- 1、[CL] Pretrained Language Models for Text Generation: A Survey
- 2、[CV] Intriguing Properties of Vision Transformers
- 3、[LG] Navigation Turing Test (NTT): Learning to Evaluate Human-Like Navigation
- 4、[CV] NeLF: Practical Novel View Synthesis with Neural Light Field
- 5、[CV] Driving-Signal Aware Full-Body Avatars
- [CV] VLM: Task-agnostic Video-Language Model Pre-training for Video Understanding
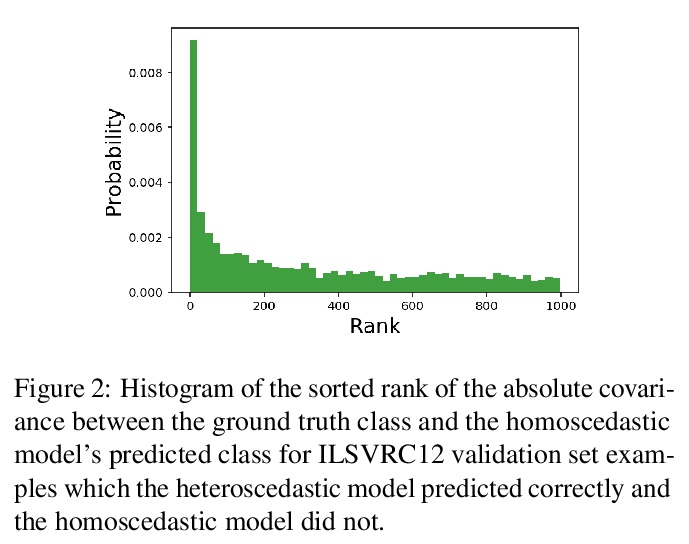
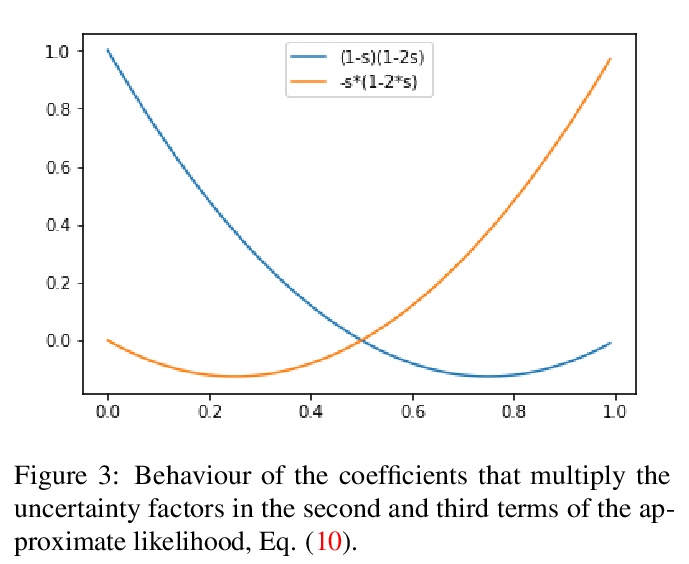
- [LG] Correlated Input-Dependent Label Noise in Large-Scale Image Classification
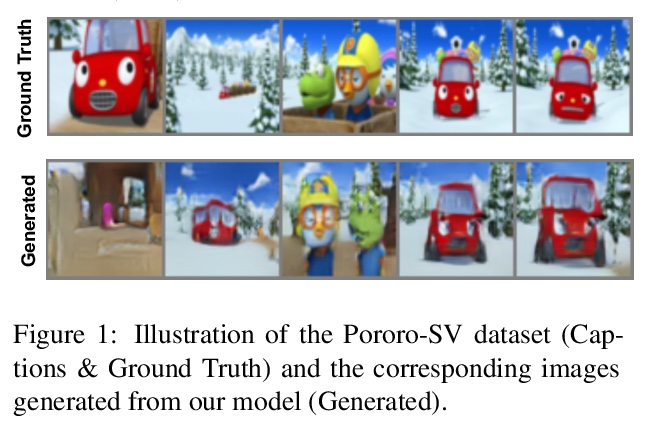
- [CL] Improving Generation and Evaluation of Visual Stories via Semantic Consistency
- [CV] Self-supervised Augmentation Consistency for Adapting Semantic Segmentation
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
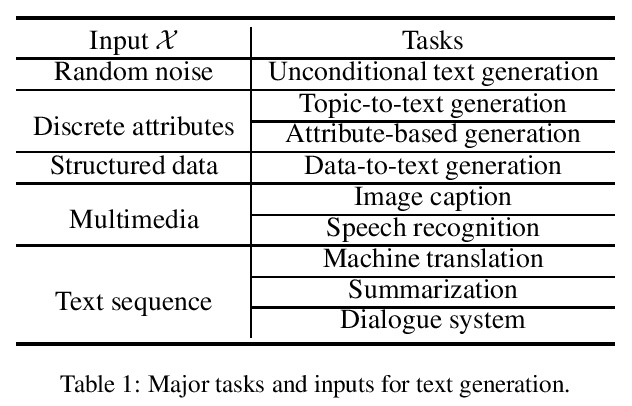
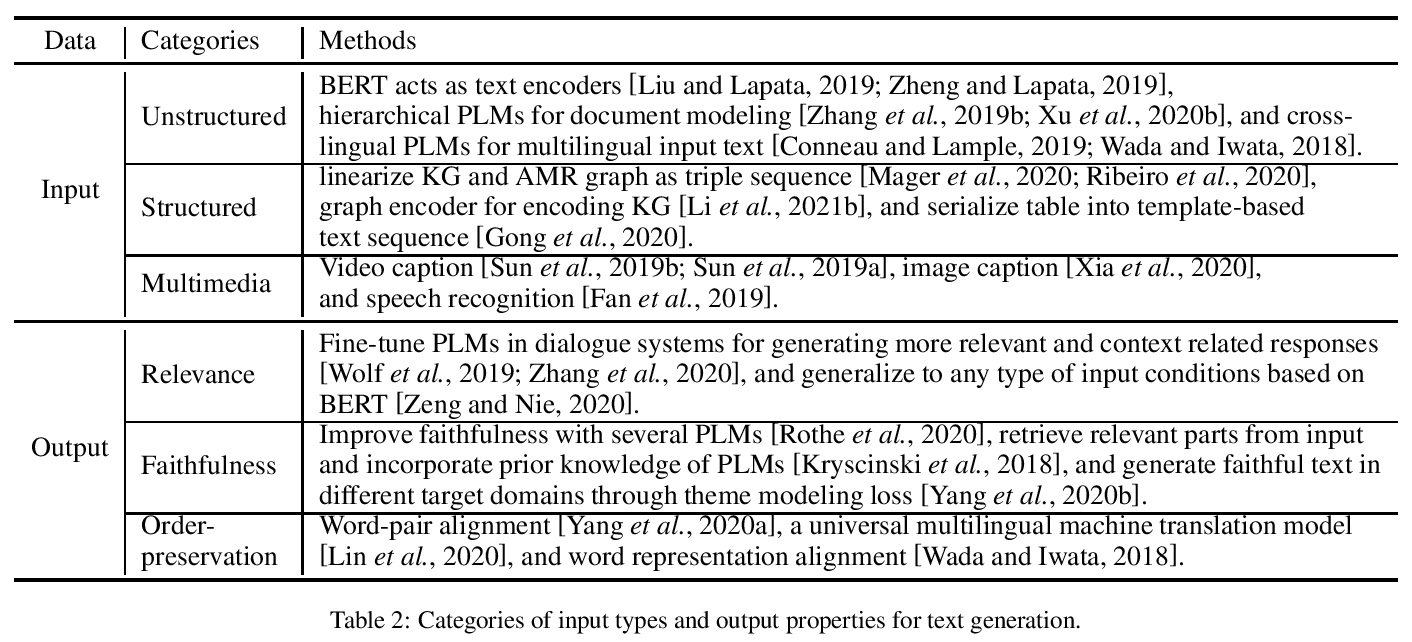
1、[CL] Pretrained Language Models for Text Generation: A Survey
J Li, T Tang, W X Zhao, J Wen
[Renmin University of China]
面向文本生成的预训练语言模型综述。文本生成已经成为自然语言处理(NLP)中最重要又最具挑战性的任务之一。深度学习的复苏通过神经生成模型,特别是预训练语言模型(PLM)的范式,大大推动了这一领域的发展。本文概述了面向文本生成的预训练语言模型取得的主要进展。序言部分提出了一般的任务定义,并简要介绍了用于文本生成的预训练语言模型的主流架构。核心内容部分讨论了如何调整现有的预训练语言模型,以对不同的输入数据进行建模,并满足生成文本的特殊属性。进一步总结了文本生成的几个重要的微调策略。提出了几个未来的方向并进行了总结。本综述旨在为文本生成研究者提供一个综合的、指向相关研究的指南。
Text generation has become one of the most important yet challenging tasks in natural language processing (NLP). The resurgence of deep learning has greatly advanced this field by neural generation models, especially the paradigm of pretrained language models (PLMs). In this paper, we present an overview of the major advances achieved in the topic of PLMs for text generation. As the preliminaries, we present the general task definition and briefly describe the mainstream architectures of PLMs for text generation. As the core content, we discuss how to adapt existing PLMs to model different input data and satisfy special properties in the generated text. We further summarize several important fine-tuning strategies for text generation. Finally, we present several future directions and conclude this paper. Our survey aims to provide text generation researchers a synthesis and pointer to related research.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kh2kfffmb
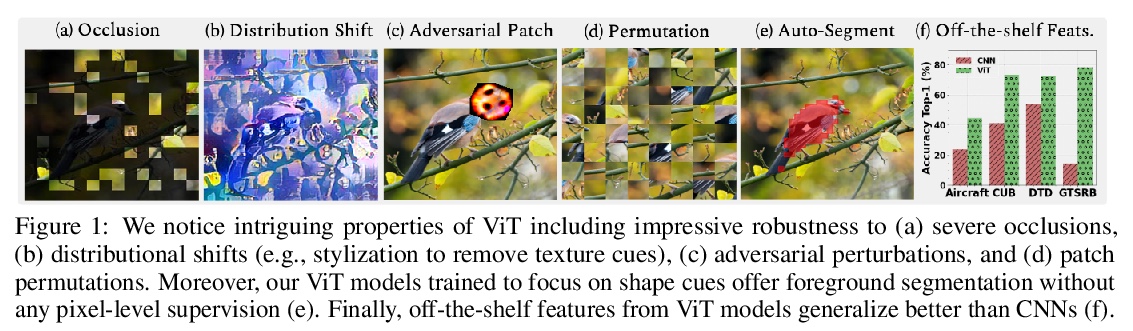
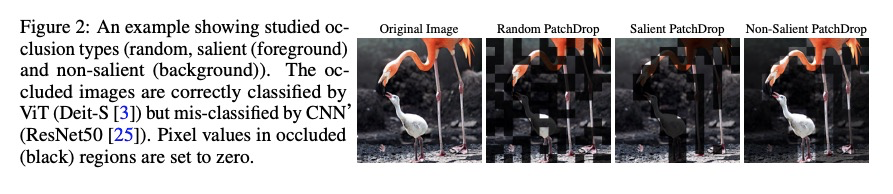
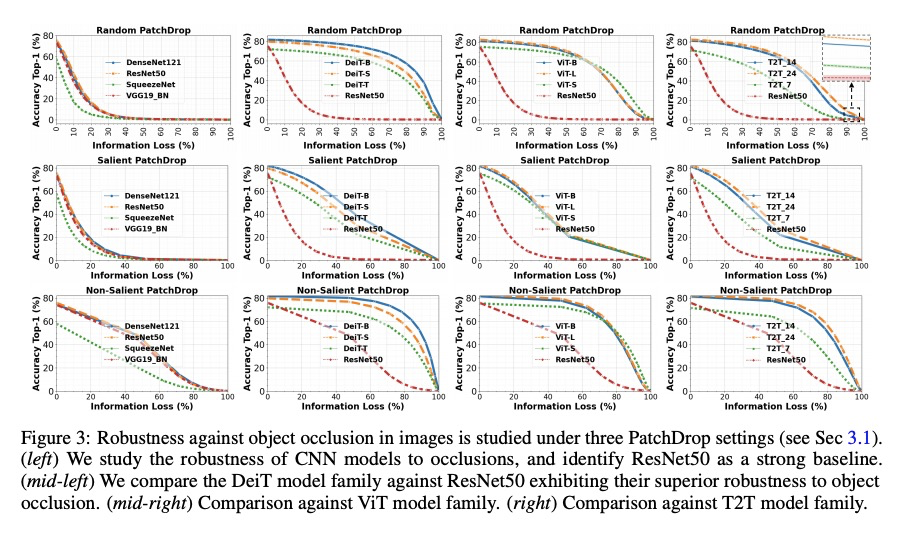
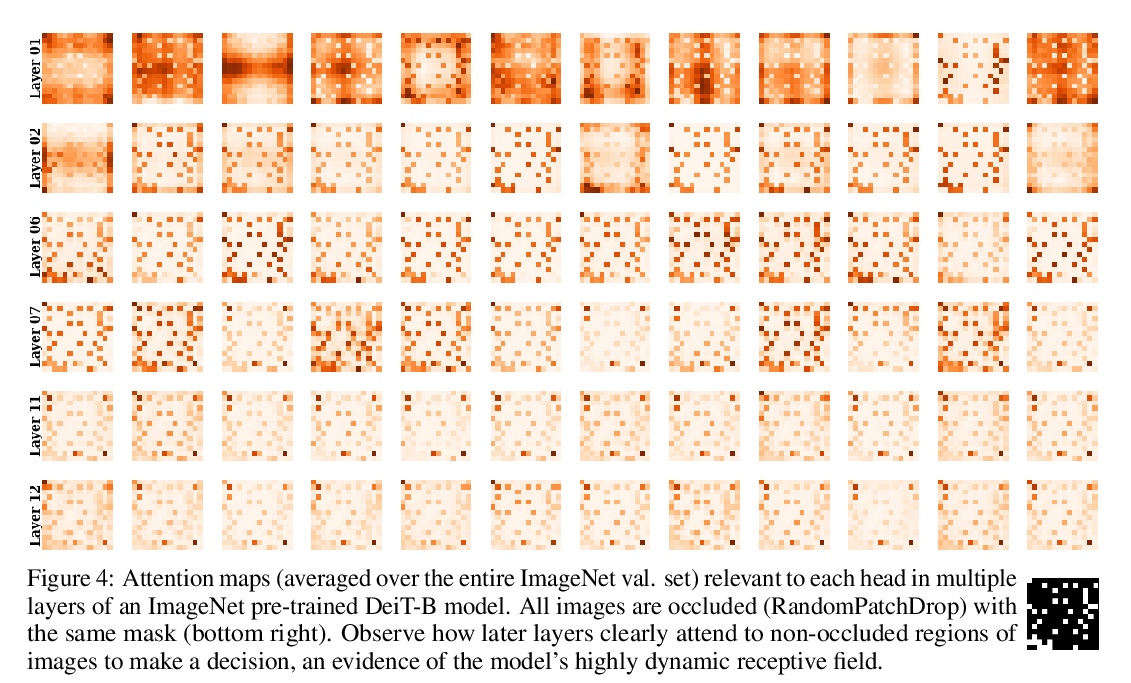
2、[CV] Intriguing Properties of Vision Transformers
M Naseer, K Ranasinghe, S Khan, M Hayat, F S Khan, M Yang
[Australian National University & Mohamed bin Zayed University of AI]
视觉Transformer的迷人特性。视觉Transformer(ViT)在各种机器视觉问题上表现出令人印象深刻的性能。这些模型基于多头的自注意里机制,可灵活地关注到图像块序列来编码上下文线索。一个重要的问题是,这种以给定图块为条件的对整个图像背景的关注的灵活性,如何能够促进自然图像中干扰的处理,例如,严重遮挡、域迁移、空间排列、对抗性和自然扰动。本文通过一组广泛实验,系统性研究了该问题,包括三个ViT系列,并与一个高性能的卷积神经网络(CNN)进行比较。展示并分析了ViT的以下特性:(a) Transformer对严重遮挡、扰动和域迁移具有高度的鲁棒性,例如,即使在随机遮挡了80%的图像内容后,仍能在ImageNet上保持高达60%的最高精度。(b) 对遮挡的鲁棒表现不是由于对局部纹理的偏差,与CNN相比,ViTs对纹理的偏差明显减少。当适当的训练来编码基于形状的特征时,ViTs表现出与人类视觉系统相当的形状识别能力。(c) 用ViT编码形状表征导致了一个有趣的结果,即无需像素级监督的准确语义分割。(d) 来自单一ViT模型的现成特征可以组合成特征集合,在传统的及少样本学习范式中的一系列分类数据集中获得高精度。本文表明ViT的有效特征,是由于通过自注意力机制可能产生的灵活和动态的感受野。
Vision transformers (ViT) have demonstrated impressive performance across various machine vision problems. These models are based on multi-head self-attention mechanisms that can flexibly attend to a sequence of image patches to encode contextual cues. An important question is how such flexibility in attending imagewide context conditioned on a given patch can facilitate handling nuisances in natural images e.g., severe occlusions, domain shifts, spatial permutations, adversarial and natural perturbations. We systematically study this question via an extensive set of experiments encompassing three ViT families and comparisons with a high-performing convolutional neural network (CNN). We show and analyze the following intriguing properties of ViT: (a) Transformers are highly robust to severe occlusions, perturbations and domain shifts, e.g., retain as high as 60% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet even after randomly occluding 80% of the image content. (b) The robust performance to occlusions is not due to a bias towards local textures, and ViTs are significantly less biased towards textures compared to CNNs. When properly trained to encode shape-based features, ViTs demonstrate shape recognition capability comparable to that of human visual system, previously unmatched in the literature. (c) Using ViTs to encode shape representation leads to an interesting consequence of accurate semantic segmentation without pixel-level supervision. (d) Off-the-shelf features from a single ViT model can be combined to create a feature ensemble, leading to high accuracy rates across a range of classification datasets in both traditional and few-shot learning paradigms. We show effective features of ViTs are due to flexible and dynamic receptive fields possible via self-attention mechanisms.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kh2oE1UHI
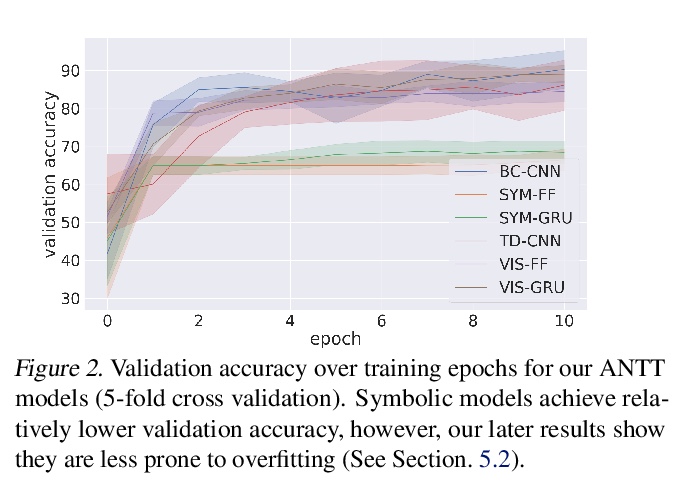
3、[LG] Navigation Turing Test (NTT): Learning to Evaluate Human-Like Navigation
S Devlin, R Georgescu, I Momennejad, J Rzepecki, E Zuniga, G Costello, G Leroy, A Shaw, K Hofmann
[Microsoft Research]
导航图灵测试(NTT):类人导航评价学习。在开发学习复杂类人行为的智能体的道路上,一个关键的挑战是需要快速和准确地量化与人类的相似性。虽然人工对这种行为的评估可以是高度准确的,但速度和可扩展性有限。本文通过一种新的自动导航图灵测试(ANTT)来解决这些限制,该测试可学习预测人工对人类相似性的判断。在一个复杂的3D环境导航任务上证明了自动NTT的有效性。研究了六个分类模型,以阐明最适合这项任务的架构类型,通过人工NTT收集的数据对其进行验证。最好的模型在区分真正的人类和智能体行为时达到了很高的精度。
A key challenge on the path to developing agents that learn complex human-like behavior is the need to quickly and accurately quantify humanlikeness. While human assessments of such behavior can be highly accurate, speed and scalability are limited. We address these limitations through a novel automated Navigation Turing Test (ANTT) that learns to predict human judgments of human-likeness. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our automated NTT on a navigation task in a complex 3D environment. We investigate six classification models to shed light on the types of architectures best suited to this task, and validate them against data collected through a human NTT. Our best models achieve high accuracy when distinguishing true human and agent behavior. At the same time, we show that predicting finer-grained human assessment of agents’ progress towards human-like behavior remains unsolved. Our work takes an important step towards agents that more effectively learn complex human-like behavior.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kh2tKrP3H


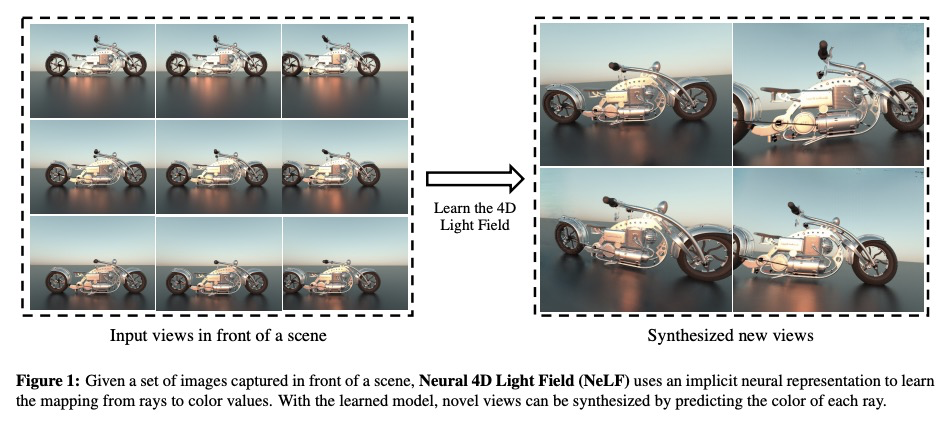
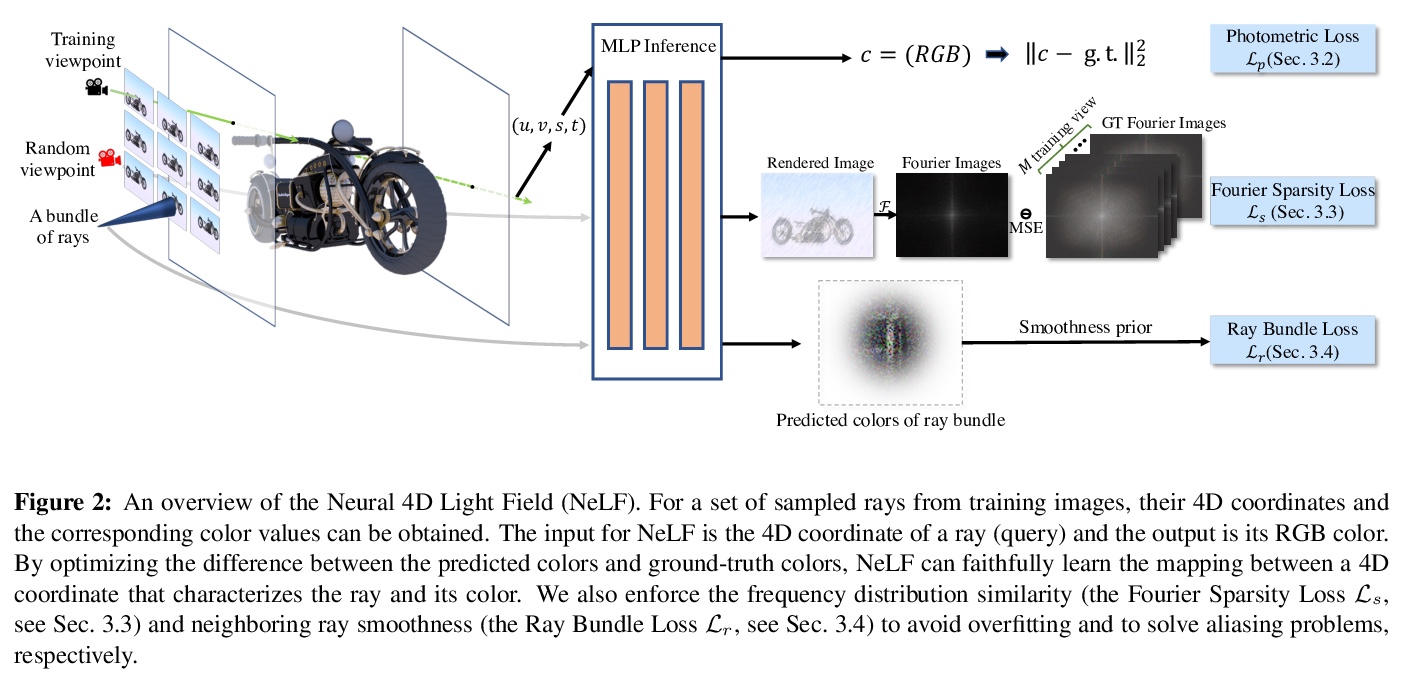
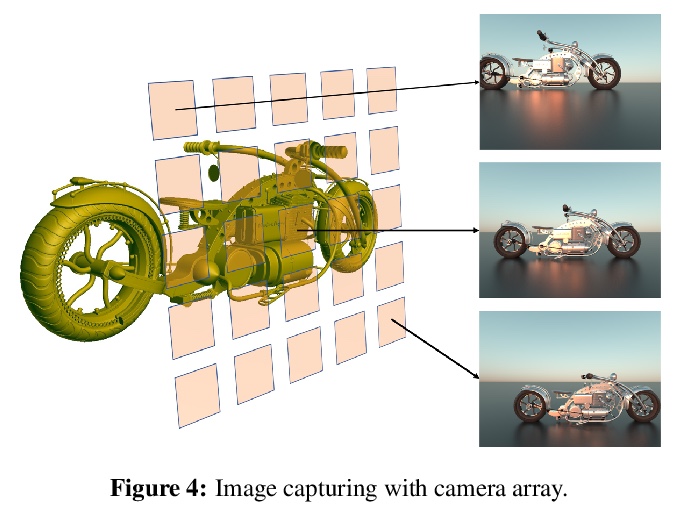
4、[CV] NeLF: Practical Novel View Synthesis with Neural Light Field
C Liu, Z Li, J Yuan, Y Xu
[InnoPeak Technology Inc & State University of New York]
NeLF:基于神经光场的实用新视图合成。本文为复杂场景新型视图合成提出了一种高效、鲁棒的深度学习解决方案,将3D场景表示为光场,即一组光线,每条光线在到达图像平面时都带有相应颜色。为有效进行新视图渲染,采用光场4D参数化,每条光线由一个4D参数来描述,将光场制定为一个4D函数,将4D坐标映射到相应的颜色值。训练一个深度全连接网络来优化该隐函数并记忆3D场景,用场景特定模型来合成新视图。与以往需要密集视图采样以可靠渲染新视图的光场方法不同,该方法可通过射线采样并直接从网络中查询每条射线颜色来渲染新视图,从而实现高质量光场渲染,而训练图像集比较稀少,在保持交互式帧率的同时,实现了最先进的新视图合成结果。
In this paper, we present an efficient and robust deep learning solution for novel view synthesis of complex scenes. In our approach, a 3D scene is represented as a light field, i.e., a set of rays, each of which has a corresponding color when reaching the image plane. For efficient novel view rendering, we adopt a 4D parameterization of the light field, where each ray is characterized by a 4D parameter. We then formulate the light field as a 4D function that maps 4D coordinates to corresponding color values. We train a deep fully connected network to optimize this implicit function and memorize the 3D scene. Then, the scene-specific model is used to synthesize novel views. Different from previous light field approaches which require dense view sampling to reliably render novel views, our method can render novel views by sampling rays and querying the color for each ray from the network directly, thus enabling highquality light field rendering with a sparser set of training images. Our method achieves state-of-the-art novel view synthesis results while maintaining an interactive frame rate.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kh2z7whKY

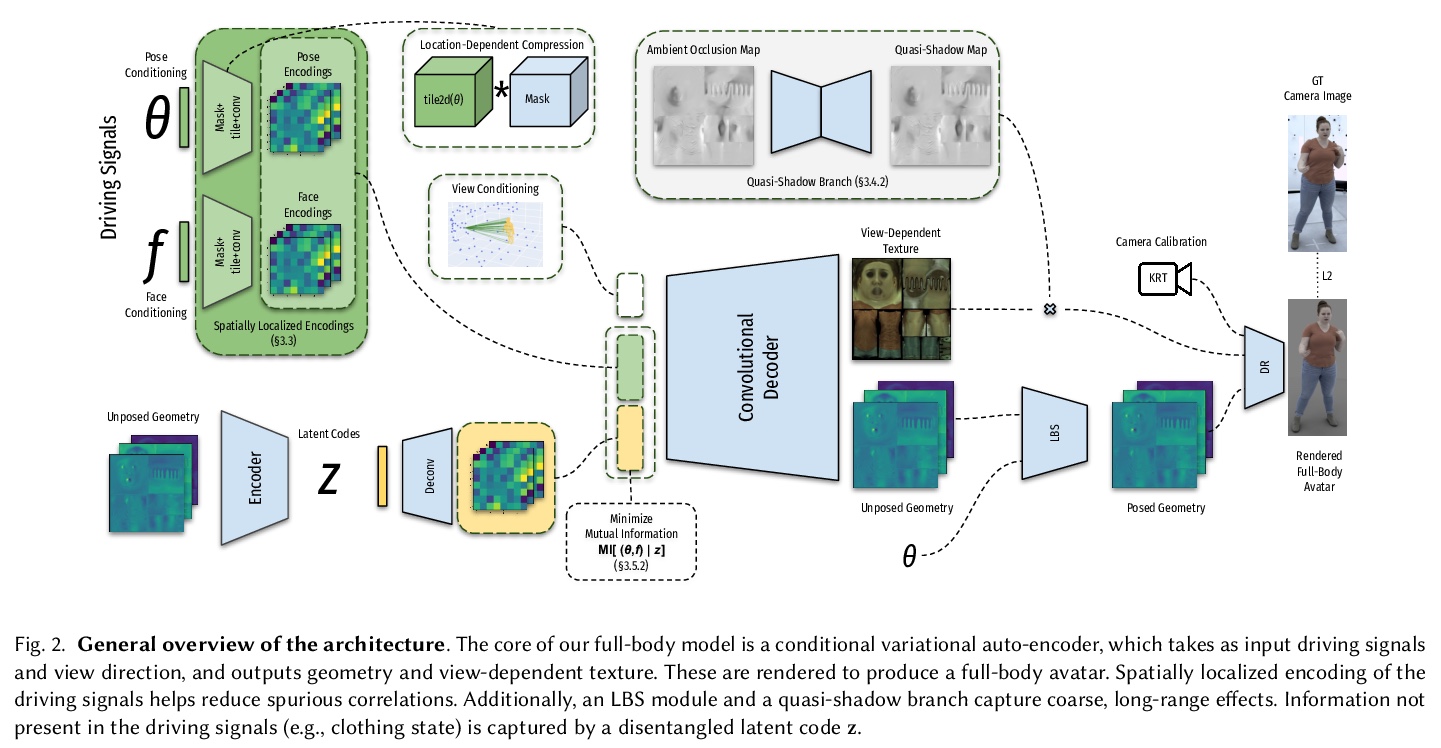
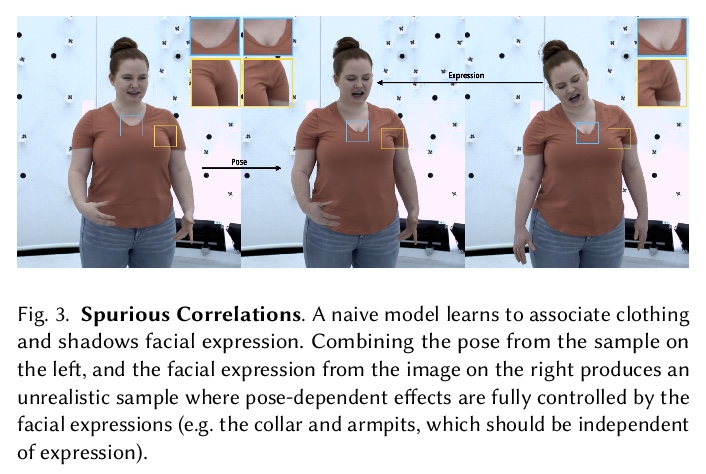
5、[CV] Driving-Signal Aware Full-Body Avatars
T Bagautdinov, C Wu, T Simon, F Prada, T Shiratori, S Wei, W Xu, Y Sheikh, J Saragih
[Facebook Reality Labs]
驱动信号感知的全身化身。提出一种基于学习的方法,用来构建驱动信号感知的全身化身,采用条件变分自编码器,用不完整驱动信号(如人体姿态和人脸关键点)制作动画,并产生高质量的人体几何和相关外观表示。该方法背后的核心是,通过解缠驱动信号和其他动画中不可用的生成式要素,实现更好的驱动性和泛化性。对于给定的驱动信号,变分模型产生紧凑的缺失因素不确定性空间,可采用最适合于特定应用的归因策略。证明了该方法在虚拟远程呈现的全身动画这一具有挑战性的问题上的有效性,由置于环境中并安装在VR头盔上的最小传感器获得驱动信号。
We present a learning-based method for building driving-signal aware full-body avatars. Our model is a conditional variational autoencoder that can be animated with incomplete driving signals, such as human pose and facial keypoints, and produces a high-quality representation of human geometry and view-dependent appearance. The core intuition behind our method is that better drivability and generalization can be achieved by disentangling the driving signals and remaining generative factors, which are not available during animation. To this end, we explicitly account for information deficiency in the driving signal by introducing a latent space that exclusively captures the remaining information, thus enabling the imputation of the missing factors required during full-body animation, while remaining faithful to the driving signal. We also propose a learnable localized compression for the driving signal which promotes better generalization, and helps minimize the influence of global chance-correlations often found in real datasets. For a given driving signal, the resulting variational model produces a compact space of uncertainty for missing factors that allows for an imputation strategy best suited to a particular application. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach on the challenging problem of full-body animation for virtual telepresence with driving signals acquired from minimal sensors placed in the environment and mounted on a VR-headset.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kh2ErvJOI


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
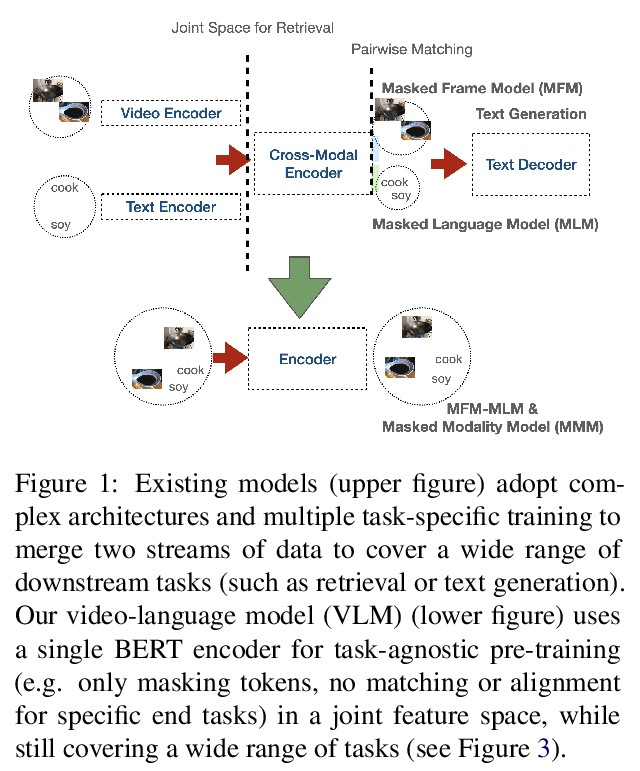
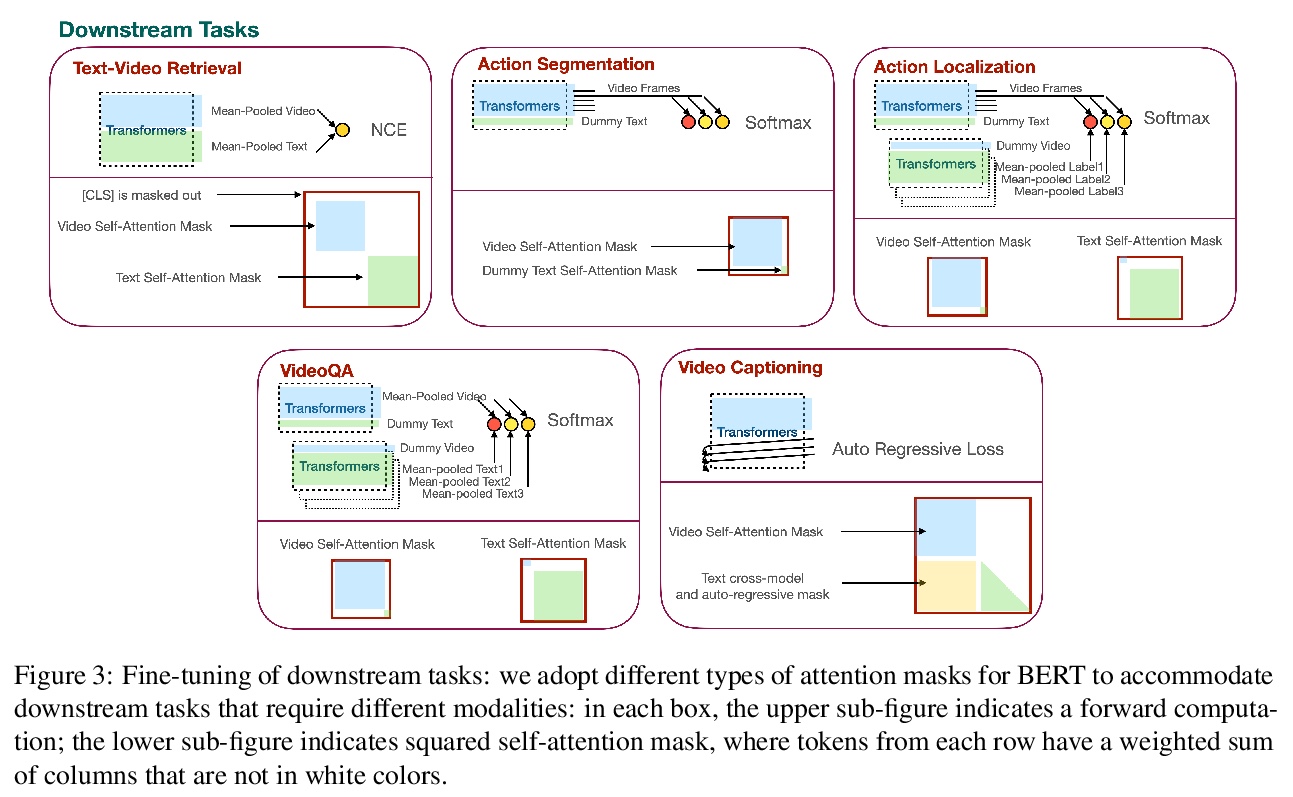
[CV] VLM: Task-agnostic Video-Language Model Pre-training for Video Understanding
VLM:面向视频理解的任务无关视频-语言模型预训练
H Xu, G Ghosh, P Huang, P Arora, M Aminzadeh, C Feichtenhofer, F Metze, L Zettlemoyer
[Facebook AI]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kh2LHxMD1

[LG] Correlated Input-Dependent Label Noise in Large-Scale Image Classification
大规模图像分类的输入依赖性相关标签噪声
M Collier, B Mustafa, E Kokiopoulou, R Jenatton, J Berent
[Google AI]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kh2Nms8kG

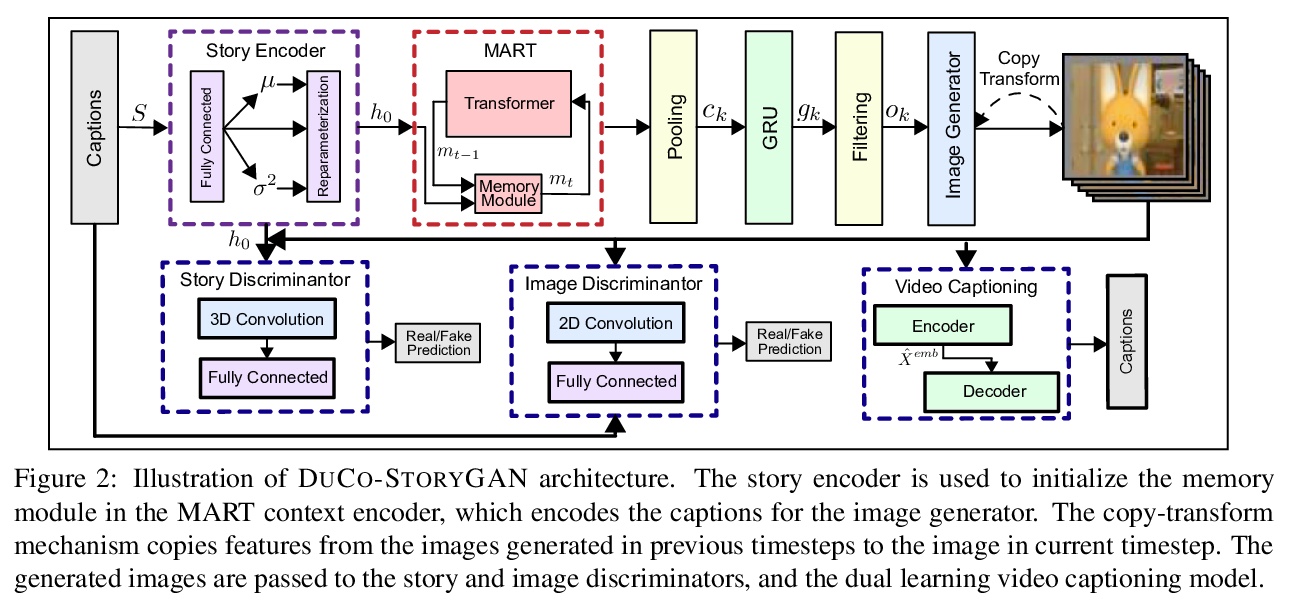
[CL] Improving Generation and Evaluation of Visual Stories via Semantic Consistency
基于语义一致性改进视觉故事的生成与评价
A Maharana, D Hannan, M Bansal
[University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kh2PnsP8y

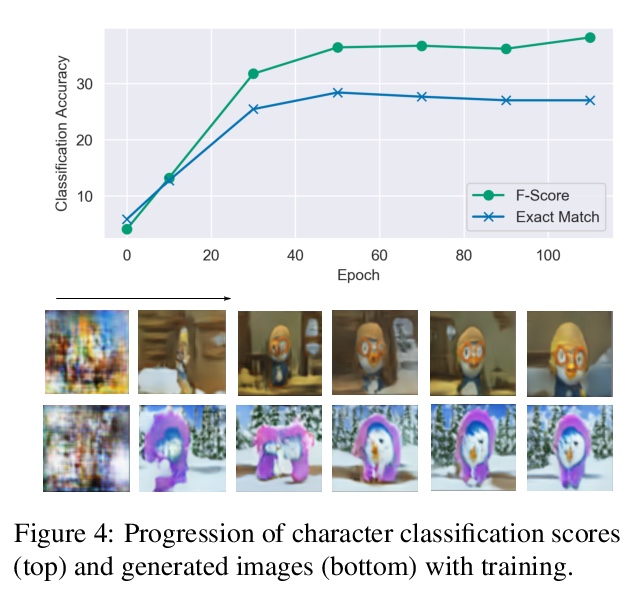
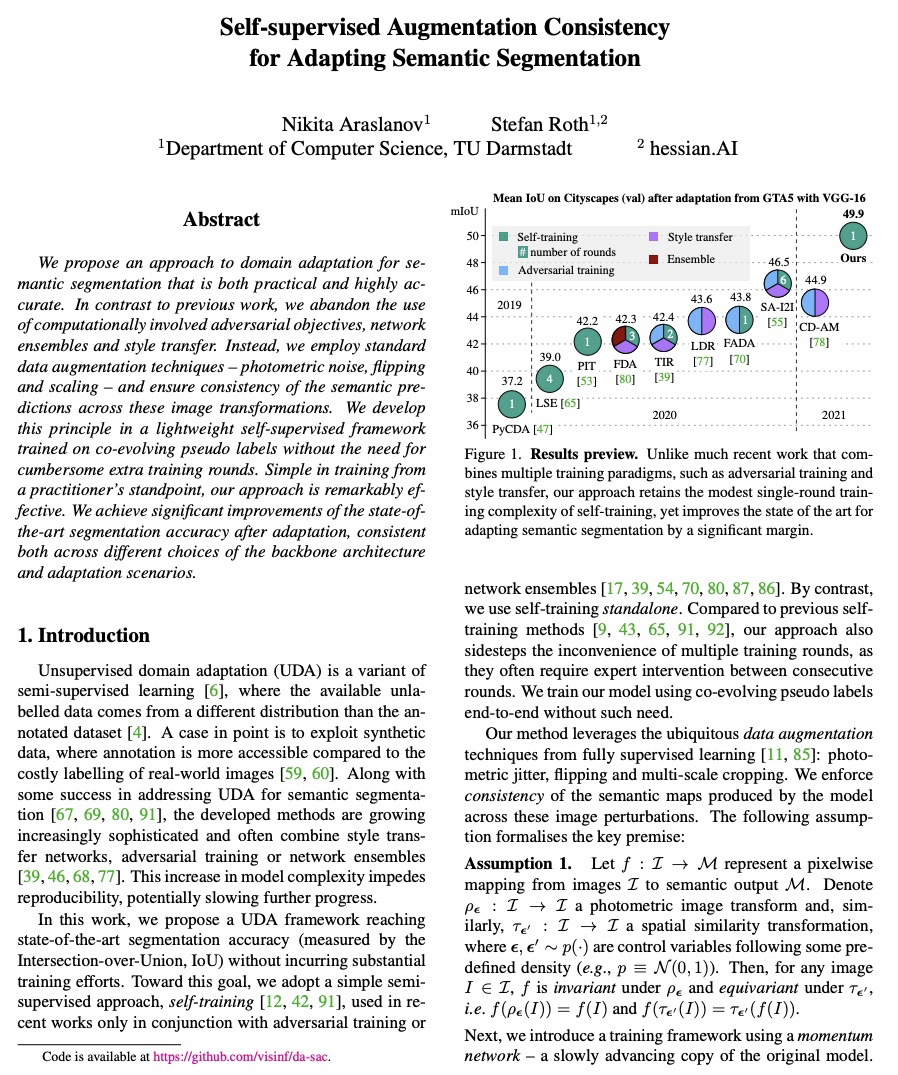
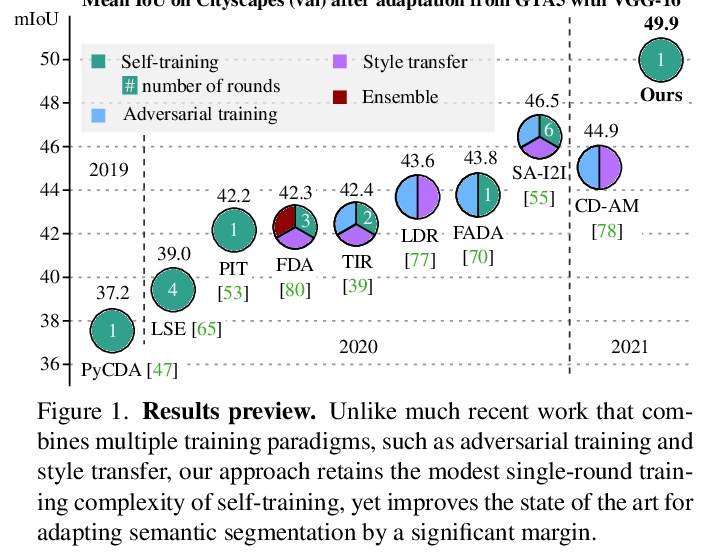
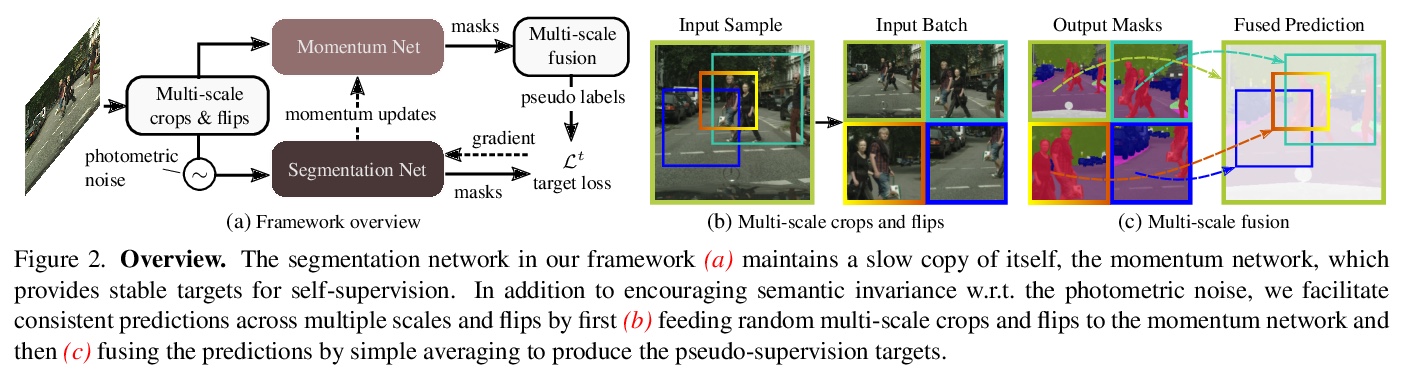
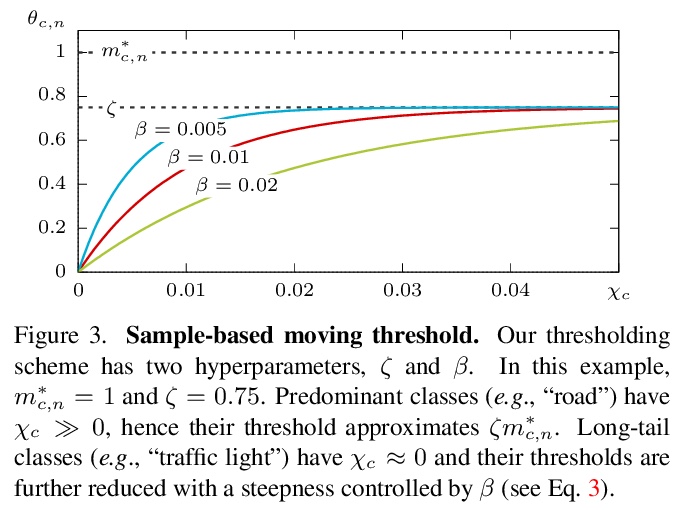
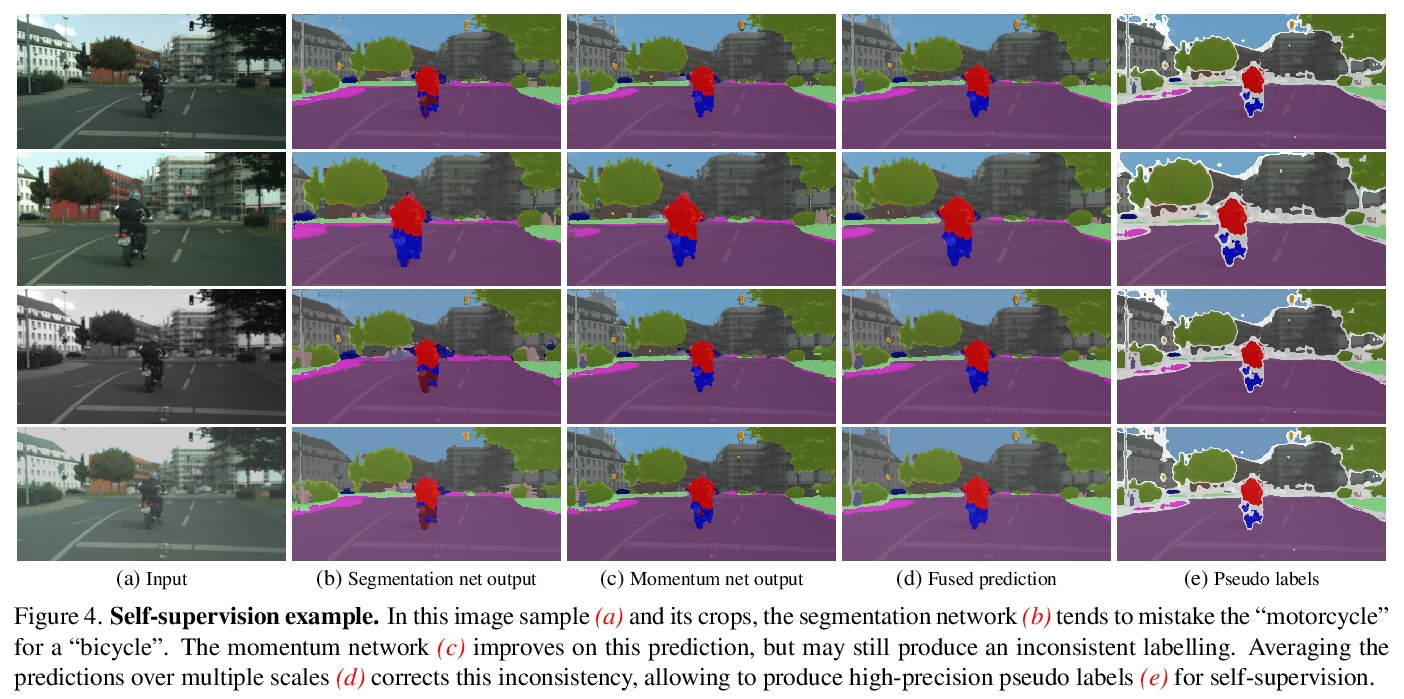
[CV] Self-supervised Augmentation Consistency for Adapting Semantic Segmentation
自监督增强一致性自适应语义分割
N Araslanov, S Roth
[TU Darmstadt]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kh2QJkKb1