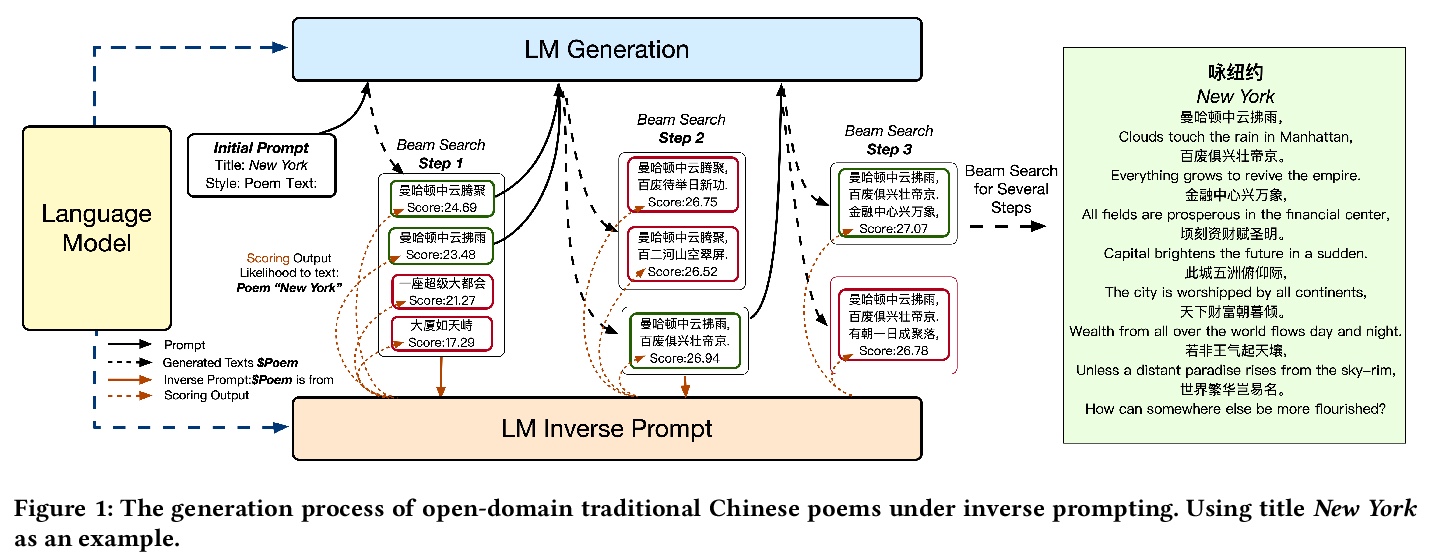
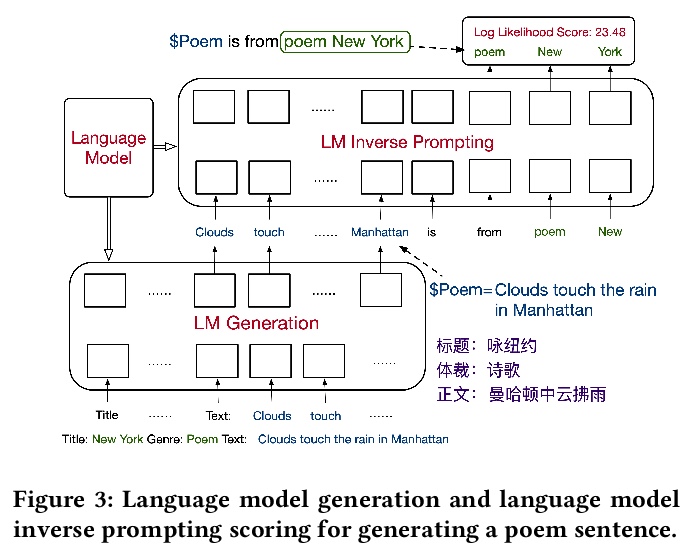
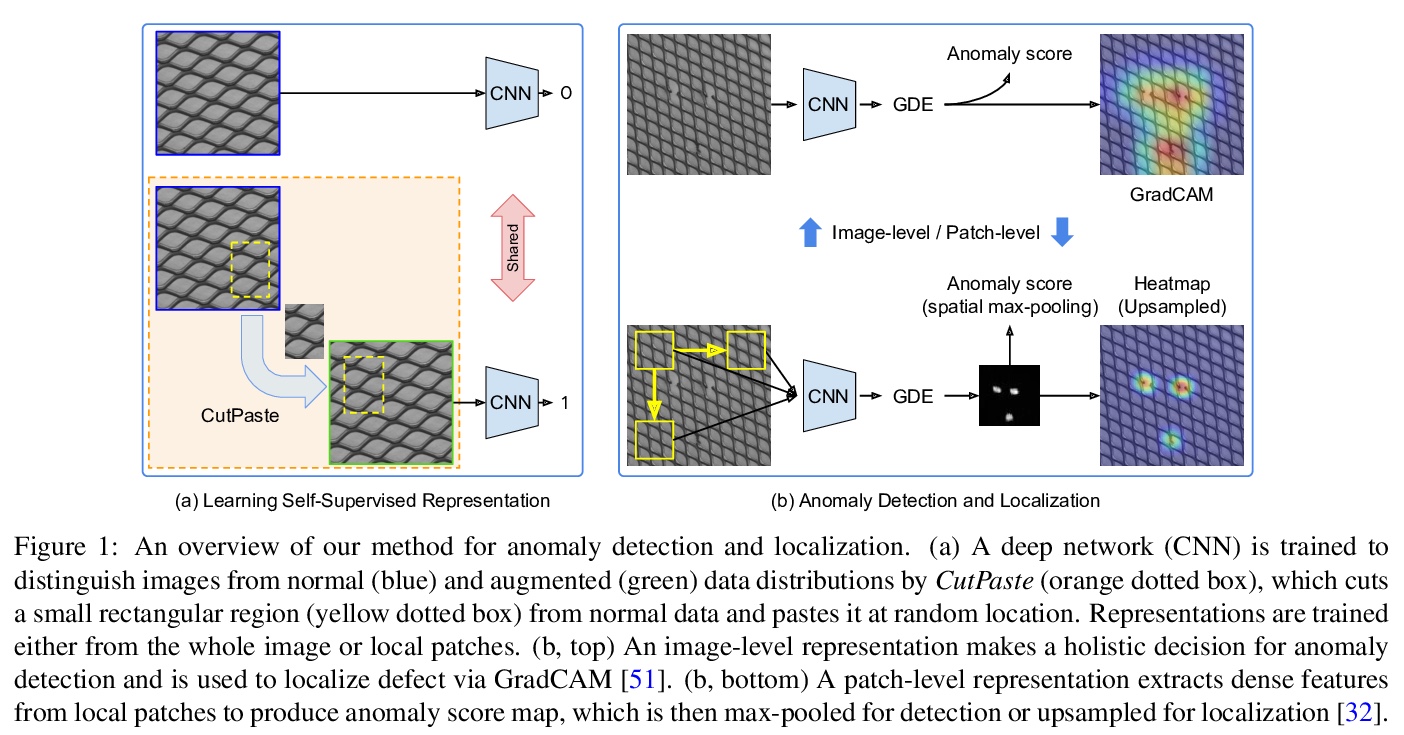
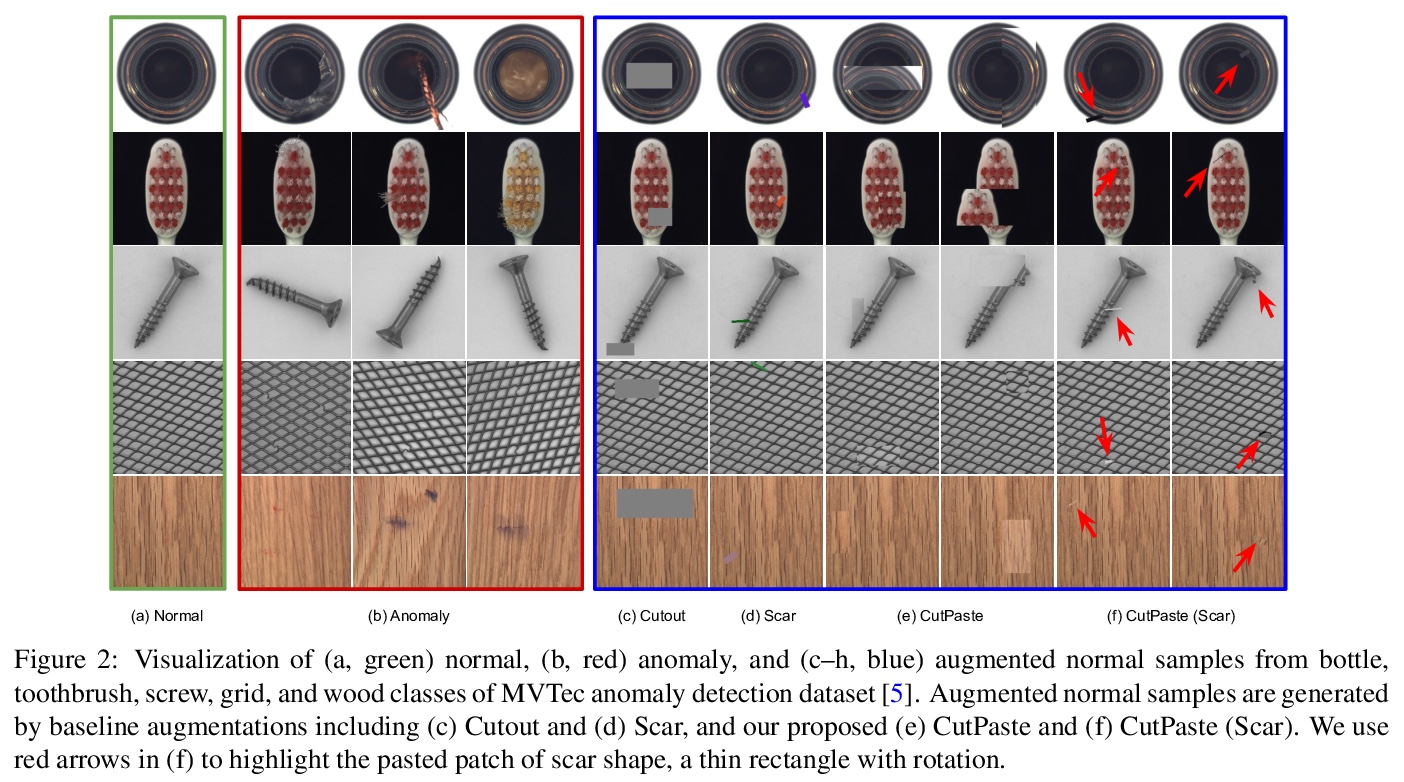
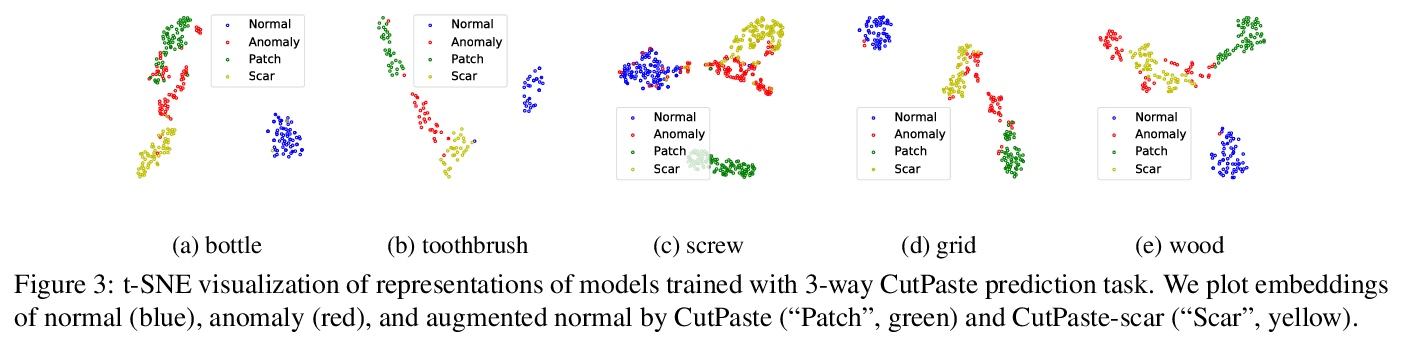
- 1、[CV] CutPaste: Self-Supervised Learning for Anomaly Detection and Localization
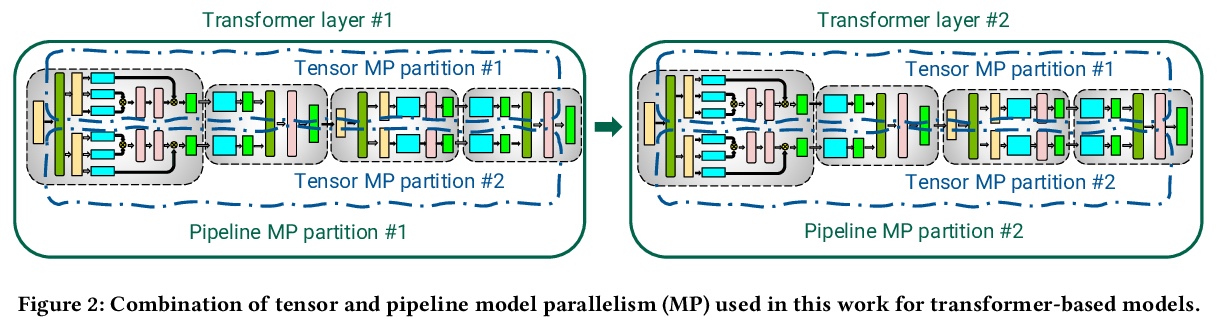
- 2、[CL] Efficient Large-Scale Language Model Training on GPU Clusters
- 3、[LG] Protein sequence design with deep generative models
- 4、[CV] SI-Score: An image dataset for fine-grained analysis of robustness to object location, rotation and size
- 5、[CV] Auxiliary Tasks and Exploration Enable ObjectNav
- [CL] An Empirical Comparison of Instance Attribution Methods for NLP
- [CL] Language model fusion for streaming end to end speech recognition
- [CV] Robust and Accurate Object Detection via Adversarial Learning
- [CL] Controllable Generation from Pre-trained Language Models via Inverse Prompting
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
(*表示值得重点关注)
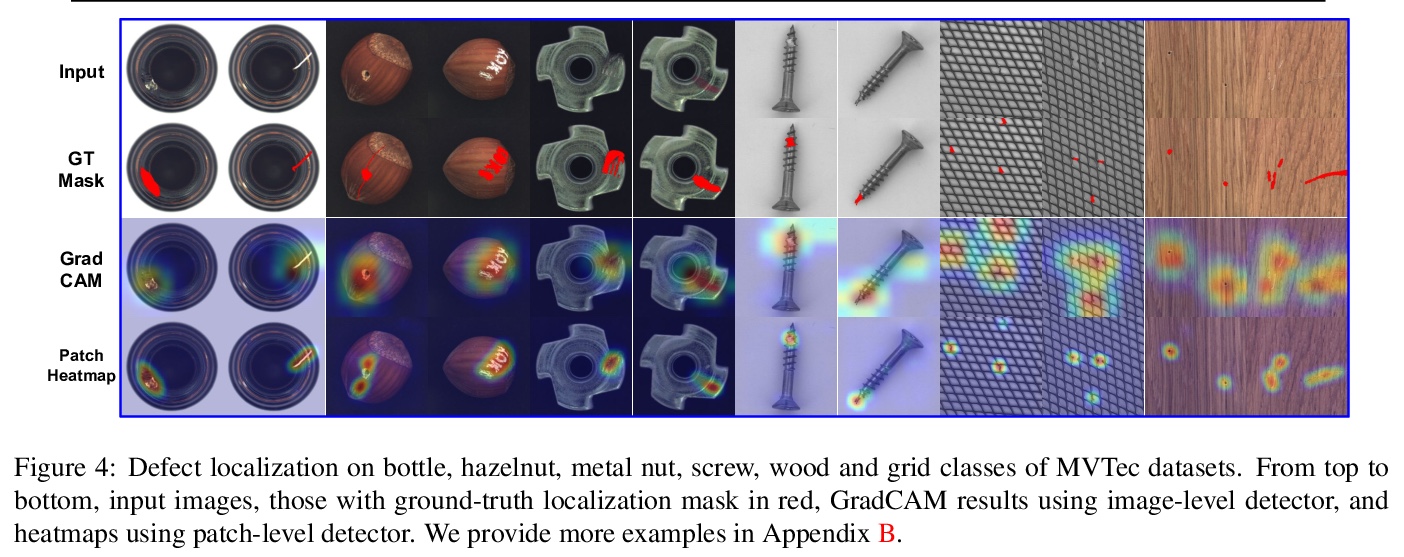
1、[CV] CutPaste: Self-Supervised Learning for Anomaly Detection and Localization
C Li, K Sohn, J Yoon, T Pfister
[Google Cloud AI Research]
CutPaste: 异常检测与定位的自监督学习。目标是构建一个高性能的缺陷检测模型,在没有异常数据的情况下检测图像的未知异常模式。提出一种数据驱动的缺陷检测和定位方法,仅使用正常训练数据构建异常检测器的两阶段框架,首先学习自监督的深度表征,然后在学习的表征上建立一个生成式的单类分类器。用CutPaste进行表征的自监督学习,一种简单有效的数据增强策略,切割一个图块并粘贴在大图像的随机位置,鼓励模型找到局部不规则的地方。在真实世界数据集上展示了卓越的图像级异常检测性能。通过学习和提取图块级表示,展示了最先进的像素级异常定位性能。对MVTec异常检测数据集的实证研究表明,所提出的算法具有通用性,能够检测各种类型的现实世界的缺陷。
We aim at constructing a high performance model for defect detection that detects unknown anomalous patterns of an image without anomalous data. To this end, we propose a two-stage framework for building anomaly detectors using normal training data only. We first learn self-supervised deep representations and then build a generative one-class classifier on learned representations. We learn representations by classifying normal data from the CutPaste, a simple data augmentation strategy that cuts an image patch and pastes at a random location of a large image. Our empirical study on MVTec anomaly detection dataset demonstrates the proposed algorithm is general to be able to detect various types of real-world defects. We bring the improvement upon previous arts by 3.1 AUCs when learning representations from scratch. By transfer learning on pretrained representations on ImageNet, we achieve a new state-of-theart 96.6 AUC. Lastly, we extend the framework to learn and extract representations from patches to allow localizing defective areas without annotations during training.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaEol21dG

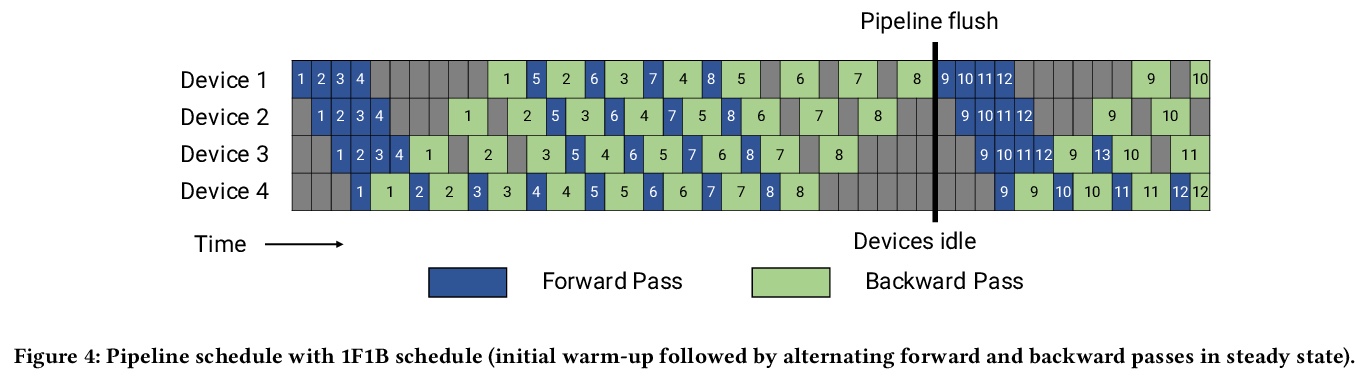
2、[CL] Efficient Large-Scale Language Model Training on GPU Clusters
D Narayanan, M Shoeybi, J Casper, P LeGresley, M Patwary, V Korthikanti, D Vainbrand, P Kashinkunti, J Bernauer, B Catanzaro, A Phanishayee, M Zaharia
[NVIDIA & Stanford University & Microsoft Research]
GPU集群上的大规模语言模型高效训练。展示了如何组成不同的并行化策略(节点内张量模型并行、节点间管线模型并行和数据并行),以扩展到数千GPU,实现高聚合吞吐量(502petaFLOP/s),同时训练万亿参数级的大型模型,与现有系统相比,可有效训练的模型大小增加了两个数量级。讨论了管线并行的各种实现,提出一种新的时间表,与之前方法相比,在内存占用相当的情况下将吞吐量提高10%以上。讨论了与这些类型并行性每一种相关的各种权衡,以及当它们组合在一起时需要如何仔细考虑它们之间的相互作用。
Large language models have led to state-of-the-art accuracies across a range of tasks. However, training these large models efficiently is challenging for two reasons: a) GPU memory capacity is limited, making it impossible to fit large models on a single GPU or even on a multi-GPU server; and b) the number of compute operations required to train these models can result in unrealistically long training times. New methods of model parallelism such as tensor and pipeline parallelism have been proposed to address these challenges; unfortunately, naive usage leads to fundamental scaling issues at thousands of GPUs due to various reasons, e.g., expensive cross-node communication or idle periods waiting on other devices.In this work, we show how to compose different types of parallelism methods (tensor, pipeline, and data paralleism) to scale to thousands of GPUs, achieving a two-order-of-magnitude increase in the sizes of models we can efficiently train compared to existing systems. We discuss various implementations of pipeline parallelism and propose a novel schedule that can improve throughput by more than 10% with comparable memory footprint compared to previously-proposed approaches. We quantitatively study the trade-offs between tensor, pipeline, and data parallelism, and provide intuition as to how to configure distributed training of a large model. The composition of these techniques allows us to perform training iterations on a model with 1 trillion parameters at 502 petaFLOP/s on 3072 GPUs with achieved per-GPU throughput of 52% of peak; previous efforts to train similar-sized models achieve much lower throughput (36% of theoretical peak). Our code has been open-sourced at > this https URL.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaEsecytg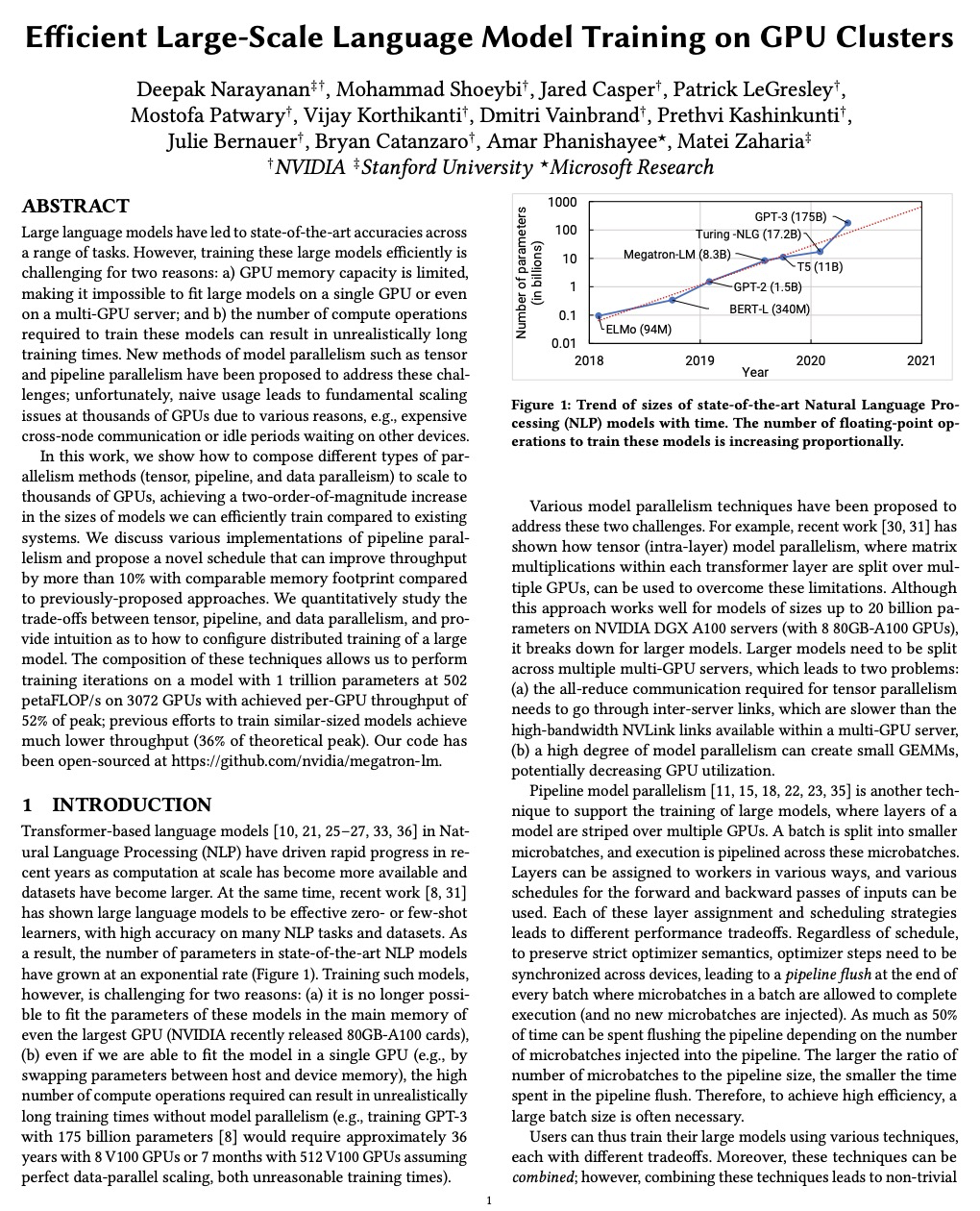
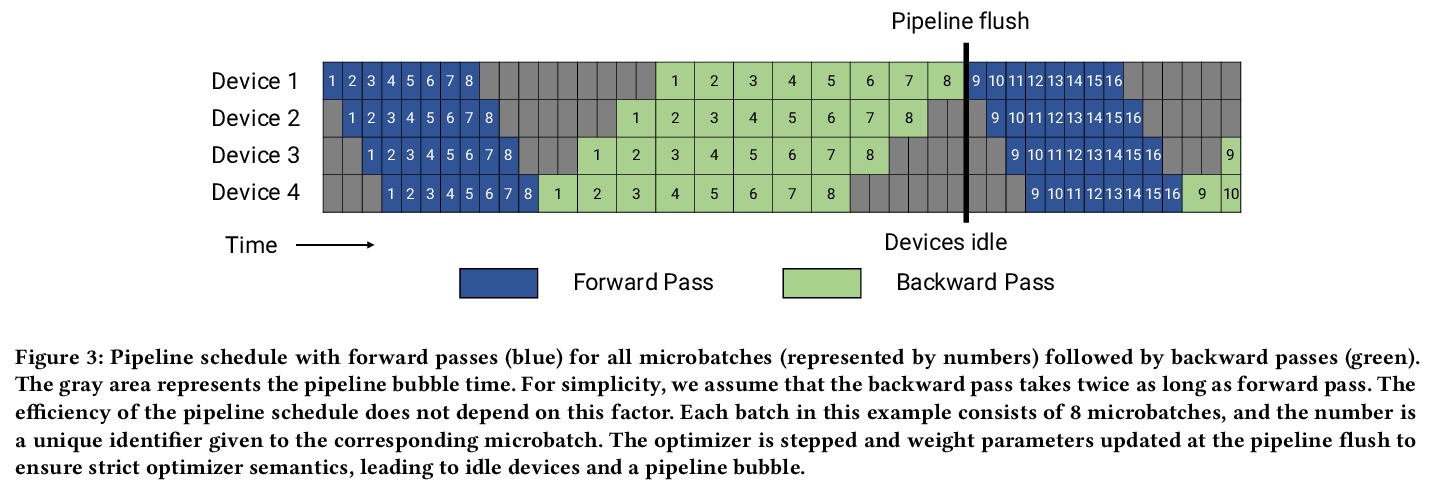
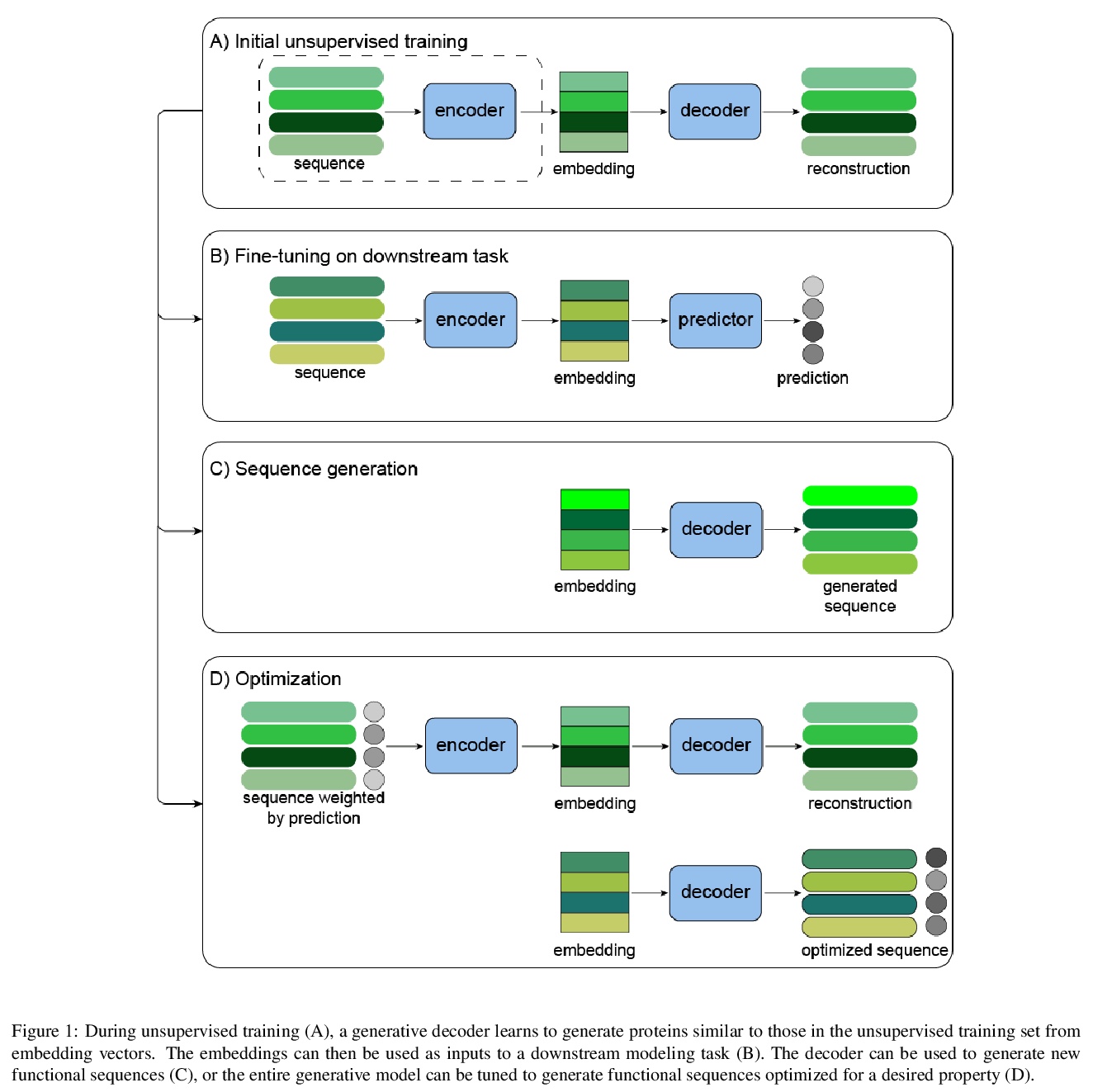
3、[LG] Protein sequence design with deep generative models
Z Wu, K E. Johnston, F H. Arnold, K K. Yang
[California Institute of Technology & Microsoft Research New England]
基于深度生成模型的蛋白质序列设计(综述)。重点介绍了机器学习生成蛋白质序列的最新应用,聚焦于深度生成式方法这一新兴领域。讨论了深度生成式模型在蛋白质工程中的三种应用:(1)在下游判别性学习任务中使用学习到的蛋白质序列表示和预训练模型,是对蛋白质工程既有框架的重要改进;(2)用生成性模型生成蛋白质序列;(3)通过调整生成性模型进行优化,使具有某种理想属性的序列被赋予更高的概率。相关目前适用于可鲁棒测量的所需蛋白质特性的子集,如存活率、荧光和结合亲和力,但如果我们希望对酶活性等更复杂的性状进行建模和理解,必须继续开发实验技术。同时,机器学习使我们能够在各种规模上生成有用的蛋白质序列。在低到中等通量的设置中,由判别模型引导的蛋白质工程能够通过学习的代偿适配函数有效地识别改进的序列。在具有较大数据量的设置中,深度生成模型具有各种优势和弱点,可根据设计和实验约束条件加以利用。通过将机器学习与多轮实验相结合,数据驱动的蛋白质工程有望从昂贵的实验室工作中获得最大的回报,使蛋白质工程师能够快速设计有用序列。
Protein engineering seeks to identify protein sequences with optimized properties. When guided by machine learning, protein sequence generation methods can draw on prior knowledge and experimental efforts to improve this process. In this review, we highlight recent applications of machine learning to generate protein sequences, focusing on the emerging field of deep generative methods.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaEwCBSCI
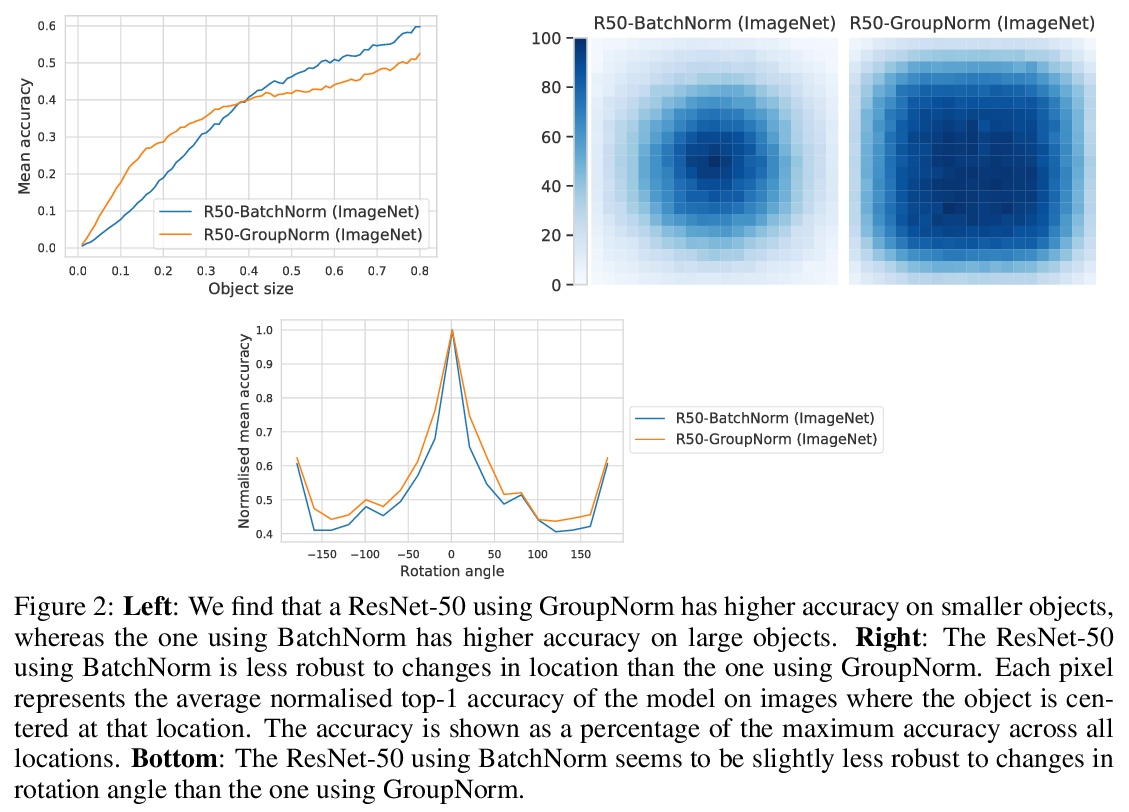
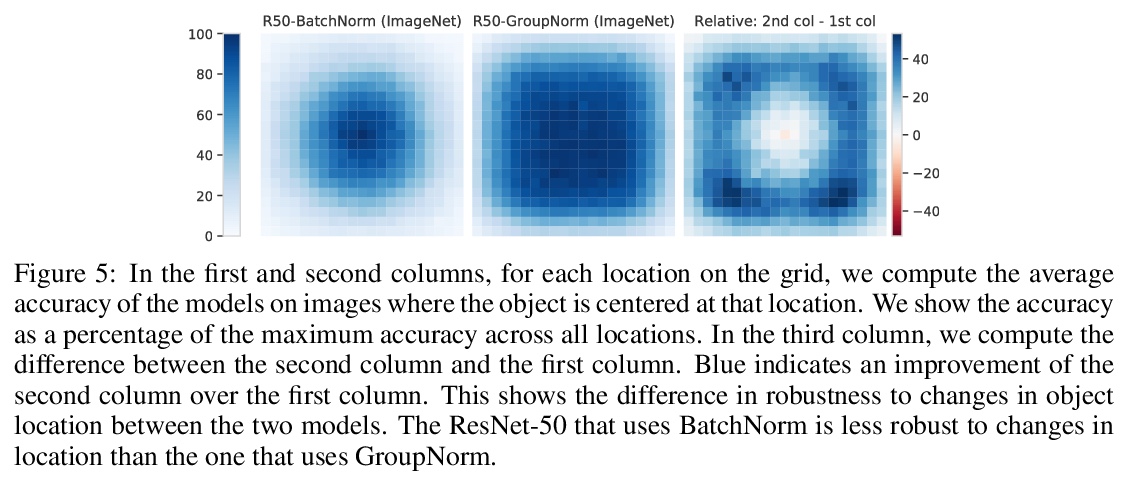
4、[CV] SI-Score: An image dataset for fine-grained analysis of robustness to object location, rotation and size
J Yung, R Romijnders, A Kolesnikov, L Beyer, J Djolonga, N Houlsby, S Gelly, M Lucic, X Zhai
[Google Research]
SI-SCORE:针对目标位置、旋转和尺寸变化鲁棒性细粒度分析图像数据集。在部署机器学习模型之前,评估其鲁棒性至关重要。在面向图像理解的深度神经网络中,改变目标位置、旋转和大小,可能会以非平凡的方式影响预测。这项工作中,使用SI-SCORE这一合成数据集,对这些变化因素的鲁棒性进行了细粒度分析。特别研究了ResNets、Vision Transformers和CLIP,并确定了其质量差异。在评估合成数据的性能时,可能存在潜在的差异和混杂因素,通过以下操作来降低风险:首先,使用真实数据的剪切和粘贴,而不是完全合成数据。其次,对超过1000个目标和背景组合进行平均,以尽量减少目标或背景的选择对结果的影响。最后,考虑的模型之间的相对性能,而不是绝对数字。
Before deploying machine learning models it is critical to assess their robustness. In the context of deep neural networks for image understanding, changing the object location, rotation and size may affect the predictions in non-trivial ways. In this work we perform a fine-grained analysis of robustness with respect to these factors of variation using SI-Score, a synthetic dataset. In particular, we investigate ResNets, Vision Transformers and CLIP, and identify interesting qualitative differences between these.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaEC23msj

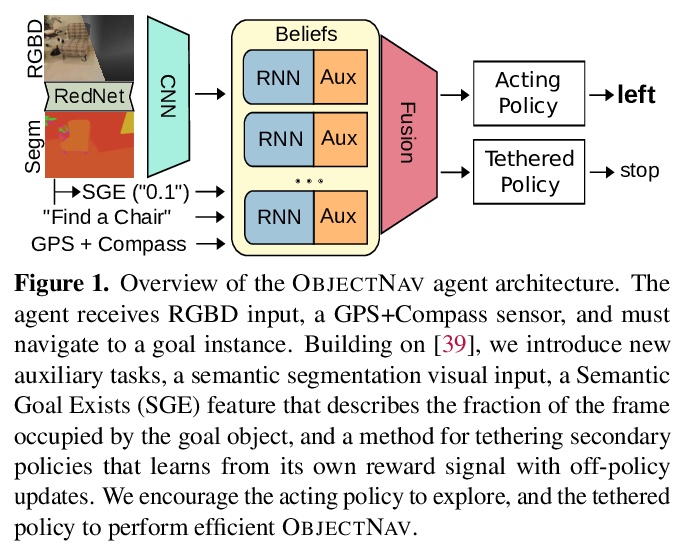
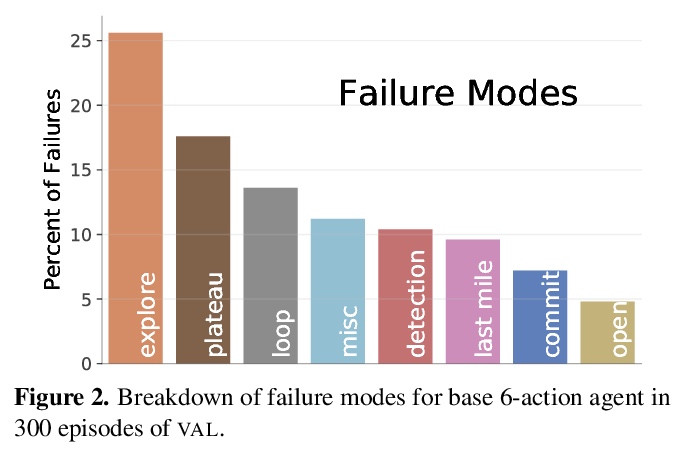
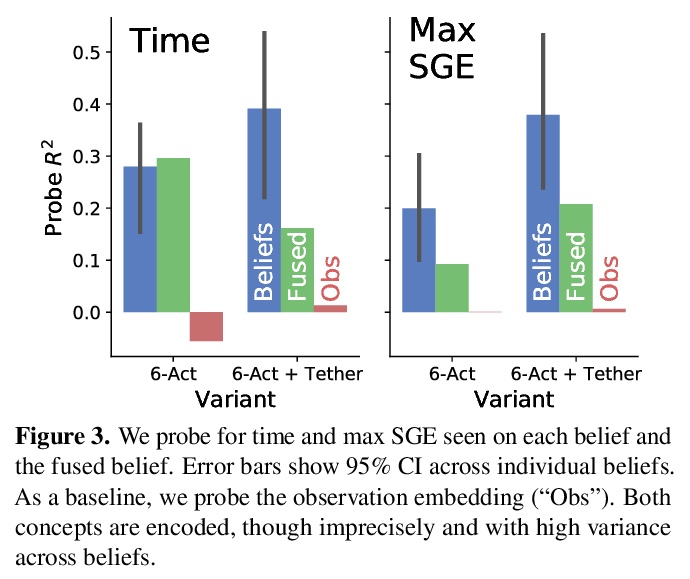
5、[CV] Auxiliary Tasks and Exploration Enable ObjectNav
J Ye, D Batra, A Das, E Wijmans
[Georgia Institute of Technology & Facebook AI Research]
辅助任务和探索使能对象目标导航。对象目标导航(ObjectGoal Navigation,OBJECTNAV)是一个具身任务,智能体要在一个不可见环境中导航到一个目标实例。通过添加辅助学习任务和探索奖励来重启一个通用学习智能体,用具有隐式环境表示的递归智能体实现了OBJECTNAV的最先进性能。目标是训练简单的CNN+RNN架构,可实现OBJECTNAV上24.5%的成功率(比之前的最先进技术相对提高了37%)。表明尽管目前显式地图很普遍,但不需要显式地图来学习复杂的具身AI任务。对智能体的的行为、表征和循环动态进行了分析,推测出执行力强的OBJECTNAV智能体一个关键要素将是平滑的、低维度的递归动态的规划能力。
ObjectGoal Navigation (ObjectNav) is an embodied task wherein agents are to navigate to an object instance in an unseen environment. Prior works have shown that end-to-end ObjectNav agents that use vanilla visual and recurrent modules, e.g. a CNN+RNN, perform poorly due to overfitting and sample inefficiency. This has motivated current state-of-the-art methods to mix analytic and learned components and operate on explicit spatial maps of the environment. We instead re-enable a generic learned agent by adding auxiliary learning tasks and an exploration reward. Our agents achieve 24.5% success and 8.1% SPL, a 37% and 8% relative improvement over prior state-of-the-art, respectively, on the Habitat ObjectNav Challenge. From our analysis, we propose that agents will act to simplify their visual inputs so as to smooth their RNN dynamics, and that auxiliary tasks reduce overfitting by minimizing effective RNN dimensionality; i.e. a performant ObjectNav agent that must maintain coherent plans over long horizons does so by learning smooth, low-dimensional recurrent dynamics. Site: > this https URL
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaEFpfLT9
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
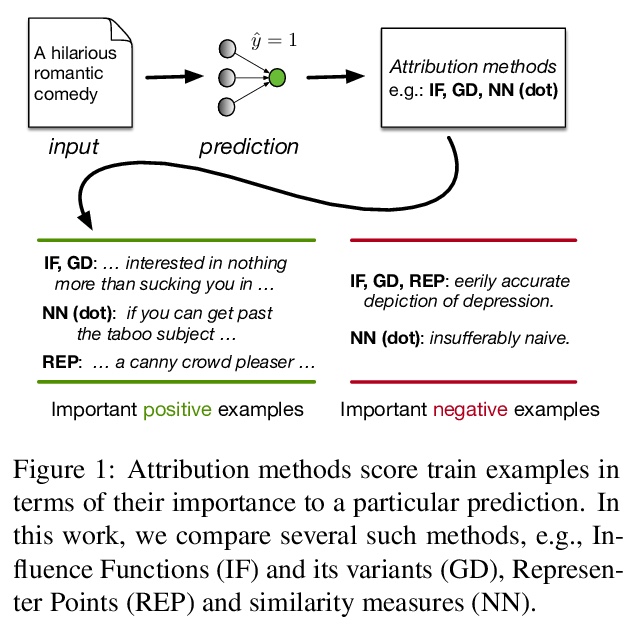
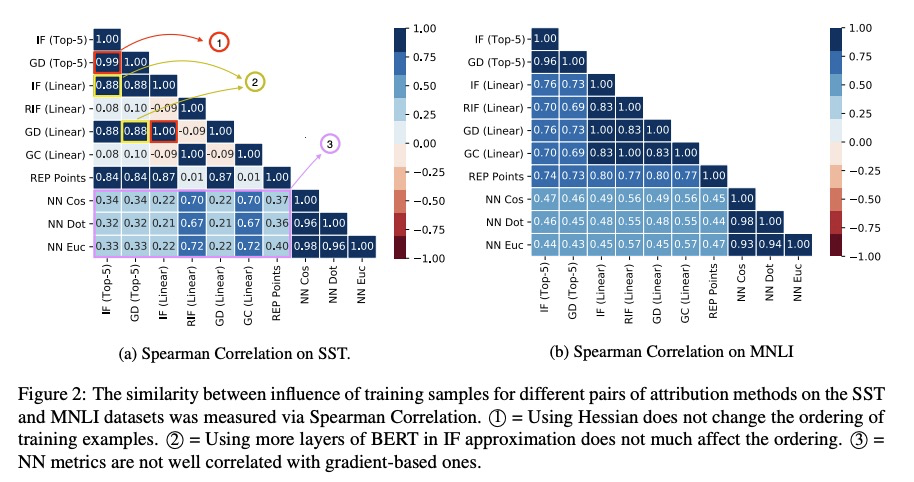
[CL] An Empirical Comparison of Instance Attribution Methods for NLP
自然语言处理实例归因方法的实证比较
P Pezeshkpour, S Jain, B C. Wallace, S Singh
[University of California, Irvine & Northeastern University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaEOumEry
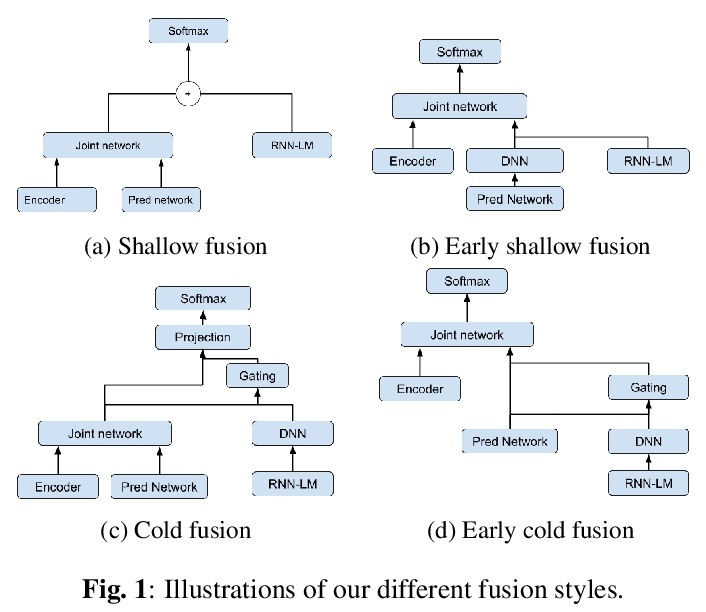
[CL] Language model fusion for streaming end to end speech recognition
面向流式端到端语音识别的语言模型融合
R Cabrera, X Liu, M Ghodsi, Z Matteson, E Weinstein, A Kannan
[Google]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaERElLxB
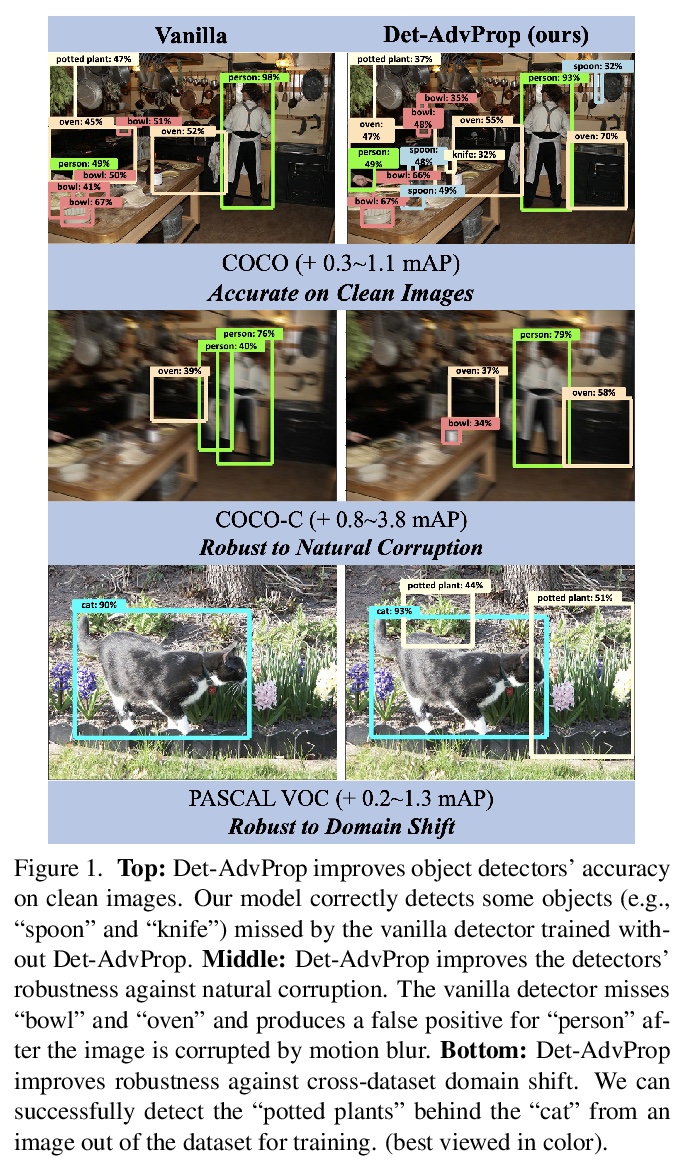
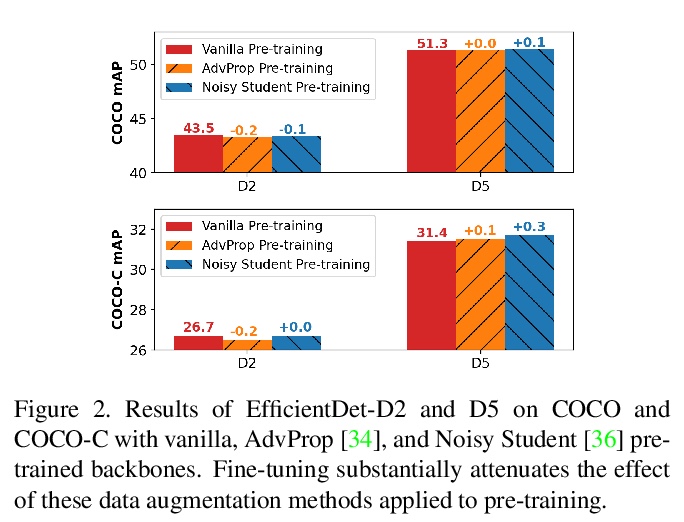
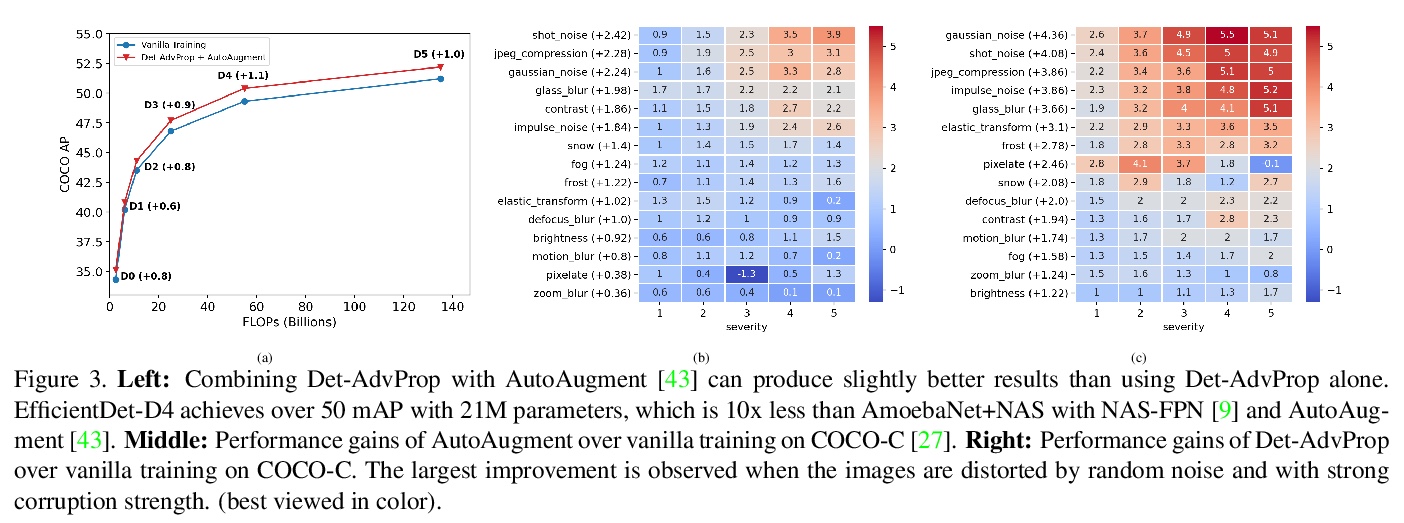
[CV] Robust and Accurate Object Detection via Adversarial Learning
基于对抗式学习的鲁棒且精确的目标检测
X Chen, C Xie, M Tan, L Zhang, C Hsieh, B Gong
[Google & UCLA & UCSC]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaEV01l5g

[CL] Controllable Generation from Pre-trained Language Models via Inverse Prompting
基于反向提示的预训练语言模型可控生成
X Zou, D Yin, Q Zhong, H Yang, Z Yang, J Tang
[Tsinghua University & Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence & Alibaba Inc]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaEWXczHj