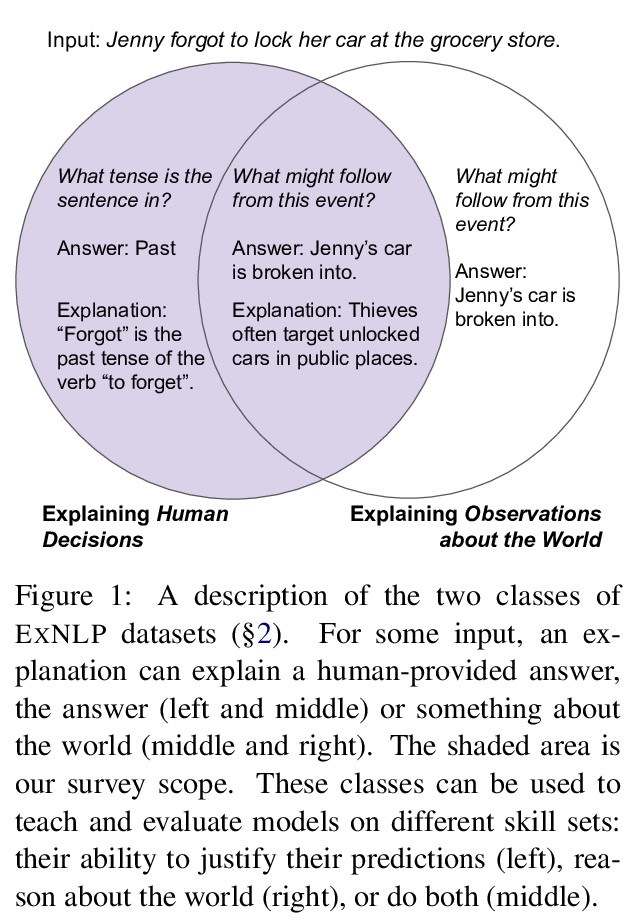
- 1、[CL] Teach Me to Explain: A Review of Datasets for Explainable NLP
- 2、[LG] Modern Koopman Theory for Dynamical Systems
- 3、[LG] Linear Transformers Are Secretly Fast Weight Memory Systems
- 4、[CV] Learning to identify image manipulations in scientific publications
- 5、[LG] E(n) Equivariant Graph Neural Networks
- [LG] Reinforcement Learning with Prototypical Representations
- [CL] When Attention Meets Fast Recurrence: Training Language Models with Reduced Compute
- [CL] Probing Classifiers: Promises, Shortcomings, and Alternatives
- [LG] Deep Policy Dynamic Programming for Vehicle Routing Problems
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[CL] Teach Me to Explain: A Review of Datasets for Explainable NLP
S Wiegreffe, A Marasović
[Georgia Institute of Technology & University of Washington]
教我解释:可解释NLP数据集综述。可解释NLP(EXNLP)越来越多地关注收集人工标注的解释。这些解释以三种方式用于下游:作为数据增强来提高预测任务性能,作为损失信号训练模型为其预测产生解释,以及作为评价模型生成的解释质量的手段。本文对可解释NLP研究的现有数据集进行了回顾,强调了数据收集中可能对下游建模产生影响的差异性,确定了三类最主要的解释(亮点、自由文本和结构化),整理了支持每种类型的文献,指出了到目前为止已经学到的,并给出了未来收集EXNLP数据集的建议。
Explainable NLP (ExNLP) has increasingly focused on collecting human-annotated explanations. These explanations are used downstream in three ways: as data augmentation to improve performance on a predictive task, as a loss signal to train models to produce explanations for their predictions, and as a means to evaluate the quality of model-generated explanations. In this review, we identify three predominant classes of explanations (highlights, free-text, and structured), organize the literature on annotating each type, point to what has been learned to date, and give recommendations for collecting ExNLP datasets in the future.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3XRclrWD
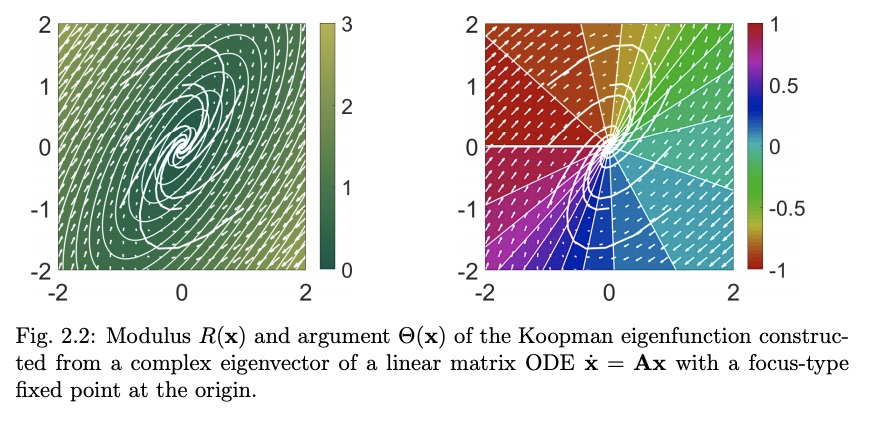
2、[LG] Modern Koopman Theory for Dynamical Systems
S L. Brunton, M Budišić, E Kaiser, J. N Kutz
[University of Washington & Clarkson University]
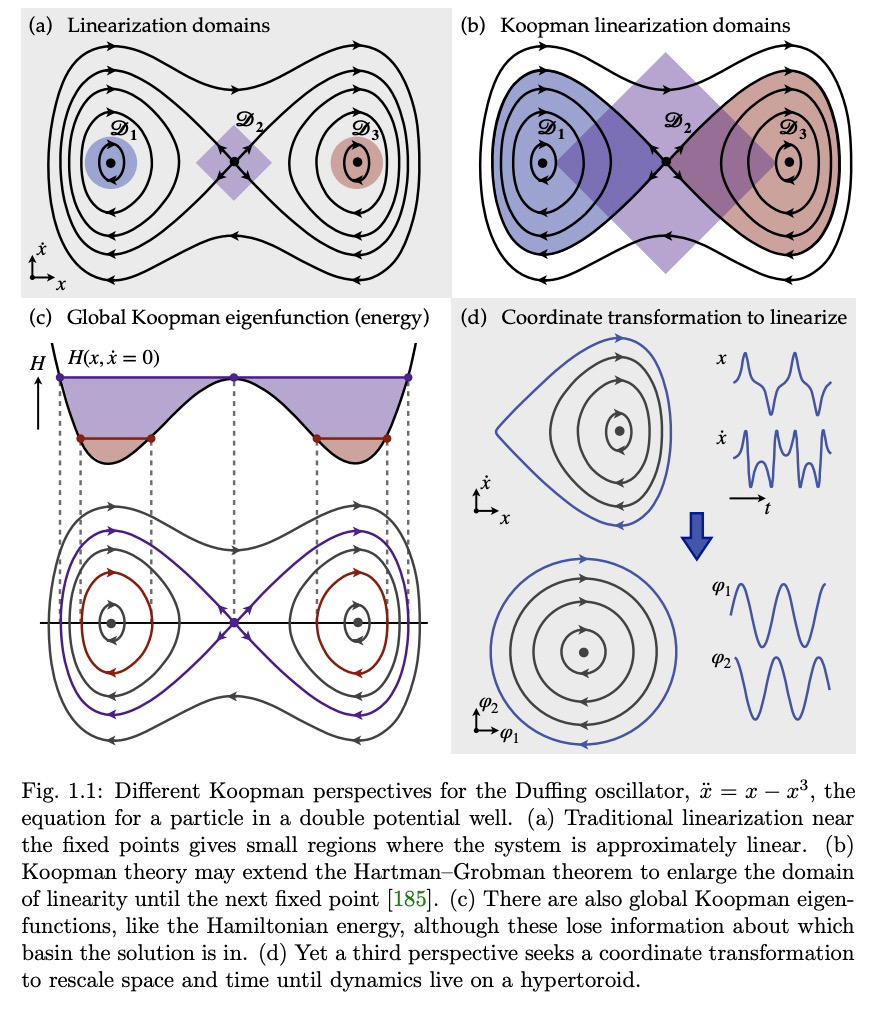
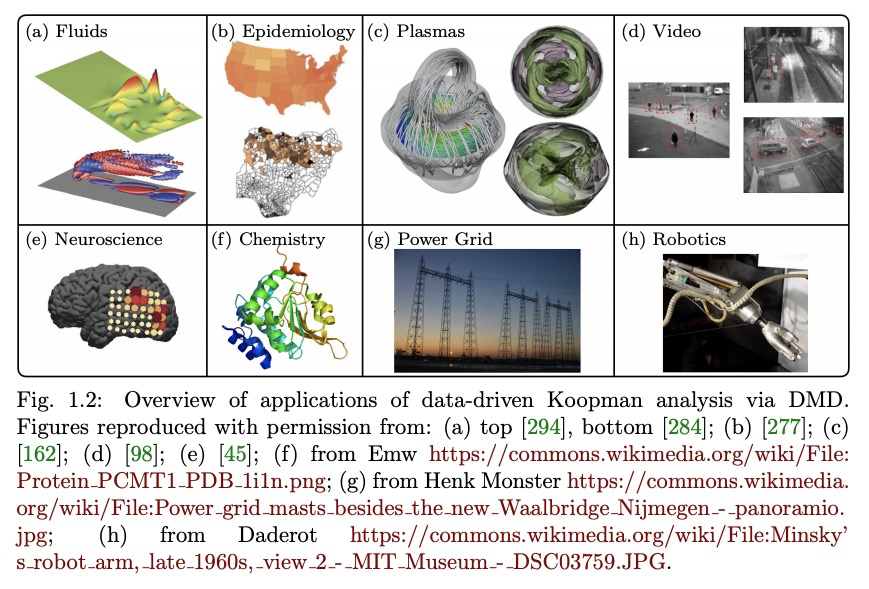
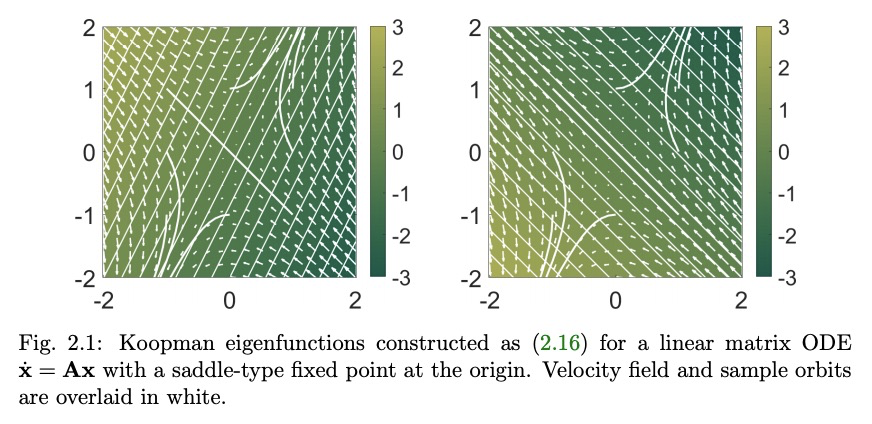
动力系统的现代Koopman理论。动力系统领域正在被现代计算和数据科学所产生的数学工具和算法所改变。第一原理推导和渐近还原正被在算子理论或概率框架中制定模型的数据驱动方法所取代。过去十年中,Koopman谱理论已经成为一种主流观点,其中非线性动力学用作用于系统所有可能的测量函数空间的无限维线性算子来表示。这种非线性动力学的线性表示法具有巨大潜力,可用为线性系统开发的标准方法来实现非线性系统的预测、估计和控制。然而,获得有限维坐标系和嵌入,使动力学看起来近似线性,仍然是一个核心的开放挑战。Koopman分析的成功主要得益于三个关键因素:1)存在严格的理论将其与动力系统的经典几何方法联系起来,2)该方法是以测量为基础制定的,使其成为利用大数据和机器学习技术的理想选择,3)简单而强大的数值算法,如动态模式分解(DMD),已经被开发和扩展,以将Koopman理论还原到实际应用中。这篇综述中,提供了现代Koopman算子理论的概述,描述了最近的理论和算法的发展,并强调了这些具有不同应用范围的方法。讨论了在快速增长的机器学习领域的关键进展和挑战,这些进展和挑战可能会推动未来的发展,并极大地改变动力系统的理论面貌。
The field of dynamical systems is being transformed by the mathematical tools and algorithms emerging from modern computing and data science. First-principles derivations and asymptotic reductions are giving way to data-driven approaches that formulate models in operator theoretic or probabilistic frameworks. Koopman spectral theory has emerged as a dominant perspective over the past decade, in which nonlinear dynamics are represented in terms of an infinite-dimensional linear operator acting on the space of all possible measurement functions of the system. This linear representation of nonlinear dynamics has tremendous potential to enable the prediction, estimation, and control of nonlinear systems with standard textbook methods developed for linear systems. However, obtaining finite-dimensional coordinate systems and embeddings in which the dynamics appear approximately linear remains a central open challenge. The success of Koopman analysis is due primarily to three key factors: 1) there exists rigorous theory connecting it to classical geometric approaches for dynamical systems, 2) the approach is formulated in terms of measurements, making it ideal for leveraging big-data and machine learning techniques, and 3) simple, yet powerful numerical algorithms, such as the dynamic mode decomposition (DMD), have been developed and extended to reduce Koopman theory to practice in real-world applications. In this review, we provide an overview of modern Koopman operator theory, describing recent theoretical and algorithmic developments and highlighting these methods with a diverse range of applications. We also discuss key advances and challenges in the rapidly growing field of machine learning that are likely to drive future developments and significantly transform the theoretical landscape of dynamical systems.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3Y1opYpt
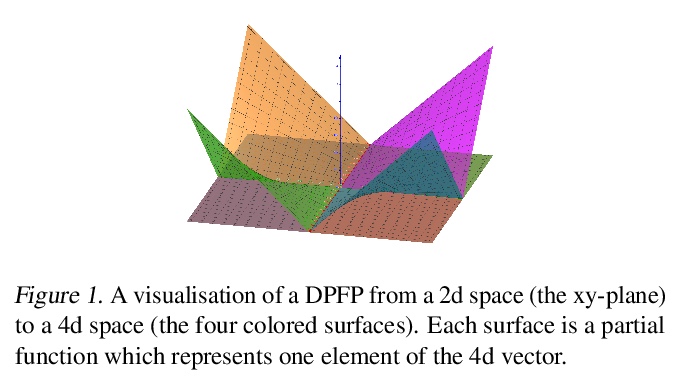
3、[LG] Linear Transformers Are Secretly Fast Weight Memory Systems
I Schlag, K Irie, J Schmidhuber
[The Swiss AI Lab IDSIA]
线性Transformer与快速权重记忆系统等价。展示了线性化自注意力机制和快速权重记忆的形式等价性,推断出线性化softmax注意力变体的记忆容量限制。在有限记忆下,快速权重记忆模型的一个理想行为是操纵记忆内容,并与之动态交互。受之前关于快速权重的工作的启发,提出用一种替代规则来替换更新规则,来动态编辑记忆。提出一个新的核函数来线性化注意力,平衡了简单性和有效性。在合成检索问题以及标准的机器翻译和语言建模任务上进行的实验,表明了该方法的优势。
We show the formal equivalence of linearised self-attention mechanisms and fast weight memories from the early ‘90s. From this observation we infer a memory capacity limitation of recent linearised softmax attention variants. With finite memory, a desirable behaviour of fast weight memory models is to manipulate the contents of memory and dynamically interact with it. Inspired by previous work on fast weights, we propose to replace the update rule with an alternative rule yielding such behaviour. We also propose a new kernel function to linearise attention, balancing simplicity and effectiveness. We conduct experiments on synthetic retrieval problems as well as standard machine translation and language modelling tasks which demonstrate the benefits of our methods.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3Y5MbHwY
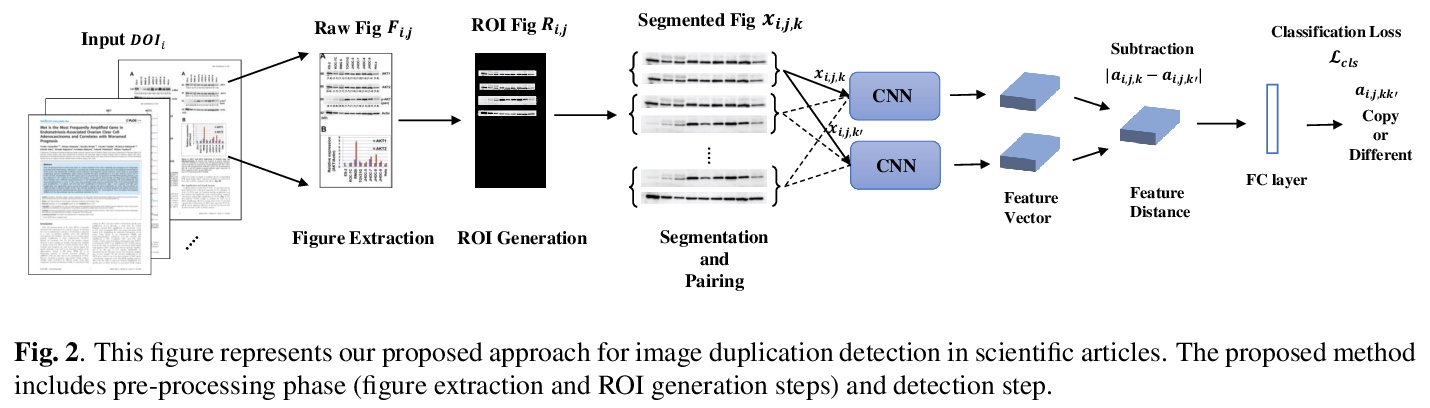
4、[CV] Learning to identify image manipulations in scientific publications
G Mazaheri, K U Avila, A K. Roy-Chowdhury
[University of California, Riverside]
科研论文图片操纵的识别学习。在图像提取、兴趣区域生成和利用Siamese网络进行复制粘贴检测三个步骤的基础上,提出一种检测科研论文中图像重复的方法,一个结合图像处理和深度学习方法的框架,将文章中的图像分类为重复的或未重复的。该框架强调了图像预处理步骤的重要性,以便在应用深度学习方法之前准备适当的数据集。实验表明,该方法检测重复图像的准确率达到90%,与其他操纵检测方法相比,检测准确率提高了13%∼。
Adherence to scientific community standards ensures objectivity, clarity, reproducibility, and helps prevent bias, fabrication, falsification, and plagiarism. To help scientific integrity officers and journal/publisher reviewers monitor if researchers stick with these standards, it is important to have a solid procedure to detect duplication as one of the most frequent types of manipulation in scientific papers. Images in scientific papers are used to support the experimental description and the discussion of the findings. Therefore, in this work we focus on detecting the duplications in images as one of the most important parts of a scientific paper. We propose a framework that combines image processing and deep learning methods to classify images in the articles as duplicated or unduplicated ones. We show that our method leads to a 90% accuracy rate of detecting duplicated images, a ~ 13% improvement in detection accuracy in comparison to other manipulation detection methods. We also show how effective the pre-processing steps are by comparing our method to other state-of-art manipulation detectors which lack these steps.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3Y9yymS9

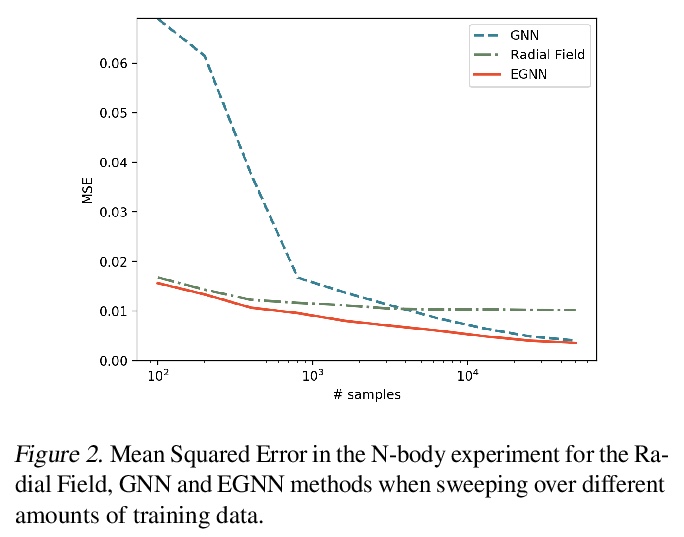
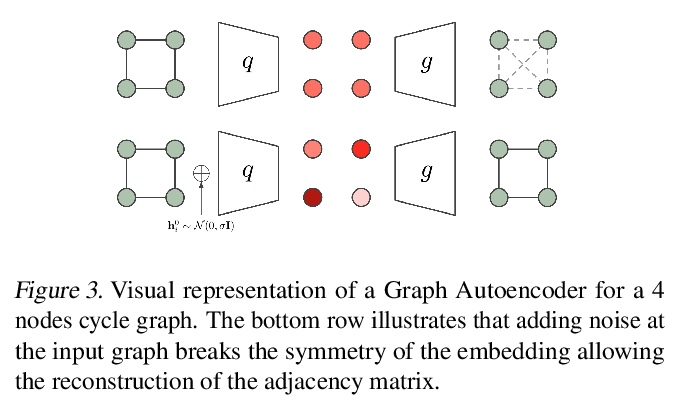
5、[LG] E(n) Equivariant Graph Neural Networks
V G Satorras, E Hoogeboom, M Welling
[University of Amsterdam]
E(n)等变图神经网络。提出一种新模型,学习对旋转、平移、反射和换元等价的图神经网络,称为E(n)等变图神经网络(EGNNs),它计算效率高,易于实现,并且在很多任务上比当前最先进的架构有显著改进。与现有方法相比,该模型不需要在中间层进行计算昂贵的高阶表示,同时仍可获得具有竞争力或更好的性能。此外,现有方法仅限于3D空间上的等价性,而该模型很容易扩展到高维空间。通过实验证明了该方法在动态系统建模、图自动编码器中的表示学习和预测分子特性上的有效性。
This paper introduces a new model to learn graph neural networks equivariant to rotations, translations, reflections and permutations called E(n)-Equivariant Graph Neural Networks (EGNNs). In contrast with existing methods, our work does not require computationally expensive higher-order representations in intermediate layers while it still achieves competitive or better performance. In addition, whereas existing methods are limited to equivariance on 3 dimensional spaces, our model is easily scaled to higher-dimensional spaces. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on dynamical systems modelling, representation learning in graph autoencoders and predicting molecular properties.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3Ydczeuj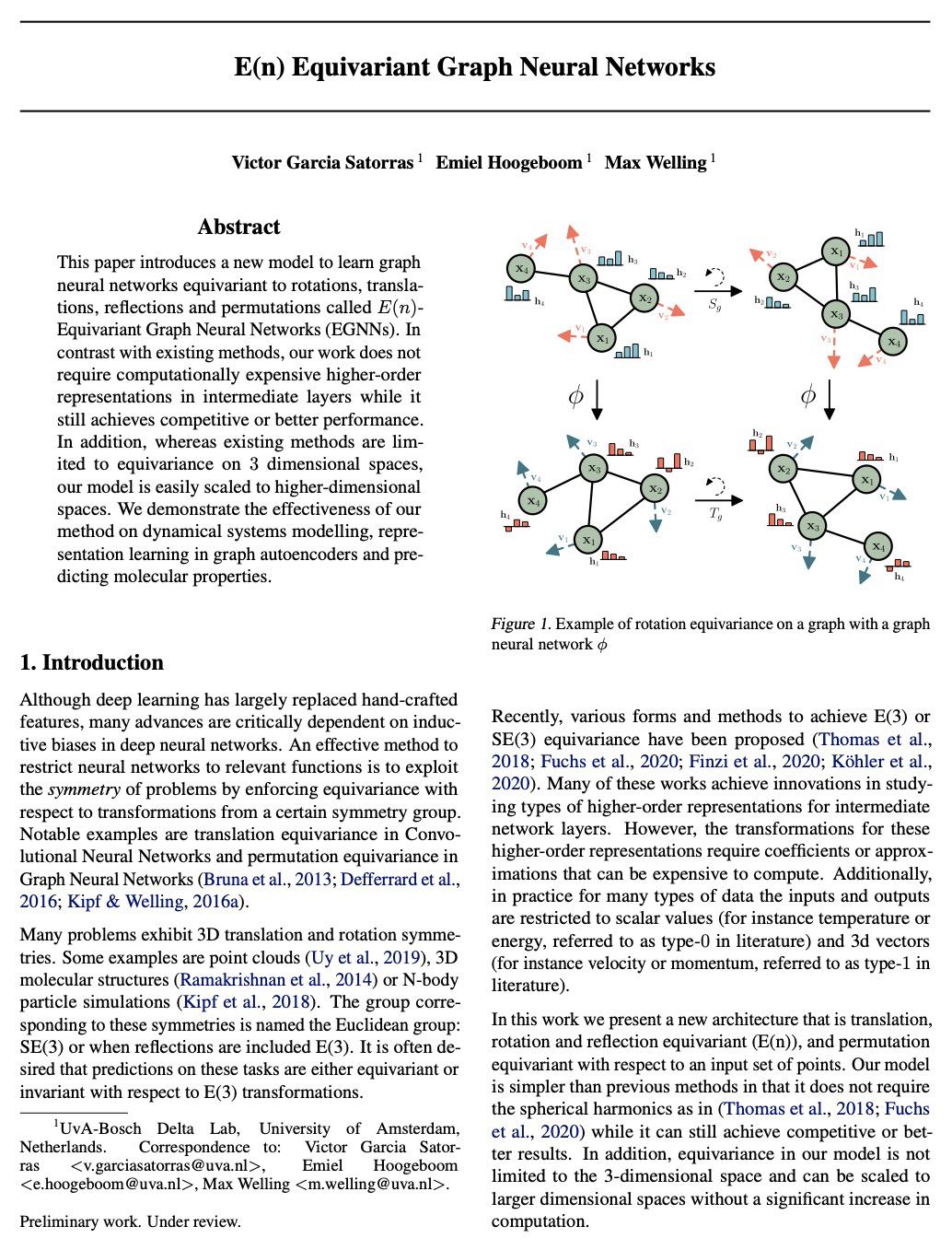
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
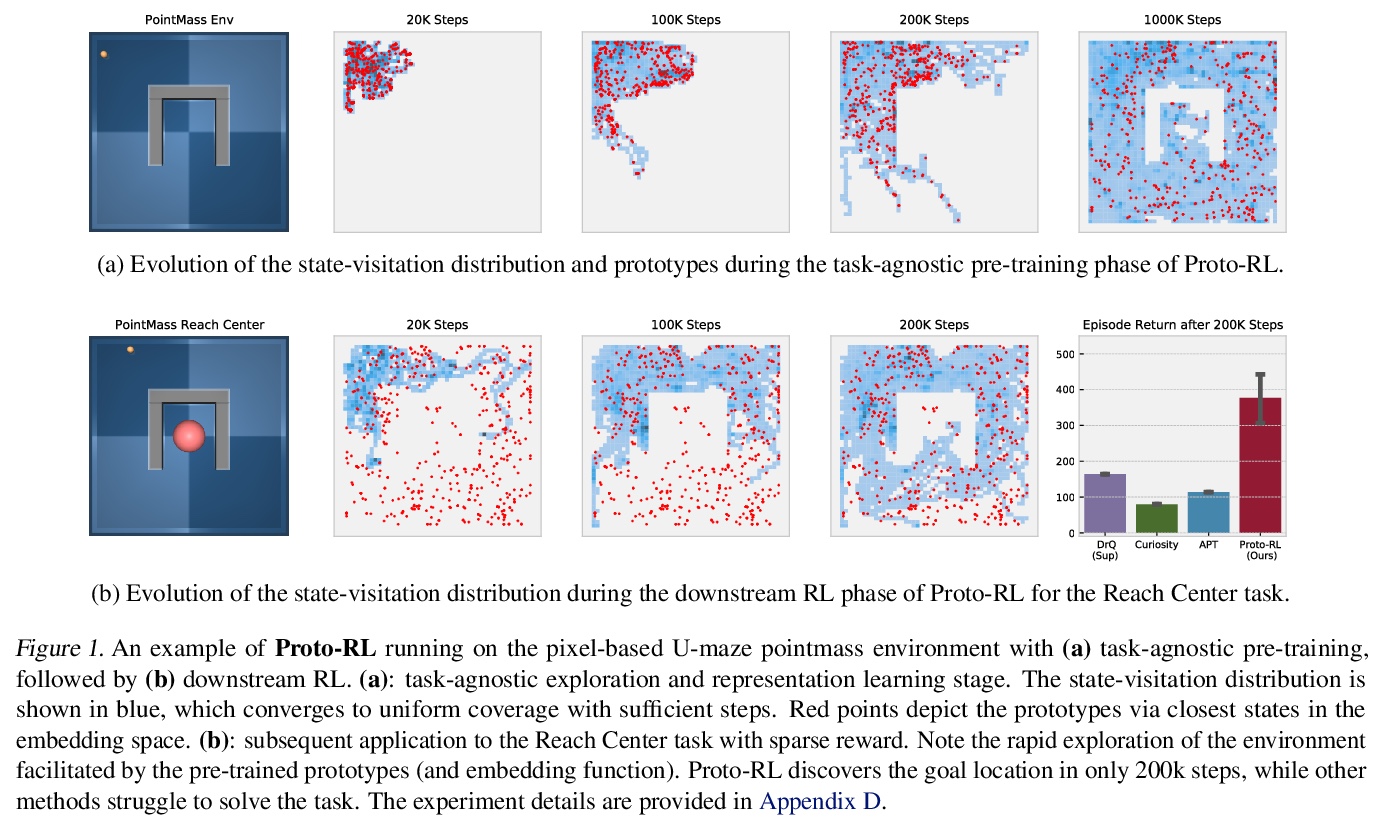
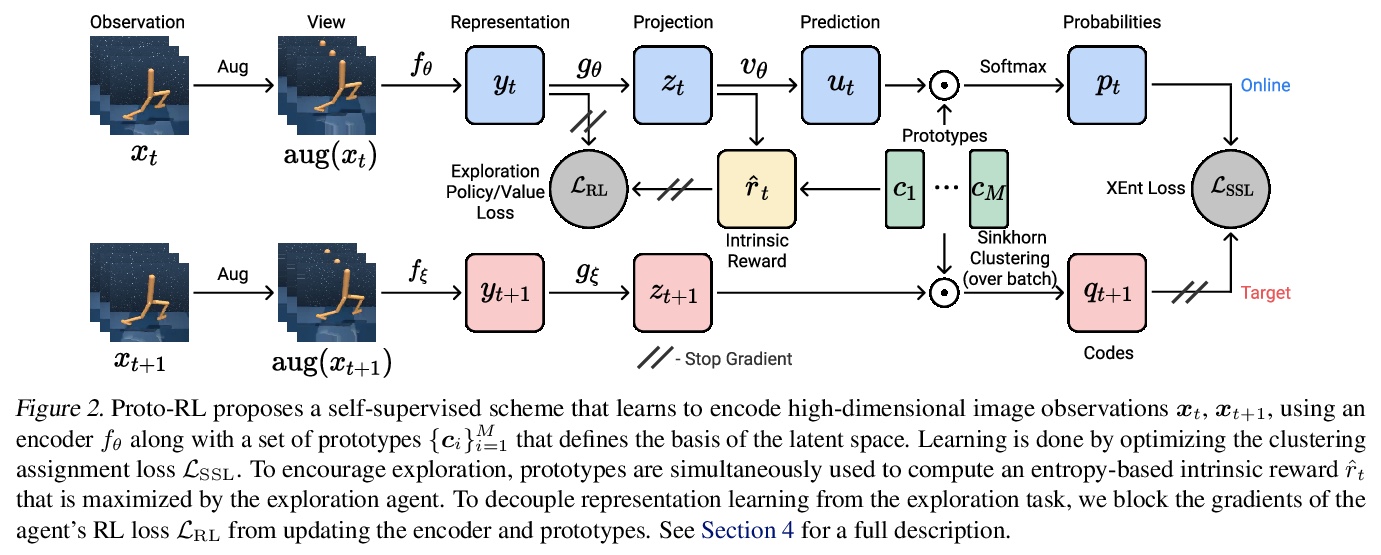
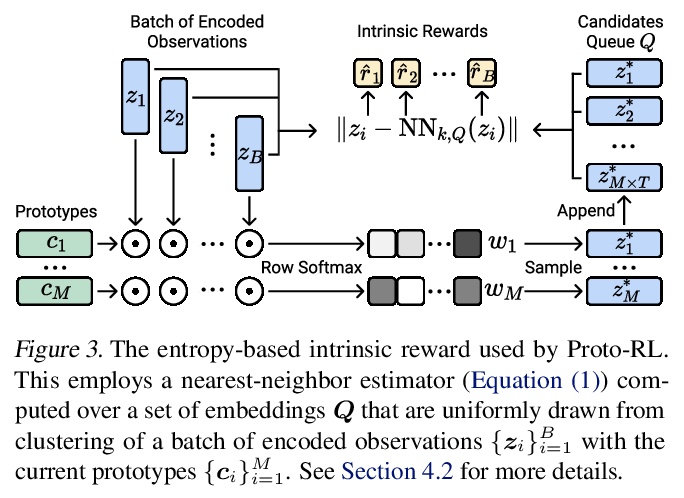
[LG] Reinforcement Learning with Prototypical Representations
原型表示强化学习
D Yarats, R Fergus, A Lazaric, L Pinto
[New York University & Facebook AI Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3Yhb5cvV
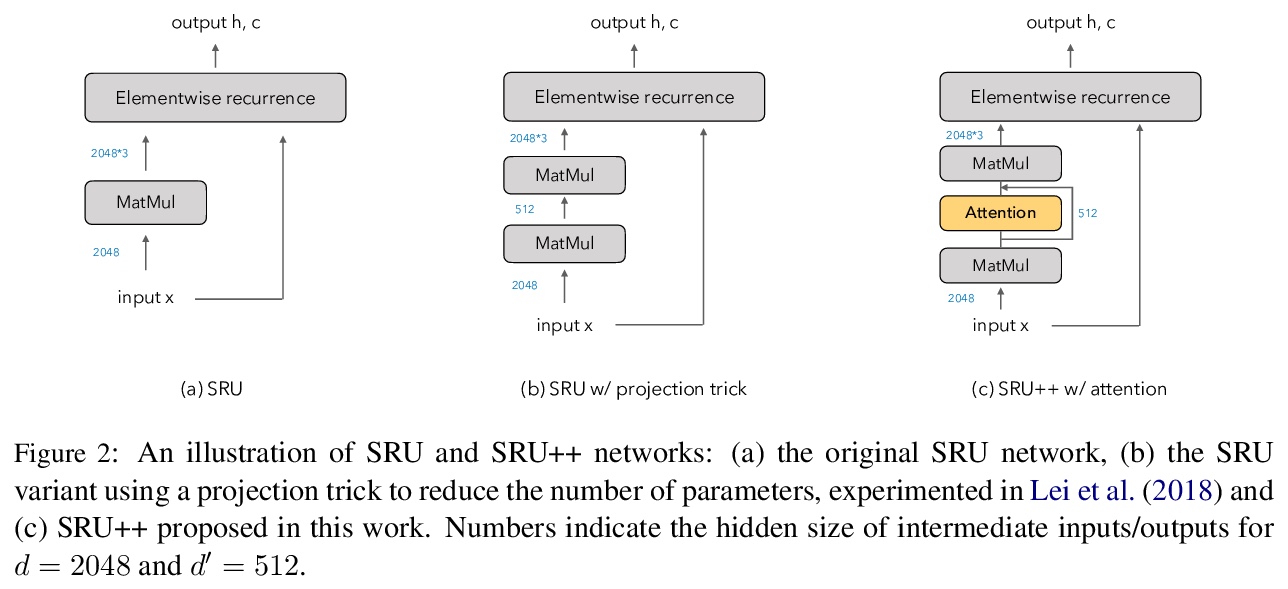
[CL] When Attention Meets Fast Recurrence: Training Language Models with Reduced Compute
注意力与快速循环:语言模型训练的计算简化
T Lei
[ASAPP, Inc]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3YizAoOl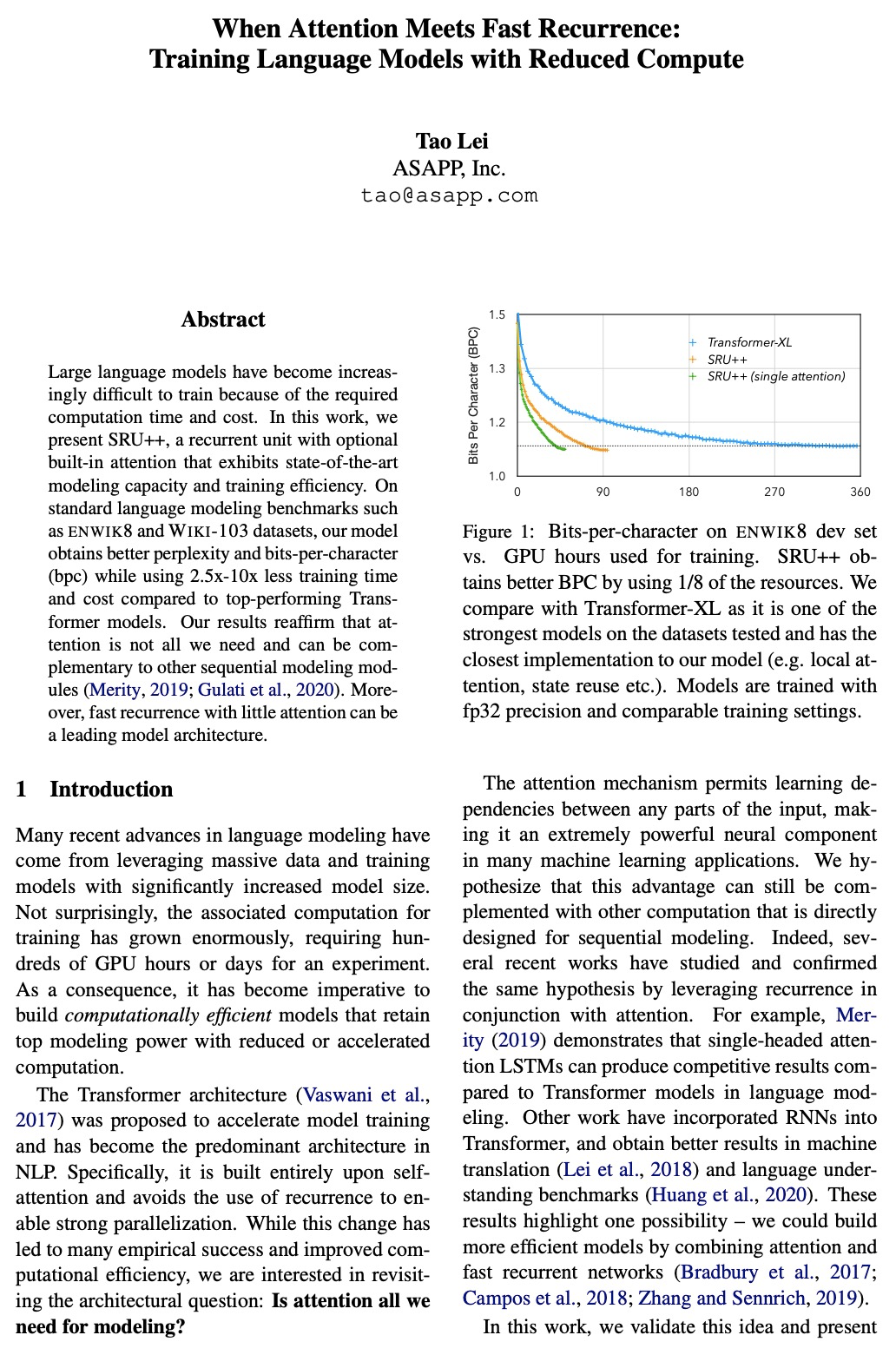
[CL] Probing Classifiers: Promises, Shortcomings, and Alternatives
探针分类器综述:承诺、缺点和替代方案
Y Belinkov
[Technion – Israel Institute of Technology]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3YlgyHoE
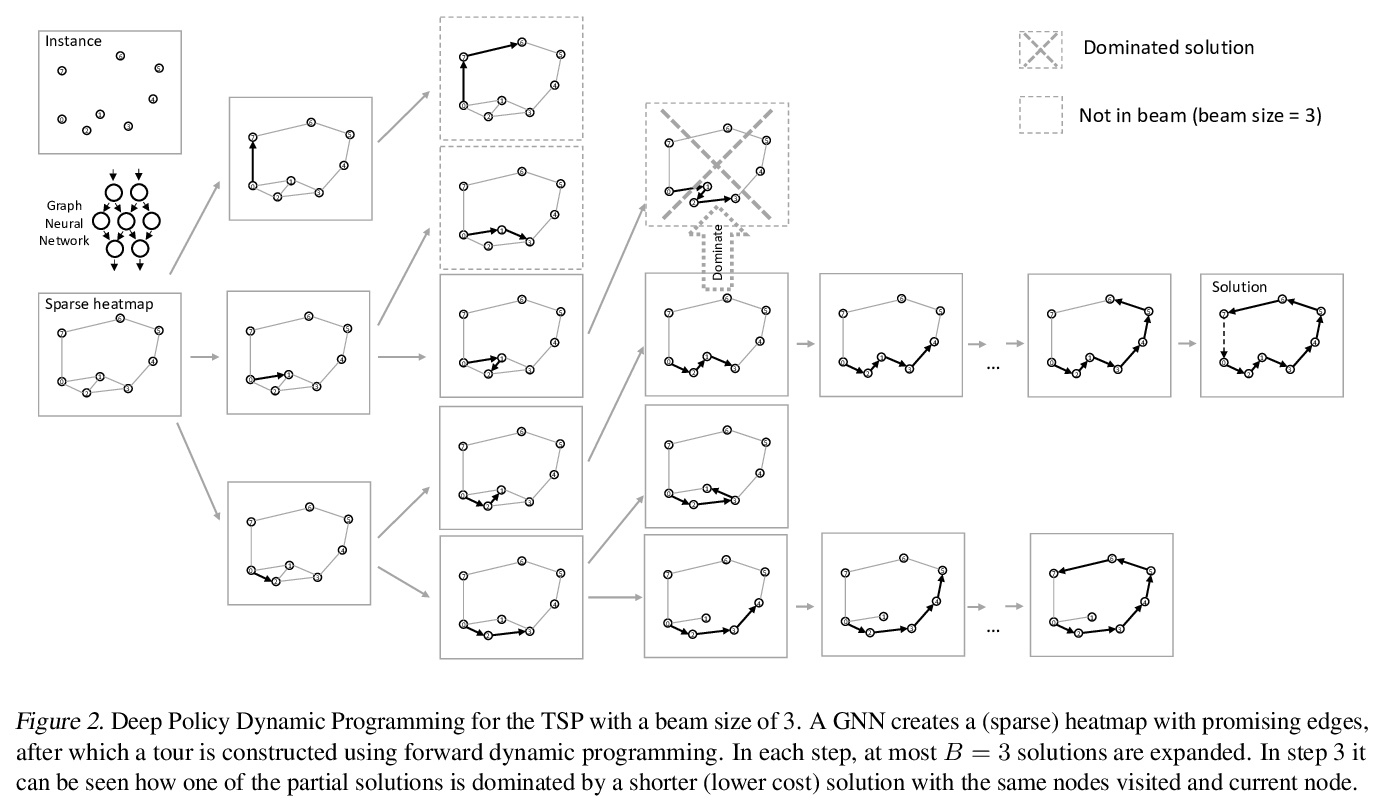
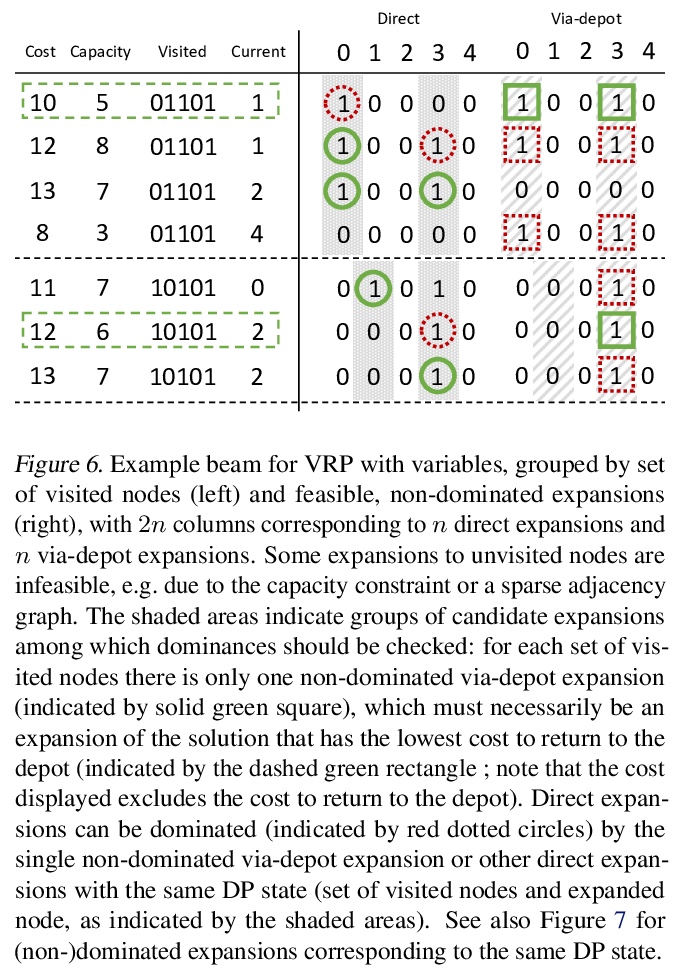
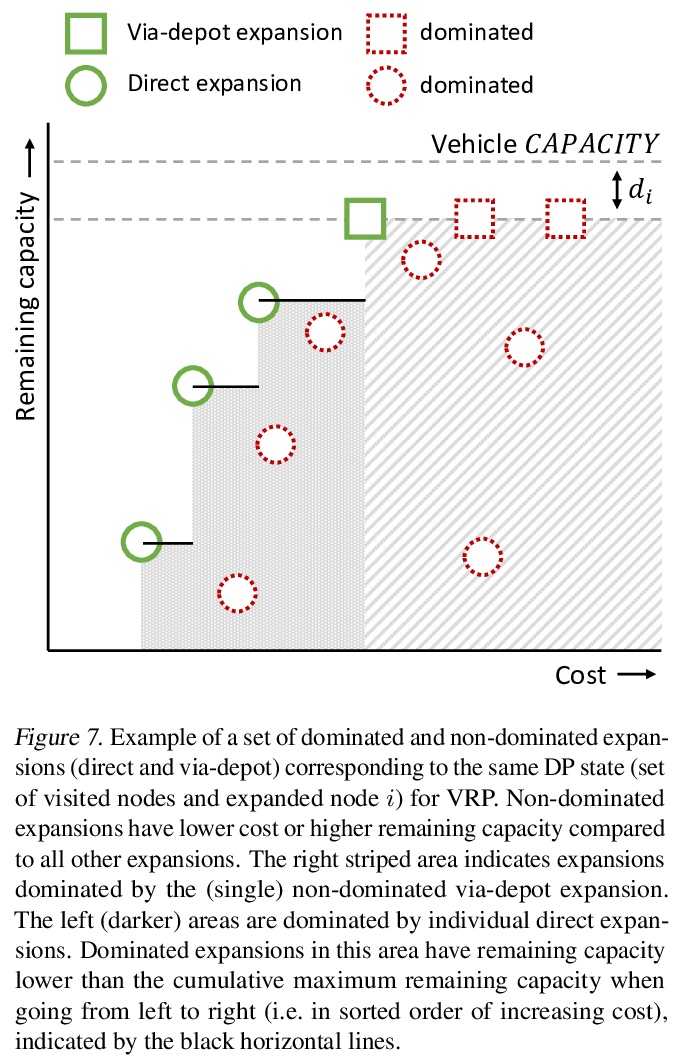
[LG] Deep Policy Dynamic Programming for Vehicle Routing Problems
车辆路径问题深度策略动态规划
W Kool, H v Hoof, J Gromicho, M Welling
[University of Amsterdam]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K3YmMe0mG