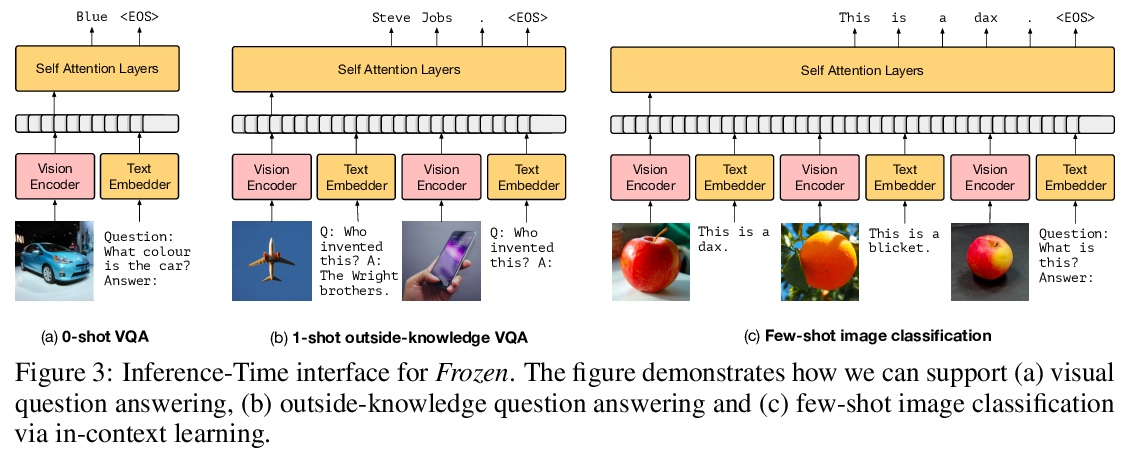
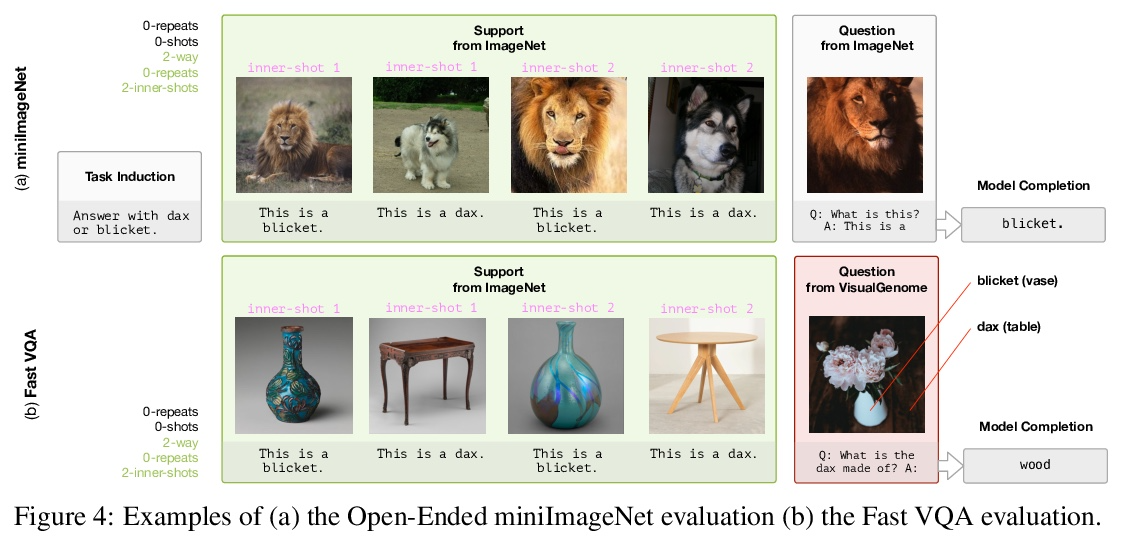
- 1、[CV] Multimodal Few-Shot Learning with Frozen Language Models
- 2、[CV] CLIPDraw: Exploring Text-to-Drawing Synthesis through Language-Image Encoders
- 3、[CV] Early Convolutions Help Transformers See Better
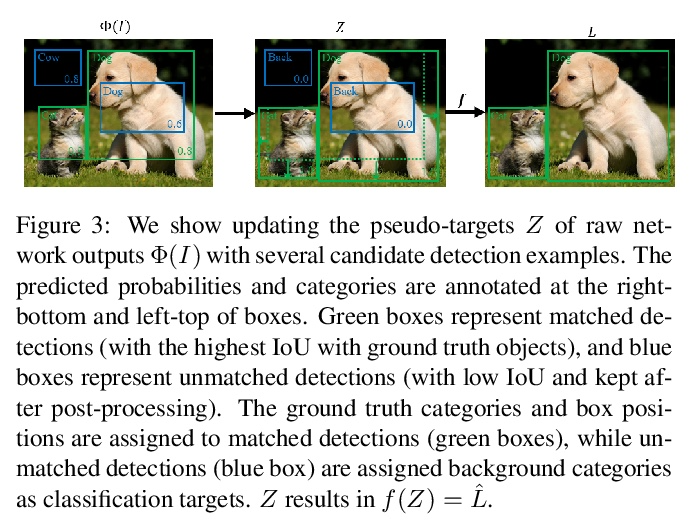
- 4、[CV] Inverting and Understanding Object Detectors
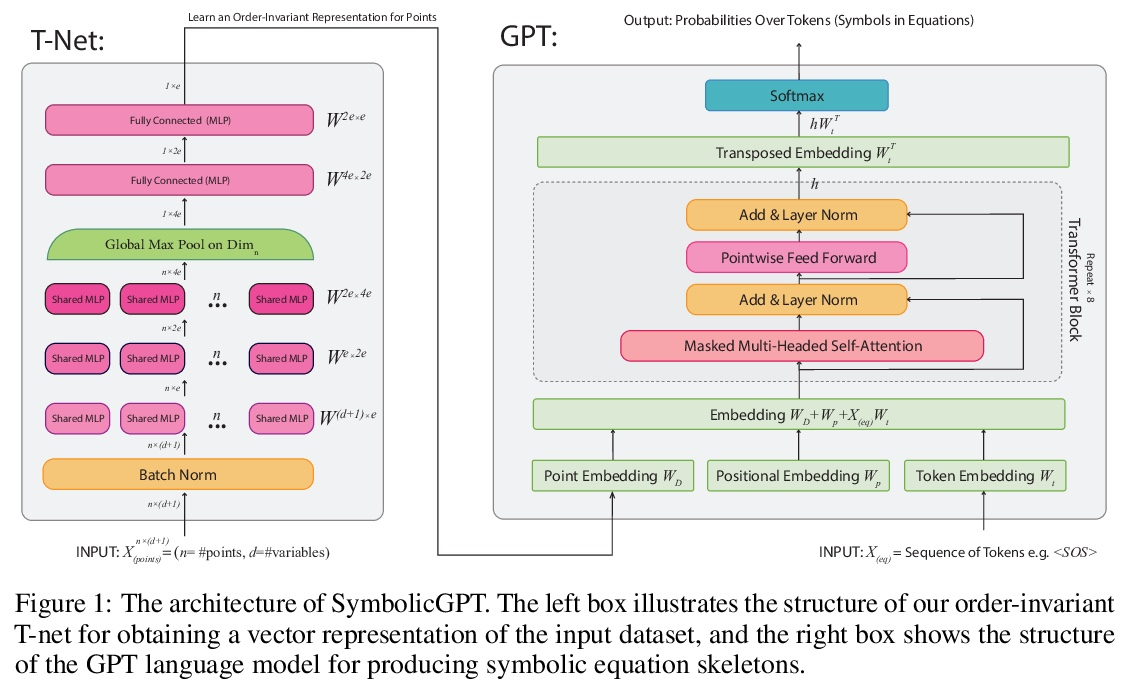
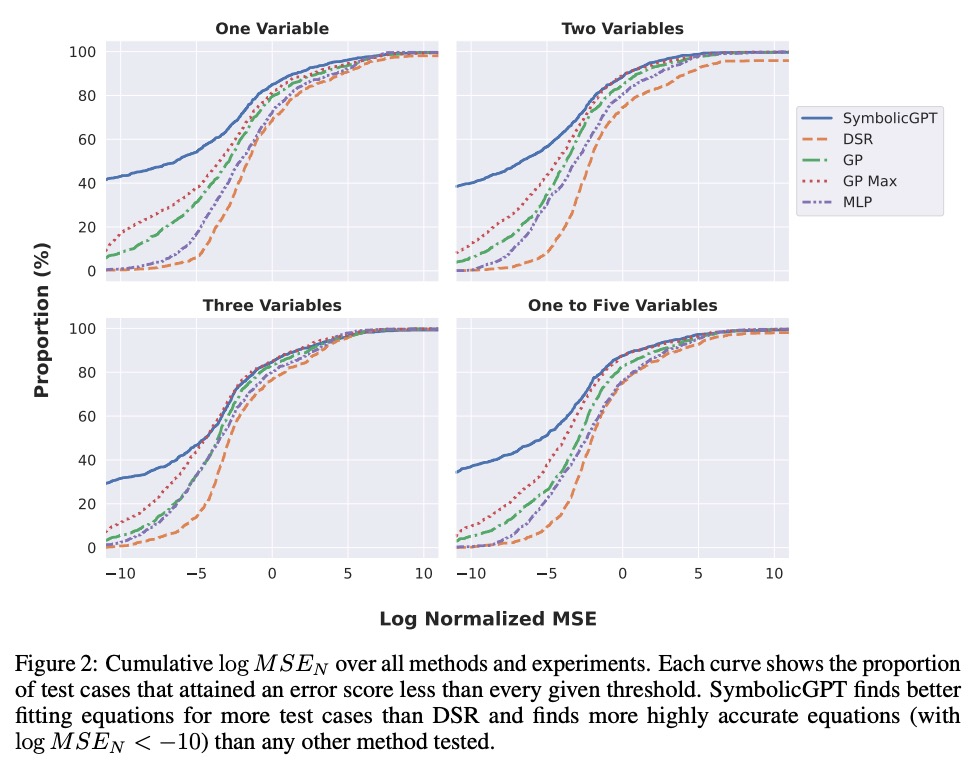
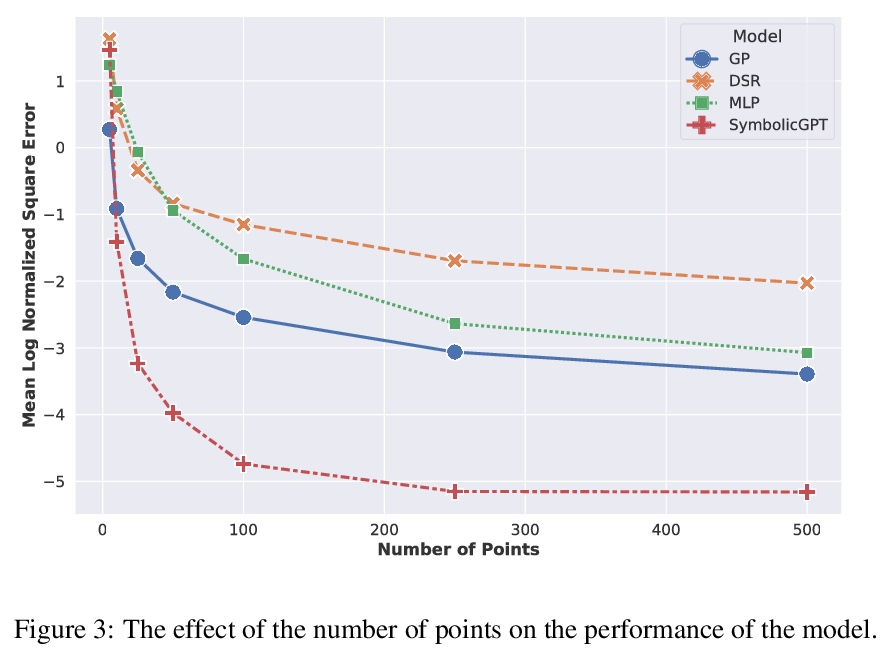
- 5、[LG] SymbolicGPT: A Generative Transformer Model for Symbolic Regression
- [LG] Multi-task curriculum learning in a complex, visual, hard-exploration domain: Minecraft
- [CV] Unsupervised Discovery of Actions in Instructional Videos
- [LG] Building population models for large-scale neural recordings: opportunities and pitfalls
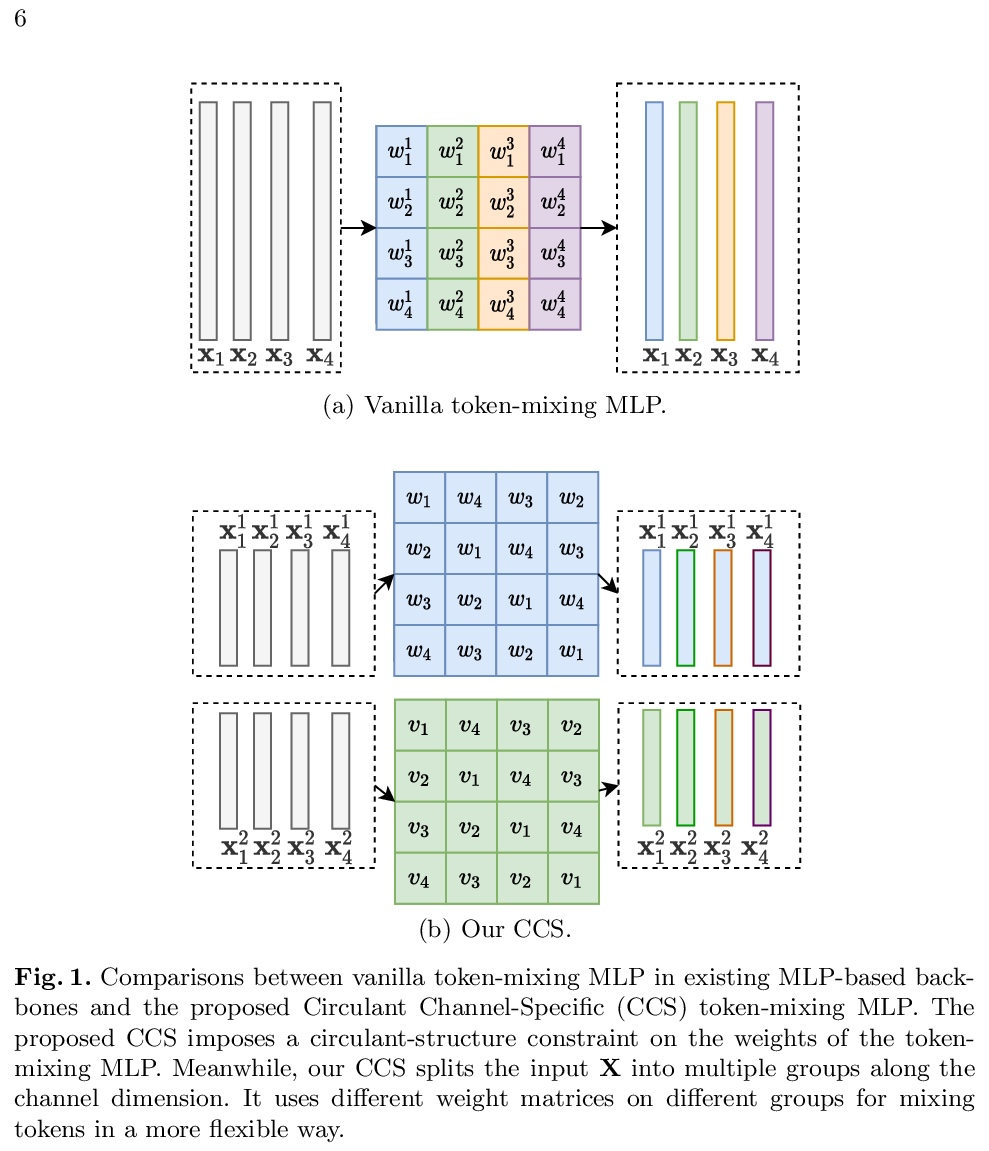
- [CV] Rethinking Token-Mixing MLP for MLP-based Vision Backbone
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CV] Multimodal Few-Shot Learning with Frozen Language Models
M Tsimpoukelli, J Menick, S Cabi, S.M. A Eslami, O Vinyals, F Hill
[DeepMind]
冻结语言模型多模态少样本学习。训练规模足够大时,自回归语言模型表现出显著的能力,在得到几个样本的提示后就能学习新的语言任务。本文提出一种简单有效的方法,将这种少样本学习能力迁移到多模态环境中(视觉和语言),将大型语言模型转化为多模态的少样本学习系统,通过将前缀调整的软提示理念扩展到有序的图像和文本集,同时保留语言模型的文本提示能力。用对齐的图像和描述数据,训练一个视觉编码器,将每张图像表示为连续的嵌入序列,这样一个预训练好的、冻结的语言模型在该前缀的提示下会生成适当的描述。由此产生的系统是一个多模态的少样本学习器,当以表示为多个交错图像文本嵌入序列的样本为条件时,对各种新任务的学习能力令人惊。实验表明,该方法可以快速学习新目标和新视觉类词汇,只用少量样本就可以利用外部知识进行视觉问题回答。
When trained at sufficient scale, auto-regressive language models exhibit the notable ability to learn a new language task after being prompted with just a few examples. Here, we present a simple, yet effective, approach for transferring this few-shot learning ability to a multimodal setting (vision and language). Using aligned image and caption data, we train a vision encoder to represent each image as a sequence of continuous embeddings, such that a pre-trained, frozen language model prompted with this prefix generates the appropriate caption. The resulting system is a multimodal few-shot learner, with the surprising ability to learn a variety of new tasks when conditioned on examples, represented as a sequence of multiple interleaved image and text embeddings. We demonstrate that it can rapidly learn words for new objects and novel visual categories, do visual question-answering with only a handful of examples, and make use of outside knowledge, by measuring a single model on a variety of established and new benchmarks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmvGBuvGa 


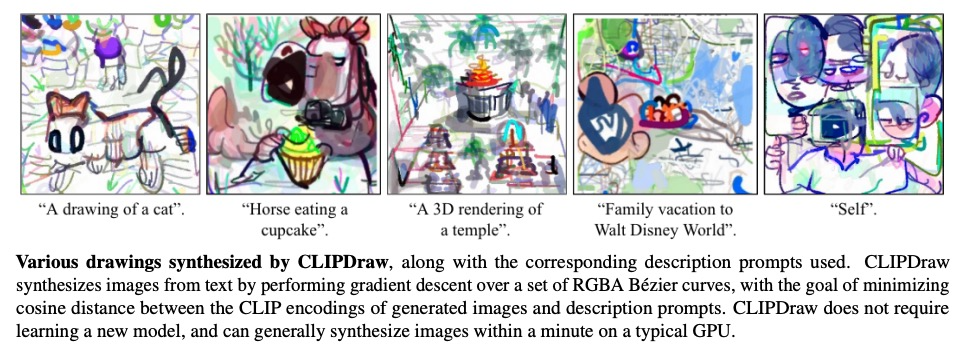
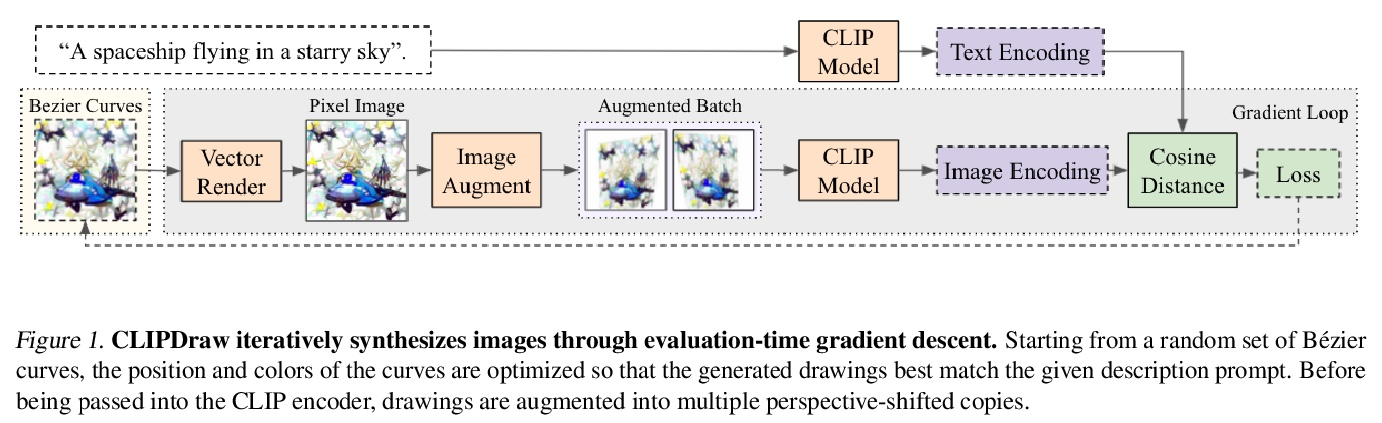
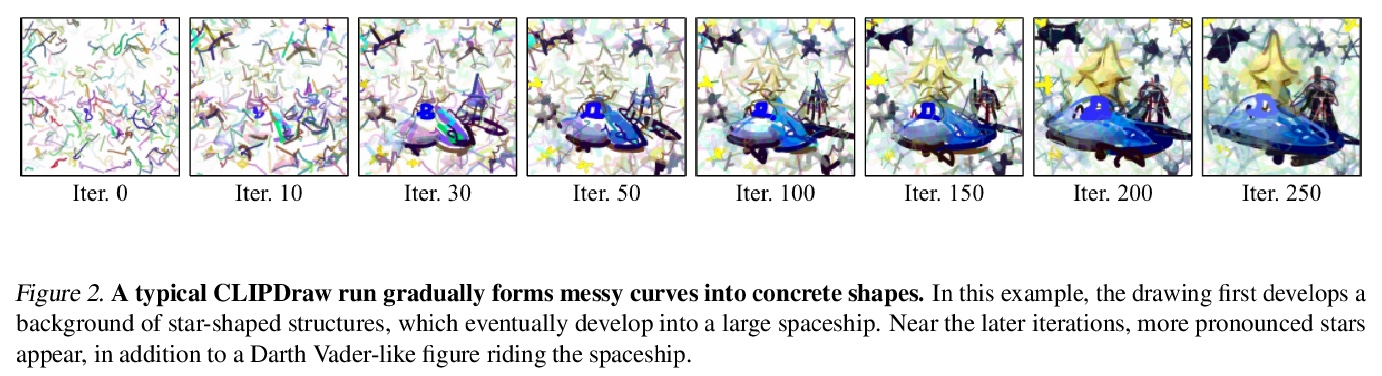
2、[CV] CLIPDraw: Exploring Text-to-Drawing Synthesis through Language-Image Encoders
K Frans, L.B. Soros, O Witkowski
[Cross Compass Ltd]
CLIPDraw: 用语言-图像编码器探索文本-图画合成。本文提出CLIPDraw,一种基于自然语言输入合成新图画的算法。CLIPDraw不需要任何训练,预训练好的CLIP语言图像编码器被用来最大化给定描述和生成图画之间相似性指标,在评估时通过迭代优化合成。CLIPDraw对矢量笔画而不是像素图像进行操作,该约束使绘画偏向于更简单的人类可识别的形状。结果比较了CLIPDraw和其他通过优化合成的方法,并强调了CLIPDraw的各种有趣的行为,例如以多种方式满足模糊的文本,可靠地产生不同艺术风格的图画,以及随着笔画数的增加从简单到复杂的视觉表现。
This work presents CLIPDraw, an algorithm that synthesizes novel drawings based on natural language input. CLIPDraw does not require any training; rather a pre-trained CLIP languageimage encoder is used as a metric for maximizing similarity between the given description and a generated drawing. Crucially, CLIPDraw operates over vector strokes rather than pixel images, a constraint that biases drawings towards simpler human-recognizable shapes. Results compare between CLIPDraw and other synthesis-throughoptimization methods, as well as highlight various interesting behaviors of CLIPDraw, such as satisfying ambiguous text in multiple ways, reliably producing drawings in diverse artistic styles, and scaling from simple to complex visual representations as stroke count is increased.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmvLcFDjF 


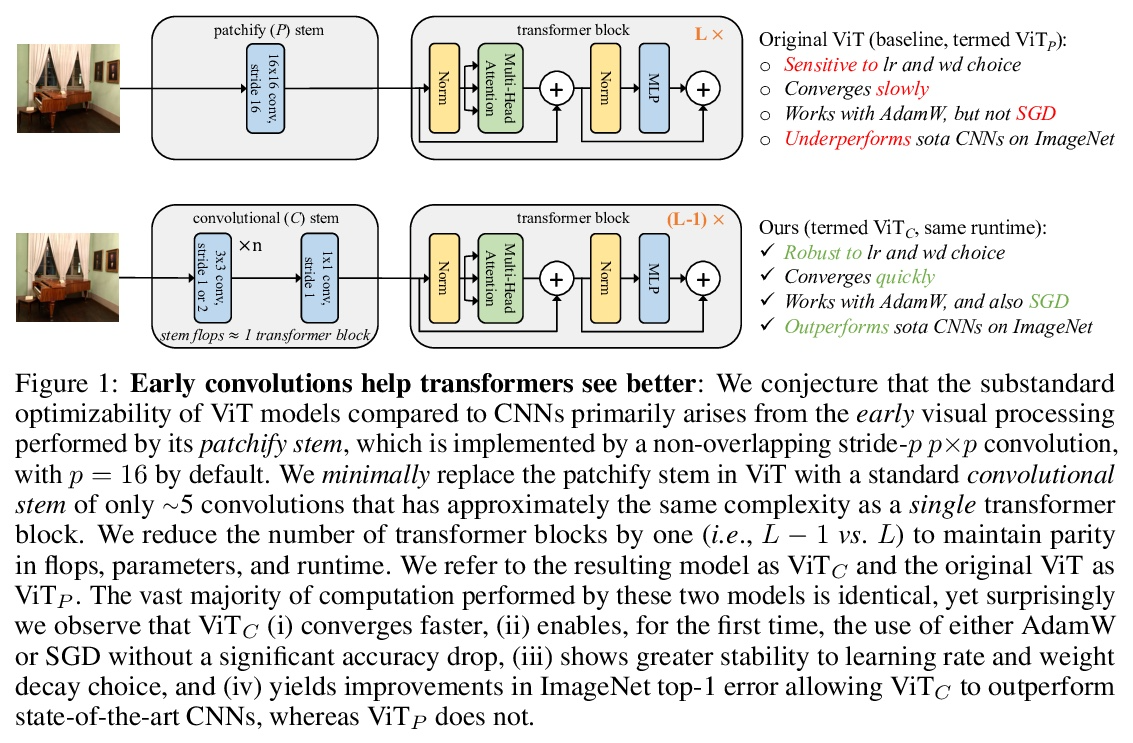
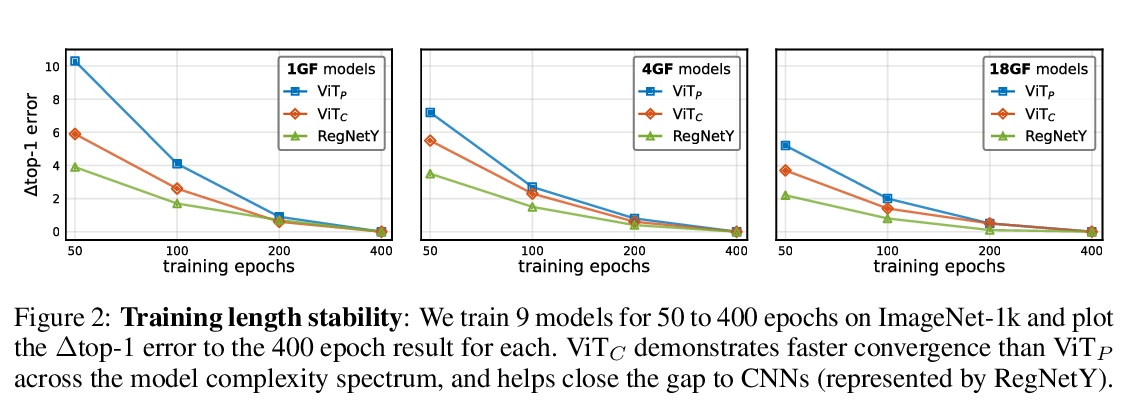
3、[CV] Early Convolutions Help Transformers See Better
T Xiao, M Singh, E Mintun, T Darrell, P Dollár, R Girshick
[Facebook AI Research & UC Berkeley]
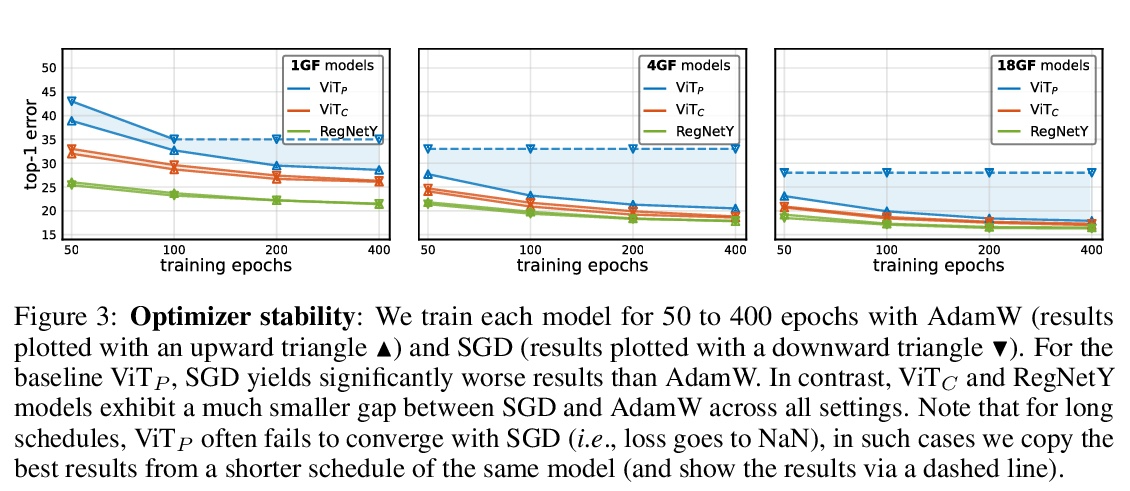
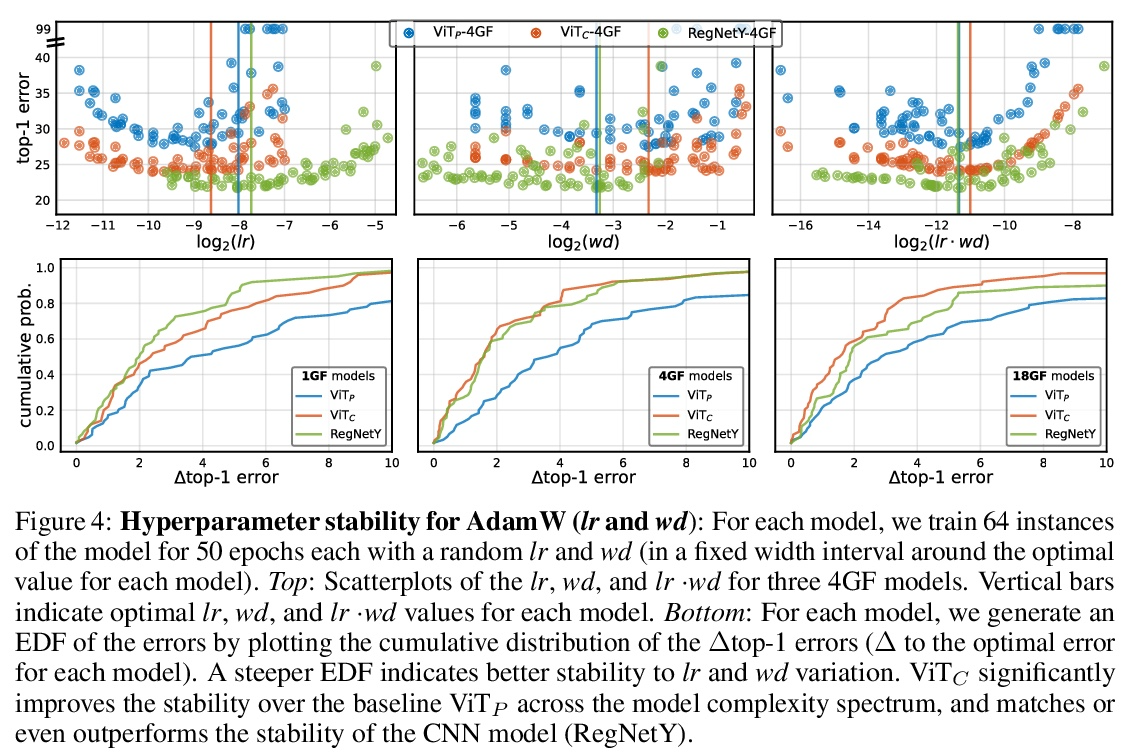
早期卷积有助于Transformer的稳定优化。视觉Transformer(ViT)模型表现出非标准的优化能力,对优化器的选择(AdamW与SGD)、优化器的超参数和训练规划长度都很敏感。相比之下,现代卷积神经网络的优化要容易得多。为什么会出现这种情况呢?本文猜测问题在于ViT模型的图块化干(patchify stem),通过应用于输入图像的p步长 p×p卷积(默认p=16)来实现。这种大核加大步长的卷积与神经网络中卷积层的典型设计选择相悖。为测试这种非典型的设计选择是否会导致问题,分析了ViT模型的优化行为,用其原始的图块化干与一个用少量堆叠的步长2 3×3卷积来取代ViT干的简单对应模型相比。虽然两种ViT设计中的绝大部分计算是相同的,但早期视觉处理的这一微小变化在对优化设置的敏感性和最终模型的准确性方面导致了明显不同的训练行为。在ViT中使用卷积干,极大提高了优化的稳定性,也提高了峰值性能(在ImageNet-1k上提高了1-2%的最高精度),同时保持了flops和运行时间。这种改进可以在广泛的模型复杂度(从1G到36G flops)和数据集规模(从ImageNet-1k到ImageNet-21k)中观察到。在ViT的早期阶段注入小剂量的卷积归纳偏差有很大的好处。这些发现使我们推荐在ViT模型中使用一个标准的、轻量级的卷积干,与原来的ViT模型设计相比,这是一个更鲁棒的架构选择。
Vision transformer (ViT) models exhibit substandard optimizability. In particular, they are sensitive to the choice of optimizer (AdamW vs. SGD), optimizer hyperparameters, and training schedule length. In comparison, modern convolutional neural networks are far easier to optimize. Why is this the case? In this work, we conjecture that the issue lies with the patchify stem of ViT models, which is implemented by a stride-p p×p convolution (p = 16 by default) applied to the input image. This large-kernel plus large-stride convolution runs counter to typical design choices of convolutional layers in neural networks. To test whether this atypical design choice causes an issue, we analyze the optimization behavior of ViT models with their original patchify stem versus a simple counterpart where we replace the ViT stem by a small number of stacked stride-two 3×3 convolutions. While the vast majority of computation in the two ViT designs is identical, we find that this small change in early visual processing results in markedly different training behavior in terms of the sensitivity to optimization settings as well as the final model accuracy. Using a convolutional stem in ViT dramatically increases optimization stability and also improves peak performance (by ∼1-2% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1k), while maintaining flops and runtime. The improvement can be observed across the wide spectrum of model complexities (from 1G to 36G flops) and dataset scales (from ImageNet-1k to ImageNet-21k). These findings lead us to recommend using a standard, lightweight convolutional stem for ViT models as a more robust architectural choice compared to the original ViT model design.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmvNXtoa3 
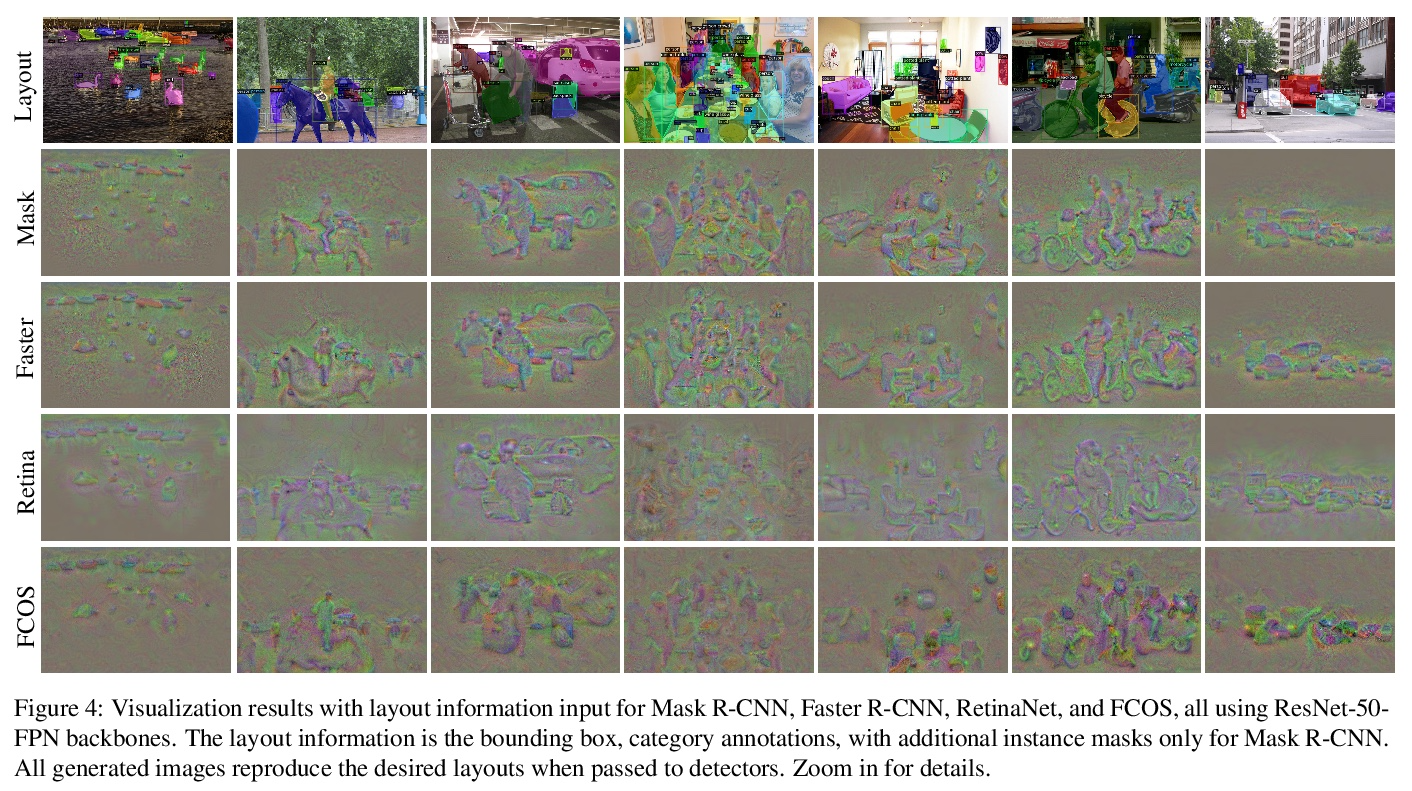
4、[CV] Inverting and Understanding Object Detectors
A Cao, J Johnson
[University of Michigan]
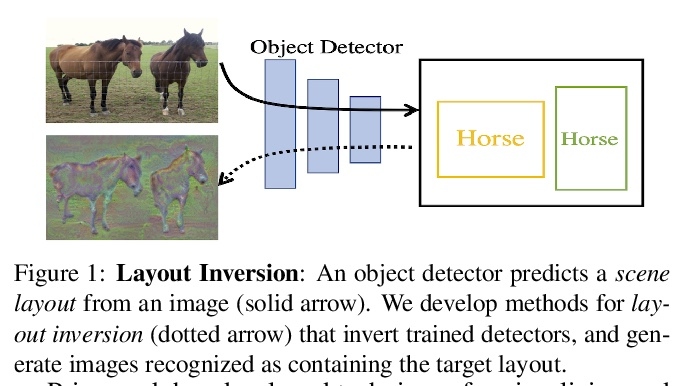
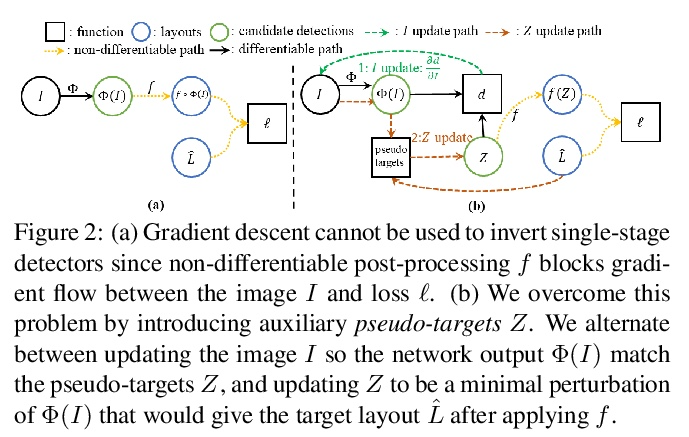
通过逆向理解目标检测器。作为计算机视觉的一个核心问题,目标检测的性能在过去几年中得到了极大改善。尽管性能令人印象深刻,但目标检测器仍缺乏可解释性。可视化技术已经被开发出来,并广泛用于分析其他类型深度学习模型做出的决定;然而,目标检测器的可视化还没有被充分开发。本文建议用逆向作为理解现代目标检测器的主要工具,开发了一种基于优化的布局逆向方法,能生成由经过训练的检测器识别为包含所需目标配置的合成图像。通过将布局逆向技术应用于各种现代目标检测器,揭示了检测器的有趣特性,依靠质量各异的特征进行分类和回归;学习通常共同出现的目标的标准化图案;用不同的视觉线索来识别不同大小的目标。
As a core problem in computer vision, the performance of object detection has improved drastically in the past few years. Despite their impressive performance, object detectors suffer from a lack of interpretability. Visualization techniques have been developed and widely applied to introspect the decisions made by other kinds of deep learning models; however visualizing object detectors has been underexplored. In this paper, we propose using inversion as a primary tool to understand modern object detectors and develop an optimization-based approach to layout inversion, allowing us to generate synthetic images recognized by trained detectors as containing a desired configuration of objects. We reveal intriguing properties of detectors by applying our layout inversion technique to a variety of modern object detectors, and further investigate them via validation experiments: they rely on qualitatively different features for classification and regression; they learn canonical motifs of commonly co-occurring objects; they use different visual cues to recognize objects of varying sizes. We hope our insights can help practitioners improve object detectors.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmvV2yjEs 

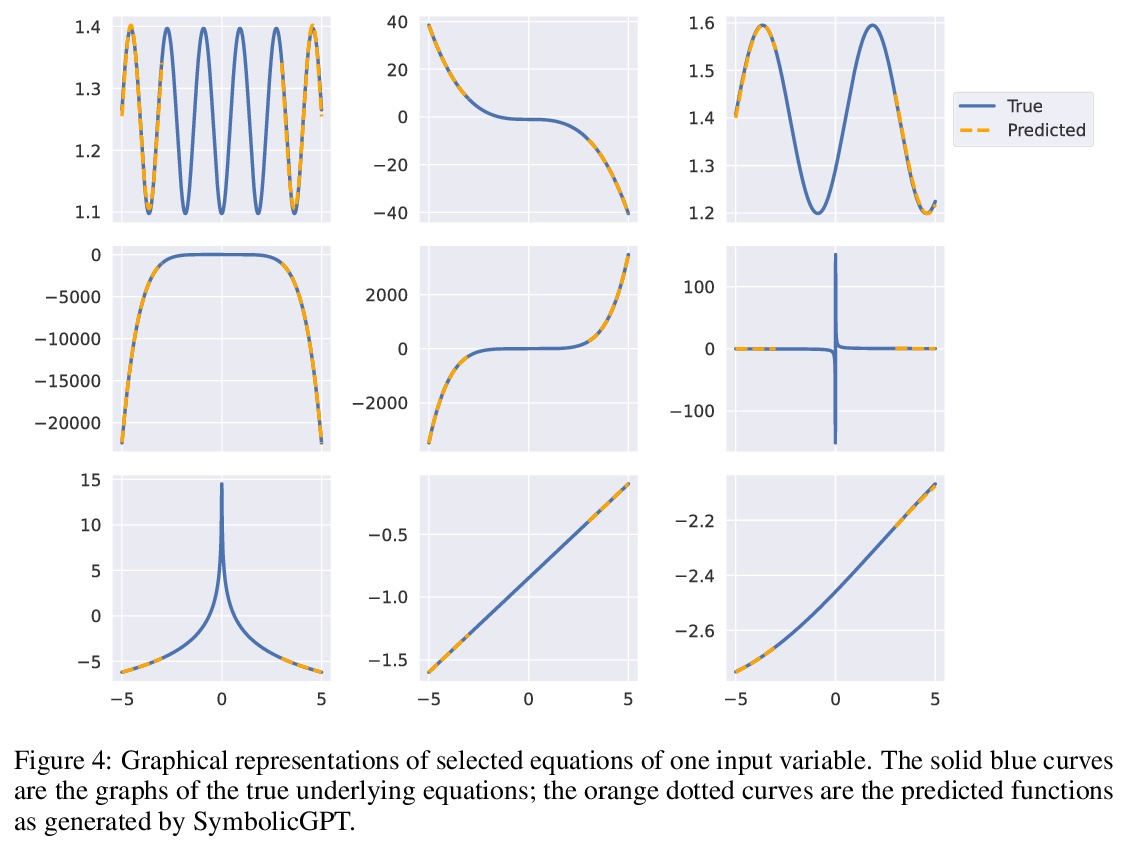
5、[LG] SymbolicGPT: A Generative Transformer Model for Symbolic Regression
M Valipour, B You, M Panju, A Ghodsi
[University of Waterloo]
SymbolicGPT: 符号回归的生成式Transformer模型。符号回归任务是确定一个最能拟合所提供输入和输出值数据集的数学表达式。由于数学表达式空间的丰富性,符号回归通常是一个具有挑战性的问题。虽然基于遗传进化算法的传统方法已经使用了几十年,但基于深度学习的方法相对较新,是一个活跃的研究领域。本文提出SymbolicGPT,一种面向符号回归的基于Transformer的新型语言模型,以一种新的方式应用语言模型,将其与符号数学和点云的阶不变表示相结合,推动了语言模型的边界,从一个新的和强大的方向接近符号回归问题。该模型利用GPT等概率语言模型包括性能和灵活性方面的优势,消除了大多数回归方法的每实例计算费用,解决了其他基于语言的回归模型所带来的输入限制。与现有的方法相比,该方法是快速的、可扩展的,并且在几种符号回归问题上表现得很好。
Symbolic regression is the task of identifying a mathematical expression that best fits a provided dataset of input and output values. Due to the richness of the space of mathematical expressions, symbolic regression is generally a challenging problem. While conventional approaches based on genetic evolution algorithms have been used for decades, deep learning-based methods are relatively new and an active research area. In this work, we present SymbolicGPT, a novel transformer-based language model for symbolic regression3. This model exploits the advantages of probabilistic language models like GPT, including strength in performance and flexibility. Through comprehensive experiments, we show that our model performs strongly compared to competing models with respect to the accuracy, running time, and data efficiency.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmvYdDRNf 
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
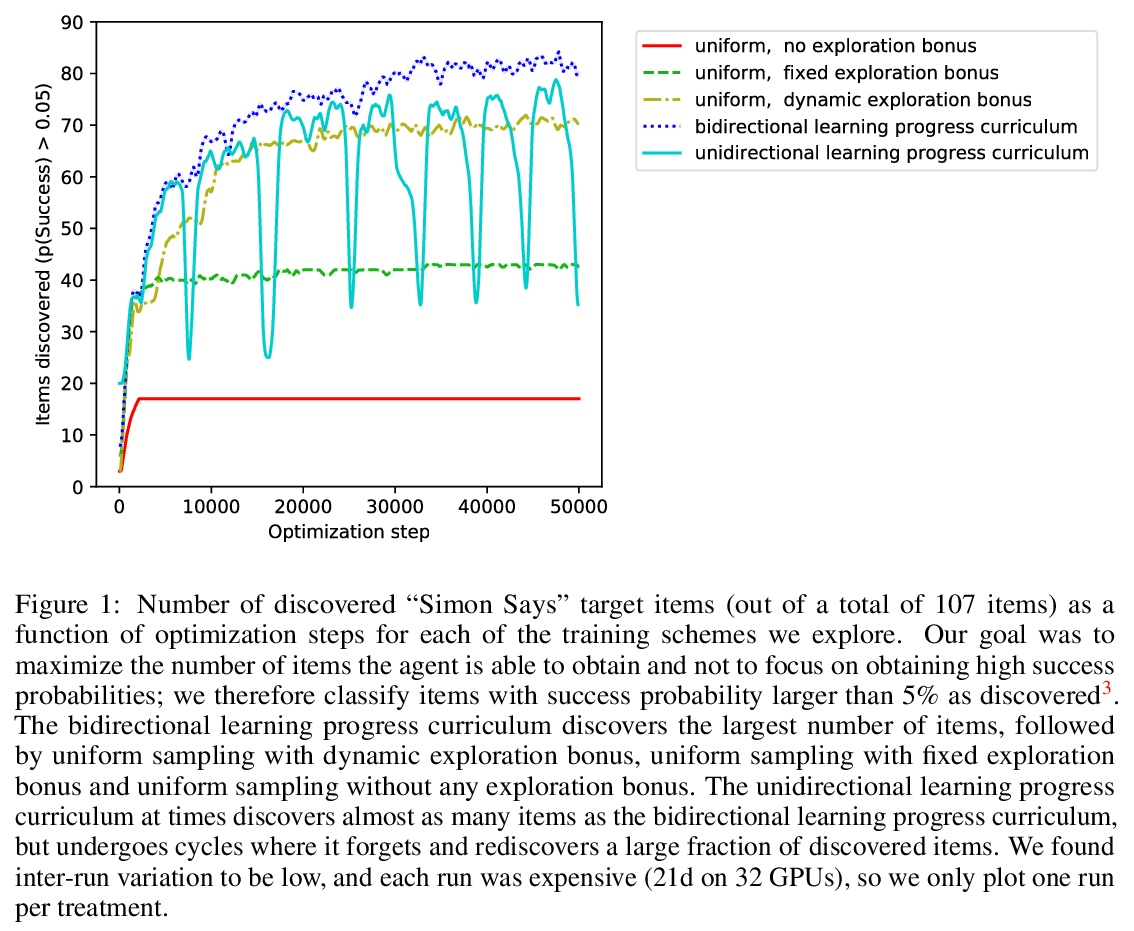
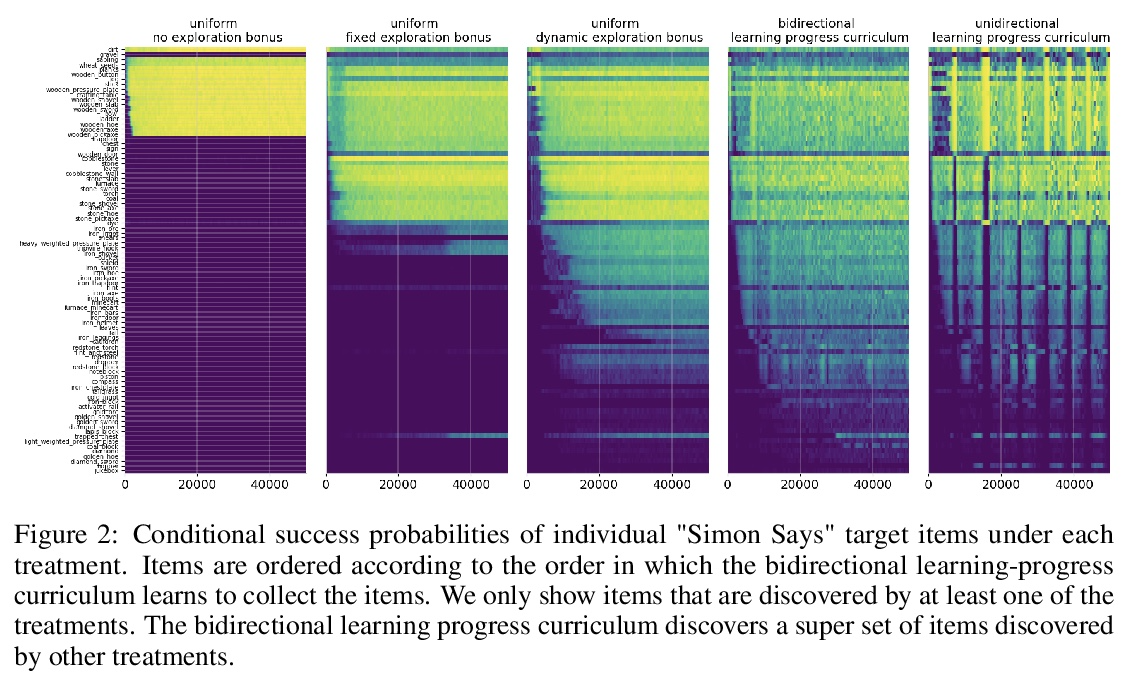
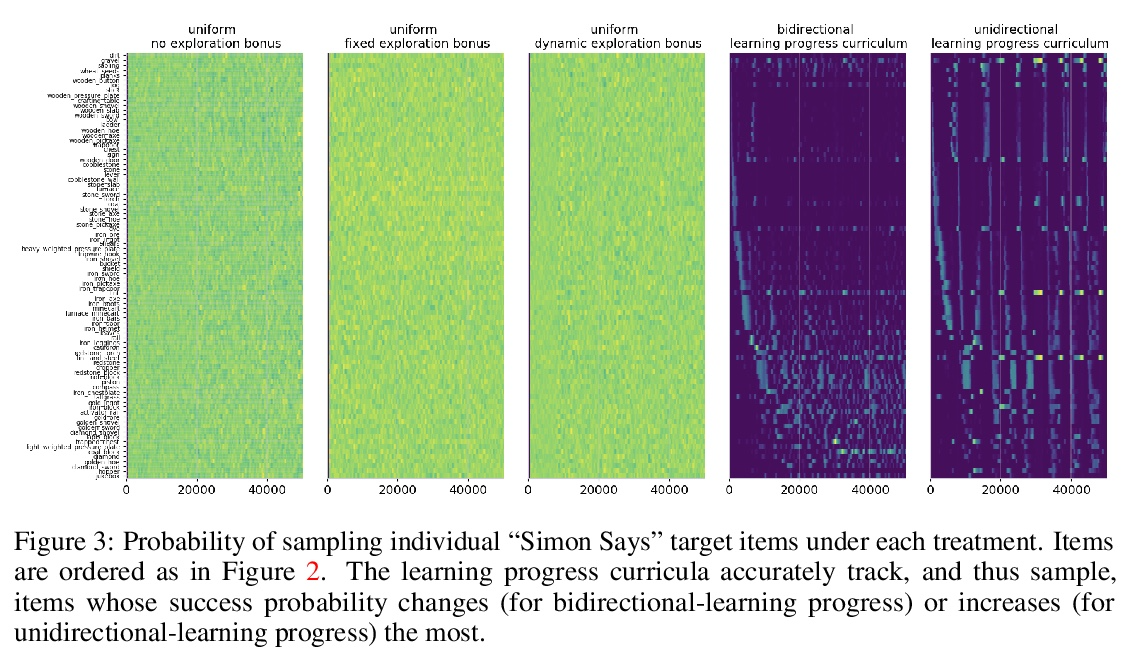
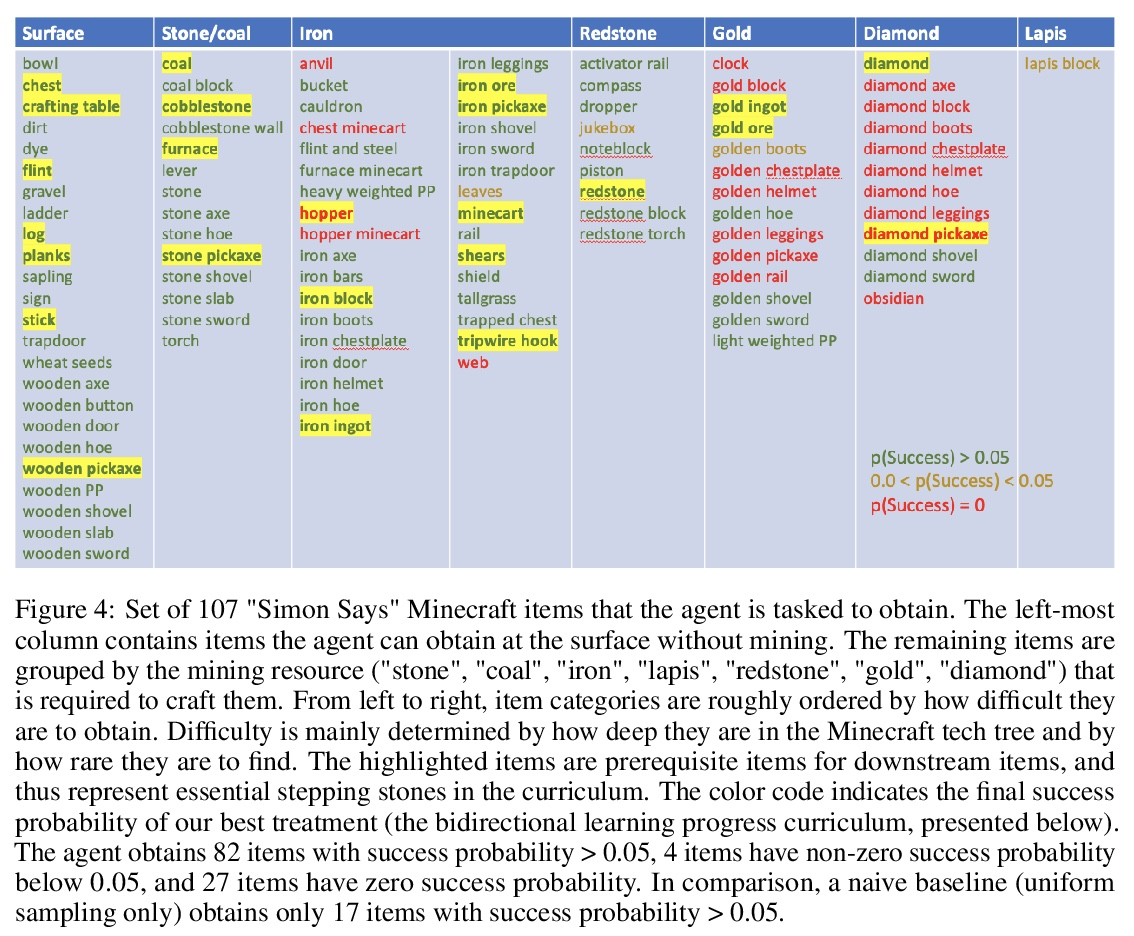
[LG] Multi-task curriculum learning in a complex, visual, hard-exploration domain: Minecraft
“我的世界”复杂、直观、难探索领域的多任务课程学习
I Kanitscheider, J Huizinga, D Farhi, W H Guss, B Houghton, R Sampedro, P Zhokhov, B Baker, A Ecoffet, J Tang, O Klimov, J Clune
[OpenAI]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kmw2etjle 
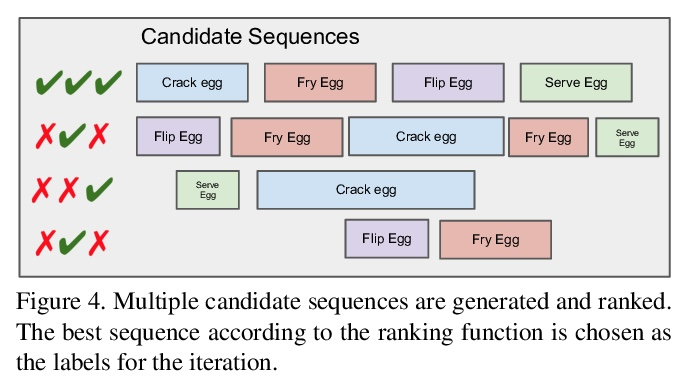
[CV] Unsupervised Discovery of Actions in Instructional Videos
教学视频中动作的无监督发现
A Piergiovanni, A Angelova, M S. Ryoo, I Essa
[Robotics at Google & Google Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kmw3Hacy1 

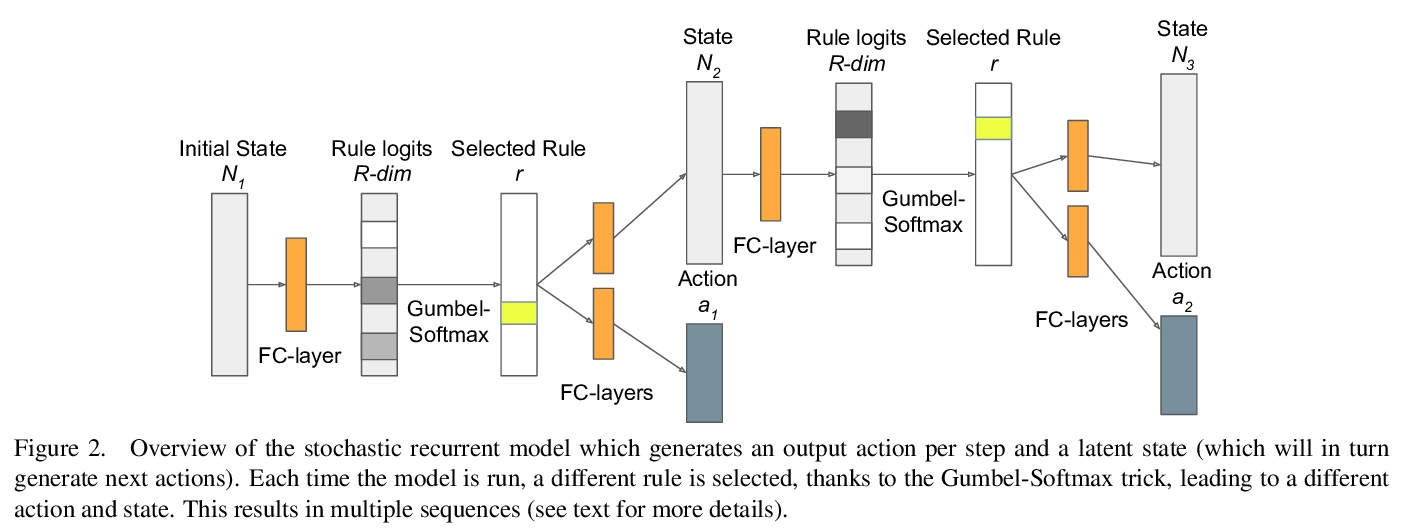
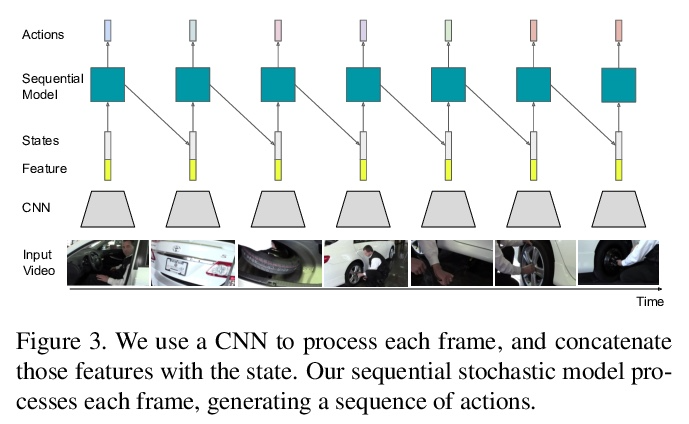
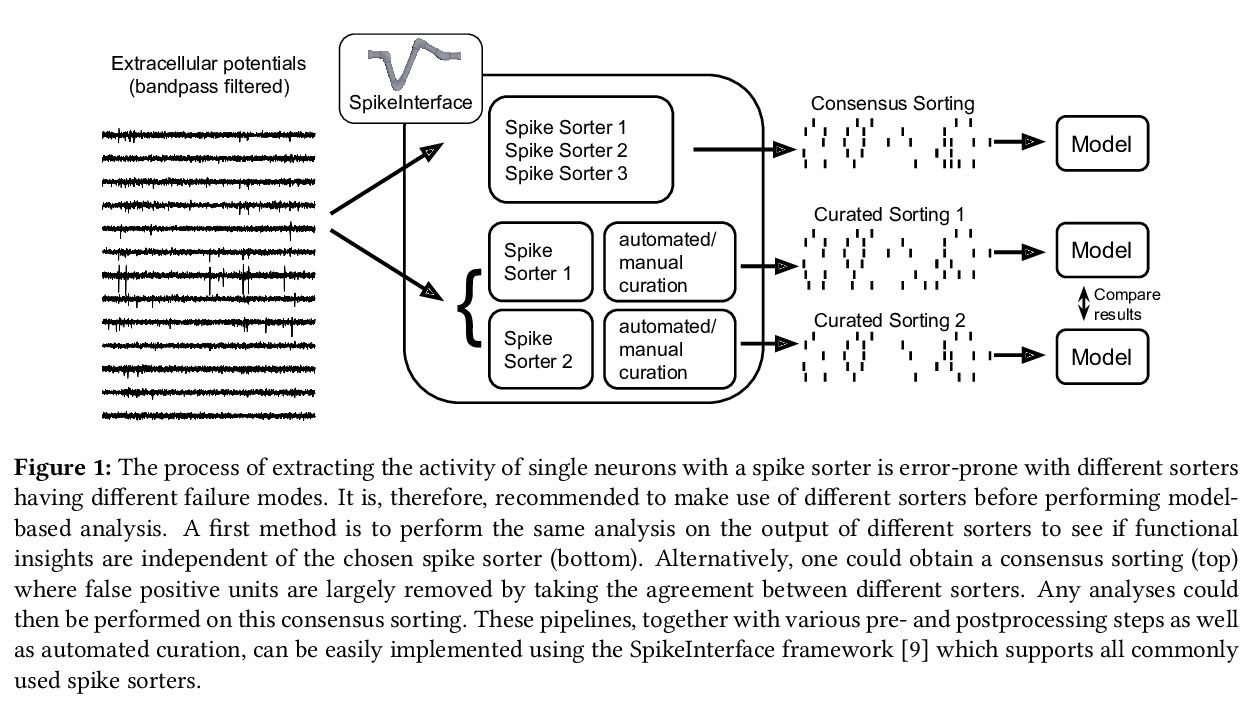
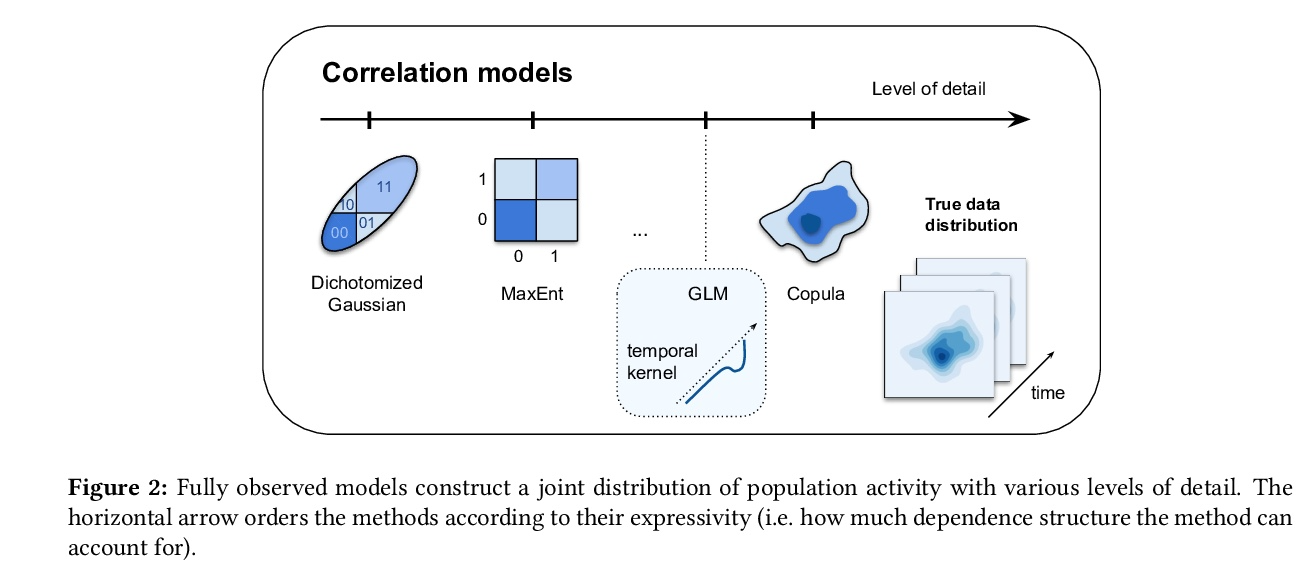
[LG] Building population models for large-scale neural recordings: opportunities and pitfalls
为大规模神经记录构建总体模型:机遇与陷阱
C Hurwitz, N Kudryashova, A Onken, M H. Hennig
[University of Edinburgh]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kmw4Wy37z 
[CV] Rethinking Token-Mixing MLP for MLP-based Vision Backbone
面向基于MLP视觉骨干的Token混合MLP的反思
T Yu, X Li, Y Cai, M Sun, P Li
[Baidu Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kmw6eqCfX