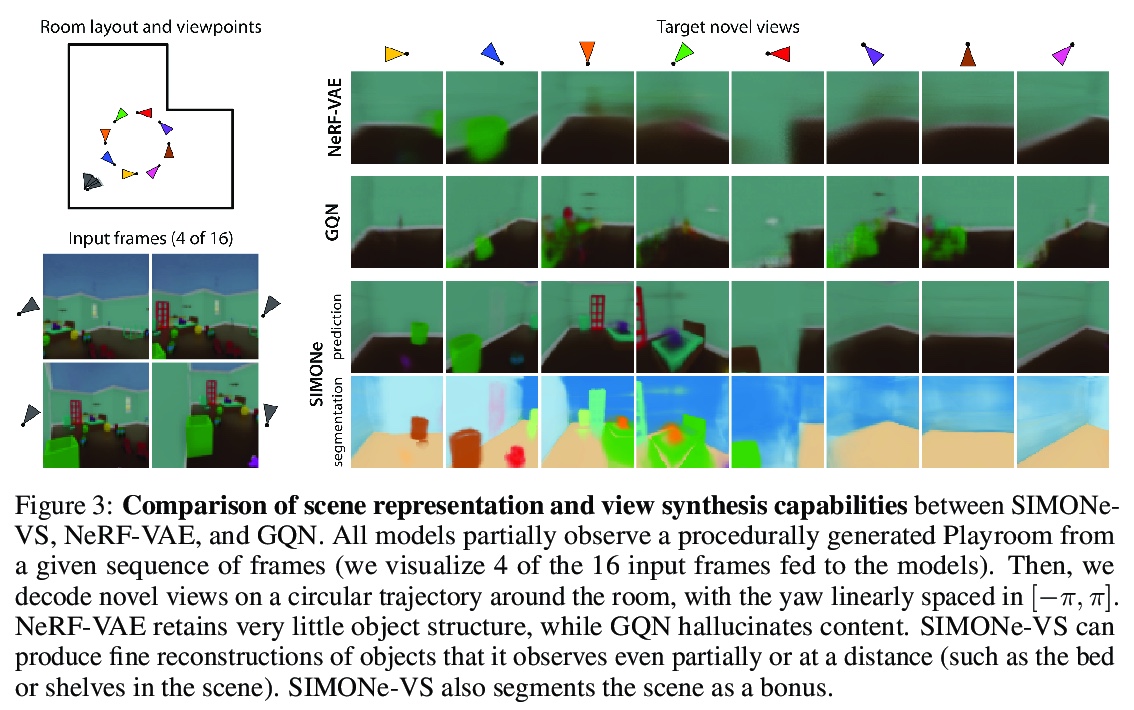
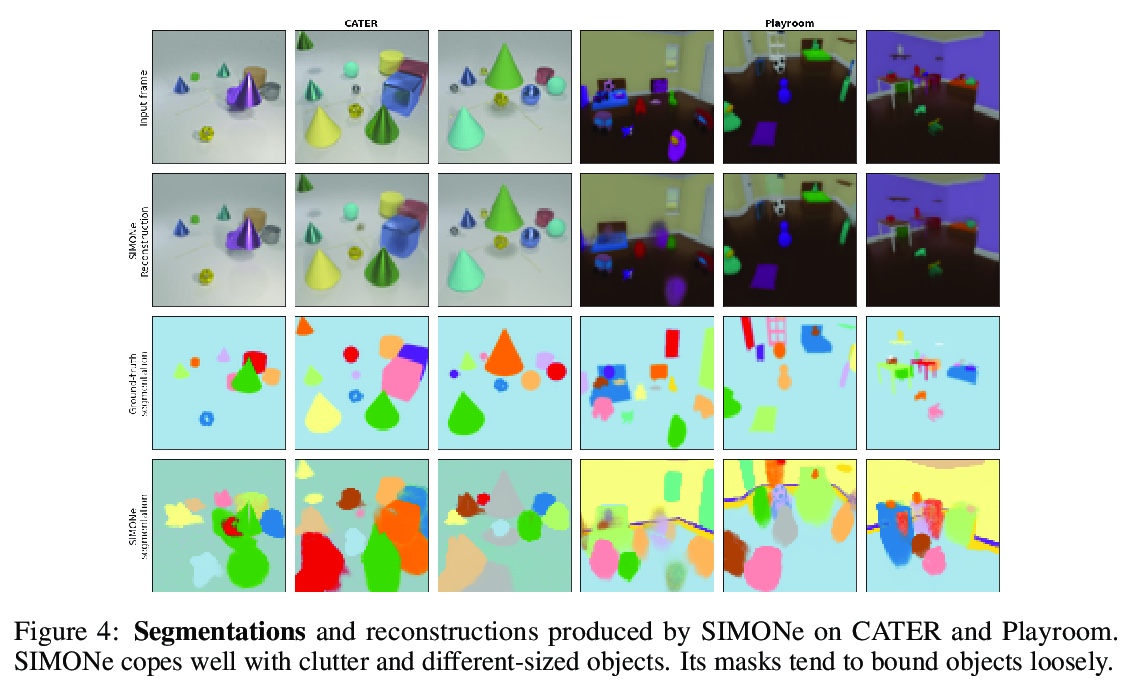
[CV] SIMONe: View-Invariant, Temporally-Abstracted Object Representations via Unsupervised Video Decomposition
SIMONe:基于无监督视频分解的视图不变时间抽象目标表示
R Kabra, D Zoran, G Erdogan, L Matthey, A Creswell, M Botvinick, A Lerchner, C P. Burgess
[DeepMind & Wayve]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kjk9Gbr94