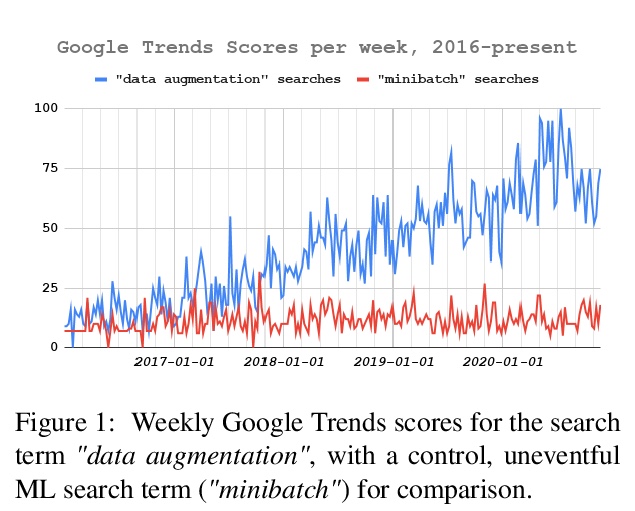
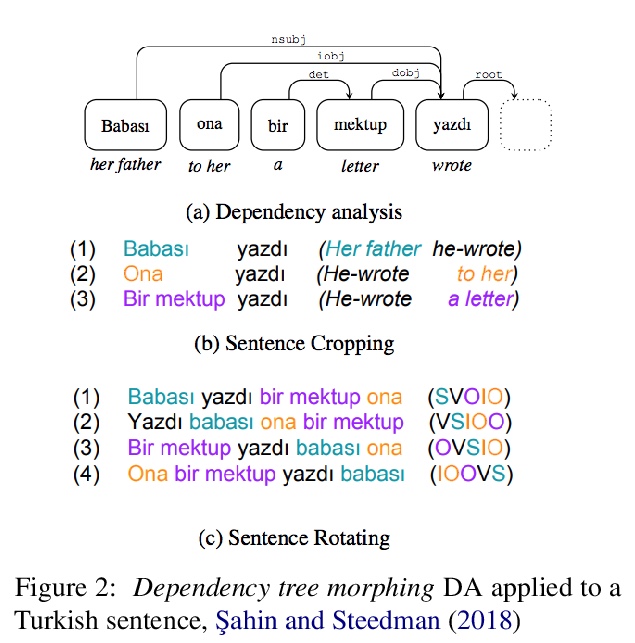
- 1、[CL] A Survey of Data Augmentation Approaches for NLP
- 2、[CV] ResMLP: Feedforward networks for image classification with data-efficient training
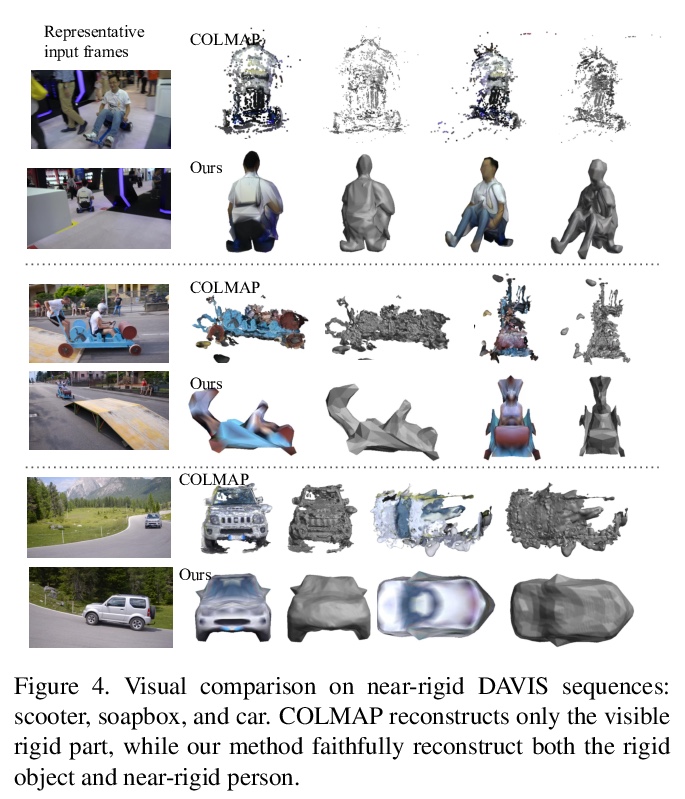
- 3、[CV] LASR: Learning Articulated Shape Reconstruction from a Monocular Video
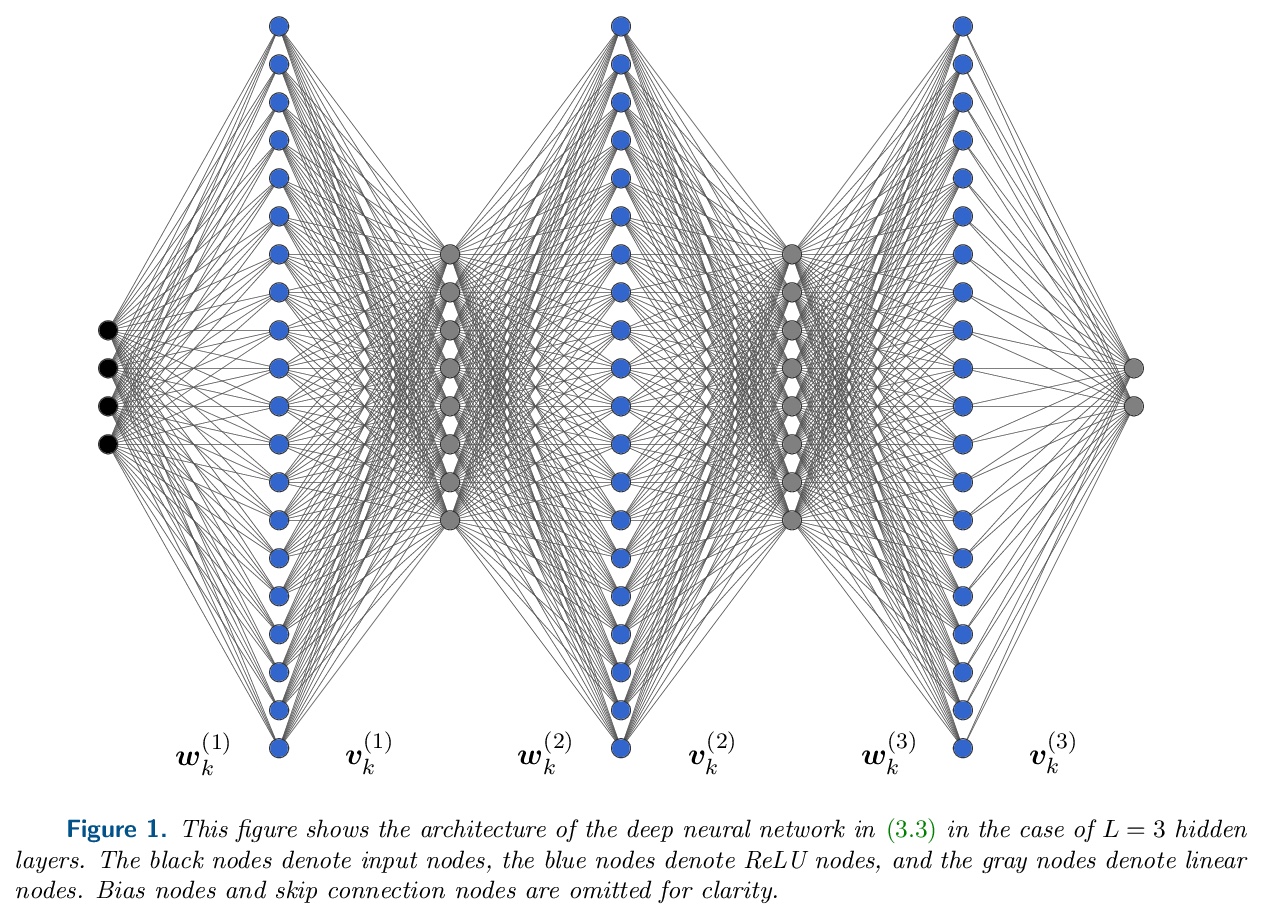
- 4、[LG] What Kinds of Functions do Deep Neural Networks Learn? Insights from Variational Spline Theory
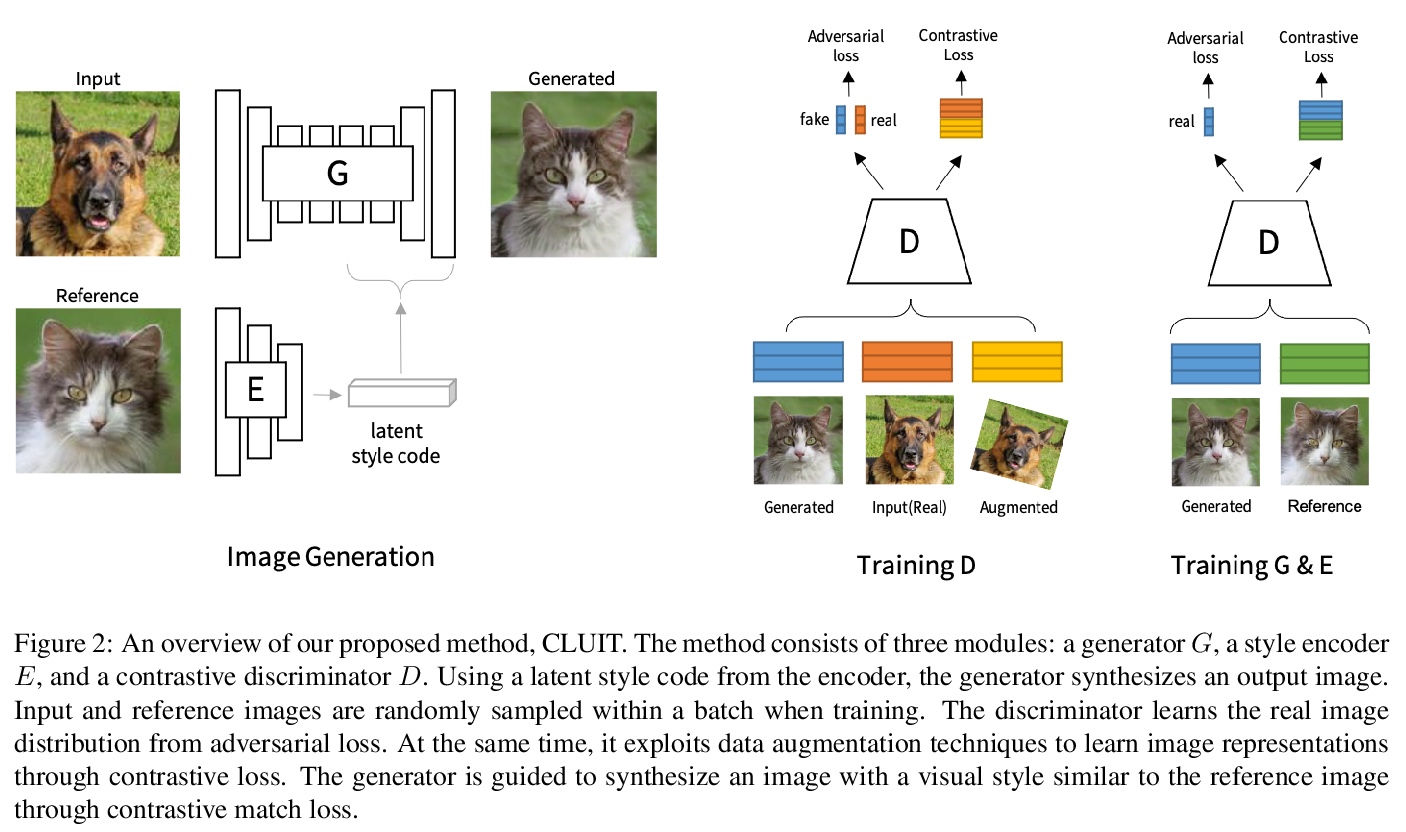
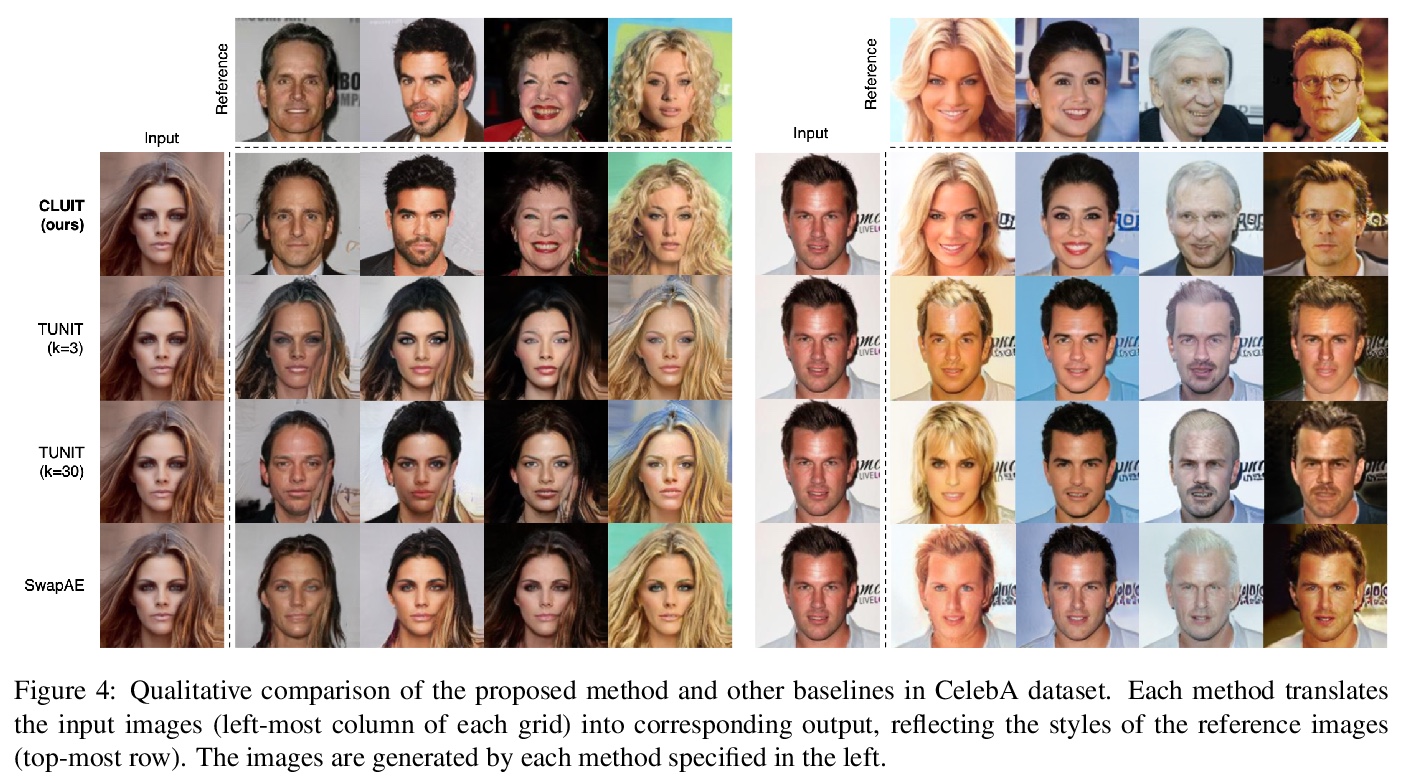
- 5、[CV] Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation
- [CL] DEXPERTS: On-the-Fly Controlled Text Generation with Experts and Anti-Experts
- [CL] A Dataset of Information-Seeking Questions and Answers Anchored in Research Papers
- [LG] Hierarchical Graph Neural Networks
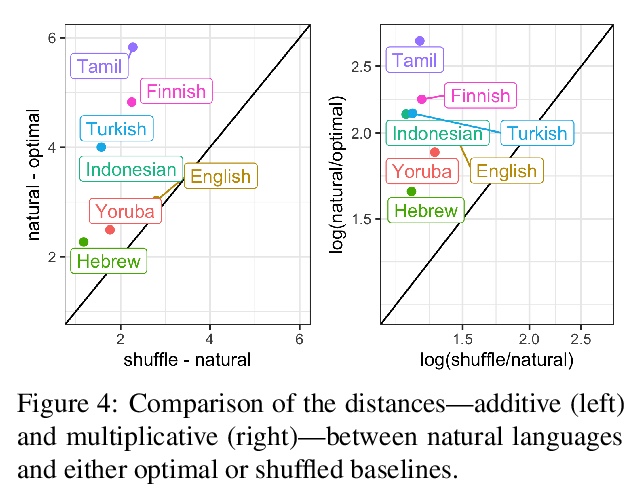
- [CL] How (Non-)Optimal is the Lexicon?
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CL] A Survey of Data Augmentation Approaches for NLP
S Y. Feng, V Gangal, J Wei, S Chandar, S Vosoughi, T Mitamura, E Hovy
[CMU & Google Research & Mila & Dartmouth College]
NLP数据增强方法综述。数据增强(DA)是指在不显式收集新数据的情况下增加训练样本多样性的策略。由于低资源领域的工作越来越多,新的任务,以及需要大量训练数据的大规模神经网络的普及,最近在NLP领域对数据增强的兴趣越来越大,但这一领域的探索仍然相对不足,这可能是由于语言数据的离散性带来的挑战。本文以结构化的方式,对文献进行了整理和总结,对NLP数据增强进行了全面和统一的综述。提供了关于数据增强的背景以及它是如何工作的,讨论了NLP的主要方法学上的代表性数据增强技术,并触及了流行的NLP应用和任务的数据增强技术。最后,概述了当前的挑战和未来的研究方向,并表明有许多进一步探索的空间,旨在澄清现有的用于NLP的数据增强文献的现状,并激励研究人员对该领域的进一步的兴趣和工作。
Data augmentation has recently seen increased interest in NLP due to more work in lowresource domains, new tasks, and the popularity of large-scale neural networks that require large amounts of training data. Despite this recent upsurge, this area is still relatively underexplored, perhaps due to the challenges posed by the discrete nature of language data. In this paper, we present a comprehensive and unifying survey of data augmentation for NLP by summarizing the literature in a structured manner. We first introduce and motivate data augmentation for NLP, and then discuss major methodologically representative approaches. Next, we highlight techniques that are used for popular NLP applications and tasks. We conclude by outlining current challenges and directions for future research. Overall, our paper aims to clarify the landscape of existing literature in data augmentation for NLP and motivate additional work in this area.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeUmrc4xd
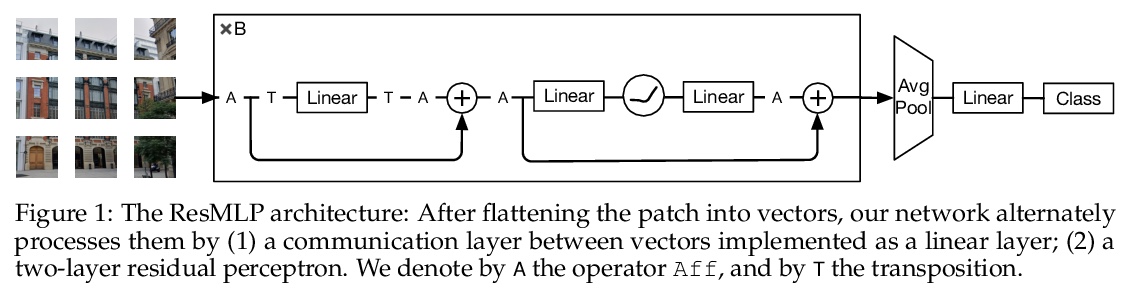
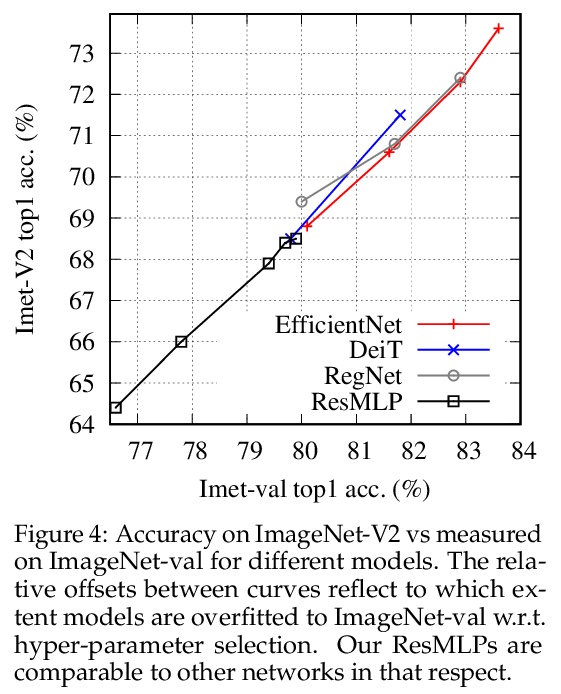
2、[CV] ResMLP: Feedforward networks for image classification with data-efficient training
H Touvron, P Bojanowski, M Caron, M Cord, A El-Nouby, E Grave, A Joulin, G Synnaeve, J Verbeek, H Jégou
[Facebook AI ]
ResMLP:面向图像分类的数据高效训练前馈网络。提出ResMLP,一个完全建立在多层感知器上的图像分类架构。它是一个简单的残差网络,交替使用(i)一个线性图块交互层,图块在各通道间独立地、一致地交互,以及(ii)一个两层前馈网络,其中各通道在每图块上独立地交互。用现代训练策略进行训练时,使用大量的数据增强和可选的蒸馏,在ImageNet上获得了令人惊讶的良好的准确性/复杂性权衡。
We present ResMLP, an architecture built entirely upon multi-layer perceptrons for image classification. It is a simple residual network that alternates (i) a linear layer in which image patches interact, independently and identically across channels, and (ii) a two-layer feed-forward network in which channels interact independently per patch. When trained with a modern training strategy using heavy data-augmentation and optionally distillation, it attains surprisingly good accuracy/complexity trade-offs on ImageNet. We will share our code based on the Timm library and pre-trained models.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeUrdfUYs
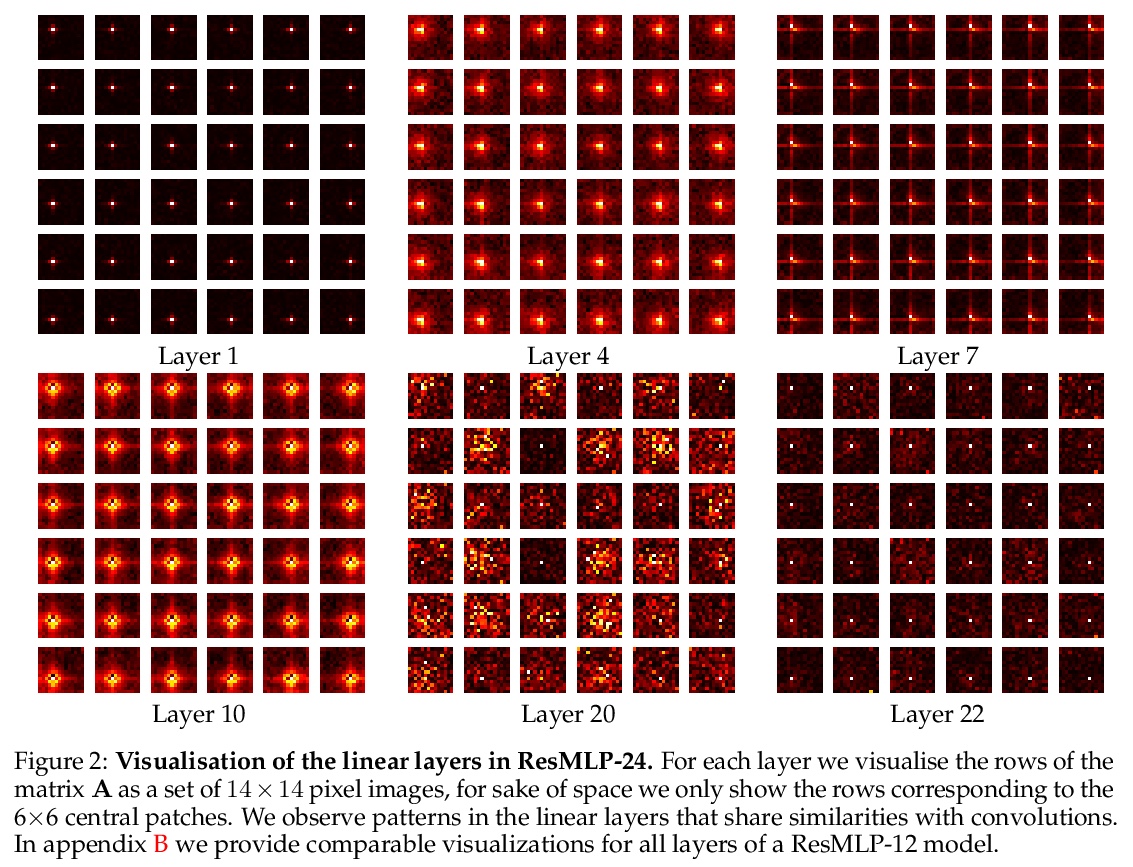
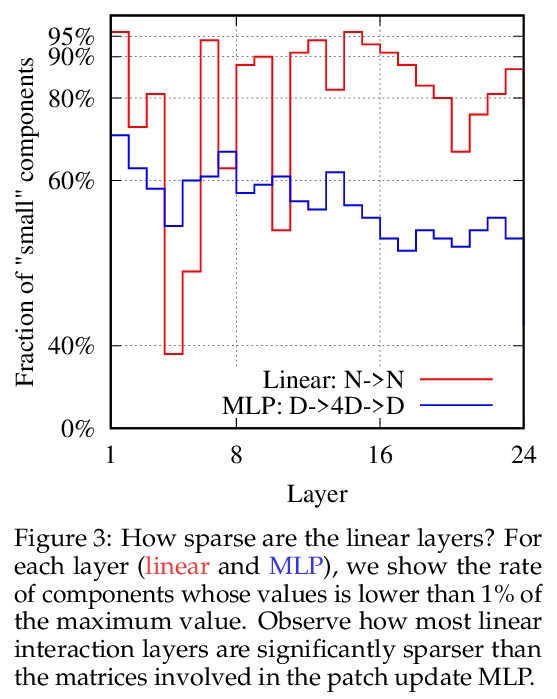
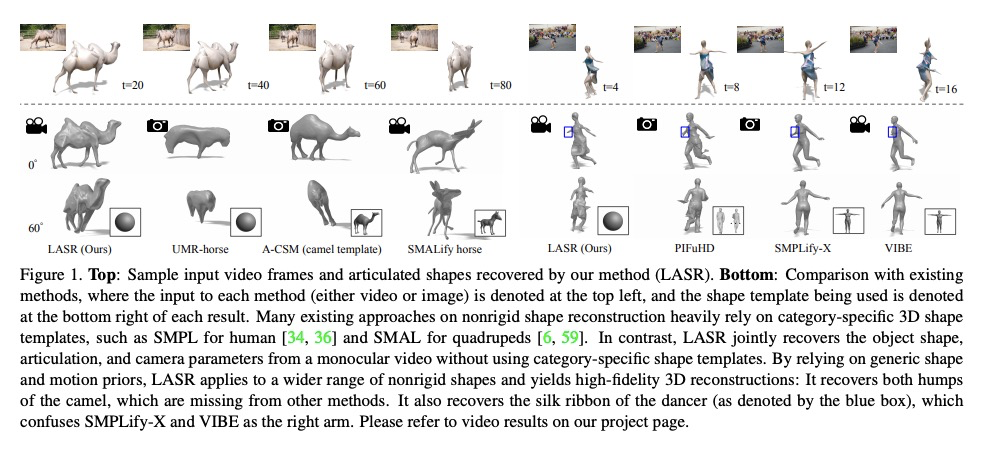
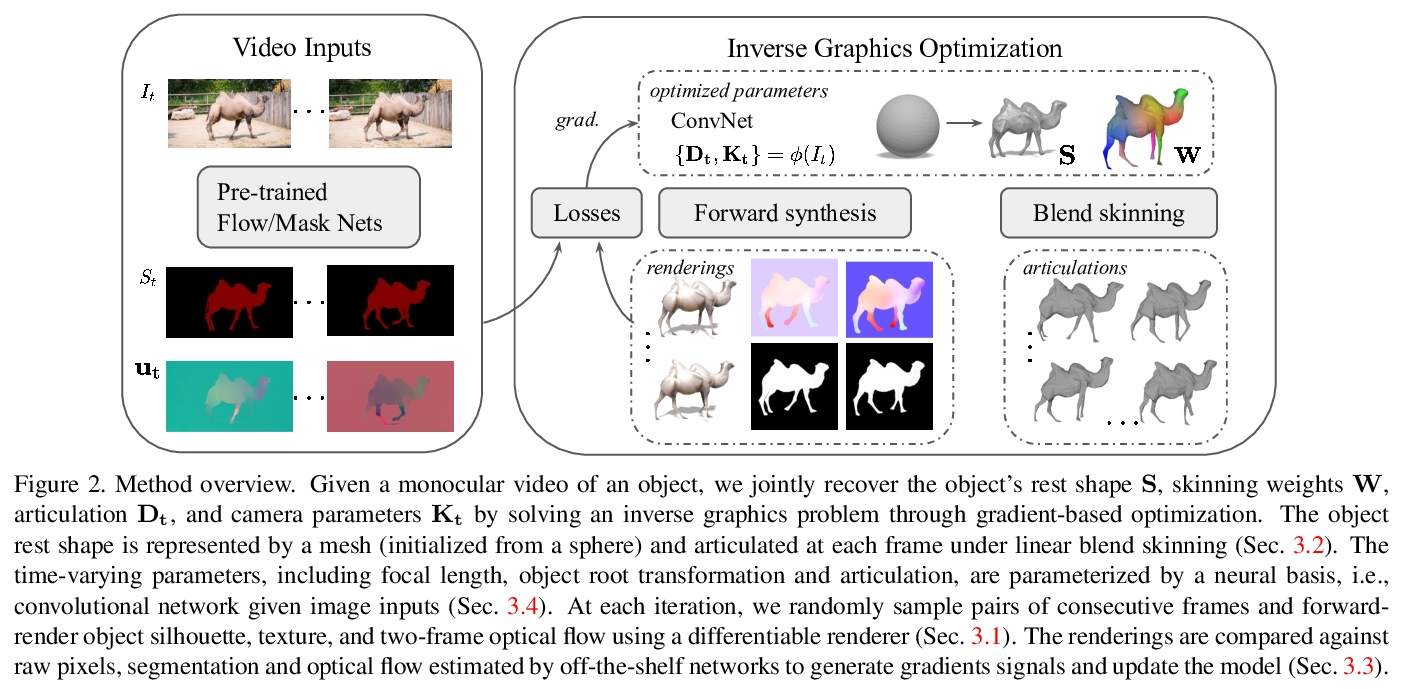
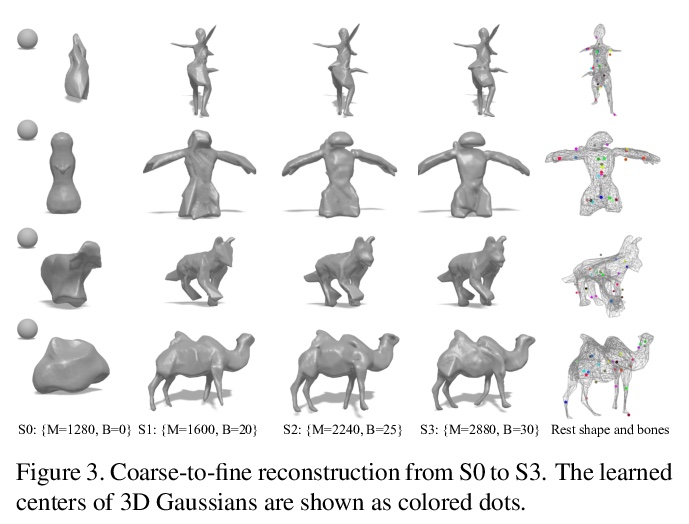
3、[CV] LASR: Learning Articulated Shape Reconstruction from a Monocular Video
G Yang, D Sun, V Jampani, D Vlasic, F Cole, H Chang, D Ramanan, W T. Freeman, C Liu
[CMU & Google Research]
LASR:单目视频的关节形状重建学习。从视频或图像集合中对刚性结构进行三维重建方面已经取得了显著的进展。然而,由于存在约束不足的状况,从RGB输入中重建非刚性结构仍然是个挑战。虽然基于模板的方法,如参数化形状模型,在为已知物体类别的”封闭世界”建模方面取得了巨大成功,但它们不能很好地处理新的物体类别或离群形状的”开放世界”。本文提出一种无模板方法,从单个视频中学习3D形状。采用一种通过合成进行分析的策略,前向渲染物体轮廓、光流和像素值,与视频观察结果进行比较,从而产生梯度来调整像机、形状和运动参数。在不使用特定类别形状模板的情况下,从人类、动物和未知类别物体的视频中,忠实重建了非刚性的3D结构。
Remarkable progress has been made in 3D reconstruction of rigid structures from a video or a collection of images. However, it is still challenging to reconstruct nonrigid structures from RGB inputs, due to its under-constrained nature. While template-based approaches, such as parametric shape models, have achieved great success in modeling the “closed world” of known object categories, they cannot well handle the “open-world” of novel object categories or outlier shapes. In this work, we introduce a template-free approach to learn 3D shapes from a single video. It adopts an analysis-by-synthesis strategy that forward-renders object silhouette, optical flow, and pixel values to compare with video observations, which generates gradients to adjust the camera, shape and motion parameters. Without using a category-specific shape template, our method faithfully reconstructs nonrigid 3D structures from videos of human, animals, and objects of unknown classes. Our code is available at lasr-google.github.io.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeUuW2M3z
4、[LG] What Kinds of Functions do Deep Neural Networks Learn? Insights from Variational Spline Theory
R Parhi, R D. Nowak
[University of Wisconsin–Madison]
深度神经网络能学到什么类型的函数?来自变分曲线理论的启示。开发了一个变分框架,来理解深度神经网络用ReLU激活函数拟合数据所学习的函数的特性。提出一个新的函数空间,和经典的有界变分空间类似,能捕捉到与深度神经网络相关的组成结构。推导出一个代表者定理,表明深度ReLU网络是这个函数空间中正则化数据拟合问题的解决方案。该函数空间由Radon域中二阶有界变化的(非反射性)Banach空间的函数组成。这些是具有促进稀疏性规范的巴拿赫空间,使我们了解到稀疏性在深度神经网络中的作用。神经网络解决方案具有跳接和阶有界的权重矩阵,为这些常见的架构选择提供了新的理论支持。本文研究的变分问题,可以被重塑为一个有限维的神经网络训练问题,其正则化方案与权重衰减和路径规范化的概念有关。
We develop a variational framework to understand the properties of functions learned by deep neural networks with ReLU activation functions fit to data. We propose a new function space, which is reminiscent of classical bounded variation spaces, that captures the compositional structure associated with deep neural networks. We derive a representer theorem showing that deep ReLU networks are solutions to regularized data fitting problems in this function space. The function space consists of compositions of functions from the (non-reflexive) Banach spaces of second-order bounded variation in the Radon domain. These are Banach spaces with sparsity-promoting norms, giving insight into the role of sparsity in deep neural networks. The neural network solutions have skip connections and rank bounded weight matrices, providing new theoretical support for these common architectural choices. The variational problem we study can be recast as a finite-dimensional neural network training problem with regularization schemes related to the notions of weight decay and path-norm regularization. Finally, our analysis builds on techniques from variational spline theory, providing new connections between deep neural networks and splines.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeUyudpax
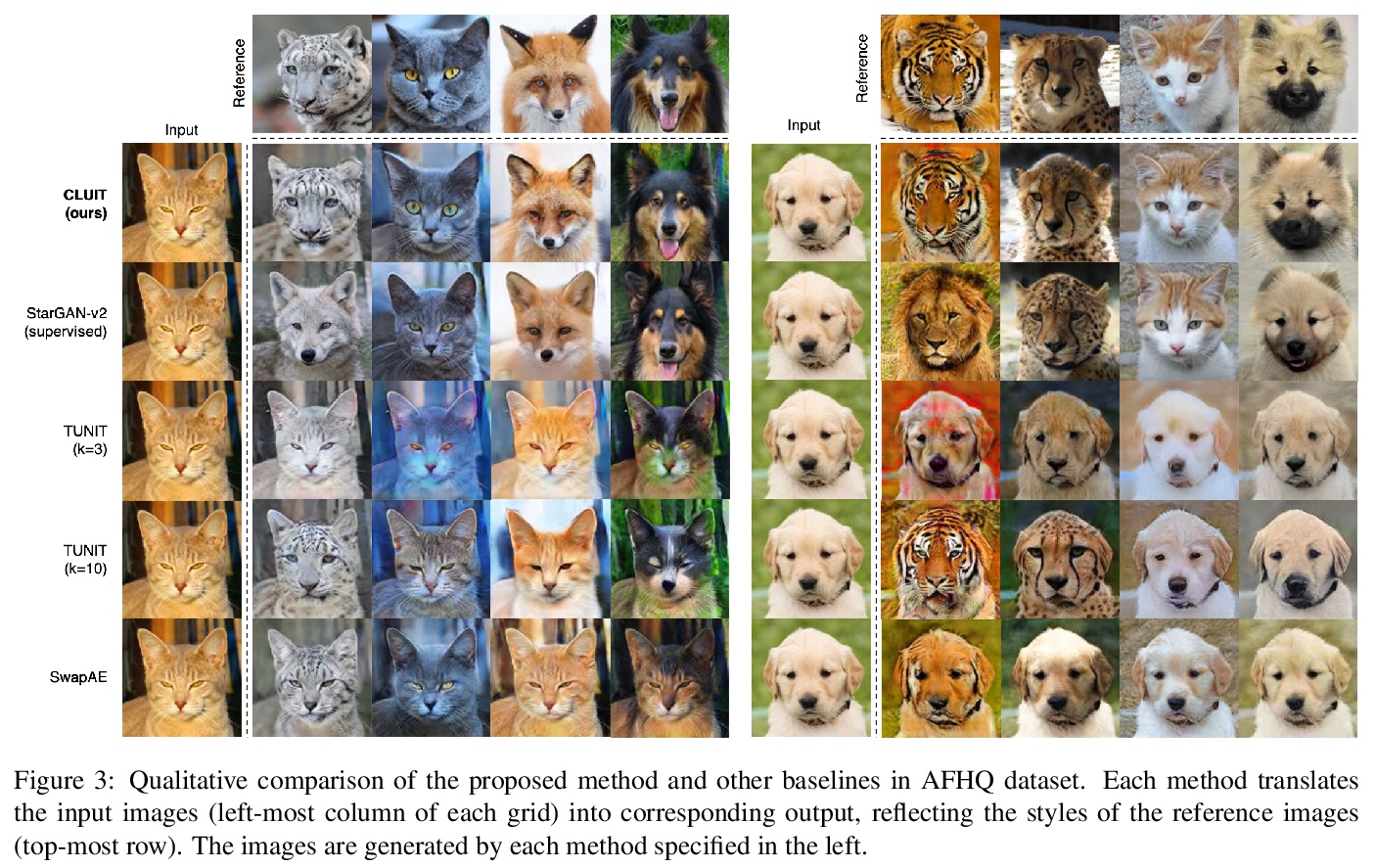
5、[CV] Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation
H Lee, J Seol, S Lee
[Seoul National University]
对比学习无监督图像到图形变换。图像到图像变换,旨在学习视觉上可区分的不同图像组之间的映射。虽然最近的方法已经显示出令人印象深刻的能力,甚至可以改变图像错综复杂的外观,但在训练模型时仍然依赖领域标签来区分不同的视觉特征。这种对标签的依赖往往大大限制了应用的范围,因为一致和高质量的标签是昂贵的。本文希望从图像本身捕获视觉特征,并应用它们来实现现实的变换,而不需要人工产生的标签,提出了一种基于对比学习的无监督的图像-图像变换方法,其关键思想是学习一个区分不同风格的鉴别器,让鉴别器监督生成器在图像间迁移这些风格。在训练过程中,随机抽取一对图像,并训练生成器在保持原始结构的情况下,将其中一个图像的外观改变为另一个。实验结果表明,该方法在视觉质量和变换准确性方面优于领先的无监督基线。
Image-to-image translation aims to learn a mapping between different groups of visually distinguishable images. While recent methods have shown impressive ability to change even intricate appearance of images, they still rely on domain labels in training a model to distinguish between distinct visual features. Such dependency on labels often significantly limits the scope of applications since consistent and high-quality labels are expensive. Instead, we wish to capture visual features from images themselves and apply them to enable realistic translation without humangenerated labels. To this end, we propose an unsupervised image-to-image translation method based on contrastive learning. The key idea is to learn a discriminator that differentiates between distinctive styles and let the discriminator supervise a generator to transfer those styles across images. During training, we randomly sample a pair of images and train the generator to change the appearance of one towards another while keeping the original structure. Experimental results show that our method outperforms the leading unsupervised baselines in terms of visual quality and translation accuracy.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeUDjymy4


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
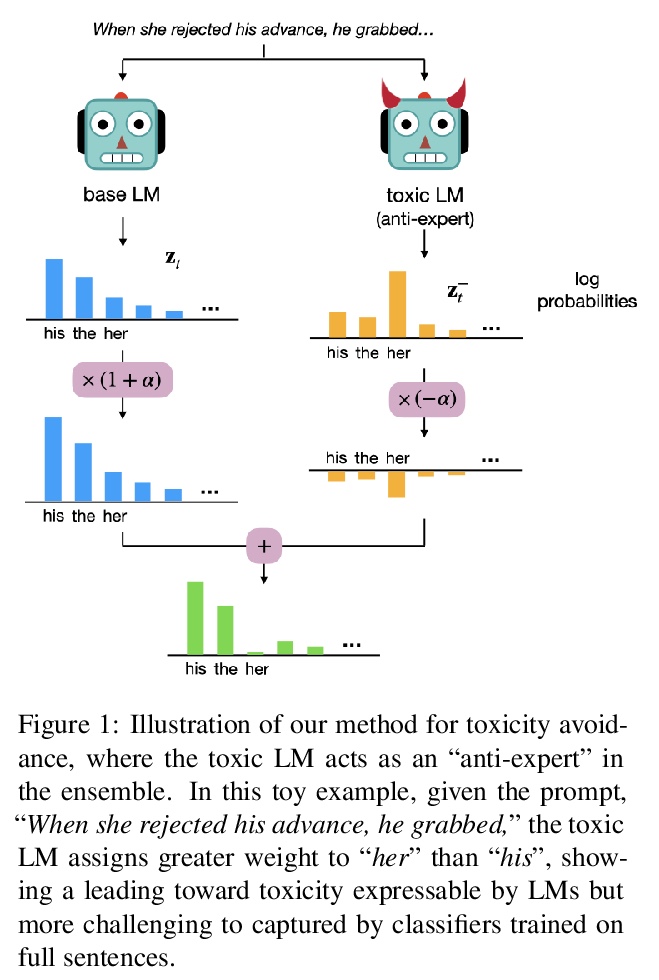
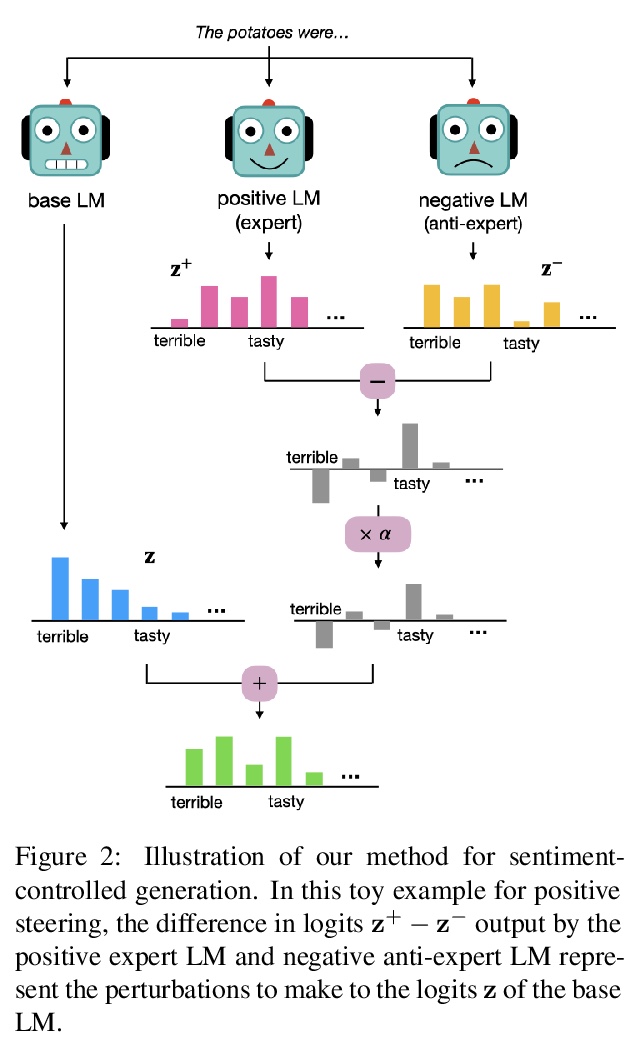
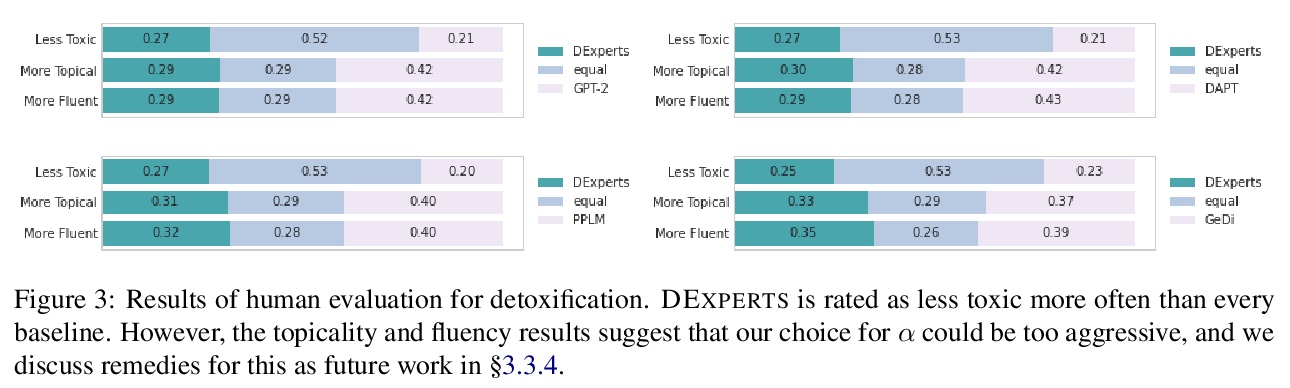
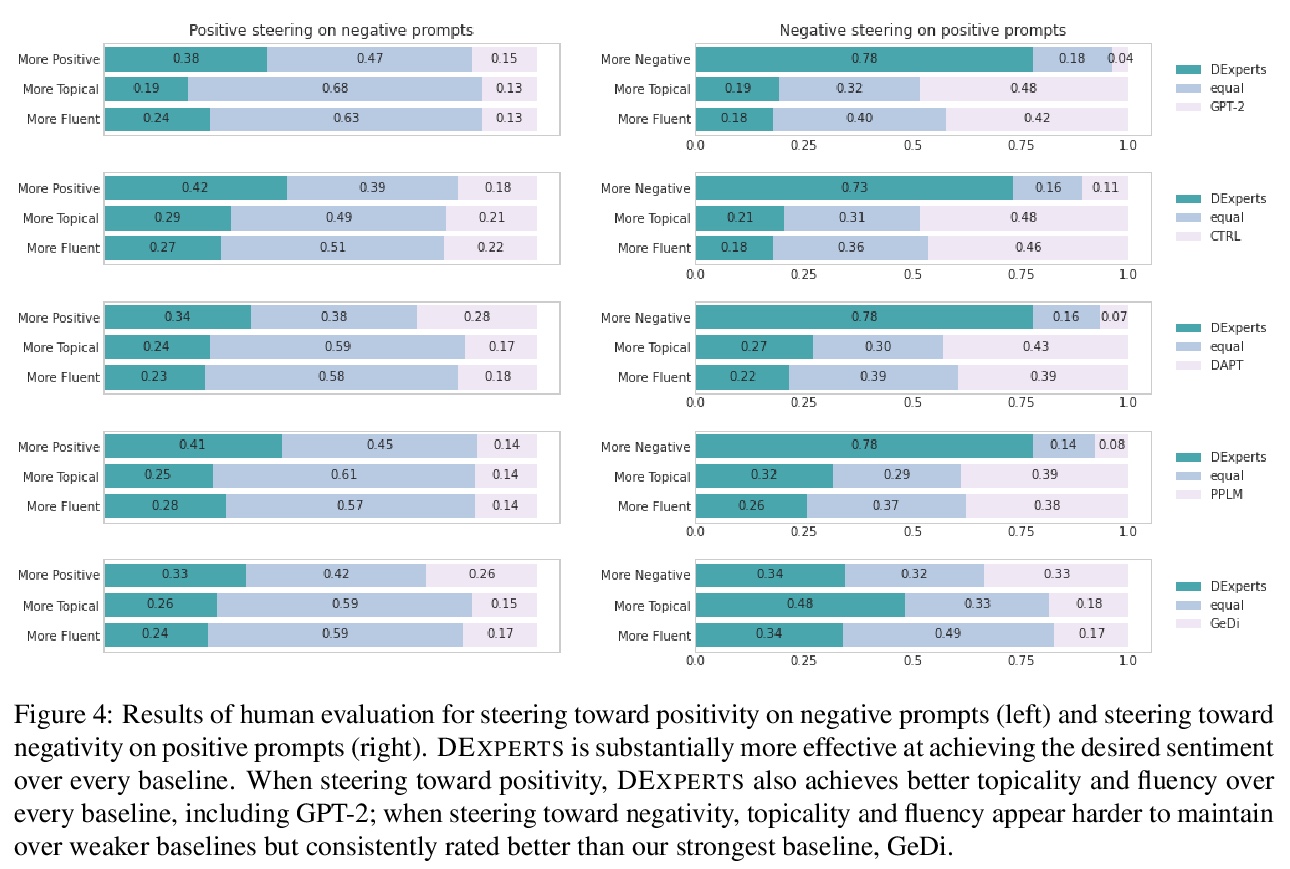
[CL] DEXPERTS: On-the-Fly Controlled Text Generation with Experts and Anti-Experts
DEXPERTS:结合专家和反专家的动态受控文本生成
A Liu, M Sap, X Lu, S Swayamdipta, C Bhagavatula, N A. Smith, Y Choi
[University of Washington & Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeUGC07Mc
[CL] A Dataset of Information-Seeking Questions and Answers Anchored in Research Papers
QASPER:学术论文信息搜寻问答锚定数据集
P Dasigi, K Lo, I Beltagy, A Cohan, N A. Smith, M Gardner
[Allen Institute for AI & University of Washington]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeUIP6zCF
[LG] Hierarchical Graph Neural Networks
层次图神经网络
S Sobolevsky
[New York University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeURZAQpx

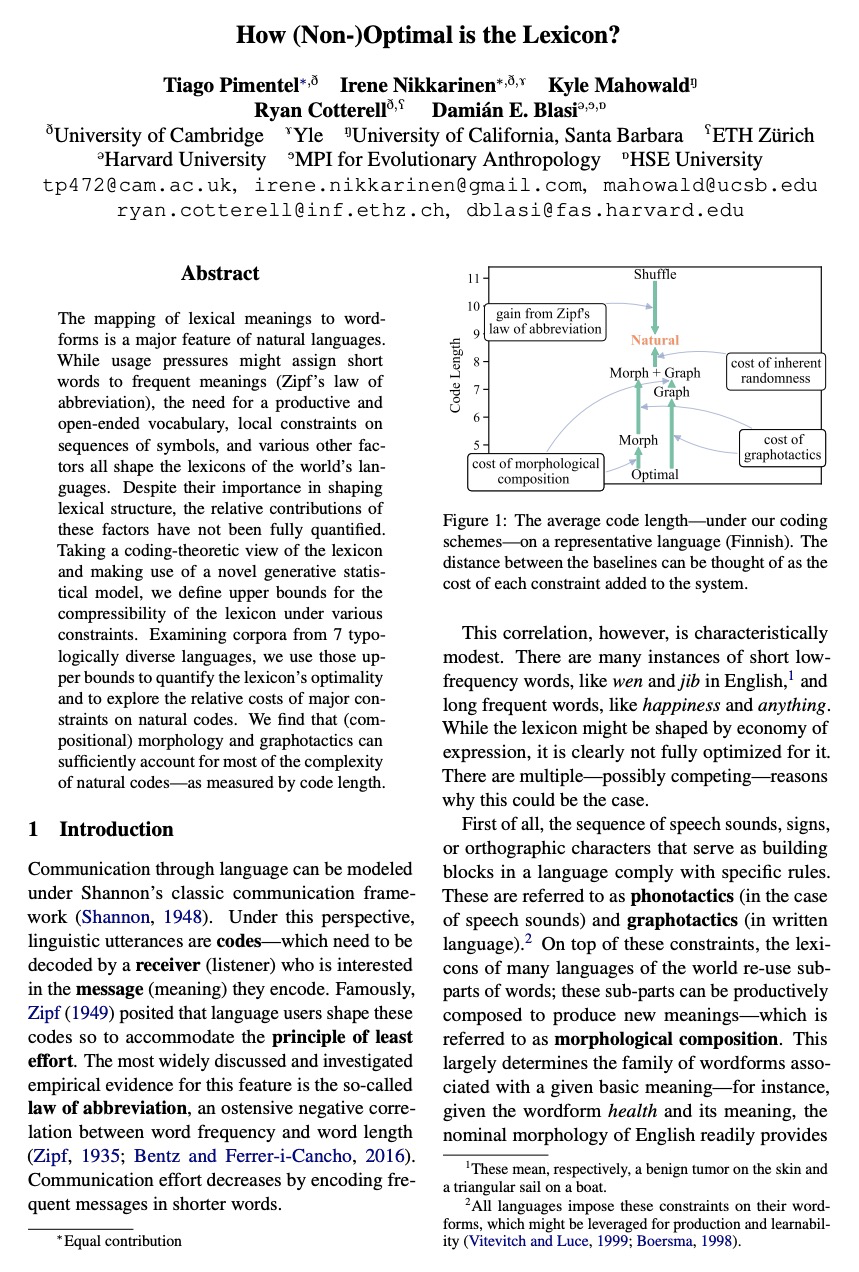
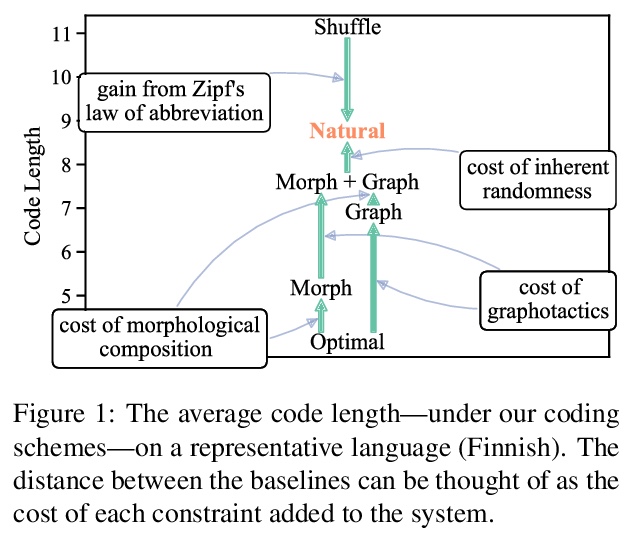
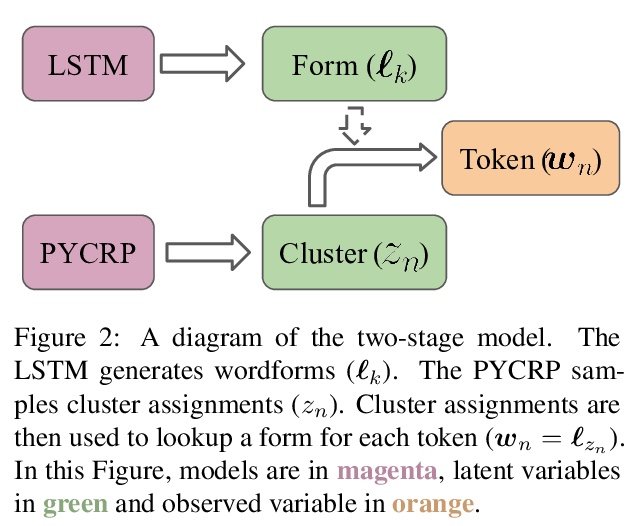
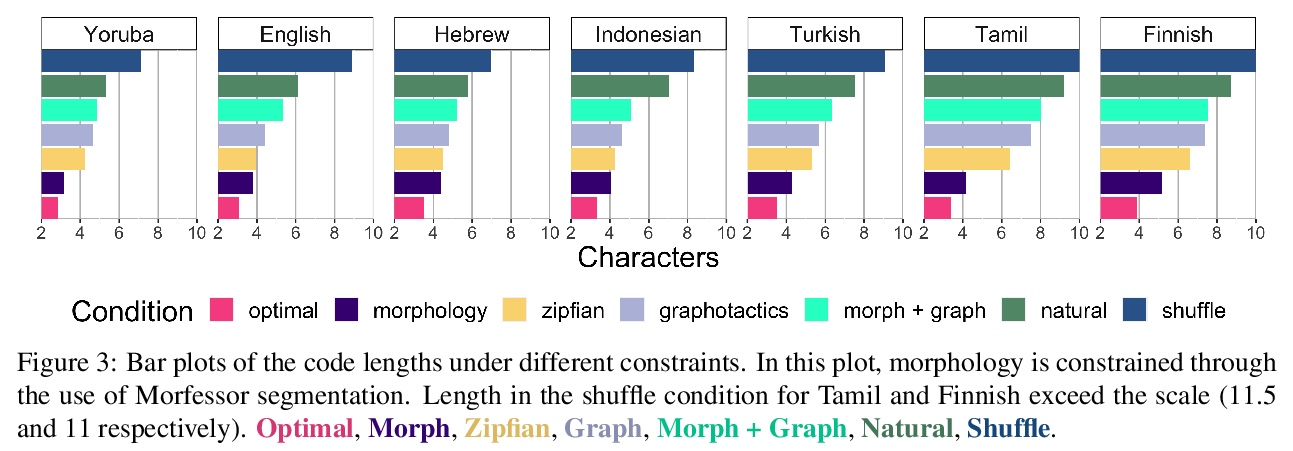
[CL] How (Non-)Optimal is the Lexicon?
从编码理论角度看词典优化
T Pimentel, I Nikkarinen, K Mahowald, R Cotterell, D Blasi
[University of Cambridge]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KeUW90DXA