- 1、[CL] Revisiting the Primacy of English in Zero-shot Cross-lingual Transfer
- 2、[CV] Focal Self-attention for Local-Global Interactions in Vision Transformers
- 3、[LG] Variational Diffusion Models
- 4、[CV] CLIP-It! Language-Guided Video Summarization
- 5、[CV] Global Filter Networks for Image Classification
- [CV] AutoFormer: Searching Transformers for Visual Recognition
- [LG] Stabilizing Deep Q-Learning with ConvNets and Vision Transformers under Data Augmentation
- [LG] Mandoline: Model Evaluation under Distribution Shift
- [RO] Offline-to-Online Reinforcement Learning via Balanced Replay and Pessimistic Q-Ensemble
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
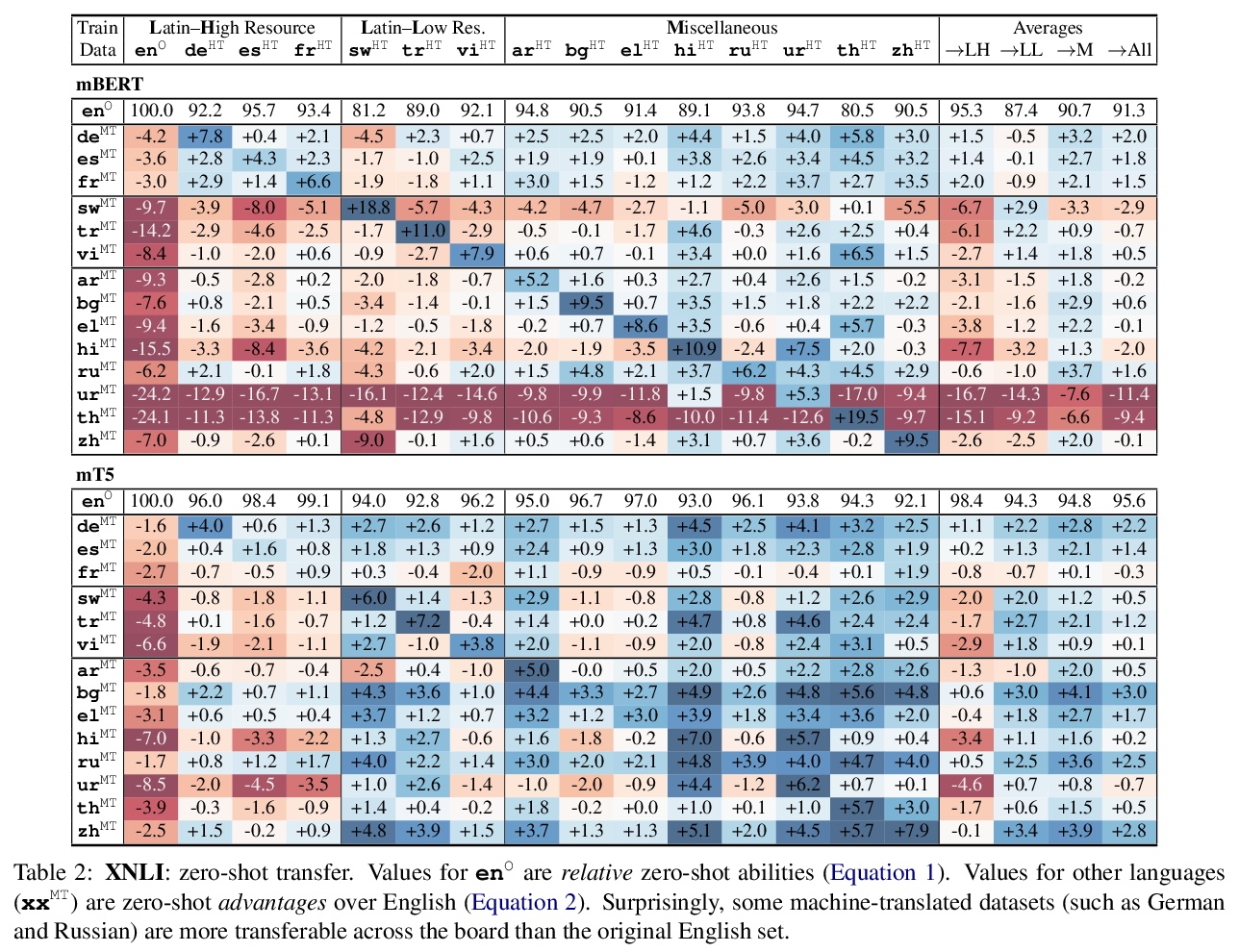
1、[CL] Revisiting the Primacy of English in Zero-shot Cross-lingual Transfer
I Turc, K Lee, J Eisenstein, M Chang, K Toutanova
[Google Research]
对零样本跨语言迁移首选英文作为源语言的重新审视。尽管大型预训练多语言模型取得了成功,但它们并没有完全缓解对标记数据的需求,收集所有目标语言的标记数据是很麻烦的。零样本跨语言迁移正在成为一种实用的解决方案:预训练好的模型,在一种迁移语言上进行微调后,在多种目标语言上测试时表现出惊人的性能。英语是迁移的主要源语言,这一点在流行的零样本测试基准中得到了加强。然而,这种默认的选择并没有得到系统的审查。本文将英语与其他用于微调的迁移语言,在两个预训练的多语言模型(mBERT和mT5)和多个分类和问答任务上进行比较。发现其他高资源语言,如德语和俄语,往往能更有效地迁移,特别是当目标语言集是多样化的或先验未知的时候。出乎意料的是,即使训练集是由英语自动翻译过来的,也会出现这种情况。
Despite their success, large pre-trained multilingual models have not completely alleviated the need for labeled data, which is cumbersome to collect for all target languages. Zero-shot cross-lingual transfer is emerging as a practical solution: pre-trained models later fine-tuned on one transfer language exhibit surprising performance when tested on many target languages. English is the dominant source language for transfer, as reinforced by popular zero-shot benchmarks. However, this default choice has not been systematically vetted. In our study, we compare English against other transfer languages for fine-tuning, on two pretrained multilingual models (mBERT and mT5) and multiple classification and question answering tasks. We find that other high-resource languages such as German and Russian often transfer more effectively, especially when the set of target languages is diverse or unknown a priori. Unexpectedly, this can be true even when the training sets were automatically translated from English. This finding can have immediate impact on multilingual zero-shot systems, and should inform future benchmark designs.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmY2s9uza 


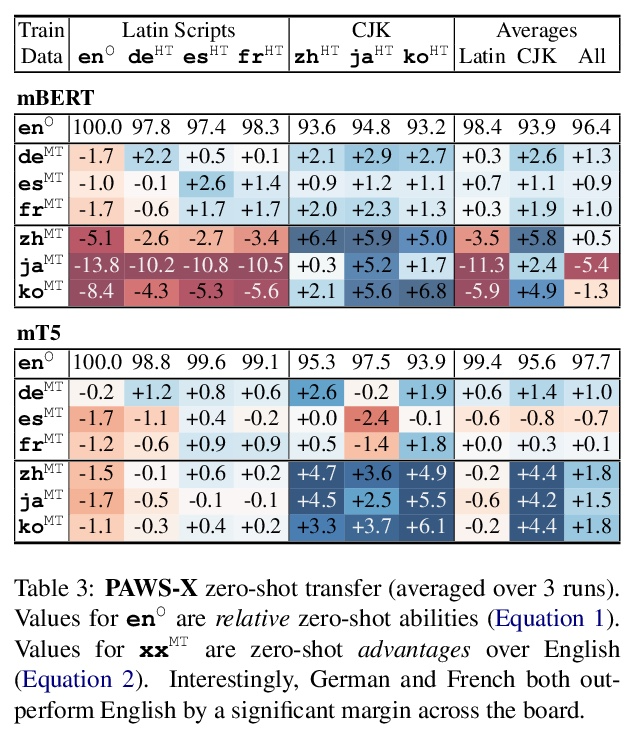
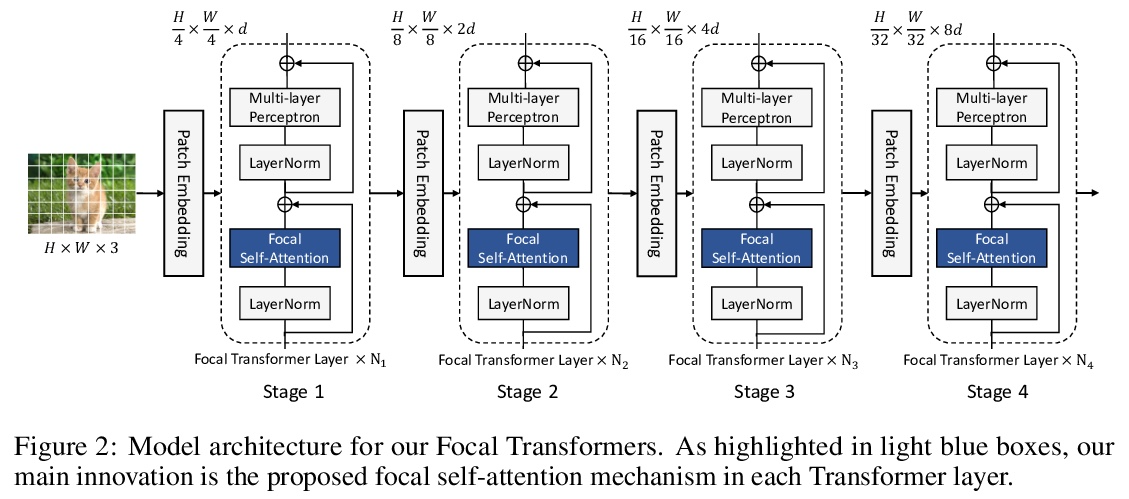
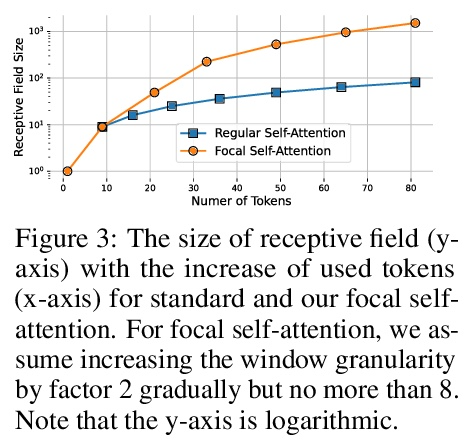
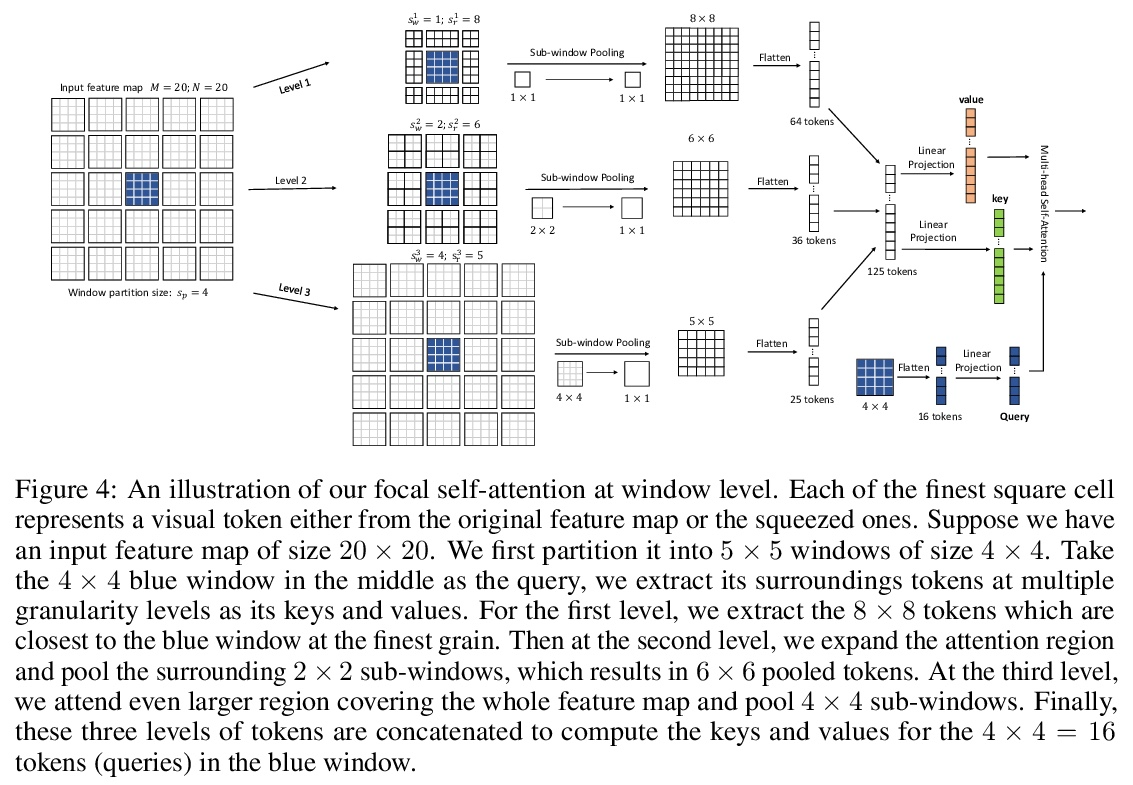
2、[CV] Focal Self-attention for Local-Global Interactions in Vision Transformers
J Yang, C Li, P Zhang, X Dai, B Xiao, L Yuan, J Gao
[Microsoft Research at Redmond & Microsoft Cloud + AI]
视觉Transformer局部-全局交互焦点自注意力。最近,视觉Transformer及其变体在各种计算机视觉任务中显示出巨大的前景。通过自注意力捕捉短程和长程视觉依赖关系的能力是成功的关键,但同时也带来了挑战,因为需要四倍的计算开销,特别是对于高分辨率的视觉任务(如目标检测)。最近的许多工作试图通过应用粗粒度的全局注意力或细粒度的局部注意力来减少计算和内存成本并提高性能。然而,这两类方法都削弱了多层Transformer原始的自注意力机制的建模能力,从而导致了次优的解决方案。本文提出焦点式自注意力,同时包含细粒度局部和粗粒度全局的交互。每个标记在细粒度上关注其周围近处的标记,在粗粒度上关注远处的标记,可有效地捕捉短程和长程的视觉依赖。基于焦点自注意力,提出一种新的视觉Transformer模型变体,Focal Transformers,在一系列公共图像分类和物体检测基准上取得了比最先进的视觉Transformer更高的性能。
Recently, Vision Transformer and its variants have shown great promise on various computer vision tasks. The ability of capturing shortand long-range visual dependencies through self-attention is the key to success. But it also brings challenges due to quadratic computational overhead, especially for the high-resolution vision tasks (e.g., object detection). Many recent works have attempted to reduce the computational and memory cost and improve performance by applying either coarse-grained global attentions or fine-grained local attentions. However, both approaches cripple the modeling power of the original self-attention mechanism of multi-layer Transformers, thus leading to sub-optimal solutions. In this paper, we present focal self-attention, a new mechanism that incorporates both fine-grained local and coarse-grained global interactions. In this new mechanism, each token attends its closest surrounding tokens at fine granularity and the tokens far away at coarse granularity, and thus can capture both shortand long-range visual dependencies efficiently and effectively. With focal self-attention, we propose a new variant of Vision Transformer models, called Focal Transformer, which achieves superior performance over the state-of-the-art (SoTA) vision Transformers on a range of public image classification and object detection benchmarks. In particular, our Focal Transformer models with a moderate size of 51.1M and a larger size of 89.8M achieve 83.5% and 83.8% Top-1 accuracy, respectively, on ImageNet classification at 224× 224. When employed as the backbones, Focal Transformers achieve consistent and substantial improvements over the current SoTA Swin Transformers [44] across 6 different object detection methods. Our largest Focal Transformer yields 58.7/58.9 box mAPs and 50.9/51.3 mask mAPs on COCO mini-val/test-dev, and 55.4 mIoU on ADE20K for semantic segmentation, creating new SoTA on three of the most challenging computer vision tasks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmY8drFTv 

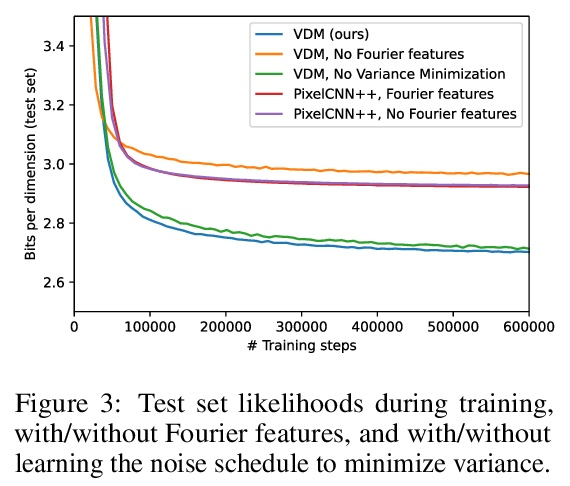
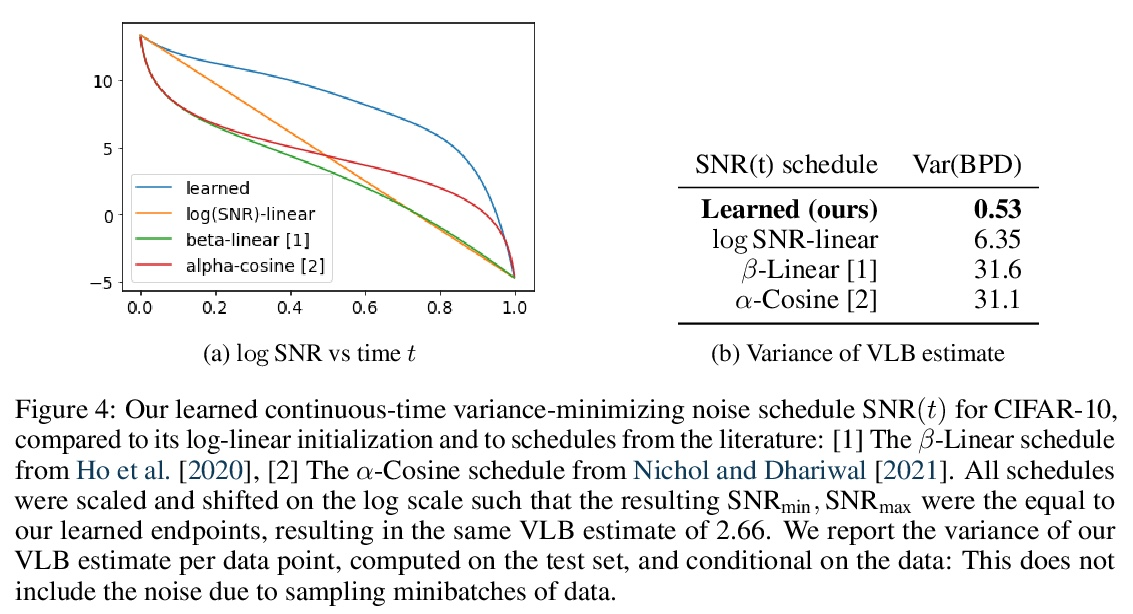
3、[LG] Variational Diffusion Models
D P. Kingma, T Salimans, B Poole, J Ho
[Google Research]
变分扩散模型。基于扩散的生成模型已经展示了在感知上令人印象深刻的综合能力,但它们也能成为基于似然的伟大模型吗?本文给出了肯定的答案,提出基于扩散的生成模型族,在标准图像密度估计的基准上获得了最先进的似然。提出了关于使用新的扩散模型族对自然图像密度进行建模的最先进的结果,包括可学习的扩散规范、用于精细建模的傅里叶特征以及其他架构创新。与其他基于扩散的模型不同,该方法允许联合模型其他部分有效优化噪声时间表。变分下限(VLB)简化为扩散数据信噪比的一个非常简短的表达,从而提高了对这一类模型的理论理解。利用这一洞察,证明了文献中提出的几个模型之间的等价性。除了其端点的信噪比外,连续时间VLB对噪声时间表是不变的。使得能够学习一个噪声时间表,使所得的VLB估计器方差最小,从而导致更快的优化。结合这些进展和架构上的改进,在图像密度估计基准上获得了最先进的似然,超过了多年来主导这些基准的自回归模型,而且优化速度往往明显加快。展示了如何将该模型转化为bits-back压缩方案,并展示了接近理论最优的无损压缩率。
Diffusion-based generative models have demonstrated a capacity for perceptually impressive synthesis, but can they also be great likelihood-based models? We answer this in the affirmative, and introduce a family of diffusion-based generative models that obtain state-of-the-art likelihoods on standard image density estimation benchmarks. Unlike other diffusion-based models, our method allows for efficient optimization of the noise schedule jointly with the rest of the model. We show that the variational lower bound (VLB) simplifies to a remarkably short expression in terms of the signal-to-noise ratio of the diffused data, thereby improving our theoretical understanding of this model class. Using this insight, we prove an equivalence between several models proposed in the literature. In addition, we show that the continuous-time VLB is invariant to the noise schedule, except for the signal-to-noise ratio at its endpoints. This enables us to learn a noise schedule that minimizes the variance of the resulting VLB estimator, leading to faster optimization. Combining these advances with architectural improvements, we obtain state-of-the-art likelihoods on image density estimation benchmarks, outperforming autoregressive models that have dominated these benchmarks for many years, with often significantly faster optimization. In addition, we show how to turn the model into a bits-back compression scheme, and demonstrate lossless compression rates close to the theoretical optimum.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmYeTF2C2 


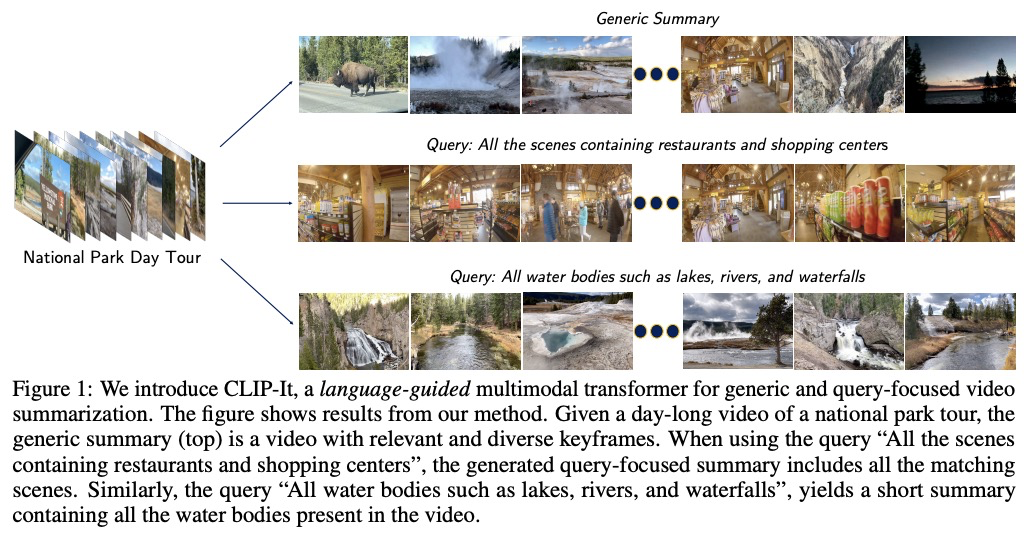
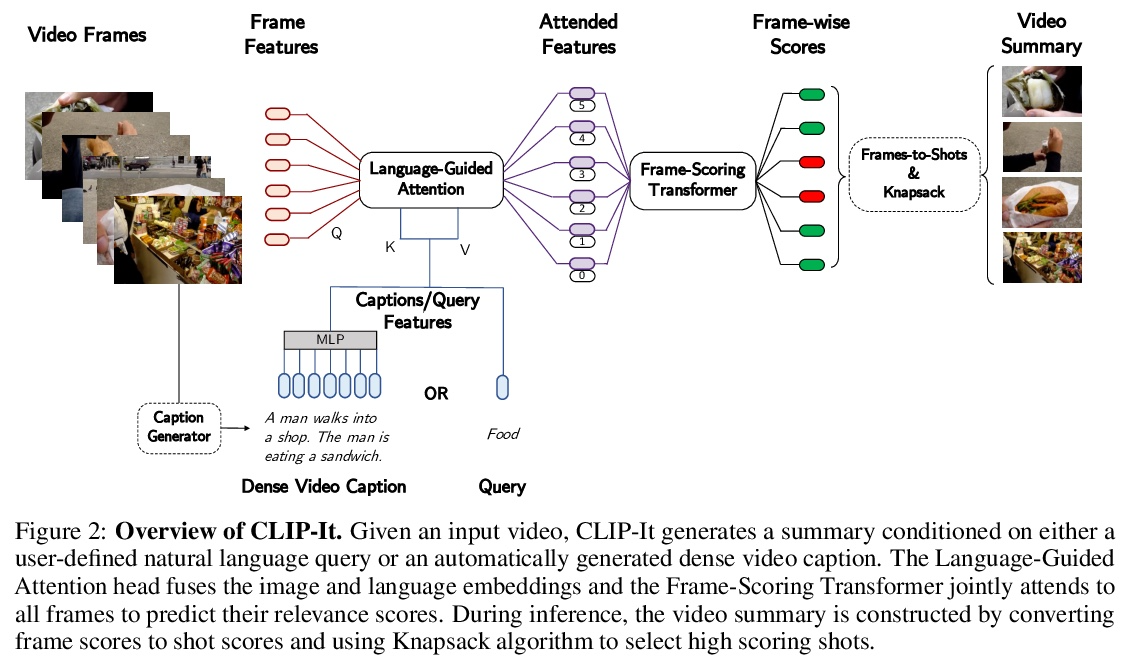
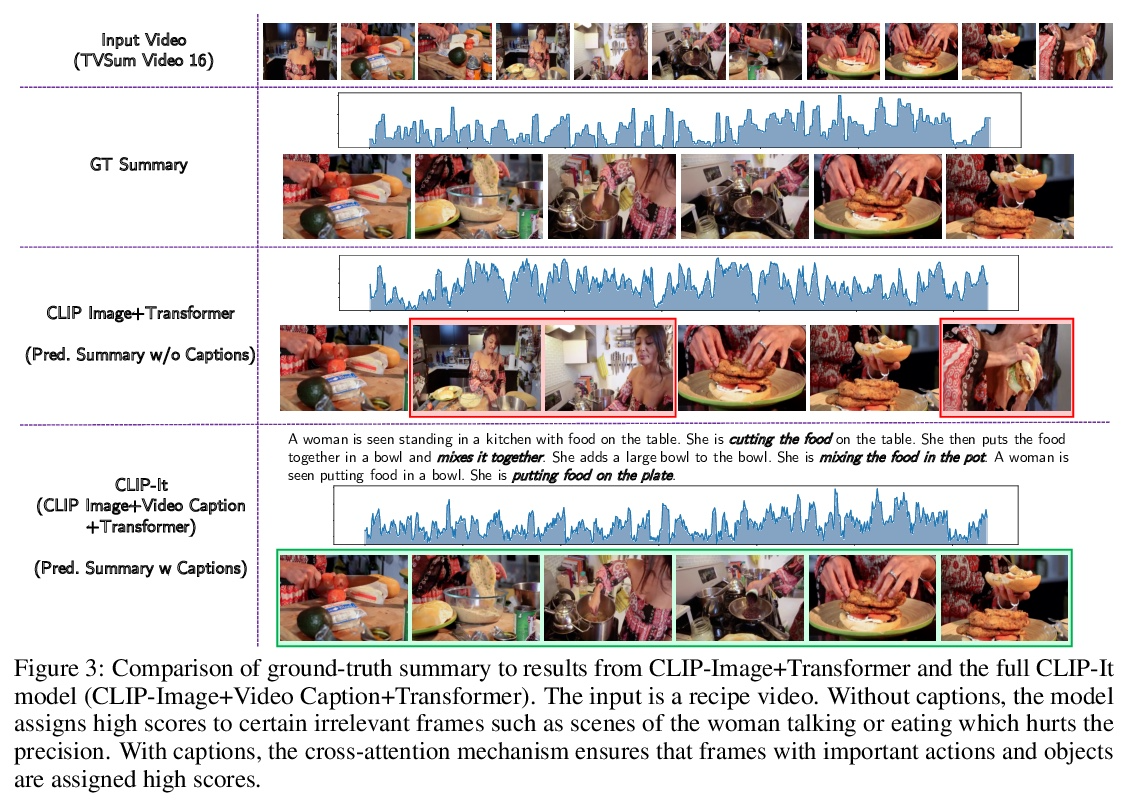
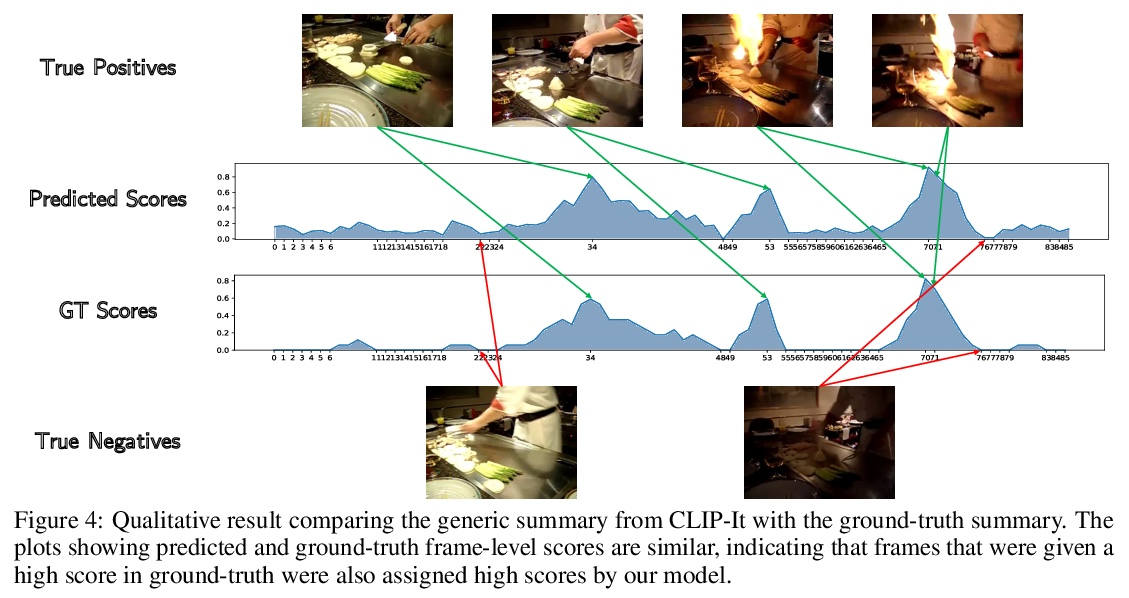
4、[CV] CLIP-It! Language-Guided Video Summarization
M Narasimhan, A Rohrbach, T Darrell
[UC Berkeley]
CLIP-It! 语言指导的视频摘要。一个通用的视频摘要是一个视频的删节版,它传达了整个故事,并保留最重要的场景。然而,视频中场景的重要性往往是主观的,用户应该可以选择通过使用自然语言来指定什么是对他们重要的,从而定制摘要。此外,现有的全自动通用摘要的模型,还没有利用现有的语言模型,而语言模型可以作为显著性的有效先验。本文提出CLIP-It,一种解决通用和以查询为重点的视频摘要的单一框架,在文献中通常是分开处理的。提出一种语言引导的多模态transformer,可以根据视频中的帧相对于彼此的重要性,以及它们与用户定义的查询(用于以查询为重点的摘要)或自动生成的密集视频标题(用于通用视频摘要)的相关性来学习评分。该模型可通过在没有真值监督的情况下进行训练扩展到无监督环境中。在标准视频摘要数据集(TVSum和SumMe)和以查询为重点的视频摘要数据集(QFVS)上的表现都明显优于基线和之前的工作。特别是,在迁移设置中取得了很大的改进,证明了该方法具有很强的泛化能力。
A generic video summary is an abridged version of a video that conveys the whole story and features the most important scenes. Yet the importance of scenes in a video is often subjective, and users should have the option of customizing the summary by using natural language to specify what is important to them. Further, existing models for fully automatic generic summarization have not exploited available language models, which can serve as an effective prior for saliency. This work introduces CLIP-It, a single framework for addressing both generic and queryfocused video summarization, typically approached separately in the literature. We propose a language-guided multimodal transformer that learns to score frames in a video based on their importance relative to one another and their correlation with a user-defined query (for query-focused summarization) or an automatically generated dense video caption (for generic video summarization). Our model can be extended to the unsupervised setting by training without ground-truth supervision. We outperform baselines and prior work by a significant margin on both standard video summarization datasets (TVSum and SumMe) and a query-focused video summarization dataset (QFVS). Particularly, we achieve large improvements in the transfer setting, attesting to our method’s strong generalization capabilities.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmYiWeLvn 
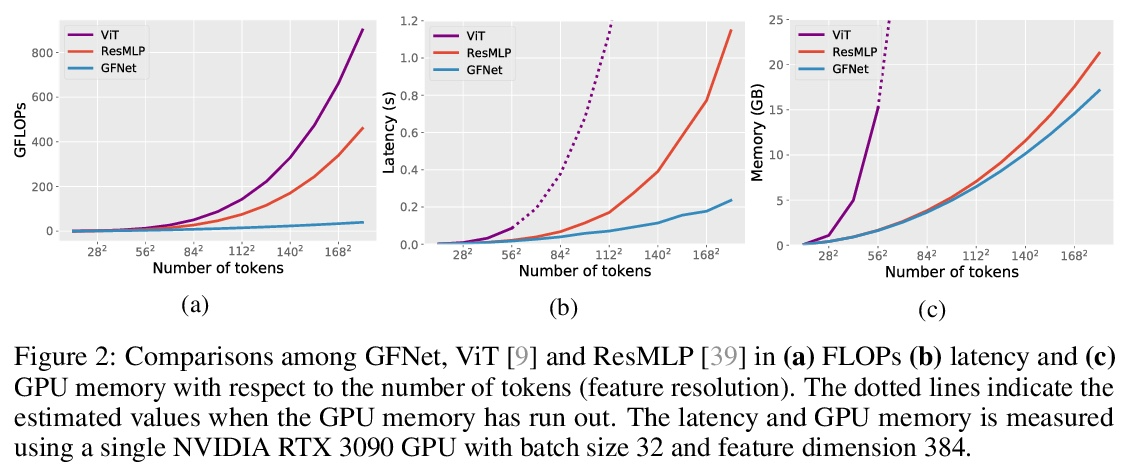
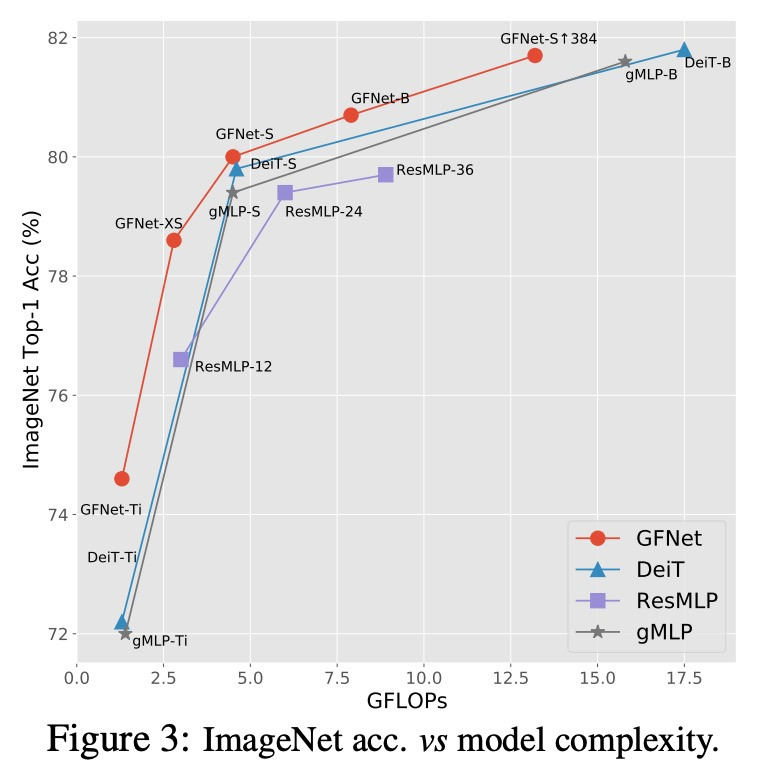
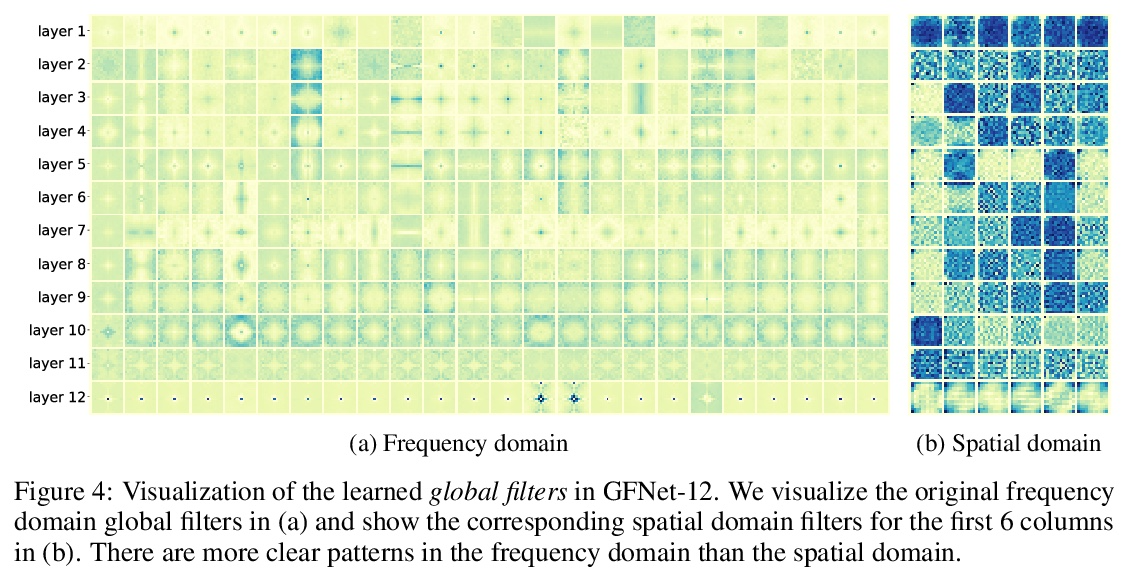
5、[CV] Global Filter Networks for Image Classification
Y Rao, W Zhao, Z Zhu, J Lu, J Zhou
[Tsinghua University]
面向图像分类的全局滤波网络。最近,用于视觉的自注意力和纯多层感知器(MLP)模型的进展显示出巨大潜力,以较少的归纳偏差实现了可喜的性能。这些模型通常是基于从原始数据中学习空间位置之间的相互作用。随着图像大小的增加,自注意力和MLP的复杂性呈四次方增长,这使得这些模型在需要高分辨率特征时难以扩大规模。本文提出全局滤波网络(GFNet),一种概念简单但计算效率高的架构,以对数线性的复杂度学习频域中的长程空间依赖关系。该架构用三个关键操作取代了视觉transformer中的自注意力层:二维离散傅里叶变换,频域特征和可学习全局滤波器之间的逐元乘法,以及二维反傅里叶变换。展示了该模型在ImageNet和下游任务中有利的准确性/复杂性权衡。实验结果表明,GFNet在效率、泛化能力和鲁棒性方面可以成为transformer式模型和CNN的一个非常有竞争力的替代方案。
Recent advances in self-attention and pure multi-layer perceptrons (MLP) models for vision have shown great potential in achieving promising performance with fewer inductive biases. These models are generally based on learning interaction among spatial locations from raw data. The complexity of self-attention and MLP grows quadratically as the image size increases, which makes these models hard to scale up when high-resolution features are required. In this paper, we present the Global Filter Network (GFNet), a conceptually simple yet computationally efficient architecture, that learns long-term spatial dependencies in the frequency domain with log-linear complexity. Our architecture replaces the self-attention layer in vision transformers with three key operations: a 2D discrete Fourier transform, an element-wise multiplication between frequency-domain features and learnable global filters, and a 2D inverse Fourier transform. We exhibit favorable accuracy/complexity trade-offs of our models on both ImageNet and downstream tasks. Our results demonstrate that GFNet can be a very competitive alternative to transformer-style models and CNNs in efficiency, generalization ability and robustness.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmYm5xQ1Q 

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
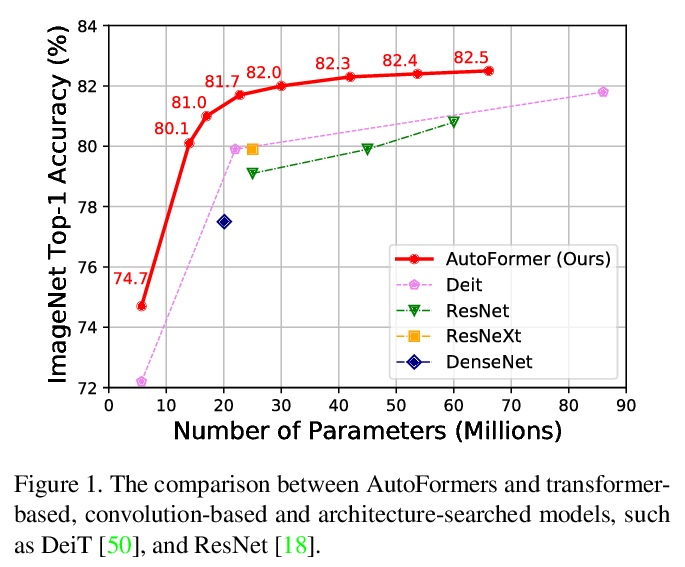
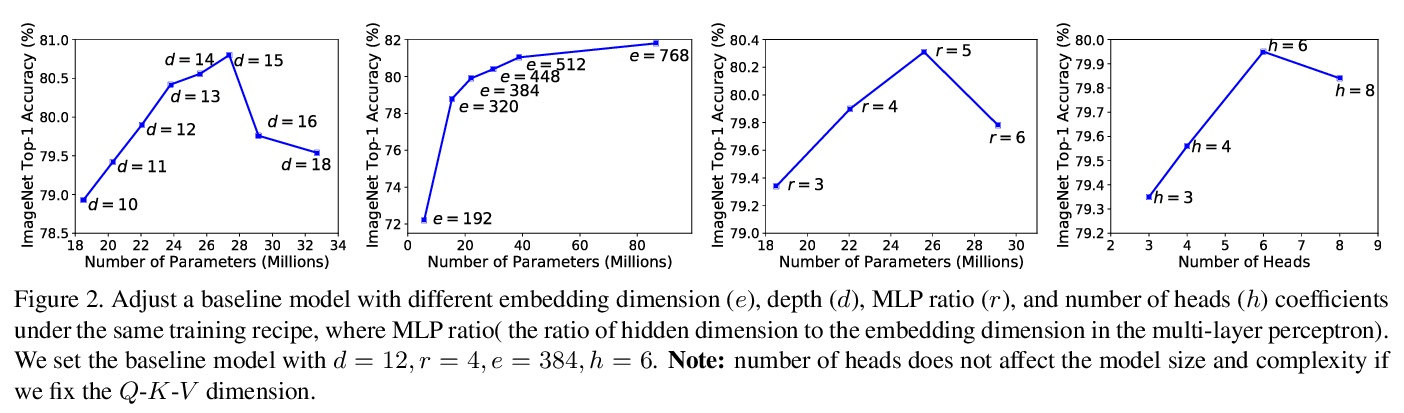
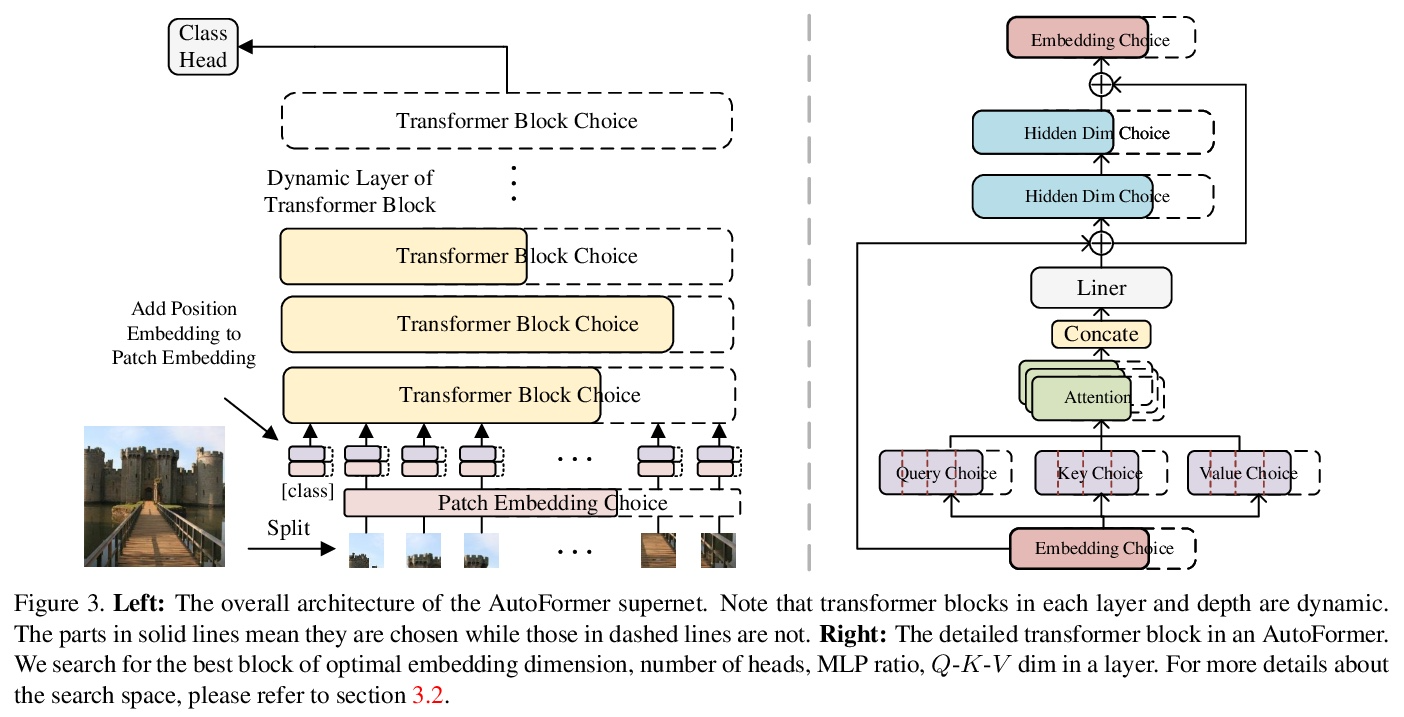
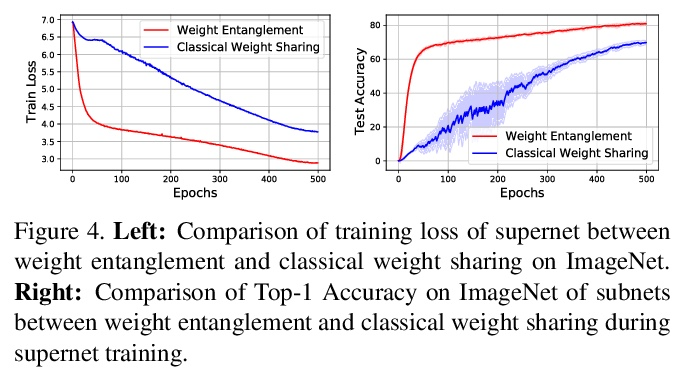
[CV] AutoFormer: Searching Transformers for Visual Recognition
AutoFormer:面向视觉识别的Transformer架构搜索
M Chen, H Peng, J Fu, H Ling
[Stony Brook University & Microsoft Research Asia]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmYoY4TT1 
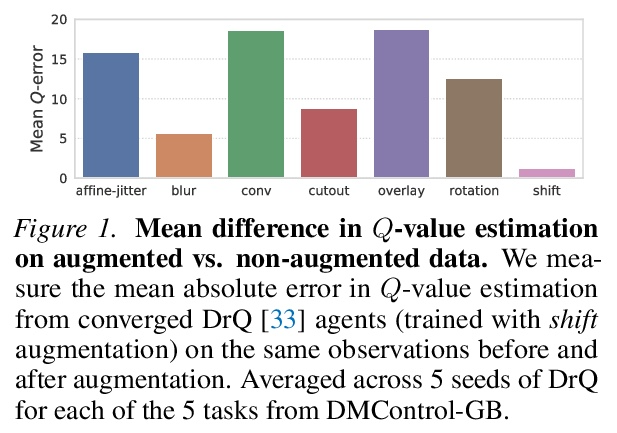
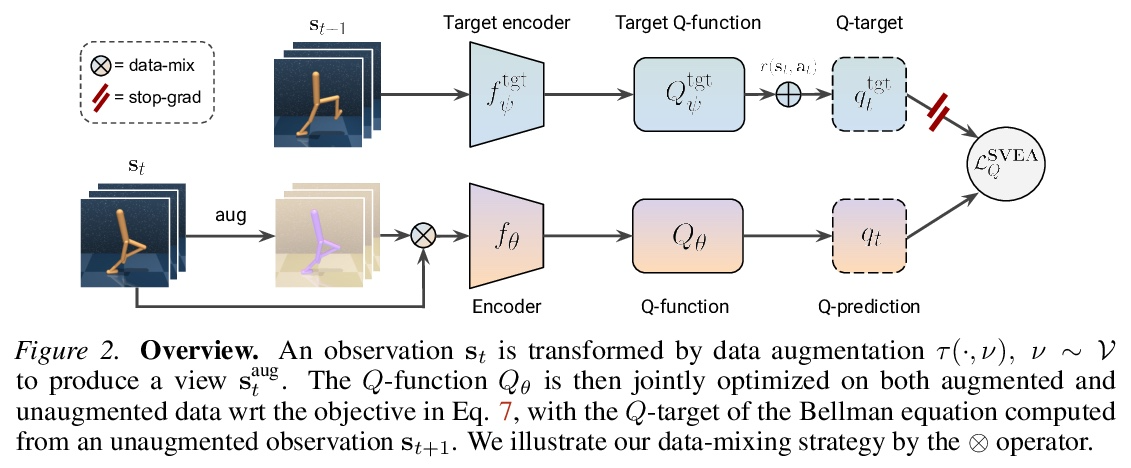
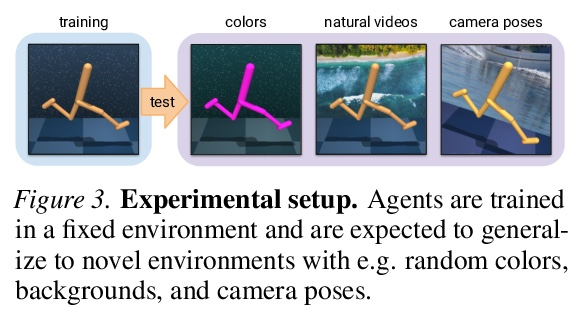
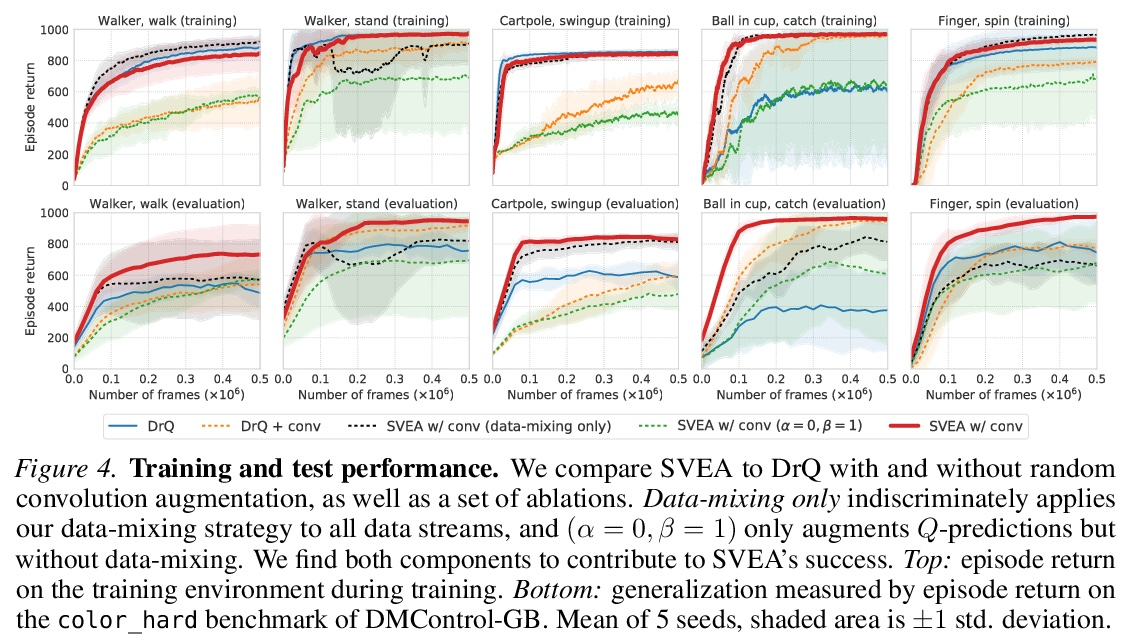
[LG] Stabilizing Deep Q-Learning with ConvNets and Vision Transformers under Data Augmentation
用ConvNets和视觉Transformer稳定数据增强深度Q-Learning
N Hansen, H Su, X Wang
[UC San Diego]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmYuZAZJf 
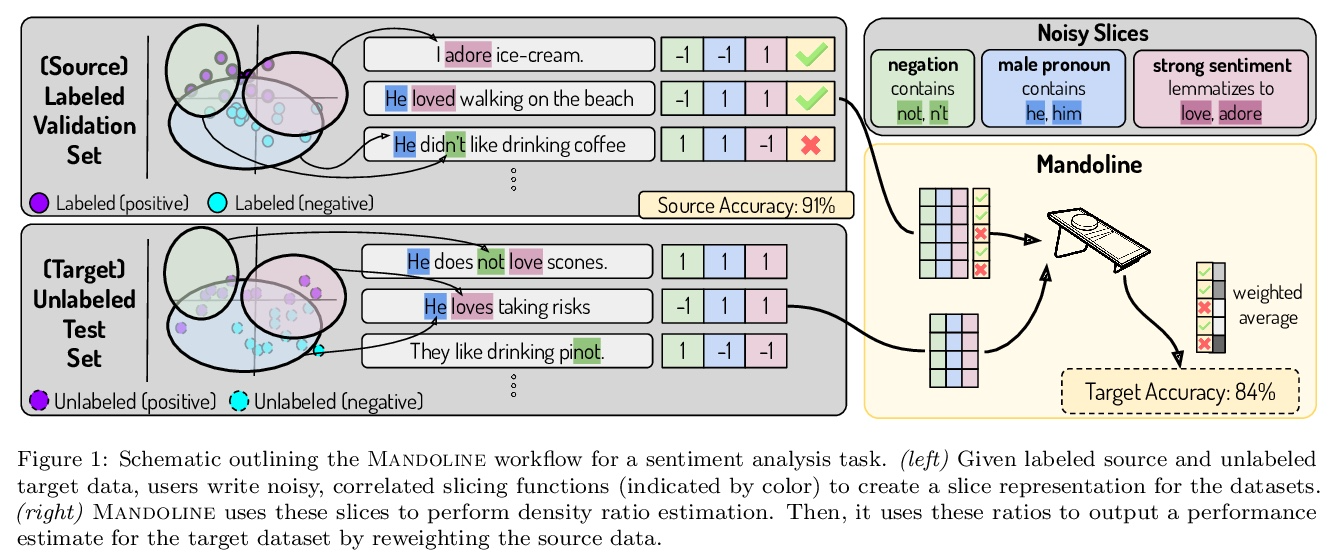
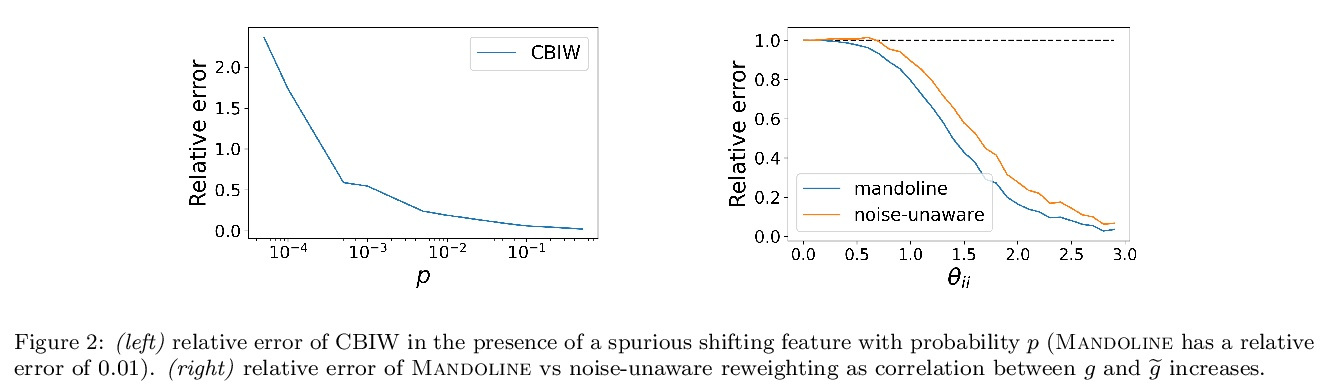
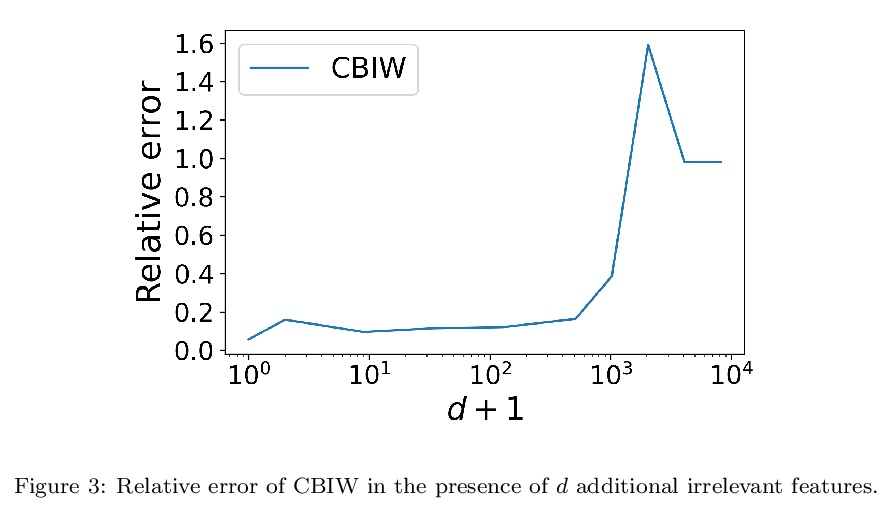
[LG] Mandoline: Model Evaluation under Distribution Shift
Mandoline:分布转移下的模型评价
M Chen, K Goel, N Sohoni, F Poms, K Fatahalian, C Ré
[Stanford University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmYyKoD3n 
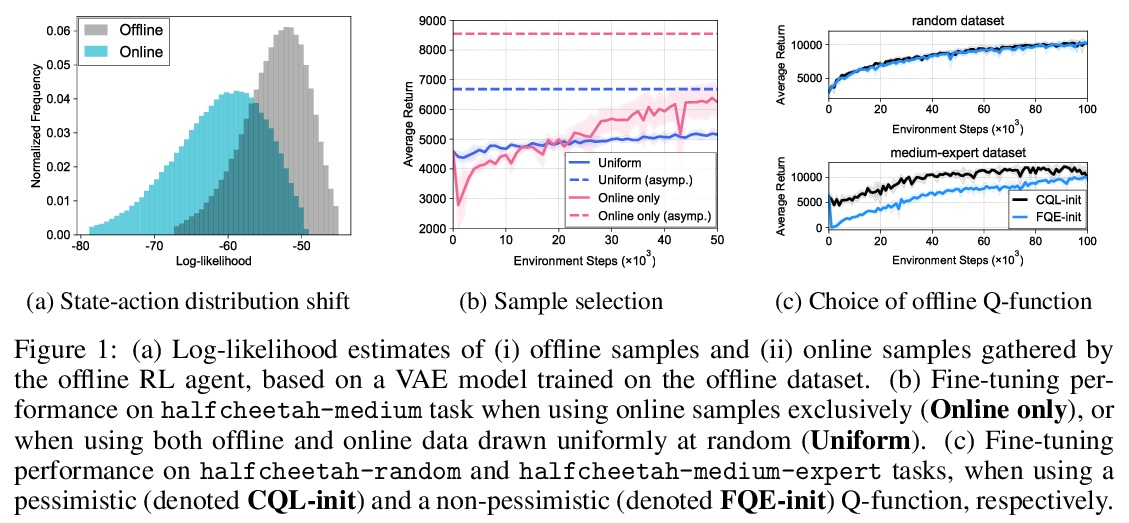
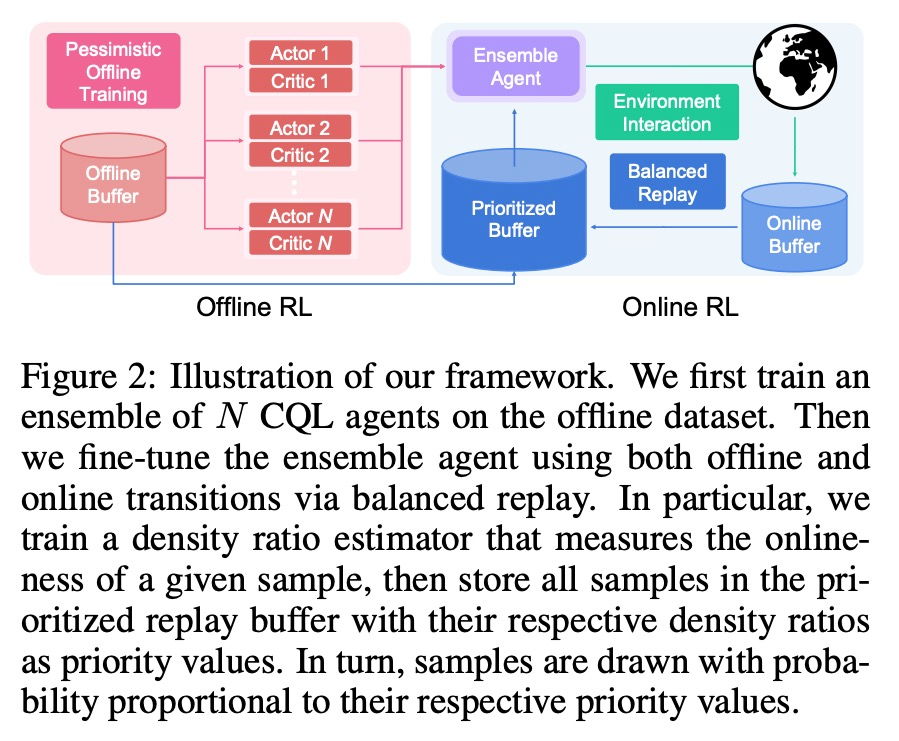
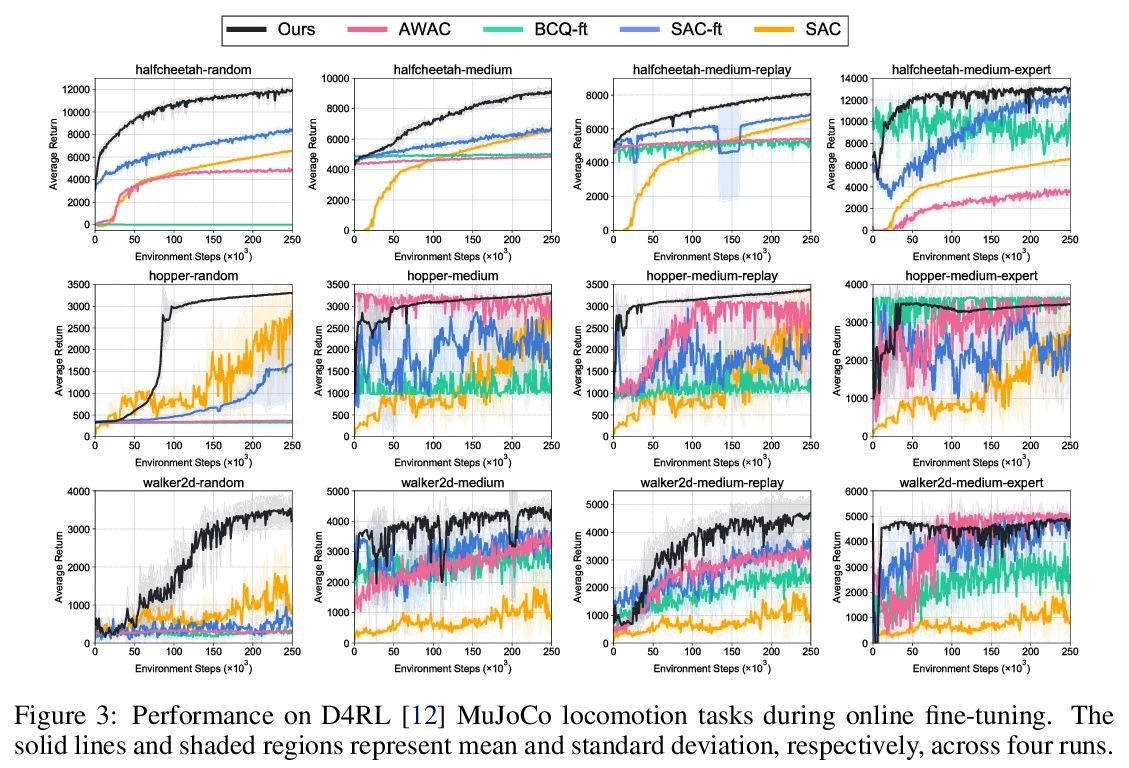
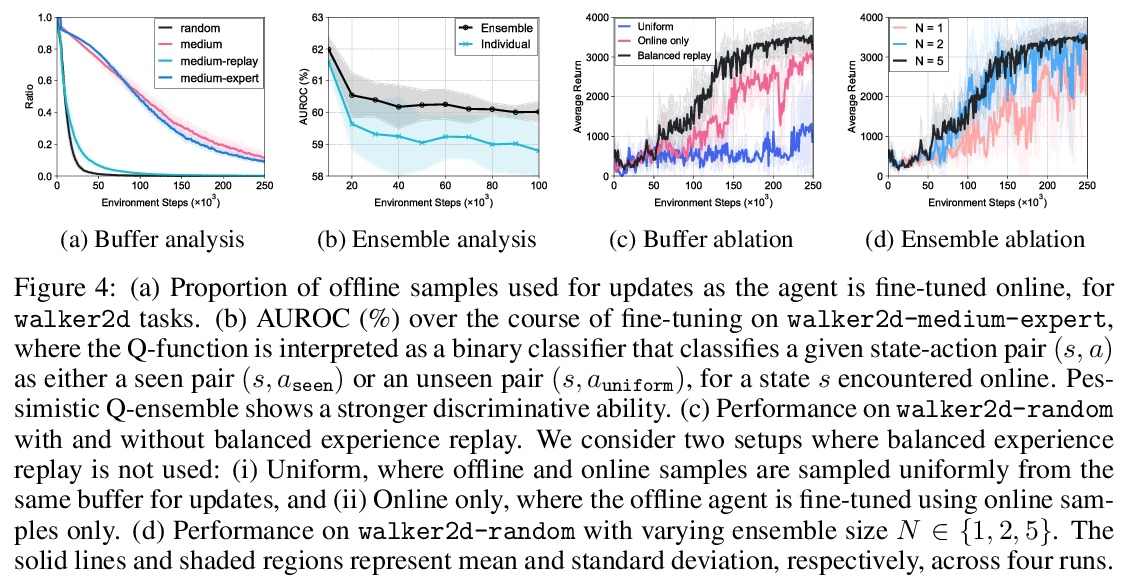
[RO] Offline-to-Online Reinforcement Learning via Balanced Replay and Pessimistic Q-Ensemble
基于平衡重放和悲观Q集成的离线-在线强化学习
S Lee, Y Seo, K Lee, P Abbeel, J Shin
[UC Berkeley & Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmYAWi2FY