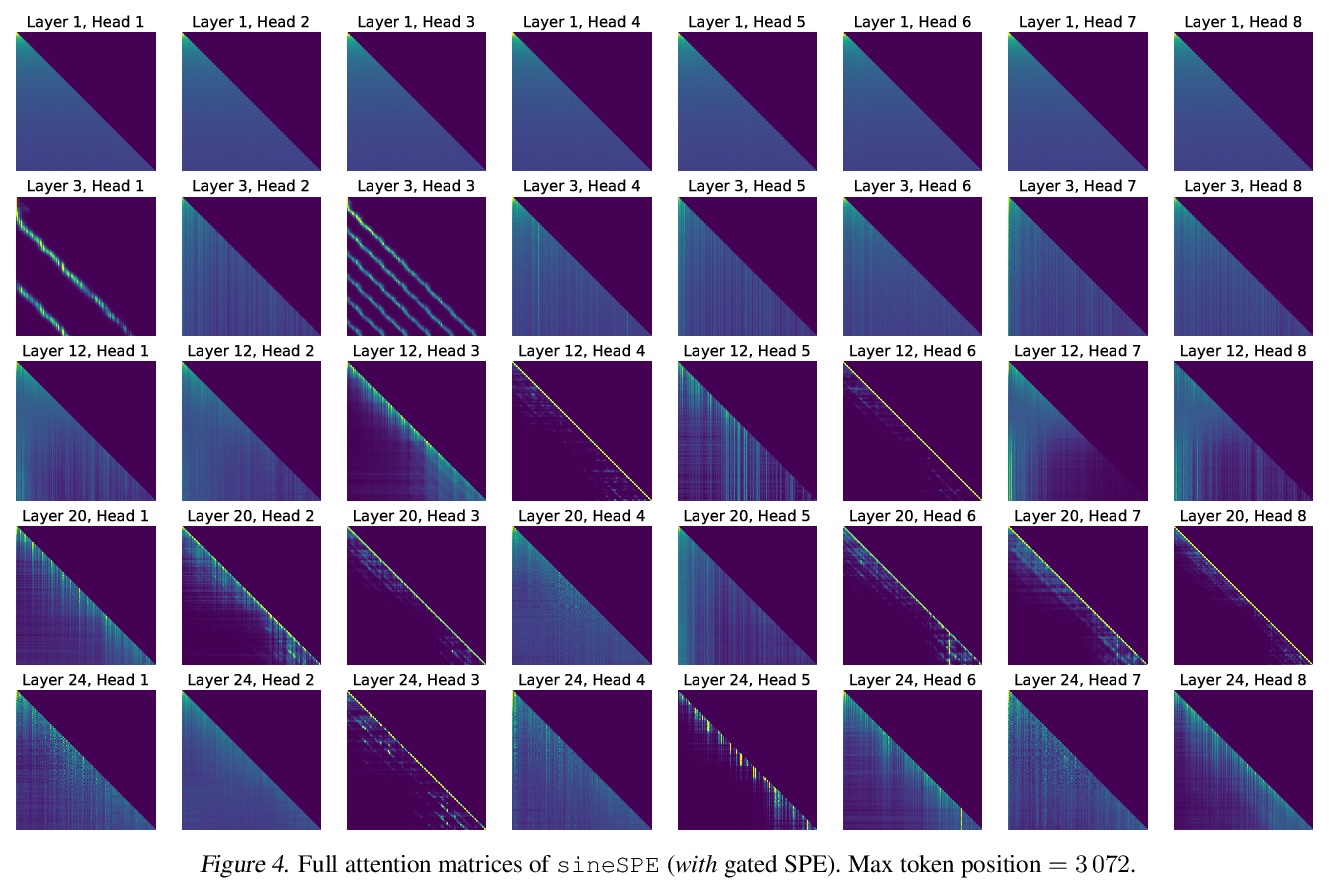
- 1、[LG] Relative Positional Encoding for Transformers with Linear Complexity
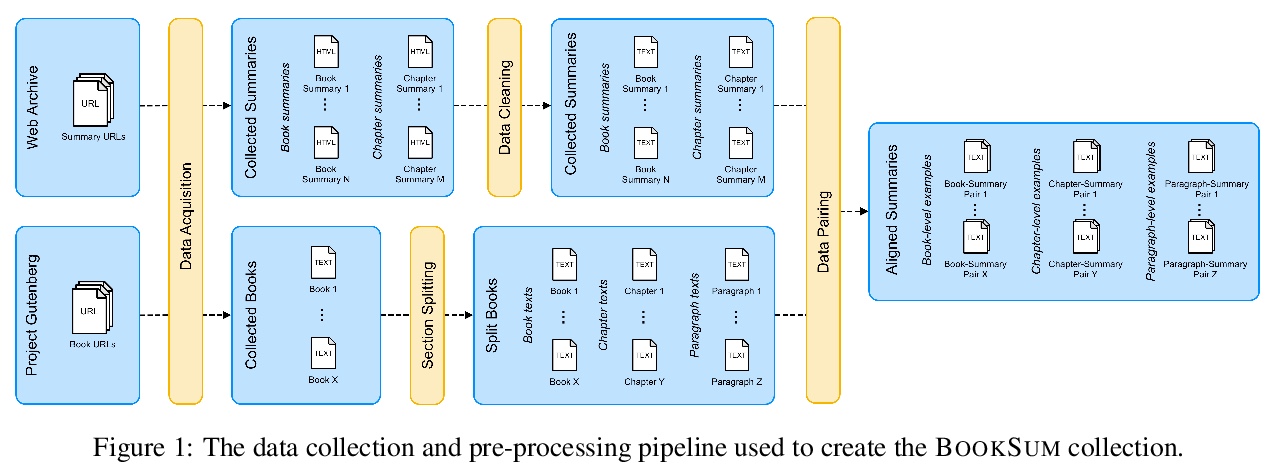
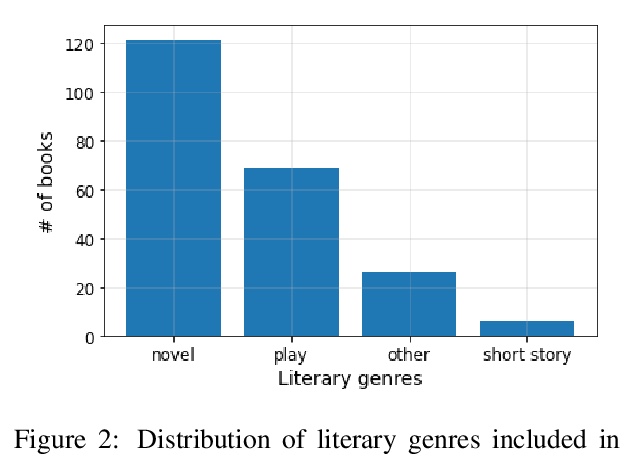
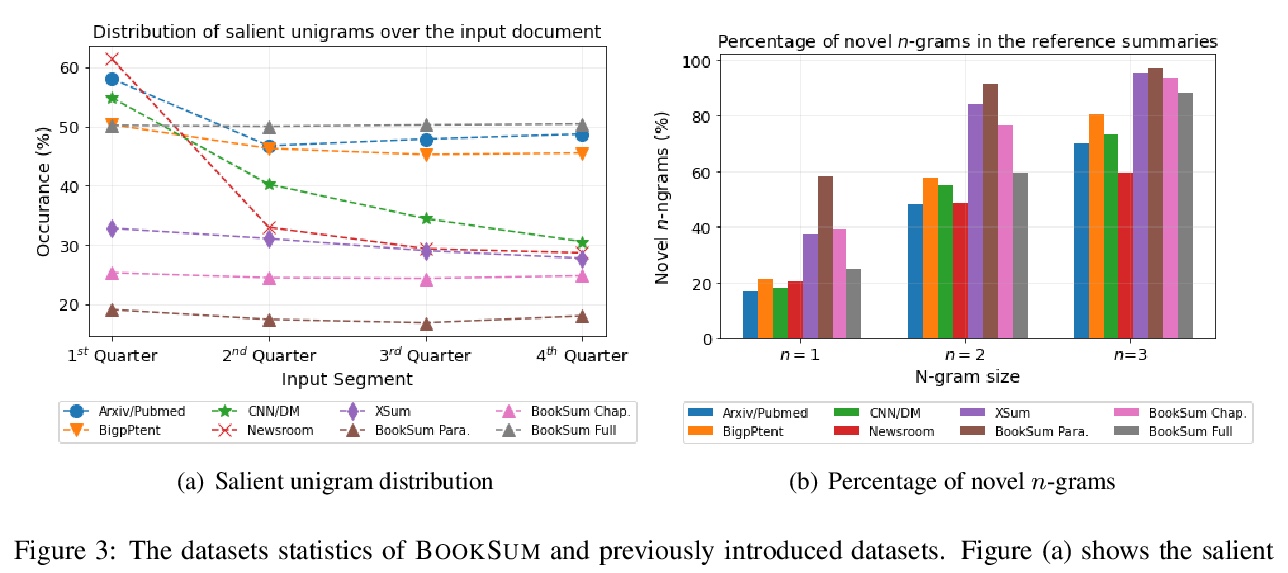
- 2、[CL] BookSum: A Collection of Datasets for Long-form Narrative Summarization
- 3、[CV] Finding an Unsupervised Image Segmenter in Each of Your Deep Generative Models
- 4、[LG] Parallel and Flexible Sampling from Autoregressive Models via Langevin Dynamics
- 5、[CV] Finding a Needle in a Haystack: Tiny Flying Object Detection in 4K Videos using a Joint Detection-and-Tracking Approach
- [CV] Exemplar-Based Open-Set Panoptic Segmentation Network
- [AI] Coach-Player Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Dynamic Team Composition
- [LG] Fast and Slow Learning of Recurrent Independent Mechanisms
- [CV] Image Cropping on Twitter: Fairness Metrics, their Limitations, and the Importance of Representation, Design, and Agency
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] Relative Positional Encoding for Transformers with Linear Complexity
A Liutkus, O Cífka, S Wu, U Şimşekli, Y Yang, G Richard
[Inria & Telecom Paris & Research Center for IT Innovation]
具有线性复杂度的Transformer相对位置编码。由于线性空间和时间复杂度,Transformer模型的最新进展可处理前所未有长度的序列。相对位置编码(RPE)被认为对经典的Transformer有益,包括利用滞后而不是绝对位置进行推理,但RPE并不适用于最近的线性Transformer变体,因为它需要明确计算注意力矩阵。本文提出了随机位置编码作为一种生成PE的方法,可以替代经典的加性(正弦)PE,可证明其行为与RPE相似,在位置编码和相关高斯过程的交叉协方差结构之间建立了联系。在长程Arena基准和音乐生成上说明了该方法的性能。
Recent advances in Transformer models allow for unprecedented sequence lengths, due to linear space and time complexity. In the meantime, relative positional encoding (RPE) was proposed as beneficial for classical Transformers and consists in exploiting lags instead of absolute positions for inference. Still, RPE is not available for the recent linear-variants of the Transformer, because it requires the explicit computation of the attention matrix, which is precisely what is avoided by such methods. In this paper, we bridge this gap and present Stochastic Positional Encoding as a way to generate PE that can be used as a replacement to the classical additive (sinusoidal) PE and provably behaves like RPE. The main theoretical contribution is to make a connection between positional encoding and cross-covariance structures of correlated Gaussian processes. We illustrate the performance of our approach on the Long-Range Arena benchmark and on music generation.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KghhtlkRm
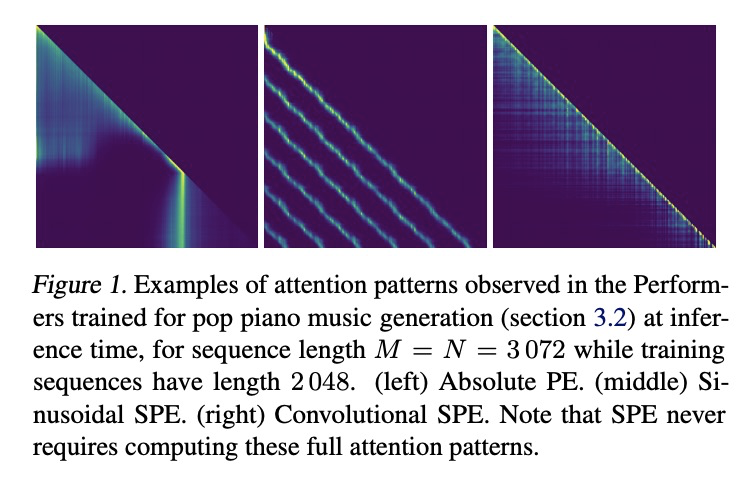
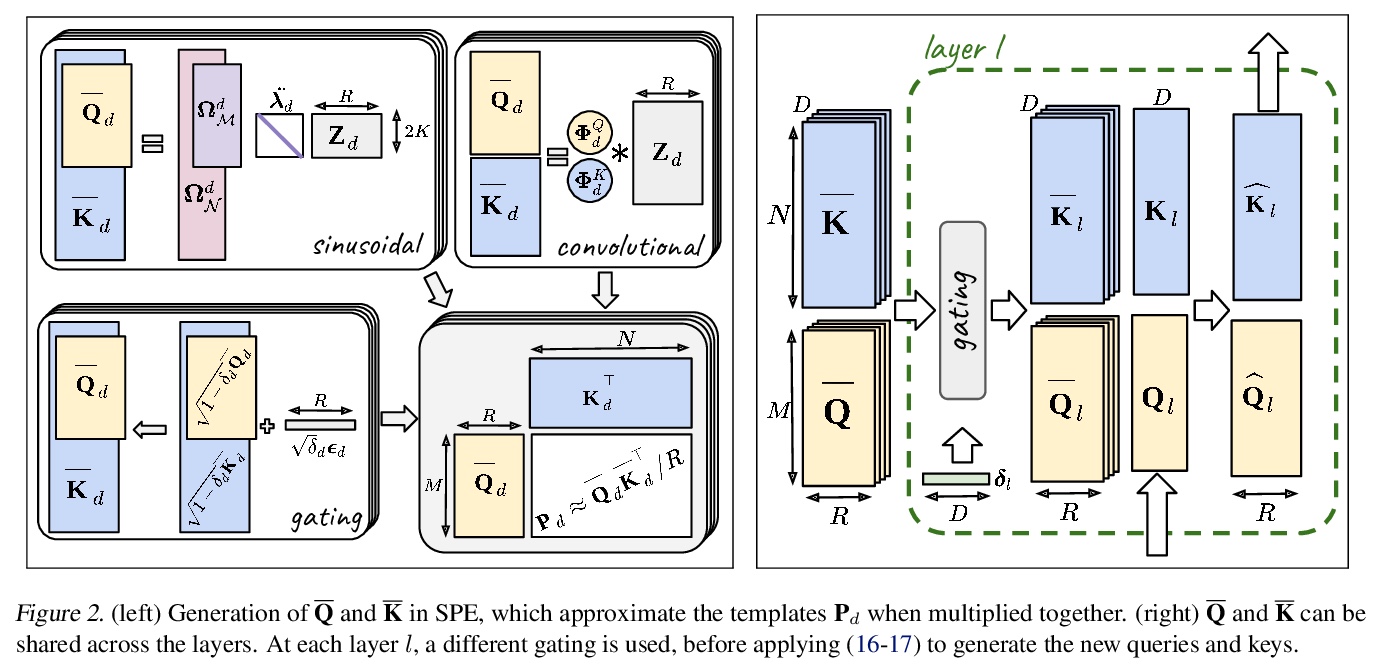
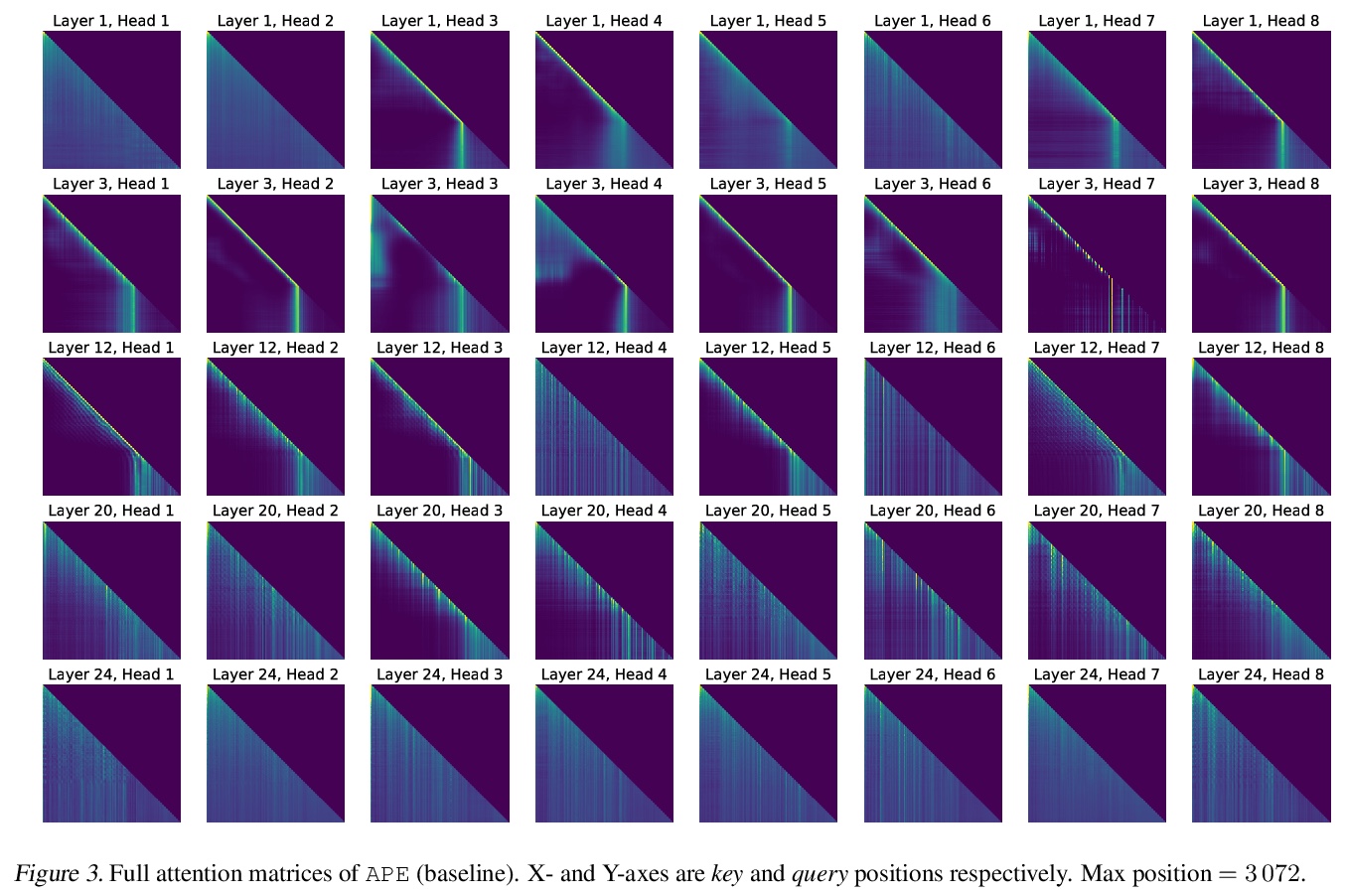
2、[CL] BookSum: A Collection of Datasets for Long-form Narrative Summarization
W Kryściński, N Rajani, D Agarwal, C Xiong, D Radev
[Salesforce Research]
BookSum:长篇叙事摘要数据集。大多数可用的文本摘要数据集,缺乏长程因果关系和时间依赖,且多为短篇源文档,往往包含强烈的布局和文体偏见,虽然相关,但这种数据集对未来几代文本摘要系统的挑战有限。本文引入BookSum来解决这些问题,BookSum是一个用于长篇叙述性摘要的数据集,涵盖了文学领域的源文档,如小说、戏剧和故事,并包括高度抽象的、人工撰写的、难度递增的三个级别的摘要:段落级、篇章级和全书级。数据集的领域和结构给总结系统带来了一系列独特的挑战,其中包括:处理很长的文件,非平凡因果和时间依赖,以及丰富的话语结构。
The majority of available text summarization datasets include short-form source documents that lack long-range causal and temporal dependencies, and often contain strong layout and stylistic biases. While relevant, such datasets will offer limited challenges for future generations of text summarization systems. We address these issues by introducing BOOKSUM, a collection of datasets for long-form narrative summarization. Our dataset covers source documents from the literature domain, such as novels, plays and stories, and includes highly abstractive, human written summaries on three levels of granularity of increasing difficulty: paragraph-, chapter-, and book-level. The domain and structure of our dataset poses a unique set of challenges for summarization systems, which include: processing very long documents, non-trivial causal and temporal dependencies, and rich discourse structures. To facilitate future work, we trained and evaluated multiple extractive and abstractive summarization models as baselines for our dataset.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KghlesLvk
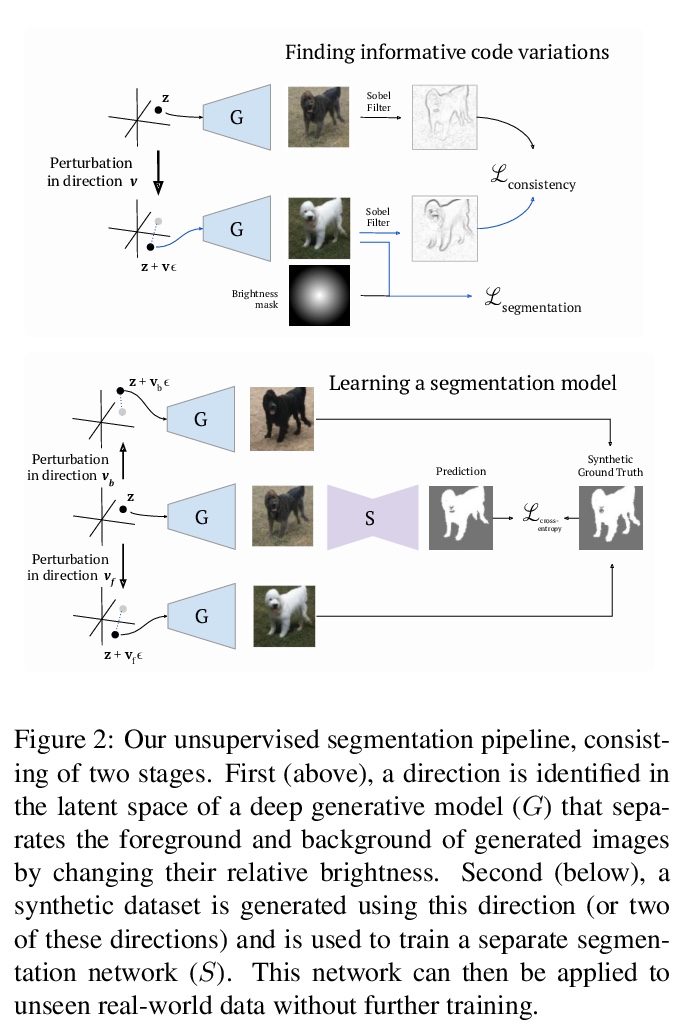
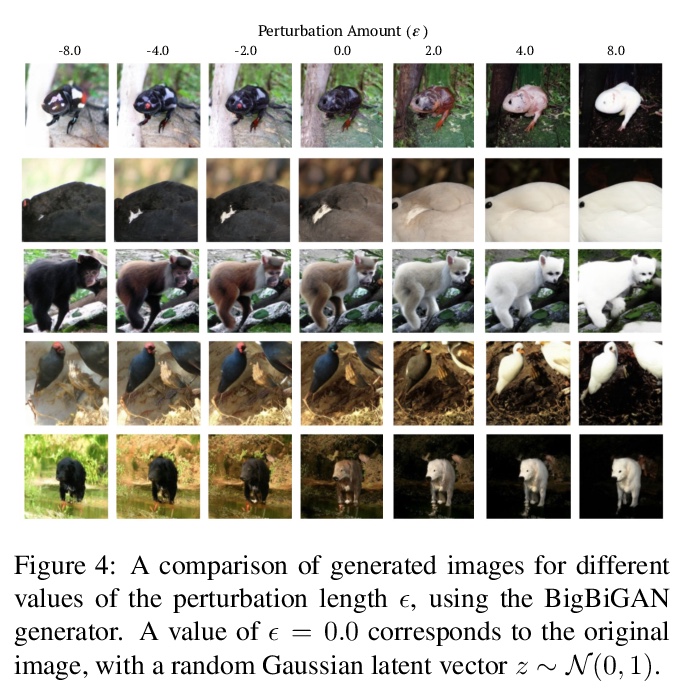
3、[CV] Finding an Unsupervised Image Segmenter in Each of Your Deep Generative Models
L Melas-Kyriazi, C Rupprecht, I Laina, A Vedaldi
[University of Oxford]
从深度生成模型提取无监督图像分割器。最近的研究表明,在GAN的潜空间中存在许多人类可理解的方向。本文开发了一种自动程序,用来寻找导致前景-背景图像分离的方向,用这些方向来训练无需人工监督的图像分割模型。该方法与生成器无关,在各种不同GAN架构下都能产生强大的分割结果。利用在ImageNet等大型数据集上预训练的GAN,可对一系列领域的图像进行分割,无需进一步训练或微调。在图像分割基准上评估了该方法,与之前的工作相比,既不需要人工监督,也不用训练数据,实验结果表明,从预训练的深度生成模型中自动提取前景-背景结构,可以作为人工监督的一个非常有效的替代。
Recent research has shown that numerous humaninterpretable directions exist in the latent space of GANs. In this paper, we develop an automatic procedure for finding directions that lead to foreground-background image separation, and we use these directions to train an image segmentation model without human supervision. Our method is generator-agnostic, producing strong segmentation results with a wide range of different GAN architectures. Furthermore, by leveraging GANs pretrained on large datasets such as ImageNet, we are able to segment images from a range of domains without further training or finetuning. Evaluating our method on image segmentation benchmarks, we compare favorably to prior work while using neither human supervision nor access to the training data. Broadly, our results demonstrate that automatically extracting foregroundbackground structure from pretrained deep generative models can serve as a remarkably effective substitute for human supervision.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KghoWDYUw


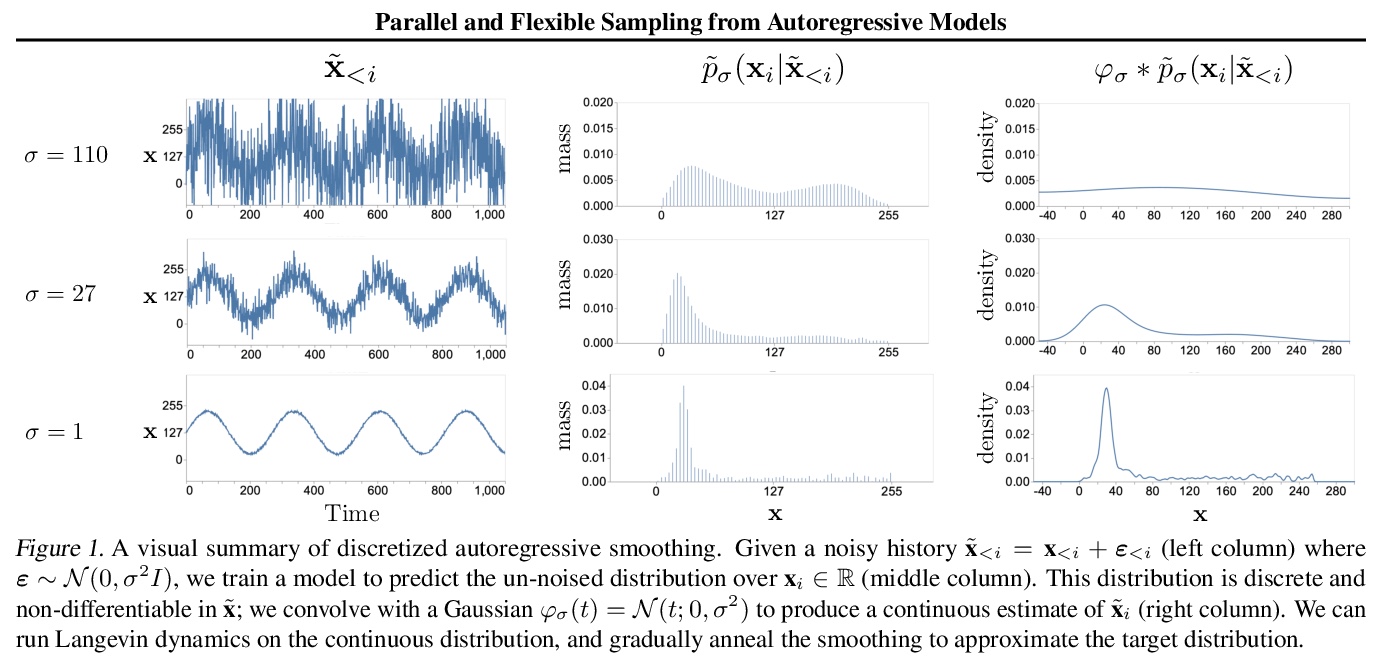
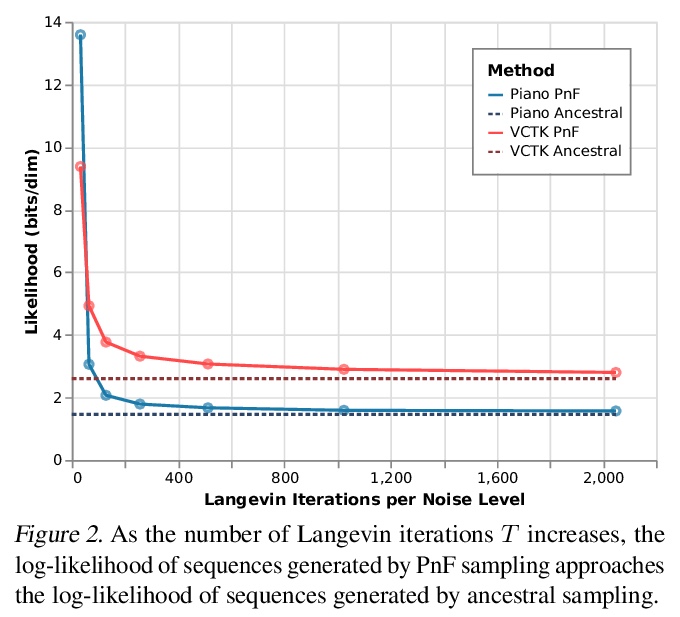
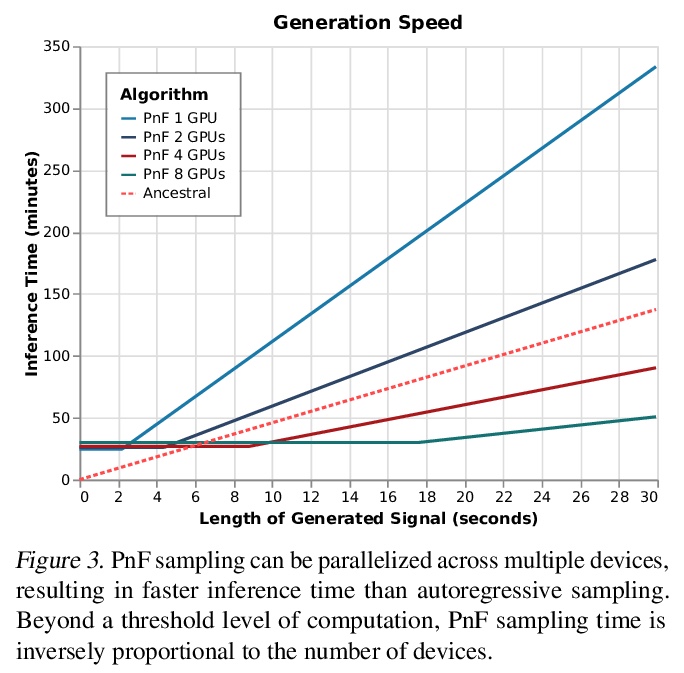
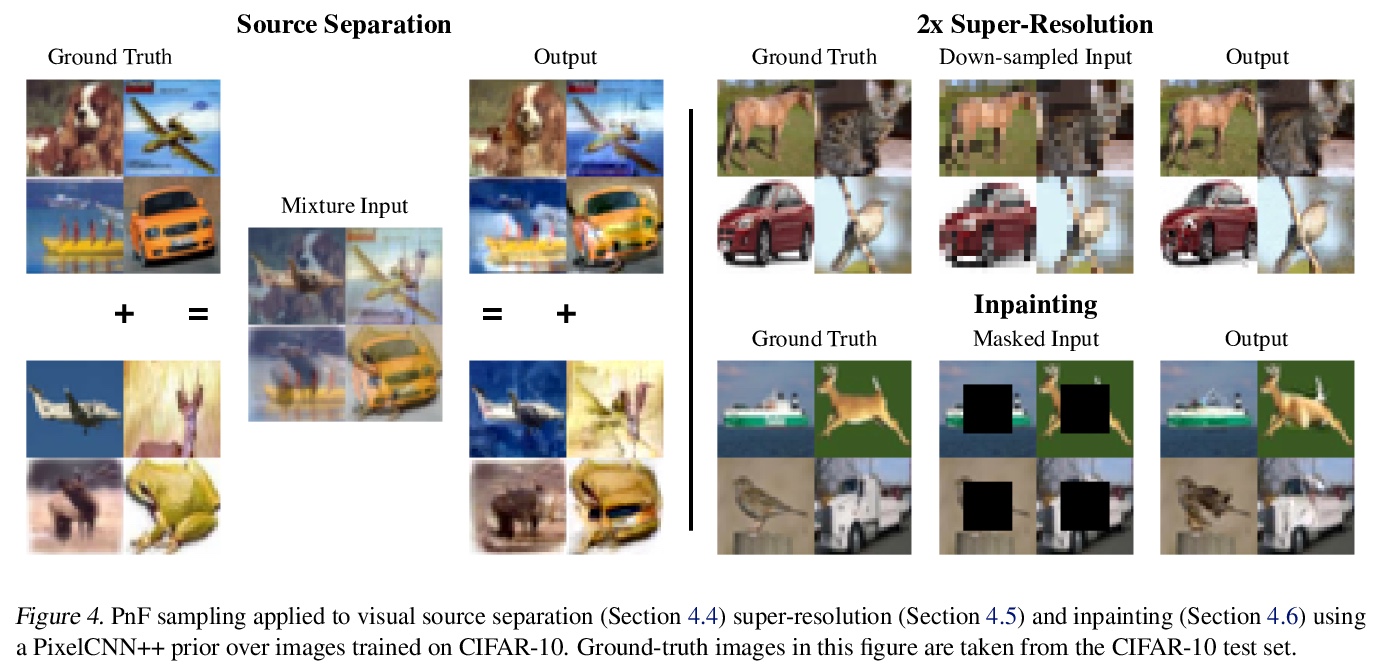
4、[LG] Parallel and Flexible Sampling from Autoregressive Models via Langevin Dynamics
V Jayaram, J Thickstun
[University of Washington]
基于朗格文动力学的自回归模型并行灵活采样。提出一种从自回归模型采样的替代方法:PnF采样。自回归模型通常按照模型定义的转变动力学顺序进行采样的。本文提出的PnF采样,用白噪声初始化序列,遵循由序列全局对数似然的朗格文动力学定义的马尔科夫链,使采样过程并行化,可推广到条件采样。PnF采样的灵活性将(无条件)生成性建模问题与具体的条件采样任务细节相分离。用自回归模型作为贝叶斯先验,可用条件似然或约束来引导生成模型的输出。将这些技术应用于视觉和音频领域的自回归模型,在音源分离、超分辨率和图像补全方面取得了有竞争力的结果。
This paper introduces an alternative approach to sampling from autoregressive models. Autoregressive models are typically sampled sequentially, according to the transition dynamics defined by the model. Instead, we propose a sampling procedure that initializes a sequence with white noise and follows a Markov chain defined by Langevin dynamics on the global loglikelihood of the sequence. This approach parallelizes the sampling process and generalizes to conditional sampling. Using an autoregressive model as a Bayesian prior, we can steer the output of a generative model using a conditional likelihood or constraints. We apply these techniques to autoregressive models in the visual and audio domains, with competitive results for audio source separation, super-resolution, and inpainting.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KghrKFycI
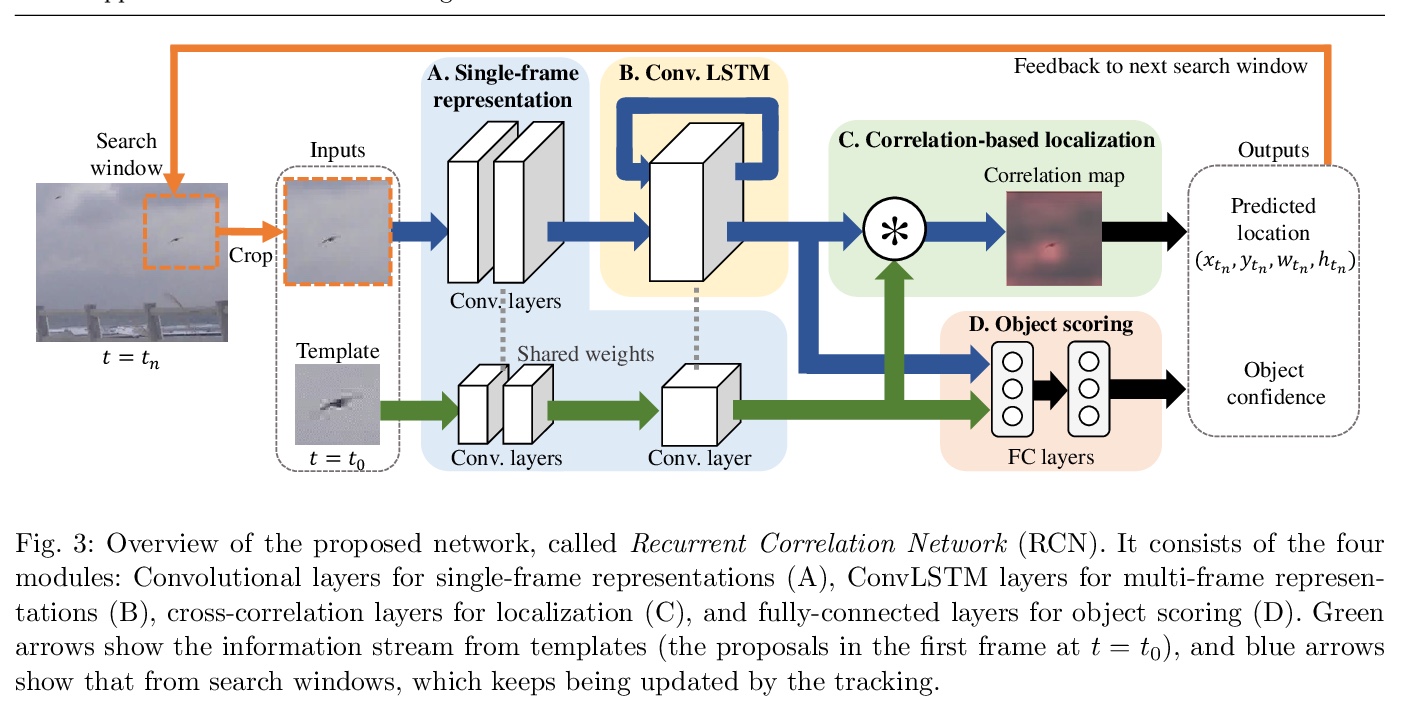
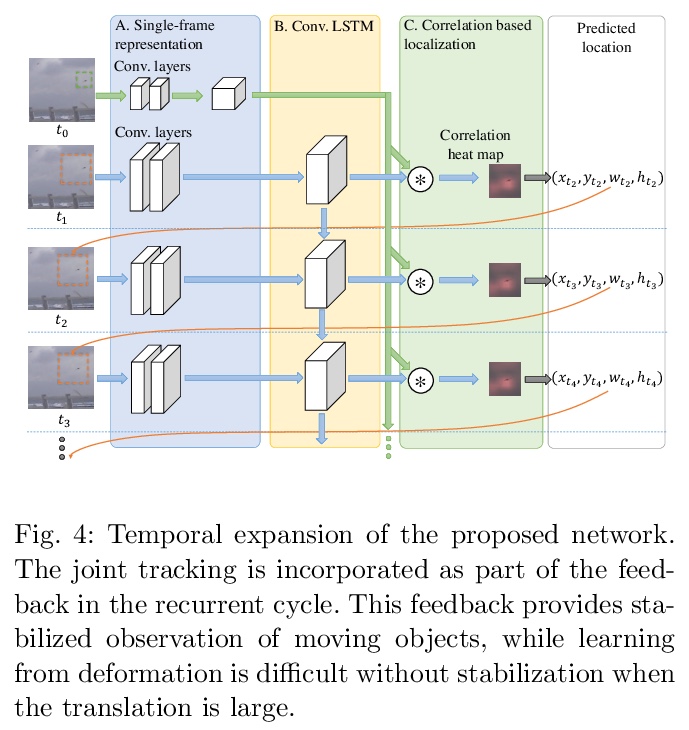
5、[CV] Finding a Needle in a Haystack: Tiny Flying Object Detection in 4K Videos using a Joint Detection-and-Tracking Approach
R Yoshihashi, R Kawakami, S You, T T Trinh, M Iida, T Naemura
[The University of Tokyo]
大海捞针:用检测和跟踪的联合方法检测4K视频中微小飞行物。检测高分辨率视频中的微小目标是一项挑战,因为视觉信息很少且不可靠。具体来说,该挑战包括目标的分辨率很低,由于压缩而产生的MPEG伪影,以及有许多硬干扰物的大搜索区域。由于不可靠的外观和不可靠的运动估计,跟踪也同样困难。通过将这两个具有挑战性的任务结合起来,会有共同的好处,本文提出一种叫做”循环关联网络”的神经网络模型,检测和跟踪通过单一的、可训练的、端到端的网络学习的多帧表示法共同进行,利用卷积长短期记忆网络来学习检测的信息性外观变化,同时在跟踪中共享所学的表征以提高性能。在对包含有小型飞行目标(如鸟和无人机)的场景图像的数据集进行的实验中,所提出的方法在检测性能上比深度单帧检测器和现有的基于运动的检测器有一致的改进。当网络被评估为鸟类图像数据集上的跟踪器时,它的表现与最先进的通用目标跟踪器一样好。
Detecting tiny objects in a high-resolution video is challenging because the visual information is little and unreliable. Specifically, the challenge includes very low resolution of the objects, MPEG artifacts due to compression and a large searching area with many hard negatives. Tracking is equally difficult because of the unreliable appearance, and the unreliable motion estimation. Luckily, we found that by combining this two challenging tasks together, there will be mutual benefits. Following the idea, in this paper, we present a neural network model called the Recurrent Correlational Network, where detection and tracking are jointly performed over a multi-frame representation learned through a single, trainable, and end-to-end network. The framework exploits a convolutional long short-term memory network for learning informative appearance changes for detection, while the learned representation is shared in tracking for enhancing its performance. In experiments with datasets containing images of scenes with small flying objects, such as birds and unmanned aerial vehicles, the proposed method yielded consistent improvements in detection performance over deep singleframe detectors and existing motion-based detectors. Furthermore, our network performs as well as state-ofthe-art generic object trackers when it was evaluated as a tracker on a bird image dataset.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KghvRDVlP


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
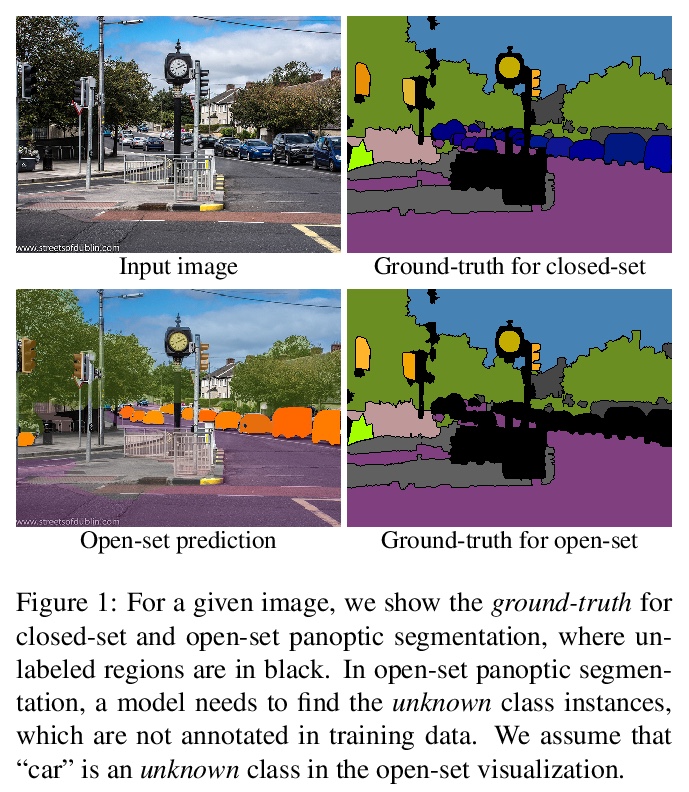
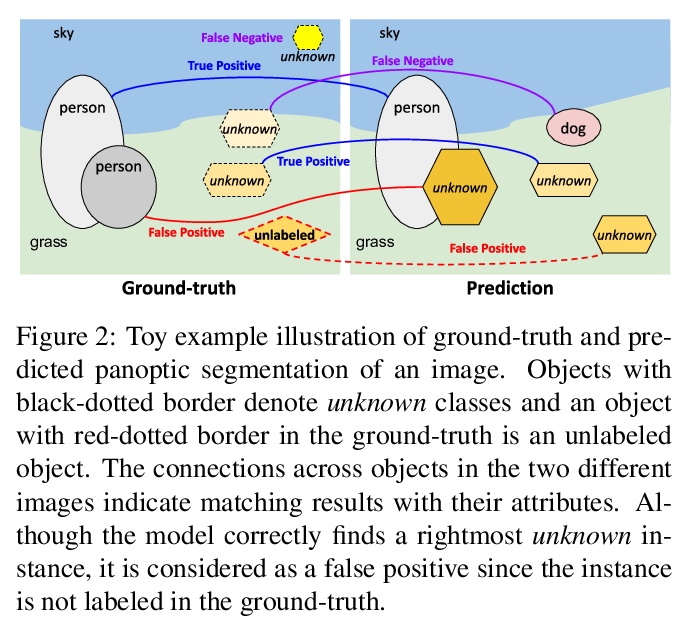
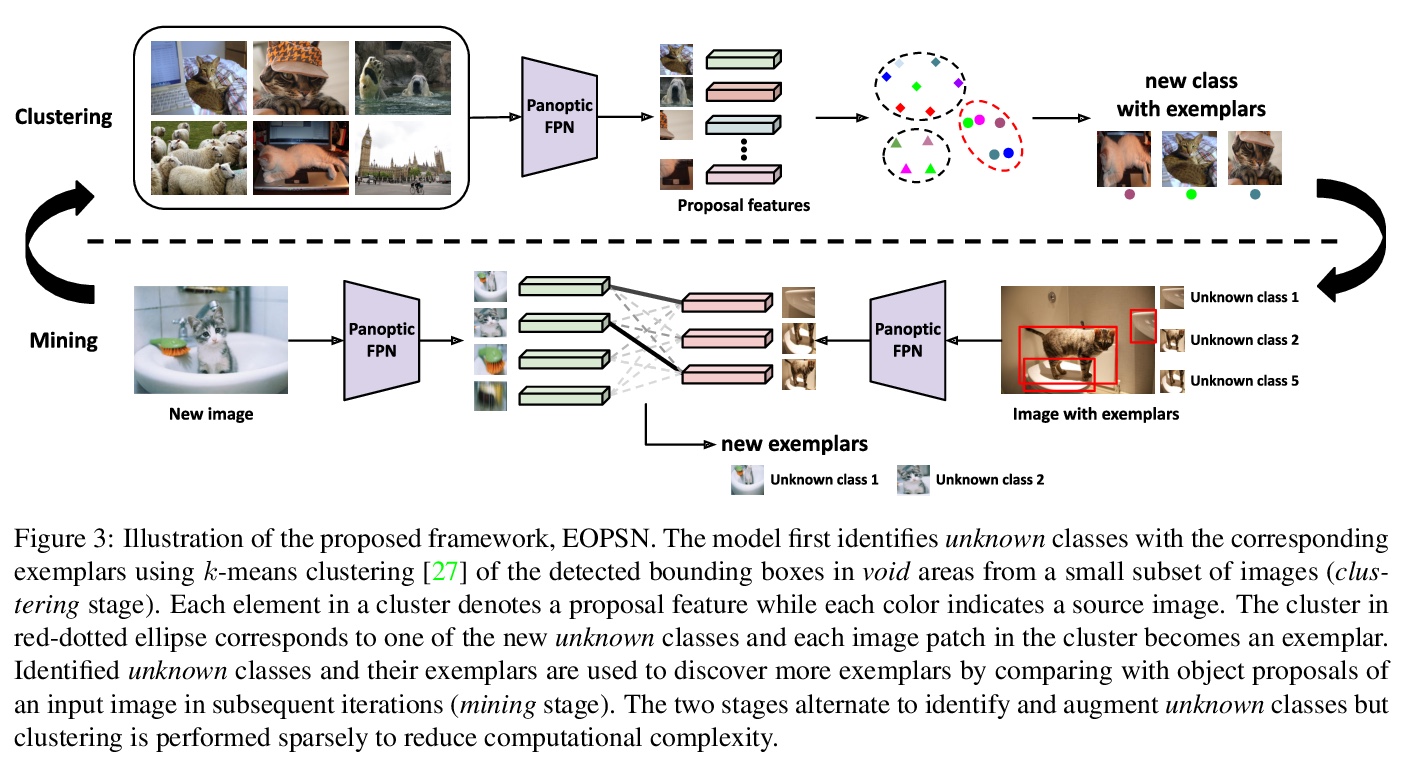
[CV] Exemplar-Based Open-Set Panoptic Segmentation Network
基于范例的开放集全景分割网络
J Hwang, S W Oh, J Lee, B Han
[Seoul National University & Adobe Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KghAt95BP

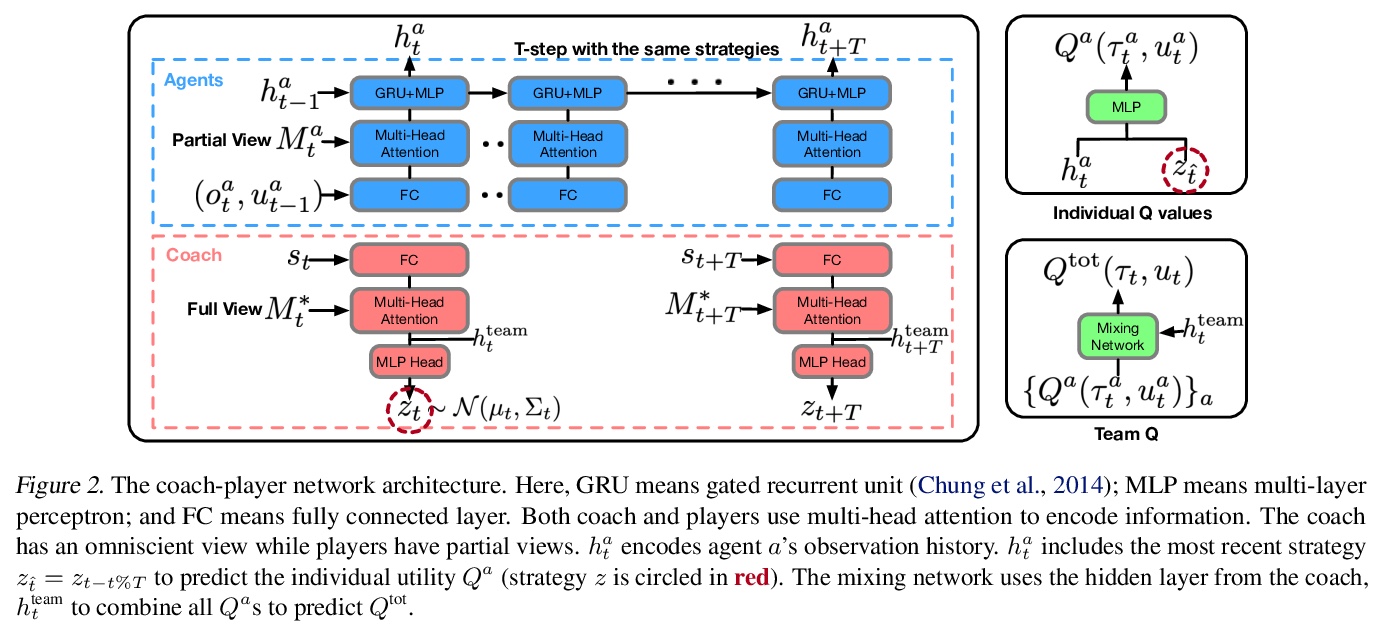
[AI] Coach-Player Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Dynamic Team Composition
面向动态团队构成的教练-玩家多智能体强化学习
B Liu, Q Liu, P Stone, A Garg, Y Zhu, A Anandkumar
[University of Texas at Austin & University of Toronto & Nvidia]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KghCCrbFZ


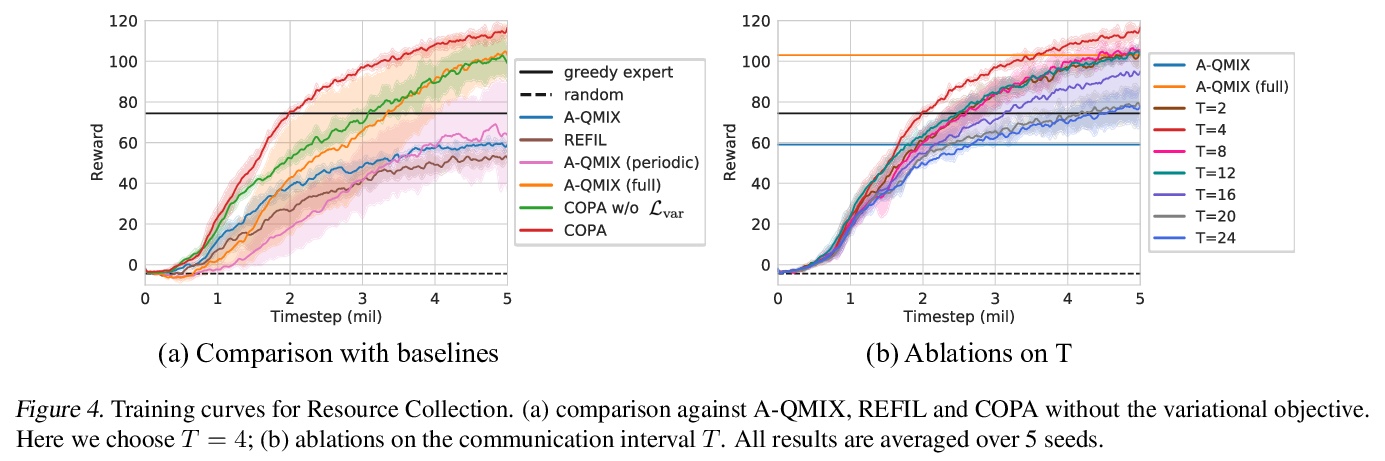
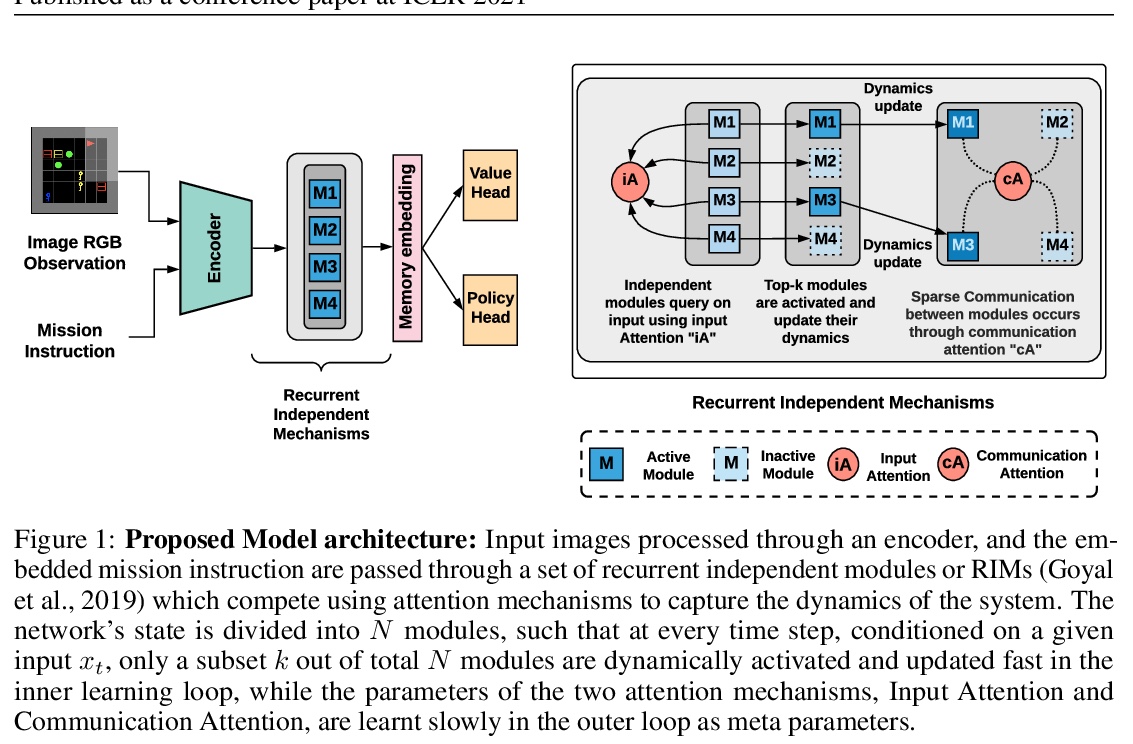
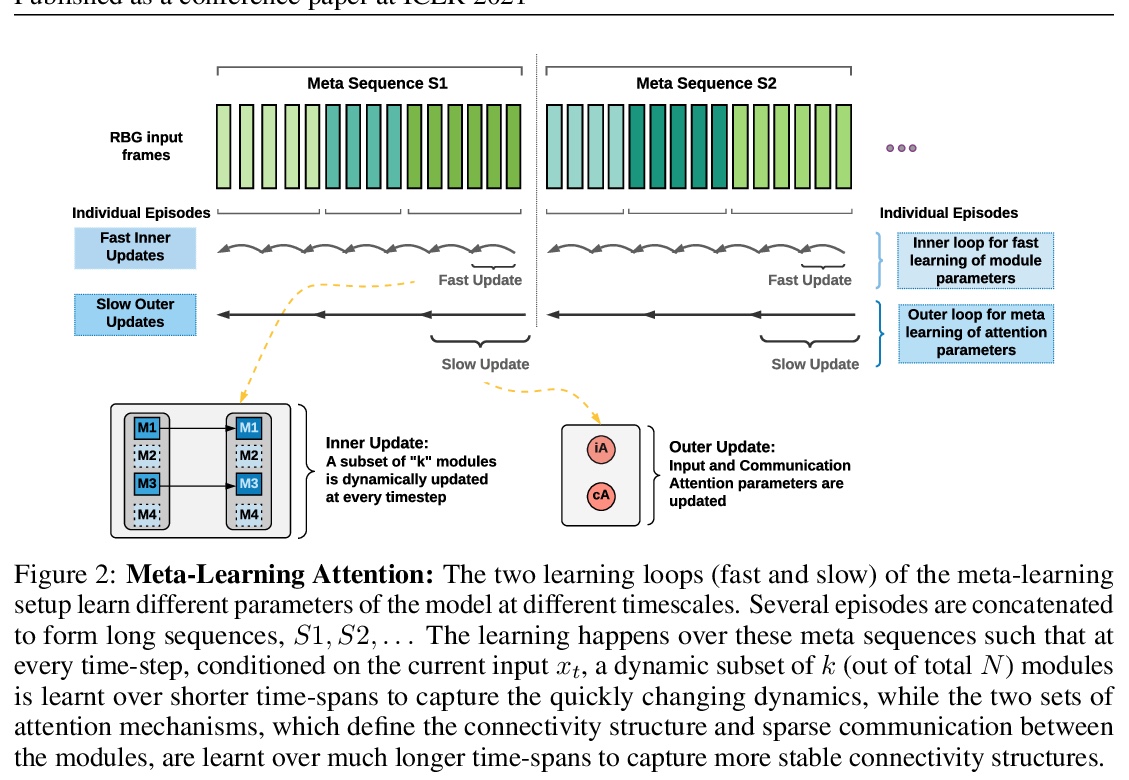
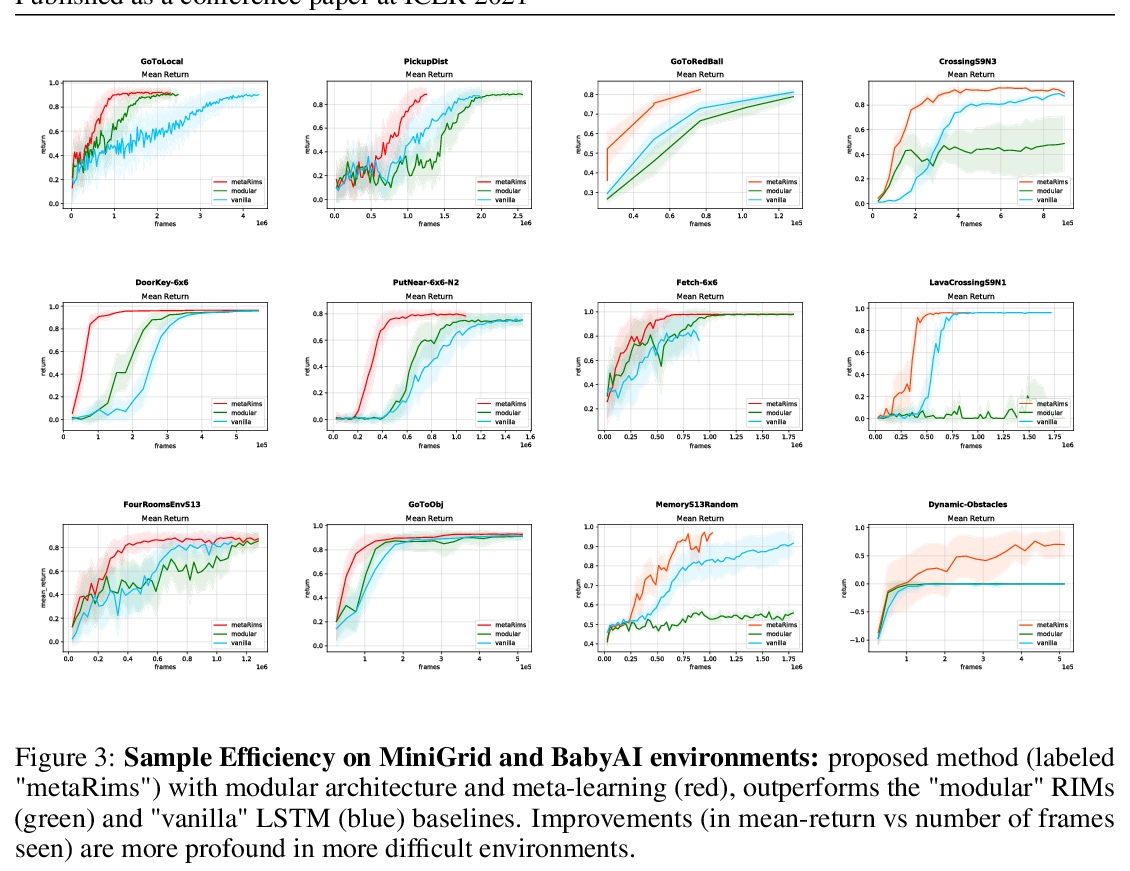
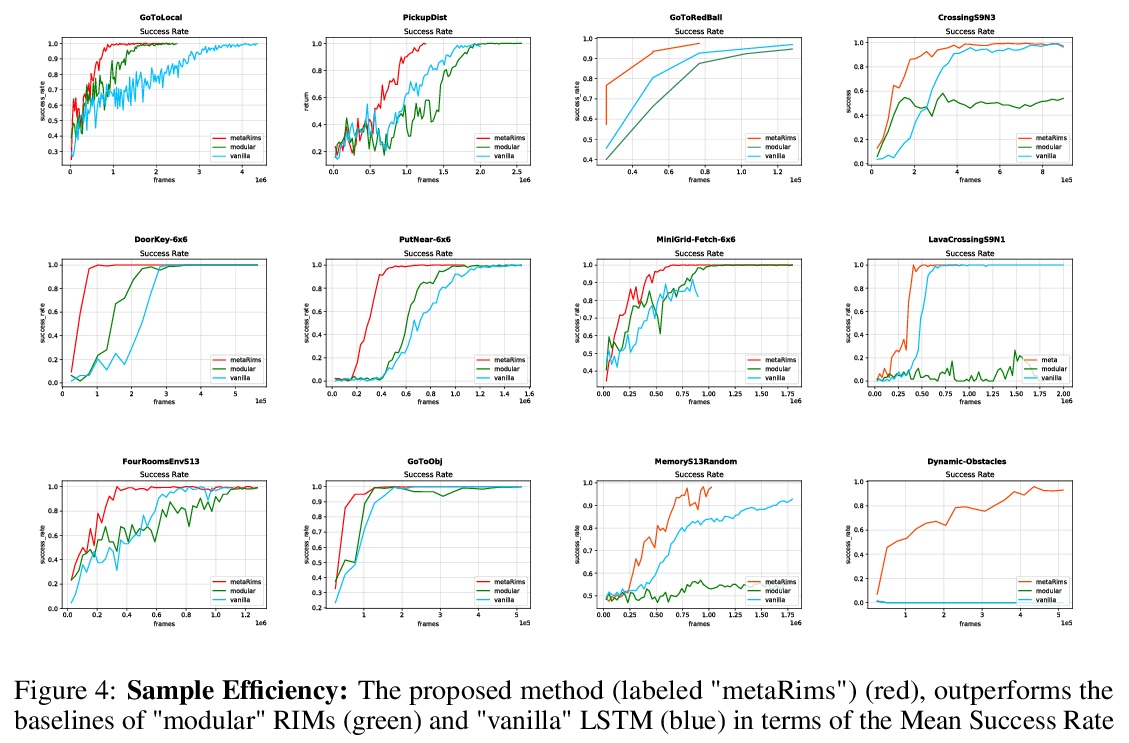
[LG] Fast and Slow Learning of Recurrent Independent Mechanisms
递归独立机制的快学习与慢学习
K Madan, R N Ke, A Goyal, B B Schölkopf, Y Bengio
[University of Monsreal & Polytechnique Montreal]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KghFbmnVJ
[CV] Image Cropping on Twitter: Fairness Metrics, their Limitations, and the Importance of Representation, Design, and Agency
推特图像裁剪:公平性度量、局限性及表现、设计和代理的重要性
K Yee, U Tantipongpipat, S Mishra
[Twitter]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KghHE8E6K