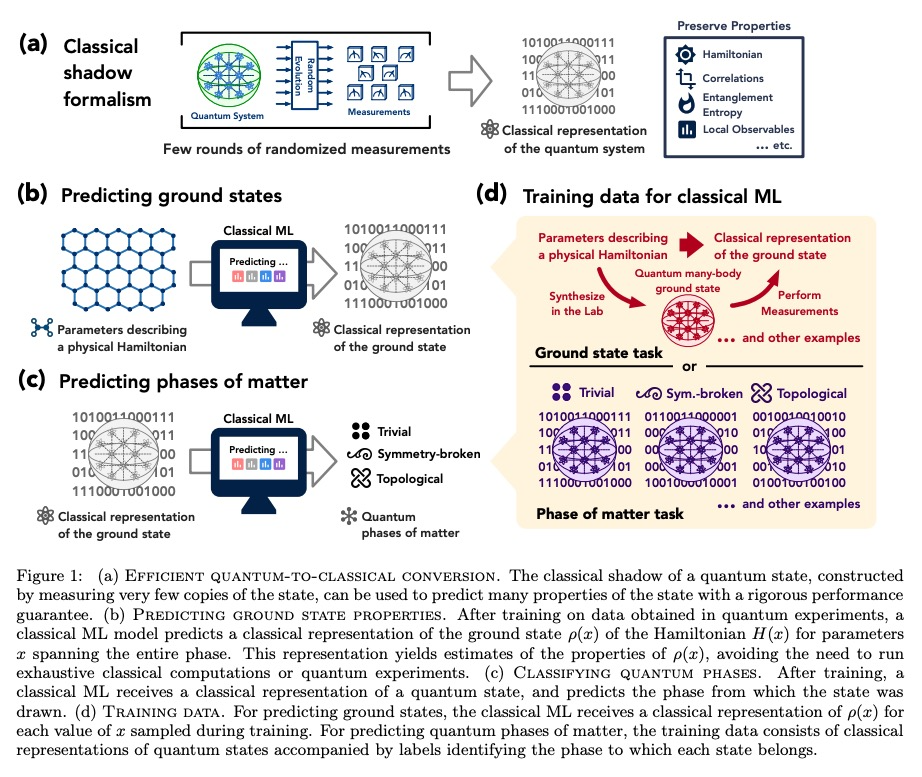
- 1、[LG] Provably efficient machine learning for quantum many-body problems
- 2、[AS] AudioCLIP: Extending CLIP to Image, Text and Audio
- 3、[CV] HyperNeRF: A Higher-Dimensional Representation for Topologically Varying Neural Radiance Fields
- 4、[CL] Charformer: Fast Character Transformers via Gradient-based Subword Tokenization
- 5、[LG] Task-agnostic Continual Learning with Hybrid Probabilistic Models
- [CV] GaussiGAN: Controllable Image Synthesis with 3D Gaussians from Unposed Silhouettes
- [CV] Video Swin Transformer
- [LG] Towards Biologically Plausible Convolutional Networks
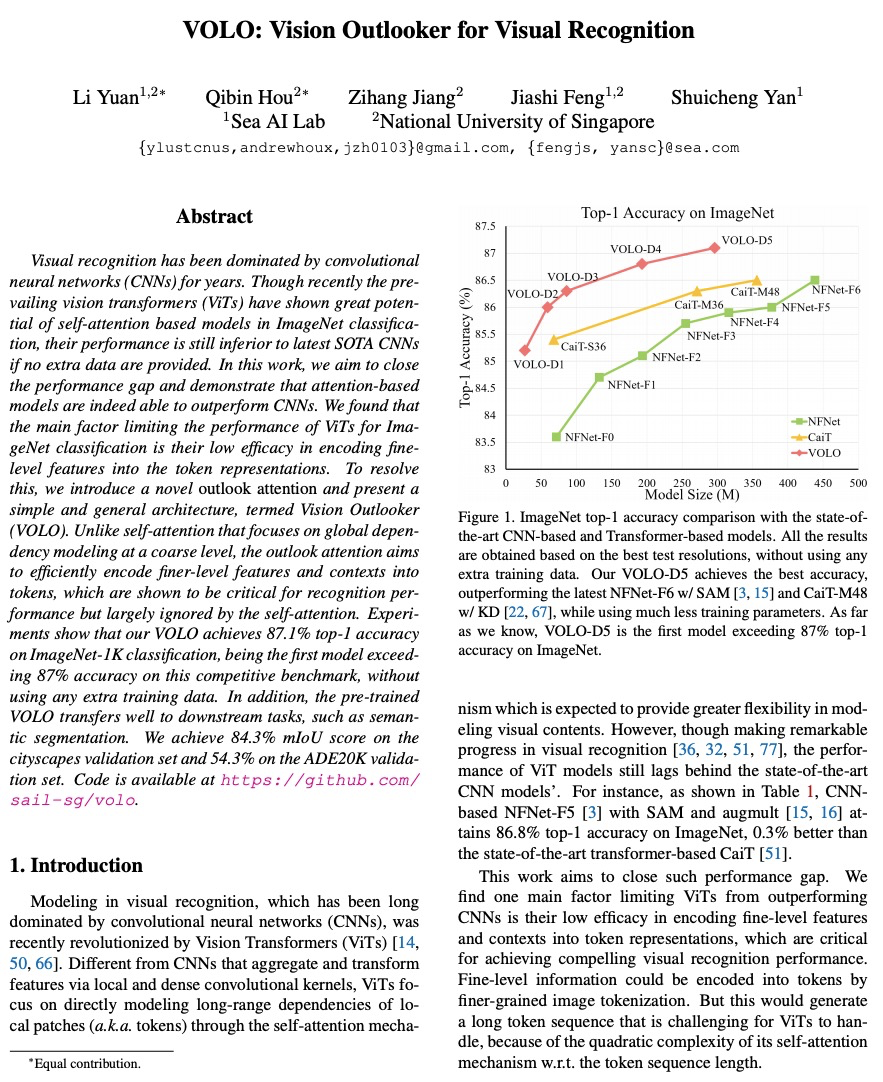
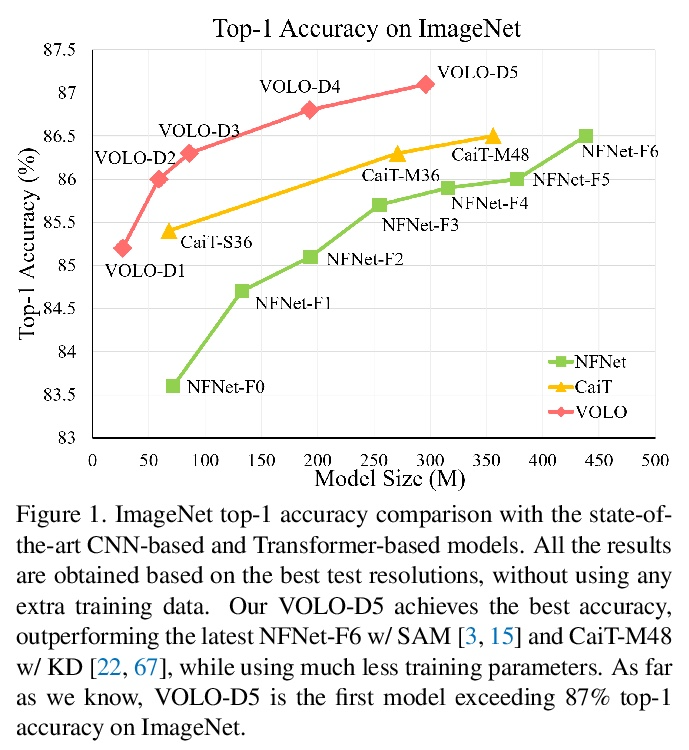
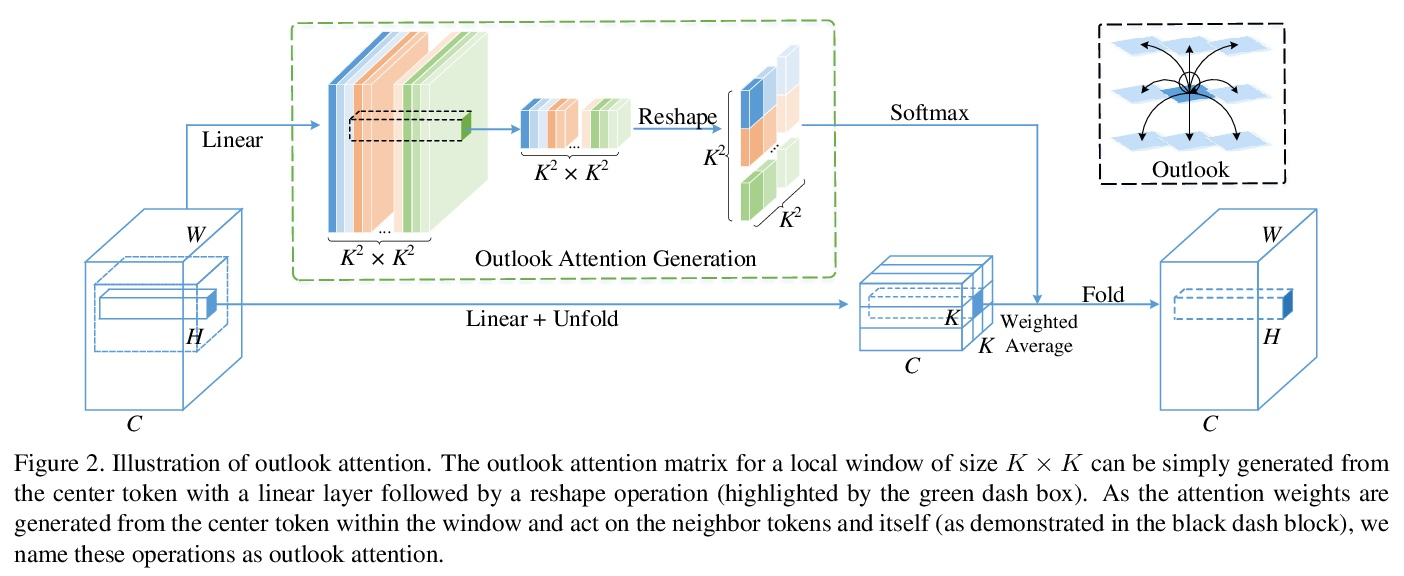
- [CV] VOLO: Vision Outlooker for Visual Recognition
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] Provably efficient machine learning for quantum many-body problems
H Huang, R Kueng, G Torlai, V V. Albert, J Preskill
[Caltech & Johannes Kepler University Linz & AWS Center for Quantum Computing,]
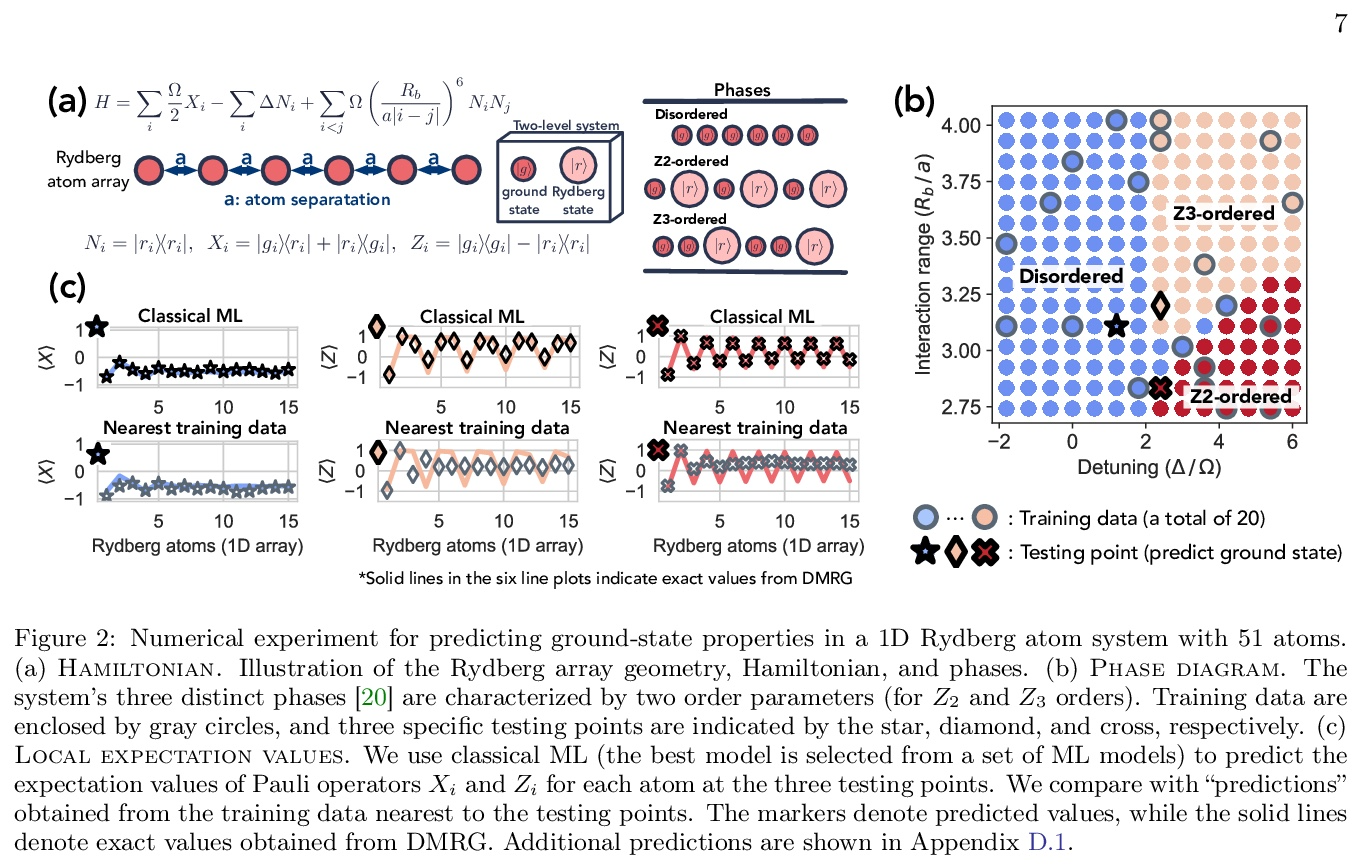
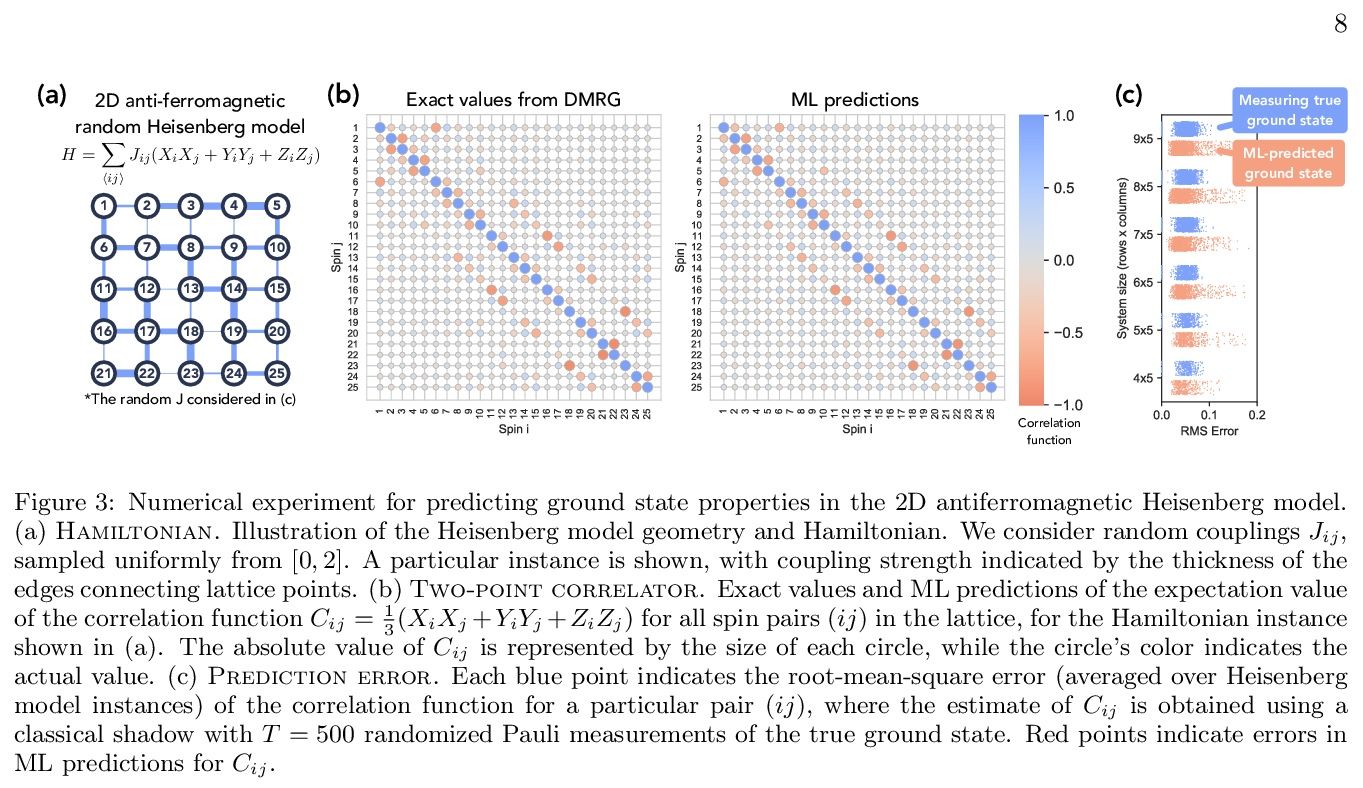
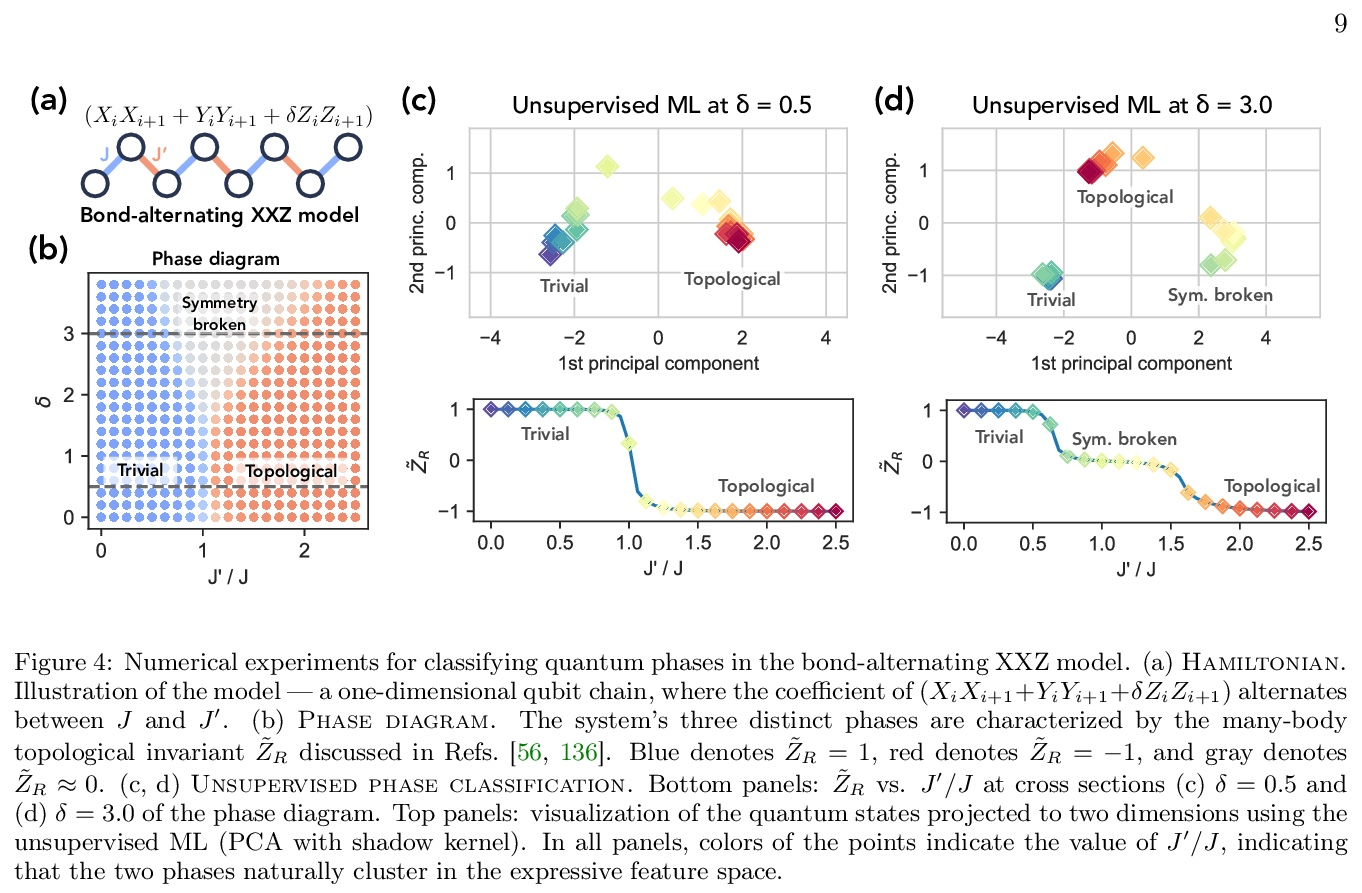
量子多体问题可证高效机器学习。经典机器学习(ML)为解决物理和化学中具有挑战性的量子多体问题提供了一种潜在的强大方法。然而,与其他传统方法相比,机器学习的优势还没有被牢固确立。本文证明了经典机器学习算法可有效预测有限空间维度中空白哈密顿量的基态特性,在学习了通过测量物质的相同量子相位中其他哈密顿量而获得的数据之后。反之,在广泛接受的复杂性理论假设下,不从数据中学习的经典算法不能获得同样的保证。本文还证明,经典机器学习算法可有效地对广泛的物质量子相进行分类,基于经典阴影的概念,一种多体量子态的简洁经典描述,可在可行的量子实验中构建,并用于预测该态的许多性质。广泛的数值实验证实了在各种情况下的理论结果,包括里德堡原子系统、2D随机海森堡模型、对称保护拓扑相和拓扑有序相。
Classical machine learning (ML) provides a potentially powerful approach to solving challenging quantum many-body problems in physics and chemistry. However, the advantages of ML over more traditional methods have not been firmly established. In this work, we prove that classical ML algorithms can efficiently predict ground state properties of gapped Hamiltonians in finite spatial dimensions, after learning from data obtained by measuring other Hamiltonians in the same quantum phase of matter. In contrast, under widely accepted complexity theory assumptions, classical algorithms that do not learn from data cannot achieve the same guarantee. We also prove that classical ML algorithms can efficiently classify a wide range of quantum phases of matter. Our arguments are based on the concept of a classical shadow, a succinct classical description of a many-body quantum state that can be constructed in feasible quantum experiments and be used to predict many properties of the state. Extensive numerical experiments corroborate our theoretical results in a variety of scenarios, including Rydberg atom systems, 2D random Heisenberg models, symmetry-protected topological phases, and topologically ordered phases.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KlU9V091H 
2、[AS] AudioCLIP: Extending CLIP to Image, Text and Audio
A Guzhov, F Raue, J Hees, A Dengel
[DFKI GmbH]
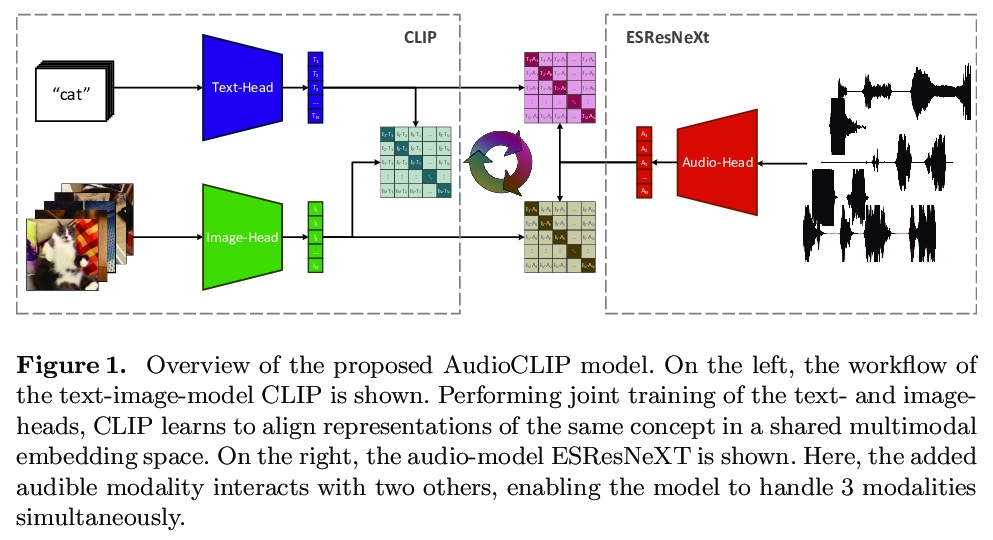
AudioCLIP:将 CLIP 扩展到图像、文本和音频。过去,快速发展的声音分类领域极大受益于其他领域方法的应用。现在,观察到将特定领域的任务和方法融合在一起的趋势,为社区提供了新的优秀模型。本文提出 CLIP 模型的扩展,除文本和图像之外,还能处理音频。所提出的模型使用 AudioSet 数据集将 ESResNeXt 音频模型合并到 CLIP 框架中。这种组合使所提出模型能执行单模态和多模态的分类和查询,同时保持 CLIP 以零样本推理方式泛化到不可见数据集的能力。AudioCLIP 在环境声音分类(ESC)任务中达到了最新水平,在 UrbanSound8K 和 ESC-50 数据集上的准确率分别达到 90.07% 和 97.15%,优于其他方法。此外,还在相同数据集的零样本 ESCtask 中达到了新基线(分别为 68.78% 和 69.40%)。最后,评估了所提出模型的跨模态查询性能,以及完全和部分训练对结果的影响。
In the past, the rapidly evolving field of sound classification greatly benefited from the application of methods from other domains. Today, we observe the trend to fuse domain-specific tasks and approaches together, which provides the community with new outstanding models. In this work, we present an extension of the CLIP model that handles audio in addition to text and images. Our proposed model incorporates the ESResNeXt audio-model into the CLIP framework using the AudioSet dataset. Such a combination enables the proposed model to perform bimodal and unimodal classification and querying, while keeping CLIP’s ability to generalize to unseen datasets in a zero-shot inference fashion. AudioCLIP achieves new state-of-the-art results in the Environmental Sound Classification (ESC) task, out-performing other approaches by reaching accuracies of 90.07% on the UrbanSound8K and 97.15% on the ESC-50 datasets. Further it sets new baselines in the zero-shot ESCtask on the same datasets (68.78% and 69.40%, respectively). Finally, we also assess the cross-modal querying performance of the proposed model as well as the influence of full and partial training on the results. For the sake of reproducibility, our code is published.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KlUgSbRBl 
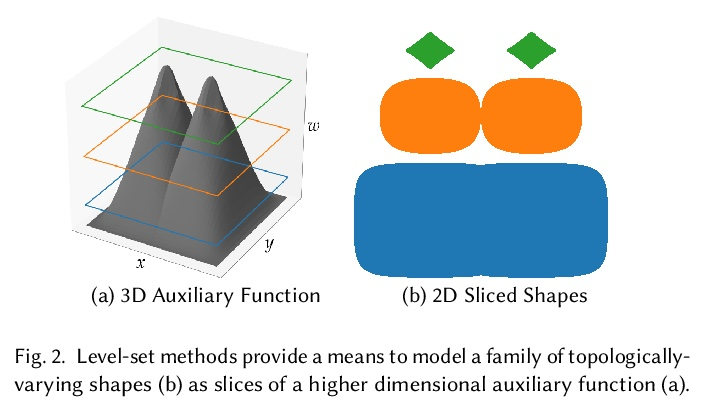
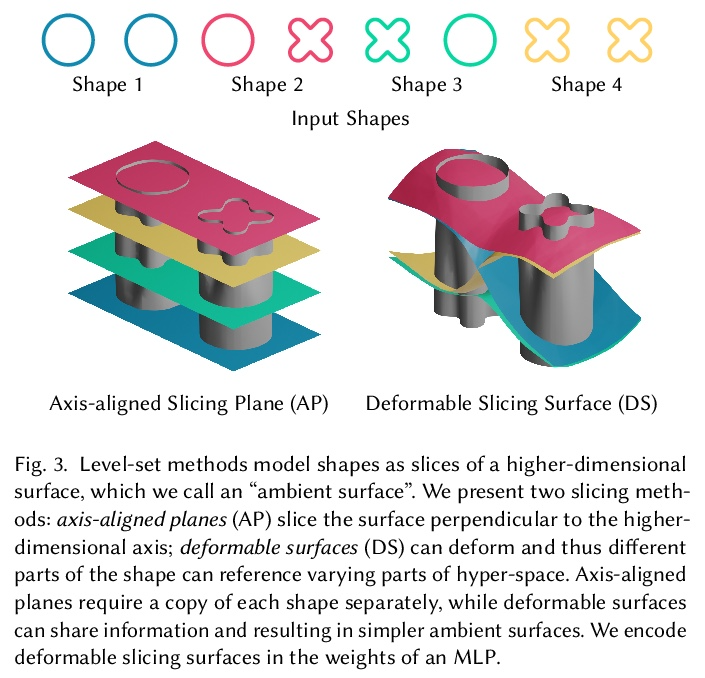
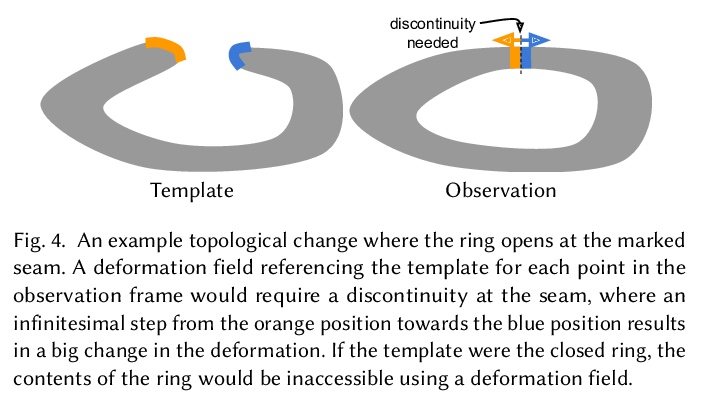
3、[CV] HyperNeRF: A Higher-Dimensional Representation for Topologically Varying Neural Radiance Fields
K Park, U Sinha, P Hedman, J T. Barron, S Bouaziz, D B Goldman, R Martin-Brualla, S M. Seitz
[University of Washington & Google Research & Facebook Reality Labs]
HyperNeRF:拓扑变化神经辐射场的更高维表示。神经辐射场(NeRF) 能以前所未有的保真度重建场景,最近的工作已将 NeRF 扩展到处理动态场景。重建此类非刚性场景的常用方法,是用从每个输入图像中的坐标到规范模板坐标空间的习得变形场映射。然而,这些基于变形的方法难以模拟拓扑变化,因为拓扑变化需要变形场的不连续性,但这些变形场必须是连续的。本文通过将 NeRF 提升到更高维空间来解决该限制,并将与每个单独输入图像对应的 5D 辐射场表示为通过该“超空间”的切片。该方法受到水平集方法的启发,将表面演变建模为通过更高维表面的切片。在两个任务上评估了所提出的方法:(i)在“时刻”间——即在输入图像中看到的场景配置间——平滑插值,同时保持视觉合理性,以及(ii)固定时刻的新视图合成。实验结果表明,称为 HyperNeRF 的方法在这两个任务上都以显著优势优于现有方法。与 Nerfies 相比,根据 LPIPS 的测量,HyperNeRF 将插值的平均错误率降低了 8.6%,将新视图合成的平均错误率降低了 8.8%。
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) are able to reconstruct scenes with unprecedented fidelity, and various recent works have extended NeRF to handle dynamic scenes. A common approach to reconstruct such non-rigid scenes is through the use of a learned deformation field mapping from coordinates in each input image into a canonical template coordinate space. However, these deformation-based approaches struggle to model changes in topology, as topological changes require a discontinuity in the deformation field, but these deformation fields are necessarily continuous. We address this limitation by lifting NeRFs into a higher dimensional space, and by representing the 5D radiance field corresponding to each individual input image as a slice through this “hyper-space”. Our method is inspired by level set methods, which model the evolution of surfaces as slices through a higher dimensional surface. We evaluate our method on two tasks: (i) interpolating smoothly between “moments”, i.e., configurations of the scene, seen in the input images while maintaining visual plausibility, and (ii) novel-view synthesis at fixed moments. We show that our method, which we dub HyperNeRF, outperforms existing methods on both tasks by significant margins. Compared to Nerfies, HyperNeRF reduces average error rates by 8.6% for interpolation and 8.8% for novel-view synthesis, as measured by LPIPS.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KlUmGlRtp 

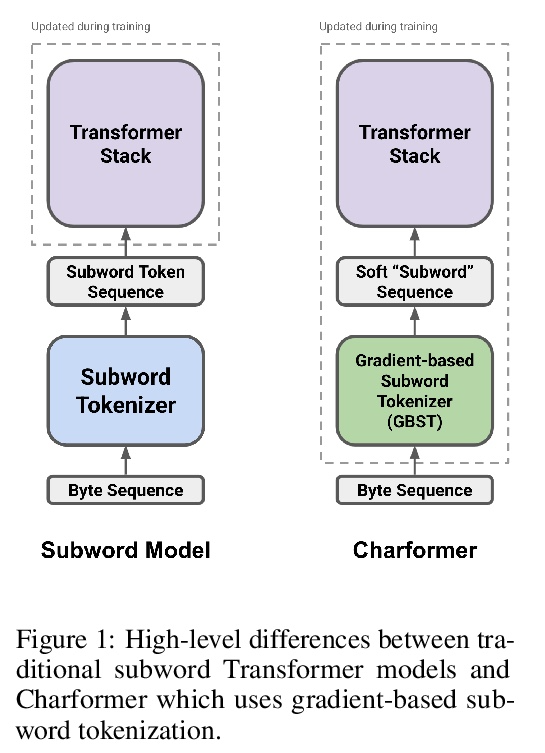
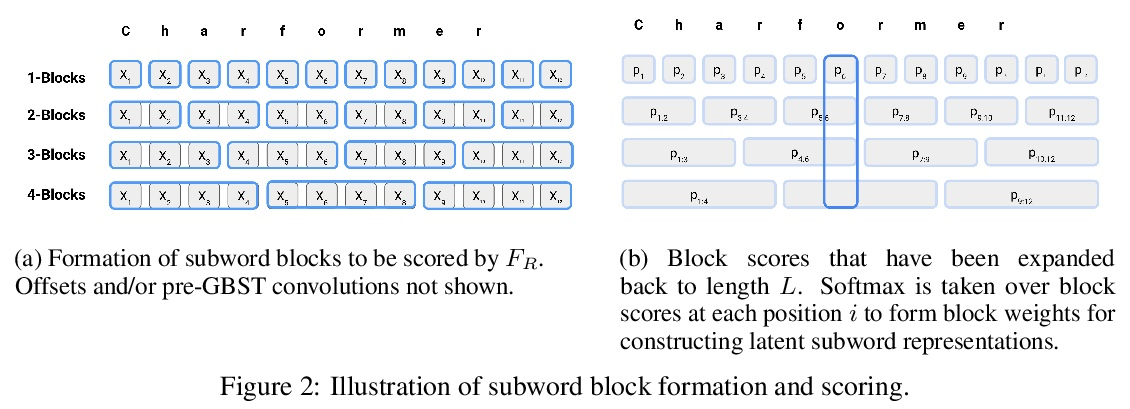
4、[CL] Charformer: Fast Character Transformers via Gradient-based Subword Tokenization
Y Tay, V Q. Tran, S Ruder, J Gupta, H W Chung, D Bahri, Z Qin, S Baumgartner, C Yu, D Metzler
[Google Research and DeepMind]
Charformer:基于梯度子词标记化的快速字符Transformer。自然语言处理中最先进的模型,依赖于单独的刚性子词标记化算法,限制了其泛化能力和对新设置的适应。本文提出一种新的模型归纳偏差,作为模型的一部分来学习端到端子词标记化。引入基于软梯度的子词标记化模块 (GBST),以数据驱动的方式自动从字符中学习潜在的子词表示。GBST 枚举候选子词块并学习用块评分网络逐位置对其进行评分。还引入了 CHARFORMER,一种深度 Transformer 模型,集成了 GBST 并在字节级别进行操作。通过对英语 GLUE、多语言和嘈杂文本数据集的大量实验,表明 CHARFORMER 优于一系列有竞争力的字节级基线,同时通常表现良好,有时甚至优于基于子词的模型。此外,CHARFORMER 速度很快,在保持有竞争力的质量的同时,将普通字节级和子词级 Transformer 的速度提高了 28-100%,为完全端到端训练高性能无Token模型铺平了道路。
State-of-the-art models in natural language processing rely on separate rigid subword tokenization algorithms, which limit their generalization ability and adaptation to new settings. In this paper, we propose a new model inductive bias that learns a subword tokenization end-to-end as part of the model. To this end, we introduce a soft gradient-based subword tokenization module (GBST) that automatically learns latent subword representations from characters in a data-driven fashion. Concretely, GBST enumerates candidate subword blocks and learns to score them in a position-wise fashion using a block scoring network. We additionally introduce CHARFORMER, a deep Transformer model that integrates GBST and operates on the byte level. Via extensive experiments on English GLUE, multilingual, and noisy text datasets, we show that CHARFORMER outperforms a series of competitive byte-level baselines while generally performing on par and sometimes outperforming subword-based models. Additionally, CHARFORMER is fast, improving the speed of both vanilla byte-level and subword-level Transformers by 28-100% while maintaining competitive quality. We believe this work paves the way for highly performant token-free models that are trained completely end-to-end.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KlUqYCfWi 

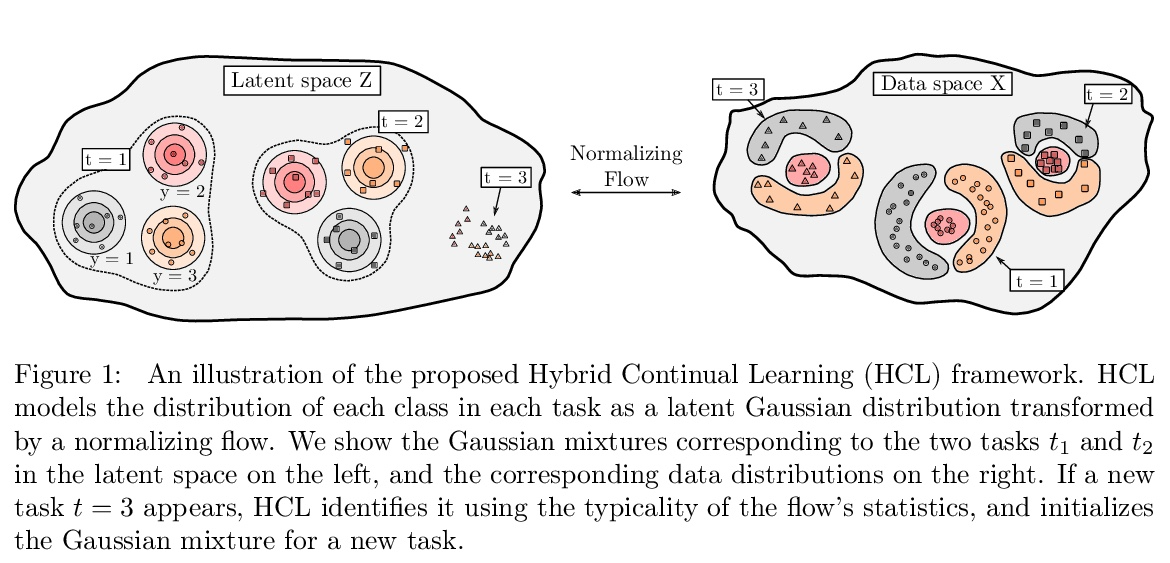
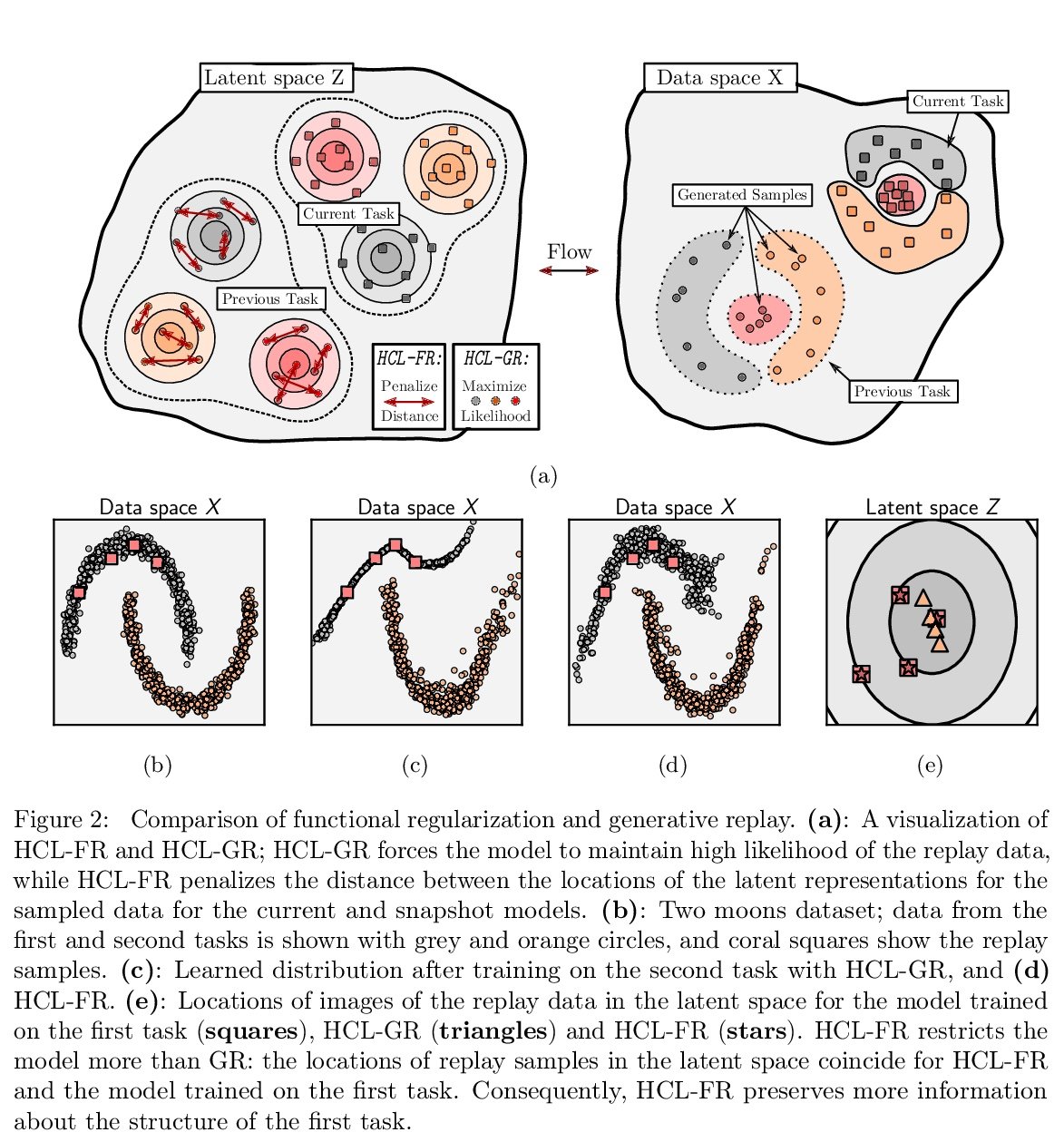
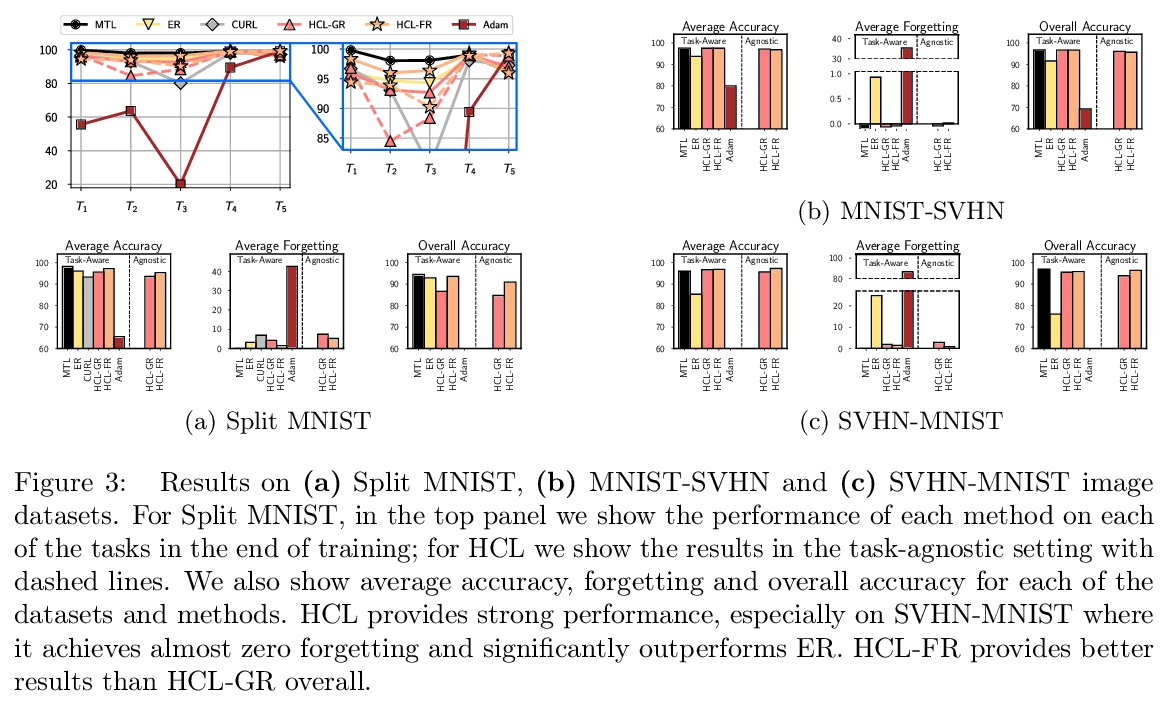
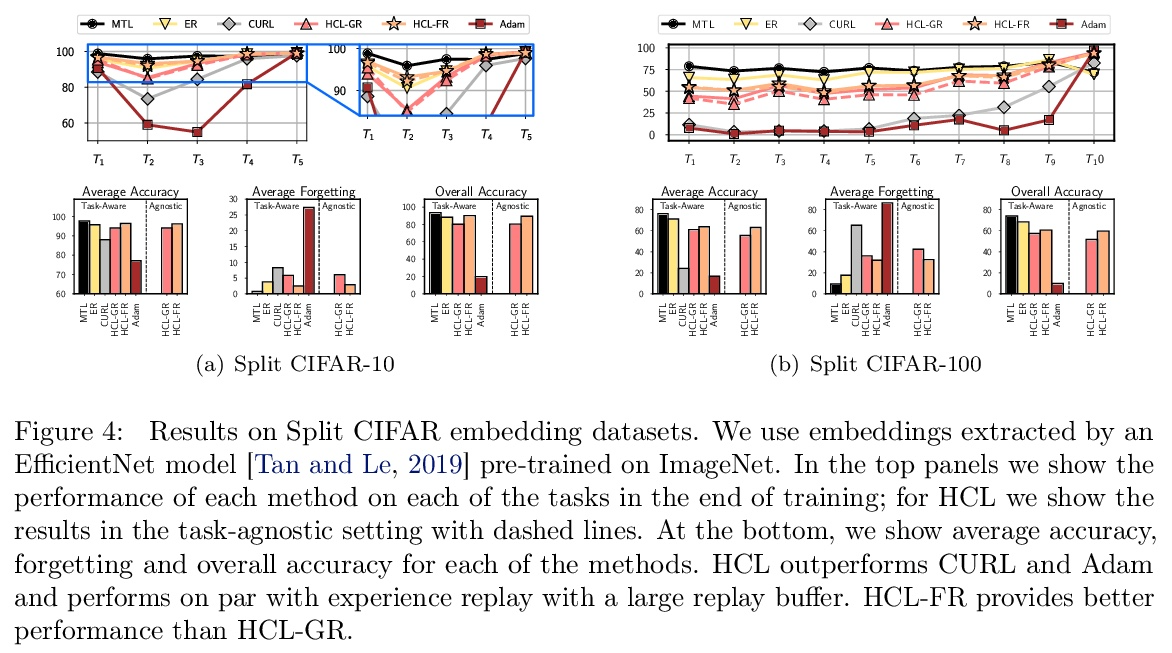
5、[LG] Task-agnostic Continual Learning with Hybrid Probabilistic Models
P Kirichenko, M Farajtabar, D Rao, B Lakshminarayanan, N Levine, A Li, H Hu, A G Wilson, R Pascanu
[New York University & DeepMind & Google Research]
混合概率模型任务不可知持续学习。不断学习新任务,而不遗忘不断变化的数据分布,对于现实世界的问题至关重要,但对于现代深度学习而言却极具挑战性。本文提出 HCL,一种用于分类的持续学习的混合生成判别方法,用归一化流对每个任务和每个类的分布进行建模。该流用于学习数据分布、执行分类、识别任务变化和避免遗忘,利用了归一化流模型唯一具有的可逆性和精确似然性。用流的生成能力通过生成重放和新的功能正则化技术来避免灾难性遗忘。对于任务识别,采用基于测量模型统计数据典型性的最先进的异常检测技术。展示了 HCL 在一系列持续学习基准(例如 split-MNIST、split-CIFAR 和 SVHN-MNIST)上的强大性能。
Learning new tasks continuously without forgetting on a constantly changing data distribution is essential for real-world problems but extremely challenging for modern deep learning. In this work we propose HCL, a Hybrid generative-discriminative approach to Continual Learning for classification. We model the distribution of each task and each class with a normalizing flow. The flow is used to learn the data distribution, perform classification, identify task changes, and avoid forgetting, all leveraging the invertibility and exact likelihood which are uniquely enabled by the normalizing flow model. We use the generative capabilities of the flow to avoid catastrophic forgetting through generative replay and a novel functional regularization technique. For task identification, we use state-of-the-art anomaly detection techniques based on measuring the typicality of the model’s statistics. We demonstrate the strong performance of HCL on a range of continual learning benchmarks such as split-MNIST, split-CIFAR, and SVHN-MNIST.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KlUuEsTJ2 
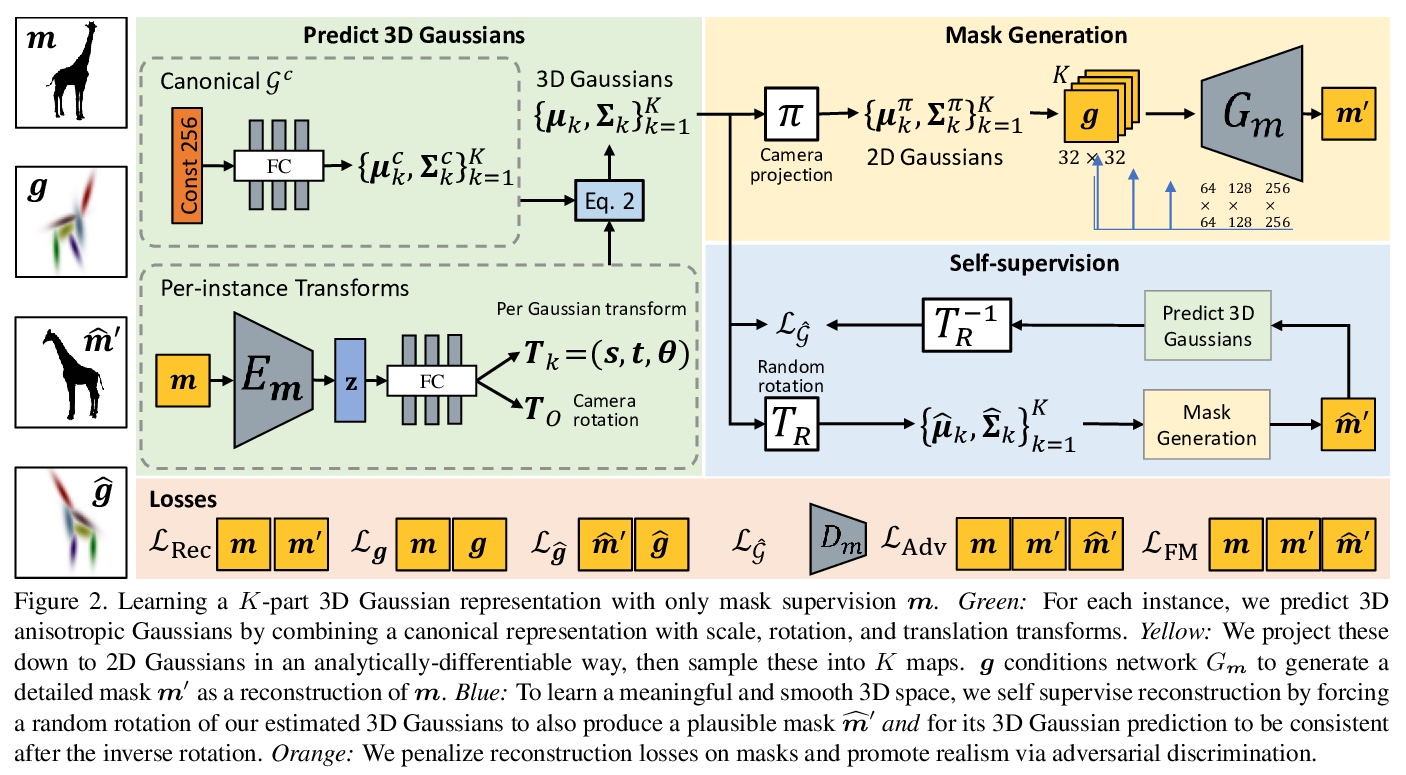
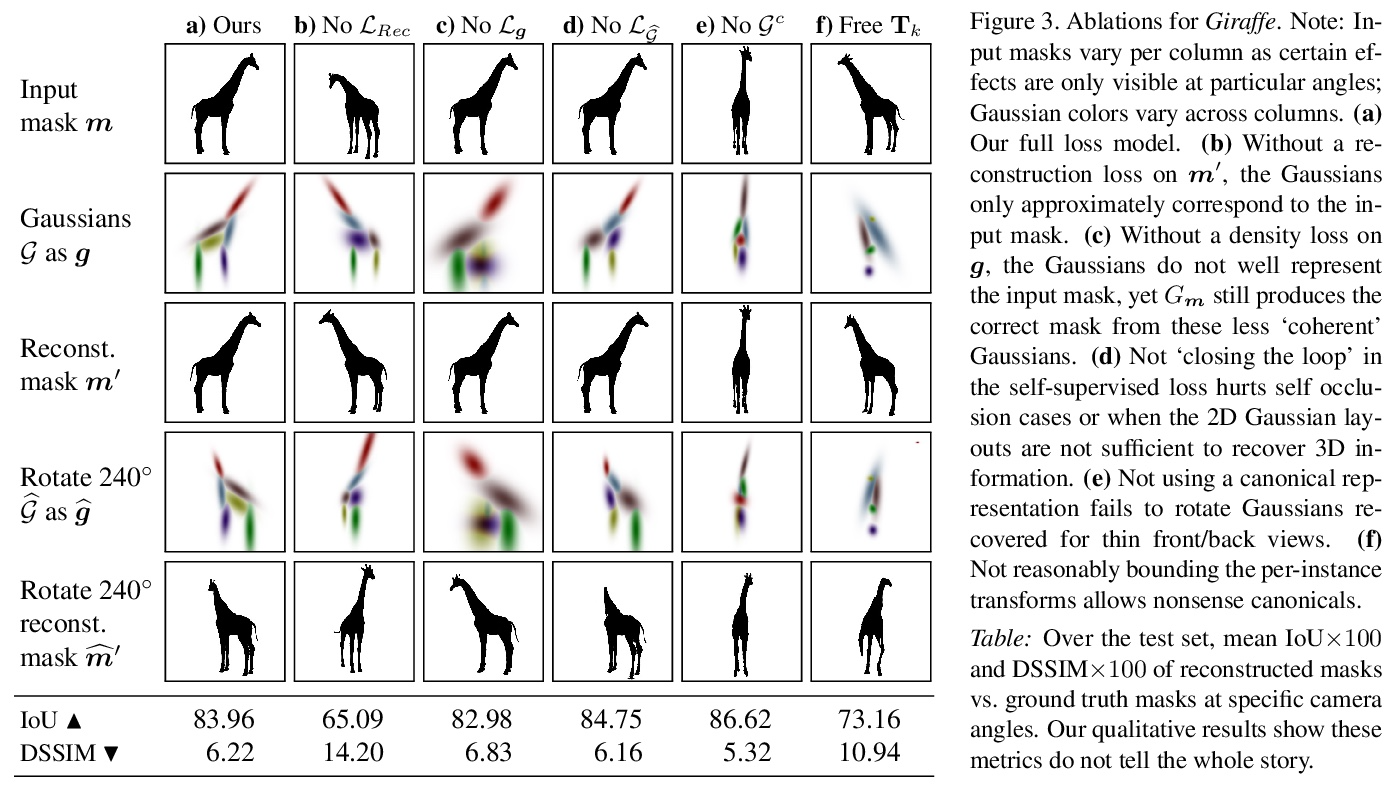
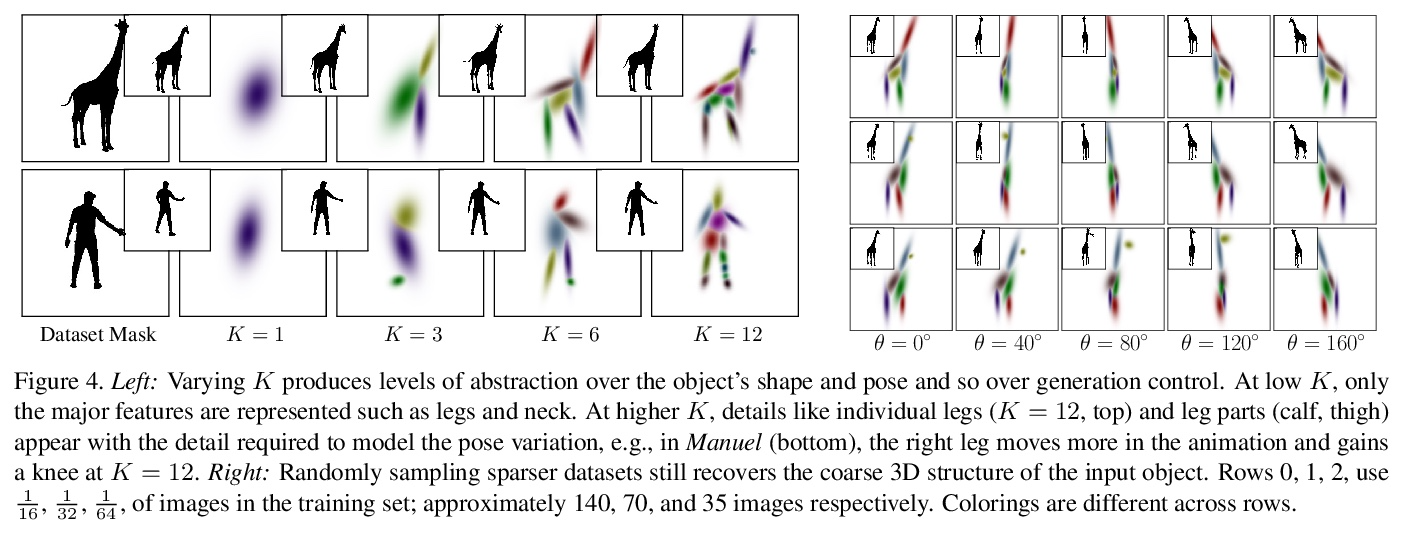
[CV] GaussiGAN: Controllable Image Synthesis with 3D Gaussians from Unposed Silhouettes
GaussiGAN:基于3D高斯的姿态未知轮廓可控图像合成
Y A.Mejjati, I Milefchik, A Gokaslan, O Wang, K I Kim, J Tompkin
[University of Bath & Cornell University & Adobe & UNIST & Brown University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KlUAu8Sin 
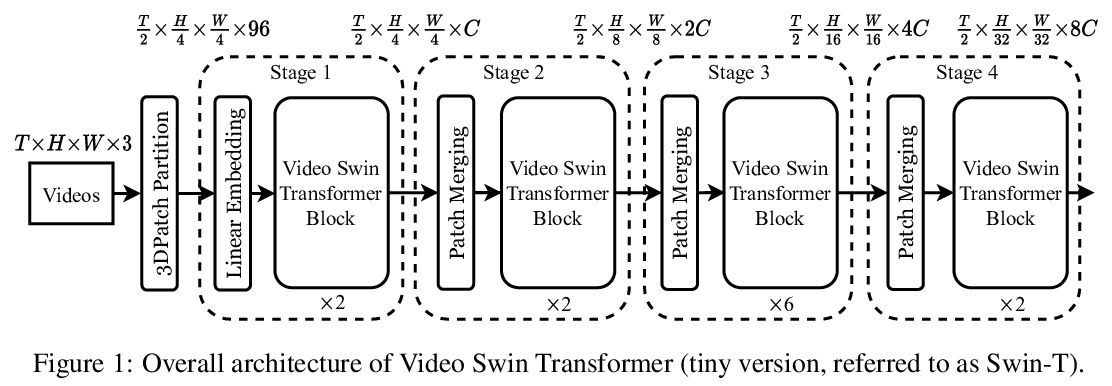
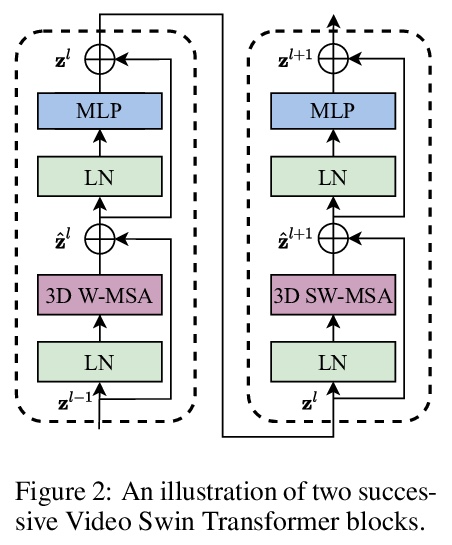
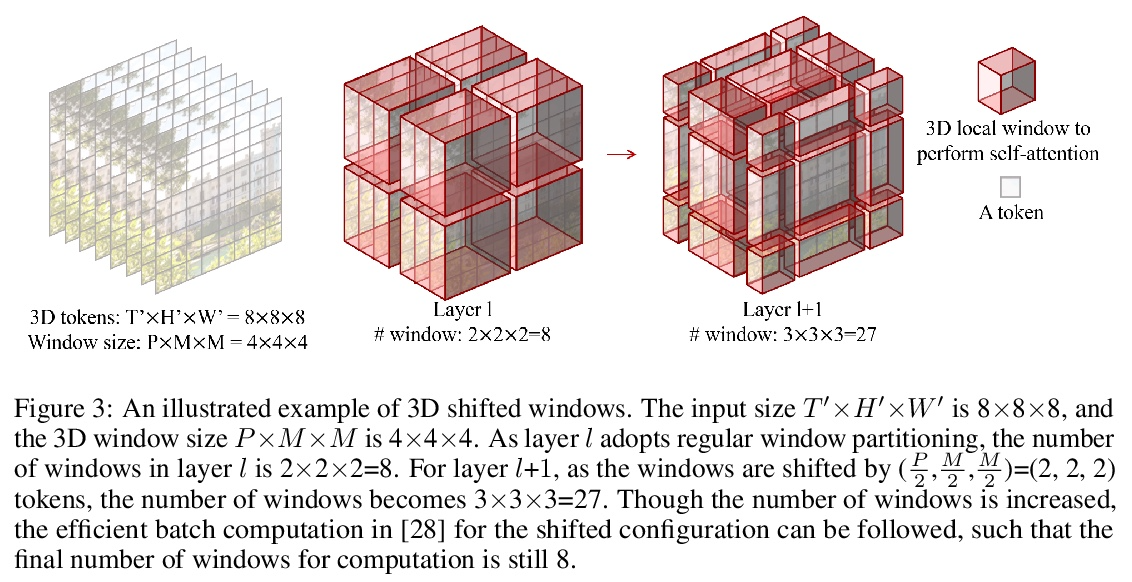
[CV] Video Swin Transformer
视频Swin Transformer
Z Liu, J Ning, Y Cao, Y Wei, Z Zhang, S Lin, H Hu
[Microsoft Research Asia]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KlUDeBusg 
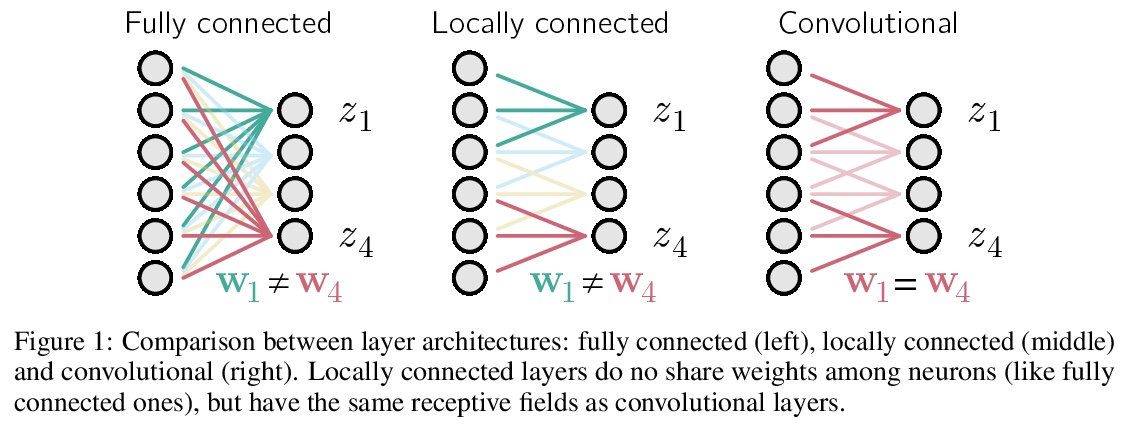
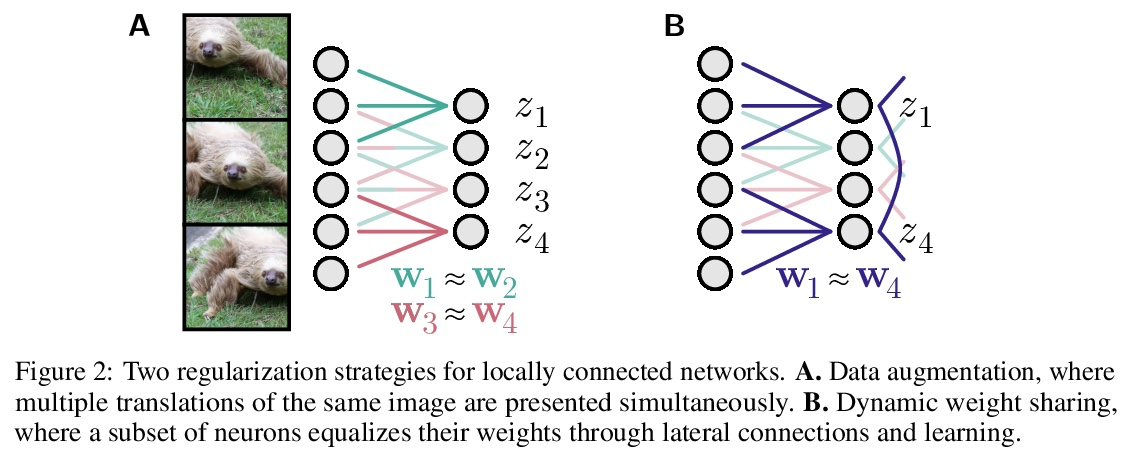
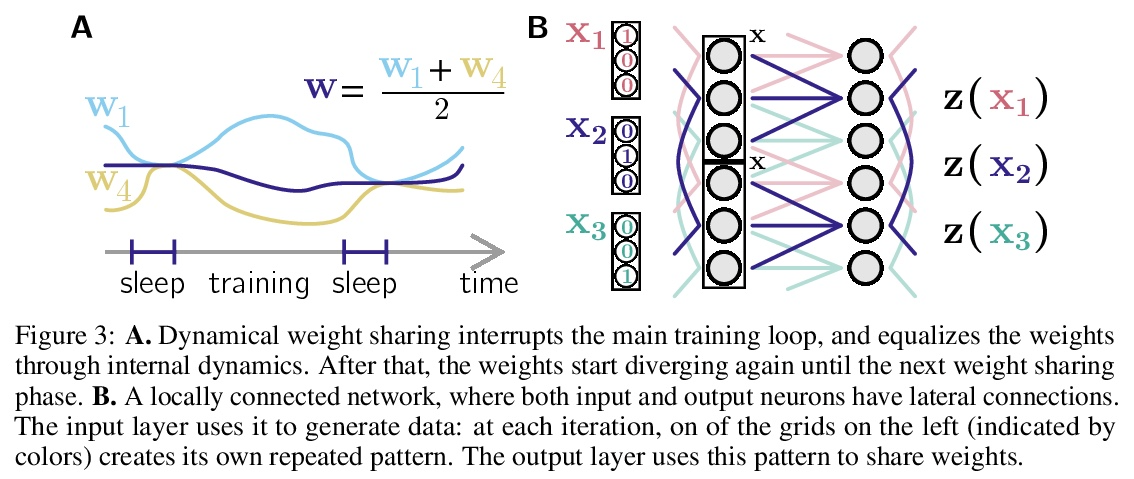
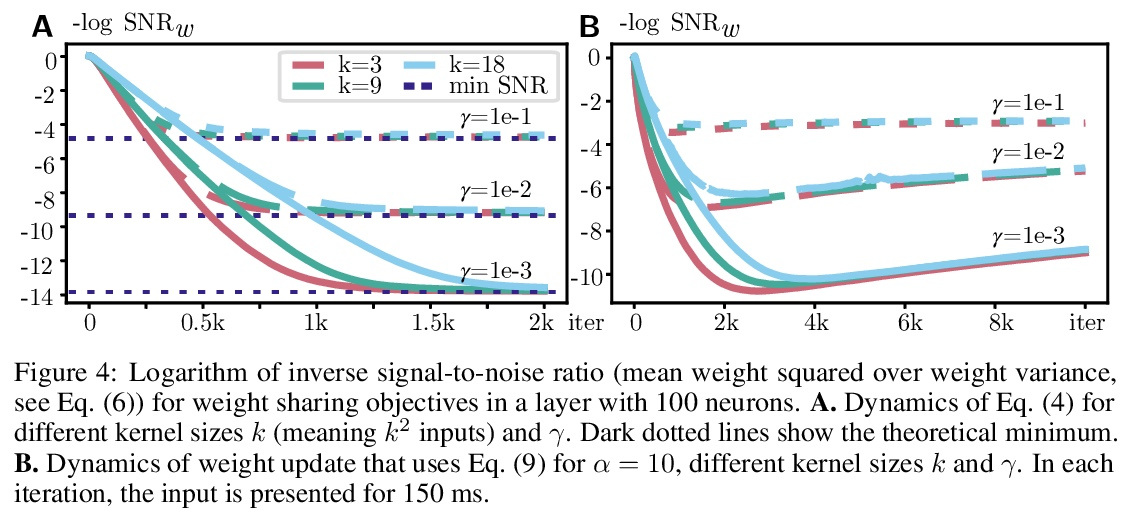
[LG] Towards Biologically Plausible Convolutional Networks
生物学上合理的卷积网络探索
R Pogodin, Y Mehta, T P. Lillicrap, P E. Latham
[UCL]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KlUEOr8Zo 
[CV] VOLO: Vision Outlooker for Visual Recognition
VOLO:面向视觉识别的Vision Outlooker
L Yuan, Q Hou, Z Jiang, J Feng, S Yan
[Sea AI Lab & National University of Singapore]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KlUGKplye