- 1、[CV] Transformer is All You Need: Multimodal Multitask Learning with a Unified Transformer
- 2、[LG] Towards Causal Representation Learning
- 3、[CL] Formal Language Theory Meets Modern NLP
- 4、[CV] VisualGPT: Data-efficient Image Captioning by Balancing Visual Input and Linguistic Knowledge from Pretraining
- 5、[CV] Style and Pose Control for Image Synthesis of Humans from a Single Monocular View
- [IR] Pyserini: An Easy-to-Use Python Toolkit to Support Replicable IR Research with Sparse and Dense Representations
- [CL] Position Information in Transformers: An Overview
- [LG] Shapley values for feature selection: The good, the bad, and the axioms
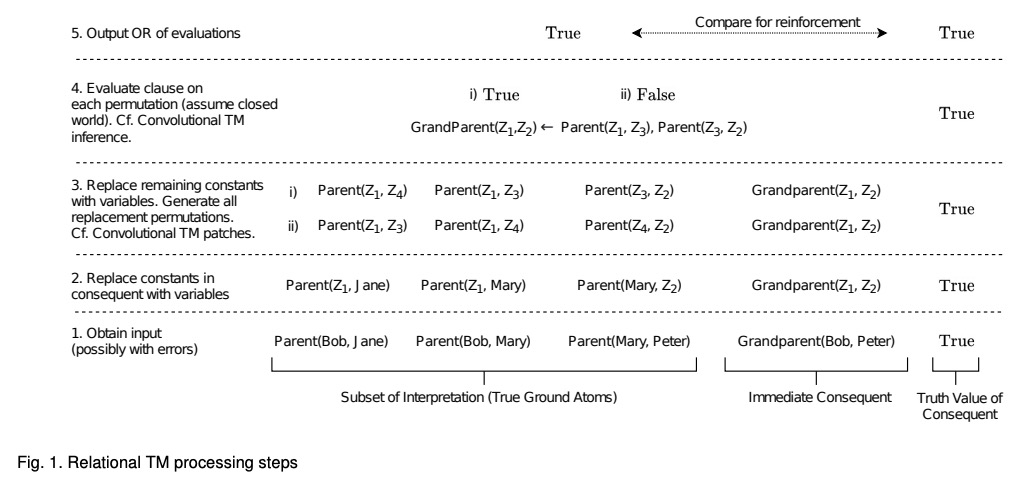
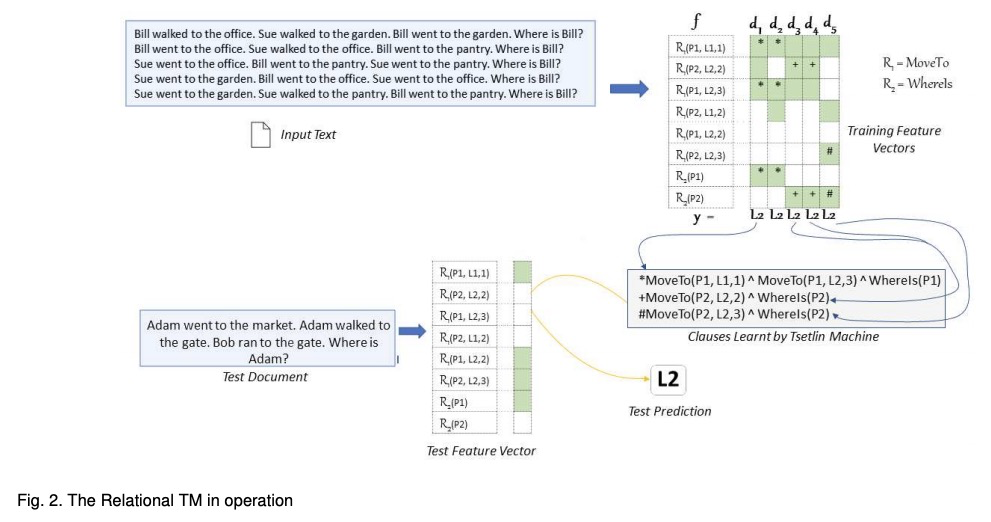
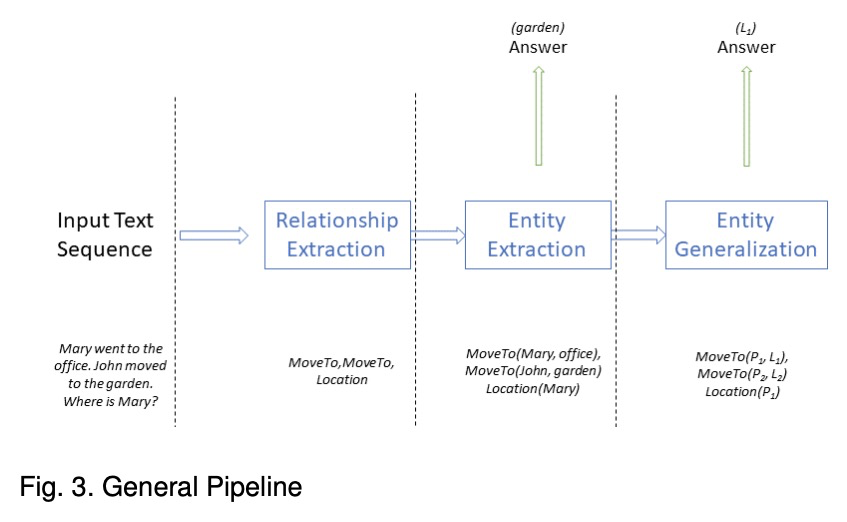
- [CL] A Relational Tsetlin Machine with Applications to Natural Language Understanding
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[CV] Transformer is All You Need: Multimodal Multitask Learning with a Unified Transformer
R Hu, A Singh
[Facebook AI Research (FAIR)]
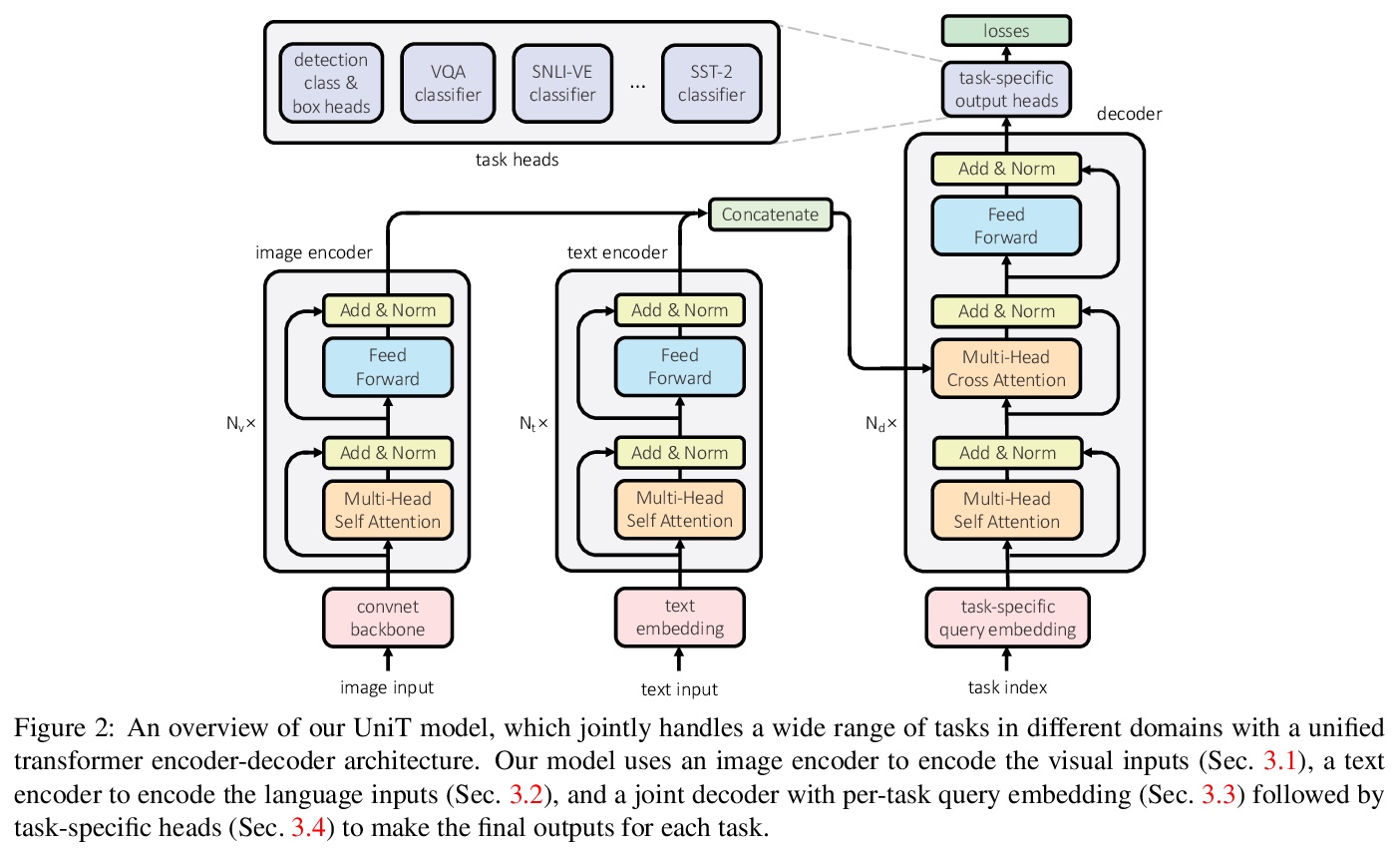
基于统一Transformer的多模态多任务学习。提出统一Transformer模型UniT,可同时学习不同领域最突出的任务,从目标检测到语言理解和多模态推理。UniT模型基于Transformer编码器-解码器架构,用编码器对每个输入模态进行编码,用共享解码器在编码后的输入表示上对各任务进行预测。整个模型是用每个任务的损失进行端到端联合训练,与之前用Transformer进行多任务学习的尝试相比,将相同模型参数共享到所有任务中,而不是单独对特定任务模型进行微调,并且处理不同领域的任务种类更多。联合学习了视觉和文本领域最主要的任务及其交叉点,即GLUE benckmark中的目标检测、视觉问题回答、视觉蕴含和自然语言理解任务,包括QNLI、MNLI、QQP和SST-2,这些不同任务可同时学习,并在UniT的训练方案下正确收敛。实验中,在8个数据集上联合学习了7个任务,在相同的监督下,通过一组紧凑的模型参数,在每个领域实现了与之前成熟工作相当的性能。通过对各种任务的分析,表明多模态任务,如VQA和视觉联想,可从单模态任务的多任务训练中获益。
We propose UniT, a Unified Transformer model to simultaneously learn the most prominent tasks across different domains, ranging from object detection to language understanding and multimodal reasoning. Based on the transformer encoder-decoder architecture, our UniT model encodes each input modality with an encoder and makes predictions on each task with a shared decoder over the encoded input representations, followed by task-specific output heads. The entire model is jointly trained end-to-end with losses from each task. Compared to previous efforts on multi-task learning with transformers, we share the same model parameters to all tasks instead of separately fine-tuning task-specific models and handle a much higher variety of tasks across different domains. In our experiments, we learn 7 tasks jointly over 8 datasets, achieving comparable performance to well-established prior work on each domain under the same supervision with a compact set of model parameters. Code will be released in MMF at > this https URL.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3m17cS75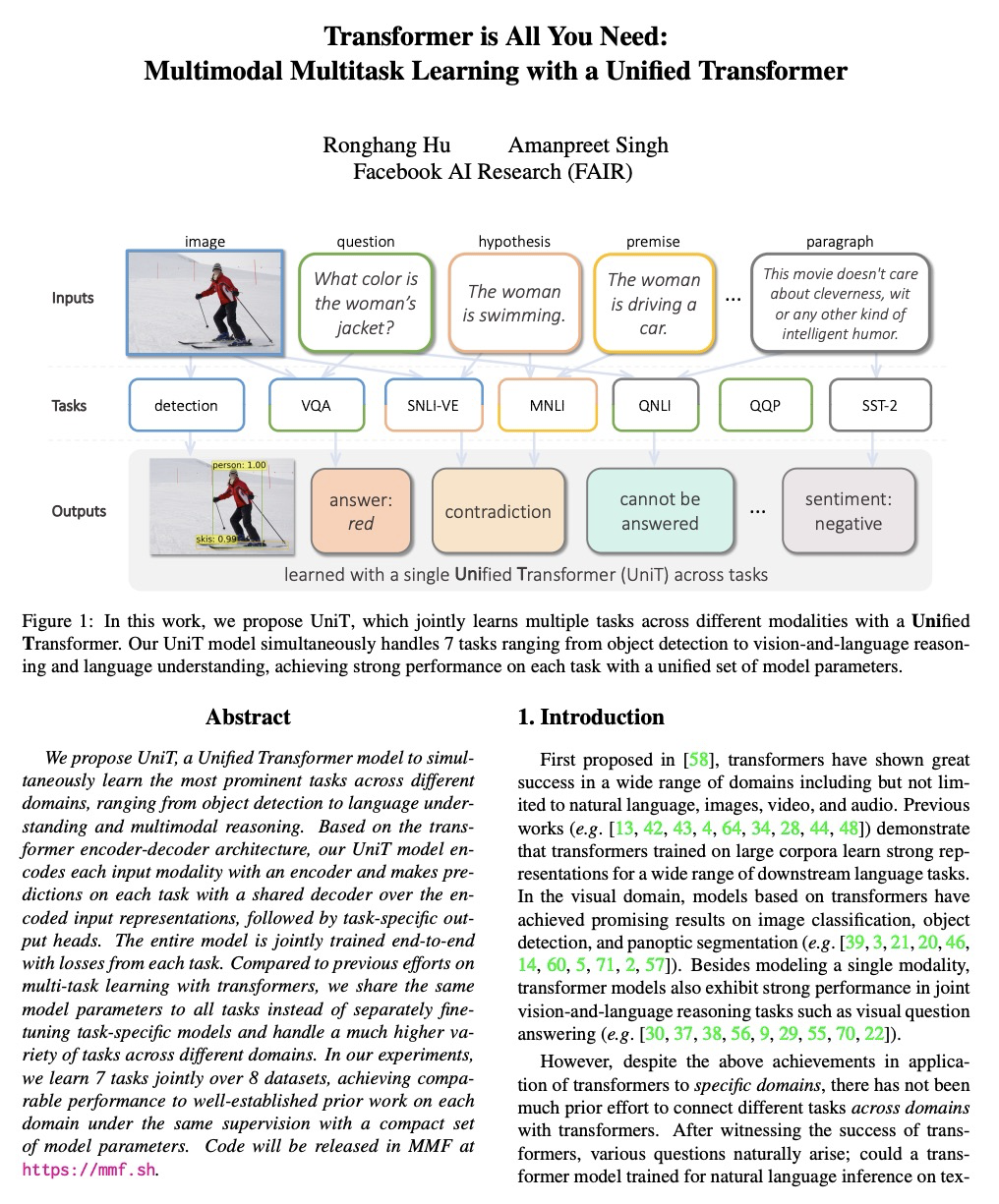

2、[LG] Towards Causal Representation Learning
B Schölkopf, F Locatello, S Bauer, N R Ke, N Kalchbrenner, A Goyal, Y Bengio
[Max-Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems & University of Montreal & Google Research Amsterdam]
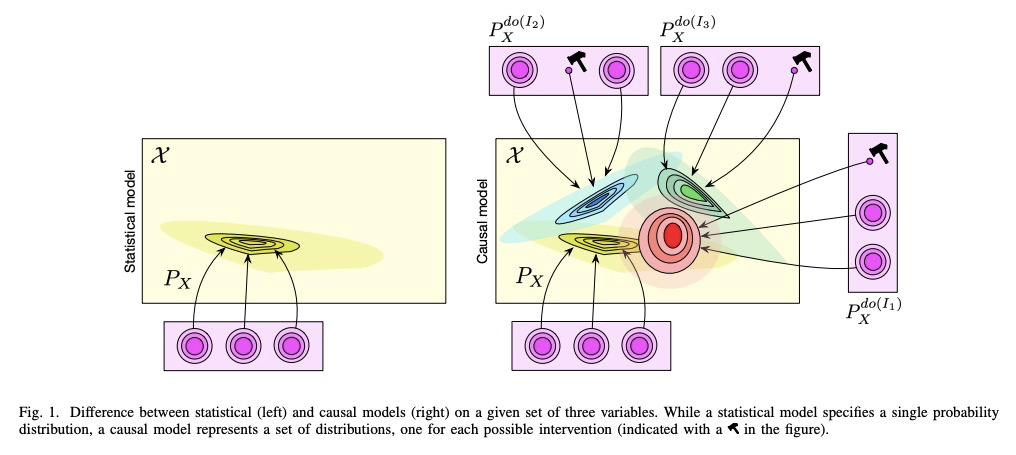
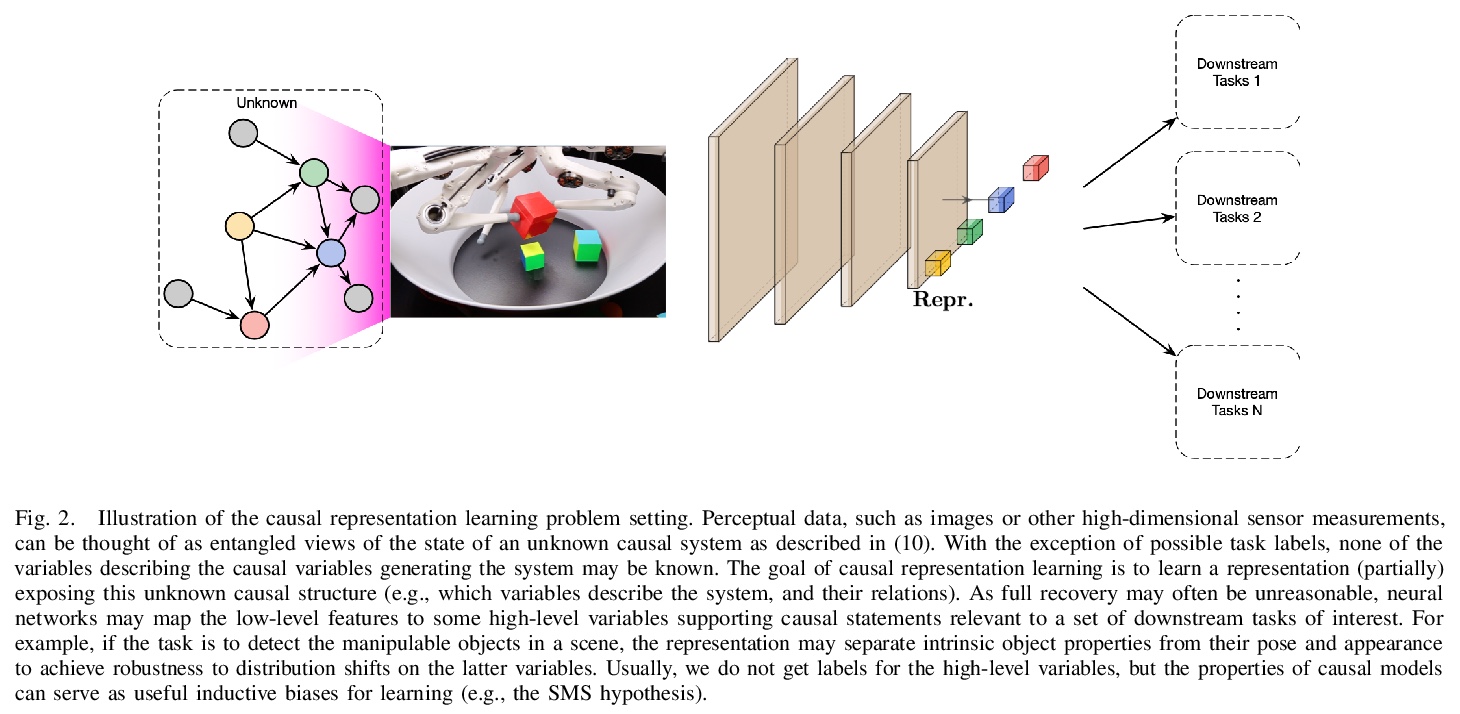
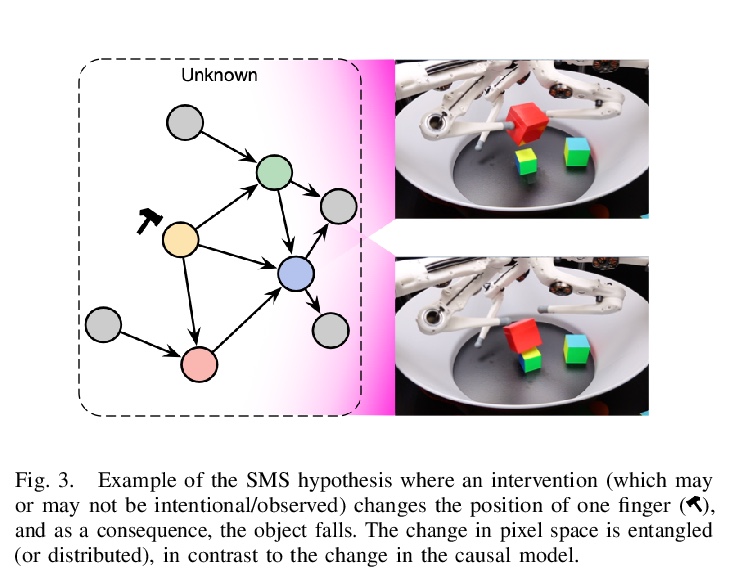
因果表示学习探索。回顾了因果推理的基本概念,并将其与机器学习的关键性开放问题联系起来,包括迁移和泛化,分析因果关系如何为现代机器学习研究做出贡献。讨论同时也涉及到相反的方向:因果方面的大多数工作都是从因果变量给定的前提开始的。因此,人工智能和因果性的一个核心问题是因果表示学习,即从低级观测值中发现高级因果变量。最后,划定了因果性对机器学习的一些影响,并提出了两个社区交叉的关键研究领域,包括在一定规模上学习非线性因果关系,因果变量的学习、理解现有深度学习方法的偏差、学习世界和智能体的因果正确模型。
The two fields of machine learning and graphical causality arose and developed separately. However, there is now cross-pollination and increasing interest in both fields to benefit from the advances of the other. In the present paper, we review fundamental concepts of causal inference and relate them to crucial open problems of machine learning, including transfer and generalization, thereby assaying how causality can contribute to modern machine learning research. This also applies in the opposite direction: we note that most work in causality starts from the premise that the causal variables are given. A central problem for AI and causality is, thus, causal representation learning, the discovery of high-level causal variables from low-level observations. Finally, we delineate some implications of causality for machine learning and propose key research areas at the intersection of both communities.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3m7Y93ZH
3、[CL] Formal Language Theory Meets Modern NLP
W Merrill
[Allen Institute for AI]
形式语言理论与现代自然语言处理。无论从概念上还是历史上看,NLP都与语言形式研究深深地交织在一起,这种联系可追溯到1957年乔姆斯基的《句法结构》。这一点在今天仍然适用,最近的一些工作从形式语言的角度建立了文本形式分析的现代神经网络方法,本文的目的是解释有关形式语言的背景,将不可避免地忽略这一领域丰富历史的大部分内容,着重于从现代基于深度学习的NLP的角度来介绍形式语言理论概念。
NLP is deeply intertwined with the formal study of language, both conceptually and historically. Arguably, this connection goes all the way back to Chomsky’s Syntactic Structures in 1957. This still holds true today, with a strand of recent works building formal analysis of modern neural networks methods in terms of formal languages. In this document, I aim to explain background about formal languages as they relate to to this recent work. I will by necessity ignore large parts of the rich history of this field, instead focusing on presenting formal language theoretic concepts from the perspective of modern deep learning-based NLP.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3mcZwu0i
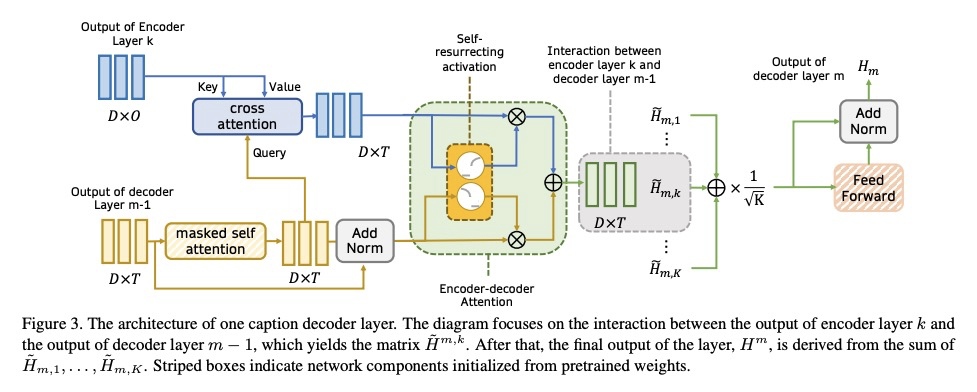
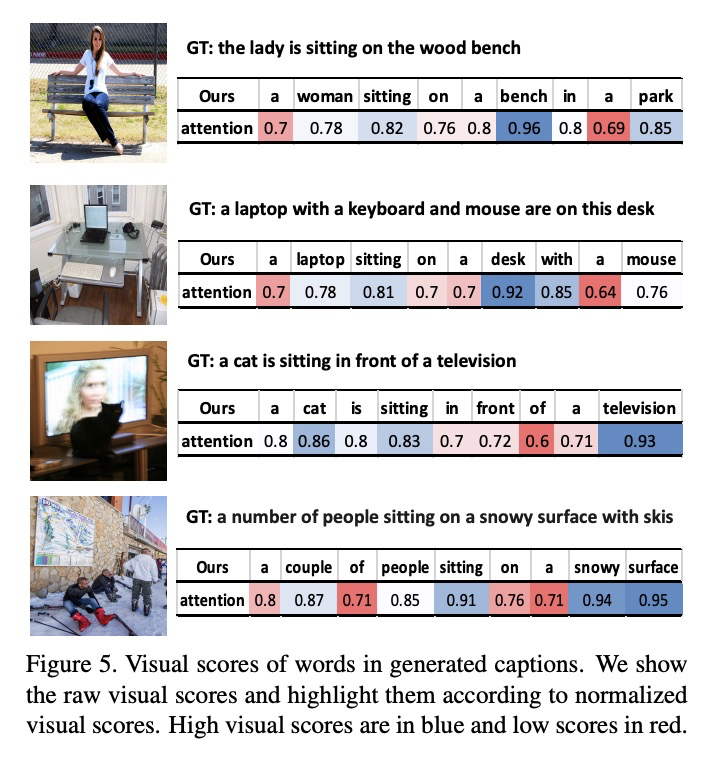
4、[CV] VisualGPT: Data-efficient Image Captioning by Balancing Visual Input and Linguistic Knowledge from Pretraining
J Chen, H Guo, K Yi, B Li, M Elhoseiny
[King Abdullah University of Science and Technology & CMU & Nanyang Technological University]
VisualGPT: 通过视觉输入和预训练语言知识的平衡实现数据高效图像描述。提出一种数据高效的图像描述模型VisualGPT,利用大型预训练语言模型(LM)中的语言知识,一个关键挑战是如何在在图像视觉信息和从预训练中获得的先验语言知识之间取得平衡。设计了一种新的自复活编码器-解码器注意力机制,并采用不饱和整流门控函数,在少量域内训练数据上快速调整预训练的语言模型作为语言解码器。所提出的自复活激活单元产生稀疏激活,不易受到零梯度的影响。
In this paper, we aim to improve the data efficiency of image captioning. We propose VisualGPT, a data-efficient image captioning model that leverages the linguistic knowledge from a large pretrained language model (LM). A crucial challenge is to balance between the use of visual information in the image and prior linguistic knowledge acquired from pretraining.We designed a novel self-resurrecting encoder-decoder attention mechanism to quickly adapt the pretrained LM as the language decoder on a small amount of in-domain training data. The pro-posed self-resurrecting activation unit produces sparse activations but is not susceptible to zero gradients. When trained on 0.1%, 0.5% and 1% of MSCOCO and Conceptual Captions, the proposed model, VisualGPT, surpasses strong image captioning baselines. VisualGPT outperforms the best baseline model by up to 10.8% CIDEr on MS COCO and up to 5.4% CIDEr on Conceptual Captions.We also perform a series of ablation studies to quantify the utility of each system component. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that improves data efficiency of image captioning by utilizing LM pretrained on unimodal data. Our code is available at: > this https URL.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3mi5sH7Y
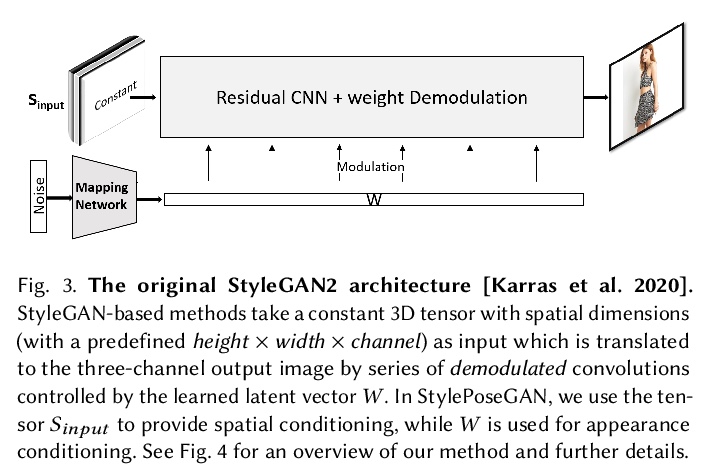
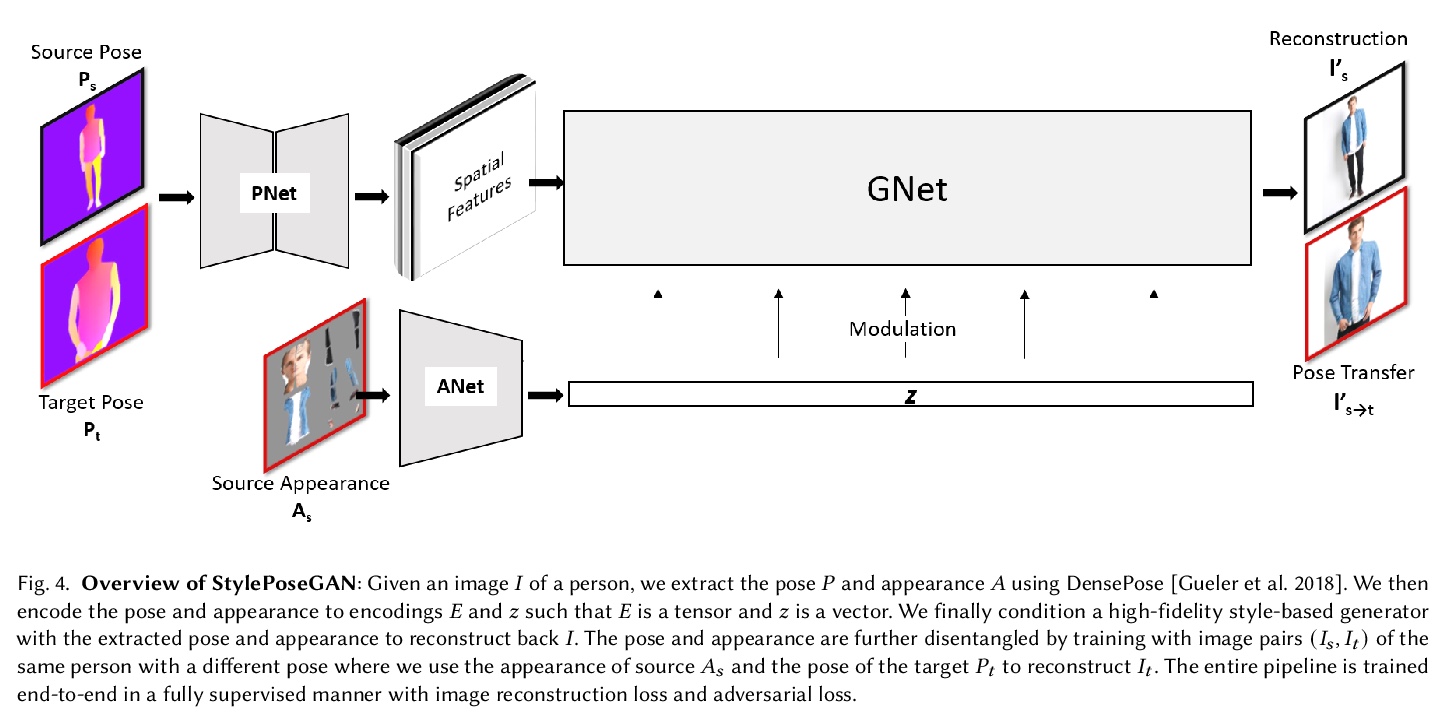
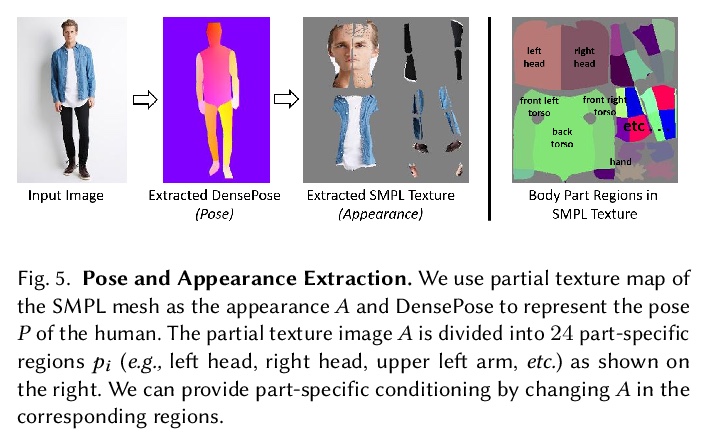
5、[CV] Style and Pose Control for Image Synthesis of Humans from a Single Monocular View
K Sarkar, V Golyanik, L Liu, C Theobalt
[Max Planck Institute for Informatics]
单一单目视图合成人类图像的风格和姿态控制。提出一种新方法StylePoseGAN,用于合成具有明确控制姿势和基于部分外观的照片级逼真的人类图像,扩展了非可控的生成器,以接受对姿态和外观的单独调节。StylePoseGAN网络可用人类图像全监督方式进行训练,以解缠姿态、外观和身体部位,性能明显优于现有的单图像重渲染方法。StylePoseGAN在常见的感知指标上实现了最先进的图像生成保真度,特别是对于细微的外观细节,如面部和纹理图案。
Photo-realistic re-rendering of a human from a single image with explicit control over body pose, shape and appearance enables a wide range of applications, such as human appearance transfer, virtual try-on, motion imitation, and novel view synthesis. While significant progress has been made in this direction using learning-based image generation tools, such as GANs, existing approaches yield noticeable artefacts such as blurring of fine details, unrealistic distortions of the body parts and garments as well as severe changes of the textures. We, therefore, propose a new method for synthesising photo-realistic human images with explicit control over pose and part-based appearance, i.e., StylePoseGAN, where we extend a non-controllable generator to accept conditioning of pose and appearance separately. Our network can be trained in a fully supervised way with human images to disentangle pose, appearance and body parts, and it significantly outperforms existing single image re-rendering methods. Our disentangled representation opens up further applications such as garment transfer, motion transfer, virtual try-on, head (identity) swap and appearance interpolation. StylePoseGAN achieves state-of-the-art image generation fidelity on common perceptual metrics compared to the current best-performing methods and convinces in a comprehensive user study.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3mpm5hJt

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[IR] Pyserini: An Easy-to-Use Python Toolkit to Support Replicable IR Research with Sparse and Dense Representations
Pyserini: 面向可复现信息检索研究支持稀疏和密集表示的Python工具包
J Lin, X Ma, S Lin, J Yang, R Pradeep, R Nogueira
[University of Waterloo]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3mt4eiBn



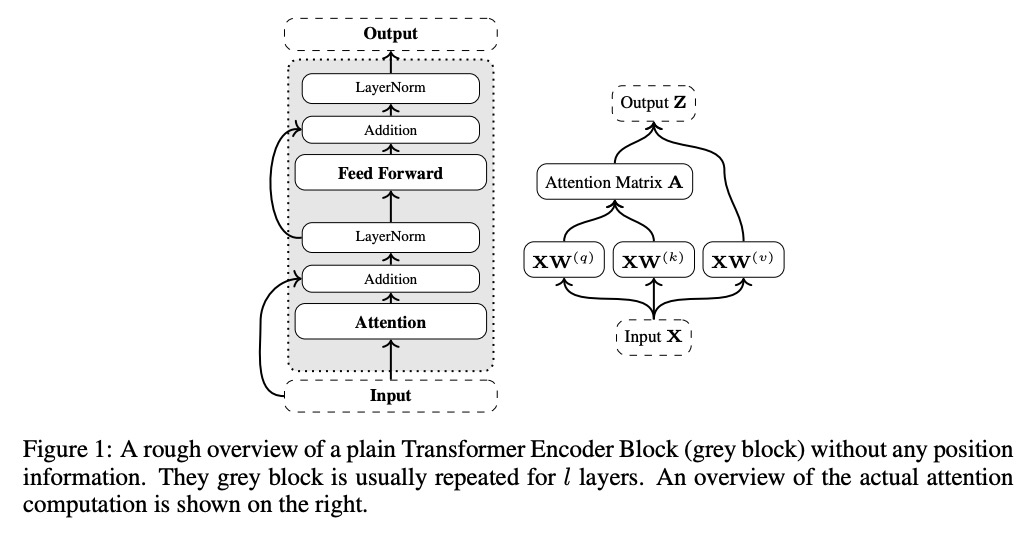
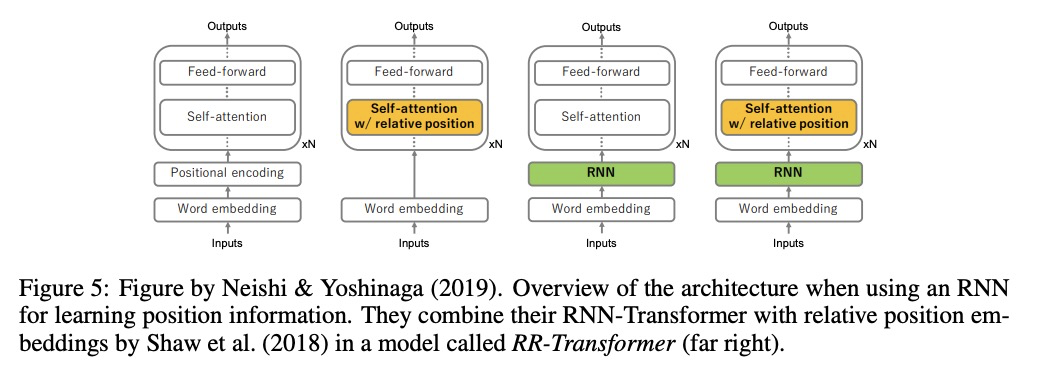
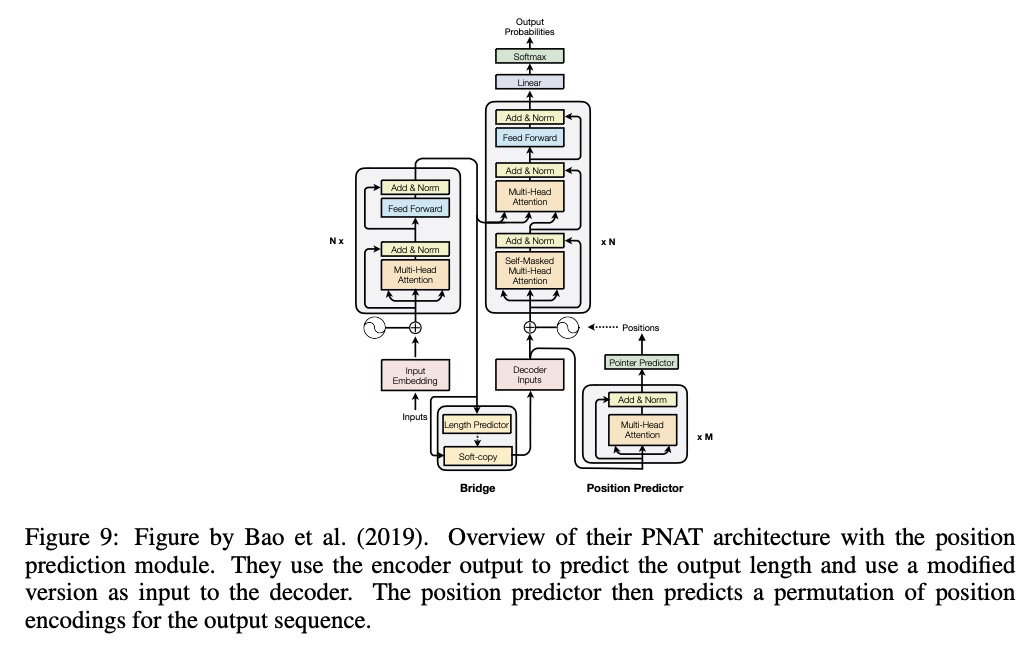
[CL] Position Information in Transformers: An Overview
Transformers位置信息概览
P Dufter, M Schmitt, H Schütze
[LMU Munich]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3mvp5a6L
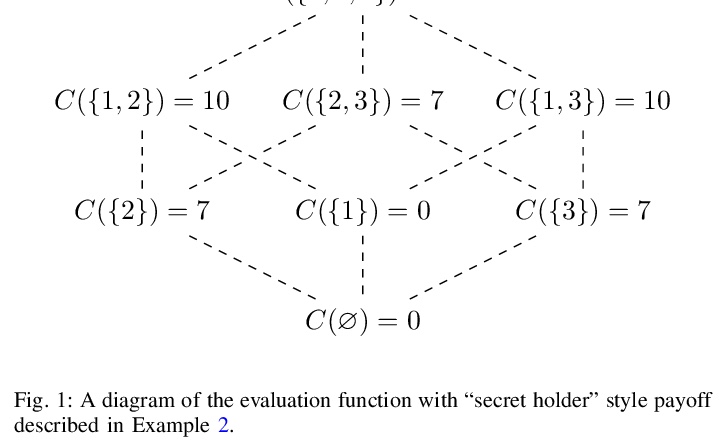
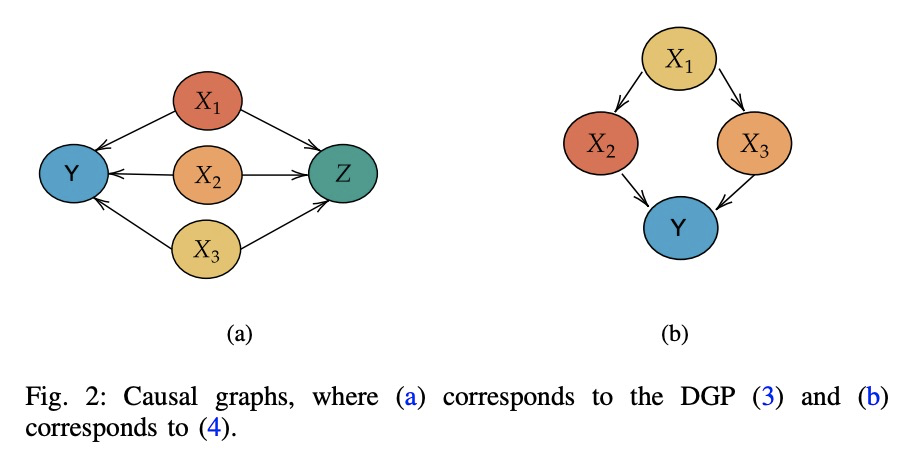
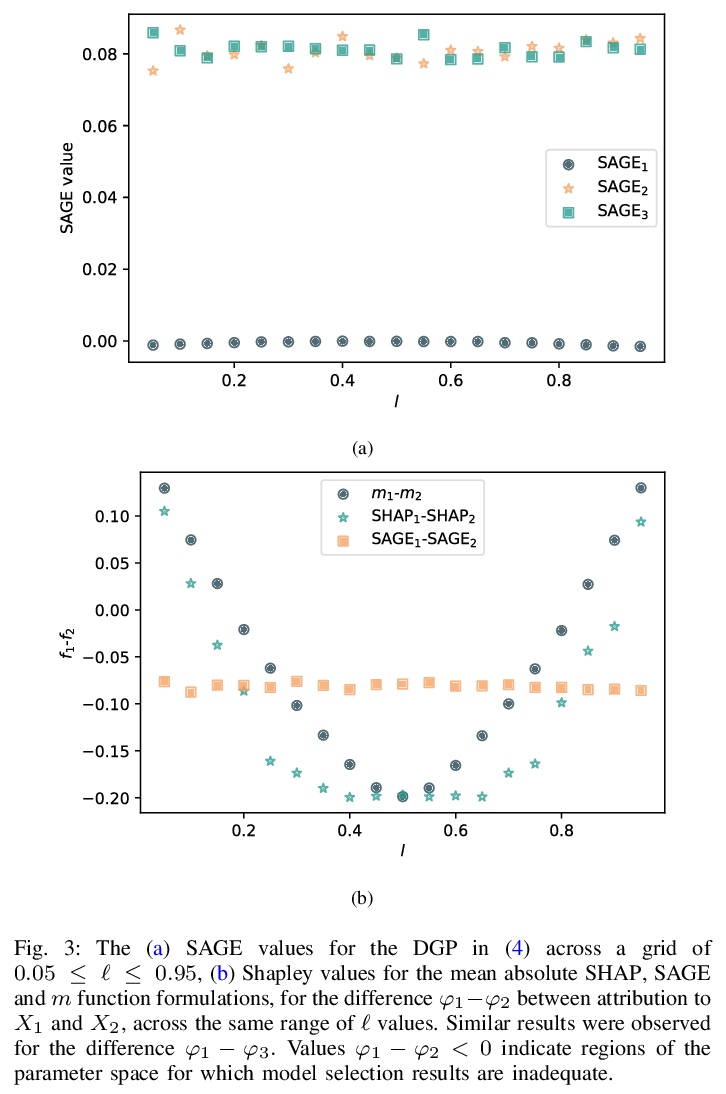
[LG] Shapley values for feature selection: The good, the bad, and the axioms
特征选择的Shapley值:好的、坏的和公理
D Fryer, I Strümke, H Nguyen
[The University of Queensland & Simula Research Laboratory & La Trobe University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3myR1mwx
[CL] A Relational Tsetlin Machine with Applications to Natural Language Understanding
关系Tsetlin机及其自然语言理解应用
R Saha, O Granmo, V I. Zadorozhny, M Goodwin
[University of Agder]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3mBFjqP5