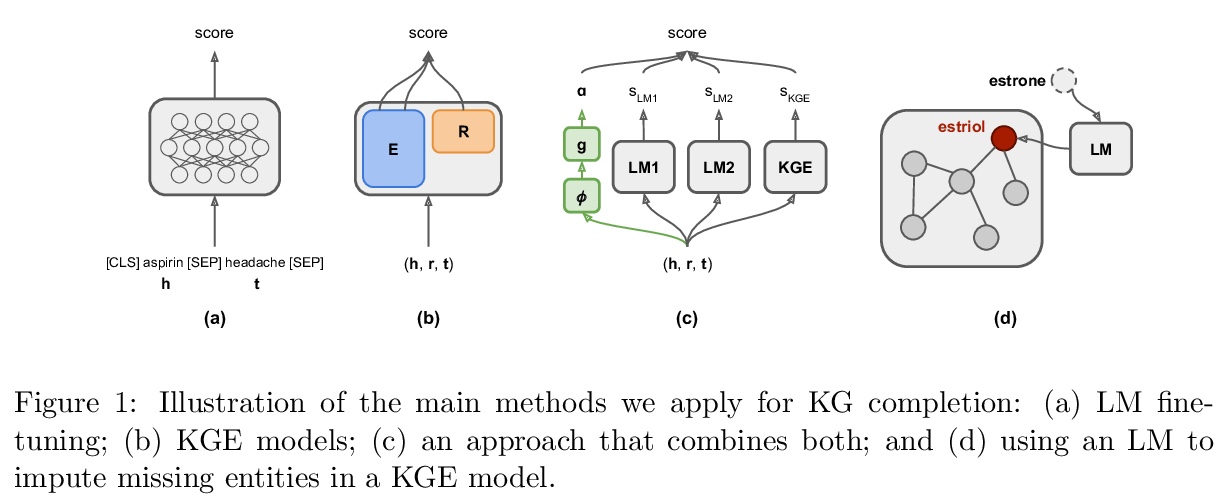
- 1、[CV] Invertible Image Signal Processing
- 2、[CV] Physion: Evaluating Physical Prediction from Vision in Humans and Machines
- 3、[CL] Learning Dense Representations of Phrases at Scale
- 4、[LG] Group Equivariant Subsampling
- 5、[CV] S²-MLP: Spatial-Shift MLP Architecture for Vision
- [LG] Preferential Temporal Difference Learning
- [LG] A Minimalist Approach to Offline Reinforcement Learning
- [CL] HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units
- [CL] Scientific Language Models for Biomedical Knowledge Base Completion: An Empirical Study
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CV] Invertible Image Signal Processing
Y Xing, Z Qian, Q Chen
[The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology]
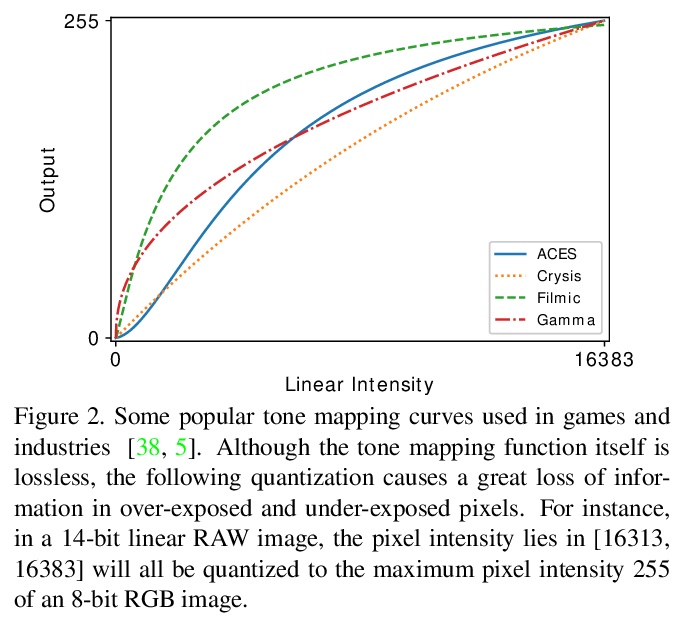
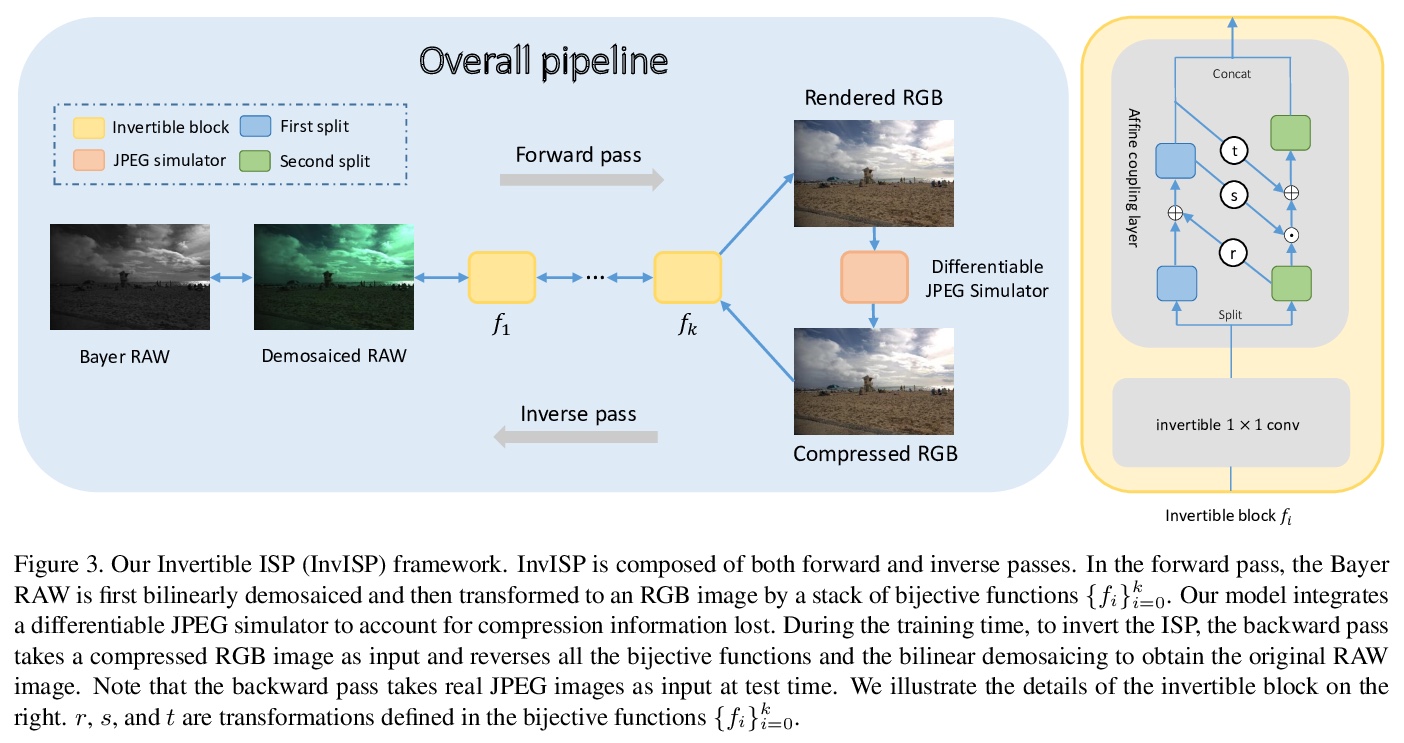
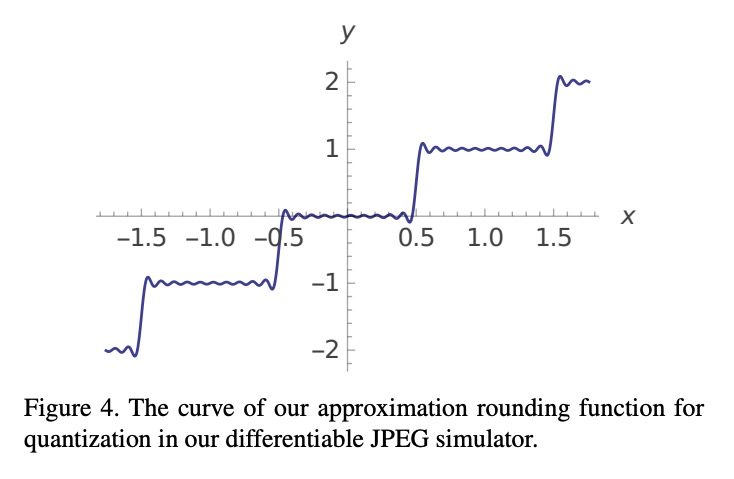
可逆图像信号处理。未经处理的RAW数据,是一种对图像编辑和计算机视觉非常有价值的图像格式。然而,由于RAW数据文件尺寸巨大,大多数用户只能获得经过处理和压缩的sRGB图像。为弥补这一差距,本文设计了一种端到端可逆图像信号处理(InvISP)管道,不仅可以渲染视觉上吸引人的sRGB图像,还可以恢复几乎完美的RAW数据。基于框架固有的可逆性,可重建真实RAW数据,而不是从sRGB图像中合成RAW数据,且无需任何内存开销。由于集成了一个可微的JPEG压缩模拟器,框架能从JPEG图像中重建RAW数据。在两台数码单反相机上进行的广泛的定量和定性实验表明,该方法在渲染的sRGB图像和重建的RAW数据上都获得了比其他方法高得多的质量。
Unprocessed RAW data is a highly valuable image format for image editing and computer vision. However, since the file size of RAW data is huge, most users can only get access to processed and compressed sRGB images. To bridge this gap, we design an Invertible Image Signal Processing (InvISP) pipeline, which not only enables rendering visually appealing sRGB images but also allows recovering nearly perfect RAW data. Due to our framework’s inherent reversibility, we can reconstruct realistic RAW data instead of synthesizing RAW data from sRGB images without any memory overhead. We also integrate a differentiable JPEG compression simulator that empowers our framework to reconstruct RAW data from JPEG images. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments on two DSLR demonstrate that our method obtains much higher quality in both rendered sRGB images and reconstructed RAW data than alternative methods.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkZspC2Fc
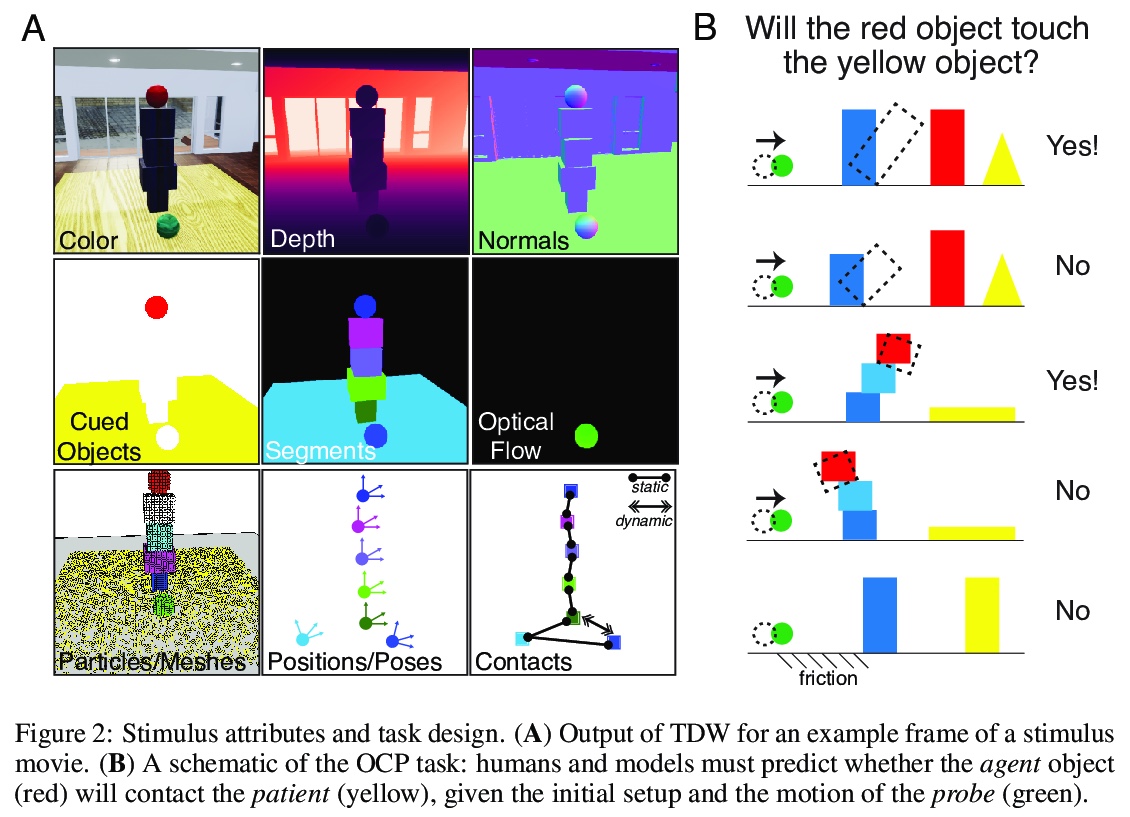
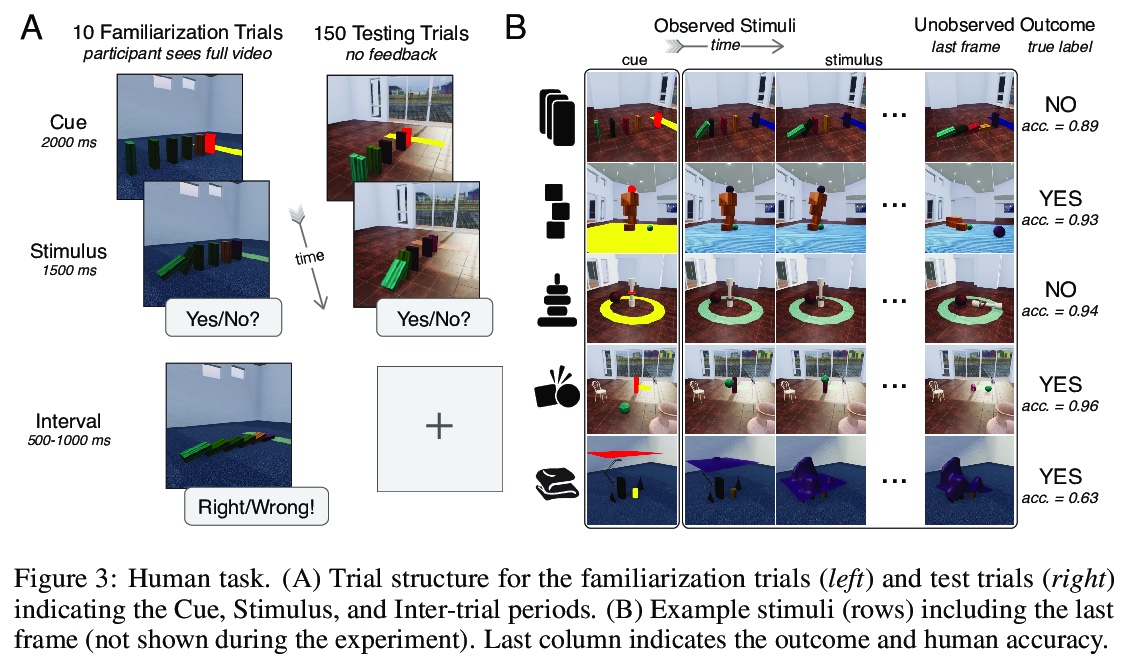
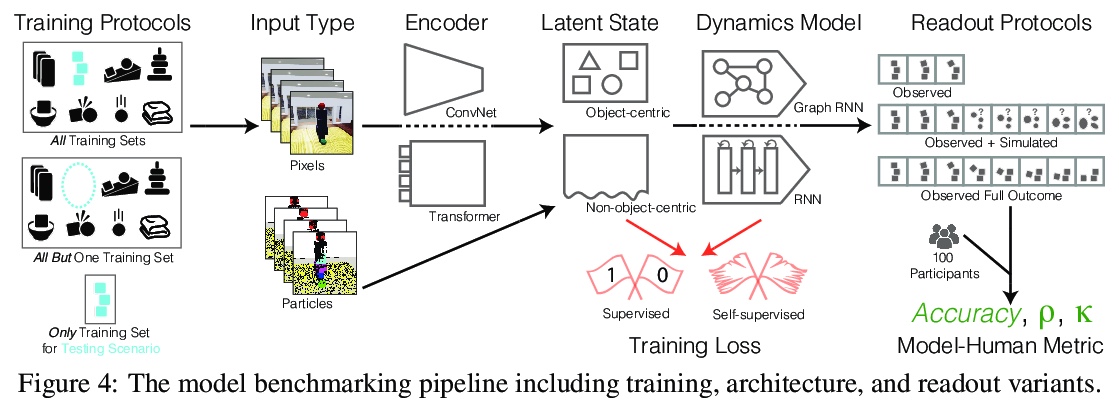
2、[CV] Physion: Evaluating Physical Prediction from Vision in Humans and Machines
D M. Bear, E Wang, D Mrowca, F J. Binder, H F Tung, R.T. Pramod, C Holdaway, S Tao, K Smith, F Sun, L Fei-Fei, N Kanwisher, J B. Tenenbaum, D L.K. Yamins, J E. Fan
[ Stanford University & UC San Diego & MIT]
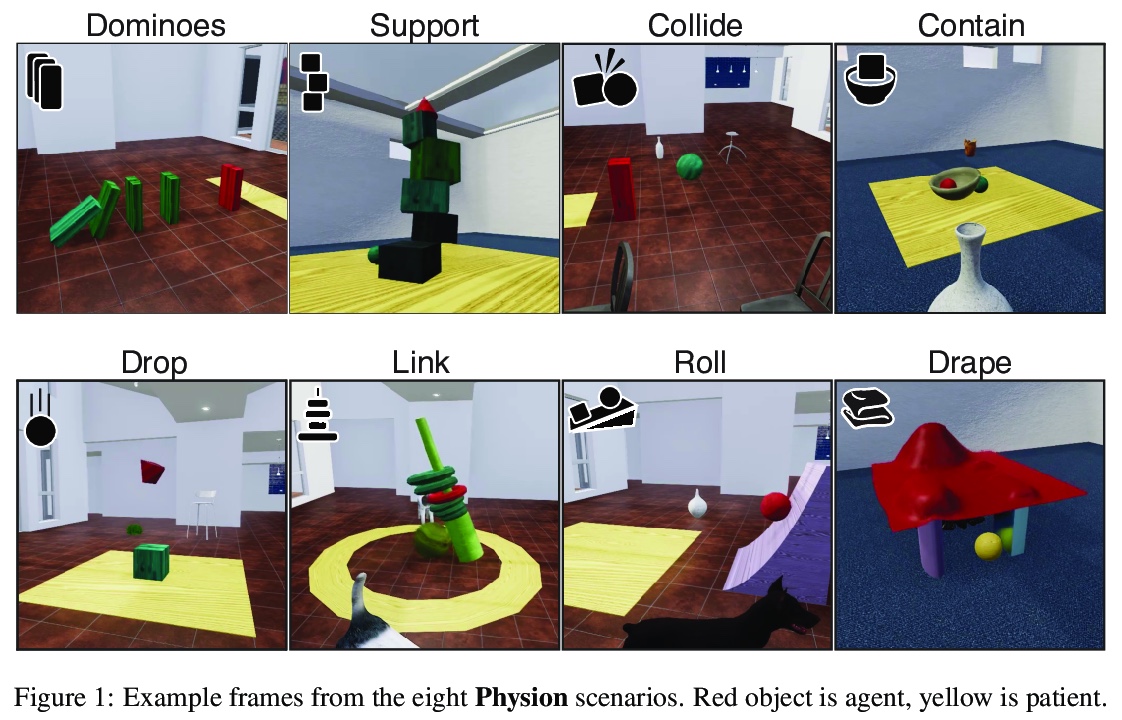
Physion: 人类视觉和机器视觉物理预测评价基准。虽然机器学习算法在许多挑战性的视觉任务中表现出色,但目前还不清楚它们是否能对现实世界中常见的物理事件做出预测。本文提出一个视觉和物理预测基准,用来精确测量这种能力。该基准真实模拟了各种物理现象——刚体和软体碰撞、稳定多物体配置、滚动和滑动、弹射运动——提出了比现有基准更全面的挑战。收集了人类对刺激的反应,因此模型的预测可直接与人工判断相比较。比较了一系列算法——其结构、学习目标、输入输出结构和训练数据方面各不相同——进行各种物理预测的能力。发现能接触到物理状态的图神经网络最能捕捉到人类行为,而在只接受视觉输入的模型中,那些具有以物体为中心的表示或预训练模型做得最好,但远远达不到人类的准确性。这表明,提取有物理意义的场景表示是实现类人视觉预测的主要瓶颈。展示了该基准如何确定需要改进的地方,并衡量在物理理解这个关键方面的进展。
While machine learning algorithms excel at many challenging visual tasks, it is unclear that they can make predictions about commonplace real world physical events. Here, we present a visual and physical prediction benchmark that precisely measures this capability. In realistically simulating a wide variety of physical phenomena – rigid and soft-body collisions, stable multi-object configurations, rolling and sliding, projectile motion – our dataset presents a more comprehensive challenge than existing benchmarks. Moreover, we have collected human responses for our stimuli so that model predictions can be directly compared to human judgments. We compare an array of algorithms – varying in their architecture, learning objective, input-output structure, and training data – on their ability to make diverse physical predictions. We find that graph neural networks with access to the physical state best capture human behavior, whereas among models that receive only visual input, those with object-centric representations or pretraining do best but fall far short of human accuracy. This suggests that extracting physically meaningful representations of scenes is the main bottleneck to achieving human-like visual prediction. We thus demonstrate how our benchmark can identify areas for improvement and measure progress on this key aspect of physical understanding.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkZvT37Eo
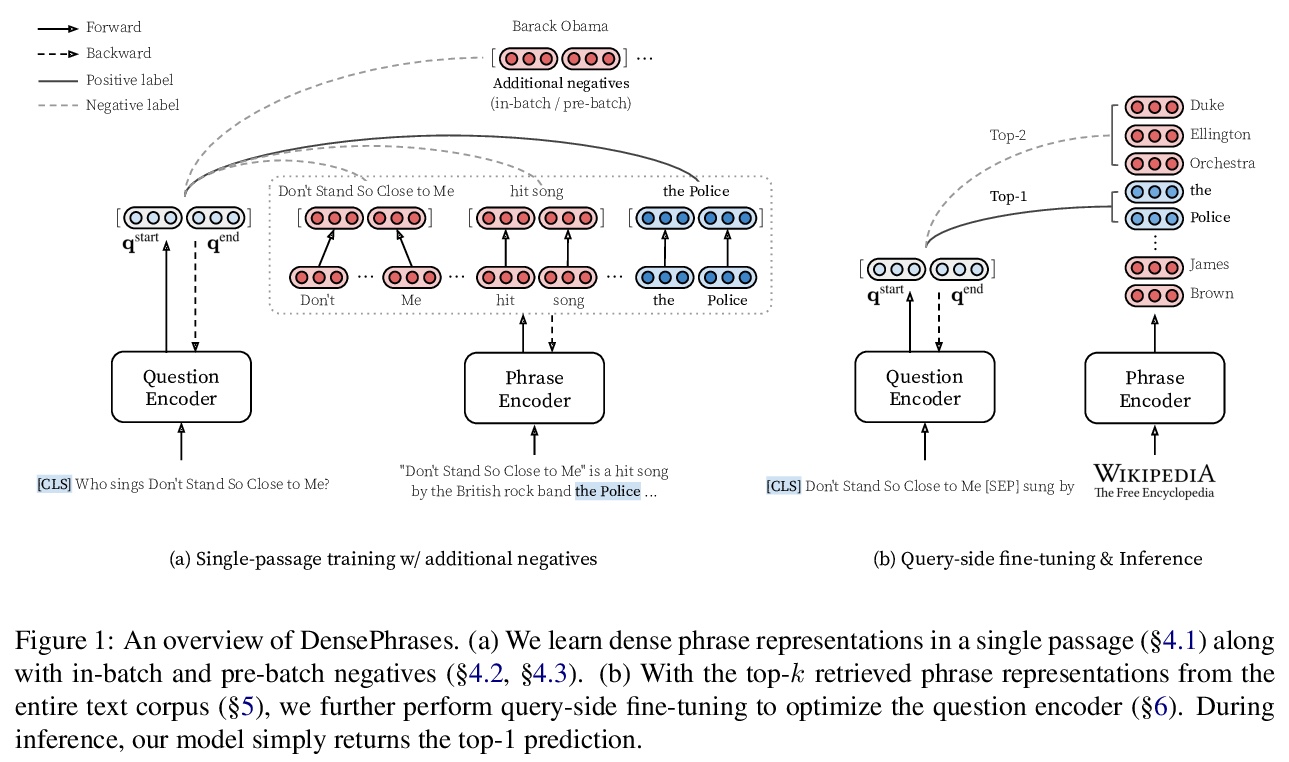
3、[CL] Learning Dense Representations of Phrases at Scale
J Lee, M Sung, J Kang, D Chen
[Korea University & Princeton University]
短语密集表示的大规模学习。开放域问答可以被重新表述为短语检索问题,无需在推理过程中按需处理文档。然而,目前的短语检索模型严重依赖稀疏表示,且仍低于检索器-阅读器方法。本文首次表明,可单独学习短语的密集表示,在开放域QA中取得更强的性能。提出一种有效方法,从阅读理解任务监督中学习短语表示,辅以新的负采样方法。提出一种查询方的微调策略,可支持迁移学习并减少训练和推理之间的差异。在五个流行的开放域QA数据集上,该模型DensePhrases比之前的短语检索模型提高了15%-25%的绝对准确率,并与最先进的检索器-阅读器模型性能相匹配。该模型由于纯密集表示而易于并行化,在CPU上每秒处理超过10个问题。直接将预先索引的密集短语表示用于两个槽填充任务,显示了利用DensePhrases作为下游任务的密集知识库的前景。
Open-domain question answering can be reformulated as a phrase retrieval problem, without the need for processing documents on-demand during inference (Seo et al., 2019). However, current phrase retrieval models heavily depend on sparse representations and still underperform retriever-reader approaches. In this work, we show for the first time that we can learn dense representations of phrases alone that achieve much stronger performance in opendomain QA. We present an effective method to learn phrase representations from the supervision of reading comprehension tasks, coupled with novel negative sampling methods. We also propose a query-side fine-tuning strategy, which can support transfer learning and reduce the discrepancy between training and inference. On five popular open-domain QA datasets, our model DensePhrases improves over previous phrase retrieval models by 15%– 25% absolute accuracy and matches the performance of state-of-the-art retriever-reader models. Our model is easy to parallelize due to pure dense representations and processes more than 10 questions per second on CPUs. Finally, we directly use our pre-indexed dense phrase representations for two slot filling tasks, showing the promise of utilizing DensePhrases as a dense knowledge base for downstream tasks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkZz9rFhQ
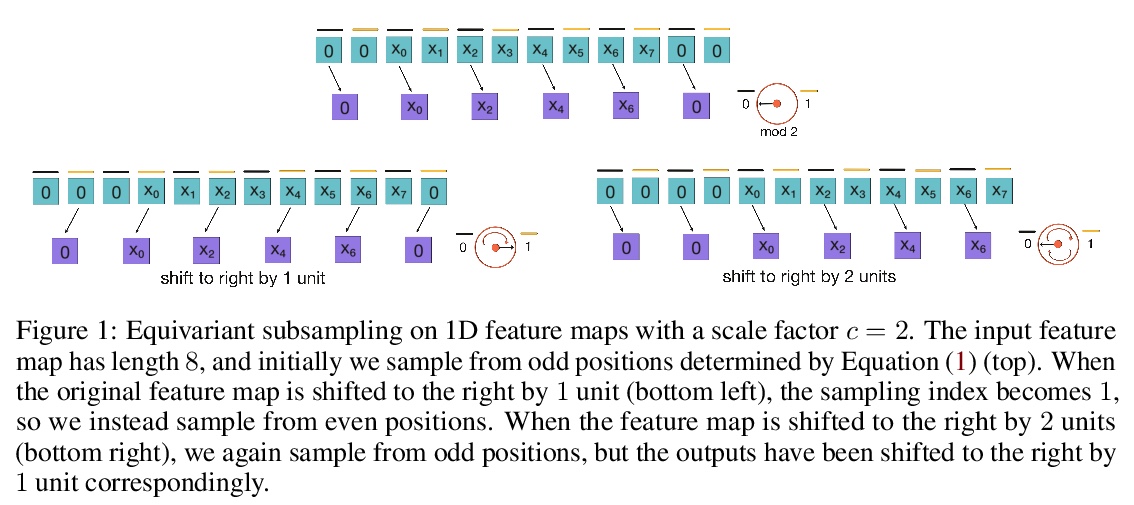
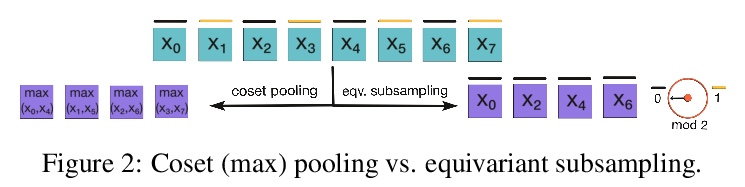
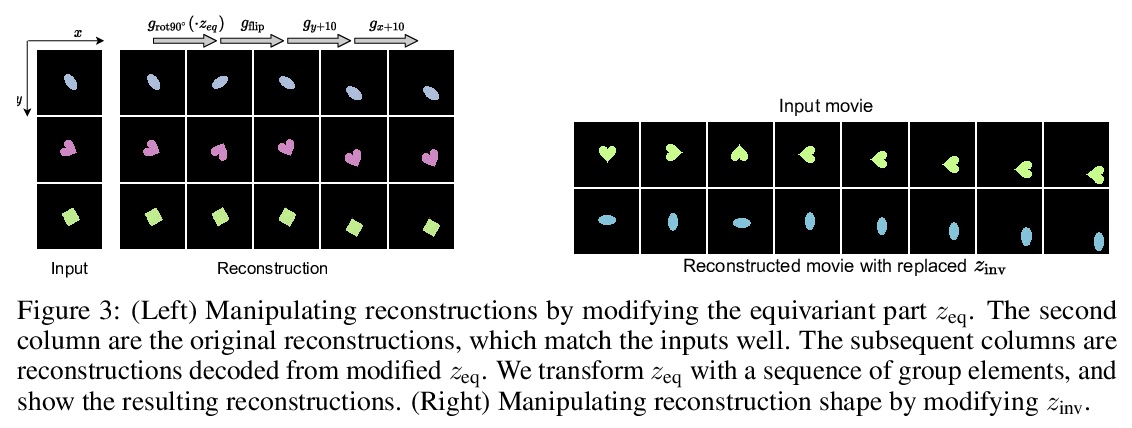
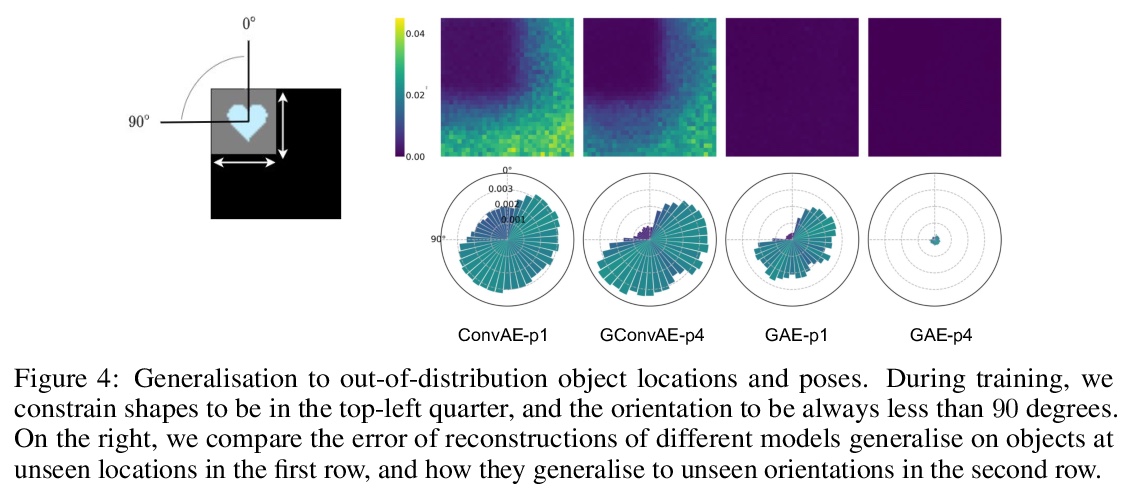
4、[LG] Group Equivariant Subsampling
J Xu, H Kim, T Rainforth, Y W Teh
[University of Oxford & DeepMind]
群等价子采样。子采样在卷积神经网络(CNN)中以池化或卷积步长的形式使用,以减少特征图的空间维度,使感受野随深度呈指数增长。然而,众所周知,这种子采样操作并不是平移等效的,与平移等效的卷积有所不同。本文提出了平移等变子采样/上采样层,可用来构建精确的平移等变CNN。将这些层从平移推广到一般群,提出群等价子采样/上采样。用这些层来构建群等价自编码器(GAE),能学习低维等价表示。在图像上经验性验证了这些表示对输入的平移和旋转确实是等价的,对未见过的位置和方向有很好的泛化作用。进一步将GAE用于在多物体数据集上学习以物体为中心的表示的模型中,与非等价基线相比,显示了更好的数据效率和分解。
Subsampling is used in convolutional neural networks (CNNs) in the form of pooling or strided convolutions, to reduce the spatial dimensions of feature maps and to allow the receptive fields to grow exponentially with depth. However, it is known that such subsampling operations are not translation equivariant, unlike convolutions that are translation equivariant. Here, we first introduce translation equivariant subsampling/upsampling layers that can be used to construct exact translation equivariant CNNs. We then generalise these layers beyond translations to general groups, thus proposing group equivariant subsampling/upsampling. We use these layers to construct group equivariant autoencoders (GAEs) that allow us to learn low-dimensional equivariant representations. We empirically verify on images that the representations are indeed equivariant to input translations and rotations, and thus generalise well to unseen positions and orientations. We further use GAEs in models that learn object-centric representations on multiobject datasets, and show improved data efficiency and decomposition compared to non-equivariant baselines.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkZC7ydv7
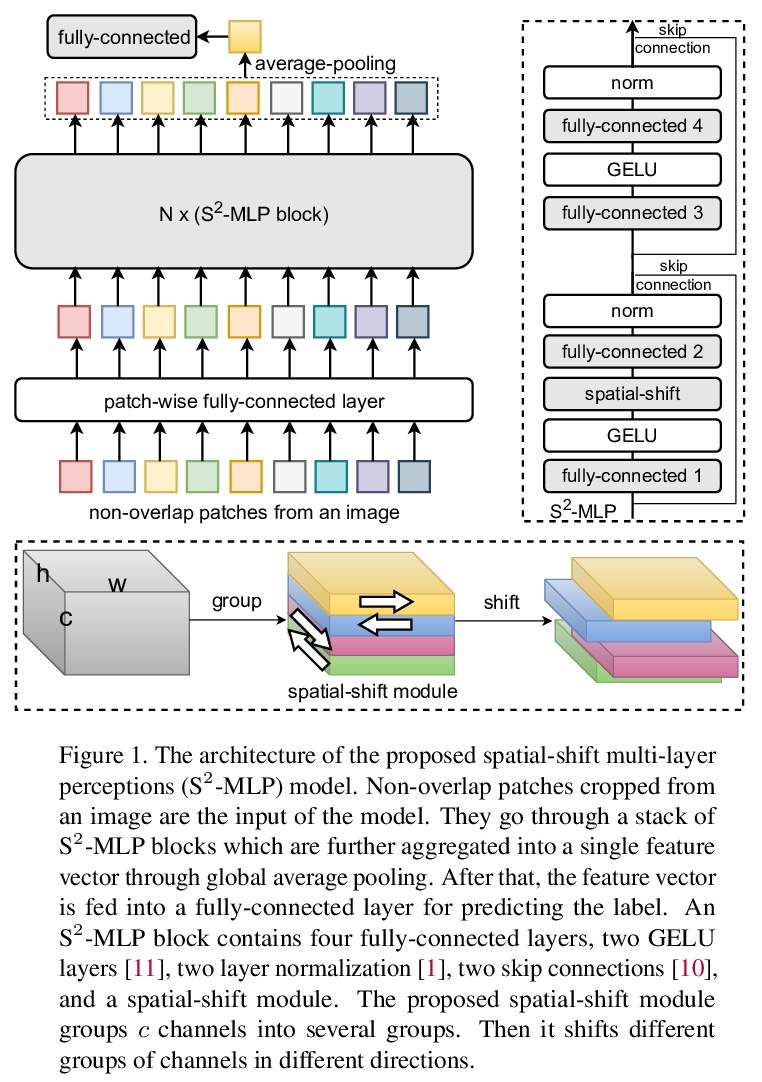
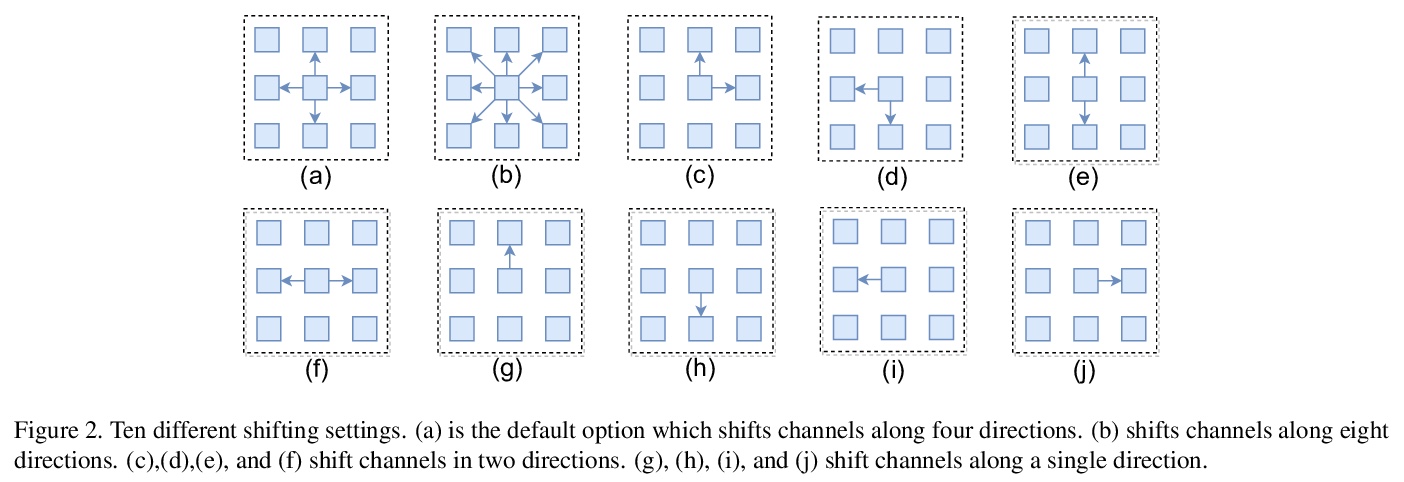
5、[CV] S²-MLP: Spatial-Shift MLP Architecture for Vision
T Yu, X Li, Y Cai, M Sun, P Li
[Baidu Research]
S²-MLP:视觉空间变换MLP架构。最近,视觉Transformer(ViT)及其后续工作放弃了卷积,利用自注意力操作,达到了与CNN相当甚至更高的精度。最近,MLP-Mixer放弃了卷积和自注意力操作,提出一种只包含MLP层的架构。为实现跨图块通信,除了通道混合MLP,还设计了一个额外的token混合MLP。在对极大规模数据集进行训练时,取得了令人鼓舞的结果。但在中等规模数据集(如ImageNet1K和ImageNet21K)上训练时,它不能像CNN和ViT的同类工作那样取得突出的性能。MLP-Mixer的性能下降,促使对token混合MLP问题的重新思考。MLP-Mixer中的token混合操作是深度卷积的一个变种,具有全局感受野和空间特定配置。但是,全局感受野和空间特定属性使得token混合MLP容易出现过拟合。本文提出一种新的纯MLP架构,即空间变换MLP(S²-MLP)。与MLP-Mixer不同,S²-MLP只包含通道混合MLP。设计了一个空间变换操作来实现图块间通信,具有一个局部感受野,并且是空间无关的。同时,还是无参数和高效的计算方式。在ImageNet-1K数据集上训练时,所提出的S²-MLP比MLP-Mixer获得了更高的识别精度。同时,S²-MLP在ImageNet-1K数据集上的表现与ViT一样出色,而且结构更简单,FLOPs和参数更少。
Recently, visual Transformer (ViT) and its following works abandon the convolution and exploit the self-attention operation, attaining a comparable or even higher accuracy than CNN. More recently, MLP-Mixer abandons both the convolution and the self-attention operation, proposing an architecture containing only MLP layers. To achieve crosspatch communications, it devises an additional token-mixing MLP besides the channel-mixing MLP. It achieves promising results when training on an extremely large-scale dataset. But it cannot achieve as outstanding performance as its CNN and ViT counterparts when training on medium-scale datasets such as ImageNet1K and ImageNet21K. The performance drop of MLP-Mixer motivates us to rethink the token-mixing MLP. We discover that token-mixing operation in MLP-Mixer is a variant of depthwise convolution with a global reception field and spatial-specific configuration. But the global reception field and the spatial-specific property make token-mixing MLP prone to over-fitting. In this paper, we propose a novel pure MLP architecture, spatial-shift MLP (S-MLP). Different from MLP-Mixer, our S-MLP only contains channel-mixing MLP. We devise a spatial-shift operation for achieving the communication between patches. It has a local reception field and is spatial-agnostic. Meanwhile, it is parameter-free and efficient for computation. The proposed S-MLP attains higher recognition accuracy than MLP-Mixer when training on ImageNet-1K dataset. Meanwhile, S-MLP accomplishes as excellent performance as ViT on ImageNet-1K dataset with considerably simpler architecture and fewer FLOPs and parameters.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkZG529gg
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
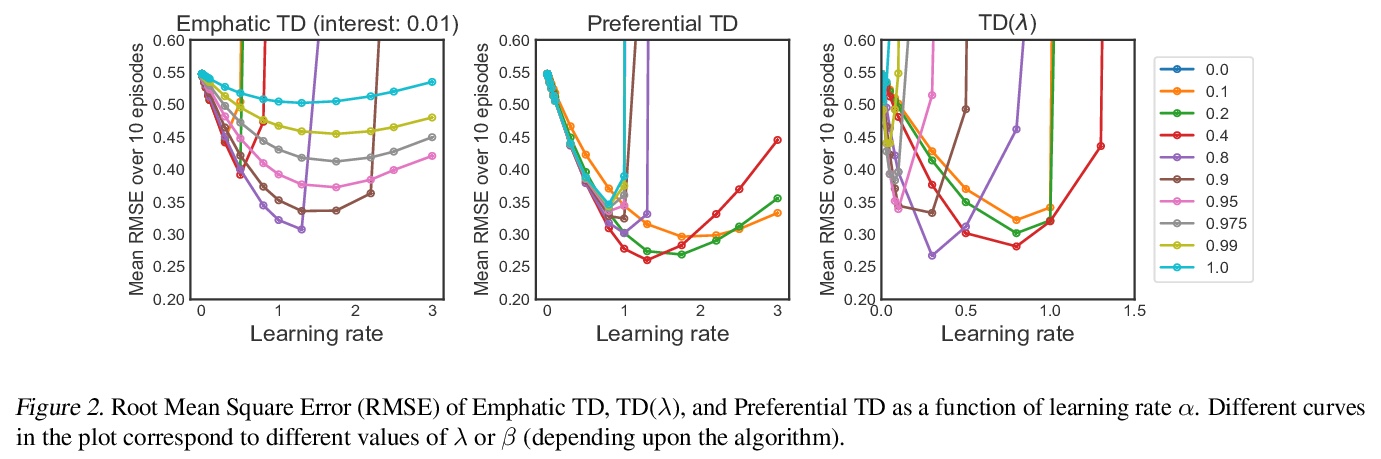
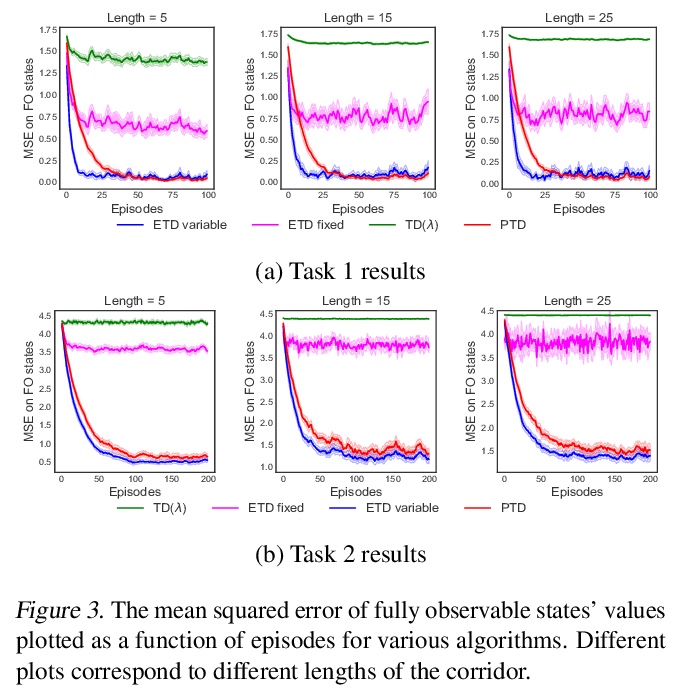
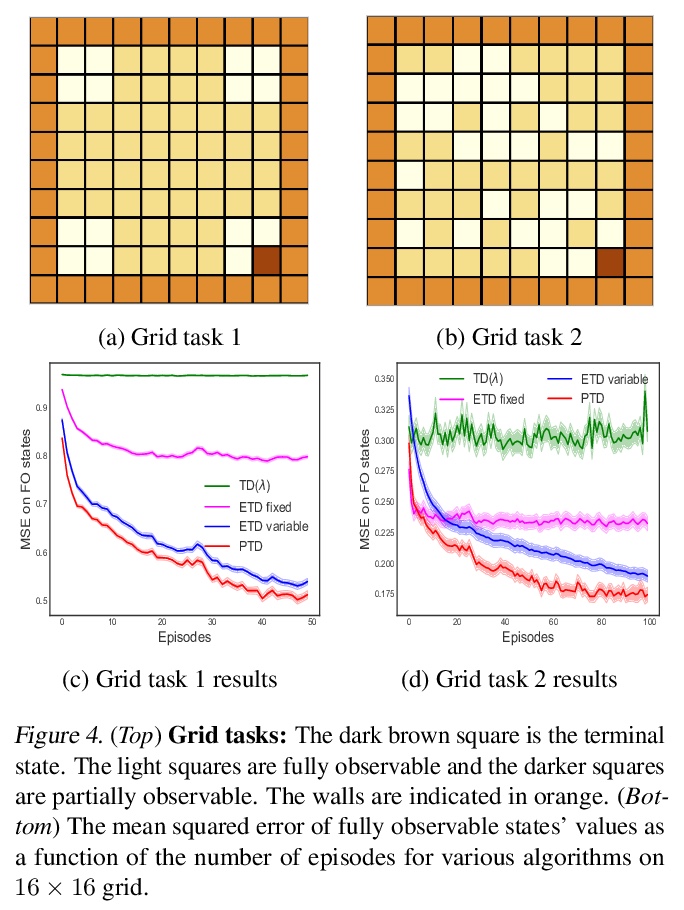
[LG] Preferential Temporal Difference Learning
倾向性时间差分学习
N Anand, D Precup
[Mila]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkZK9svnO

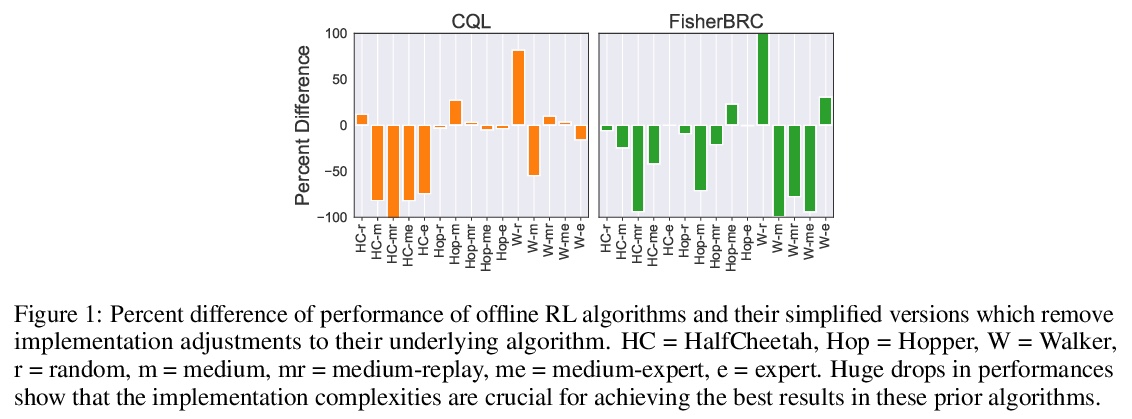
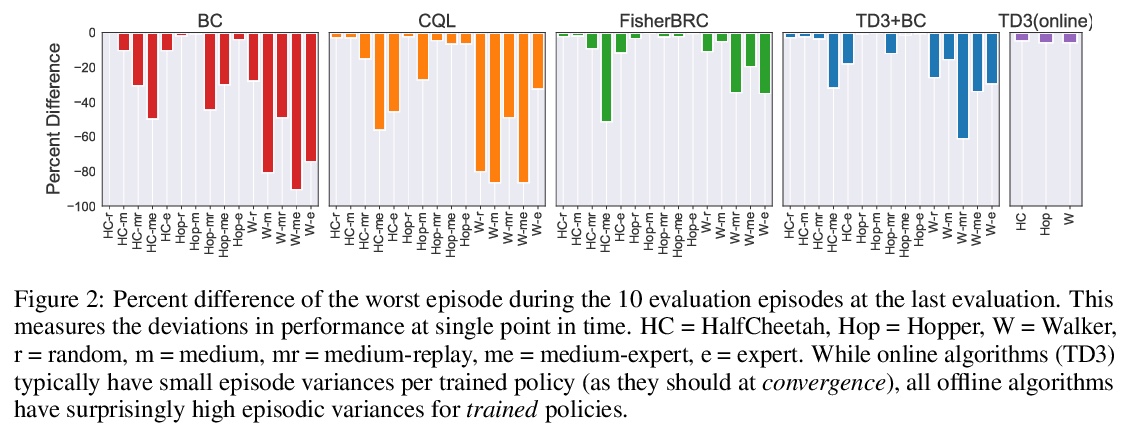
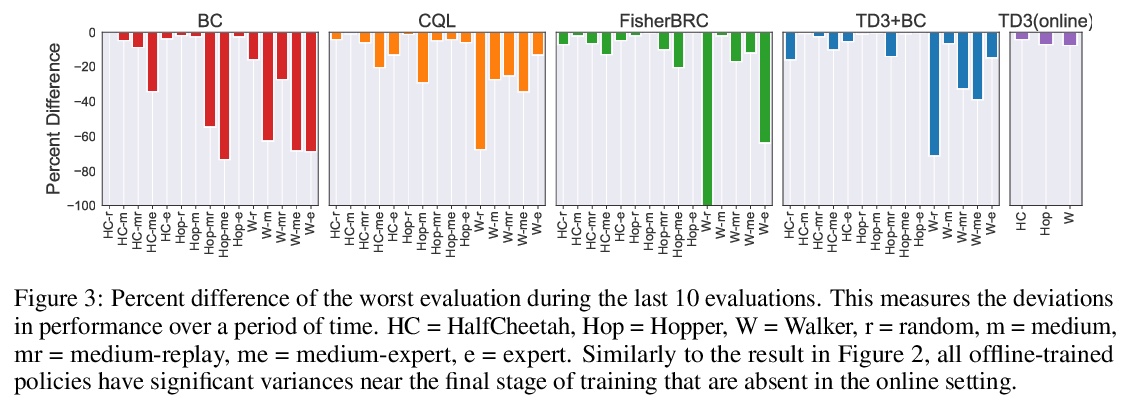
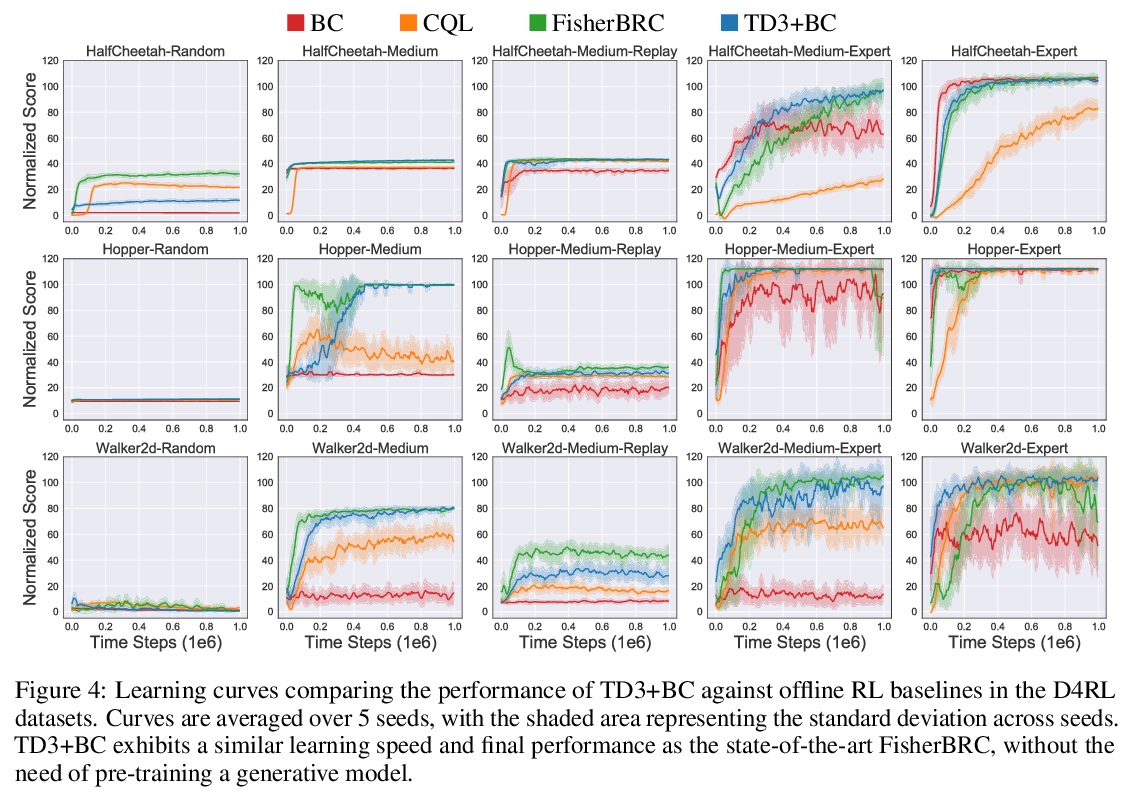
[LG] A Minimalist Approach to Offline Reinforcement Learning
离线强化学习最简方案
S Fujimoto, S S Gu
[Mila & Google Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkZLQ4VOr
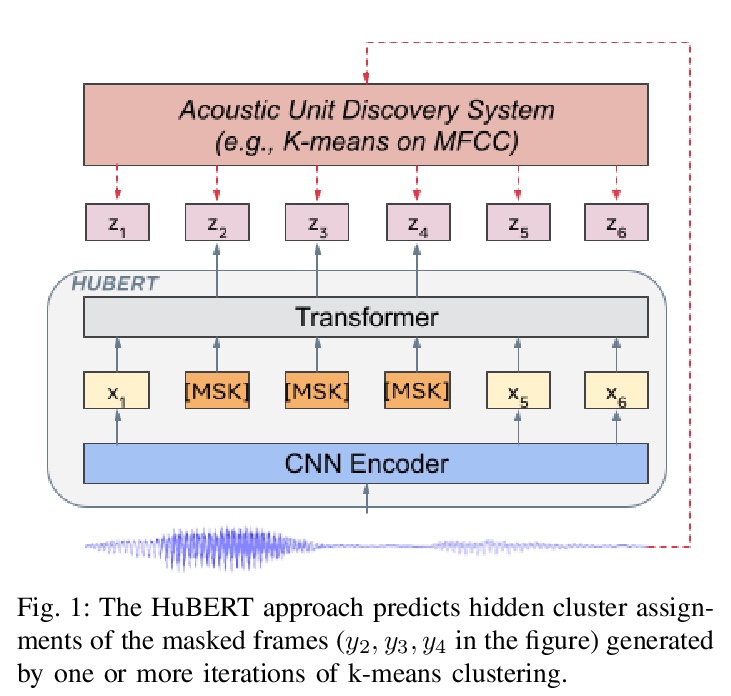
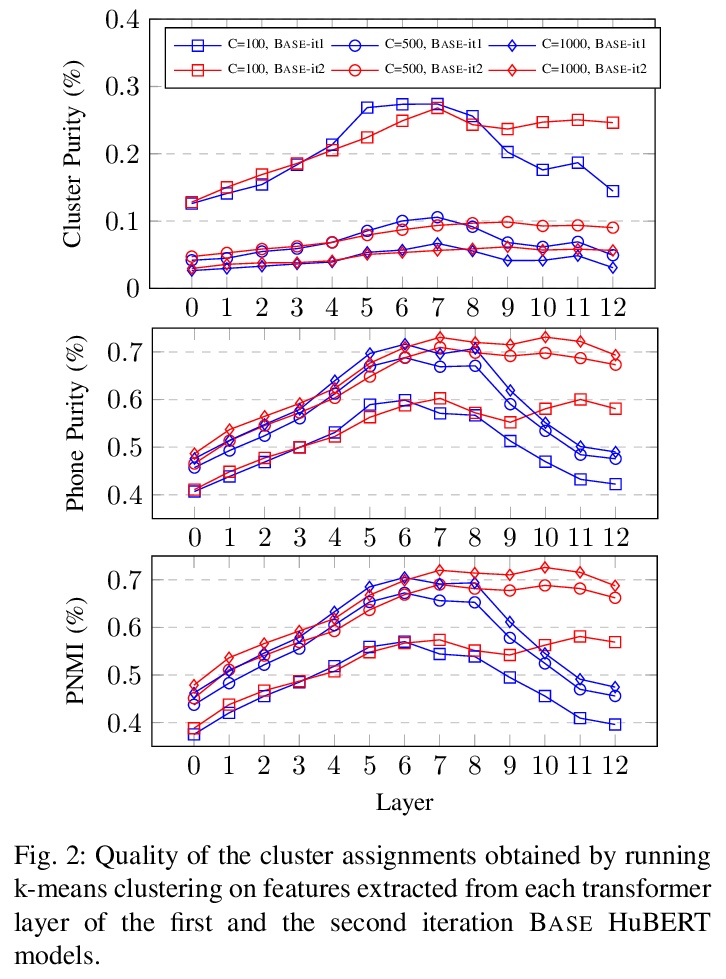
[CL] HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units
HuBERT:基于隐单元掩蔽预测的自监督语音表示学习
W Hsu, B Bolte, Y H Tsai, K Lakhotia, R Salakhutdinov, A Mohamed
[CMU]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkZO960QM
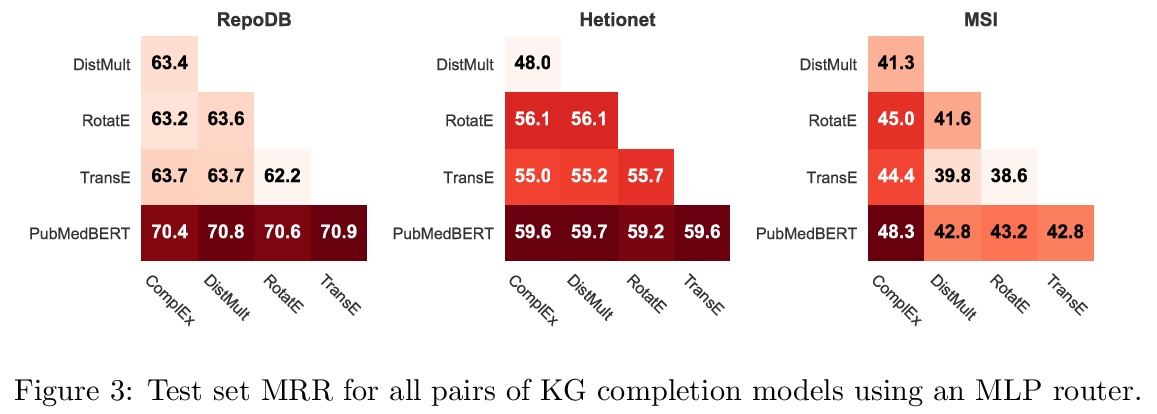
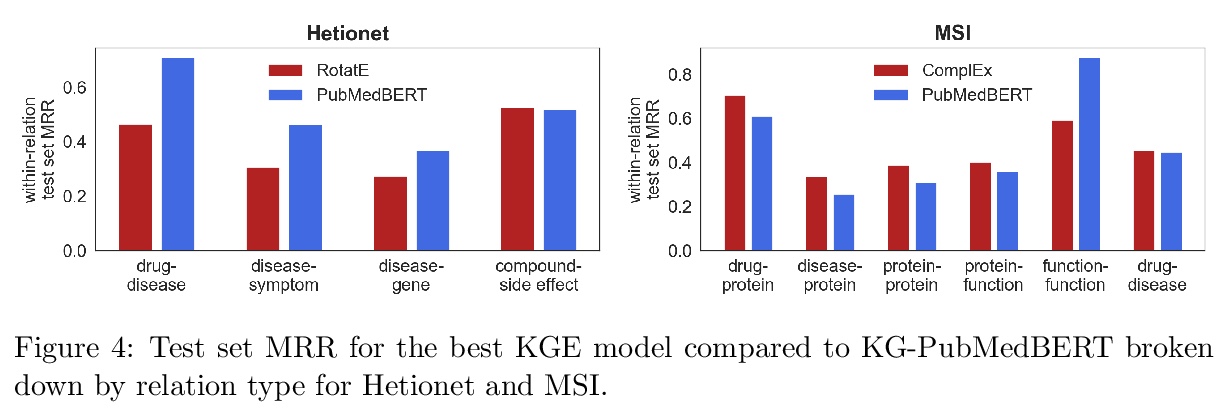
[CL] Scientific Language Models for Biomedical Knowledge Base Completion: An Empirical Study
生物医学知识图谱补全的科学语言模型实证研究
R Nadkarni, D Wadden, I Beltagy, N A. Smith, H Hajishirzi, T Hope
[University of Washington]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkZPlg30P