- 1、[AI] Symbolic Behaviour in Artificial Intelligence
- 2、[CV] CharacterGAN: Few-Shot Keypoint Character Animation and Reposing
- 3、[CV] SwiftNet: Real-time Video Object Segmentation
- 4、[CL] Bayesian Transformer Language Models for Speech Recognition
- 5、[CV] DEFT: Detection Embeddings for Tracking
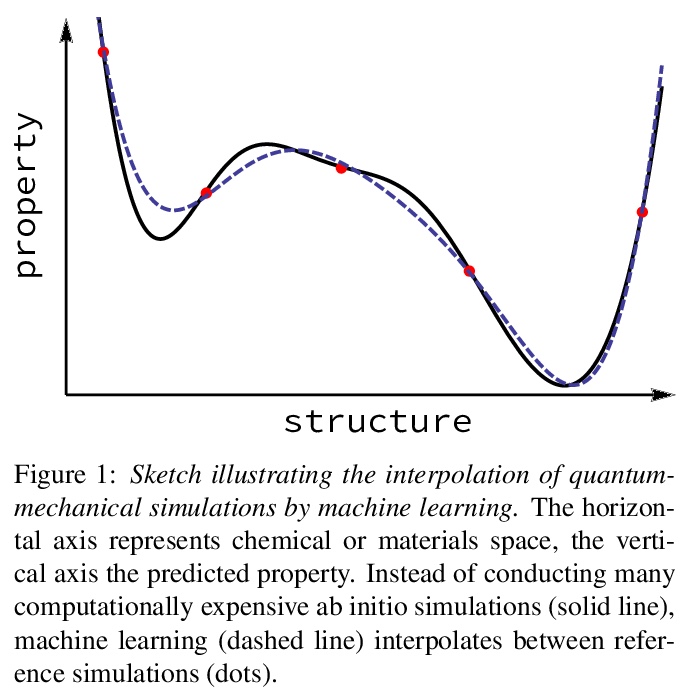
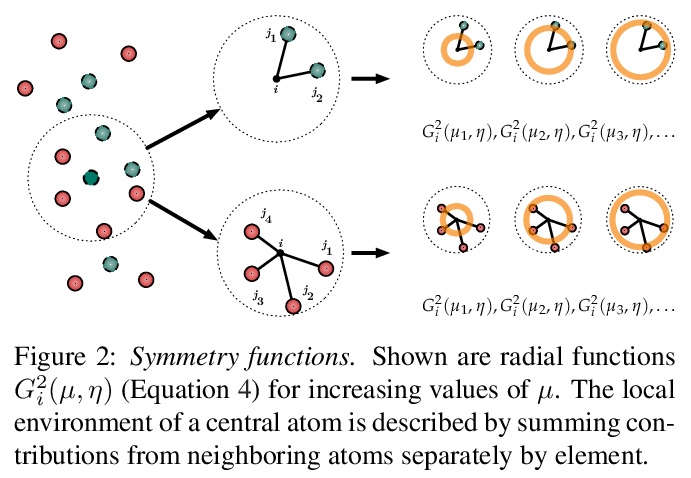
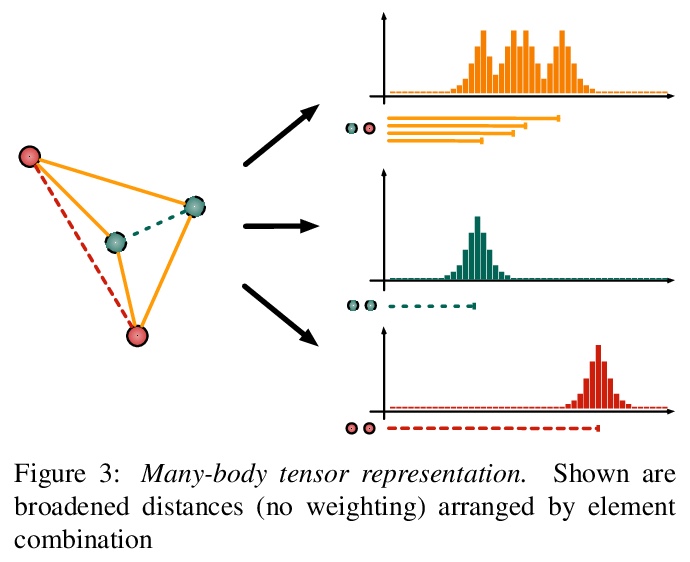
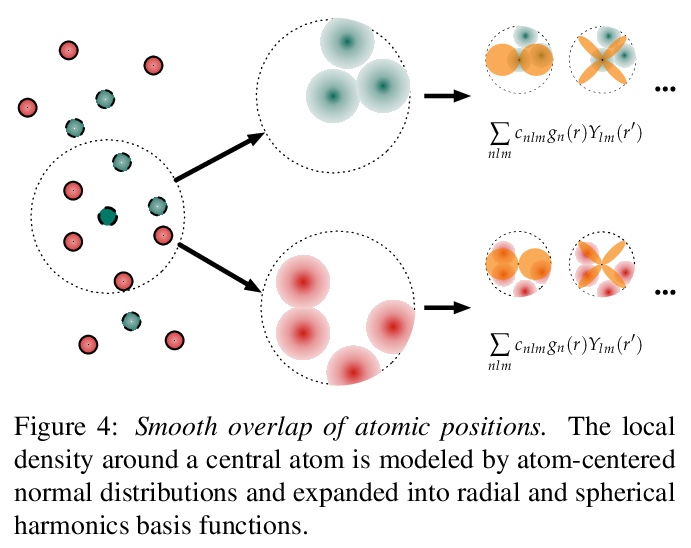
- [LG] Representations of molecules and materials for interpolation of quantum-mechanical simulations via machine learning
- [CV] Telling the What while Pointing the Where: Fine-grained Mouse Trace and Language Supervision for Improved Image Retrieval
- [LG] When does gradient descent with logistic loss interpolate using deep networks with smoothed ReLU activations?
- [CV] Unlocking Pixels for Reinforcement Learning via Implicit Attention
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[AI] Symbolic Behaviour in Artificial Intelligence
A Santoro, A Lampinen, K Mathewson, T Lillicrap, D Raposo
[DeepMind]
人工智能的符号化行为。使用符号的能力是人类智慧的巅峰,但尚未在机器中完全复制。要达到符号流畅的人工智能,首先要重新解释什么是符号,它们是如何存在的,以及系统在使用它们时的行为。首先提供了一种解释,将符号解释为实体,其意义是约定俗成的,而且只有对那些明确地、积极地参与这种约定的人来说,某物才是一个符号。之后,概述了这种解释如何在主题上统一了人类在使用符号时表现出的行为特征,包括接受性、建构性、嵌入性、可塑性、可分离性、意义性和分级性。应更多地强调符号化行为,而不是由更严格的符号解释所激发的特定计算机制。最后,建议人工智能研究探索社会和文化参与,作为发展符号行为出现所需的认知机制的工具。将使人工智能能够自行将某一事物解释为符号,而不是简单地操纵那些对人类旁观者来说只是符号的事物,从而最终使人工智能具有更类似人类的符号流畅性。我们需要的人工智能,是由对符号的深刻理解所驱动的,符号是按惯例作为意义基础设施的成员,它表现为细微的、灵活的、受各种塑造力量影响的行为。如果希望人工智能一些像人类一样融合伦理、推理、甚至美感等问题,就应该注重在人工智能中灌输符号行为。
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K1nLF7FKY
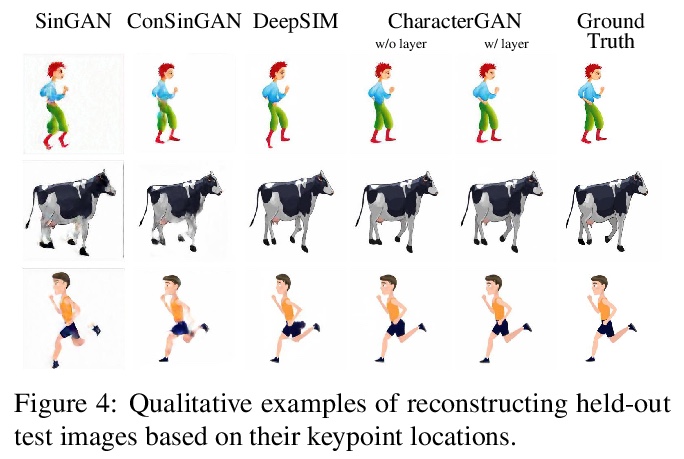
2、[CV] CharacterGAN: Few-Shot Keypoint Character Animation and Reposing
T Hinz, M Fisher, O Wang, E Shechtman, S Wermter
[University of Hamburg & Adobe Research]
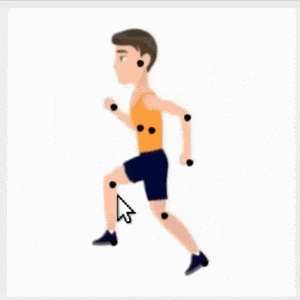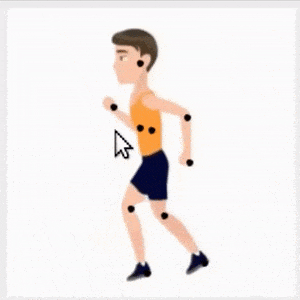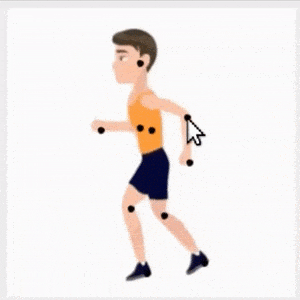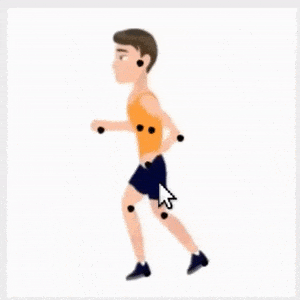
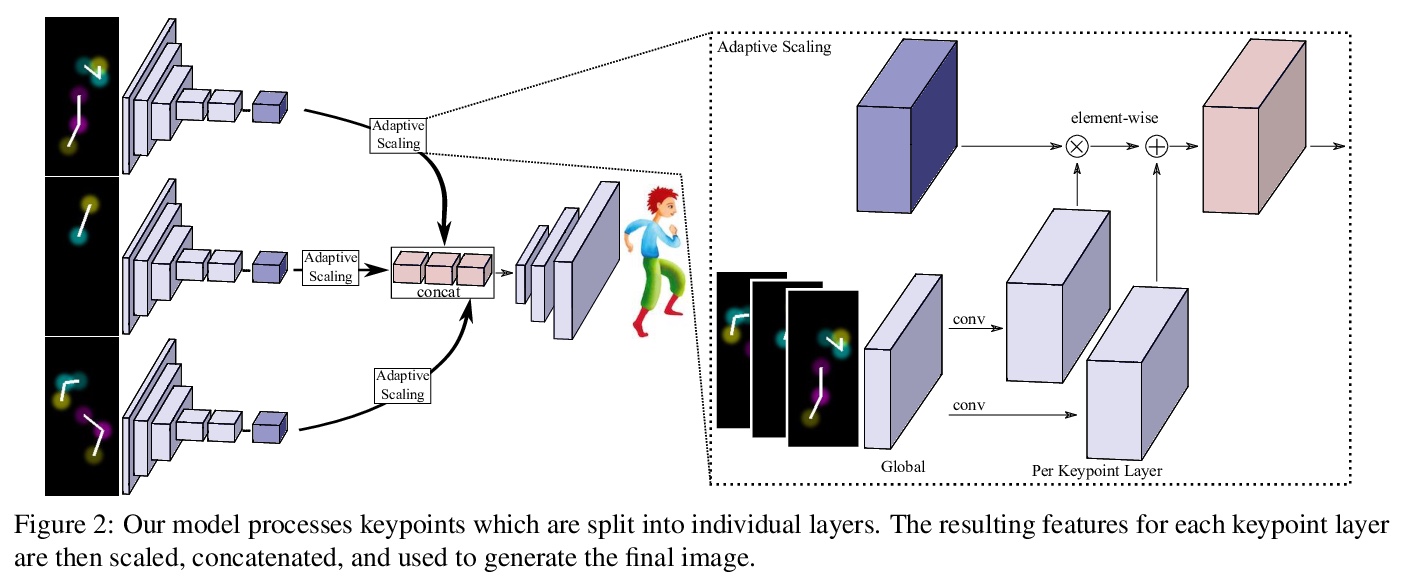
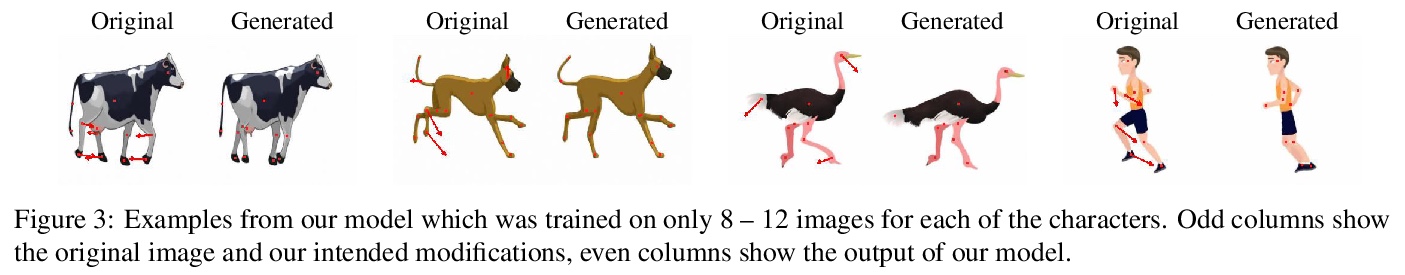
CharacterGAN:少样本关键点角色动画和姿态重排。提出了生成式模型CharacterGAN,可以在给定角色少数几张图像(8-15张)上训练GAN,实现少样本角色姿态重排和动画。仅对关键点(而不是语义图)进行训练,模型可在没有专家知识的情况下进行实时角色姿态重排。通过使用明确编码不同关键点顺序的分层方法,模型能够仅用非常有限的训练数据来模拟遮挡。引入了掩模连通性约束,在测试时可以使用共同预测的掩模来自动修复模型产生不现实输出的关键点布局。CharacterGAN可通过移动关键点来进行实时的角色姿态重排,并可以通过插值关键点来进行角色动画,处理离散的状态变化。
We introduce CharacterGAN, a generative model that can be trained on only a few samples (8 - 15) of a given character. Our model generates novel poses based on keypoint locations, which can be modified in real time while providing interactive feedback, allowing for intuitive reposing and animation. Since we only have very limited training samples, one of the key challenges lies in how to address (dis)occlusions, e.g. when a hand moves behind or in front of a body. To address this, we introduce a novel layering approach which explicitly splits the input keypoints into different layers which are processed independently. These layers represent different parts of the character and provide a strong implicit bias that helps to obtain realistic results even with strong (dis)occlusions. To combine the features of individual layers we use an adaptive scaling approach conditioned on all keypoints. Finally, we introduce a mask connectivity constraint to reduce distortion artifacts that occur with extreme out-of-distribution poses at test time. We show that our approach outperforms recent baselines and creates realistic animations for diverse characters. We also show that our model can handle discrete state changes, for example a profile facing left or right, that the different layers do indeed learn features specific for the respective keypoints in those layers, and that our model scales to larger datasets when more data is available.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K1nTh6afK

3、[CV] SwiftNet: Real-time Video Object Segmentation
H Wang, X Jiang, H Ren, Y Hu, S Bai
[Alibaba Youku Cognitive and Intelligent Lab & University of Oxford]
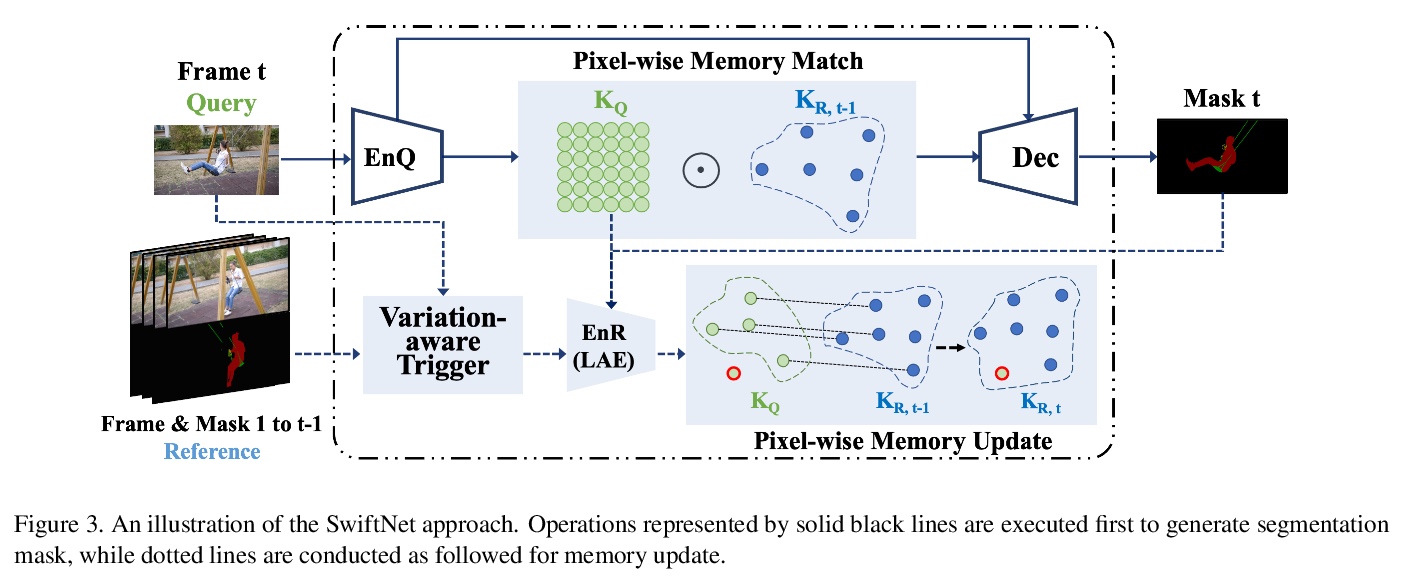
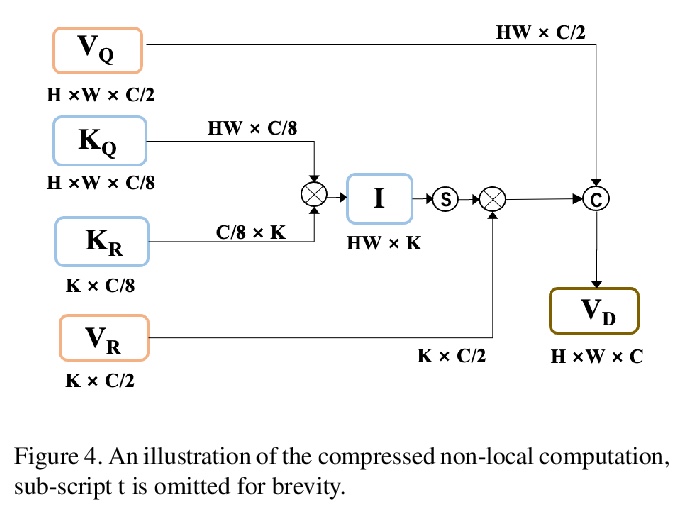
SwiftNet: 实时视频目标分割。提出了一种实时半监督视频目标分割解决方案SwiftNet,能提供最佳的整体精度和性能。SwiftNet通过显式压缩基于匹配的视频目标分割的时空冗余与像素自适应存储器(PAM)来实现实时分割。在PAM中,使用变化感知触发器减少时间冗余,自适应地选择增量帧进行内存更新,同时忽略静态帧。空间冗余通过像素化的内存更新和匹配模块来消除,放弃了全帧操作,只对时变像素进行增量处理。还设计了光聚合编码器(LAE),以彻底、快速进行参考帧编码。在DAVIS2016&2017和YouTube-VOS数据集上部署各种骨干进行了大量的实验,在DAVIS2017 test-dev上达到了77.8%的J&F和70 FPS的最佳整体分割精度和性能。
In this work we present SwiftNet for real-time semi-supervised video object segmentation (one-shot VOS), which reports 77.8% J&F and 70 FPS on DAVIS 2017 validation dataset, leading all present solutions in overall accuracy and speed performance. We achieve this by elaborately compressing spatiotemporal redundancy in matching-based VOS via Pixel-Adaptive Memory (PAM). Temporally, PAM adaptively triggers memory updates on frames where objects display noteworthy inter-frame variations. Spatially, PAM selectively performs memory update and match on dynamic pixels while ignoring the static ones, significantly reducing redundant computations wasted on segmentation-irrelevant pixels. To promote efficient reference encoding, light-aggregation encoder is also introduced in SwiftNet deploying reversed sub-pixel. We hope SwiftNet could set a strong and efficient baseline for real-time VOS and facilitate its application in mobile vision.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K1nZIAgcq

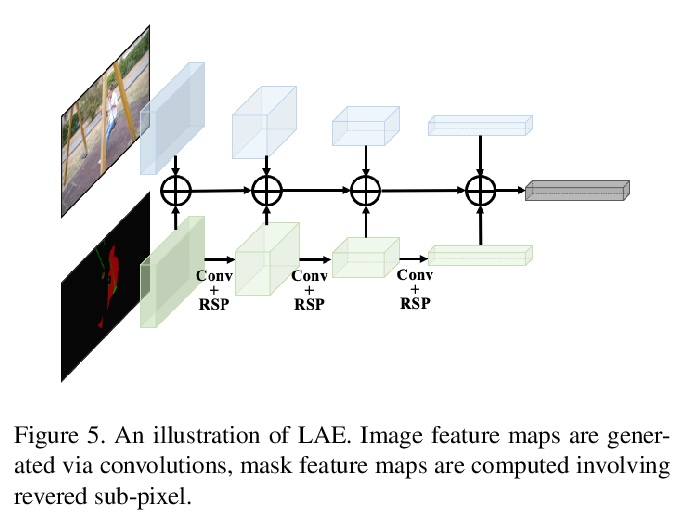
4、[CL] Bayesian Transformer Language Models for Speech Recognition
B Xue, J Yu, J Xu, S Liu, S Hu, Z Ye, M Geng, X Liu, H Meng
[The Chinese University of Hong Kong]
面向语音识别的贝叶斯Transformer语言模型。提出了一个用于Transformer语言模型估计的贝叶斯学习框架,以提高其泛化性能。采用了基于变分推断的高效方法来估计潜参数后验分布。对Transformer模型架构的不同部分(包括自注意力层、前馈层和嵌入层)贝叶斯估计的效果进行了系统研究。在Swithboard和DementiaBank Pitt数据集上,在困惑度和WER方面都获得了一致的性能改进,证明了所提出的贝叶斯Transformer语言模型在语音识别方面的优势。
State-of-the-art neural language models (LMs) represented by Transformers are highly complex. Their use of fixed, deterministic parameter estimates fail to account for model uncertainty and lead to over-fitting and poor generalization when given limited training data. In order to address these issues, this paper proposes a full Bayesian learning framework for Transformer LM estimation. Efficient variational inference based approaches are used to estimate the latent parameter posterior distributions associated with different parts of the Transformer model architecture including multi-head self-attention, feed forward and embedding layers. Statistically significant word error rate (WER) reductions up to 0.5\% absolute (3.18\% relative) and consistent perplexity gains were obtained over the baseline Transformer LMs on state-of-the-art Switchboard corpus trained LF-MMI factored TDNN systems with i-Vector speaker adaptation. Performance improvements were also obtained on a cross domain LM adaptation task requiring porting a Transformer LM trained on the Switchboard and Fisher data to a low-resource DementiaBank elderly speech corpus.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K1o2K9aLe
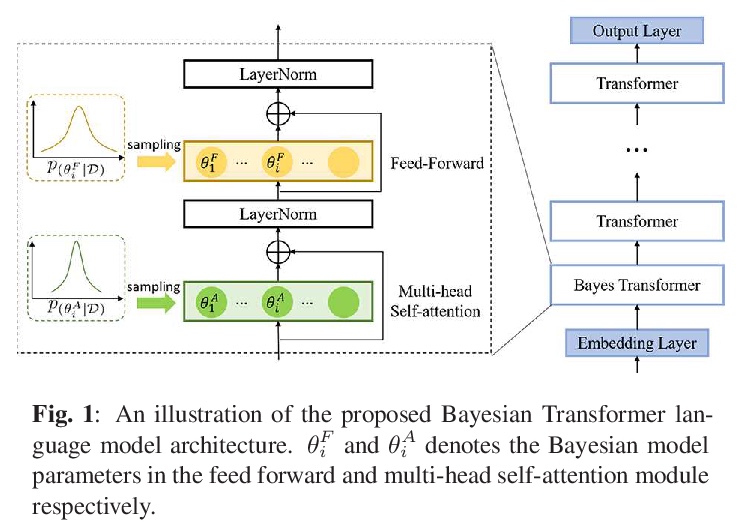
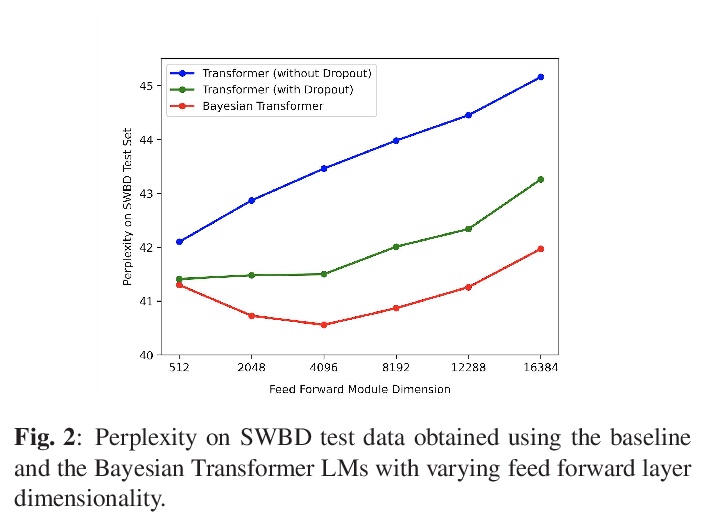
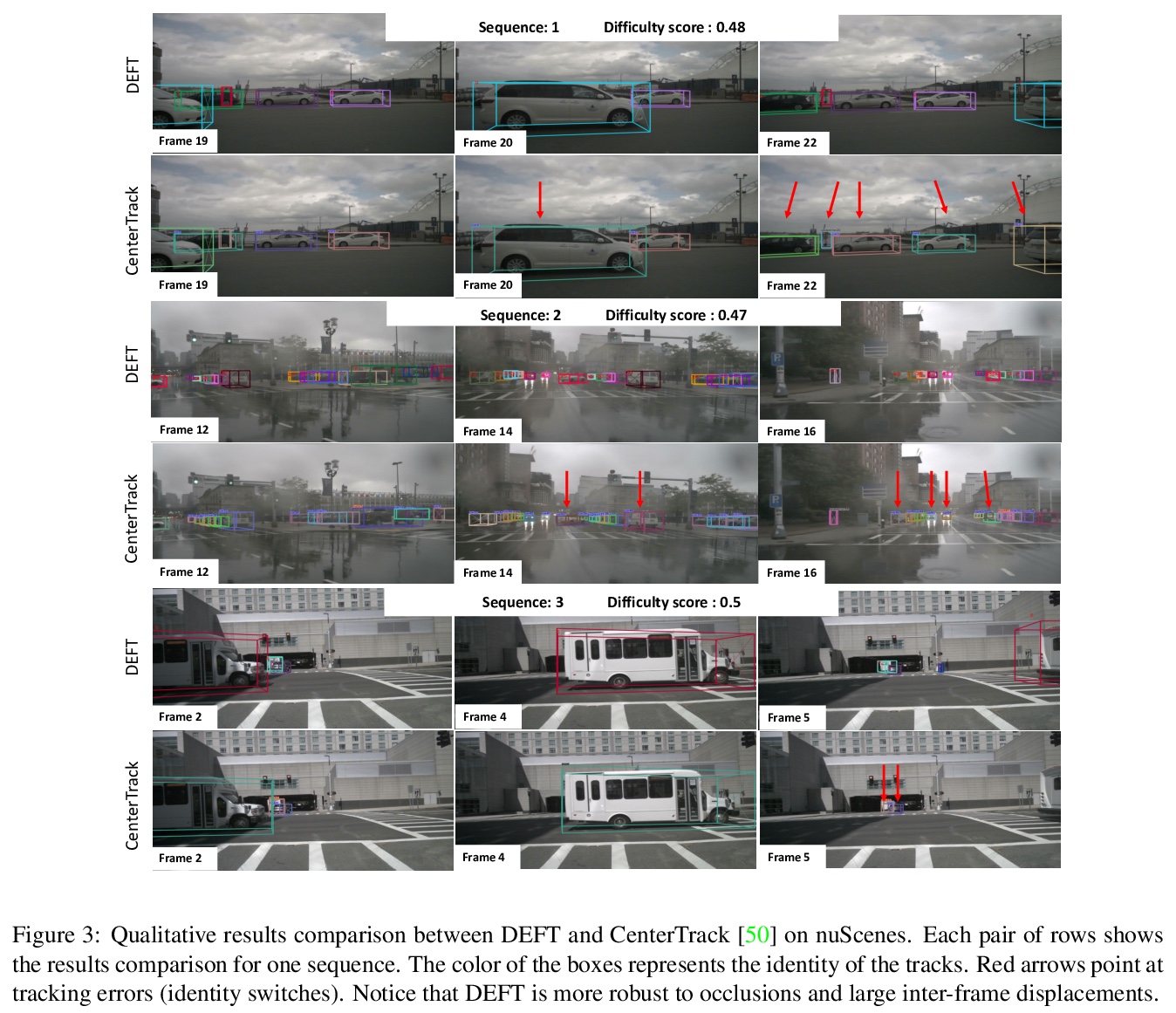
5、[CV] DEFT: Detection Embeddings for Tracking
M Chaabane, P Zhang, J. R Beveridge, S O’Hara
[Uber ATG & Aurora & Colorado State University]
DEFT:面向追踪的检测嵌入。提出一种高效的检测和跟踪联合模型DEFT(面向追踪的检测嵌入)。依赖于一个基于外观的目标匹配网络与底层目标检测网络联合学习,每个目标的嵌入是从检测器网络的多尺度骨干中提取出来的,并在追踪目标关联子网络中作为外观特征使用,添加了一个LSTM来捕捉运动约束。DEFT的精度和速度与2D在线追踪排行榜上的最先进方法相当,同时在应用于更具挑战性的追踪数据时,在鲁棒性方面具有显著优势。DEFT提高了nuScenes单目3D追踪挑战的门槛,比之前的顶级方法性能提高了一倍多。
Most modern multiple object tracking (MOT) systems follow the tracking-by-detection paradigm, consisting of a detector followed by a method for associating detections into tracks. There is a long history in tracking of combining motion and appearance features to provide robustness to occlusions and other challenges, but typically this comes with the trade-off of a more complex and slower implementation. Recent successes on popular 2D tracking benchmarks indicate that top-scores can be achieved using a state-of-the-art detector and relatively simple associations relying on single-frame spatial offsets — notably outperforming contemporary methods that leverage learned appearance features to help re-identify lost tracks. In this paper, we propose an efficient joint detection and tracking model named DEFT, or “Detection Embeddings for Tracking.” Our approach relies on an appearance-based object matching network jointly-learned with an underlying object detection network. An LSTM is also added to capture motion constraints. DEFT has comparable accuracy and speed to the top methods on 2D online tracking leaderboards while having significant advantages in robustness when applied to more challenging tracking data. DEFT raises the bar on the nuScenes monocular 3D tracking challenge, more than doubling the performance of the previous top method. Code is publicly available.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K1o5IfIpJ
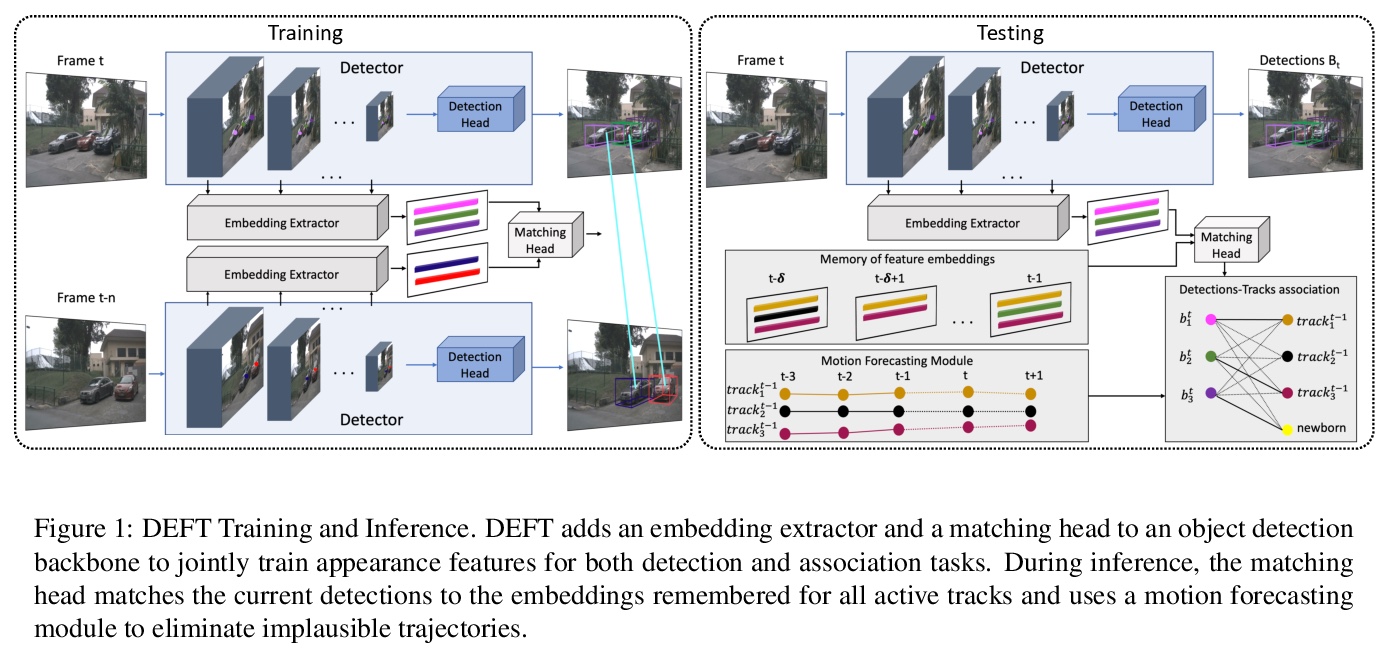

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[LG] Representations of molecules and materials for interpolation of quantum-mechanical simulations via machine learning
用机器学习进行量子力学模拟插值的分子和材料表示
M F. Langer, A Goeßmann, M Rupp
[Fritz Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K1oa5eOue
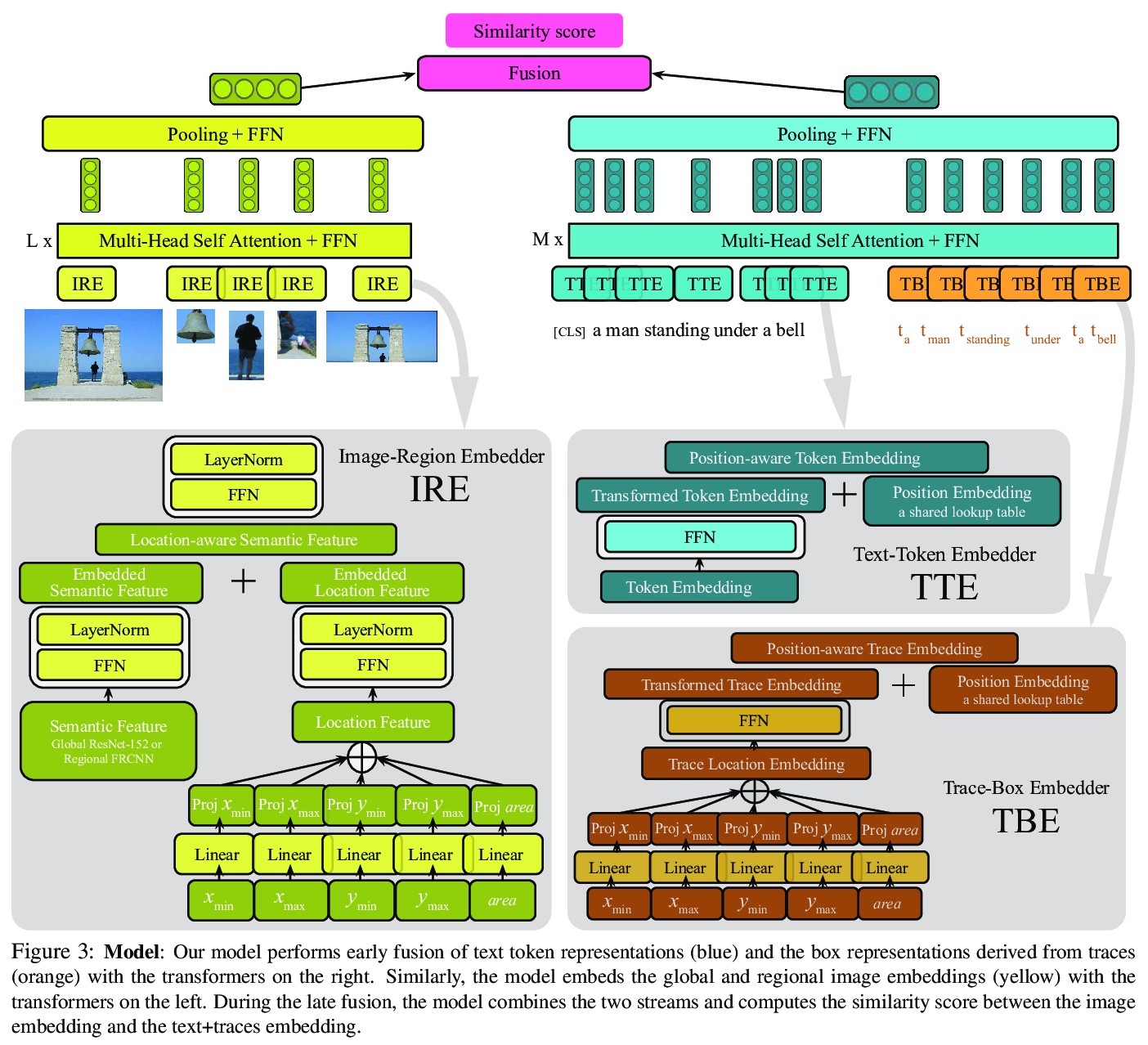
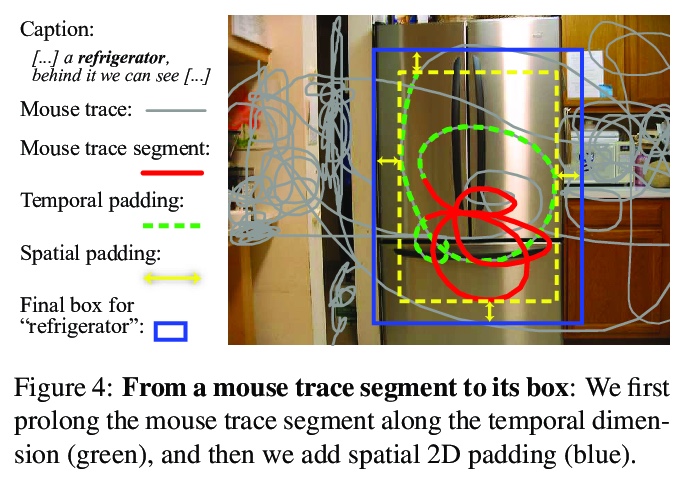
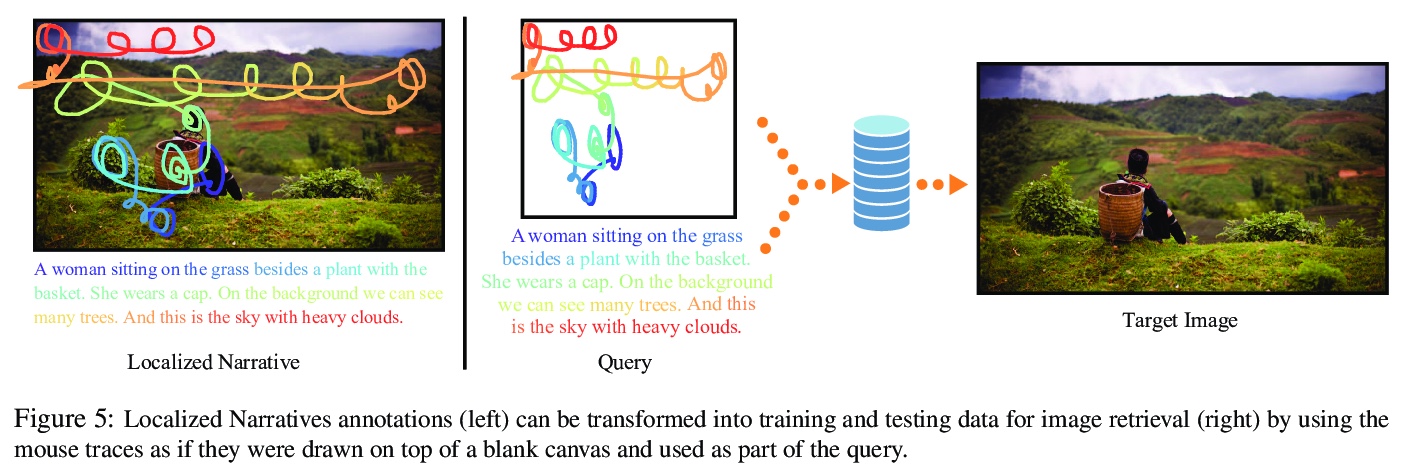
[CV] Telling the What while Pointing the Where: Fine-grained Mouse Trace and Language Supervision for Improved Image Retrieval
指出”在哪”还要说出“是啥”:面向改进图像检索的细粒度鼠标跟踪和语言监督
S Changpinyo, J Pont-Tuset, V Ferrari, R Soricut
[Google Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K1obUEycO

[LG] When does gradient descent with logistic loss interpolate using deep networks with smoothed ReLU activations?
固定宽度深度网络梯度下降logistic损失为零的条件及收敛速度的界
N S. Chatterji, P M. Long, P L. Bartlett
[UC Berkeley & Google]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K1oebolaq
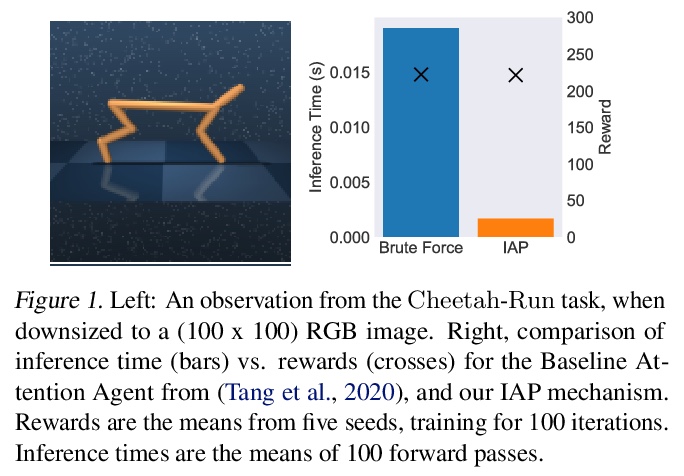
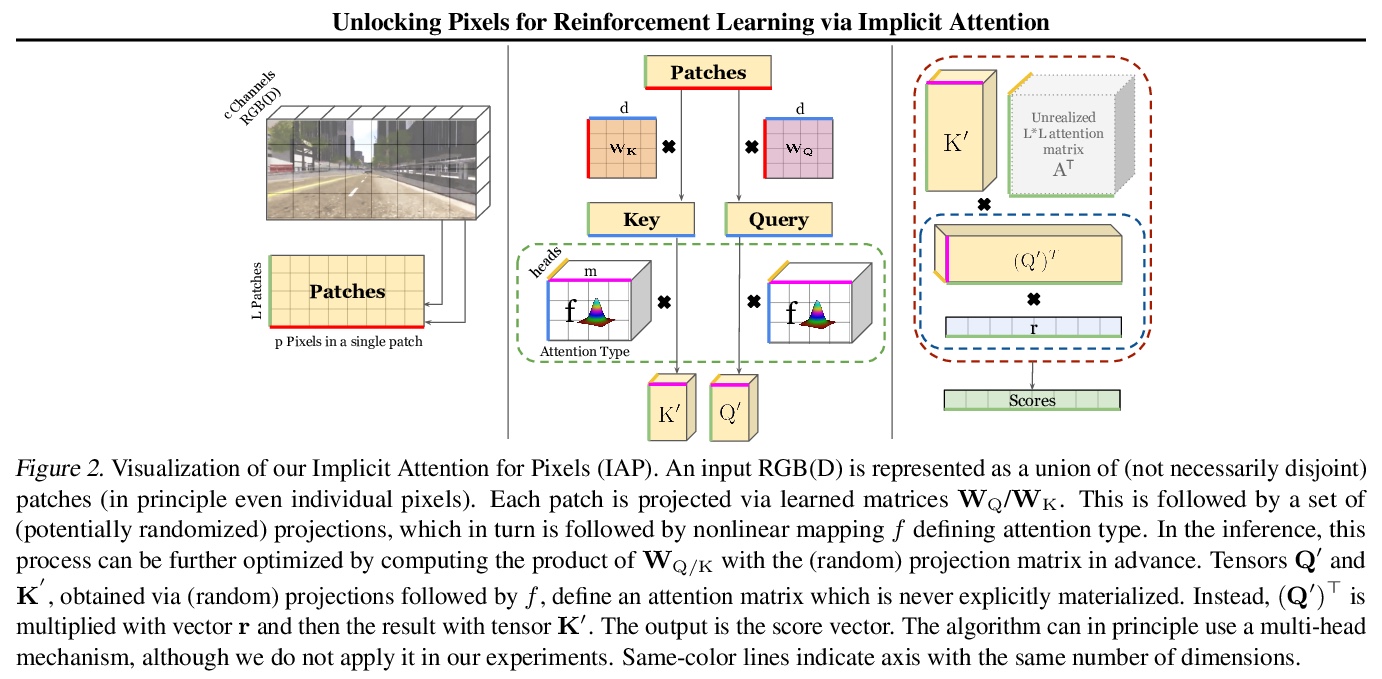
[CV] Unlocking Pixels for Reinforcement Learning via Implicit Attention
基于隐注意力的强化学习像素解锁
K Choromanski, D Jain, J Parker-Holder, X Song, V Likhosherstov, A Santara, A Pacchiano, Y Tang, A Weller
[Google & University of Oxford & University of Cambridge & UC Berkeley]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/K1ohd3QEC