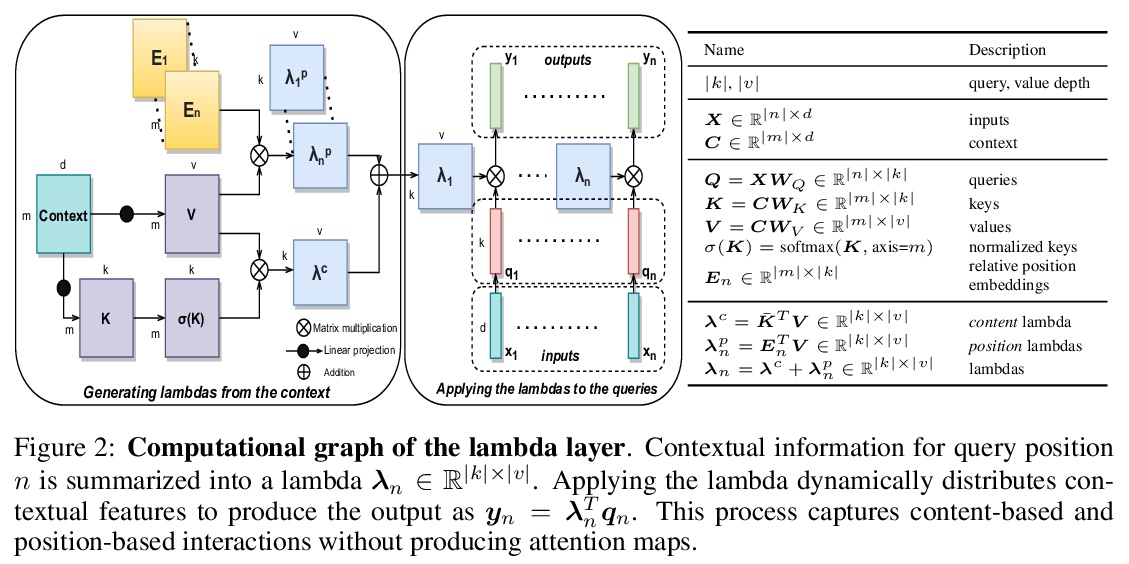
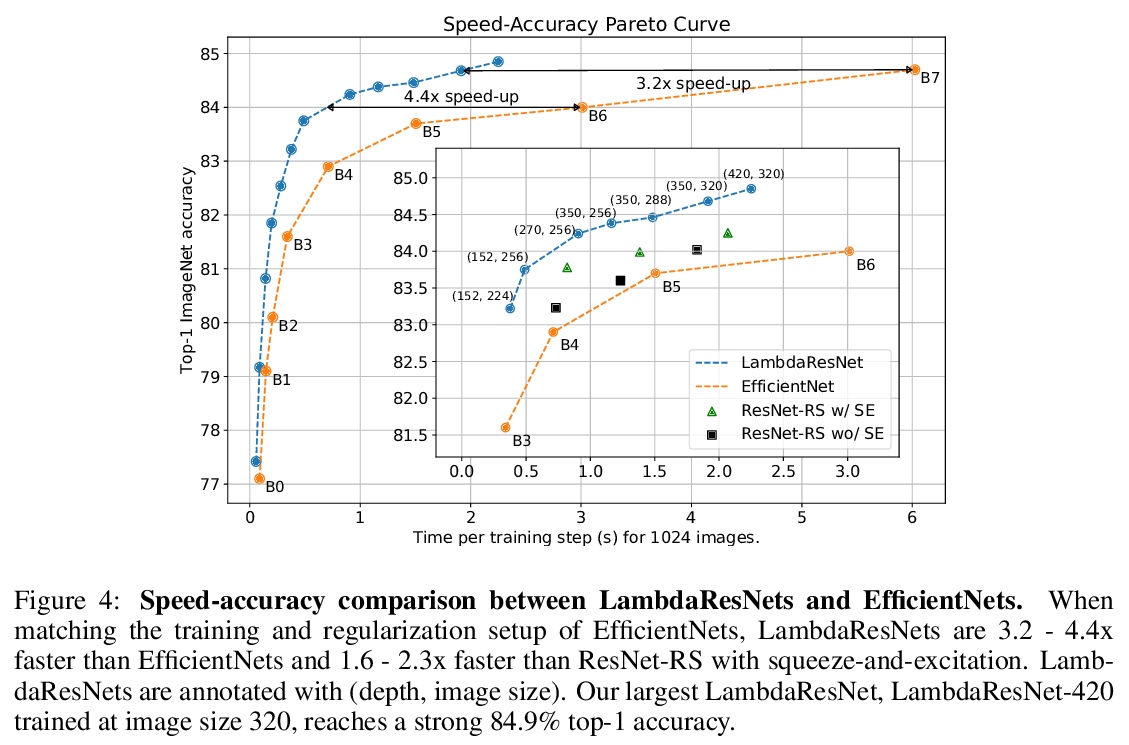
- 1、[CV] LambdaNetworks: Modeling Long-Range Interactions Without Attention
- 2、[LG] Intermediate Layer Optimization for Inverse Problems using Deep Generative Models
- 3、[LG] Bayesian Neural Network Priors Revisited
- 4、[CV] Mobile Computational Photography: A Tour
- 5、[LG] Online hyperparameter optimization by real-time recurrent learning
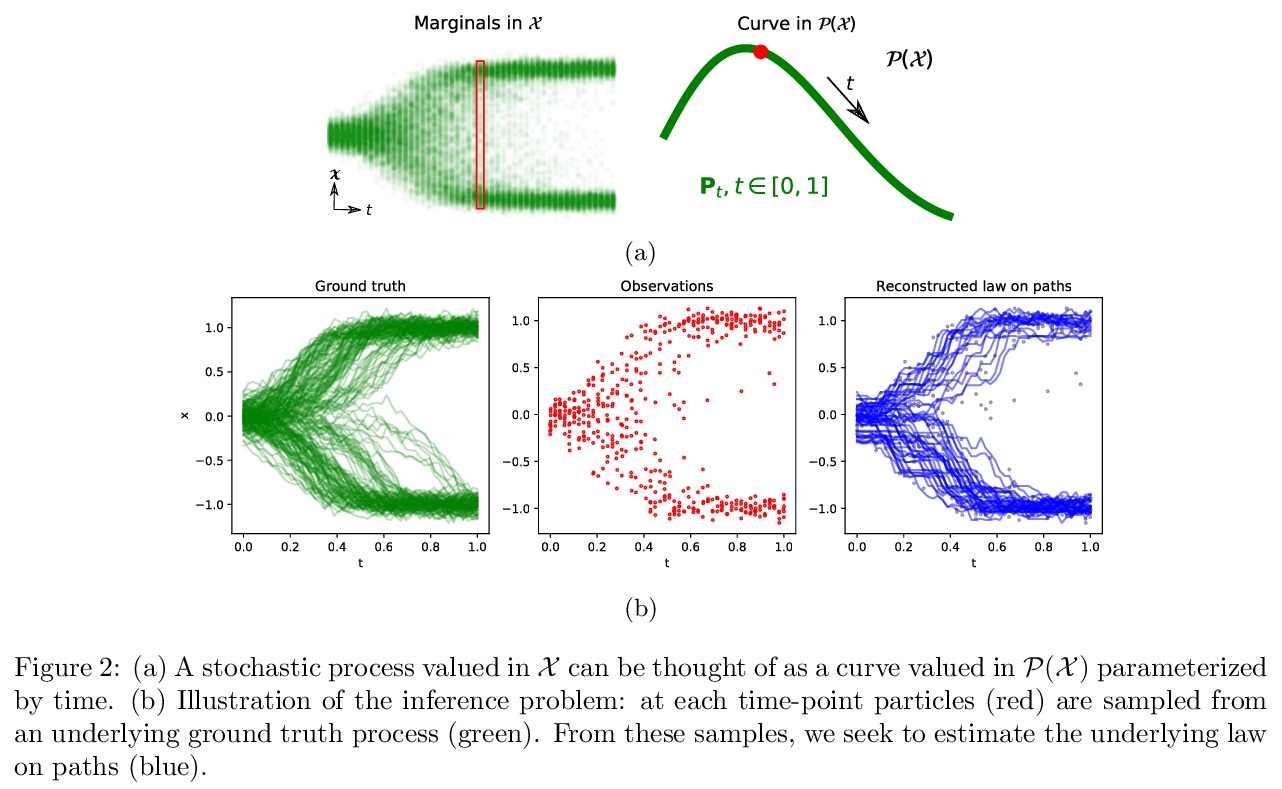
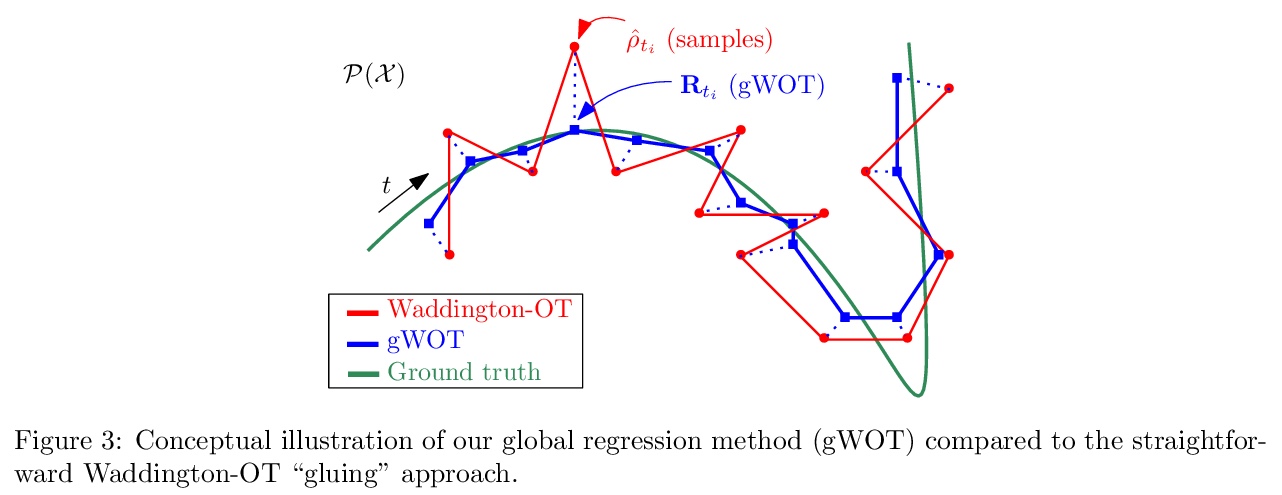
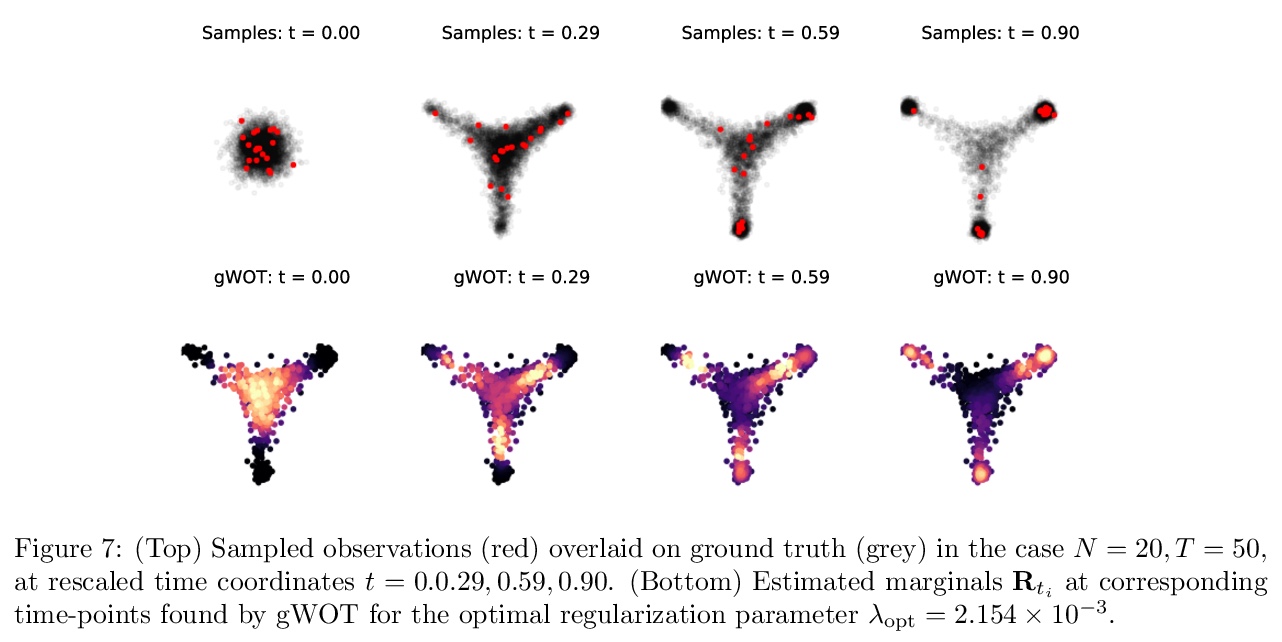
- [LG] Towards a mathematical theory of trajectory inference
- [LG] HYDRA: Hypergradient Data Relevance Analysis for Interpreting Deep Neural Networks
- [CV] Galaxy Zoo DECaLS: Detailed Visual Morphology Measurements from Volunteers and Deep Learning for 314,000 Galaxies
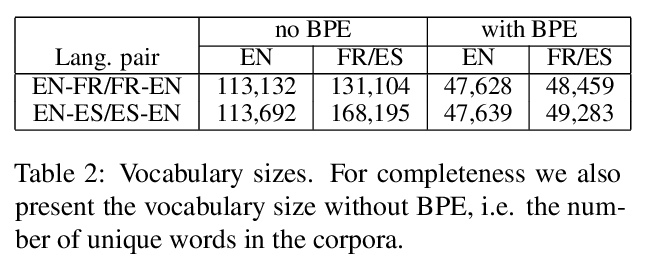
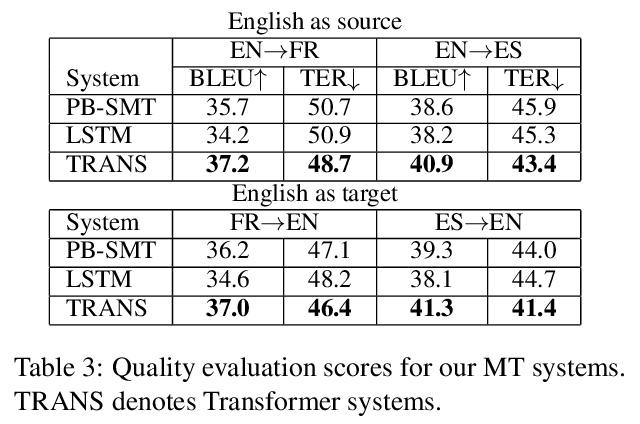
- [CL] Machine Translationese: Effects of Algorithmic Bias on Linguistic Complexity in Machine Translation
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[CV] LambdaNetworks: Modeling Long-Range Interactions Without Attention
I Bello
[Google Research]
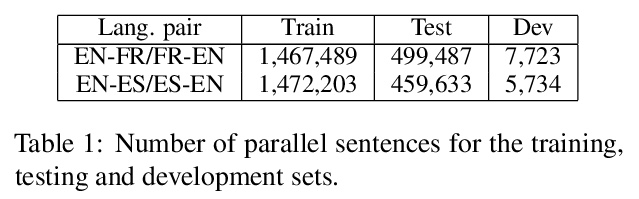
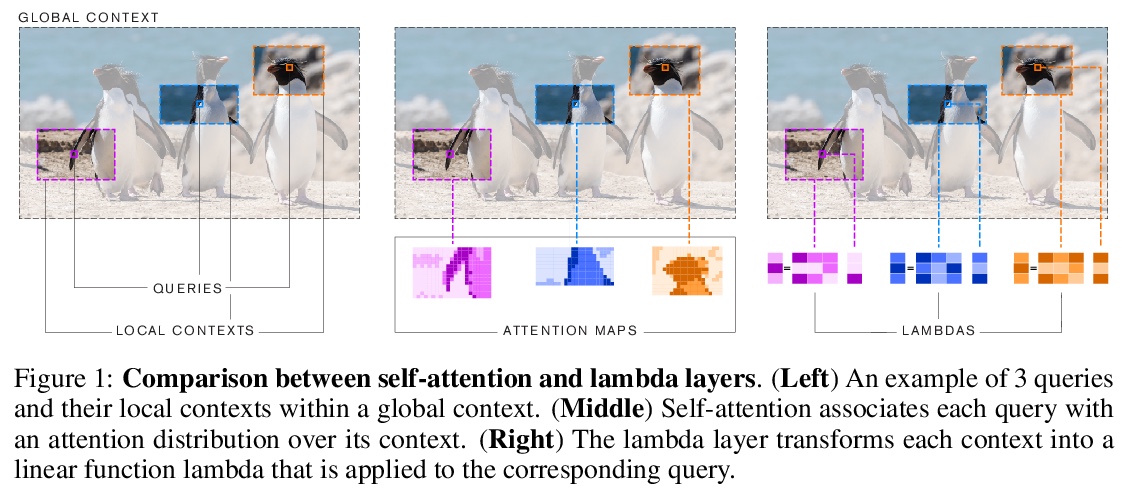
LambdaNetworks:非注意力长程交互建模。提出自注意力的替代框架lambda层,用于捕捉输入和结构化上下文信息(如被其他像素包围的像素)之间的长程交互。lambda层通过将可用的上下文转化为线性函数(称为lambdas),并将这些线性函数分别应用于每个输入来捕捉这种交互,可在无需注意力图的情况下,模拟基于内容和位置的交互,提供通道、空间和线性注意力的统一视角。设计了LambdaResNets,跨越不同尺度的混合架构系列,大大改善了图像分类模型的速度-精度权衡。LambdaResNets在ImageNet上达到了优秀的精度,同时比现代机器学习加速器上流行的EfficientNets快了3.2 4.4倍。
We present lambda layers — an alternative framework to self-attention — for capturing long-range interactions between an input and structured contextual information (e.g. a pixel surrounded by other pixels). Lambda layers capture such interactions by transforming available contexts into linear functions, termed lambdas, and applying these linear functions to each input separately. Similar to linear attention, lambda layers bypass expensive attention maps, but in contrast, they model both content and position-based interactions which enables their application to large structured inputs such as images. The resulting neural network architectures, LambdaNetworks, significantly outperform their convolutional and attentional counterparts on ImageNet classification, COCO object detection and COCO instance segmentation, while being more computationally efficient. Additionally, we design LambdaResNets, a family of hybrid architectures across different scales, that considerably improves the speed-accuracy tradeoff of image classification models. LambdaResNets reach excellent accuracies on ImageNet while being 3.2 - 4.4x faster than the popular EfficientNets on modern machine learning accelerators. When training with an additional 130M pseudo-labeled images, LambdaResNets achieve up to a 9.5x speed-up over the corresponding EfficientNet checkpoints.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K2TOWlAEw
2、[LG] Intermediate Layer Optimization for Inverse Problems using Deep Generative Models
G Daras, J Dean, A Jalal, A G. Dimakis
[The University of Texas at Austin]
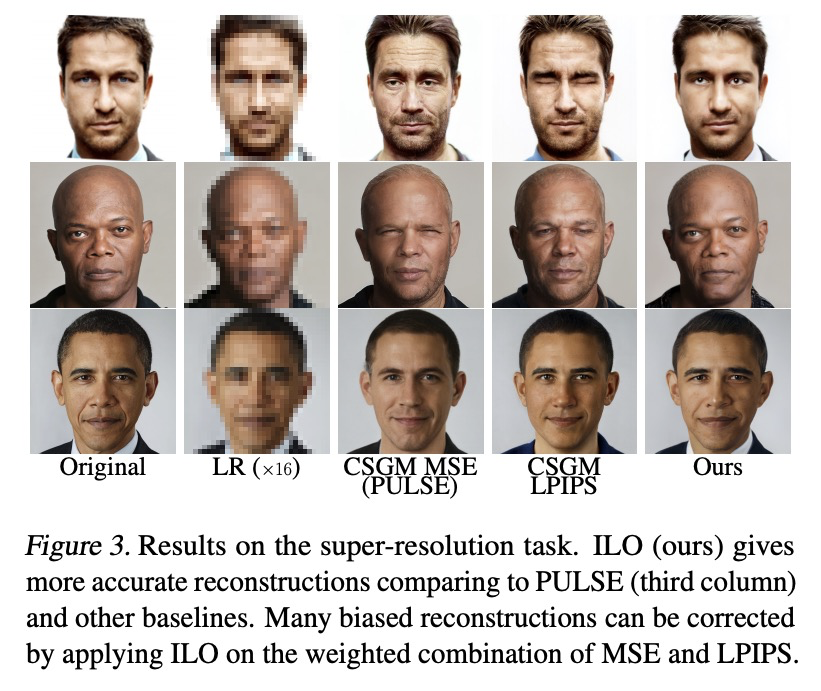
基于深度生成模型的逆向问题中间层优化。提出中间层优化(ILO),一种新型的优化算法,通过优化不同的中间层来扩大生成器范围。实证表明,该方法在包括补全、去噪、超分辨率和压缩传感在内的广泛的逆向问题上优于StyleGAN-2和PULSE中引入的最先进方法。
We propose Intermediate Layer Optimization (ILO), a novel optimization algorithm for solving inverse problems with deep generative models. Instead of optimizing only over the initial latent code, we progressively change the input layer obtaining successively more expressive generators. To explore the higher dimensional spaces, our method searches for latent codes that lie within a small > l1 ball around the manifold induced by the previous layer. Our theoretical analysis shows that by keeping the radius of the ball relatively small, we can improve the established error bound for compressed sensing with deep generative models. We empirically show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods introduced in StyleGAN-2 and PULSE for a wide range of inverse problems including inpainting, denoising, super-resolution and compressed sensing.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K2TUTveAb



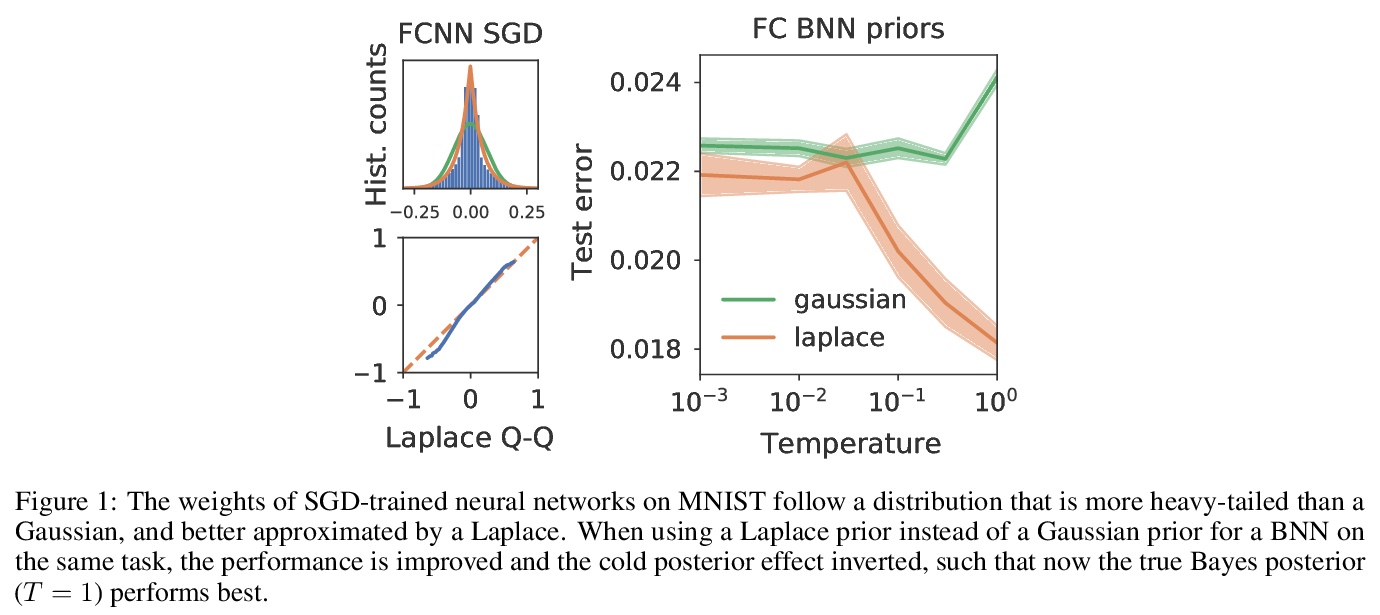
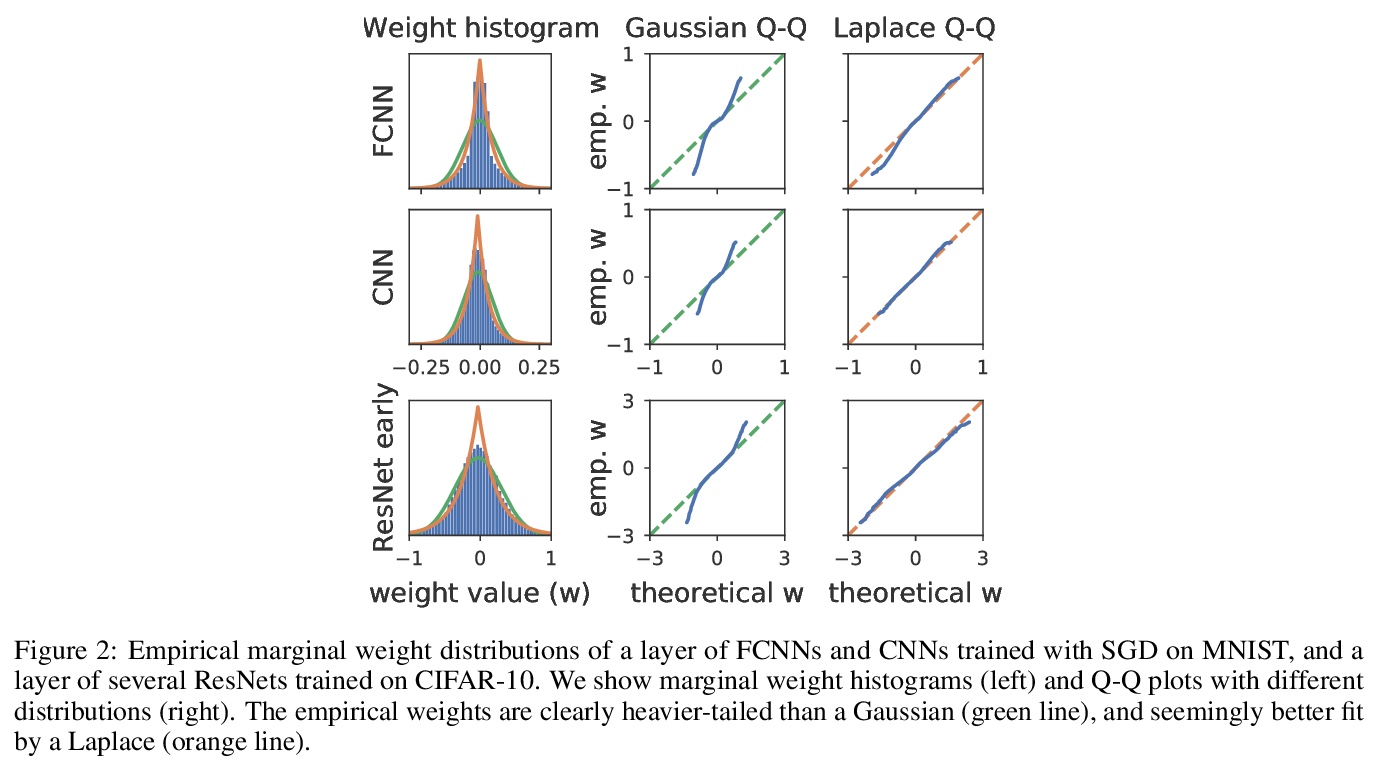
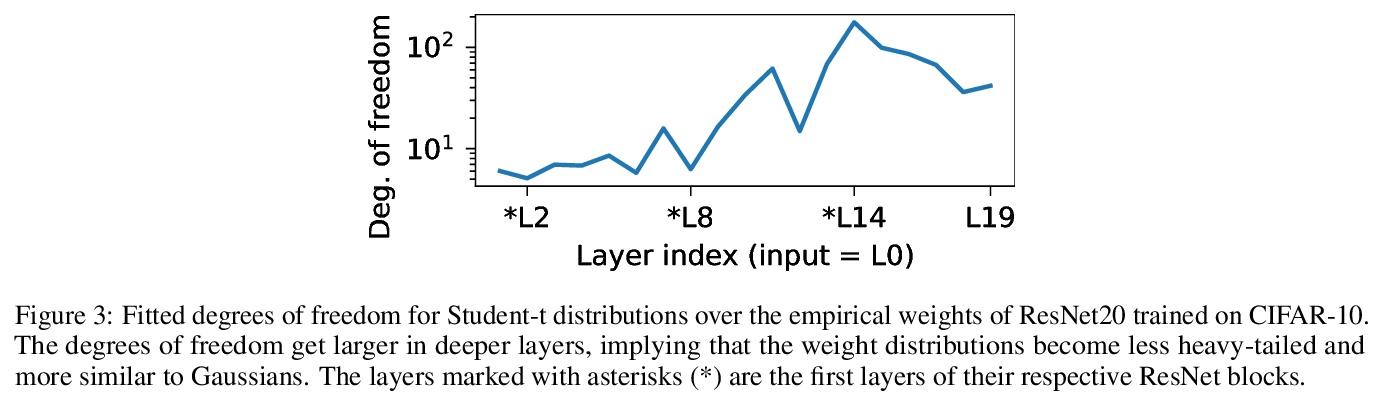
3、[LG] Bayesian Neural Network Priors Revisited
V Fortuin, A Garriga-Alonso, F Wenzel, G Rätsch, R Turner, M v d Wilk, L Aitchison
[ETH Zurich & University of Cambridge & Humboldt University of Berlin & Imperial College London]
贝叶斯神经网络先验的反思。研究了用SGD训练的不同网络中神经网络权重的汇总统计。发现全连接网络(FCNN)显示重尾权重分布,而卷积网络(CNN)权重显示出强烈的空间相关性。提出一种新的经验方法,来设计适合现代BNN架构的先验,可提高各种图像分类数据集的性能,还可减轻FCNN中的冷后效应。
Isotropic Gaussian priors are the de facto standard for modern Bayesian neural network inference. However, such simplistic priors are unlikely to either accurately reflect our true beliefs about the weight distributions, or to give optimal performance. We study summary statistics of neural network weights in different networks trained using SGD. We find that fully connected networks (FCNNs) display heavy-tailed weight distributions, while convolutional neural network (CNN) weights display strong spatial correlations. Building these observations into the respective priors leads to improved performance on a variety of image classification datasets. Moreover, we find that these priors also mitigate the cold posterior effect in FCNNs, while in CNNs we see strong improvements at all temperatures, and hence no reduction in the cold posterior effect.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K2TYTDxHQ

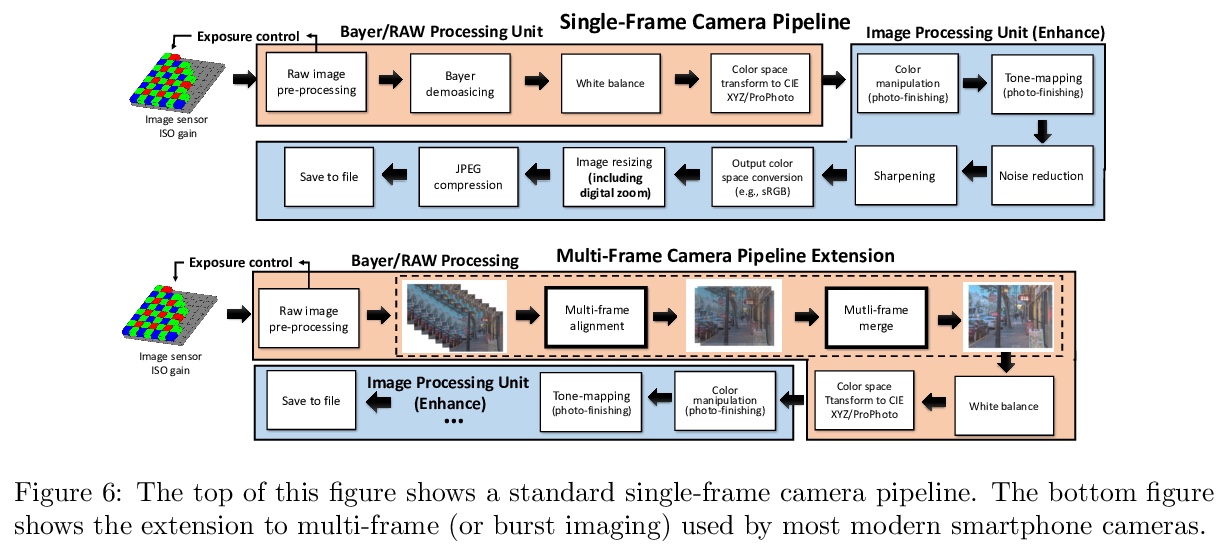
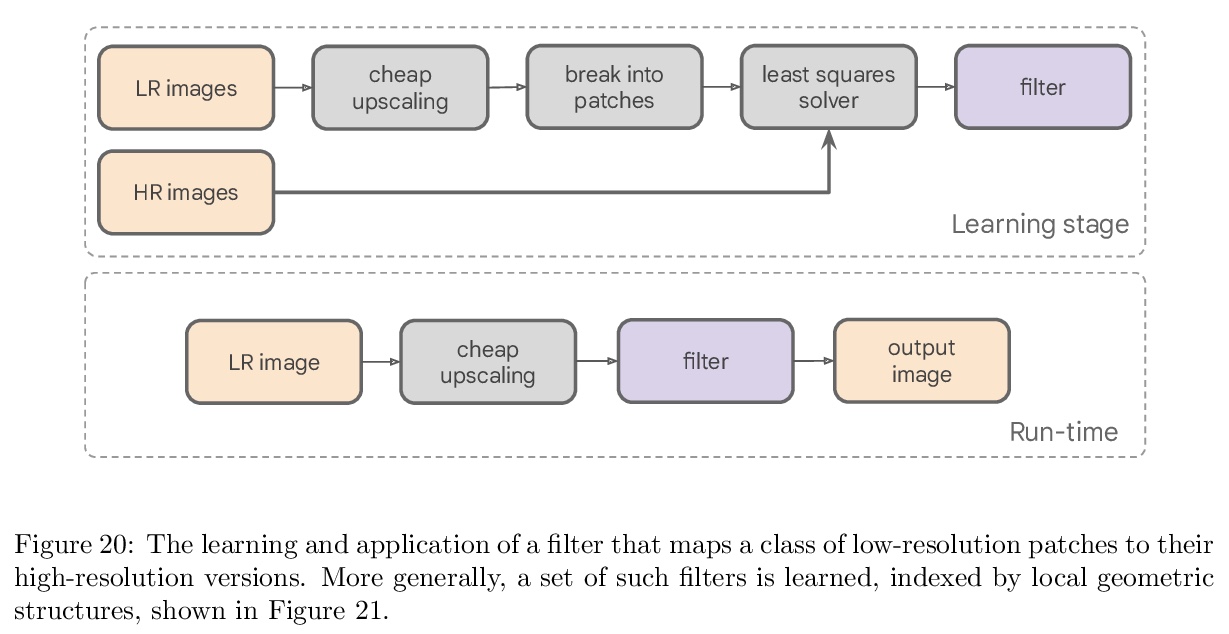
4、[CV] Mobile Computational Photography: A Tour
M Delbracio, D Kelly, M S. Brown, P Milanfar
[Google Research & York University]
移动计算影像综述。相比手机,如今的智能手机更像是相机,这一转变得益于计算影像的进步——用小尺寸移动相机拍摄精彩图像的科学和工程。现代算法和计算的进步,包括机器学习,已经改变了摄影的规则,为其带来了新的捕捉、后处理、存储和分享模式。本文简要介绍移动计算影像的历史,以及一些关键的技术内容,包括抓拍、降噪和超分辨率。在每一步,都尽可能与人类的视觉系统相联系。强调了移动成像平台与独立设备相比的一些主要局限性,并综述了在研究和实践中如何应对这些挑战。
The first mobile camera phone was sold only 20 years ago, when taking pictures with one’s phone was an oddity, and sharing pictures online was unheard of. Today, the smartphone is more camera than phone. How did this happen? This transformation was enabled by advances in computational photography -the science and engineering of making great images from small form factor, mobile cameras. Modern algorithmic and computing advances, including machine learning, have changed the rules of photography, bringing to it new modes of capture, post-processing, storage, and sharing. In this paper, we give a brief history of mobile computational photography and describe some of the key technological components, including burst photography, noise reduction, and super-resolution. At each step, we may draw naive parallels to the human visual system.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K2U37anZg

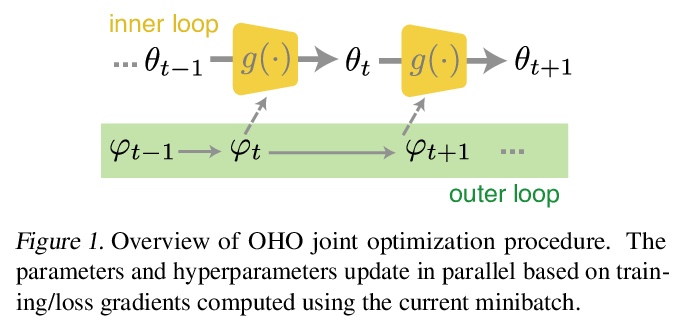
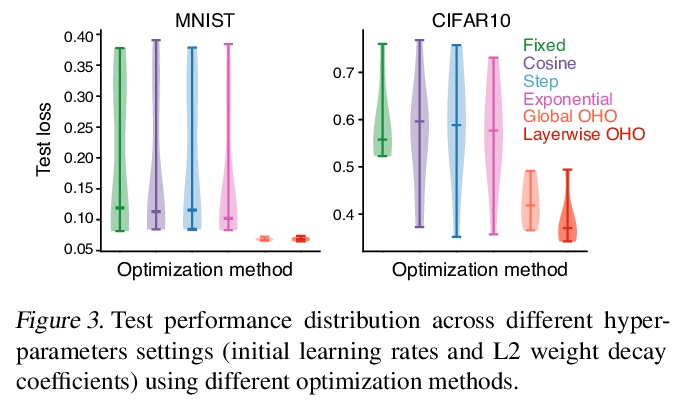
5、[LG] Online hyperparameter optimization by real-time recurrent learning
D J Im, C Savin, K Cho
[New York University]
基于实时循环学习的在线超参数优化。提出一种在线超参数优化算法OHO,无论从理论上还是从实践上都是渐近精确的,并且在计算上是可行的。该框架利用循环神经网络(RNN)中超参数优化和参数学习之间的相似性,适应已深入研究的RNN在线学习算法族,以同时调整超参数和网络参数,无需重复推出迭代优化。除了自动收缩学习率以避免过拟合外,OHO还能快速适应超参数,以补偿突发变化,如超参数扰动,并使学习过程能够可靠地找到更好的模型。OHO更新的在线性质使其广泛适用于固定和非固定学习问题。与标准离线超参数优化方法相比,该例程能产生更系统性的泛化性能,只需一小部分时间。
Conventional hyperparameter optimization methods are computationally intensive and hard to generalize to scenarios that require dynamically adapting hyperparameters, such as life-long learning. Here, we propose an online hyperparameter optimization algorithm that is asymptotically exact and computationally tractable, both theoretically and practically. Our framework takes advantage of the analogy between hyperparameter optimization and parameter learning in recurrent neural networks (RNNs). It adapts a well-studied family of online learning algorithms for RNNs to tune hyperparameters and network parameters simultaneously, without repeatedly rolling out iterative optimization. This procedure yields systematically better generalization performance compared to standard methods, at a fraction of wallclock time.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K2U7o0xMs

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
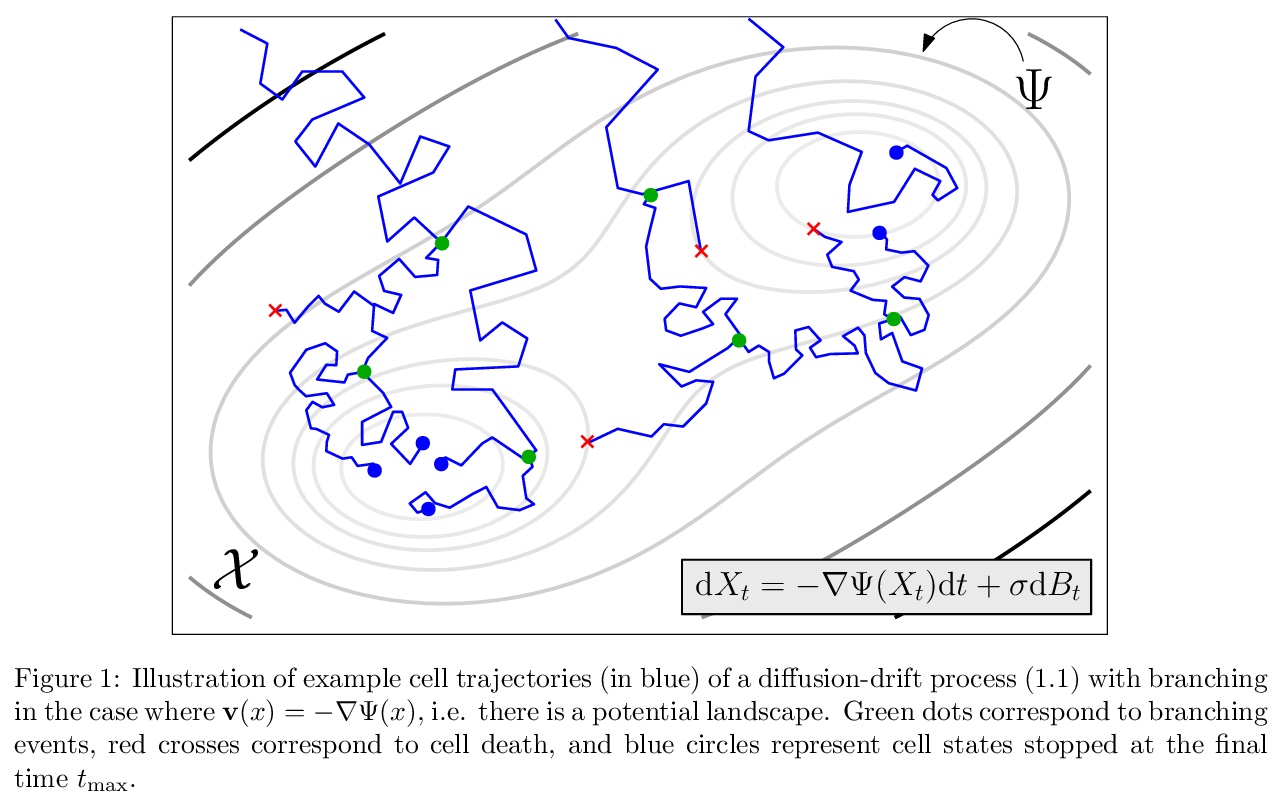
[LG] Towards a mathematical theory of trajectory inference
轨迹推断数学理论探索
H Lavenant, S Zhang, Y Kim, G Schiebinger
[Bocconi University & University of British Columbia]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K2UcIzc8m
[LG] HYDRA: Hypergradient Data Relevance Analysis for Interpreting Deep Neural Networks
HYDRA:用超参梯度数据相关性分析解释深度网络
Y Chen, B Li, H Yu, P Wu, C Miao
[Nanyang Technological University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K2UeOhtFD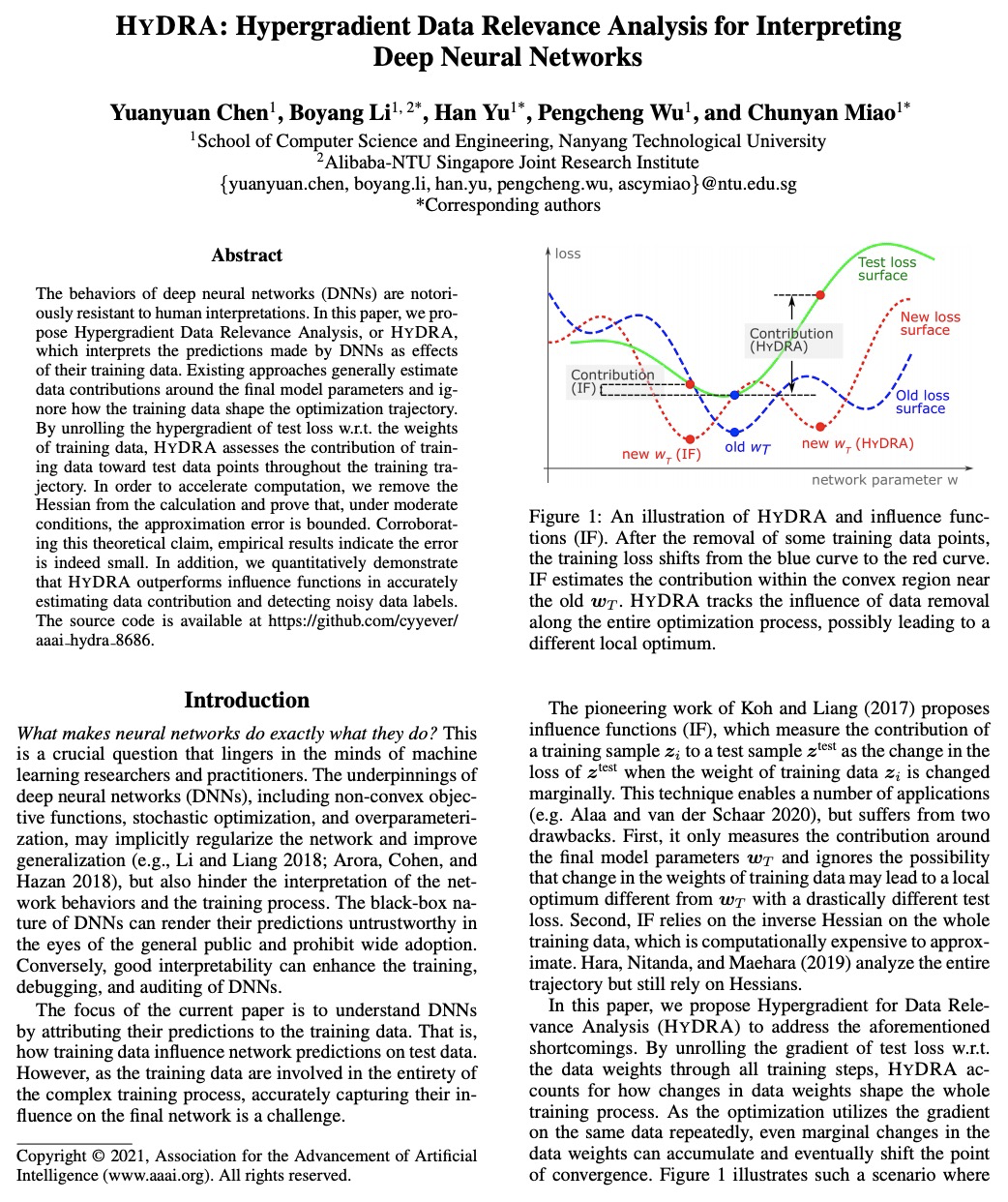
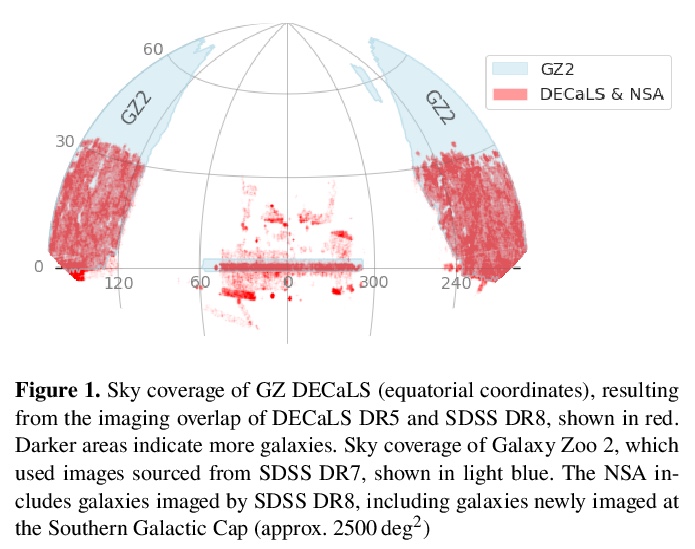
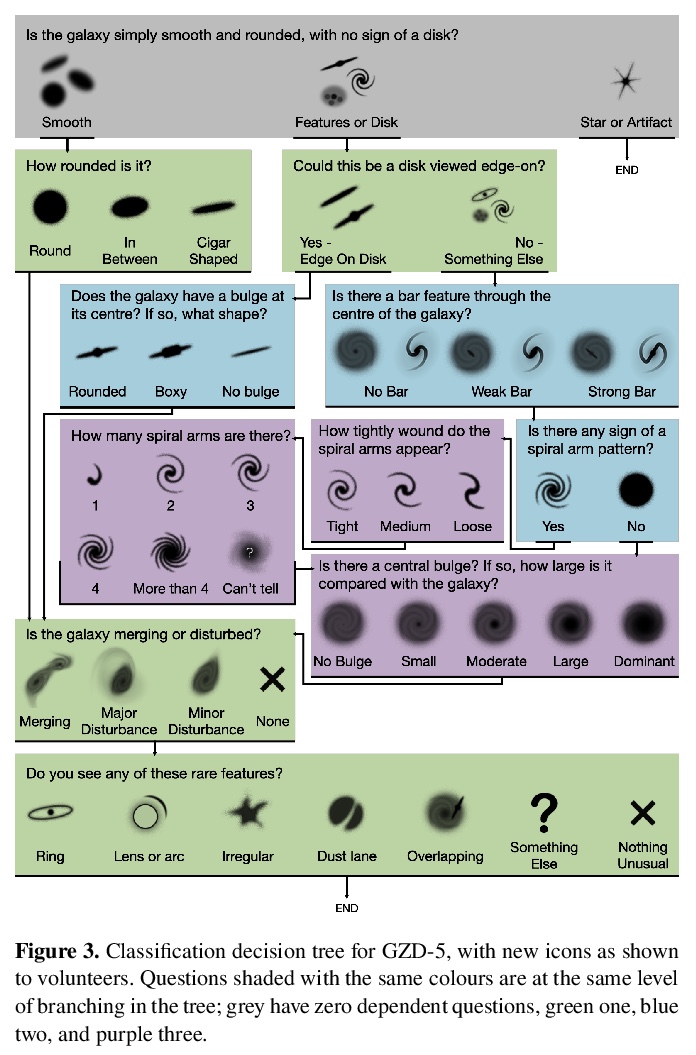
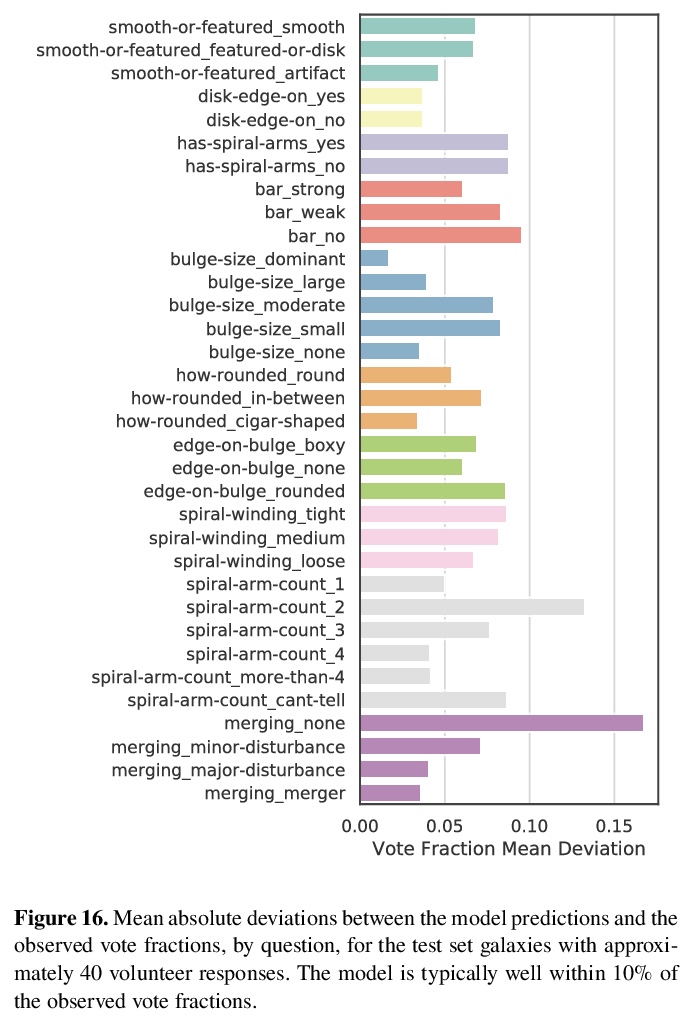
[CV] Galaxy Zoo DECaLS: Detailed Visual Morphology Measurements from Volunteers and Deep Learning for 314,000 Galaxies
Galaxy Zoo DECaLS:314,000个星系的志愿者/深度学习详细视觉形态学测量
M Walmsley, C Lintott, T Geron, S Kruk, C Krawczyk, K W. Willett, S Bamford, W Keel, L S. Kelvin, L Fortson, K L. Masters, V Mehta, B D. Simmons, R Smethurst, E M. Baeten, C Macmillan
[University of Oxford & ESTEC & University of Portsmouth Dennis Sciama Building…]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K2Uj1zM9p
[CL] Machine Translationese: Effects of Algorithmic Bias on Linguistic Complexity in Machine Translation
机器翻译腔:算法偏差对机器翻译语言复杂性的影响
E Vanmassenhove, D Shterionov, M Gwilliam
[Tilburg University & University of Maryland]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K2Un9o5zf