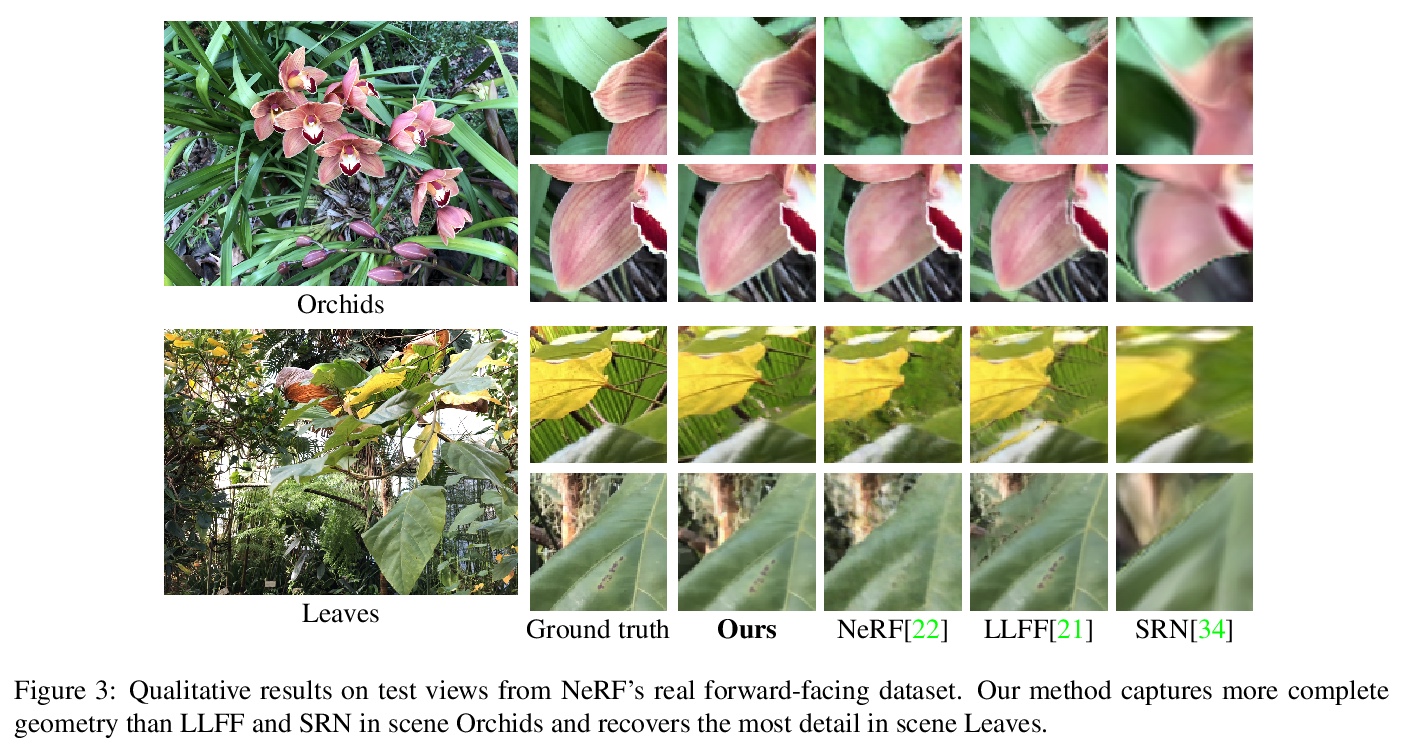
- 1、[CV] NeX: Real-time View Synthesis with Neural Basis Expansion
- 2、[RO] Advances in Inference and Representation for Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
- 3、[CV] Measuring Model Biases in the Absence of Ground Truth
- 4、[CV] Pixel-wise Anomaly Detection in Complex Driving Scenes
- 5、[CV] Knowledge Evolution in Neural Networks
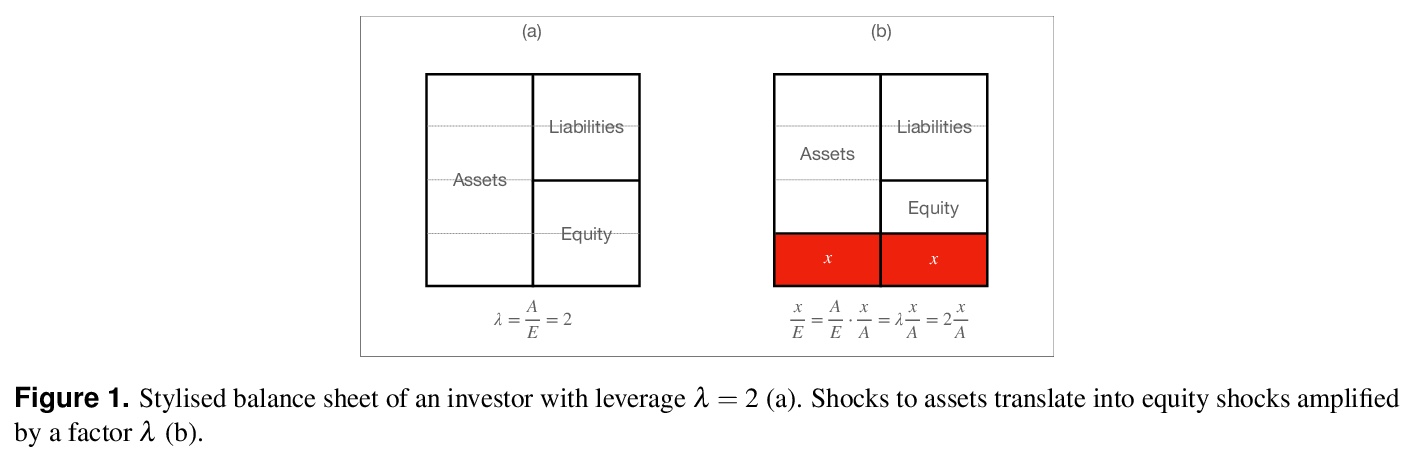
- [SI] The Physics of Financial Networks
- [CV] ForgeryNet: A Versatile Benchmark for Comprehensive Forgery Analysis
- [CV] QPIC: Query-Based Pairwise Human-Object Interaction Detection with Image-Wide Contextual Information
- [CL] BERTese: Learning to Speak to BERT
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 SI - 社交网络分析 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[CV] NeX: Real-time View Synthesis with Neural Basis Expansion
S Wizadwongsa, P Phongthawee, J Yenphraphai, S Suwajanakorn
[VISTEC]
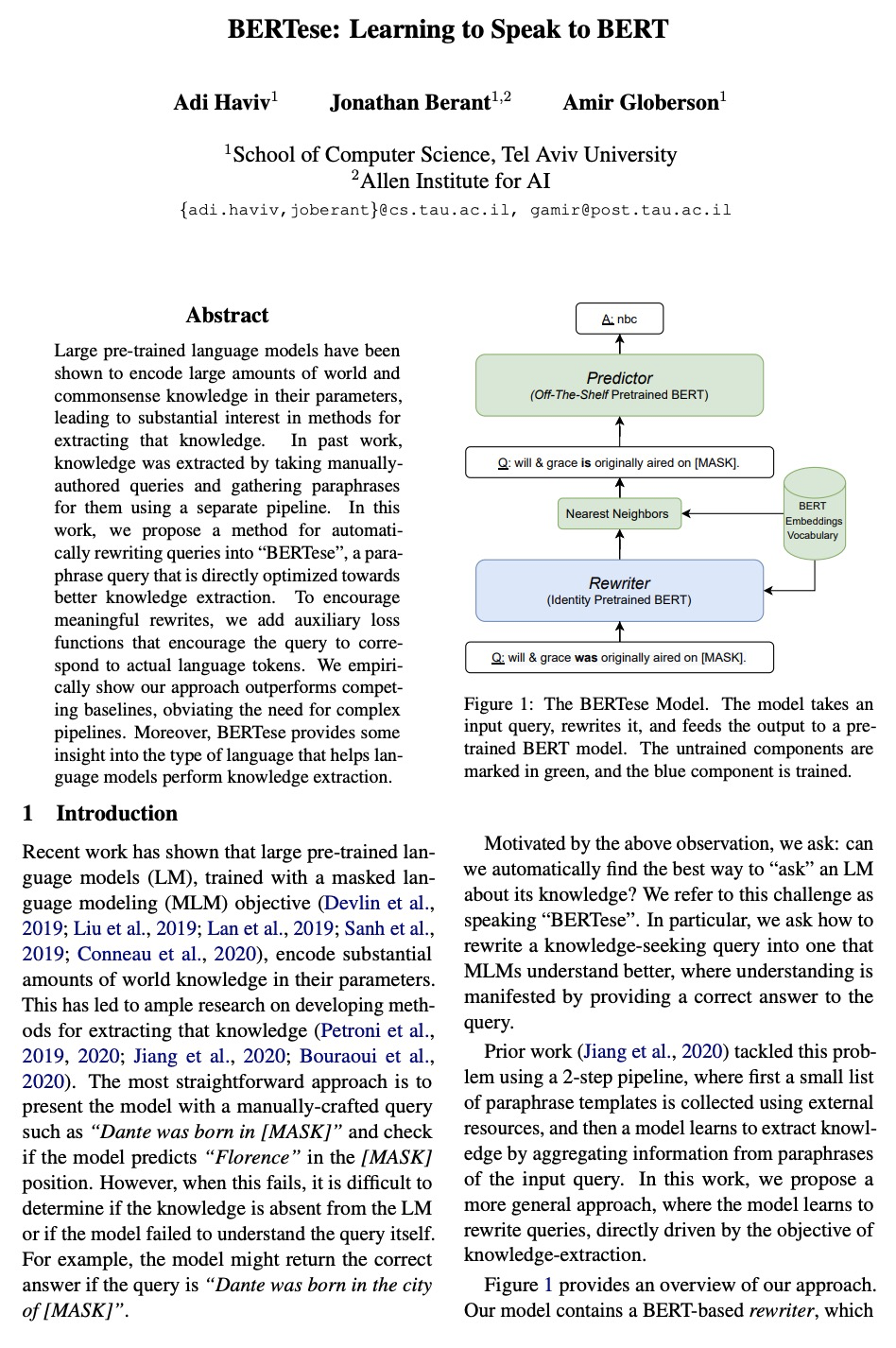
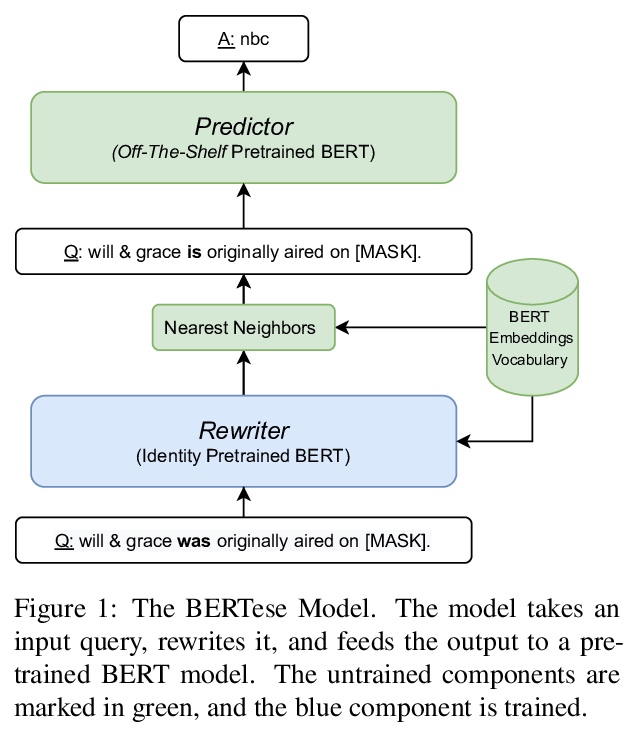
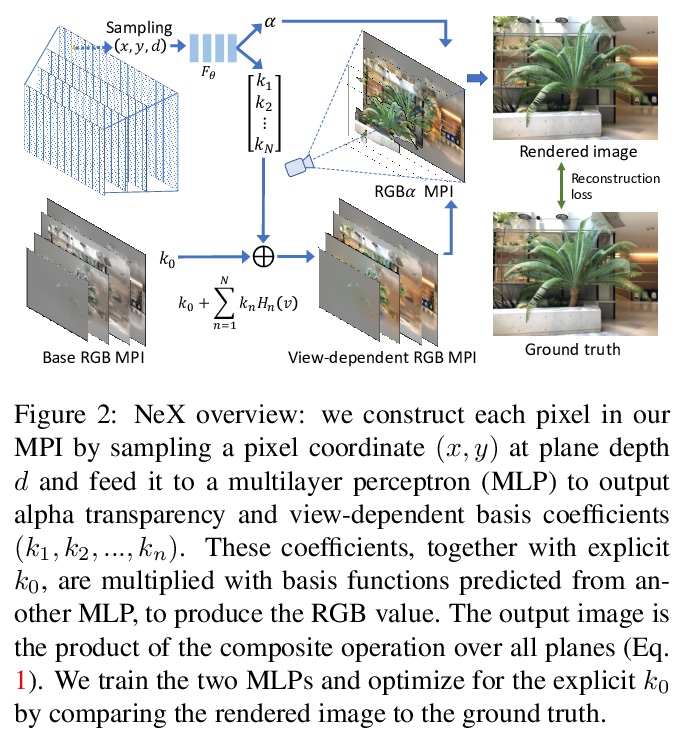
NeX: 基于神经基扩展的实时视图合成。提出一种基于多平面图像(MPI)增强的新视图合成方法NeX,能有效捕捉和重现复杂视图依赖性效果,在标准图形硬件上高效计算,实现实时渲染。与传统MPI用一组简单RGBα平面不同,NeX将每个像素参数化为神经网络学到的基函数的线性组合,来模拟视图相关的效果。提出一种混合的隐式-显式建模策略,以改善细节并产生最先进结果。在基准的前向数据集以及新引入的旨在测试视图依赖性建模极限的数据集上进行评价,具有显著的挑战性效果,如CD上的彩虹反射效果,NeX方法在所有主要指标上取得了最好的总体成绩,渲染时间比最先进的方法快1000多倍。
We present NeX, a new approach to novel view synthesis based on enhancements of multiplane image (MPI) that can reproduce next-level view-dependent effects — in real time. Unlike traditional MPI that uses a set of simple RGB> α planes, our technique models view-dependent effects by instead parameterizing each pixel as a linear combination of basis functions learned from a neural network. Moreover, we propose a hybrid implicit-explicit modeling strategy that improves upon fine detail and produces state-of-the-art results. Our method is evaluated on benchmark forward-facing datasets as well as our newly-introduced dataset designed to test the limit of view-dependent modeling with significantly more challenging effects such as rainbow reflections on a CD. Our method achieves the best overall scores across all major metrics on these datasets with more than 1000> × faster rendering time than the state of the art. For real-time demos, visit > this https URL
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K5DiWfYW8

2、[RO] Advances in Inference and Representation for Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
D M. Rosen, K J. Doherty, A T Espinoza, J J. Leonard
[MIT]
面向同步定位与制图(SLAM)的推理及表示的最新进展。同步定位和制图(SLAM)是根据对环境的局部观测建立环境全局模型的过程,也是移动机器人的一种基础能力,用以支持规划、导航和控制等核心功能。本文回顾了SLAM的最新进展,重点关注SLAM系统中使用的环境模型的表达能力(表示)和用于从数据中估计这些模型(推理)的算法的性能方面的进展。最近SLAM研究的一个突出主题是追求环境表征(包括学习的表征),这些表征超越了几何和外观的经典属性,而成为包括诸如层次组织、负担能力、动态和语义的模型属性,这些进展使自主智能体对世界有了更全面的理解,实现了更多的通用性和智能操作。第二个主要主题是对SLAM估计问题本身的数学特性(包括计算和信息论性能极限)的兴趣重新复苏,导致了新型的可认证和鲁棒推理方法的发展,极大提高了SLAM系统在实际操作中的可靠性。本文调研了这些进展,重点是它们对实现鲁棒性、长期自主性的影响。展望未来,SLAM研究面临的三大关键挑战是:长期自主性、终身地图学习、SLAM与深度学习。
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is the process of constructing a global model of an environment from local observations of it; this is a foundational capability for mobile robots, supporting such core functions as planning, navigation, and control. This article reviews recent progress in SLAM, focusing on advances in the expressive capacity of the environmental models used in SLAM systems (representation) and the performance of the algorithms used to estimate these models from data (inference). A prominent theme of recent SLAM research is the pursuit of environmental representations (including learned representations) that go beyond the classical attributes of geometry and appearance to model properties such as hierarchical organization, affordance, dynamics, and semantics; these advances equip autonomous agents with a more comprehensive understanding of the world, enabling more versatile and intelligent operation. A second major theme is a revitalized interest in the mathematical properties of the SLAM estimation problem itself (including its computational and information-theoretic performance limits); this work has led to the development of novel classes of certifiable and robust inference methods that dramatically improve the reliability of SLAM systems in real-world operation. We survey these advances with an emphasis on their ramifications for achieving robust, long-duration autonomy, and conclude with a discussion of open challenges and a perspective on future research directions.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K5Dnp7va3

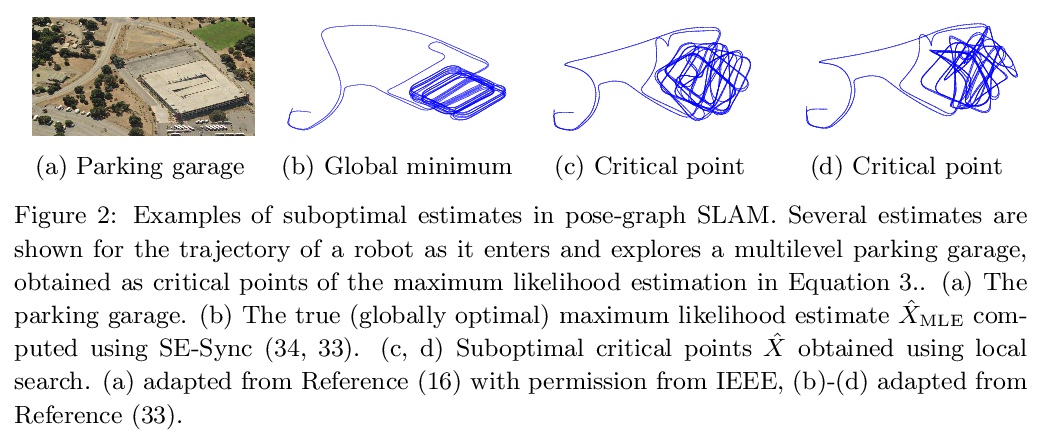
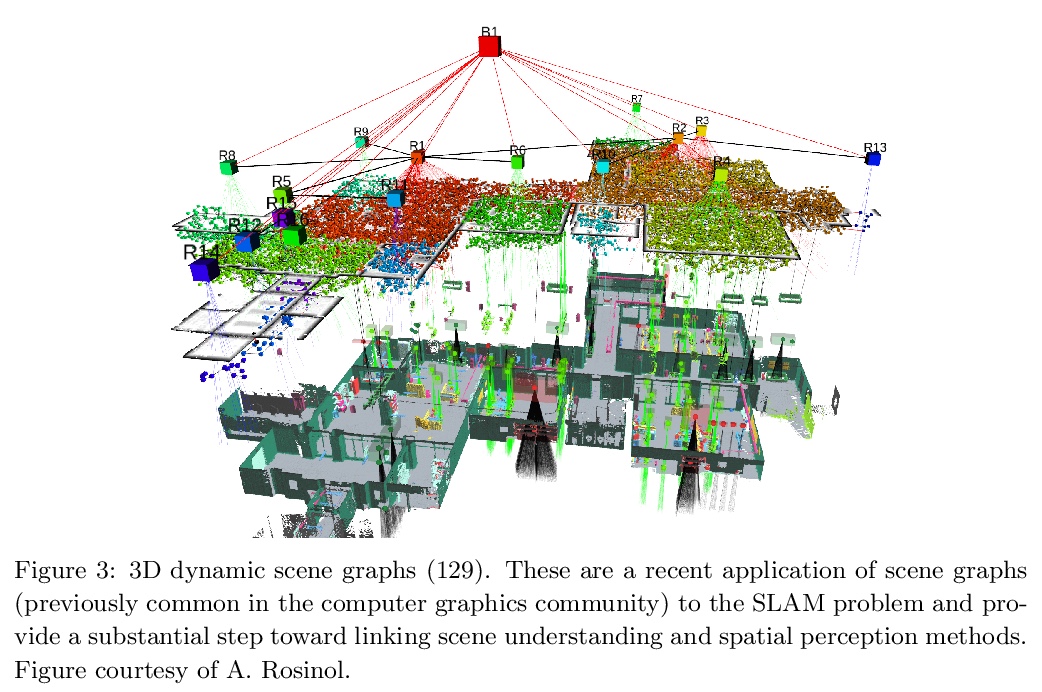
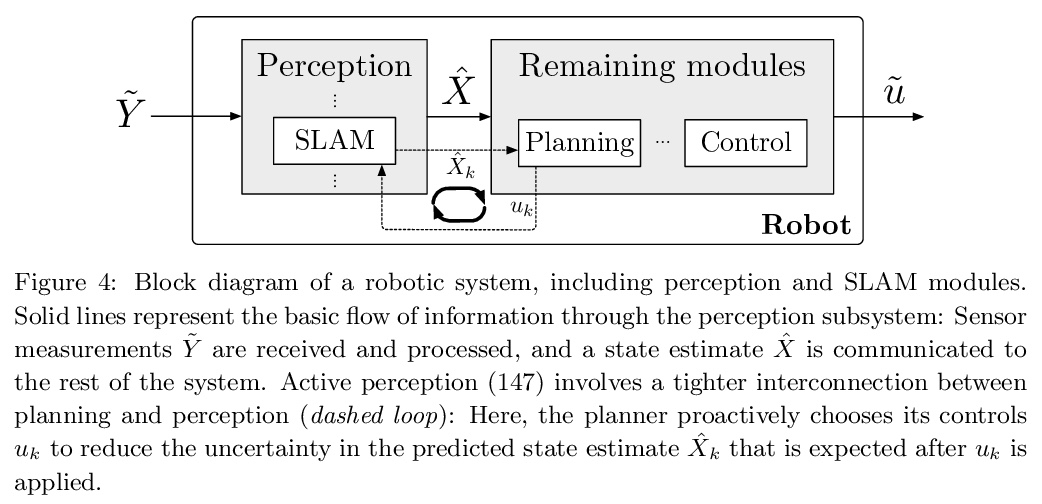
3、[CV] Measuring Model Biases in the Absence of Ground Truth
O Aka, K Burke, A Bäuerle, C Greer, M Mitchell
[Google]
在缺乏基本事实的情况下测量模型偏差。在实践中,图像通常只有稀疏的标注,可能会导致收集到的基本事实标签的分布出现问题性偏差。这种潜在的标注偏差,可能会限制依赖于基本事实的公平性度量(例如Equalized Odds)的效果。为解决该问题,引入一个新的不依赖于基本事实标签的框架来测量公平性和偏差,将给定图像的模型预测视为一组标签,类似于自然语言处理(NLP)中使用的”词袋”方法,可探索预测集间的不同关联度量,以检测偏差模式。应用这种方法来检查身份标签,和数据集中所有其他标签之间的关系。展示了不同关联度量的统计属性(尤其是归一化)是如何导致不同的标签集被检测为具有”性别偏见”的。证明了尽管标签的边际频率存在差异,但通过联合概率(nPMI)归一化的点向互信息,能检测出许多具有显著性别偏差的标签。公布了一个采用TensorBoard的开源nPMI可视化工具。
Recent advances in computer vision have led to the development of image classification models that can predict tens of thousands of object classes. Training these models can require millions of examples, leading to a demand of potentially billions of annotations. In practice, however, images are typically sparsely annotated, which can lead to problematic biases in the distribution of ground truth labels that are collected. This potential for annotation bias may then limit the utility of ground truth-dependent fairness metrics (e.g., Equalized Odds). To address this problem, in this work we introduce a new framing to the measurement of fairness and bias that does not rely on ground truth labels. Instead, we treat the model predictions for a given image as a set of labels, analogous to a ‘bag of words’ approach used in Natural Language Processing (NLP). This allows us to explore different association metrics between prediction sets in order to detect patterns of bias. We apply this approach to examine the relationship between identity labels, and all other labels in the dataset, using labels associated with ‘male’ and ‘female’) as a concrete example. We demonstrate how the statistical properties (especially normalization) of the different association metrics can lead to different sets of labels detected as having “gender bias”. We conclude by demonstrating that pointwise mutual information normalized by joint probability (nPMI) is able to detect many labels with significant gender bias despite differences in the labels’ marginal frequencies. Finally, we announce an open-sourced nPMI visualization tool using TensorBoard.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K5DqDuae4
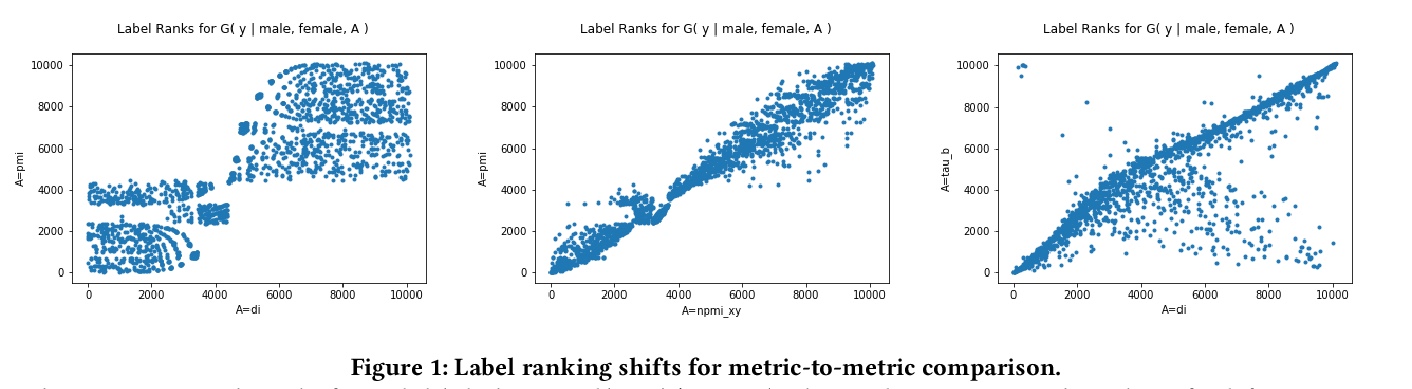
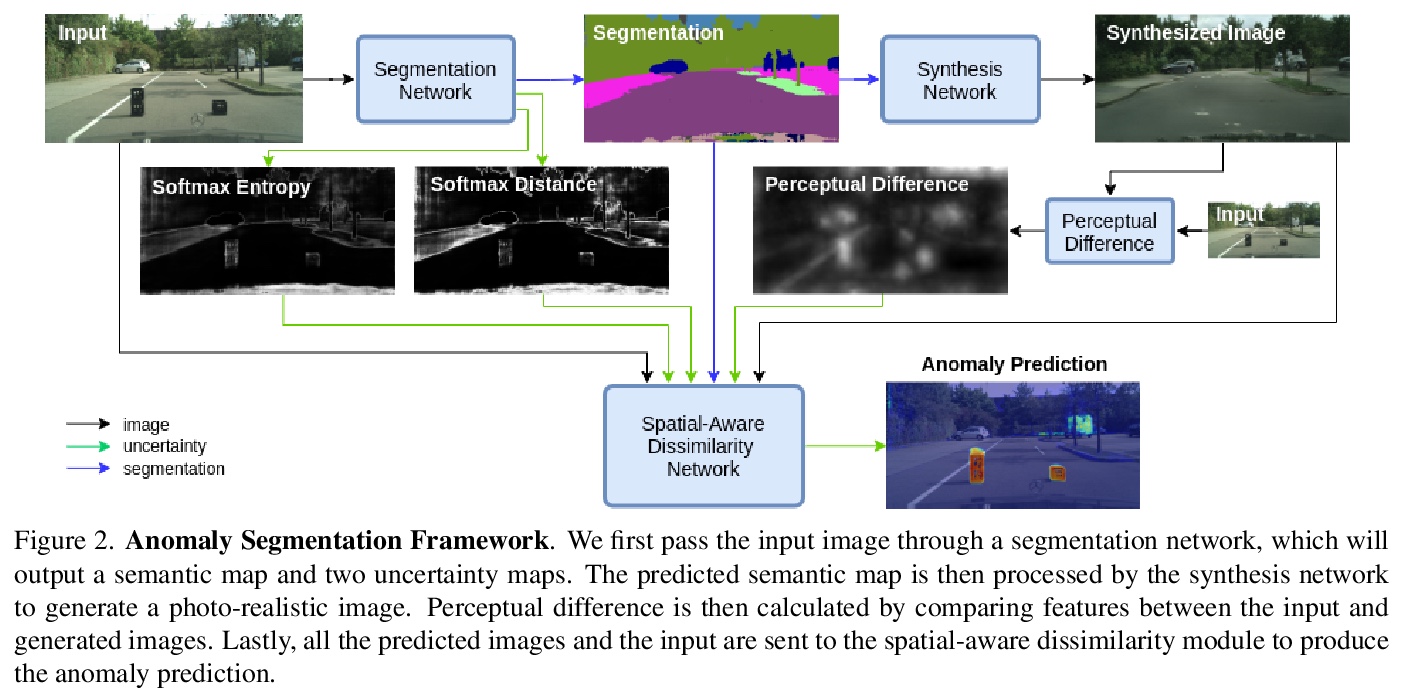
4、[CV] Pixel-wise Anomaly Detection in Complex Driving Scenes
G D Biase, H Blum, R Siegwart, C Cadena
[ETH Zurich]
复杂驾驶场景像素级异常检测。提出了结合现有最佳不确定性特征和再合成方法的像素级异常检测框架,利用不确定性测量图(软最大熵、软最大距离和感知差异)引导异构网络从预测语义图中找到输入和生成图像之间的差异,对各种异常场景具有鲁棒性,在Fishyscapes基准上实现了最先进的性能,同时保持了最先进的分割精度。提出的框架能推广到不同的分割和合成网络,作为现有分割管道的封装方法。
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K5DwHiSt0
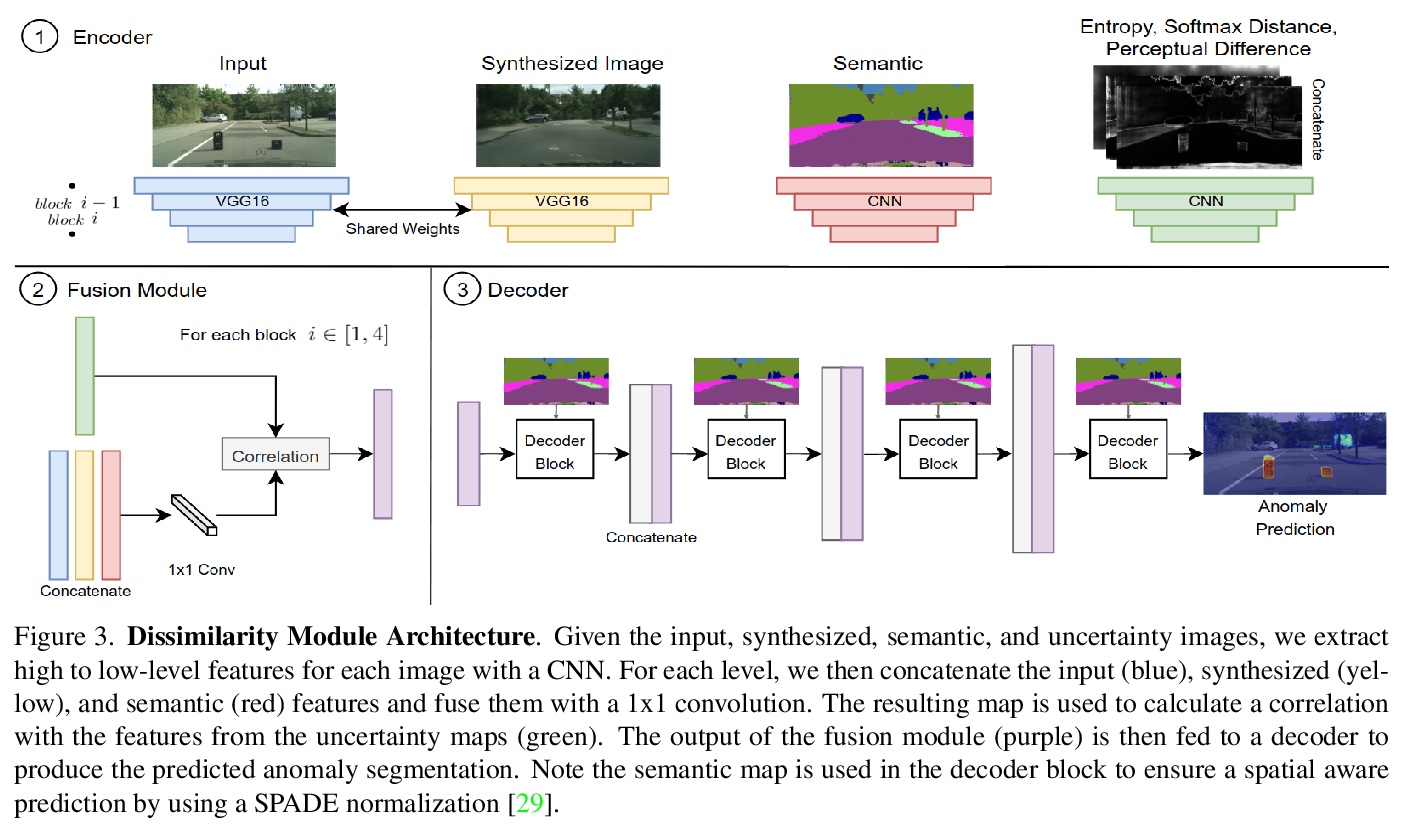

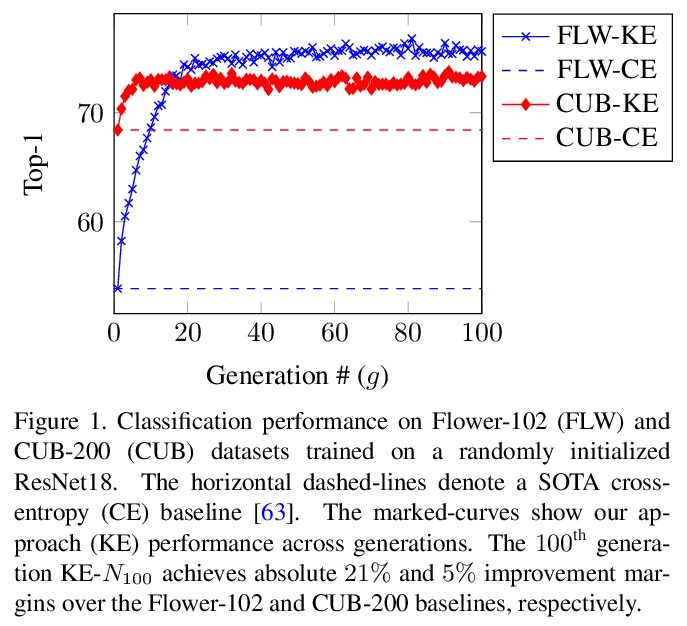
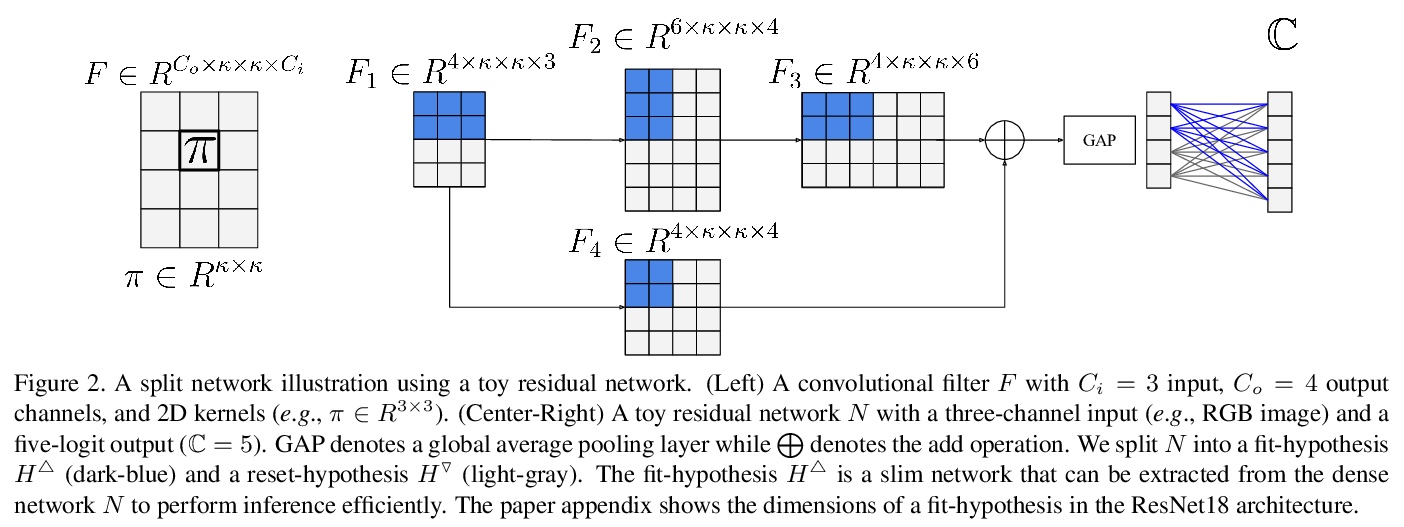
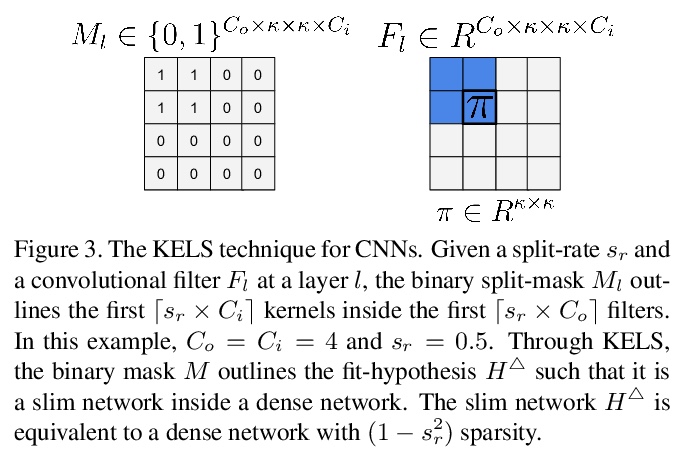
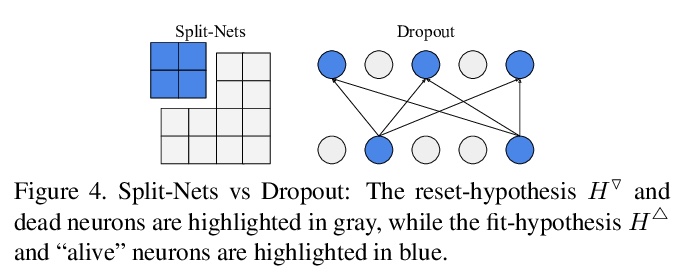
5、[CV] Knowledge Evolution in Neural Networks
A Taha, A Shrivastava, L Davis
[University of Maryland]
神经网络知识进化。提出一种进化启发的训练方法,以提高在相对较小数据集上神经网络的性能。知识进化(KE)方法将深度网络分为两个假设:fit-hypothesis和reset-hypothesis。通过对reset-hypothesis进行多代扰动,对fit-hypothesis内部的知识进行迭代进化,不仅提升了性能,还能以更小的推理成本学习到一个简单网络。KE可与vanilla和残差卷积网络无缝集成,减少了过拟合和数据收集的负担。在各种网络架构和损失函数上评价了KE,用相对较小的数据集(如CUB-200)和随机初始化的深度网络来评价KE,在最先进的基线上实现了21%的绝对改进幅度。这种性能改进伴随着推理成本的相对降低73%。KE在分类和度量学习基准上取得了最先进的结果。
Deep learning relies on the availability of a large corpus of data (labeled or unlabeled). Thus, one challenging unsettled question is: how to train a deep network on a relatively small dataset? To tackle this question, we propose an evolution-inspired training approach to boost performance on relatively small datasets. The knowledge evolution (KE) approach splits a deep network into two hypotheses: the fit-hypothesis and the reset-hypothesis. We iteratively evolve the knowledge inside the fit-hypothesis by perturbing the reset-hypothesis for multiple generations. This approach not only boosts performance, but also learns a slim network with a smaller inference cost. KE integrates seamlessly with both vanilla and residual convolutional networks. KE reduces both overfitting and the burden for data collection.We evaluate KE on various network architectures and loss functions. We evaluate KE using relatively small datasets (e.g., CUB-200) and randomly initialized deep networks. KE achieves an absolute 21% improvement margin on a state-of-the-art baseline. This performance improvement is accompanied by a relative 73% reduction in inference cost. KE achieves state-of-the-art results on classification and metric learning benchmarks. Code available at > this http URL
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K5DAfbUFj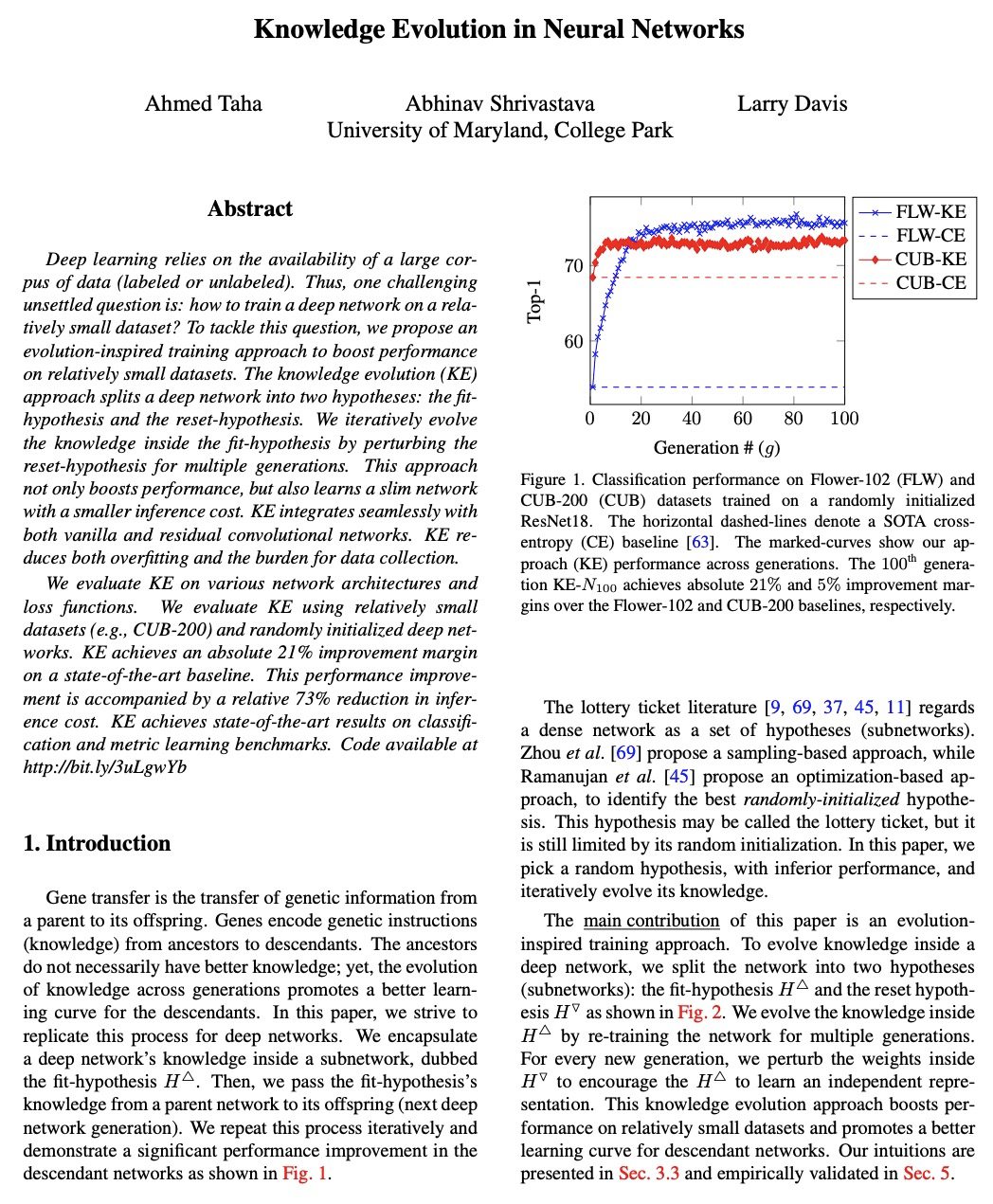
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[SI] The Physics of Financial Networks
金融网络的物理学
M Bardoscia, P Barucca, S Battiston, F Caccioli, G Cimini, D Garlaschelli, F Saracco, T Squartini, G Caldarelli
[Bank of England & University College London & University of Zurich]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K5Dv8amsW

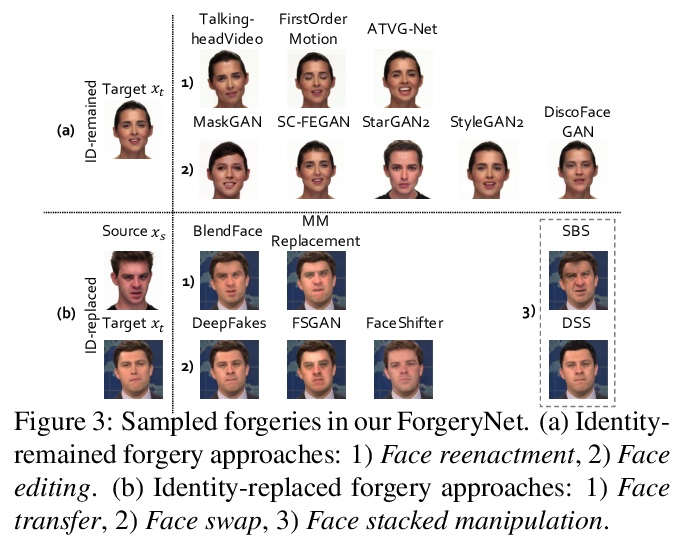
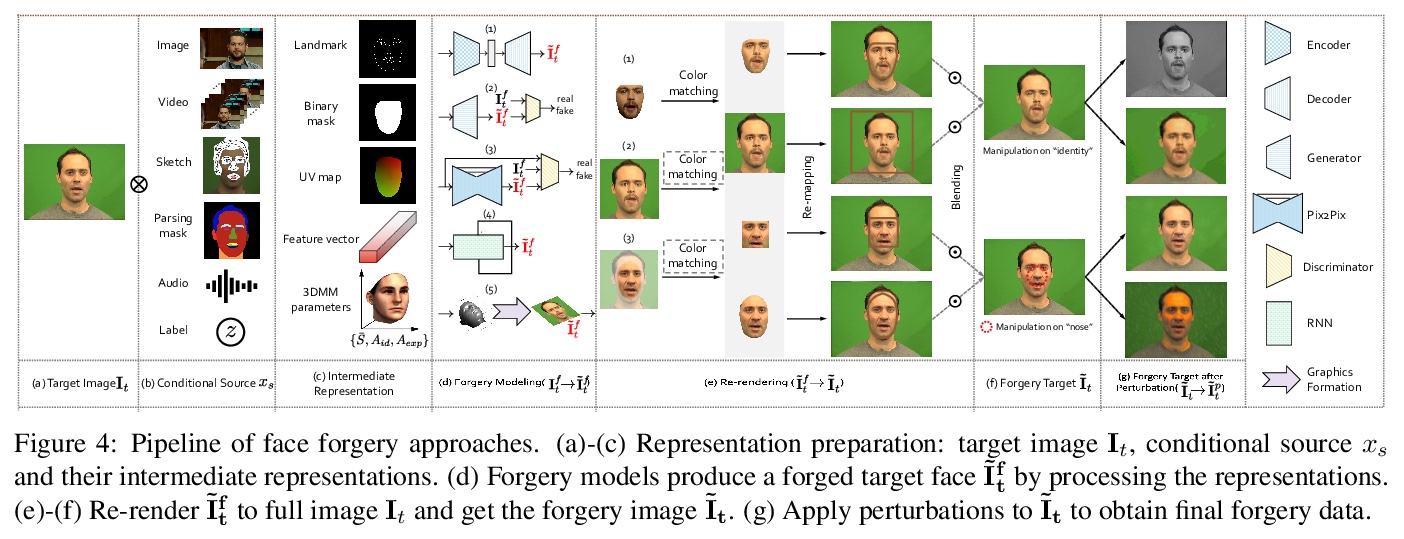
[CV] ForgeryNet: A Versatile Benchmark for Comprehensive Forgery Analysis
ForgeryNet:伪造分析的全面通用基准(数据集)
Y He, B Gan, S Chen, Y Zhou, G Yin, L Song, L Sheng, J Shao, Z Liu
[Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications & SenseTime Research & Beihang University & University of Science and Technology of China & Nanyang Technological University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K5DFGDVxc

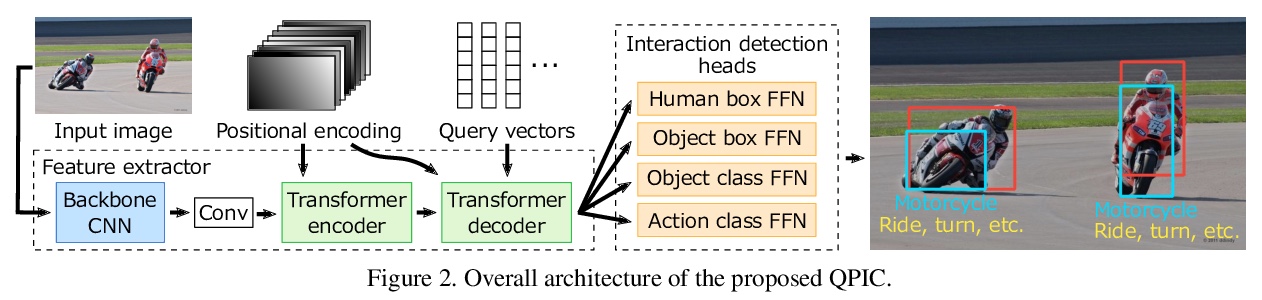
[CV] QPIC: Query-Based Pairwise Human-Object Interaction Detection with Image-Wide Contextual Information
QPIC:基于图像范围上下文信息的基于查询成对人-物交互检测
M Tamura, H Ohashi, T Yoshinaga
[Hitachi]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K5DHU17vx

[CL] BERTese: Learning to Speak to BERT
BERTese:学习与BERT对话(将知识查询自动重写成”BERTese”)
A Haviv, J Berant, A Globerson
[Tel Aviv University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K5DJi3IrL