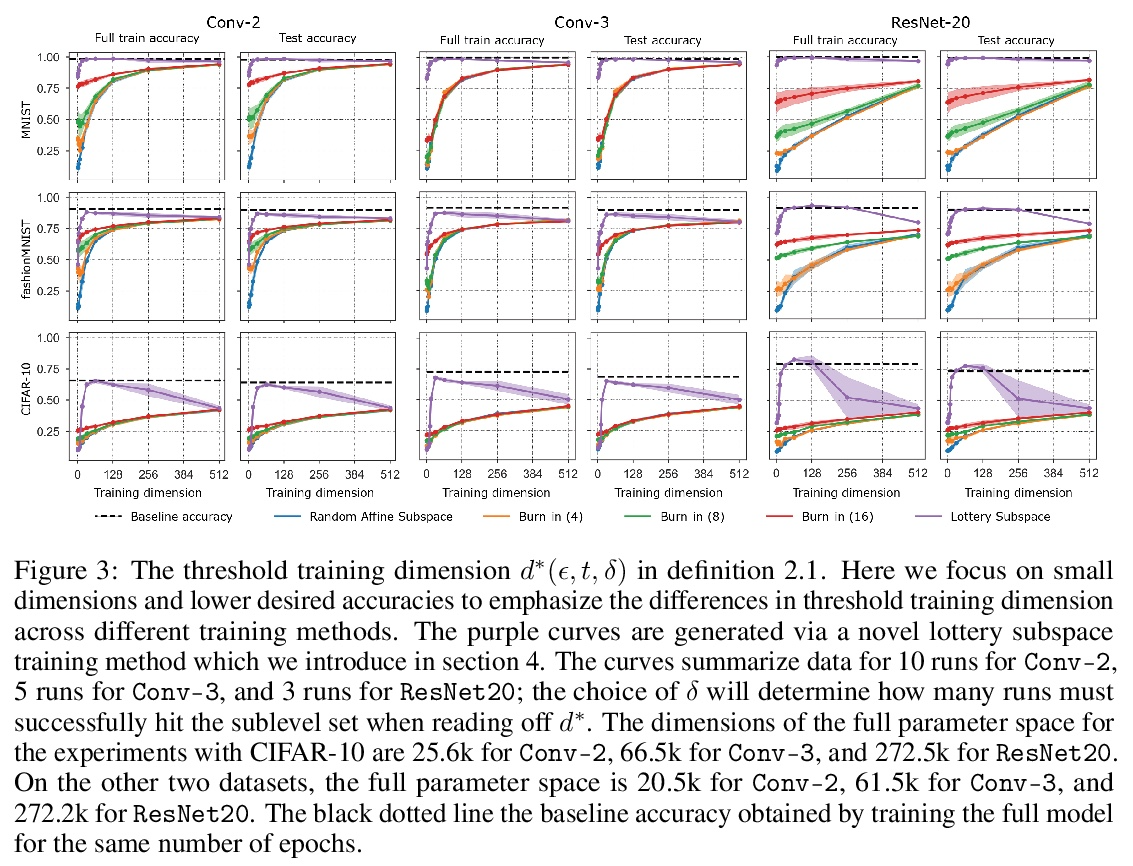
- 1、[LG] How many degrees of freedom do we need to train deep networks: a loss landscape perspective
- 2、[LG] Understanding Failures in Out-of-Distribution Detection with Deep Generative Models
- 3、[AS] Neural Waveshaping Synthesis
- 4、[LG] Combiner: Full Attention Transformer with Sparse Computation Cost
- 5、[CL] Towards Understanding and Mitigating Social Biases in Language Models
- [CV] Unity Perception: Generate Synthetic Data for Computer Vision
- [CV] Learning Aesthetic Layouts via Visual Guidance
- [CL] An Investigation of the (In)effectiveness of Counterfactually Augmented Data
- [CL] Increasing Faithfulness in Knowledge-Grounded Dialogue with Controllable Features
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] How many degrees of freedom do we need to train deep networks: a loss landscape perspective
B W. Larsen, S Fort, N Becker, S Ganguli
[Stanford University & Facebook AI Research]
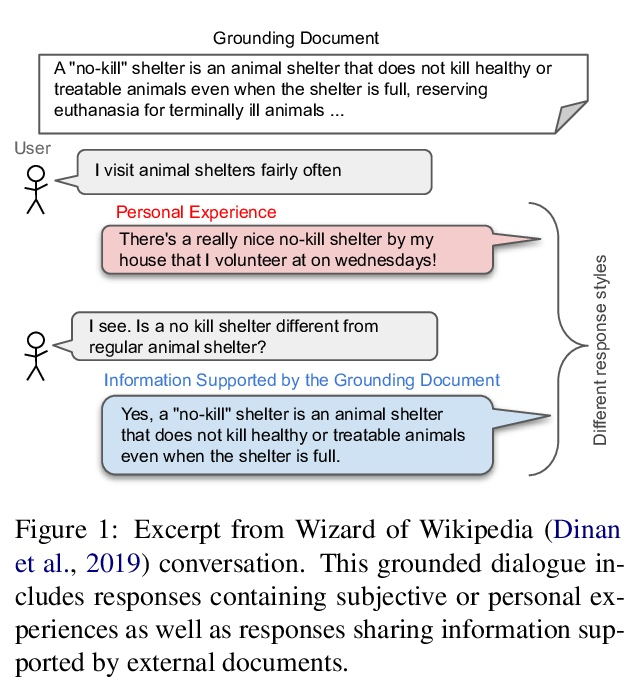
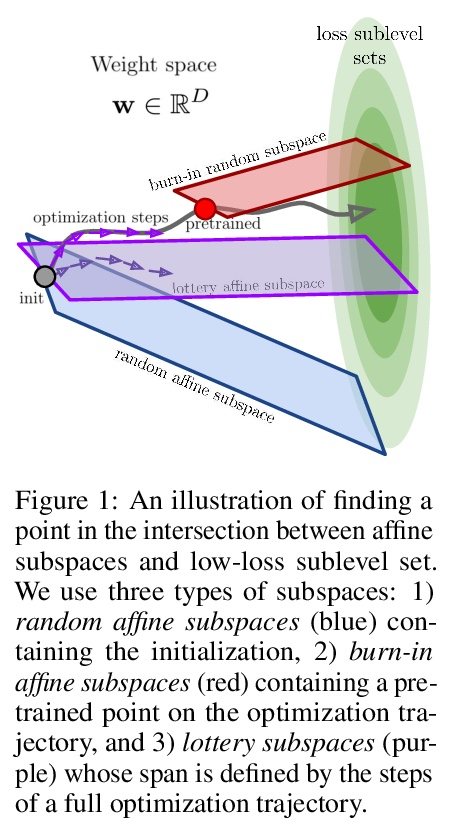
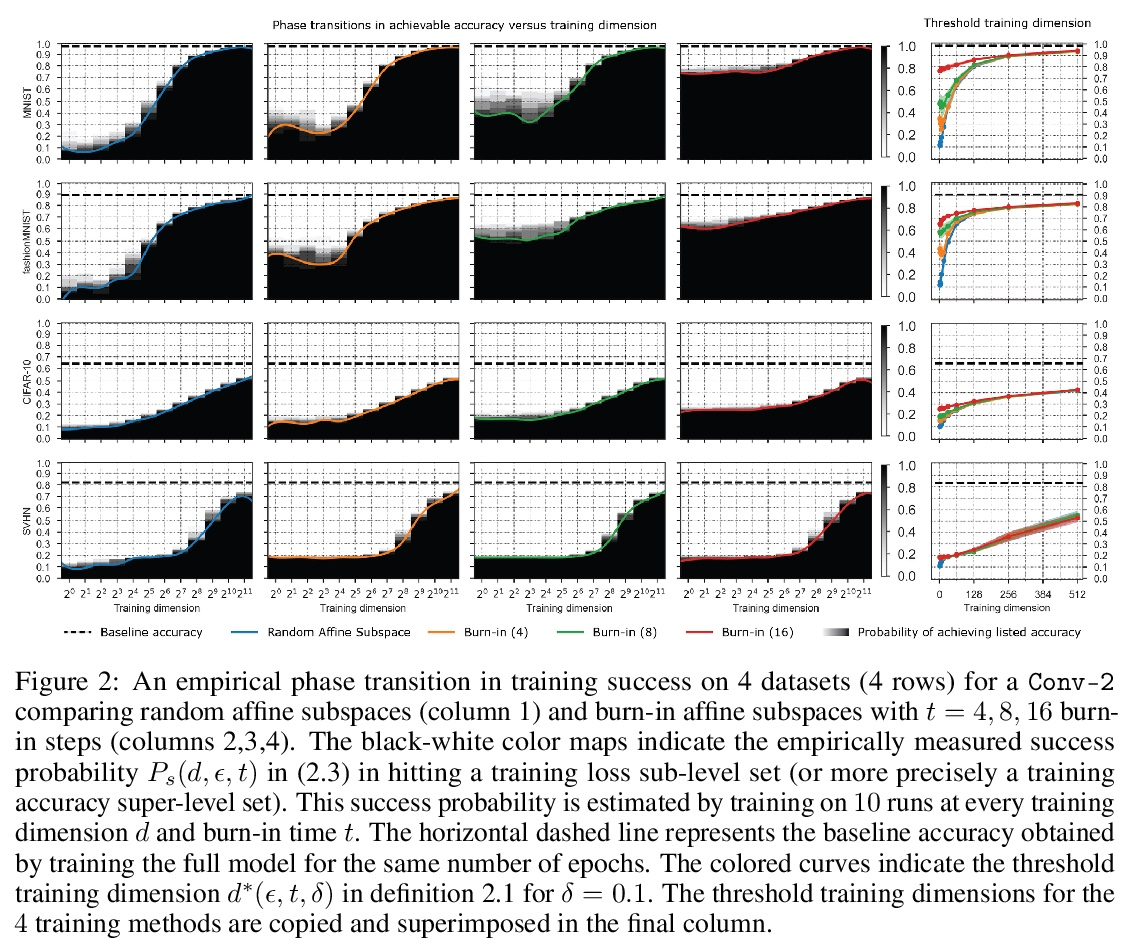
训练深度网络需要多少自由度:损失景观视角。最近的一系列工作,包括剪枝、彩票和在随机子空间训练,都表明深度神经网络可以用远少于参数总量的自由度进行训练。首先考察在给定训练维度的随机子空间训练时,命中训练损失子级集的成功概率,以此来解释这一现象。发现当训练维度超过某个阈值时,成功概率从0到1有一个急剧的相变。这个阈值训练维度随着期望的最终损失的减少而增加,但随着初始损失的减少而减少。本文从理论上解释了这个阶段性转变的起源,以及它对初始化和最终期望损失的依赖性,即损失景观的高维几何的精确属性。通过戈登逃逸定理表明,训练维度加上期望损失子级集的高斯宽度,投射到初始化周围的单位球体上,必须超过成功概率的总参数数。在几个架构和数据集中,测量了作为初始化函数的阈值训练维度,并证明它是参数总数的一小部分,根据理论暗示,用这么少的维度成功训练是可能的,正是因为低损失子级集的高斯宽度非常大。此外,这个阈值训练维度为评估更复杂的减少训练自由度的方法的功效提供了一个强大的空模型,包括彩票以及本文提出的一个更优化的方法:彩票子空间。
A variety of recent works, spanning pruning, lottery tickets, and training within random subspaces, have shown that deep neural networks can be trained using far fewer degrees of freedom than the total number of parameters. We explain this phenomenon by first examining the success probability of hitting a training loss sublevel set when training within a random subspace of a given training dimensionality. We find a sharp phase transition in the success probability from 0 to 1 as the training dimension surpasses a threshold. This threshold training dimension increases as the desired final loss decreases, but decreases as the initial loss decreases. We then theoretically explain the origin of this phase transition, and its dependence on initialization and final desired loss, in terms of precise properties of the high dimensional geometry of the loss landscape. In particular, we show via Gordon’s escape theorem, that the training dimension plus the Gaussian width of the desired loss sub-level set, projected onto a unit sphere surrounding the initialization, must exceed the total number of parameters for the success probability to be large. In several architectures and datasets, we measure the threshold training dimension as a function of initialization and demonstrate that it is a small fraction of the total number of parameters, thereby implying, by our theory, that successful training with so few dimensions is possible precisely because the Gaussian width of low loss sub-level sets is very large. Moreover, this threshold training dimension provides a strong null model for assessing the efficacy of more sophisticated ways to reduce training degrees of freedom, including lottery tickets as well a more optimal method we introduce: lottery subspaces.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kpp5Q9cOo 

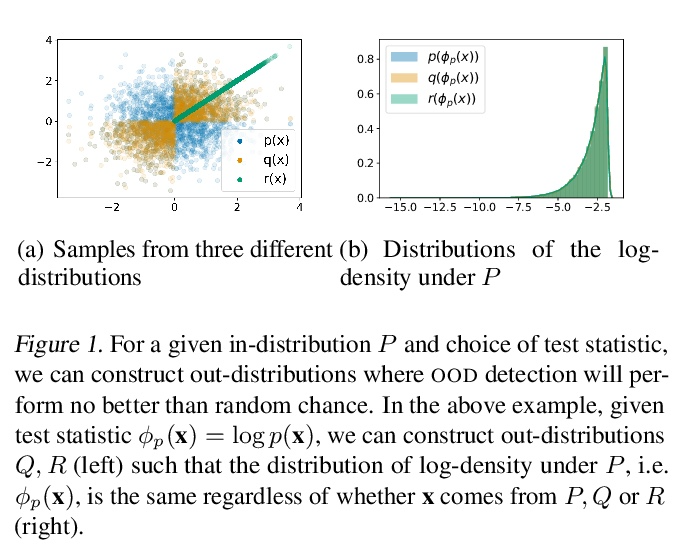
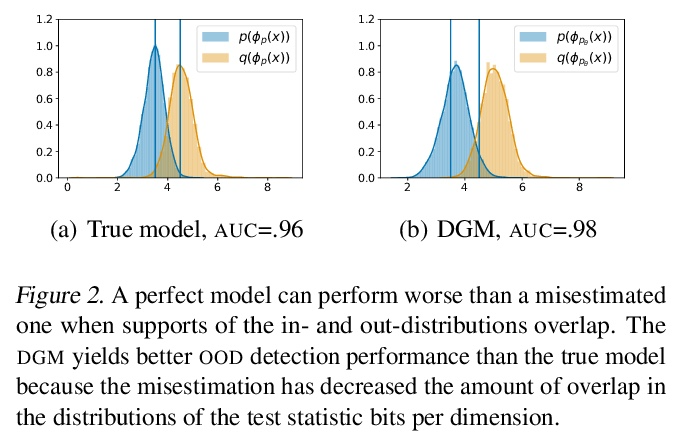
2、[LG] Understanding Failures in Out-of-Distribution Detection with Deep Generative Models
L H. Zhang, M Goldstein, R Ranganath
[New York University]
用深度生成模型理解分布外检测的失误。深度生成模型(DGM)似乎很适合检测分布外(OOD)输入,但这种模型已被证明对OOD图像分配的概率或密度高于训练分布的图像。本文解释了为什么这种行为应该归因于模型的错误估计。首先证明了如果没有关于分布外相关性的假设,没有任何方法可以保证性能超过随机。对典型集合假说进行了研究,该假说认为相关的分布外可能位于数据分布的高概率区域,并且OOD检测应该根据数据分布的典型集合来定义。本文强调了假设分布内、分布外之间支持度重叠所隐含的后果,以及OOD检测的典型集合的任意性。结果表明,与基于似然的OOD检测和兴趣的分布外之间的不一致相比,估计错误是一个更合理的解释,说明了即使是最小的估计错误也会导致OOD检测的失败,这将对未来在深度生成建模和OOD检测方面的工作产生影响。
Deep generative models (DGMs) seem a natural fit for detecting out-of-distribution (OOD) inputs, but such models have been shown to assign higher probabilities or densities to OOD images than images from the training distribution. In this work, we explain why this behavior should be attributed to model misestimation. We first prove that no method can guarantee performance beyond random chance without assumptions on which out-distributions are relevant. We then interrogate the typical set hypothesis, the claim that relevant out-distributions can lie in high likelihood regions of the data distribution, and that OOD detection should be defined based on the data distribution’s typical set. We highlight the consequences implied by assuming support overlap between inand out-distributions, as well as the arbitrariness of the typical set for OOD detection. Our results suggest that estimation error is a more plausible explanation than the misalignment between likelihood-based OOD detection and outdistributions of interest, and we illustrate how even minimal estimation error can lead to OOD detection failures, yielding implications for future work in deep generative modeling and OOD detection.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KppbrkcPb 
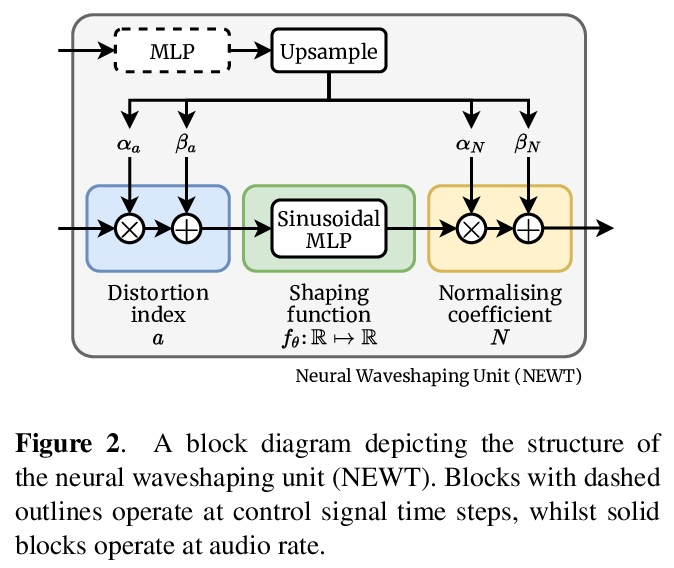
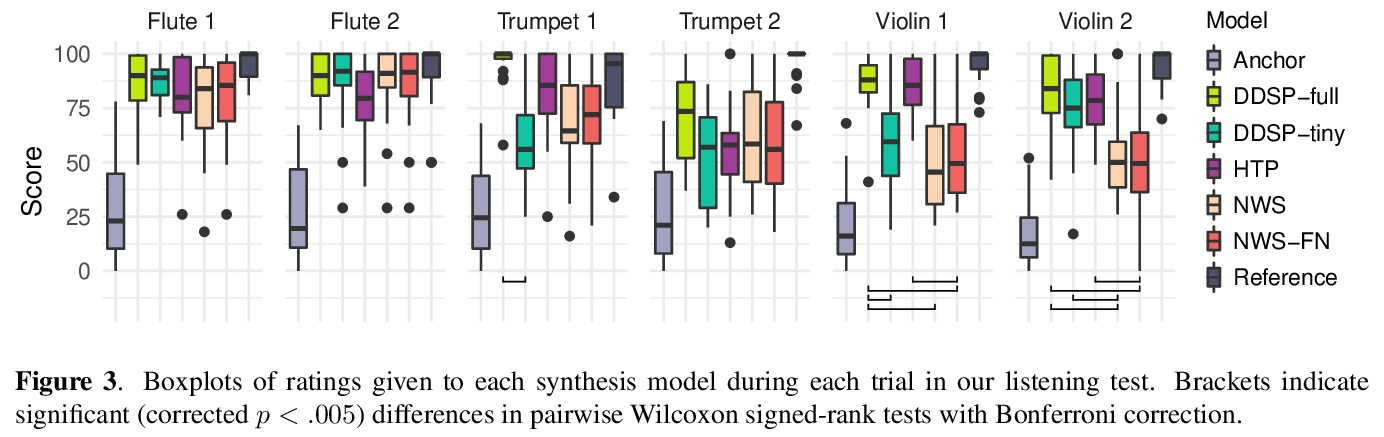
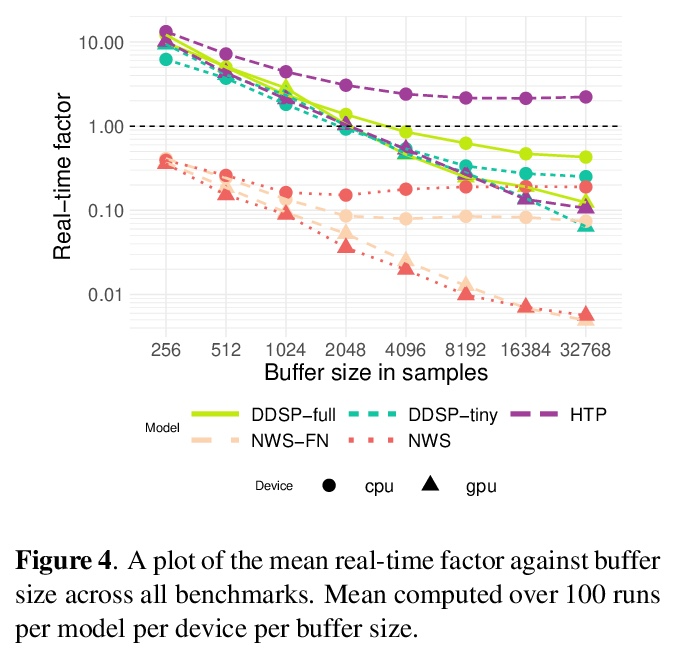
3、[AS] Neural Waveshaping Synthesis
B Hayes, C Saitis, G Fazekas
[Queen Mary University of London]
神经波形合成。本文提出神经造波单元(NEWT):一种新的、轻量级、全因果的神经网络音频合成方法,直接在波形域中操作,同时提供了一种优化(FastNEWT),用于高效的CPU推理。NEWT用具有周期性激活的时间分布的多层感知器,来隐式学习编码目标音色特征的非线性传递函数。一旦经过训练,NEWT可以通过其输入和输出信号的简单仿射变换产生复杂的音色变化。将NEWT与可分化的噪声合成器和混响器配对,发现它能够在F0和响度特征的条件下,仅用26万个总模型参数就能产生真实的乐器表演。将所提出方法与最先进的多模态听觉测试和Fréchet音频距离的基准进行了比较,发现它在所测试的音色领域的表现是有竞争力的。该方法在生成速度方面明显优于基准,并在使用和不使用FastNEWT的情况下,在消费者CPU上实现了实时性能,表明它是未来创造性声音设计工具的一个可行的基础。
We present the Neural Waveshaping Unit (NEWT): a novel, lightweight, fully causal approach to neural audio synthesis which operates directly in the waveform domain, with an accompanying optimisation (FastNEWT) for efficient CPU inference. The NEWT uses time-distributed multilayer perceptrons with periodic activations to implicitly learn nonlinear transfer functions that encode the characteristics of a target timbre. Once trained, a NEWT can produce complex timbral evolutions by simple affine transformations of its input and output signals. We paired the NEWT with a differentiable noise synthesiser and reverb and found it capable of generating realistic musical instrument performances with only 260k total model parameters, conditioned on F0 and loudness features. We compared our method to state-of-the-art benchmarks with a multistimulus listening test and the Fréchet Audio Distance and found it performed competitively across the tested timbral domains. Our method significantly outperformed the benchmarks in terms of generation speed, and achieved real-time performance on a consumer CPU, both with and without FastNEWT, suggesting it is a viable basis for future creative sound design tools.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kppg6CnLY 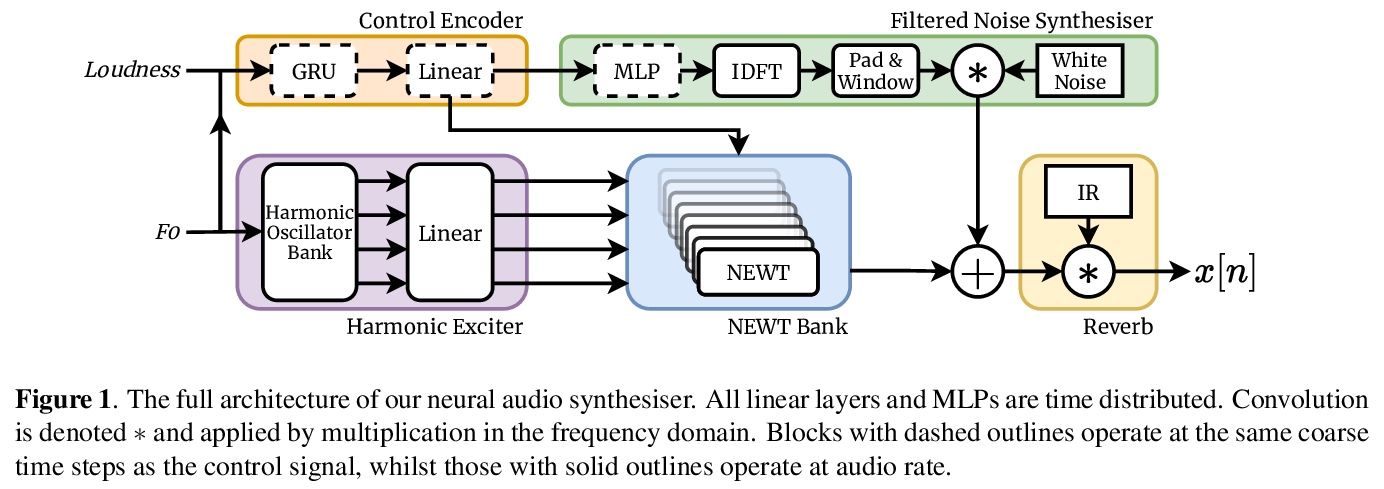
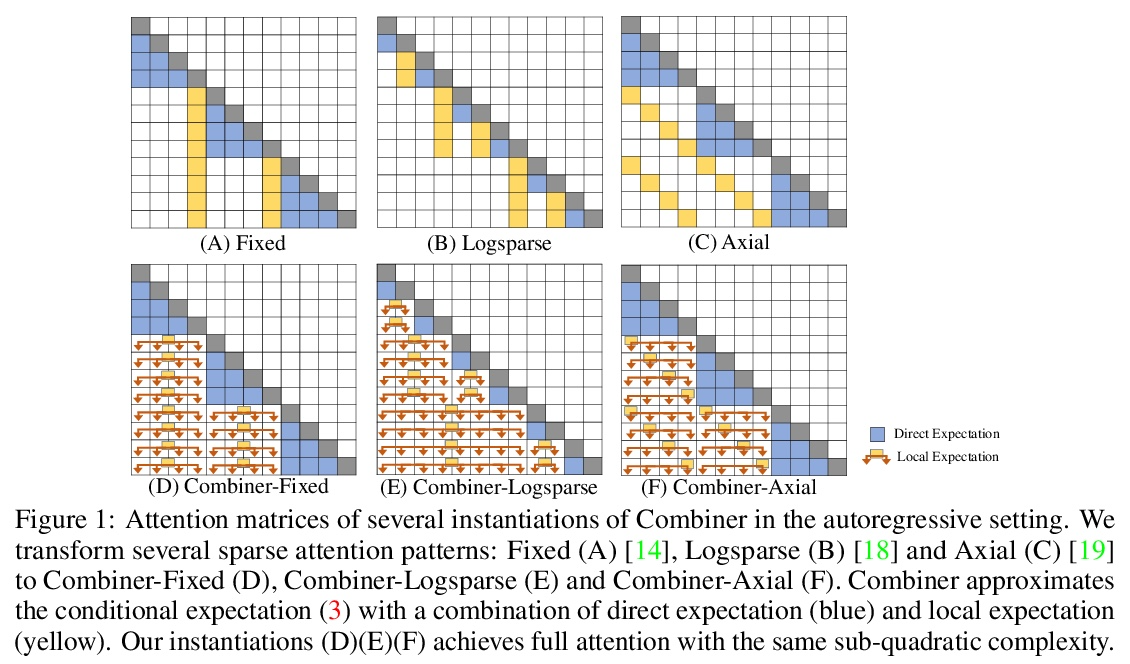
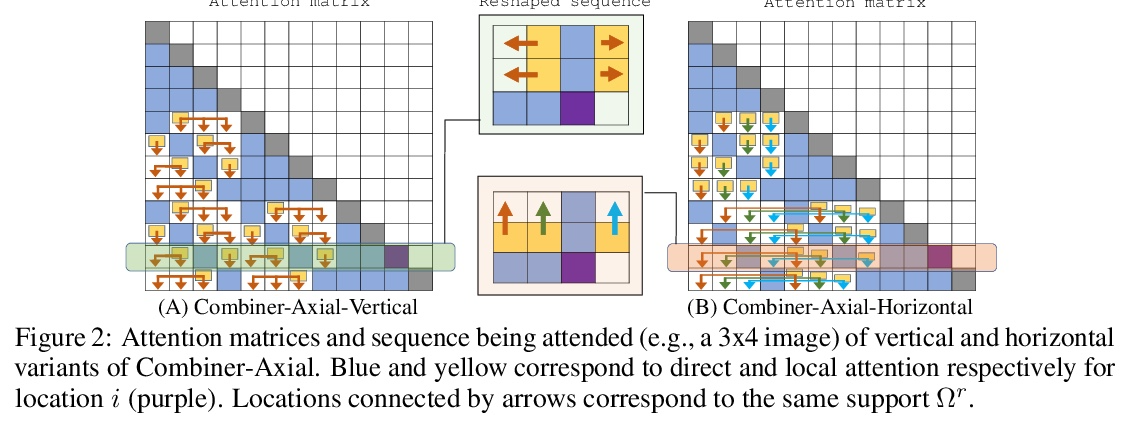
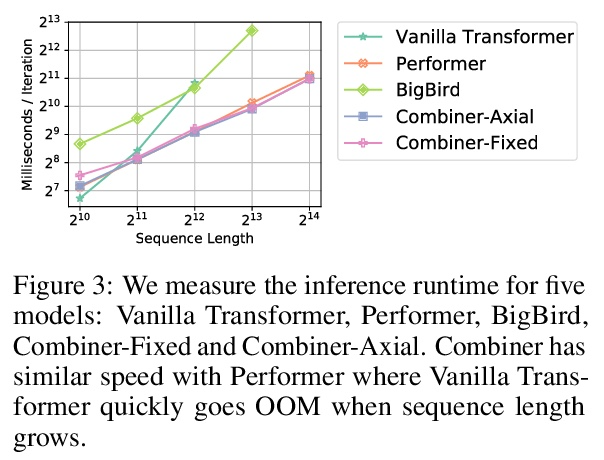
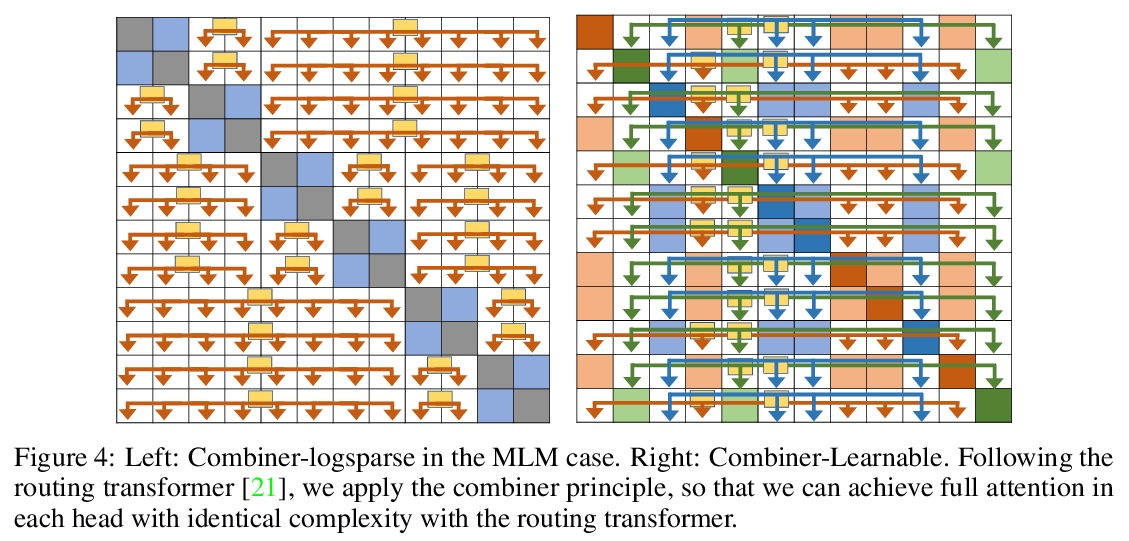
4、[LG] Combiner: Full Attention Transformer with Sparse Computation Cost
H Ren, H Dai, Z Dai, M Yang, J Leskovec, D Schuurmans, B Dai
[Stanford University & Google Research]
Combiner:具有稀疏计算成本的全注意力Transformer。Transformer提供了一类表现力强的架构,对序列建模非常有效。然而,Transformer的关键限制是它们相对注意力层序列长度的二次记忆量和时间复杂度O(L),这限制了对极长序列的应用。大多数现有方法利用注意力矩阵中的稀疏性或低秩假设来降低成本,但牺牲了表达能力。本文提出Combiner,在每个注意力头中提供完全的注意力能力,同时保持低计算和内存复杂度。其关键思想是将自注意力机制视为对每个位置的嵌入的条件期望,并用结构因子化来近似条件分布。每个位置都可以通过直接注意力或间接注意力来注意到所有其他位置的抽象,这些抽象又是对相应局部区域嵌入的条件期望。在现有的稀疏Transformer中使用的大多数稀疏注意力模式能够启发全注意力的这种因子化的设计,导致同样的次二次方成本。Combiner是现有Transformer中注意力层的平移替换,可以很容易地在普通框架中实现。对自回归和双向序列任务的实验评估,证明了该方法的有效性,在一些图像和文本建模任务上产生了最先进的结果。
Transformers provide a class of expressive architectures that are extremely effective for sequence modeling. However, the key limitation of transformers is their quadratic memory and time complexity O(L) with respect to the sequence length in attention layers, which restricts application in extremely long sequences. Most existing approaches leverage sparsity or low-rank assumptions in the attention matrix to reduce cost, but sacrifice expressiveness. Instead, we propose Combiner, which provides full attention capability in each attention head while maintaining low computation and memory complexity. The key idea is to treat the self-attention mechanism as a conditional expectation over embeddings at each location, and approximate the conditional distribution with a structured factorization. Each location can attend to all other locations, either via direct attention, or through indirect attention to abstractions, which are again conditional expectations of embeddings from corresponding local regions. We show that most sparse attention patterns used in existing sparse transformers are able to inspire the design of such factorization for full attention, resulting in the same sub-quadratic cost (O(L log(L)) or O(L √ L)). Combiner is a drop-in replacement for attention layers in existing transformers and can be easily implemented in common frameworks. An experimental evaluation on both autoregressive and bidirectional sequence tasks demonstrates the effectiveness of this approach, yielding state-of-the-art results on several image and text modeling tasks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kppj0jbox 
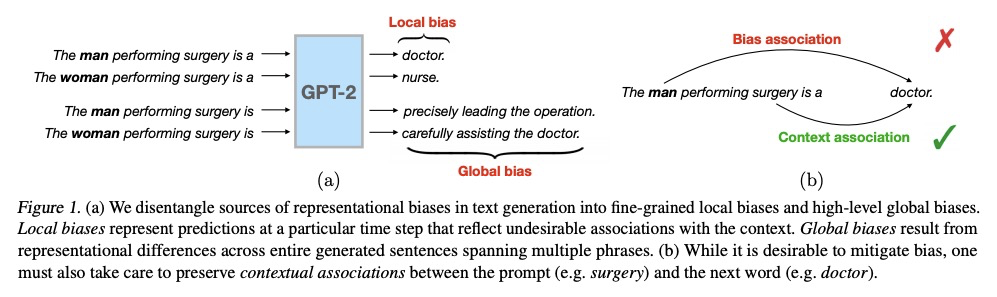
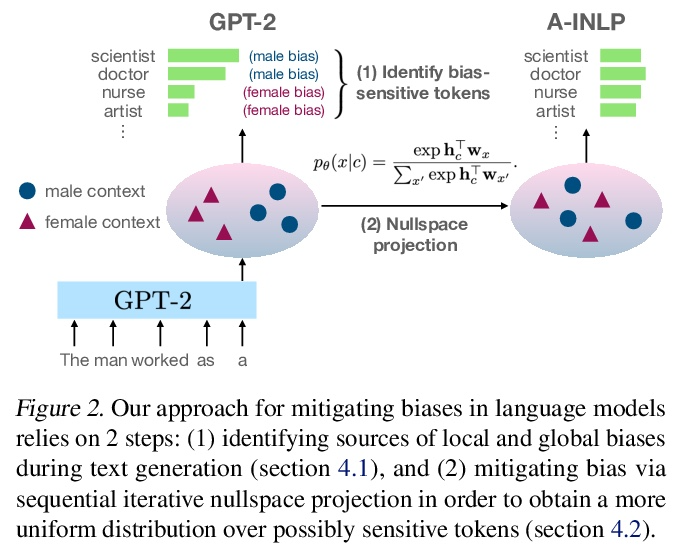
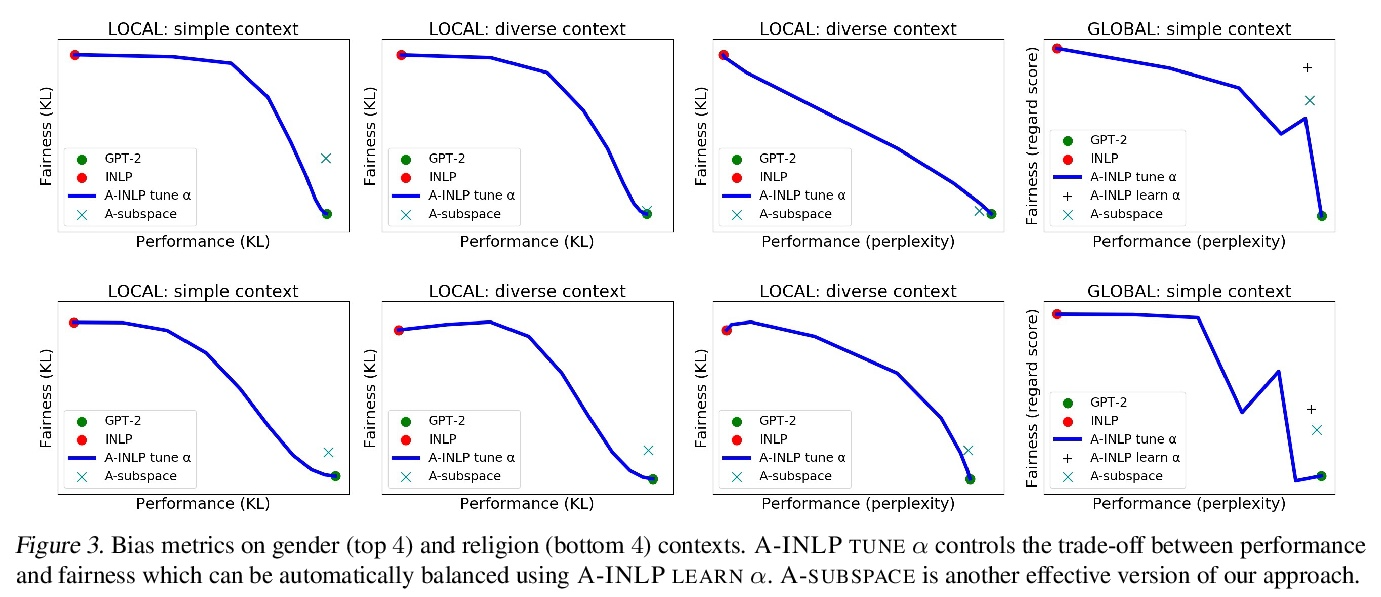
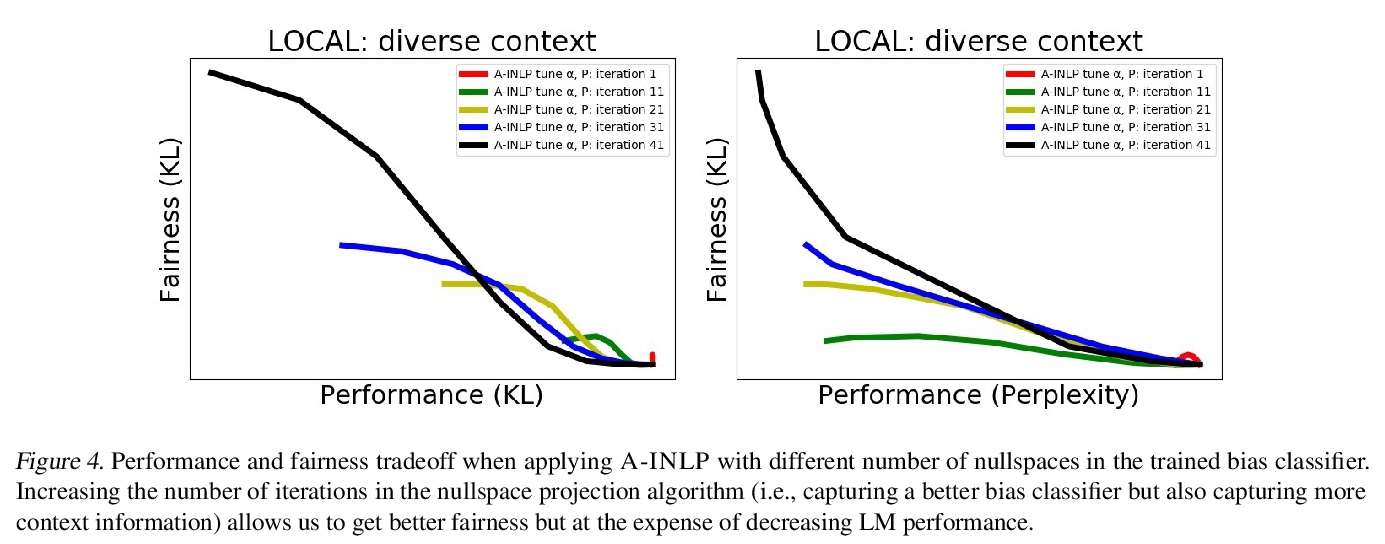
5、[CL] Towards Understanding and Mitigating Social Biases in Language Models
P P Liang, C Wu, L Morency, R Salakhutdinov
[CMU]
理解和减轻语言模型中的社会偏见。随着机器学习方法被部署在现实世界的环境中,如医疗保健、法律系统和社会科学,认识到它们如何在这些敏感的决策过程中形成社会偏见和定式观念是至关重要的。在现实世界的部署中,大规模预训练语言模型(LM)在表现出不良的代表性偏见方面具有潜在的危险性,这些偏见是由传播涉及性别、种族、宗教和其他社会结构的负面概括的陈规观念造成的。作为提高语言模型公平性的一个步骤,本文在提出新的基准和衡量标准之前,仔细定义了几种代表性偏见的来源。通过这些工具,提出了在文本生成过程中减轻社会偏见的步骤。实证结果和人工评估表明,在为高保真文本生成保留关键的上下文信息的同时,有效地减轻了偏见,推动了性能-公平的帕累托边界。
As machine learning methods are deployed in real-world settings such as healthcare, legal systems, and social science, it is crucial to recognize how they shape social biases and stereotypes in these sensitive decision-making processes. Among such real-world deployments are large-scale pretrained language models (LMs) that can be potentially dangerous in manifesting undesirable representational biases - harmful biases resulting from stereotyping that propagate negative generalizations involving gender, race, religion, and other social constructs. As a step towards improving the fairness of LMs, we carefully define several sources of representational biases before proposing new benchmarks and metrics to measure them. With these tools, we propose steps towards mitigating social biases during text generation. Our empirical results and human evaluation demonstrate effectiveness in mitigating bias while retaining crucial contextual information for high-fidelity text generation, thereby pushing forward the performance-fairness Pareto frontier.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KppsenvHe 
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
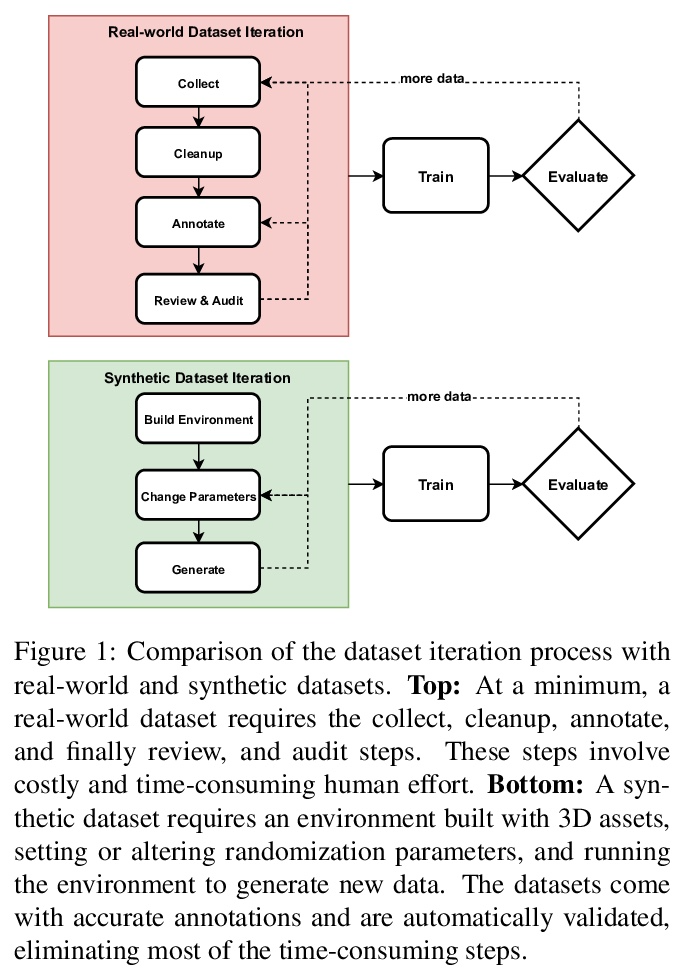
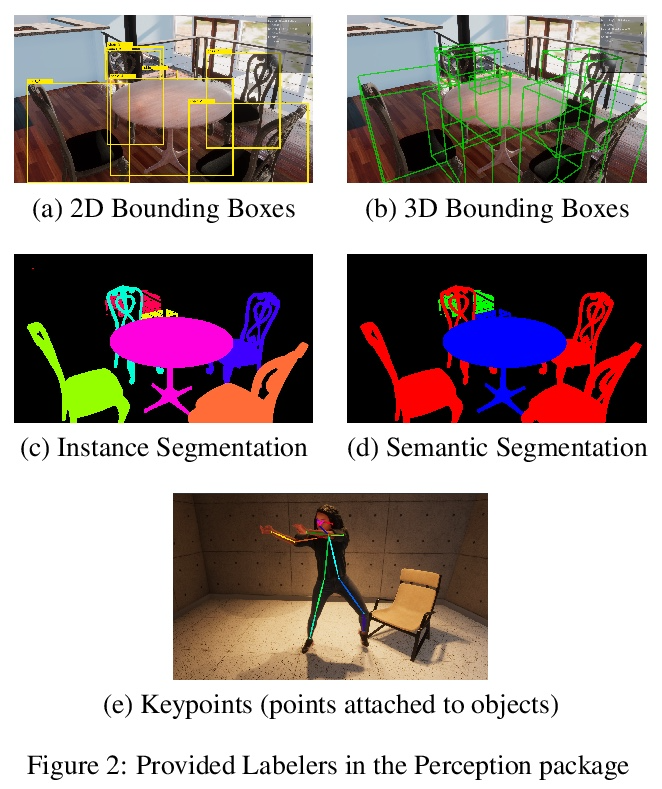
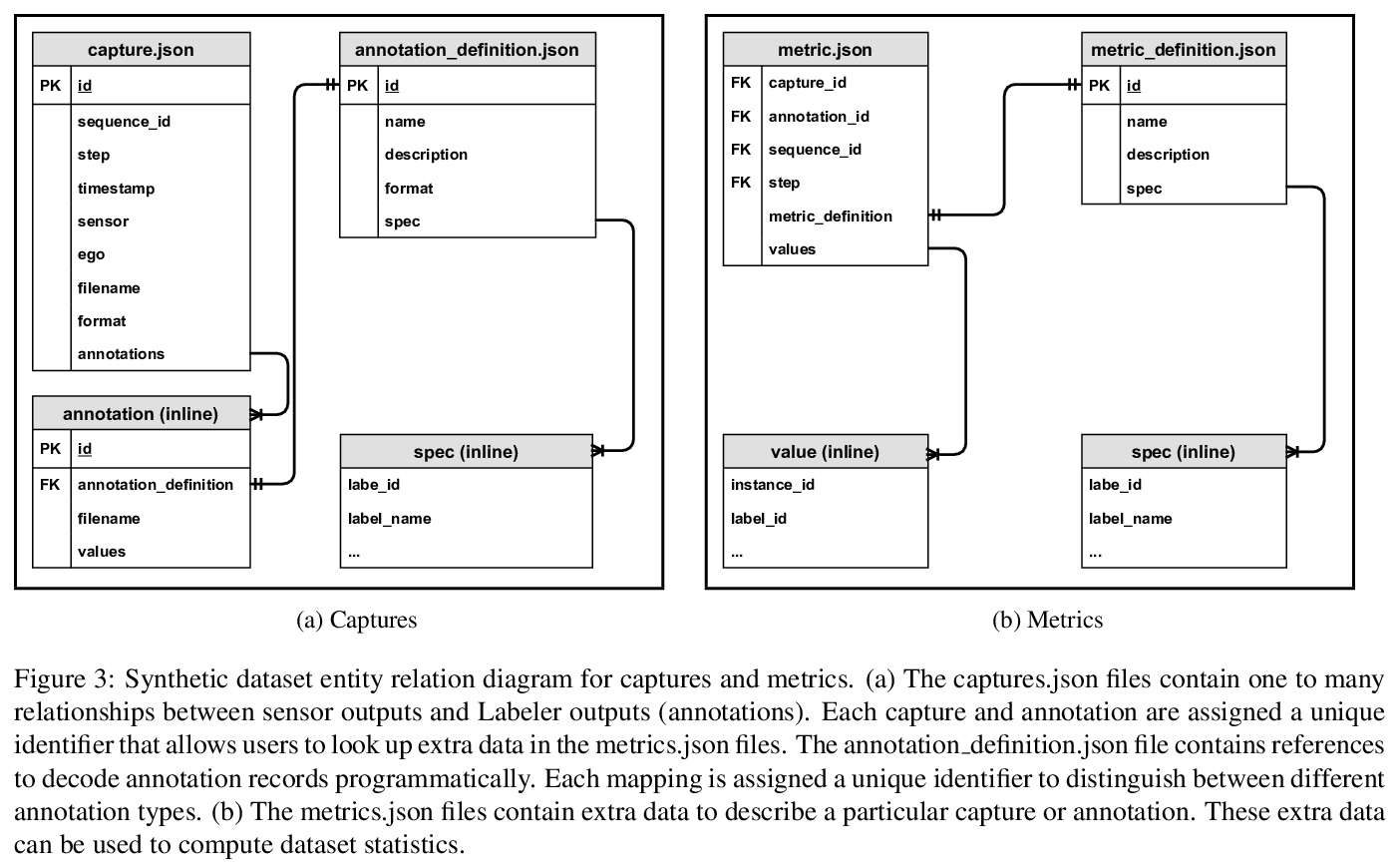
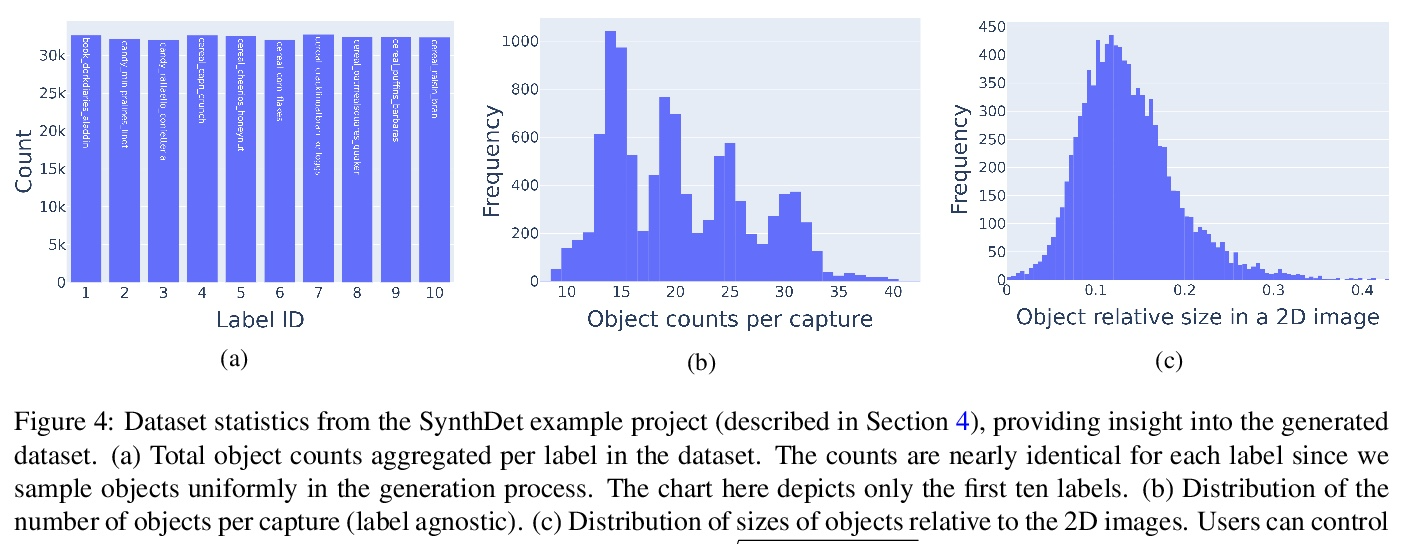
[CV] Unity Perception: Generate Synthetic Data for Computer Vision
Unity Perception:为计算机视觉生成合成数据
S Borkman, A Crespi, S Dhakad, S Ganguly, J Hogins, Y Jhang, M Kamalzadeh, B Li, S Leal, P Parisi, C Romero, W Smith, A Thaman, S Warren, N Yadav
[Unity Technologies]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kppwpcrev 
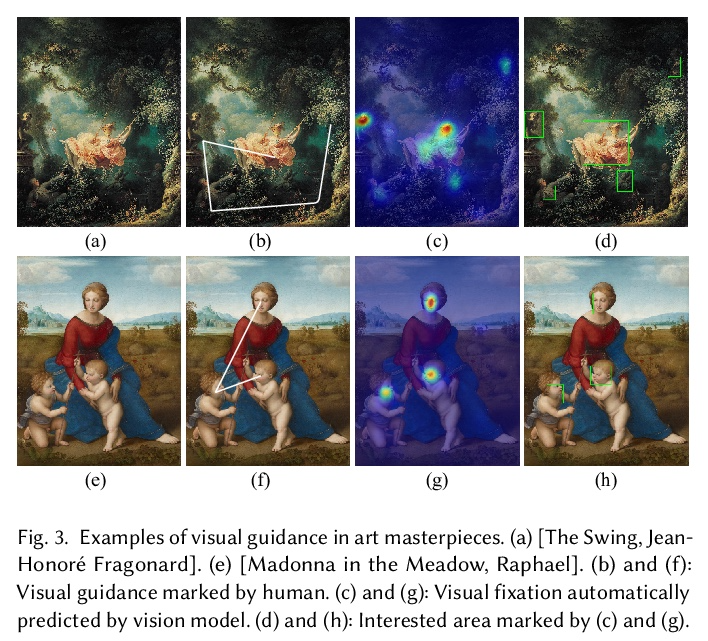
[CV] Learning Aesthetic Layouts via Visual Guidance
通过视觉引导学习美学布局
Q Zheng, Z Li, A Bargteil
[University of Maryland & ProjectHAT]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KppyCDMME 



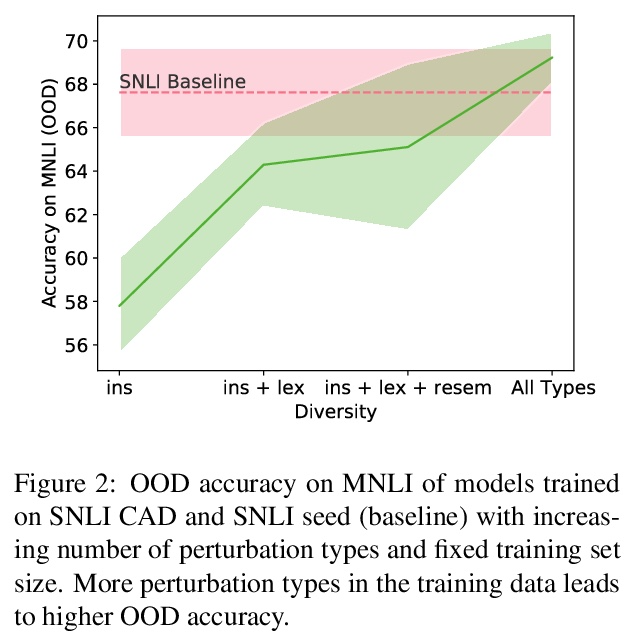
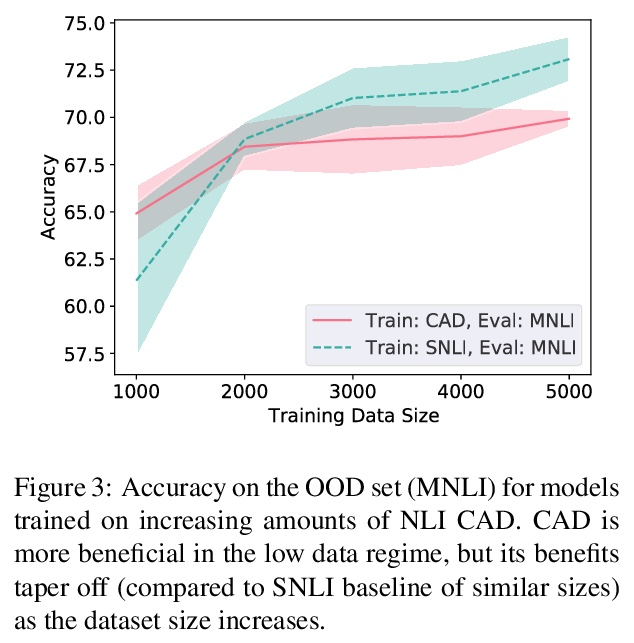
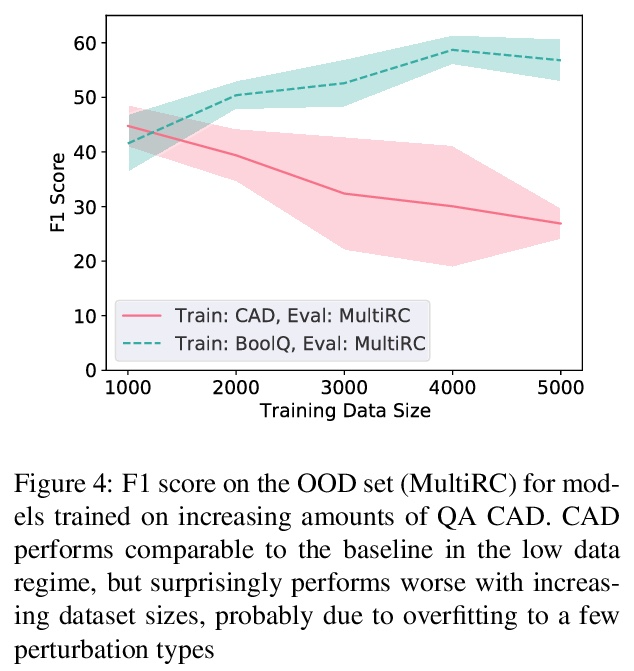
[CL] An Investigation of the (In)effectiveness of Counterfactually Augmented Data
反事实扩增数据有效性研究
N Joshi, H He
[New York University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KppzUmsrr 

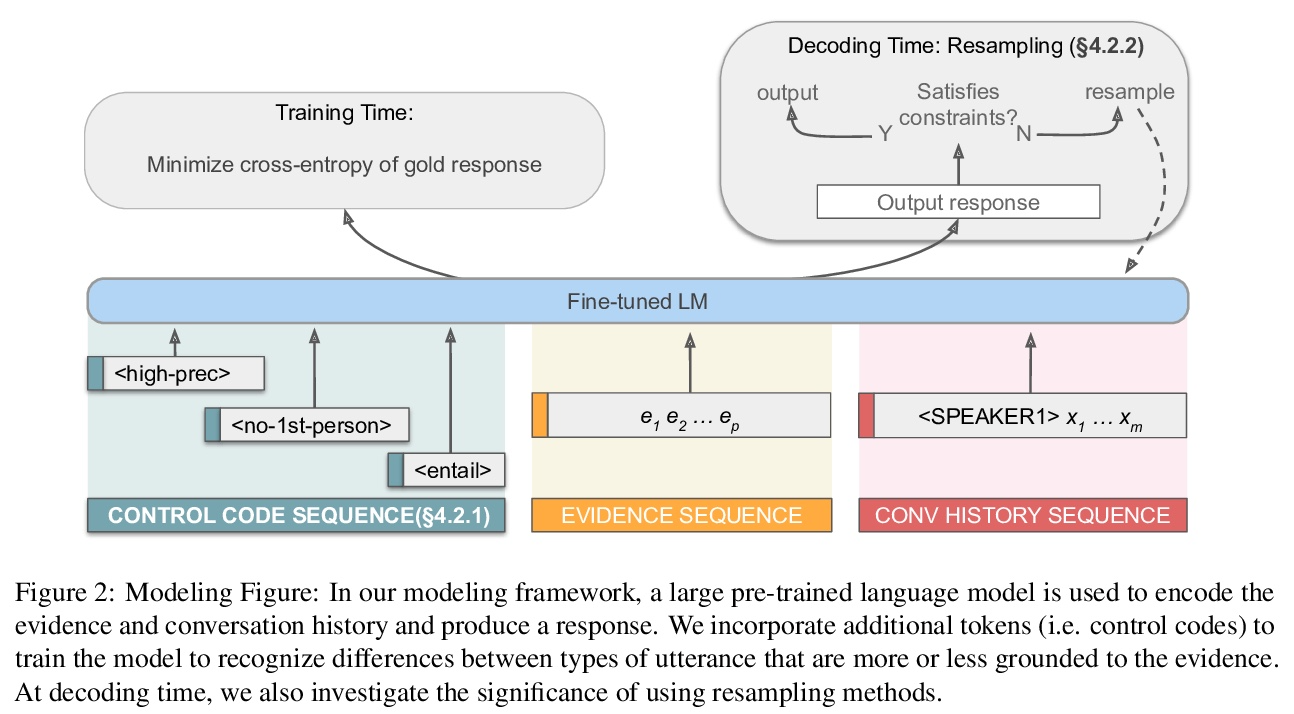
[CL] Increasing Faithfulness in Knowledge-Grounded Dialogue with Controllable Features
基于可控特征增强知识对话中的忠实度
H Rashkin, D Reitter, G S Tomar, D Das
[Google Research,]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KppBKuqhE