- 1、[CV] MLP-Mixer: An all-MLP Architecture for Vision
- 2、[LG] Data-driven discovery of physical laws with human-understandable deep learning
- 3、[AS] Audio Transformers:Transformer Architectures For Large Scale Audio Understanding. Adieu Convolutions
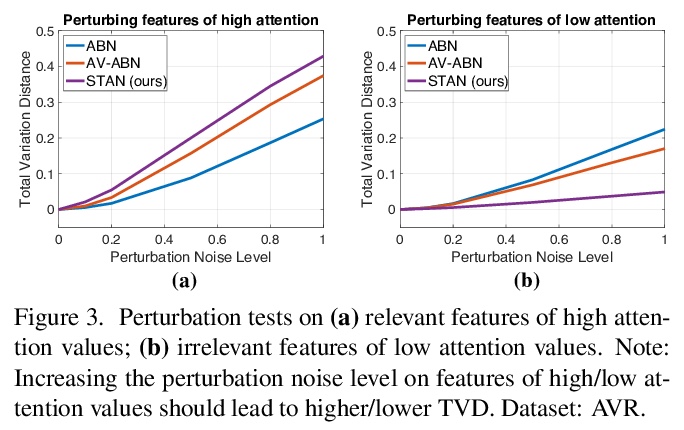
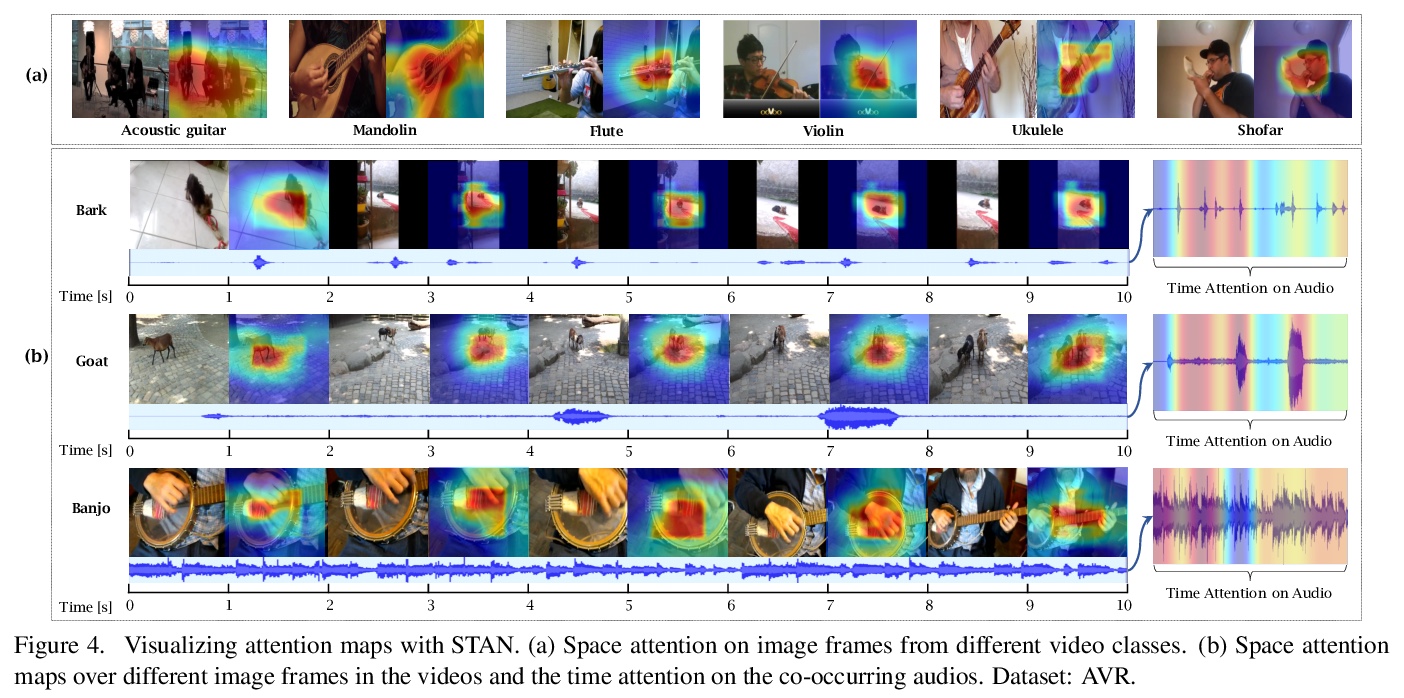
- 4、[CV] Where and When: Space-Time Attention for Audio-Visual Explanations
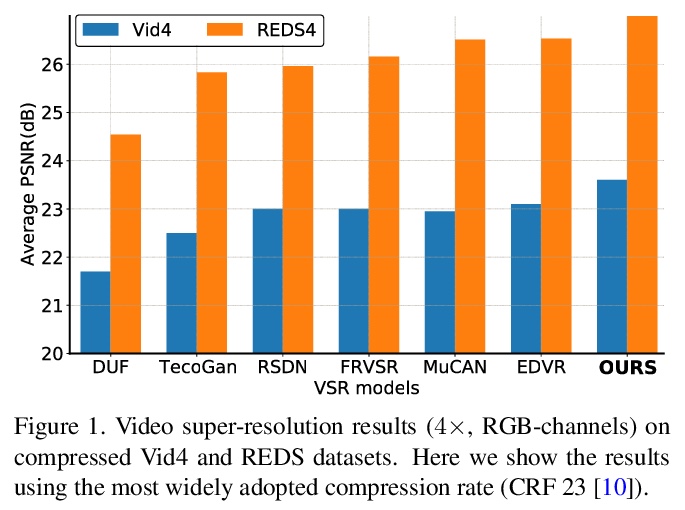
- 5、[CV] COMISR: Compression-Informed Video Super-Resolution
- [CV] Motion-Augmented Self-Training for Video Recognition at Smaller Scale
- [CL] Inferring the Reader: Guiding Automated Story Generation with Commonsense Reasoning
- [CV] Modulated Periodic Activations for Generalizable Local Functional Representations
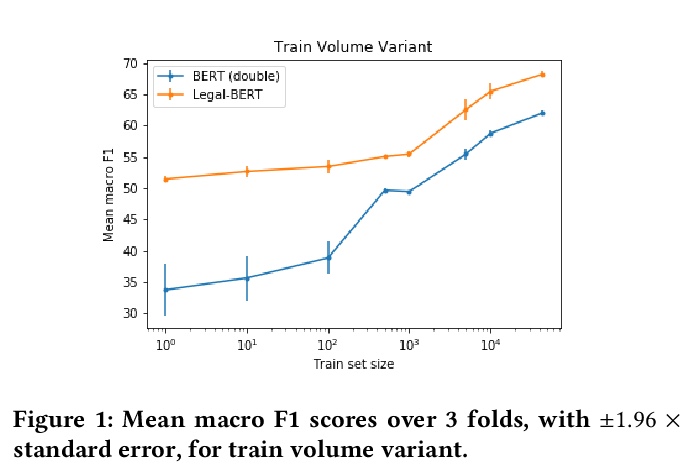
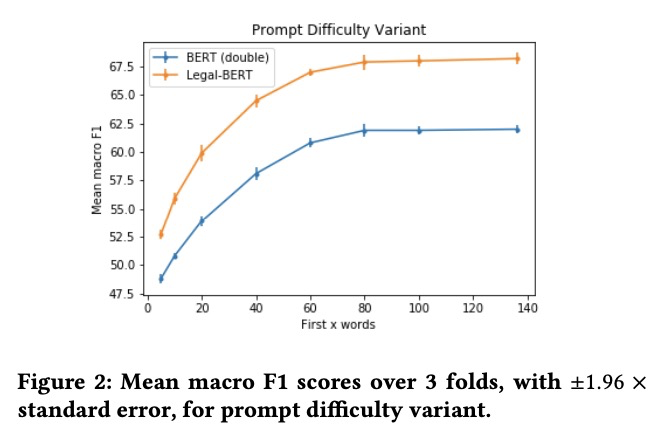
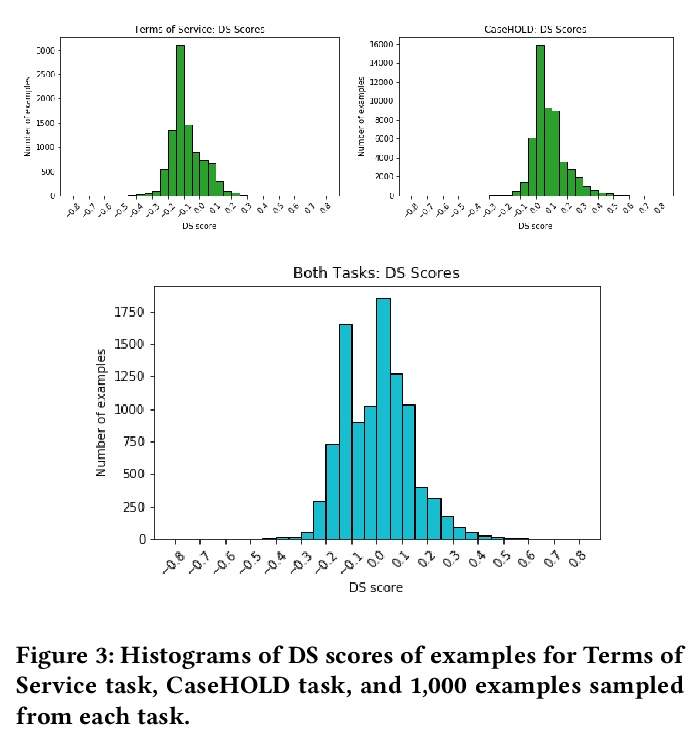
- [CL] When Does Pretraining Help? Assessing Self-Supervised Learning for Law and the CaseHOLD Dataset
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
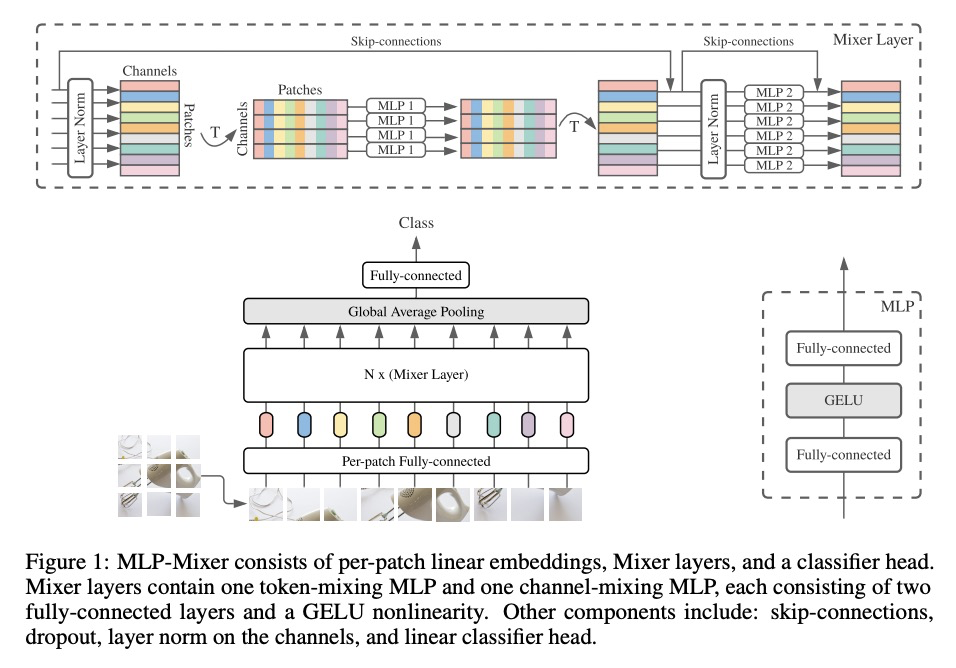
1、[CV] MLP-Mixer: An all-MLP Architecture for Vision
I Tolstikhin, N Houlsby, A Kolesnikov, L Beyer, X Zhai, T Unterthiner, J Yung, D Keysers, J Uszkoreit, M Lucic, A Dosovitskiy
[Google Research]
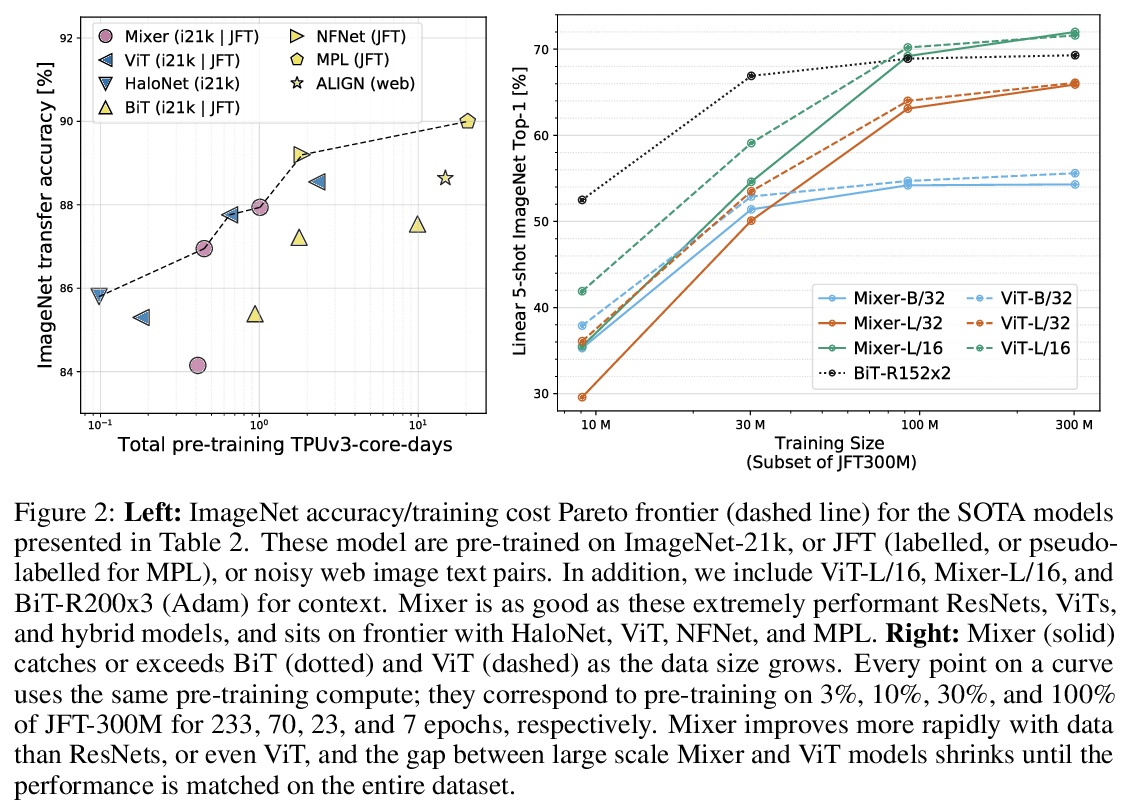
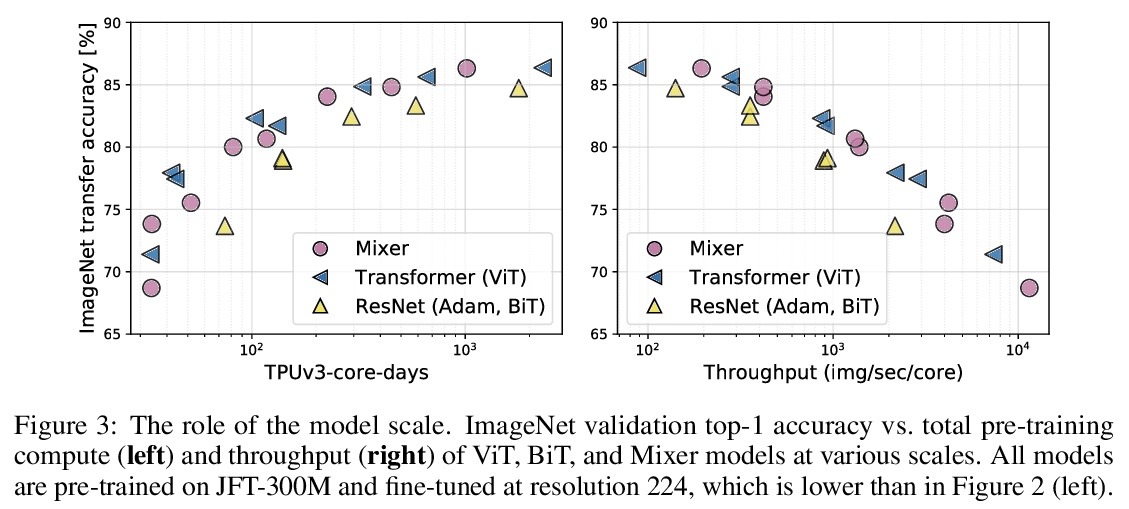
MLP-Mixer:视觉全MLP架构。卷积神经网络(CNN)是计算机视觉的首选模型。最近,基于注意力的网络,如视觉Transformer,也开始流行起来。虽然卷积和注意力都可以实现良好的性能,但都不是必要的。本文提出MLP-Mixer,一种完全基于多层感知器(MLP)的架构,包含两种类型的层:一种是独立应用于图块的MLP(用于位置级特征”混合”),另一种是跨图块应用的MLP(用于空间信息”混合”)。在大型数据集上进行训练,或使用现代正则化方案时,MLP-Mixer在图像分类基准上获得了有竞争力的分数,其预训练和推理的计算资源开销与最先进的模型相当。
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are the go-to model for computer vision. Recently, attention-based networks, such as the Vision Transformer, have also become popular. In this paper we show that while convolutions and attention are both sufficient for good performance, neither of them are necessary. We present MLP-Mixer, an architecture based exclusively on multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs). MLP-Mixer contains two types of layers: one with MLPs applied independently to image patches (i.e. “mixing” the per-location features), and one with MLPs applied across patches (i.e. “mixing” spatial information). When trained on large datasets, or with modern regularization schemes, MLP-Mixer attains competitive scores on image classification benchmarks, with pre-training and inference cost comparable to state-of-the-art models. We hope that these results spark further research beyond the realms of well established CNNs and Transformers.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke9mutsZA

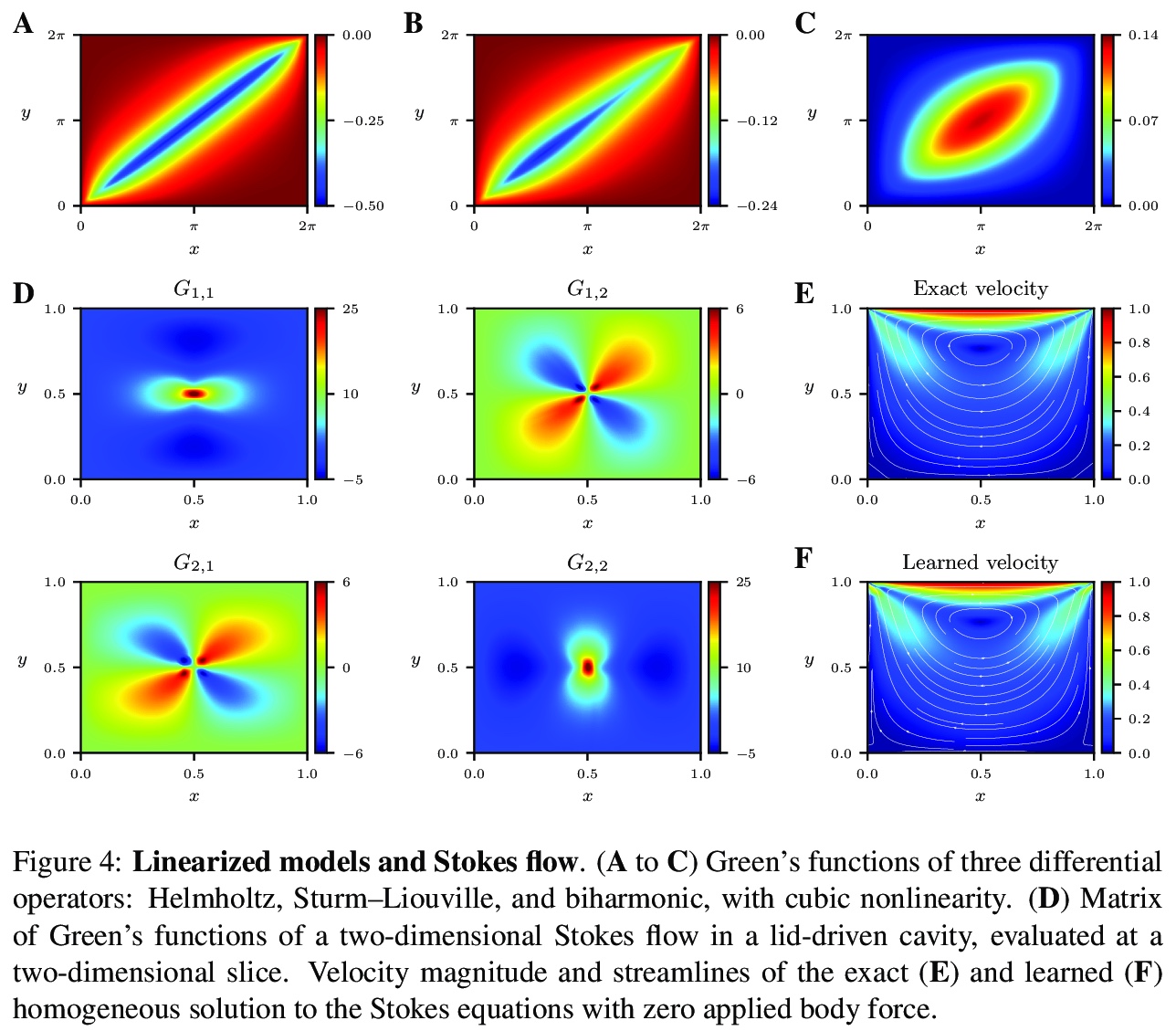
2、[LG] Data-driven discovery of physical laws with human-understandable deep learning
N Boullé, C J. Earls, A Townsend
[University of Oxford & Cornell University]
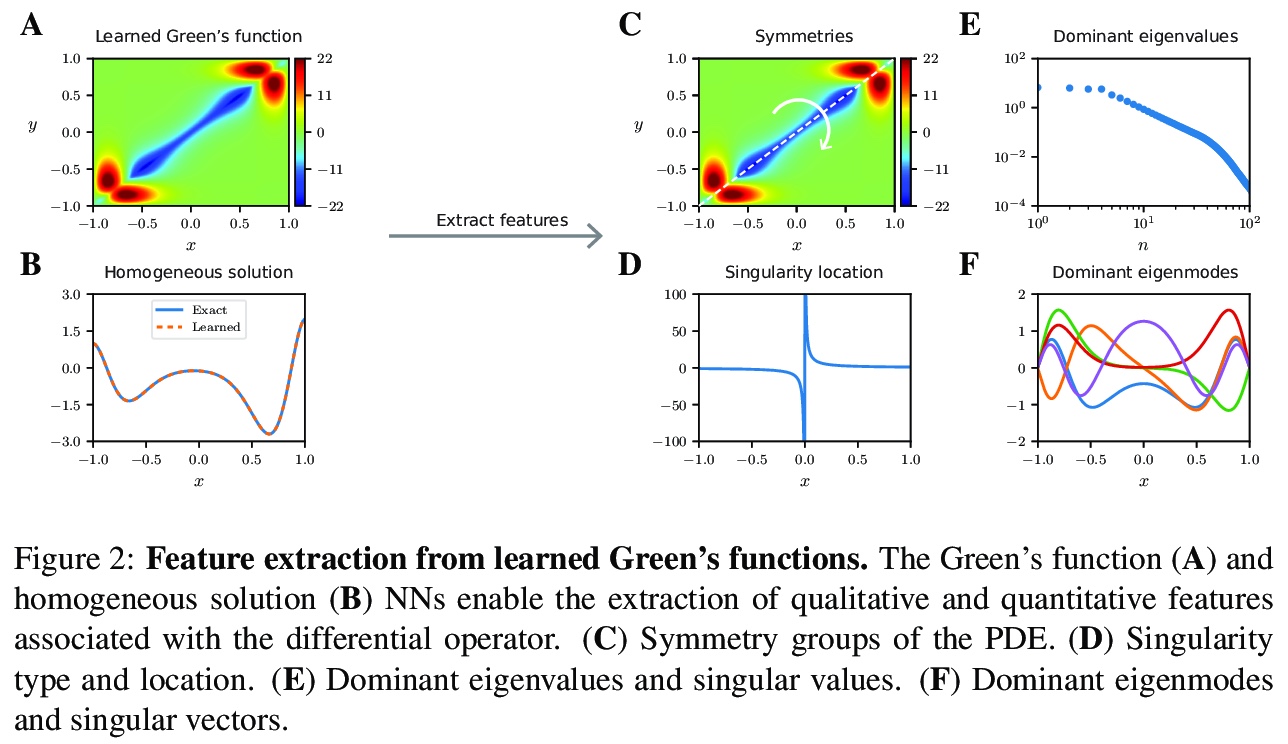
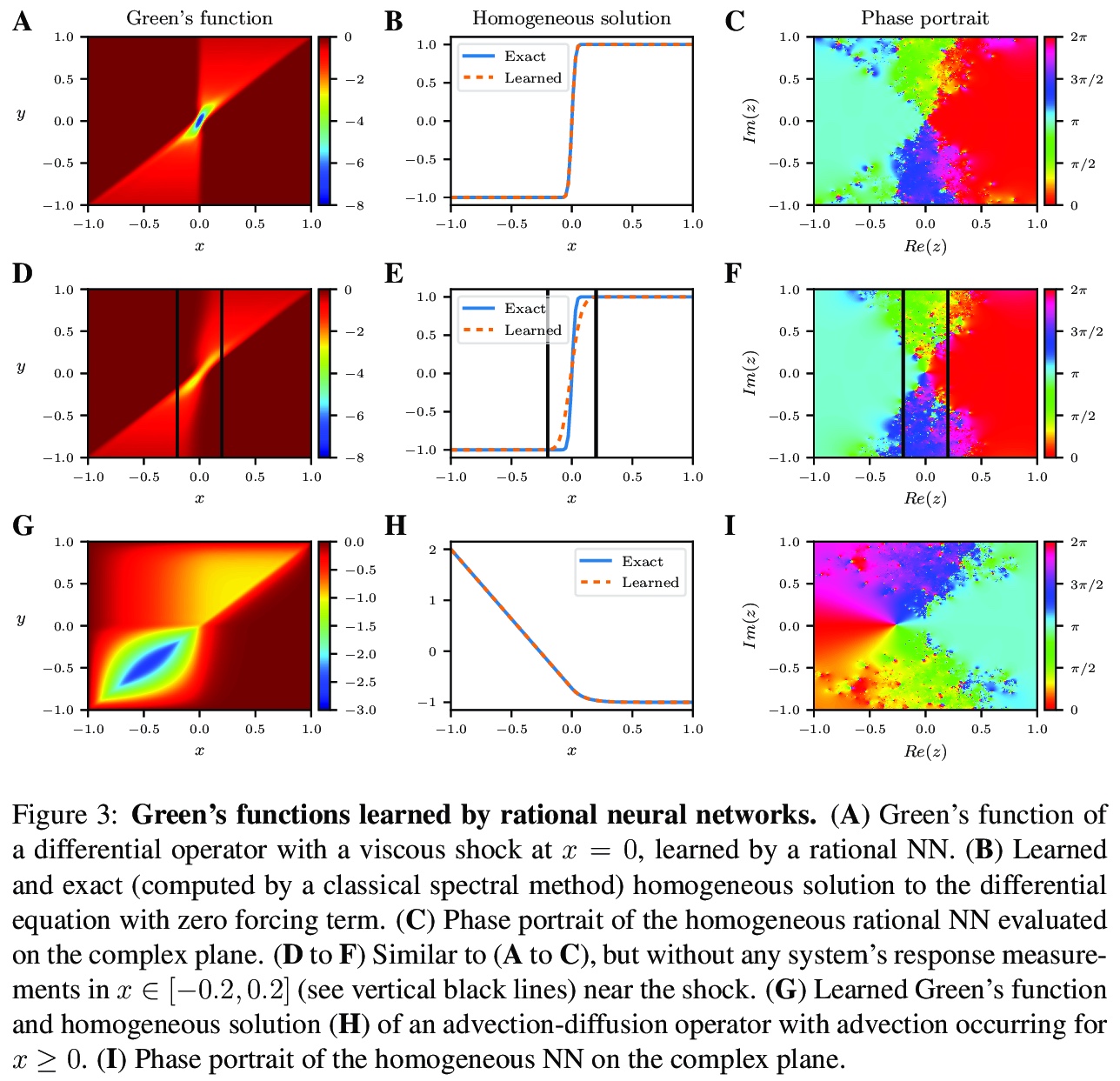
用人类可理解的深度学习进行数据驱动的物理规律发现。深度学习有机会通过以人类可解释的方式揭示其发现,来彻底改变科学和技术。本文开发了一种新的数据驱动方法,通过人机合作,加速科学发现。通过收集物理系统的反应,在精心选择的激励下,训练合理的神经网络来学习隐式偏微分方程的格林函数。这些解决方案揭示了人类可以理解的属性和特征,如线性守恒定律和对称性,以及激波和奇异点定位、边界效应和主模。在几个例子上说明了这一技术,并捕捉到了一系列的物理现象。
There is an opportunity for deep learning to revolutionize science and technology by revealing its findings in a human interpretable manner. We develop a novel data-driven approach for creating a human-machine partnership to accelerate scientific discovery. By collecting physical system responses, under carefully selected excitations, we train rational neural networks to learn Green’s functions of hidden partial differential equation. These solutions reveal human-understandable properties and features, such as linear conservation laws, and symmetries, along with shock and singularity locations, boundary effects, and dominant modes. We illustrate this technique on several examples and capture a range of physics, including advection-diffusion, viscous shocks, and Stokes flow in a lid-driven cavity.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke9smcq9S

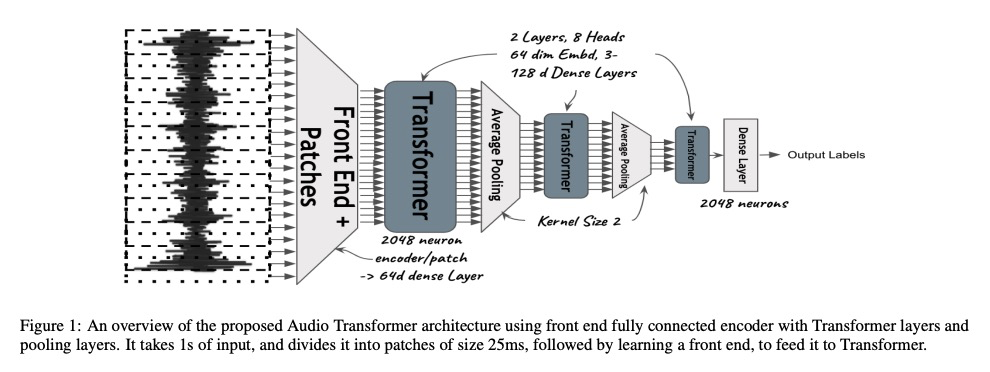
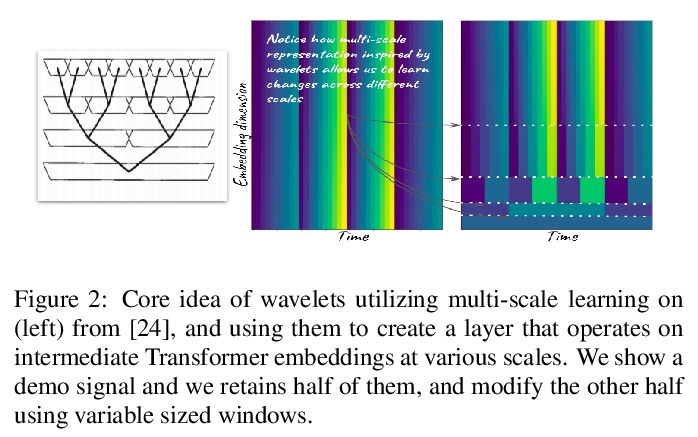
3、[AS] Audio Transformers:Transformer Architectures For Large Scale Audio Understanding. Adieu Convolutions
P Verma, J Berger
[Stanford University]
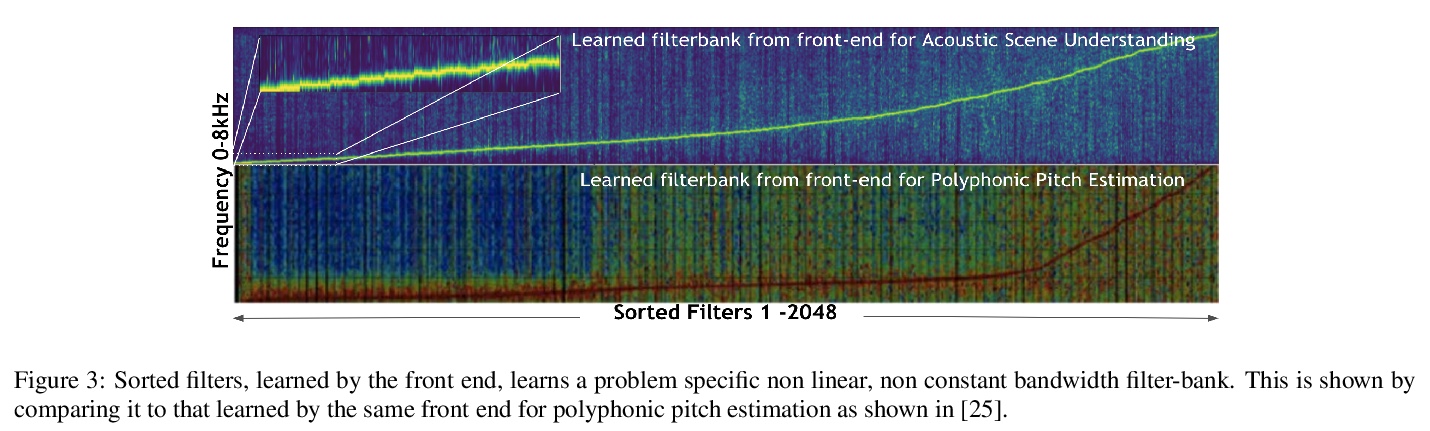
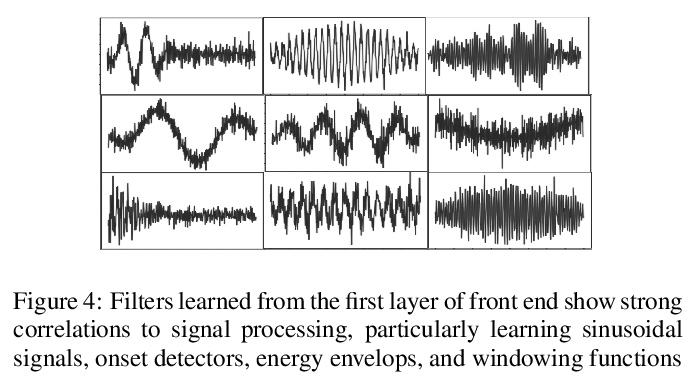
音频Transformer:用于大规模音频理解的Transformer架构。过去20年中,CNN架构通过学习特征的分层组织,产生了令人信服的声音感知和认知模型。类似于计算机视觉的成功,音频特征分类可在各种数据集和标签上针对特定的兴趣任务进行优化。为图像理解设计的类似架构已被证明对声学场景分析有效。本文将基于Transformer的架构应用于原始音频信号,不需要使用卷积层。在由200个类别组成的标准数据集Free Sound 50K上,所提出模型优于卷积模型,产生了最先进的结果。通过使用从过去几年设计的卷积网络中获得灵感的池化等技术,进一步提高了Transformer架构的性能。展示了如何将受小波启发的多速率信号处理思想应用于Transformer嵌入以改善结果,展示了模型是如何学习非线性非恒定带宽滤波器库,显示了一个适应音频理解任务的时间频率前端表示。
Over the past two decades, CNN architectures have produced compelling models of sound perception and cognition, learning hierarchical organizations of features. Analogous to successes in computer vision, audio feature classification can be optimized for a particular task of interest, over a wide variety of datasets and labels. In fact similar architectures designed for image understanding have proven effective for acoustic scene analysis. Here we propose applying Transformer based architectures without convolutional layers to raw audio signals. On a standard dataset of Free Sound 50K, comprising of 200 categories, our model outperforms convolutional models to produce state of the art results. This is significant as unlike in natural language processing and computer vision, we do not perform unsupervised pre-training for outperforming convolutional architectures. On the same training set, with respect mean average precision benchmarks, we show a significant improvement. We further improve the performance of Transformer architectures by using techniques such as pooling inspired from convolutional network designed in the past few years. In addition, we also show how multi-rate signal processing ideas inspired from wavelets, can be applied to the Transformer embeddings to improve the results. We also show how our models learns a non-linear non constant bandwidth filter-bank, which shows an adaptable time frequency front end representation for the task of audio understanding, different from other tasks e.g. pitch estimation.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke9vAebAd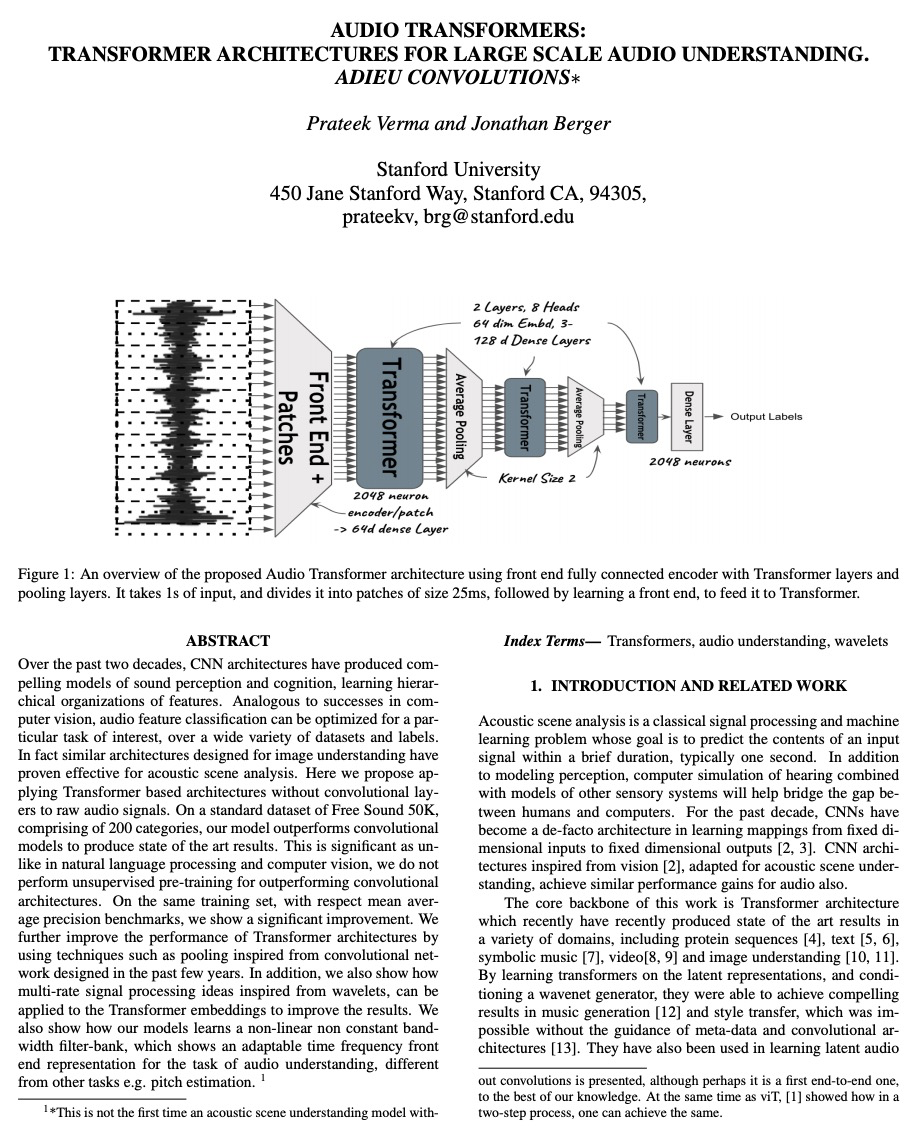
4、[CV] Where and When: Space-Time Attention for Audio-Visual Explanations
Y Chen, T Hummel, A. S Koepke, Z Akata
[University of Tubingen]
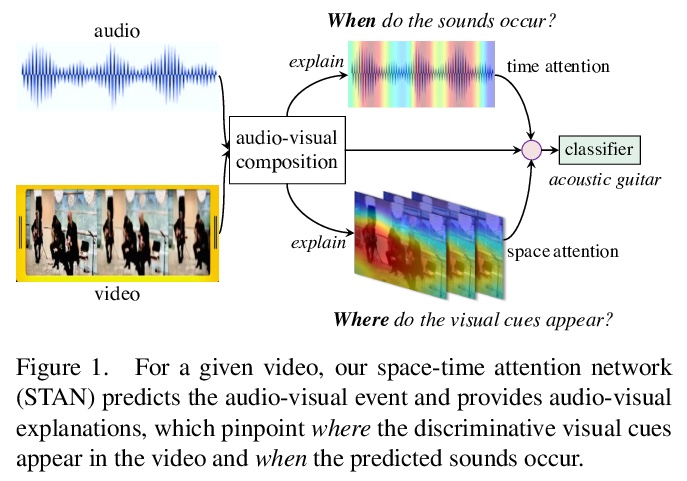
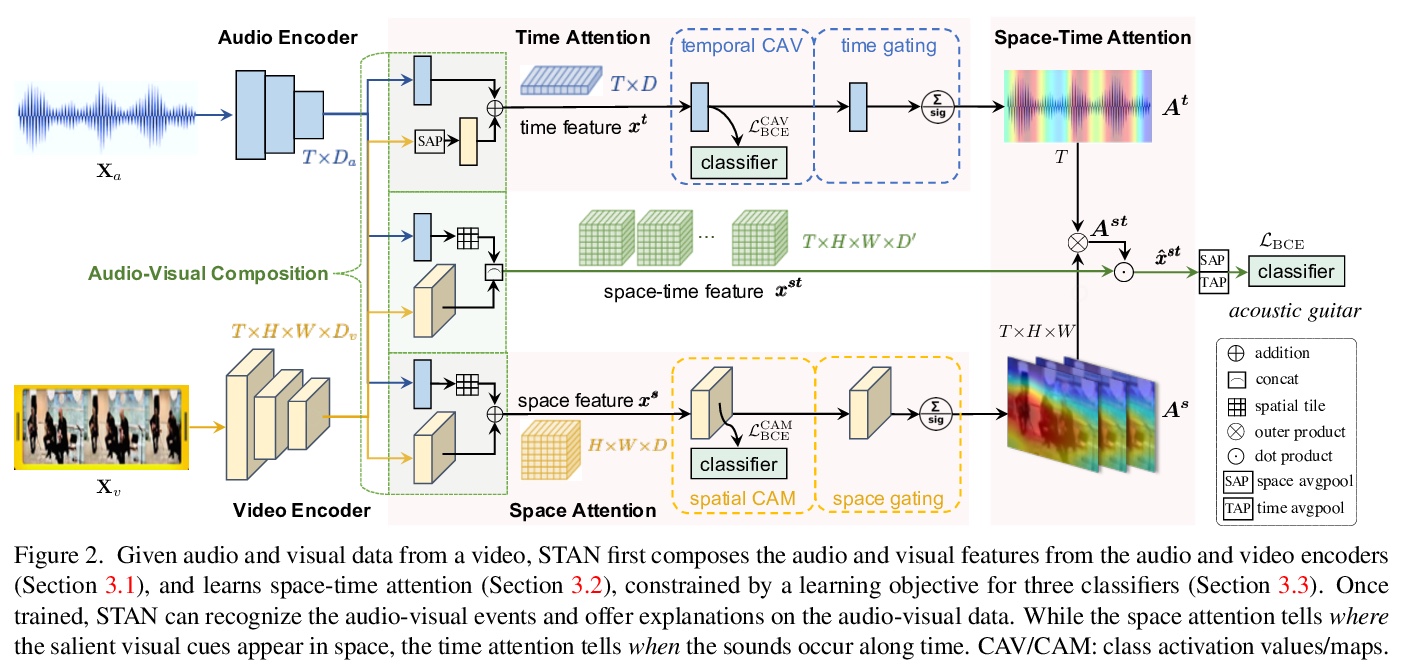
音频-视觉解释的时空注意力。解释一个多模态决策器的决定,需要确定来自两种模态的证据。可解释AI的最新进展为在静态图像上训练的模型提供了解释。但涉及到在动态世界中对多种感官模态进行建模时,如何解开复杂的多模态模型的神秘动态仍然没有得到充分的探索。本文探索音频-视觉识别的可学习解释,提出一种新的时空注意力网络,在空间和时间上揭示了音频和视觉数据的协同动态。该模型能预测音频-视觉视频事件,同时通过定位相关视觉线索出现的位置,以及预测的声音在视频中出现的时间,来证明其决策。在三个音频-视觉视频事件数据集上对模型进行了基准测试,与最近的多个多模态表示学习器和内在解释模型进行了广泛的比较。实验结果表明,该模型在视听视频事件识别方面的性能明显优于现有方法。
Explaining the decision of a multi-modal decision maker requires to determine the evidence from both modalities. Recent advances in XAI provide explanations for models trained on still images. However, when it comes to modeling multiple sensory modalities in a dynamic world, it remains underexplored how to demystify the mysterious dynamics of a complex multi-modal model. In this work, we take a crucial step forward and explore learnable explanations for audio-visual recognition. Specifically, we propose a novel space-time attention network that uncovers the synergistic dynamics of audio and visual data over both space and time. Our model is capable of predicting the audio-visual video events, while justifying its decision by localizing where the relevant visual cues appear, and when the predicted sounds occur in videos. We benchmark our model on three audiovisual video event datasets, comparing extensively to multiple recent multi-modal representation learners and intrinsic explanation models. Experimental results demonstrate the clear superior performance of our model over the existing methods on audio-visual video event recognition. Moreover, we conduct an in-depth study to analyze the explainability of our model based on robustness analysis via perturbation tests and pointing games using human annotations.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke9zItZT0
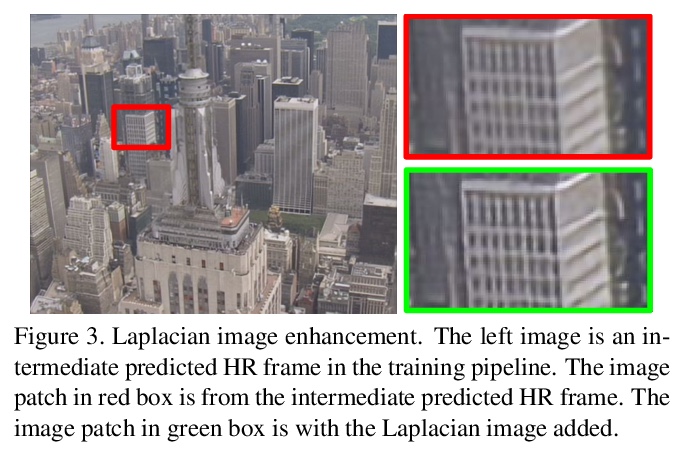
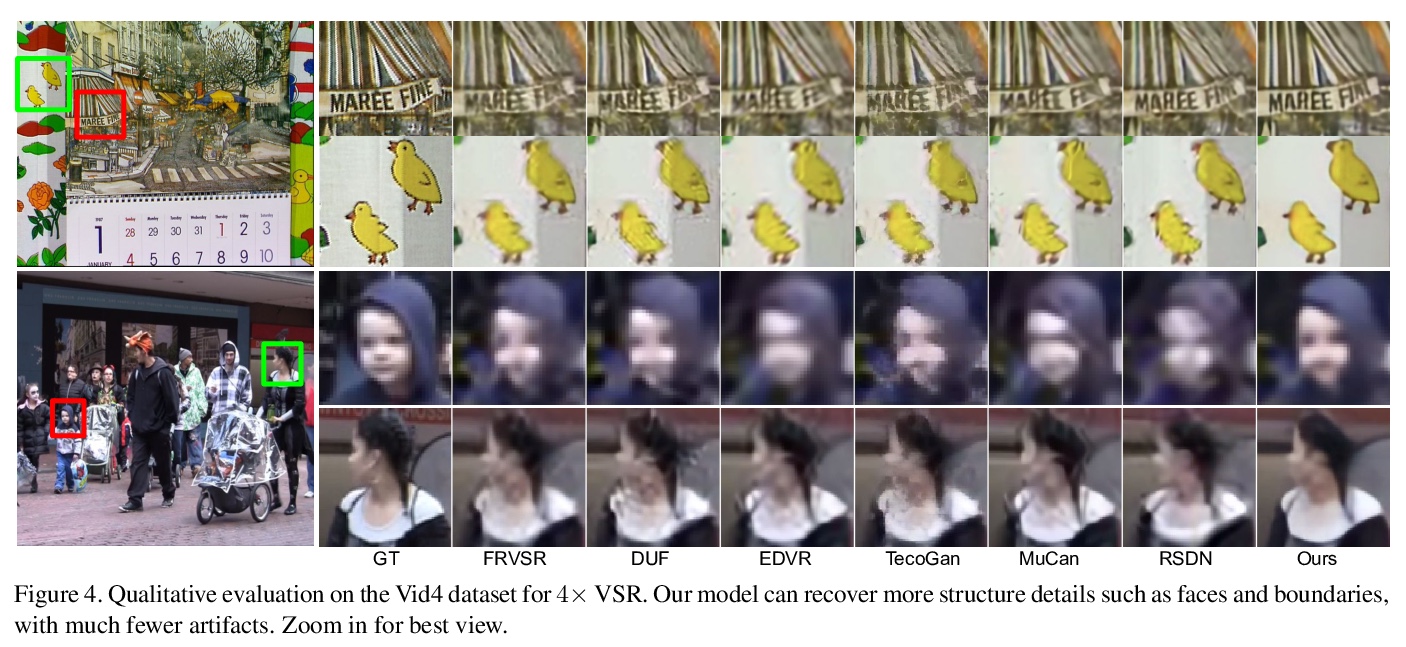
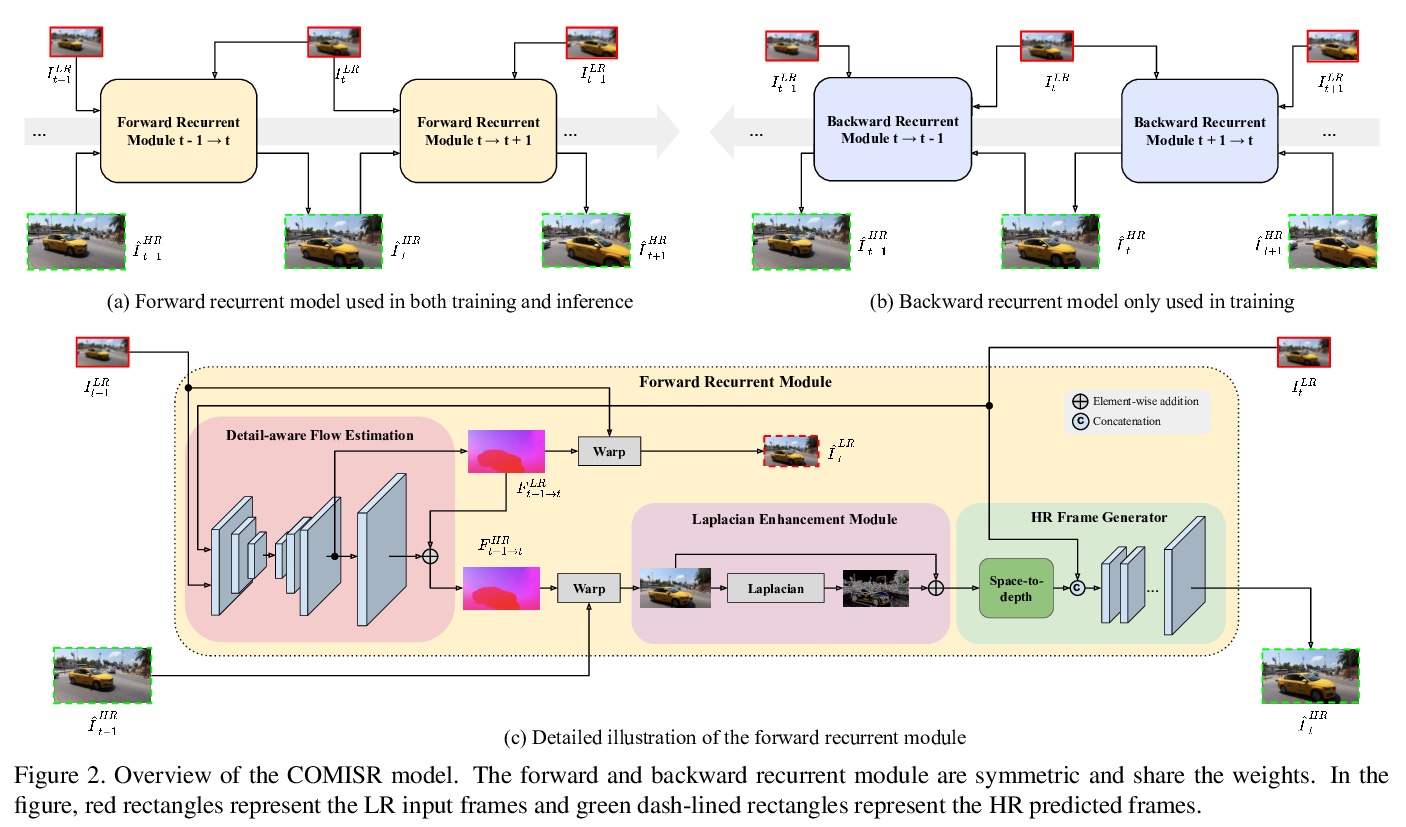
5、[CV] COMISR: Compression-Informed Video Super-Resolution
Y Li, P Jin, F Yang, C Liu, M Yang, P Milanfar
[Google]
COMISR:压缩特性感知视频超分辨率。大多数视频超分辨率方法,侧重于从低分辨率视频中恢复高分辨率视频帧,而没有考虑压缩。然而,网络和移动设备上大多数视频都被压缩了,在带宽有限的情况下,压缩会很严重。本文提出一种新的压缩特性感知的视频超分辨率模型,恢复高分辨率内容的同时,不引入由压缩引起的伪影。提出的模型由三个模块组成:双向递归变形、细节保持流估计和拉普拉斯增强,三个模块都用于处理压缩特性,如输入帧内的位置和输出帧的平滑度。对具有广泛压缩率的标准数据集进行了广泛的实验,涵盖了许多真实的视频使用案例,该方法不仅在广泛使用的基准数据集的未压缩帧上恢复了高分辨率的内容,而且在基于许多定量指标的超解压缩视频中实现了最先进的性能。通过仿真YouTube的流媒体来评估所提出的方法,证明了其有效性和鲁棒性。
Most video super-resolution methods focus on restoring high-resolution video frames from low-resolution videos without taking into account compression. However, most videos on the web or mobile devices are compressed, and the compression can be severe when the bandwidth is limited. In this paper, we propose a new compressioninformed video super-resolution model to restore highresolution content without introducing artifacts caused by compression. The proposed model consists of three modules for video super-resolution: bi-directional recurrent warping, detail-preserving flow estimation, and Laplacian enhancement. All these three modules are used to deal with compression properties such as the location of the intra-frames in the input and smoothness in the output frames. For thorough performance evaluation, we conducted extensive experiments on standard datasets with a wide range of compression rates, covering many real video use cases. We showed that our method not only recovers high-resolution content on uncompressed frames from the widely-used benchmark datasets, but also achieves state-ofthe-art performance in super-resolving compressed videos based on numerous quantitative metrics. We also evaluated the proposed method by simulating streaming from YouTube to demonstrate its effectiveness and robustness.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke9EOhpOl


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
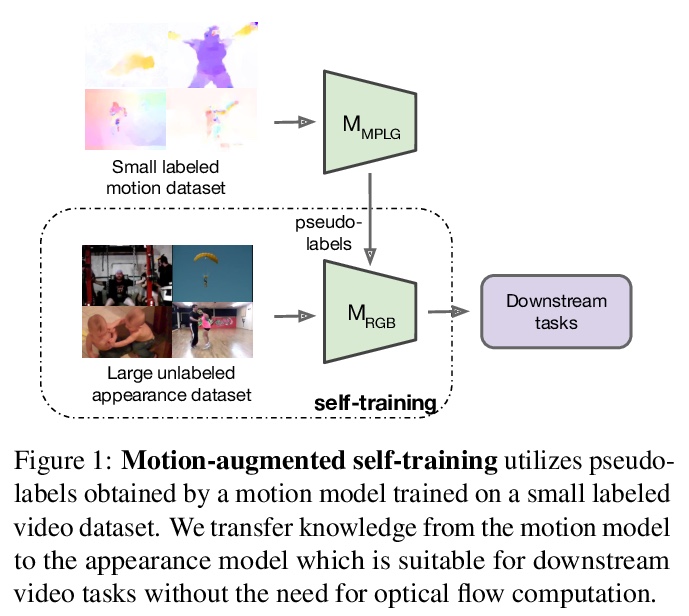
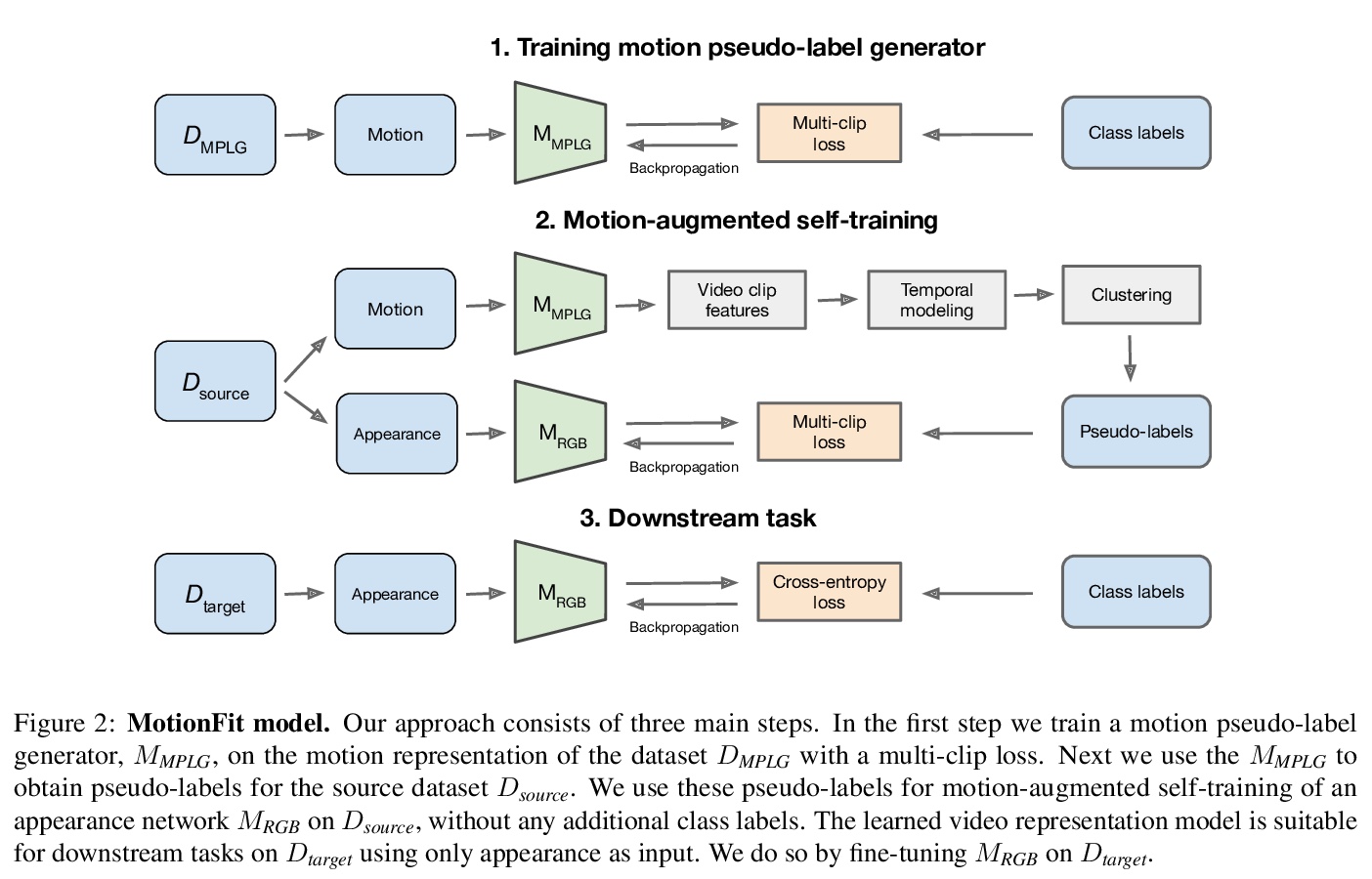
[CV] Motion-Augmented Self-Training for Video Recognition at Smaller Scale
面向更小规模视频识别的运动增强自训练
K Gavrilyuk, M Jain, I Karmanov, C G. M. Snoek
[University of Amsterdam & Qualcomm AI Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke9J6f74F
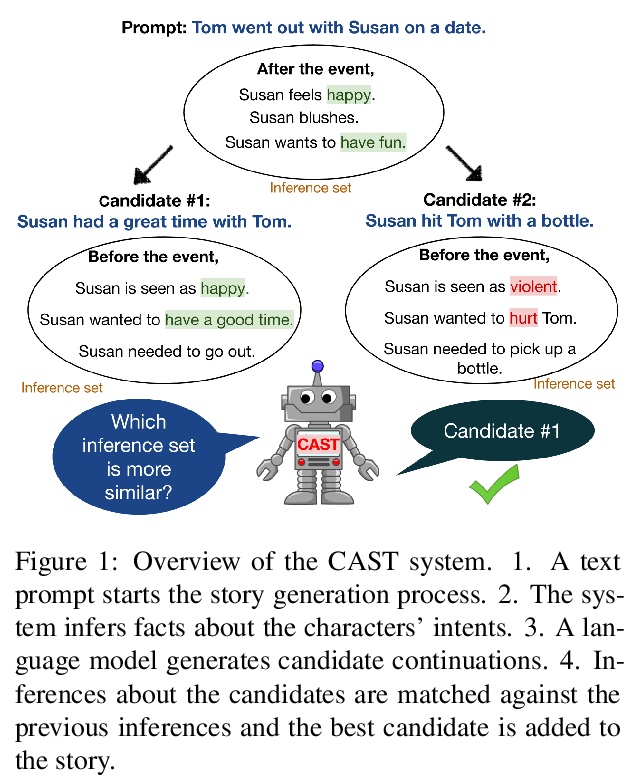
[CL] Inferring the Reader: Guiding Automated Story Generation with Commonsense Reasoning
推断读者:基于常识推理引导自动故事生成
X Peng, S Li, S Wiegreffe, M Riedl
[Georgia Institute of Technology]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke9KB4tu3
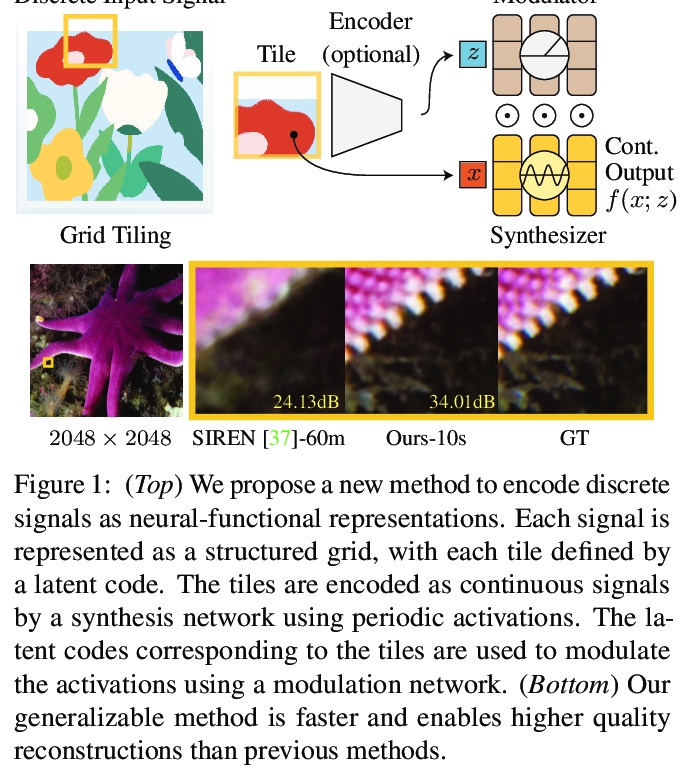
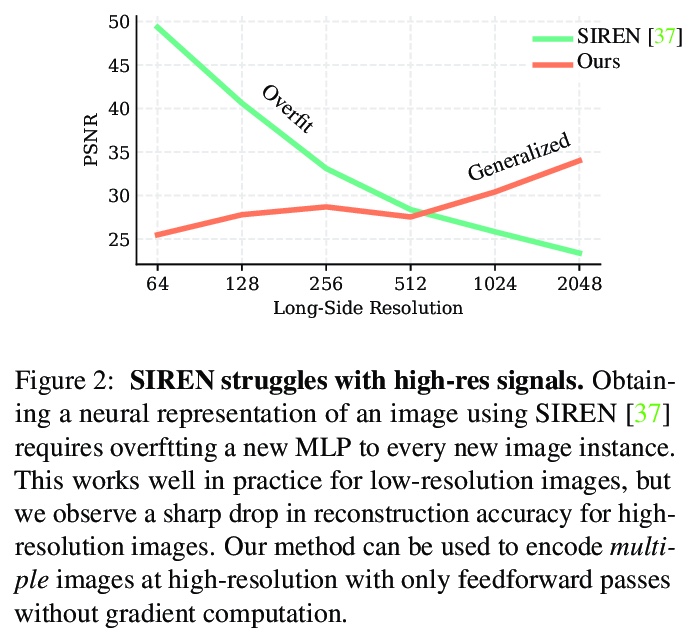
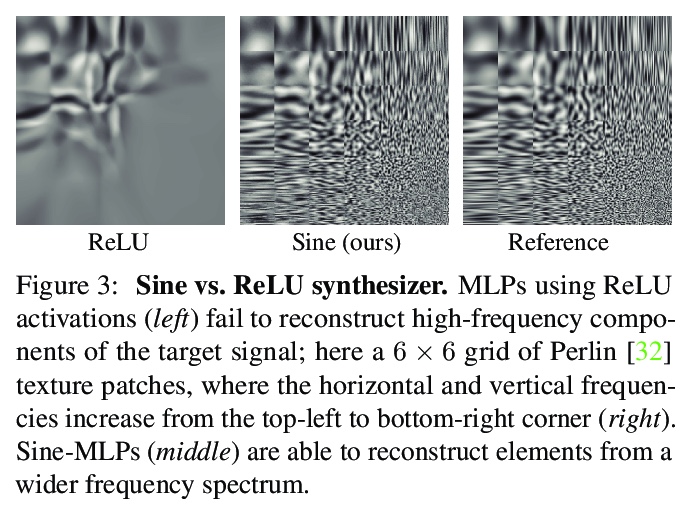
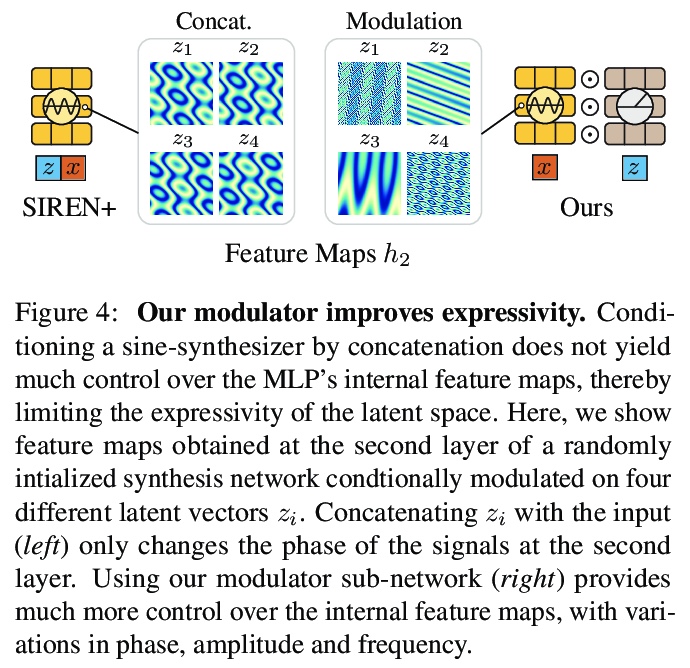
[CV] Modulated Periodic Activations for Generalizable Local Functional Representations
面向可泛化局部功能性表示的调制周期性激活
I Mehta, M Gharbi, C Barnes, E Shechtman, R Ramamoorthi, M Chandraker
[UC San Diego & Adobe Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke9O1xZZw
[CL] When Does Pretraining Help? Assessing Self-Supervised Learning for Law and the CaseHOLD Dataset
预训练何时有效?面向法律和CaseHOLD数据集的自监督学习评价
L Zheng, N Guha, B R. Anderson, P Henderson, D E. Ho
[Stanford University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Ke9QqsBVH