- 1、[CV] VidTr: Video Transformer Without Convolutions
- 2、[CV] Skip-Convolutions for Efficient Video Processing
- 3、[CV] SRWarp: Generalized Image Super-Resolution under Arbitrary Transformation
- 4、[CV] Motion Representations for Articulated Animation
- 5、[CV] Sketch-based Normal Map Generation with Geometric Sampling
- [CV] Skeletor: Skeletal Transformers for Robust Body-Pose Estimation
- [SI] What are higher-order networks?
- [LG] DisCo RL: Distribution-Conditioned Reinforcement Learning for General-Purpose Policies
- [CL] MS2: Multi-Document Summarization of Medical Studies
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[CV] VidTr: Video Transformer Without Convolutions
X Li, Y Zhang, C Liu, B Shuai, Y Zhu, B Brattoli, H Chen, I Marsic, J Tighe
[Rutgers University & Amazon Web Services]
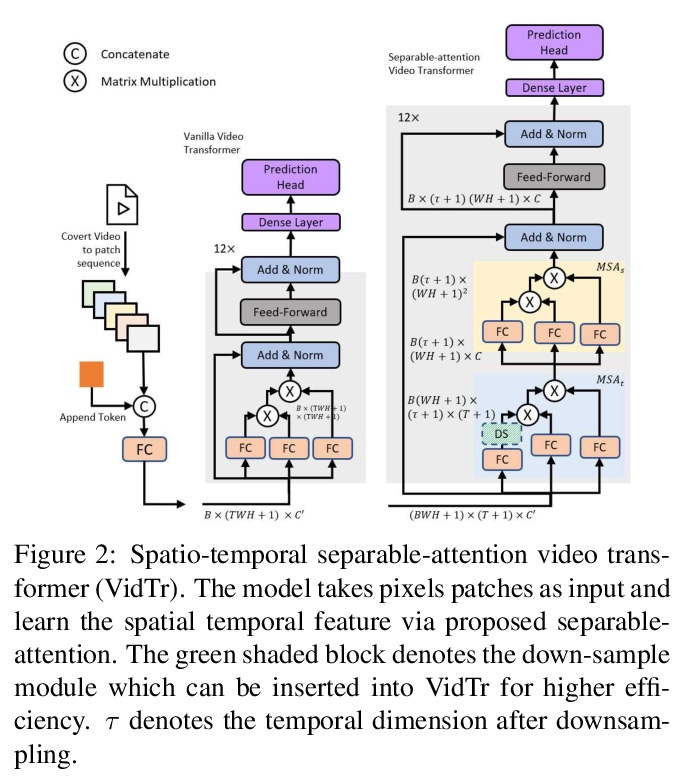
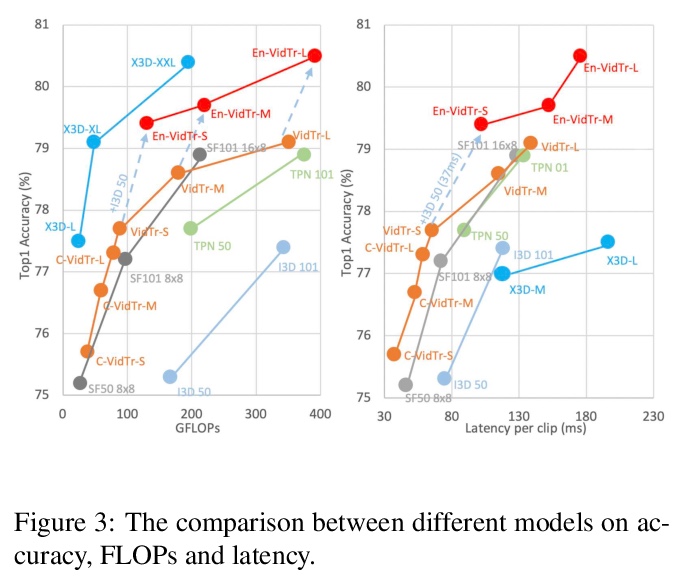
VidTr: 无卷积视频Transformer。提出用于视频分类的可分离注意力的视频Transformer(VidTr),与基于卷积的方法相比,VidTr能通过叠加注意力来聚合时空信息,以更高的效率提供更好的性能。VidTr及其变体,包括具有SOTA性能的VidTr和使用所提出的基于标准差的池化方法大幅降低计算成本的紧凑型VidTr,适用于不同的应用场景。提供了6种常用数据集的详细结果和分析,预训练模型可用于许多下游任务。
We introduce Video Transformer (VidTr) with separable-attention for video classification. Comparing with commonly used 3D networks, VidTr is able to aggregate spatio-temporal information via stacked attentions and provide better performance with higher efficiency. We first introduce the vanilla video transformer and show that transformer module is able to perform spatio-temporal modeling from raw pixels, but with heavy memory usage. We then present VidTr which reduces the memory cost by 3.3×while keeping the same performance. To further compact the model, we propose the standard deviation based topK pooling attention, which reduces the computation by dropping non-informative features. VidTr achieves state-of-the-art performance on five commonly used dataset with lower computational requirement, showing both the efficiency and effectiveness of our design. Finally, error analysis and visualization show that VidTr is especially good at predicting actions that require long-term temporal reasoning. The code and pre-trained weights will be released.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcMvLqxlw


2、[CV] Skip-Convolutions for Efficient Video Processing
A Habibian, D Abati, T S. Cohen, B E Bejnordi
[Qualcomm AI Research]
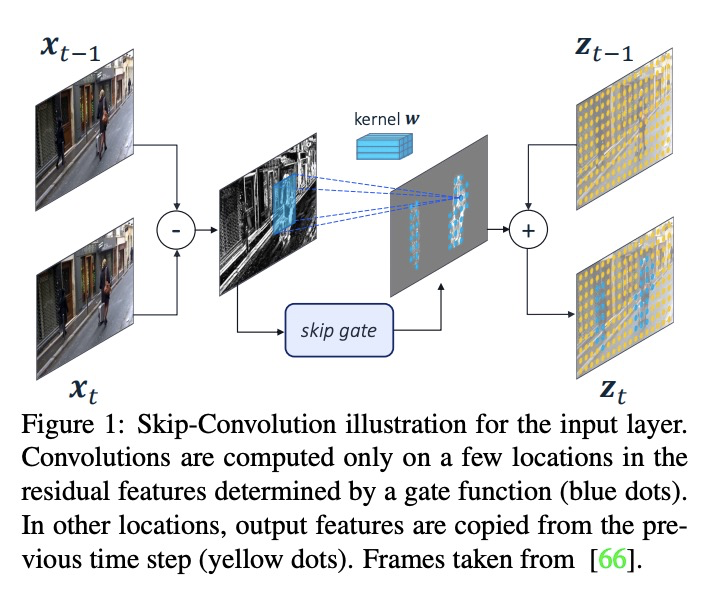
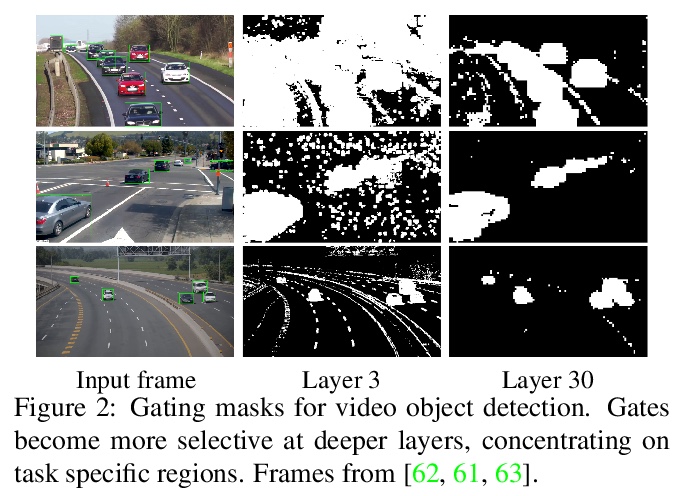
跳卷积高效视频处理。提出了跳卷积(Skip-Convolutions),利用视频流中大量冗余并节省计算。每个视频表示为一系列跨帧和网络激活的变化,用残差表示。重新表述标准卷积,以便在残差帧上进行有效计算:每一层都有一个二进制门,决定一个残差对模型预测是否重要,如前景区域,或是可以安全跳过,如背景区域。这些门既可实现为一个与卷积核联合训练的高效网络,也可根据残差大小简单跳过。门控函数可纳入块状稀疏结构,在硬件平台高效实施。通过在EfficientDet和HRNet两个先进架构中用跳卷积代替所有卷积,在两个不同的任务中把计算成本持续降低了3∼4倍,而精度没有任何下降。与现有的模型压缩以及图像和视频高效方法的广泛比较表明,Skip-Convolutions通过有效地利用视频中的时间冗余,达到了新的技术水平。
We propose Skip-Convolutions to leverage the large amount of redundancies in video streams and save computations. Each video is represented as a series of changes across frames and network activations, denoted as residuals. We reformulate standard convolution to be efficiently computed on residual frames: each layer is coupled with a binary gate deciding whether a residual is important to the model prediction,~\eg foreground regions, or it can be safely skipped, e.g. background regions. These gates can either be implemented as an efficient network trained jointly with convolution kernels, or can simply skip the residuals based on their magnitude. Gating functions can also incorporate block-wise sparsity structures, as required for efficient implementation on hardware platforms. By replacing all convolutions with Skip-Convolutions in two state-of-the-art architectures, namely EfficientDet and HRNet, we reduce their computational cost consistently by a factor of 3~4x for two different tasks, without any accuracy drop. Extensive comparisons with existing model compression, as well as image and video efficiency methods demonstrate that Skip-Convolutions set a new state-of-the-art by effectively exploiting the temporal redundancies in videos.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcMBhA987


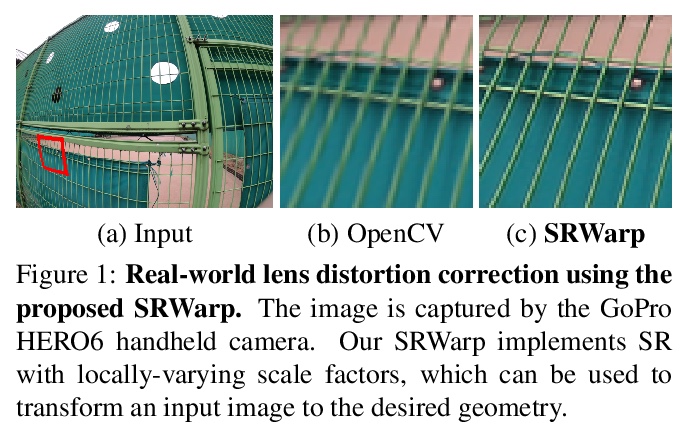
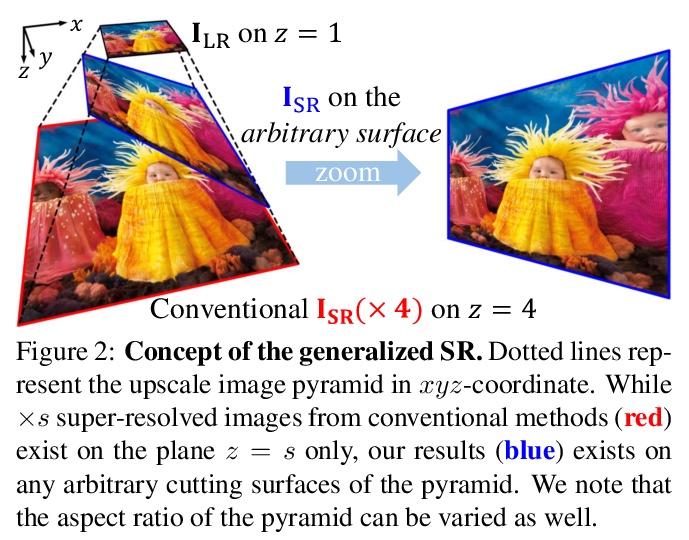
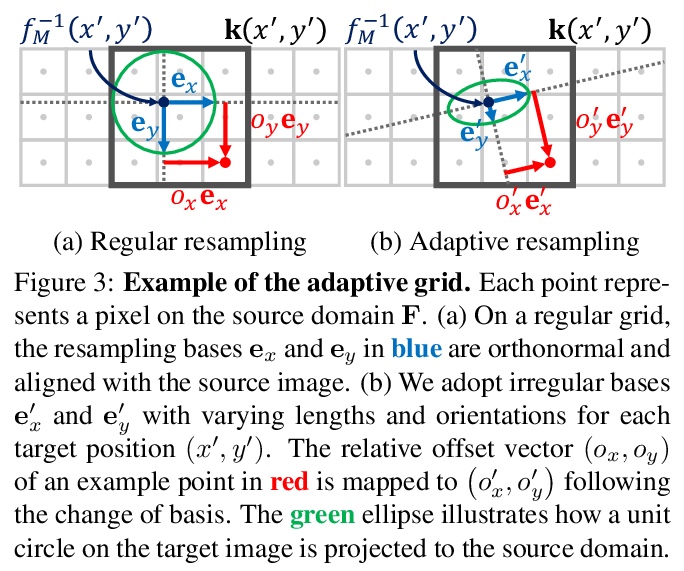
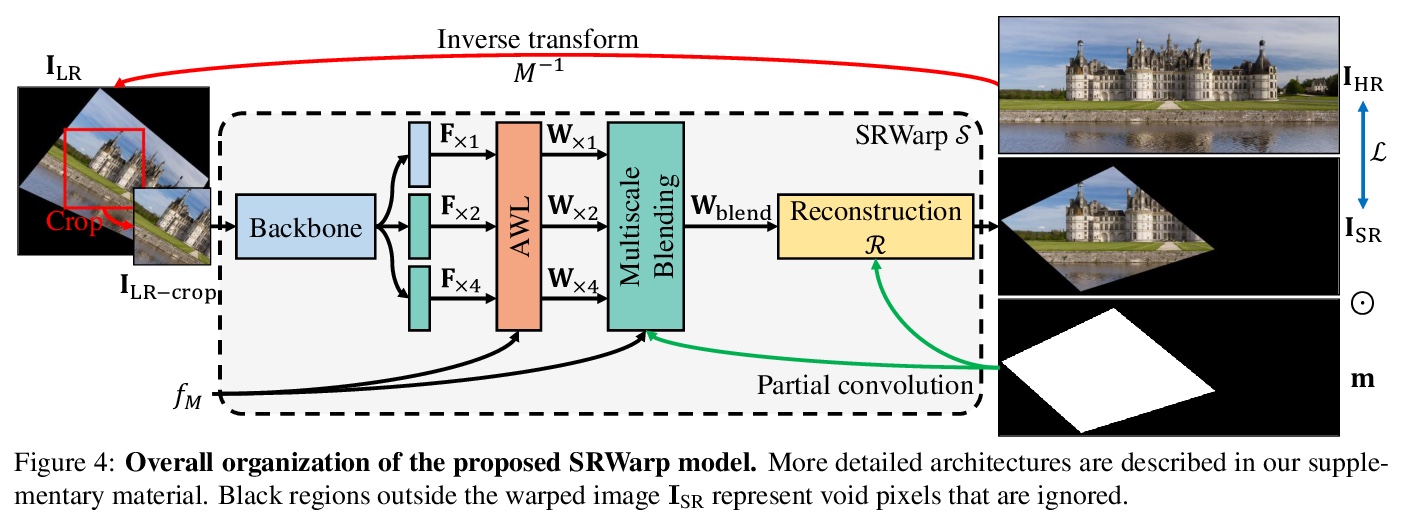
3、[CV] SRWarp: Generalized Image Super-Resolution under Arbitrary Transformation
S Son, K M Lee
[Seoul National University]
SRWarp: 任意变换下的通用图像超分辨率。深度卷积网络在图像处理及其应用方面取得了重大成就,包括单幅图像超分辨率(SR)。然而,传统方法仍然依赖一些预先确定的整数缩放因子,如×2或×4,当需要任意的目标分辨率时,很难被应用。最近的方法将范围扩大到实值升采样因子,甚至用不同的长宽比来突破这个限制。本文提出SRWarp框架,将超分辨率任务进一步向任意图像变换的方向推广。将传统的图像扭曲任务,特别是当输入被放大时,解释为一个空间变化的超分辨率问题。提出几个新的公式,包括自适应翘曲层和多尺度混合,以便在变换过程中重建视觉上有利的结果。与以前的方法相比,没有将超分辨率模型约束在一个规则的网格上,而是允许无数可能的变形,以实现灵活多样的图像编辑。广泛的实验证明了所提出的SRWarp方法的必要性,并证明了其在各种变换下的优势。
Deep CNNs have achieved significant successes in image processing and its applications, including single image super-resolution (SR). However, conventional methods still resort to some predetermined integer scaling factors, e.g., x2 or x4. Thus, they are difficult to be applied when arbitrary target resolutions are required. Recent approaches extend the scope to real-valued upsampling factors, even with varying aspect ratios to handle the limitation. In this paper, we propose the SRWarp framework to further generalize the SR tasks toward an arbitrary image transformation. We interpret the traditional image warping task, specifically when the input is enlarged, as a spatially-varying SR problem. We also propose several novel formulations, including the adaptive warping layer and multiscale blending, to reconstruct visually favorable results in the transformation process. Compared with previous methods, we do not constrain the SR model on a regular grid but allow numerous possible deformations for flexible and diverse image editing. Extensive experiments and ablation studies justify the necessity and demonstrate the advantage of the proposed SRWarp method under various transformations.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcMFyo6Ap
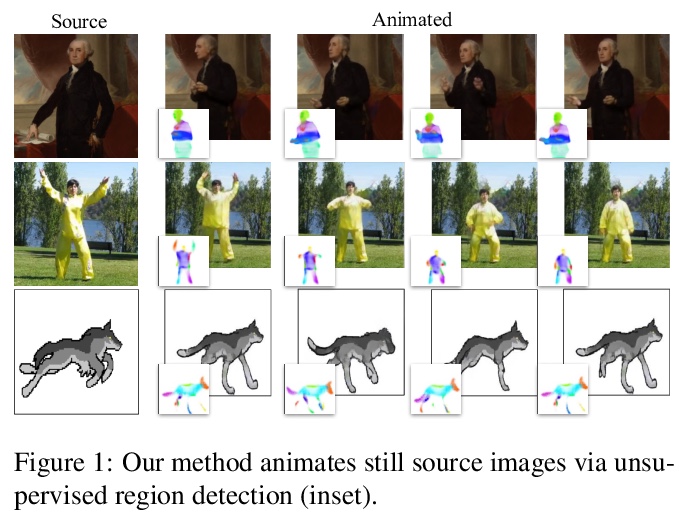
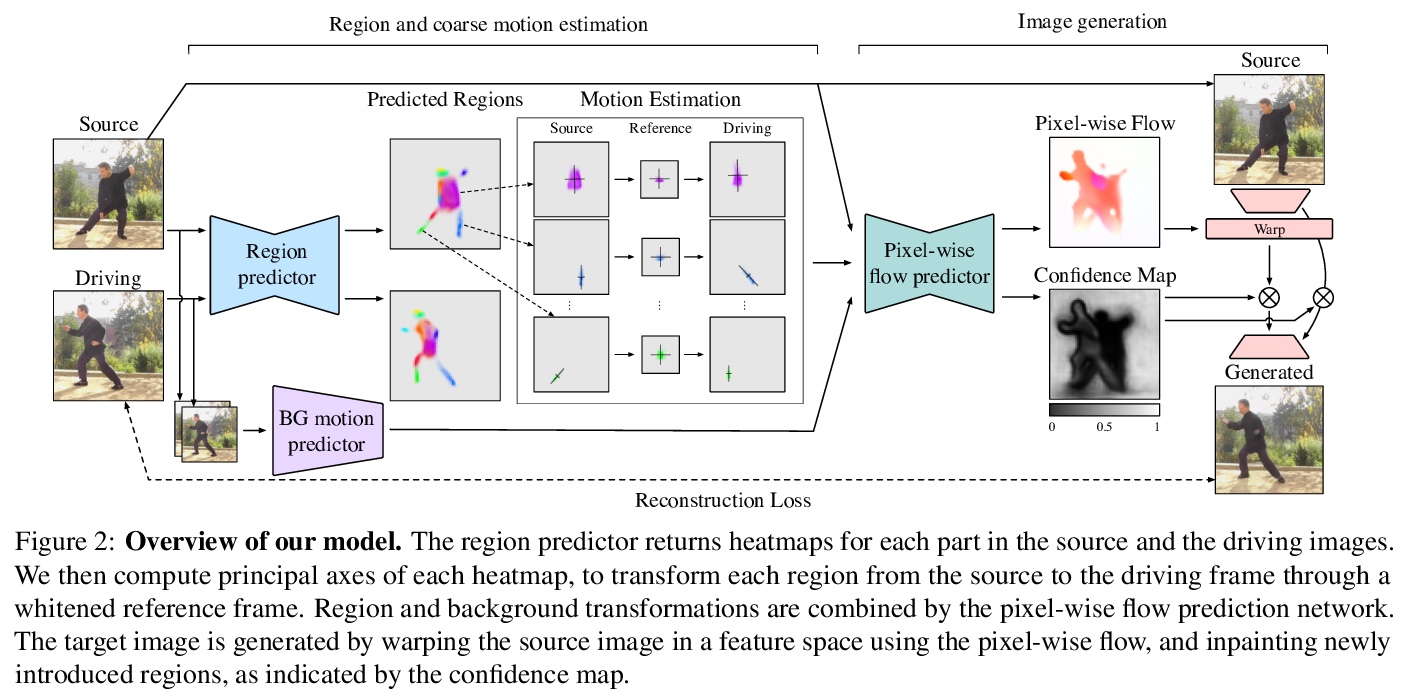
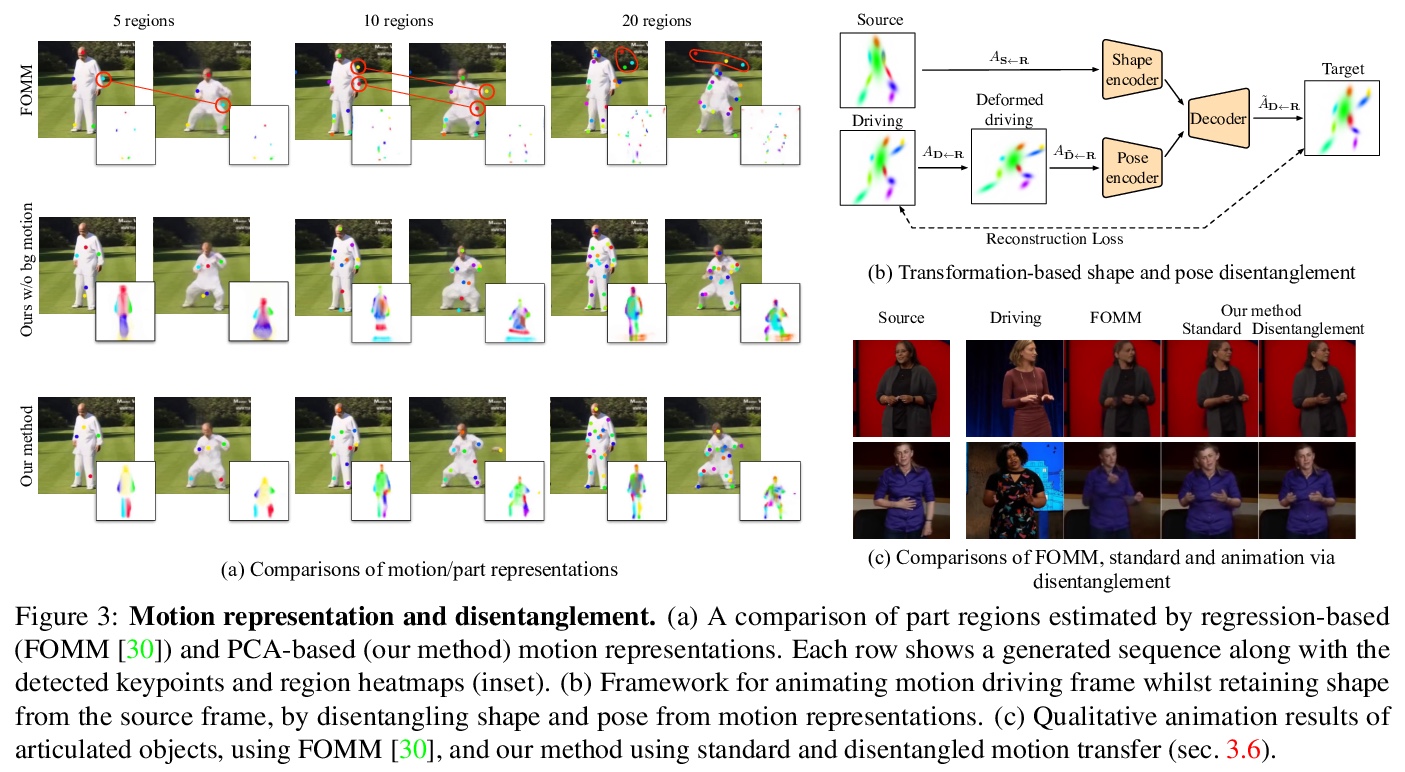
4、[CV] Motion Representations for Articulated Animation
A Siarohin, O J. Woodford, J Ren, M Chai, S Tulyakov
[University of Trento & Snap Inc]
关节动画的运动表示。之前的无监督动画框架,在有关节物体上效果不佳,主要在于表示方法。本文提出一种新的、基于PCA的区域运动表示,既能使网络更容易地学习区域运动,又能鼓励学习有语义的物体部分。提出了背景运动估计模块,以解耦前景和背景运动。在一系列数据集和任务上的定性和定量结果,表明了几个关键的优势:改善了区域分布和稳定性,提高了重建精度和用户感知质量,有能力扩展到更多的区域。引入一个新的、更具挑战性的数据集—TED-talks,以作为未来改进这一任务的基准。
We propose novel motion representations for animating articulated objects consisting of distinct parts. In a completely unsupervised manner, our method identifies object parts, tracks them in a driving video, and infers their motions by considering their principal axes. In contrast to the previous keypoint-based works, our method extracts meaningful and consistent regions, describing locations, shape, and pose. The regions correspond to semantically relevant and distinct object parts, that are more easily detected in frames of the driving video. To force decoupling of foreground from background, we model non-object related global motion with an additional affine transformation. To facilitate animation and prevent the leakage of the shape of the driving object, we disentangle shape and pose of objects in the region space. Our model can animate a variety of objects, surpassing previous methods by a large margin on existing benchmarks. We present a challenging new benchmark with high-resolution videos and show that the improvement is particularly pronounced when articulated objects are considered, reaching 96.6% user preference vs. the state of the art.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcMJ0jcVD


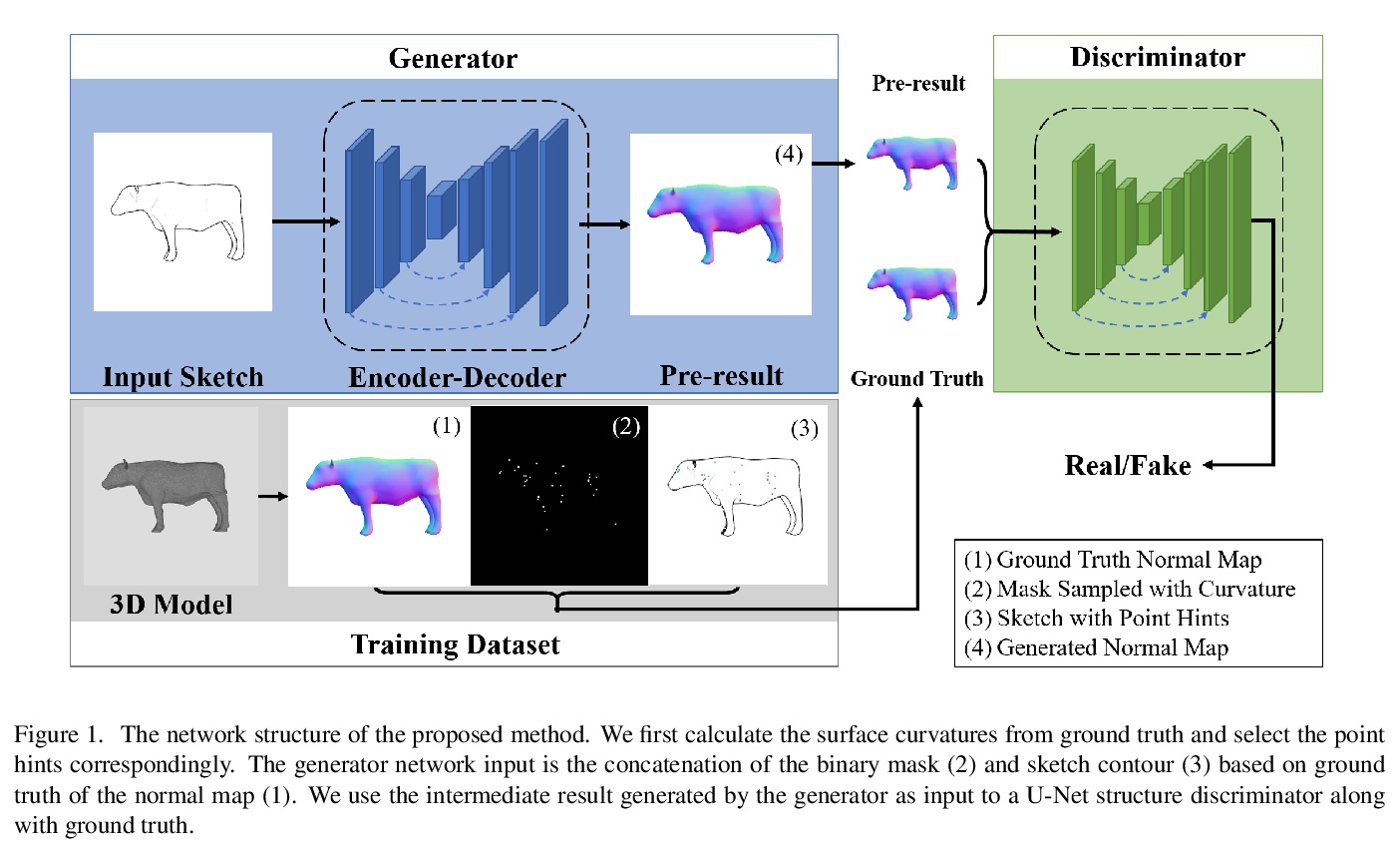
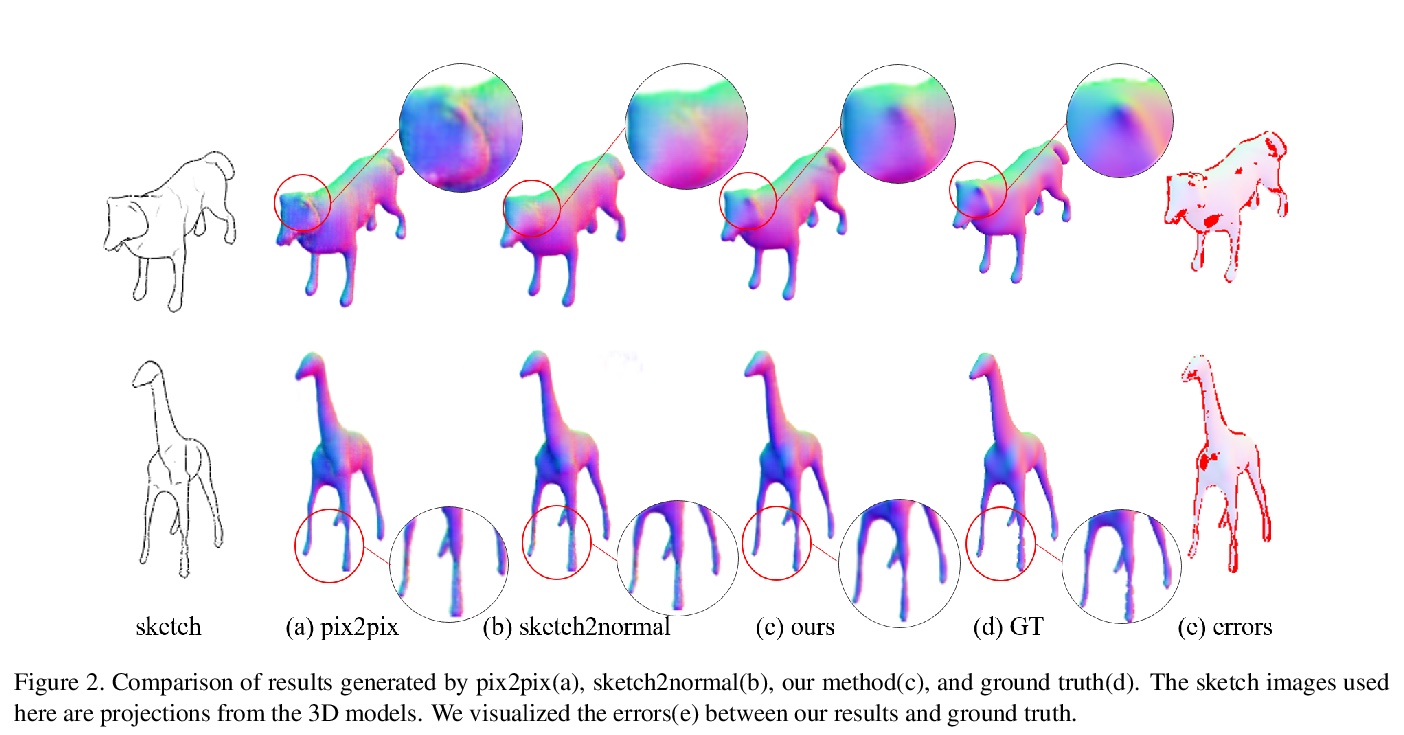
5、[CV] Sketch-based Normal Map Generation with Geometric Sampling
Y He, H Xie, C Zhang, X Yang, K Miyata
[JAIST & University of Fukui & The University of Tokyo]
基于草图的几何采样法线图生成。法线图是表示复杂三维模型的一种重要而有效的方法。在3D内容创作中,设计师可从自由手绘的草图中自动生成高质量和准确的法线图而大大受益。本文提出一种深度生成模型,用于从用户的草图中生成几何采样法线图,可生成边界清晰、法线纹理流畅的法线图。生成模型基于条件生成对抗网络和条件掩码的曲率敏感点采样。这种采样过程可以帮助消除作为网络输入的生成结果的模糊性。采用U-Net结构判别器,以帮助生成器得到更好的训练。经验证,所提出的框架可以生成更准确的法线图。
Normal map is an important and efficient way to represent complex 3D models. A designer may benefit from the auto-generation of high quality and accurate normal maps from freehand sketches in 3D content creation. This paper proposes a deep generative model for generating normal maps from users sketch with geometric sampling. Our generative model is based on Conditional Generative Adversarial Network with the curvature-sensitive points sampling of conditional masks. This sampling process can help eliminate the ambiguity of generation results as network input. In addition, we adopted a U-Net structure discriminator to help the generator be better trained. It is verified that the proposed framework can generate more accurate normal maps.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcMLzycqq
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
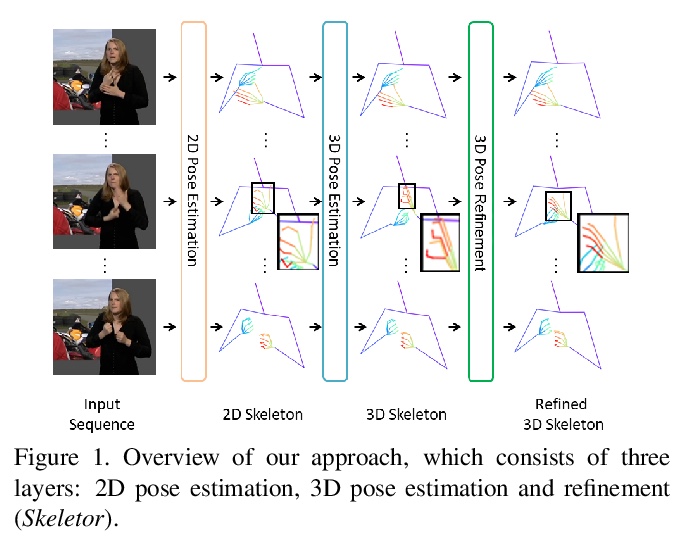
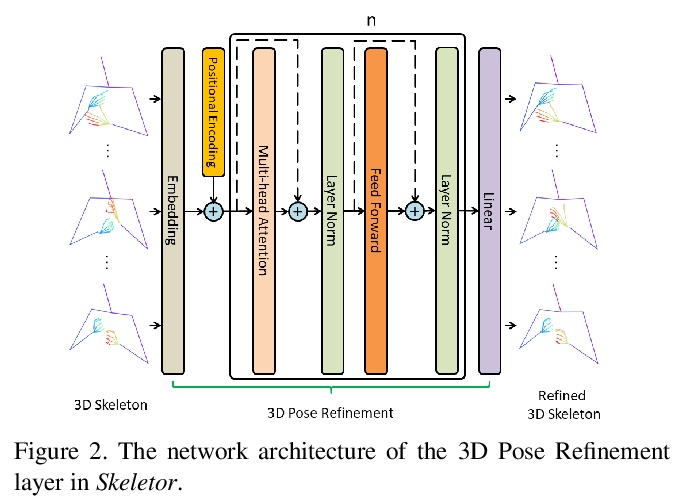
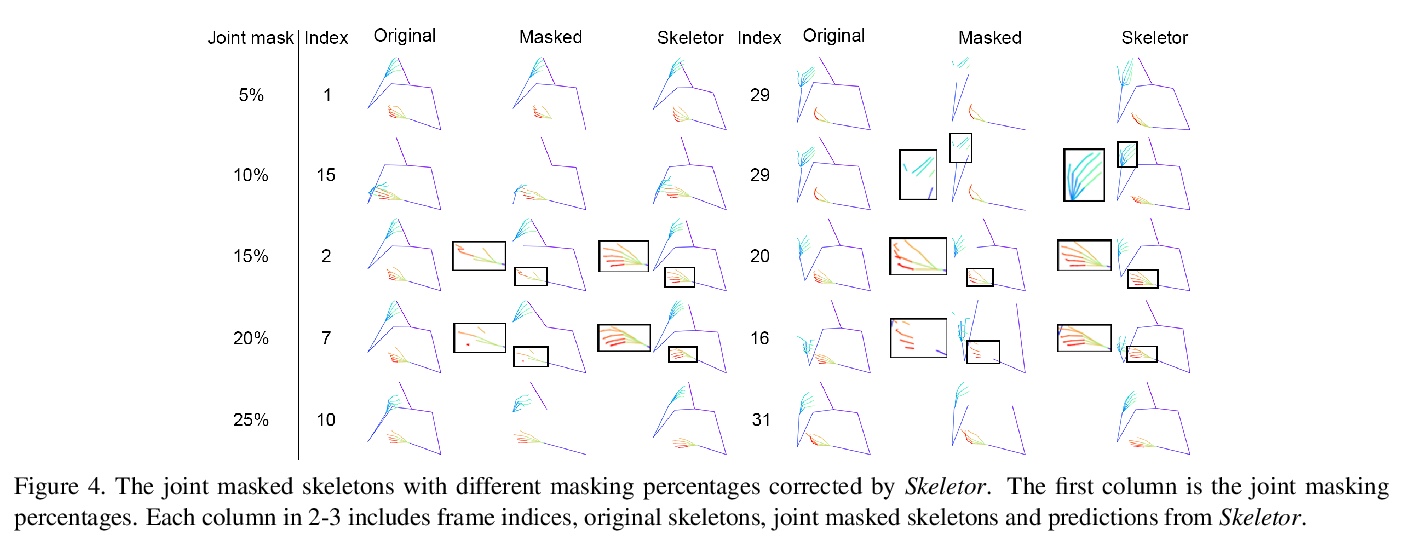
[CV] Skeletor: Skeletal Transformers for Robust Body-Pose Estimation
Skeletor:面向鲁棒人体姿态估计的骨架Transformer
T Jiang, N C Camgoz, R Bowden
[University of Surrey]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcMOCoy4Y

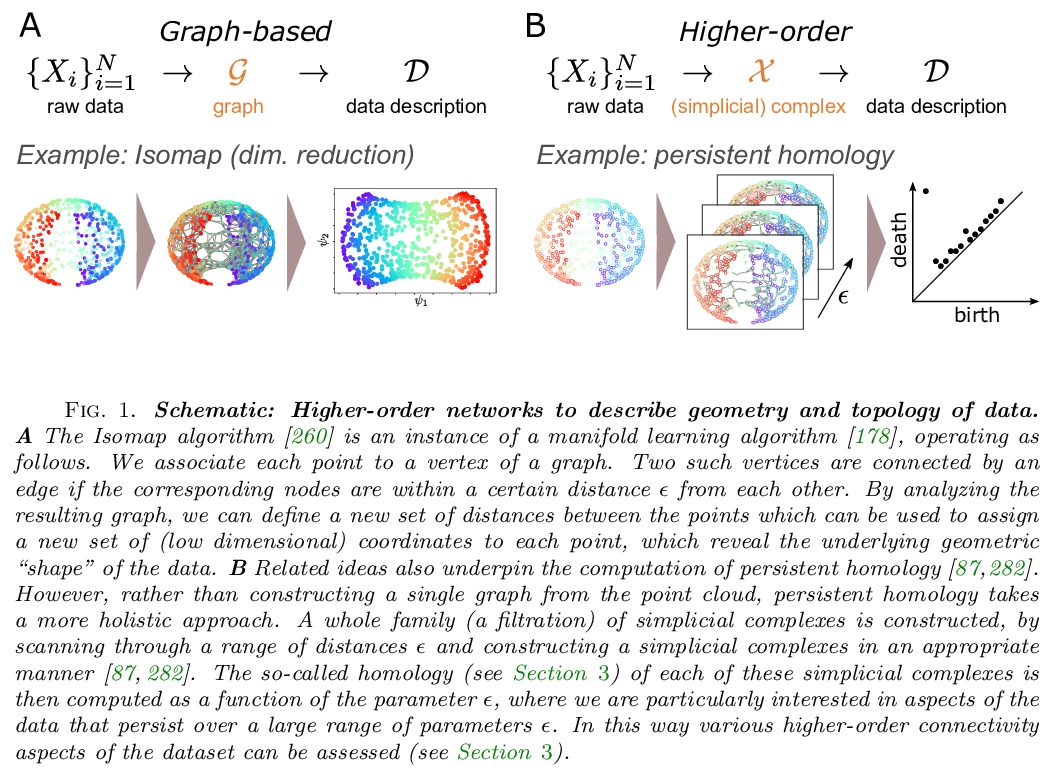
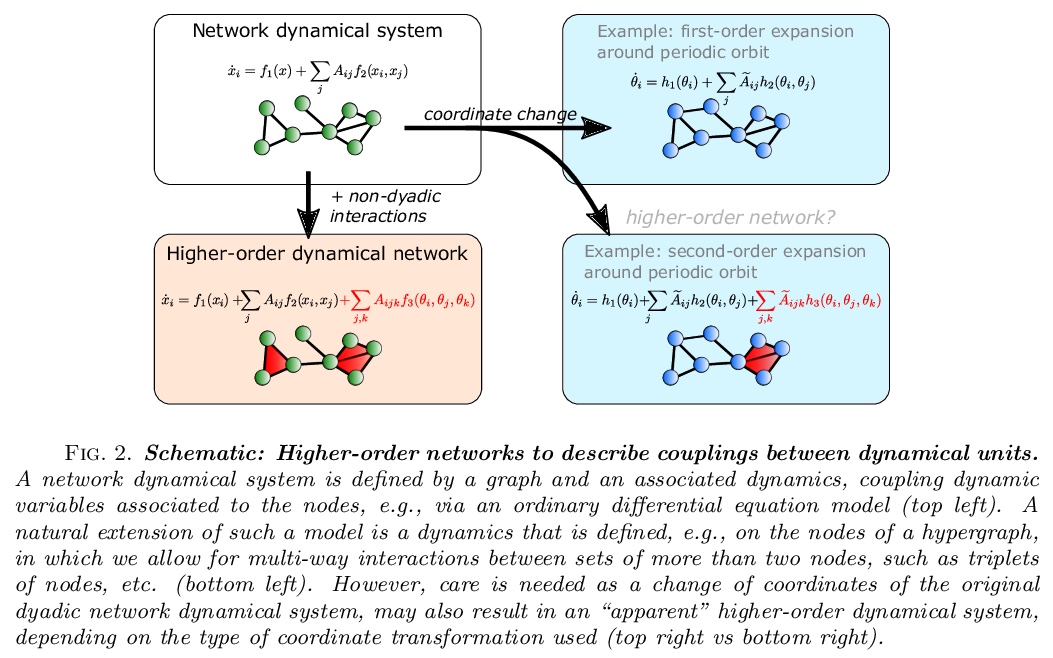
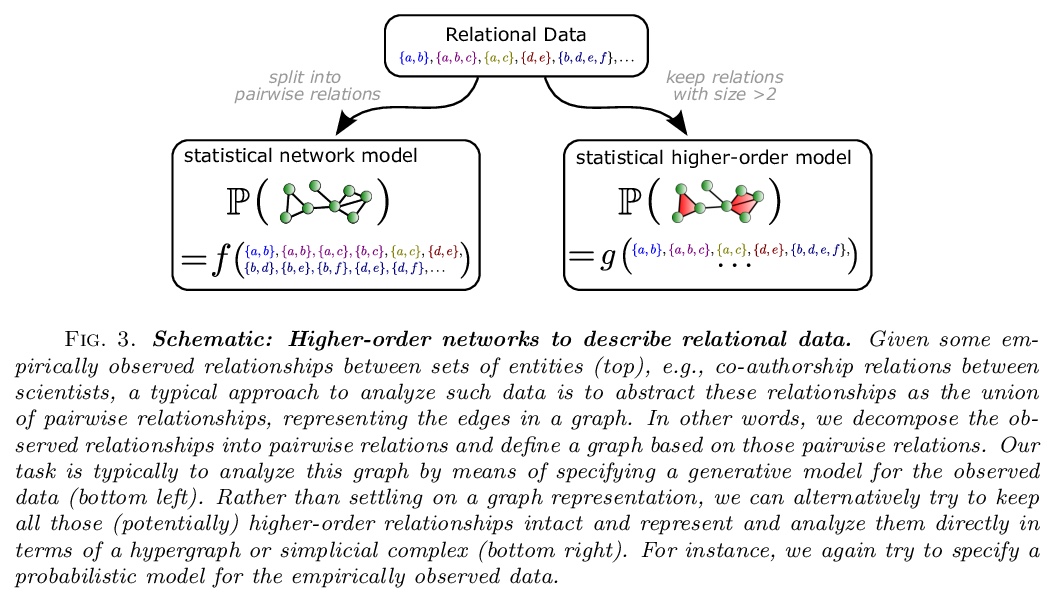
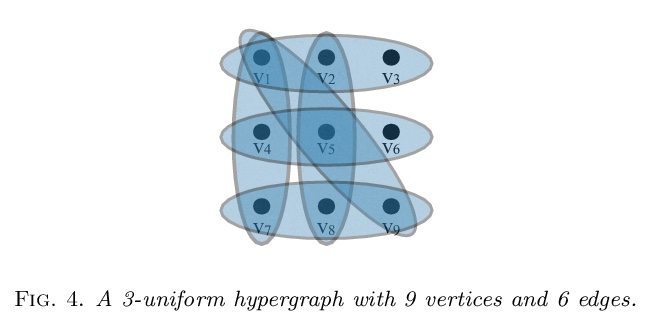
[SI] What are higher-order networks?
什么是高阶网络?
C Bick, E Gross, H A. Harrington, M T. Schaub
[Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam & University of Hawai‘i at Manoa & University of Oxford & RWTH Aachen University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcMQT2QX6
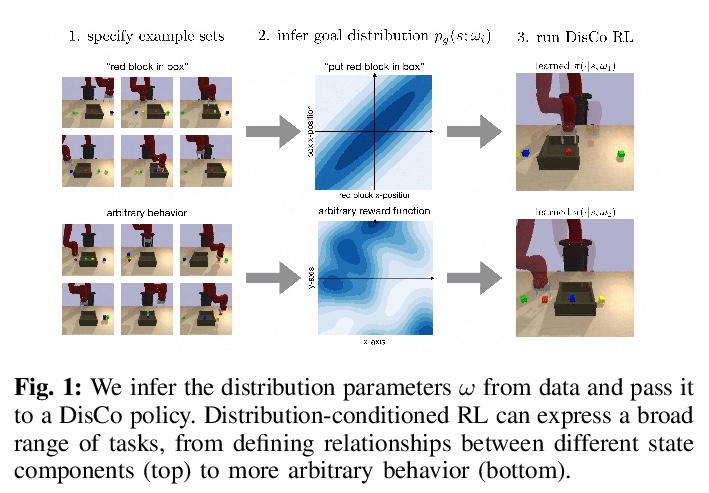
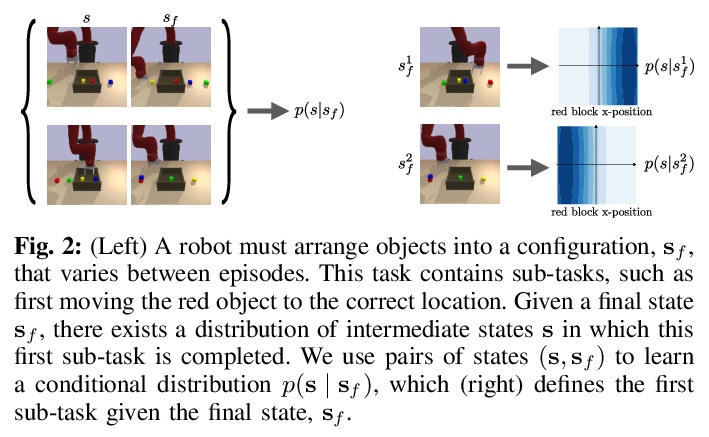
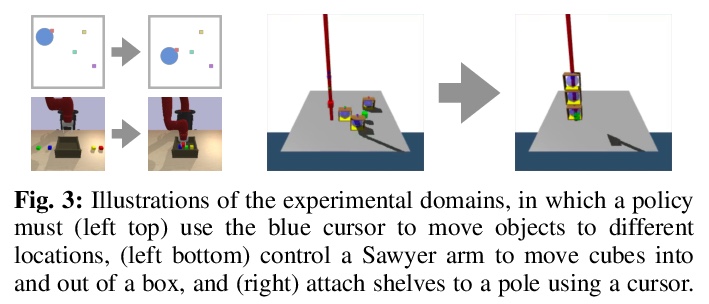
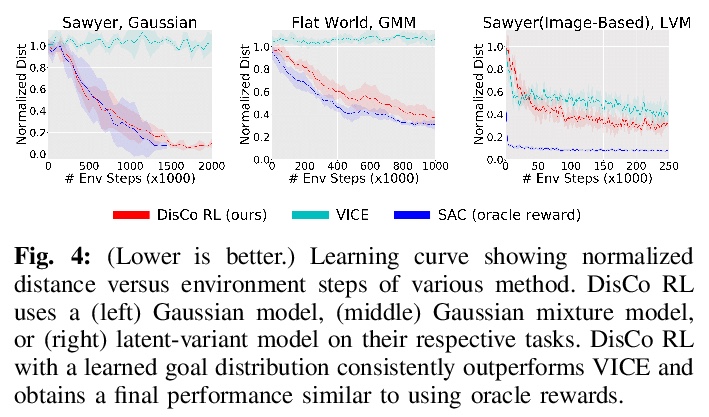
[LG] DisCo RL: Distribution-Conditioned Reinforcement Learning for General-Purpose Policies
DisCo RL:通用策略分布条件强化学习
S Nasiriany, V H. Pong, A Nair, A Khazatsky, G Berseth, S Levine
[UC Berkeley]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcMS3b0Wi
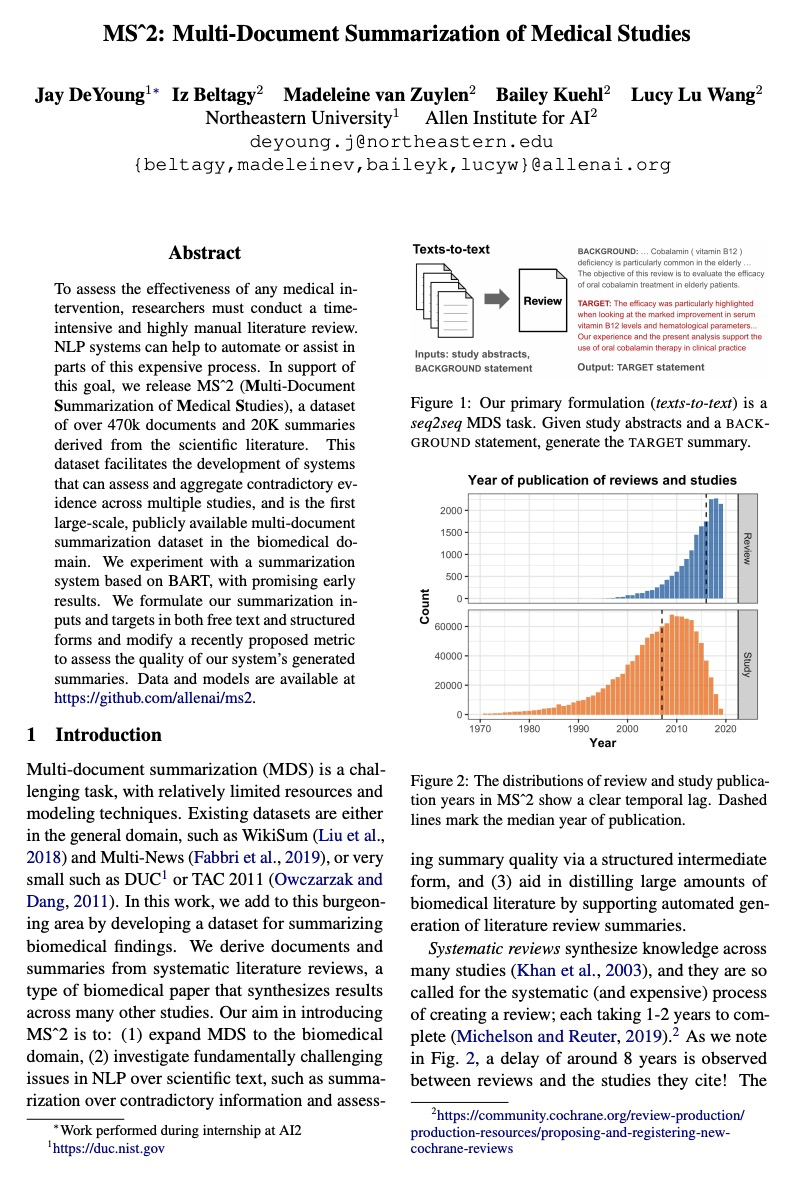
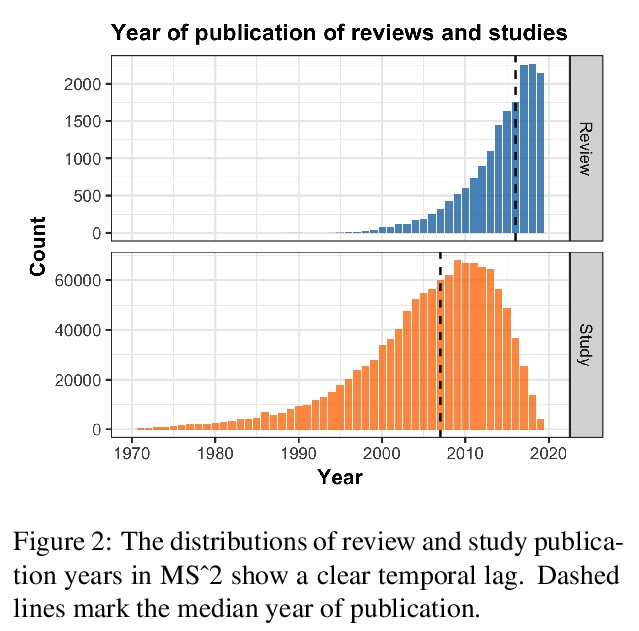
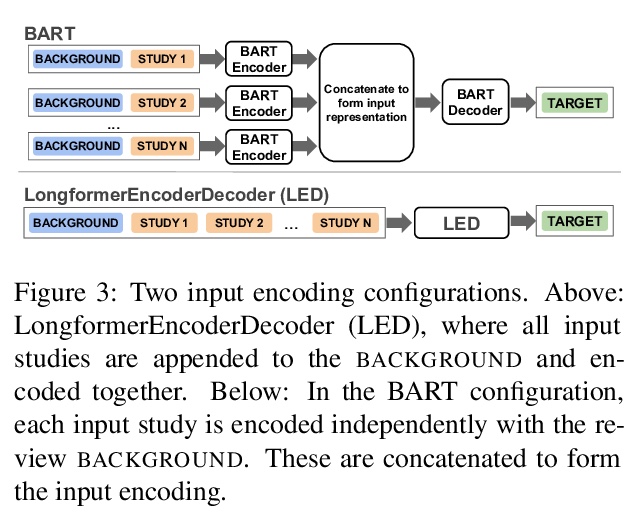
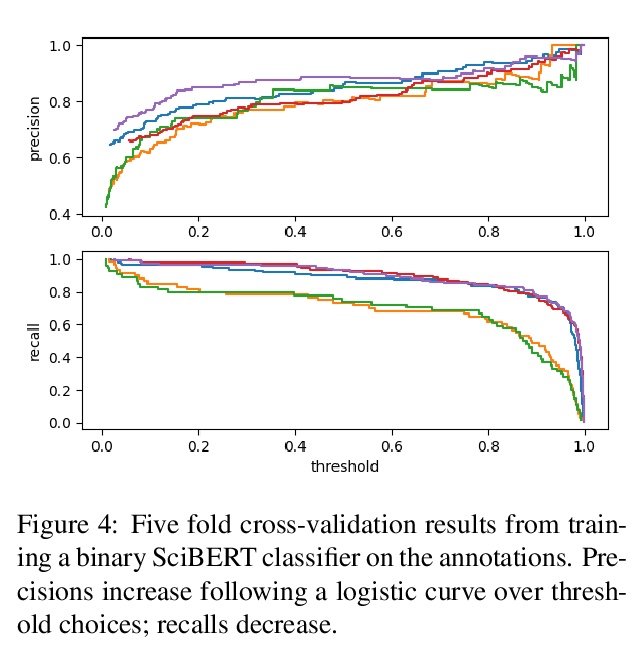
[CL] MS2: Multi-Document Summarization of Medical Studies
MS2:医学研究多文档综述
J DeYoung, I Beltagy, M v Zuylen, B Kuehl, L L Wang
[Northeastern University & Allen Institute for AI]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcMU83mgQ