- 1、[CV] High-Resolution Complex Scene Synthesis with Transformers
- 2、[LG] Grad-TTS: A Diffusion Probabilistic Model for Text-to-Speech
- 3、[CL] Maximal Multiverse Learning for Promoting Cross-Task Generalization of Fine-Tuned Language Models
- 4、[CV] Representation Learning via Global Temporal Alignment and Cycle-Consistency
- 5、[CV] Connecting What to Say With Where to Look by Modeling Human Attention Traces
- [CV] Structured dataset documentation: a datasheet for CheXpert
- [CV] 3D Spatial Recognition without Spatially Labeled 3D
- [CV] Neural Trajectory Fields for Dynamic Novel View Synthesis
- [CV] Episodic Transformer for Vision-and-Language Navigation
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CV] High-Resolution Complex Scene Synthesis with Transformers
M Jahn, R Rombach, B Ommer
[Heidelberg University]
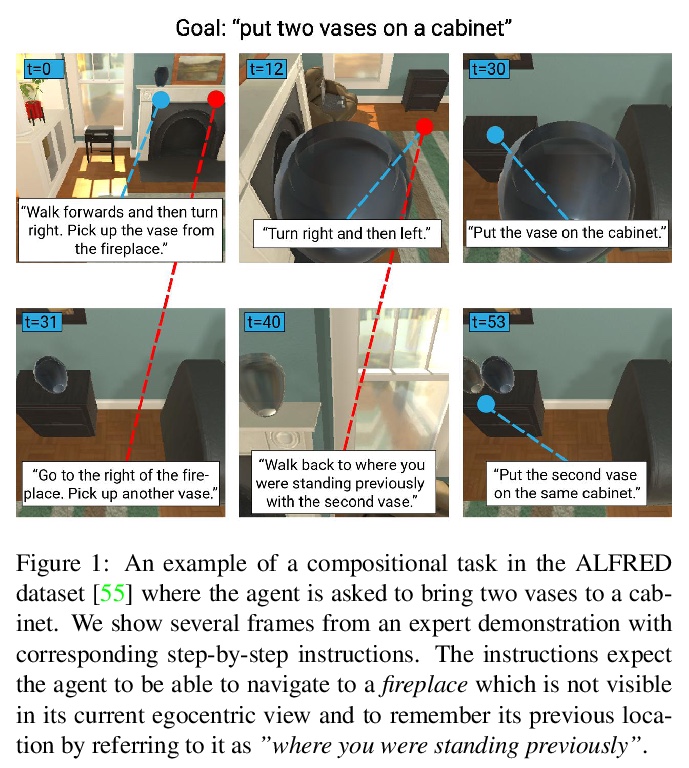
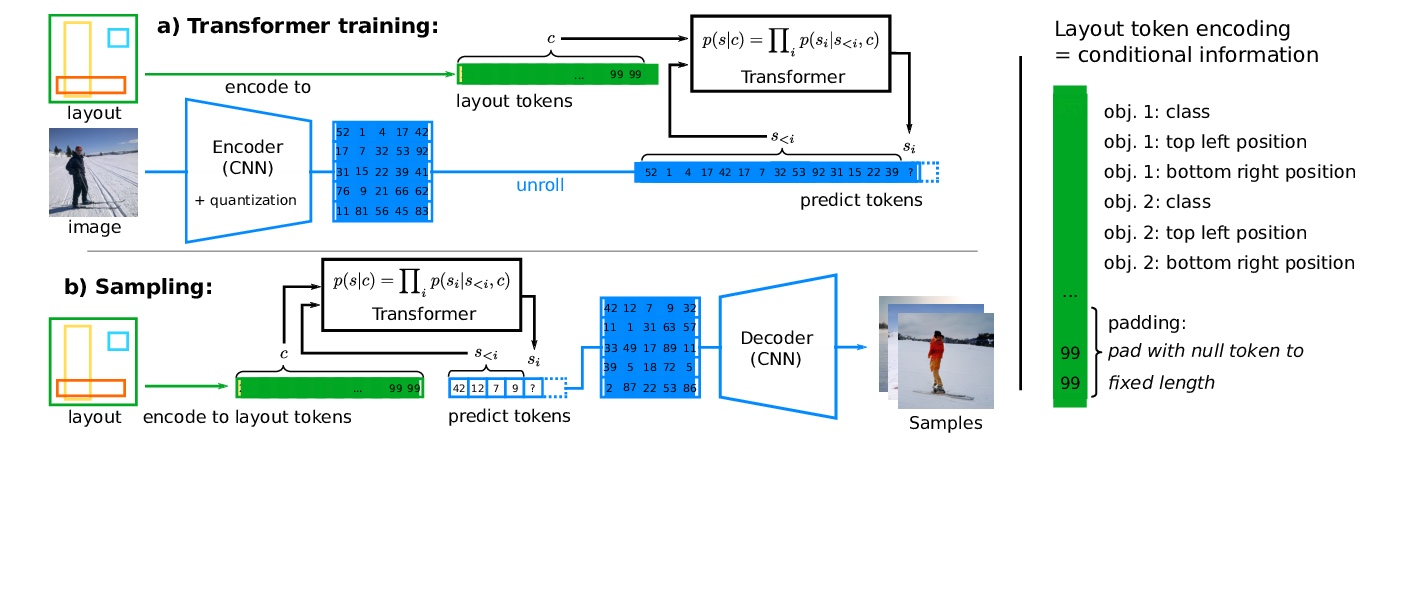
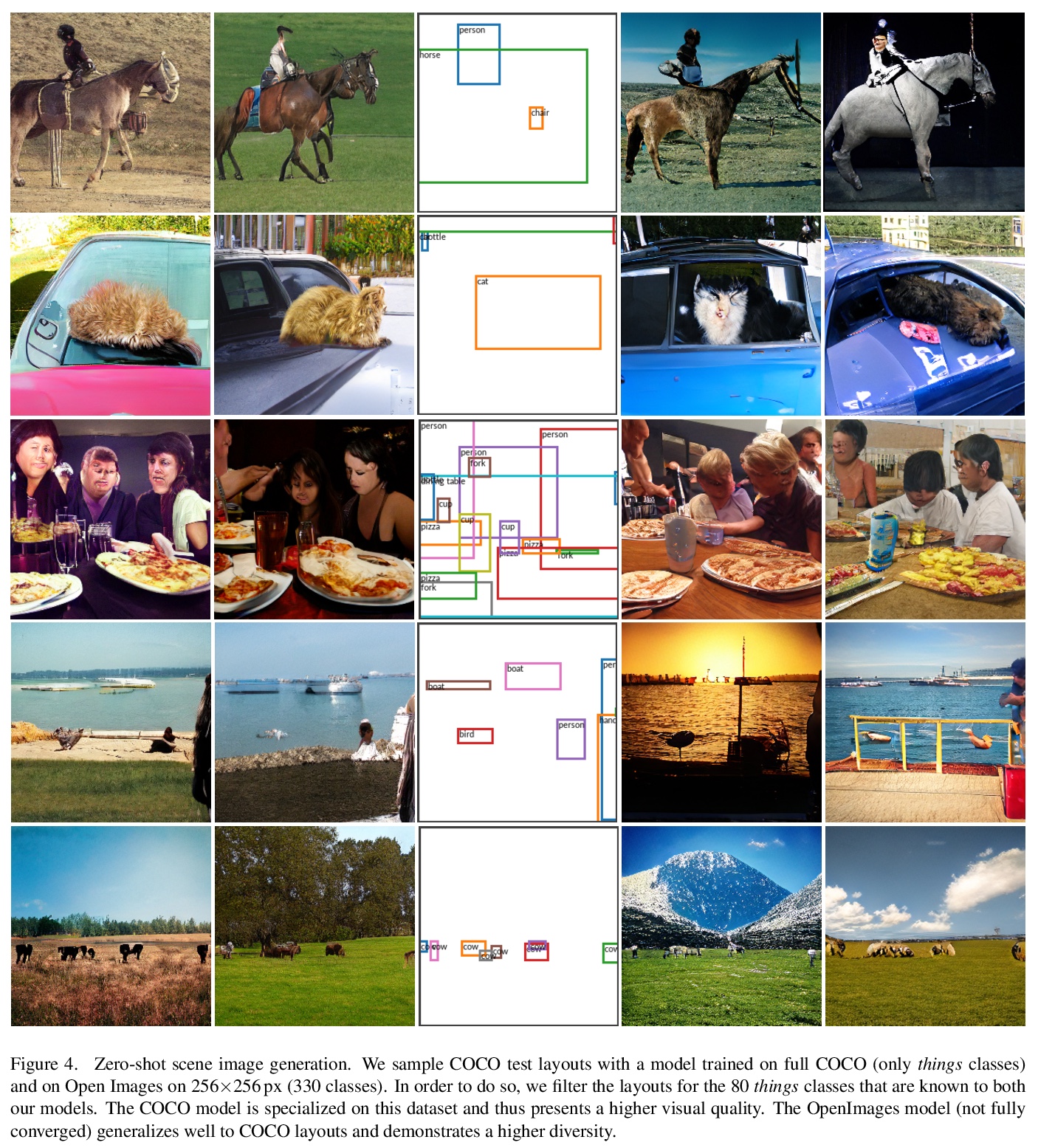
Transformer高分辨率复杂场景合成。最近,通过深度生成模型用粗粒度布局进行复杂场景图像的可控合成已经得到了普及。然而,目前方法的结果仍然没有达到其对高分辨率合成的承诺。这主要是由于这些方法的高度工程化性质,其往往依赖于辅助损失和中间步骤,如掩码生成器。本文提出一种正交方法,其中生成模型基于纯似然训练,没有额外目标。优化一个具有对抗性训练的强大的压缩模型,该模型学会通过离散的潜瓶颈重建其输入,从而有效剥离高频细节(如纹理)的潜表示。训练一个自回归Transformers模型,以学习离散图像表示的分布,条件是布局的标记化版本。实验表明,所产生的系统能合成与给定布局一致的高质量图像。在COCO-Stuff和Visual Genome上将最先进的FID得分提高了19%和53%,并在COCO和Open Images上展示了高达512×512 px的图像的合成。
The use of coarse-grained layouts for controllable synthesis of complex scene images via deep generative models has recently gained popularity. However, results of current approaches still fall short of their promise of highresolution synthesis. We hypothesize that this is mostly due to the highly engineered nature of these approaches which often rely on auxiliary losses and intermediate steps such as mask generators. In this note, we present an orthogonal approach to this task, where the generative model is based on pure likelihood training without additional objectives. To do so, we first optimize a powerful compression model with adversarial training which learns to reconstruct its inputs via a discrete latent bottleneck and thereby effectively strips the latent representation of high-frequency details such as texture. Subsequently, we train an autoregressive transformer model to learn the distribution of the discrete image representations conditioned on a tokenized version of the layouts. Our experiments show that the resulting system is able to synthesize high-quality images consistent with the given layouts. In particular, we improve the state-of-the-art FID score on COCO-Stuff and on Visual Genome by up to 19% and 53% and demonstrate the synthesis of images up to 512×512 px on COCO and Open Images.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kfw5d0o4I


2、[LG] Grad-TTS: A Diffusion Probabilistic Model for Text-to-Speech
V Popov, I Vovk, V Gogoryan, T Sadekova, M Kudinov
[Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab]
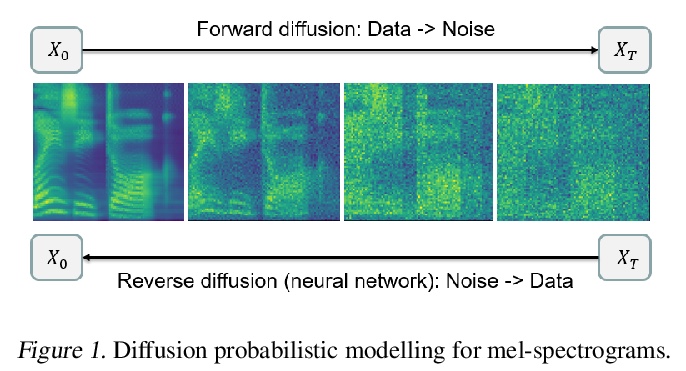
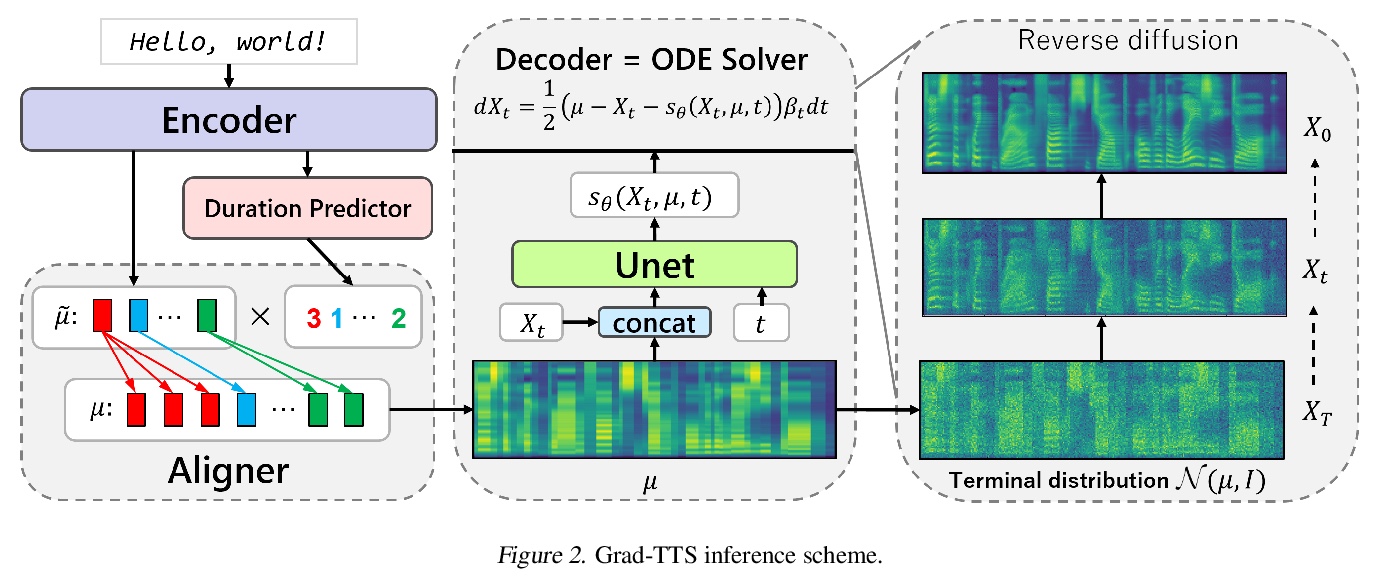
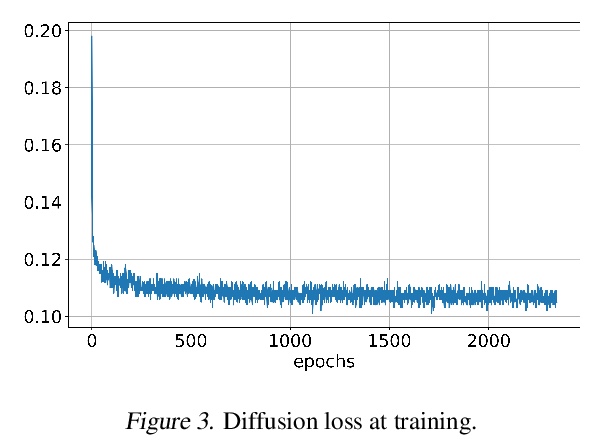
Grad-TTS:面向文本语音合成的扩散概率模型。最近,去噪扩散概率模型和生成性得分匹配在复杂的数据分布建模方面显示出很大潜力,而随机微积分为这些技术提供了统一视角,可实现灵活的推理方案。本文提出一种新的文本-语音合成模型Grad-TTS,也是第一个利用扩散概率建模概念的声学特征发生器,其主要生成引擎是基于扩散的解码器,将以编码器输出为参数的高斯噪声转化为梅尔谱图,同时用单调对齐搜索法进行对齐。随机微分方程的框架将传统的扩散概率模型推广到从具有不同参数的噪声中重建数据的场景,可通过明确控制声音质量和推理速度之间的权衡使这种重建变得灵活。能以比Tacotron2快两倍的速度生成梅尔谱图,同时保持与普通TTS基线竞争的合成质量。人工主观评价表明,Grad-TTS在平均意见得分方面与先进的文本到语音方法相比具有竞争力。
Recently, denoising diffusion probabilistic models and generative score matching have shown high potential in modelling complex data distributions while stochastic calculus has provided a unified point of view on these techniques allowing for flexible inference schemes. In this paper we introduce Grad-TTS, a novel text-tospeech model with score-based decoder producing mel-spectrograms by gradually transforming noise predicted by encoder and aligned with text input by means of Monotonic Alignment Search. The framework of stochastic differential equations helps us to generalize conventional diffusion probabilistic models to the case of reconstructing data from noise with different parameters and allows to make this reconstruction flexible by explicitly controlling trade-off between sound quality and inference speed. Subjective human evaluation shows that Grad-TTS is competitive with stateof-the-art text-to-speech approaches in terms of Mean Opinion Score. We will make the code publicly available shortly.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kfw93u6Ji

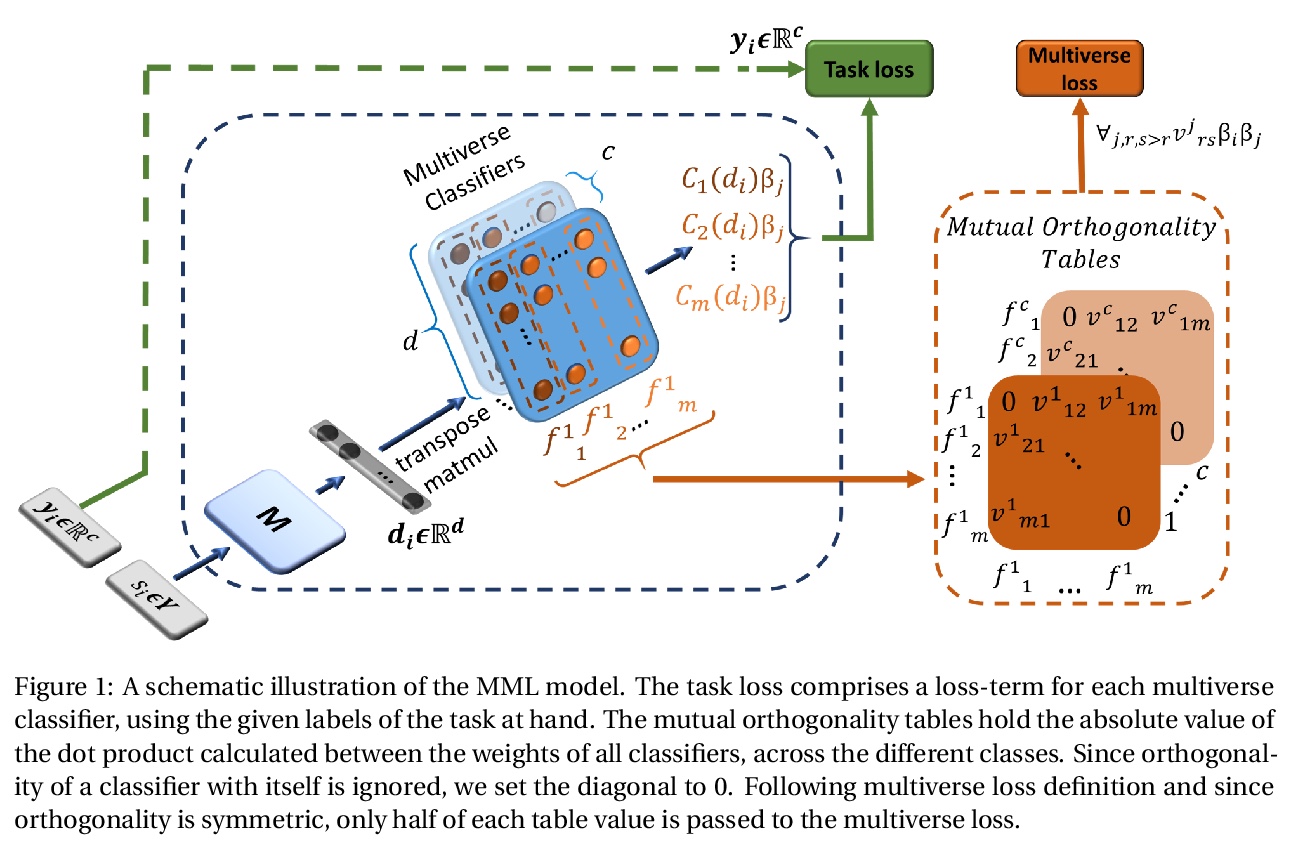
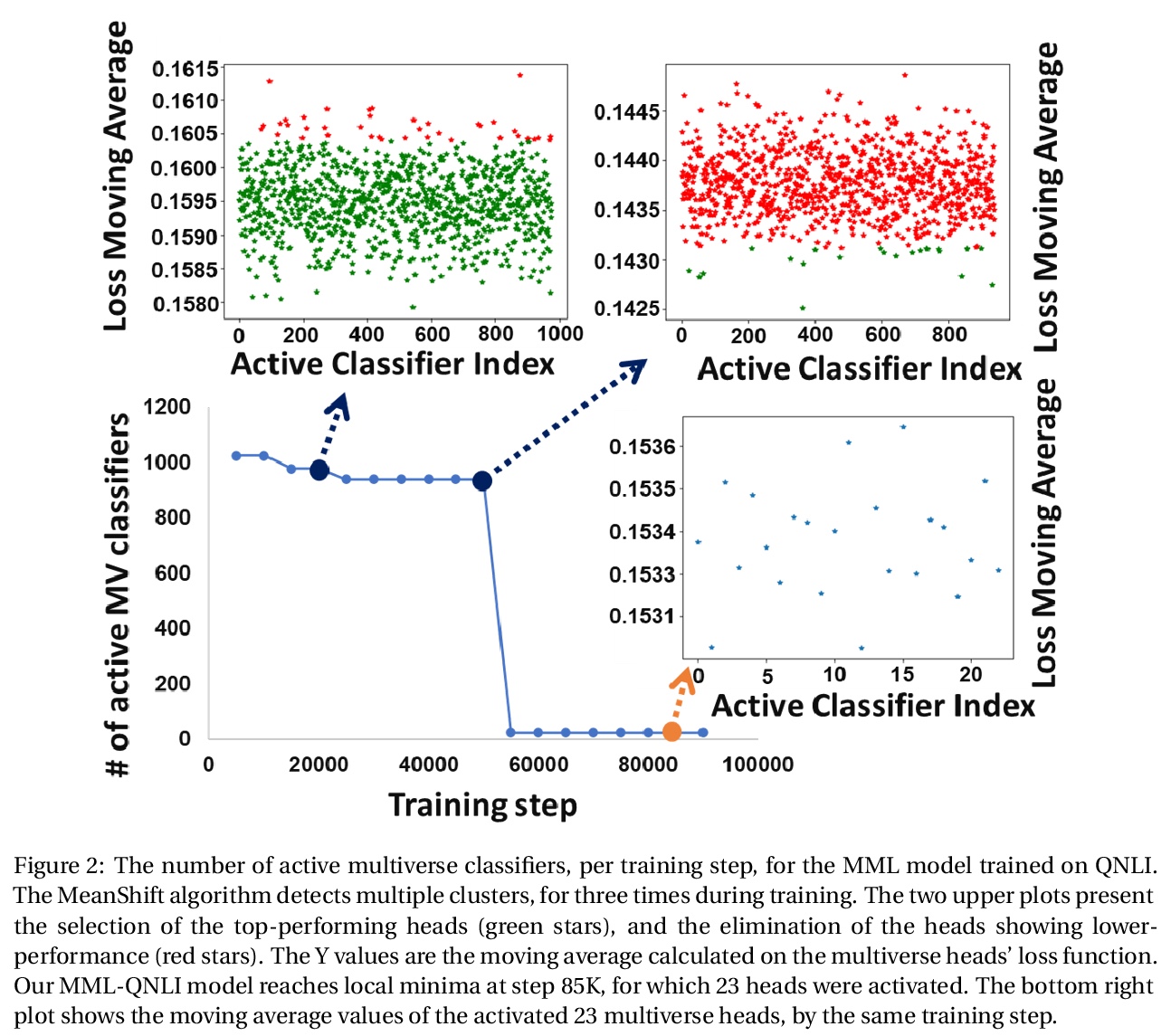
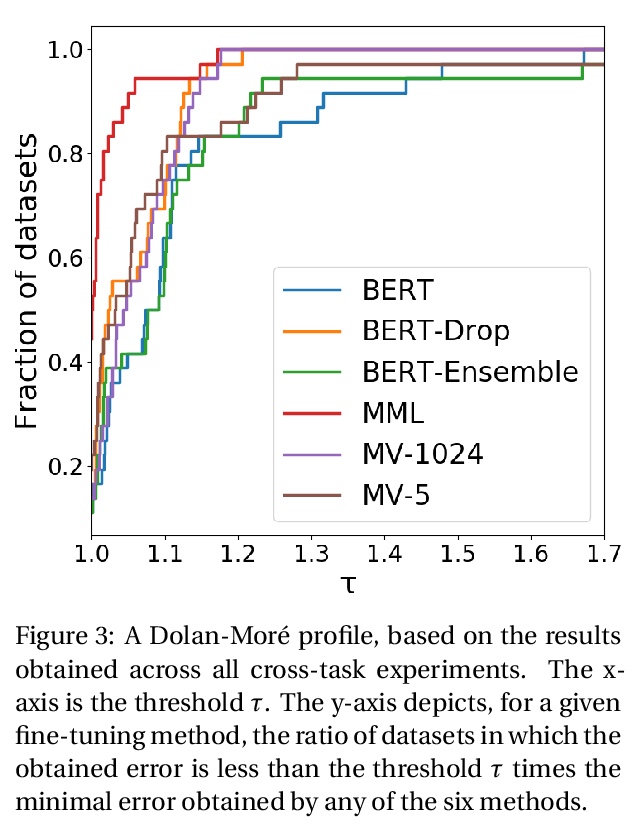
3、[CL] Maximal Multiverse Learning for Promoting Cross-Task Generalization of Fine-Tuned Language Models
I Malkiel, L Wolf
[Tel Aviv University]
用最大多元学习促进微调语言模型跨任务泛化。基于BERT的语言建模包括两个阶段:(i)在未标记文本上进行无监督预训练,以及(ii)为特定监督任务进行微调。本文提出一种方法,用大量的平行分类器头,充分发挥第二阶段的作用,这些分类器头被强制要求是正交的,同时在训练过程中自适应消除较弱的分类器头。其本质是,给定一个预训练语言模型和带有标记数据的下游任务,用最大数量的多元分类器对模型进行微调,目标是使任务损失和应用于分类头的正交性损失都最小。当强制执行正交性阻碍了分类器的性能时,会检测并消除效果较差的分类头。广泛的数据集间和数据集内的评估表明,该方法提高了BERT的泛化能力,有时会导致+9%的精度提高。这些结果强调了适当的微调程序的重要性,特别是对于相对较小的数据集。
Language modeling with BERT consists of two phases of (i) unsupervised pre-training on unlabeled text, and (ii) fine-tuning for a specific supervised task. We present a method that leverages the second phase to its fullest, by applying an extensive number of parallel classifier heads, which are enforced to be orthogonal, while adaptively eliminating the weaker heads during training. We conduct an extensive interand intradataset evaluation, showing that our method improves the generalization ability of BERT, sometimes leading to a +9% gain in accuracy. These results highlight the importance of a proper fine-tuning procedure, especially for relatively smaller-sized datasets. Our code is attached as supplementary.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfwfQh2Yd
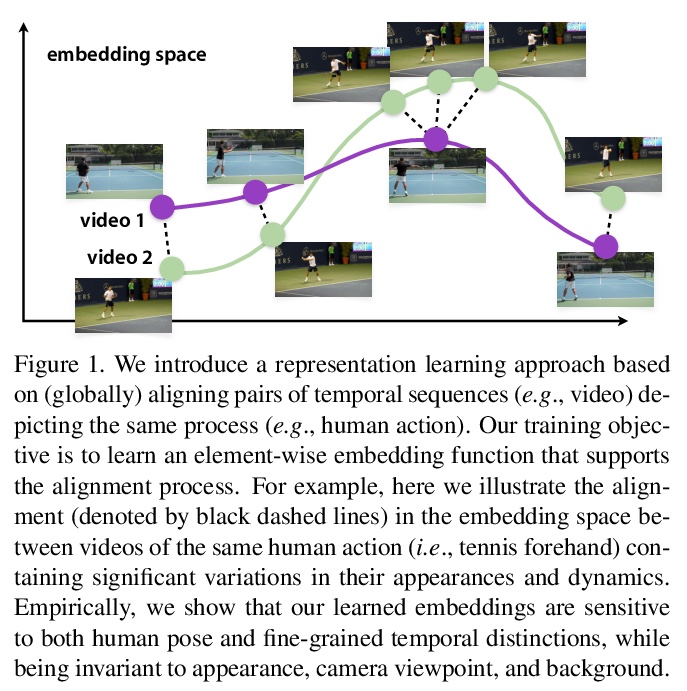
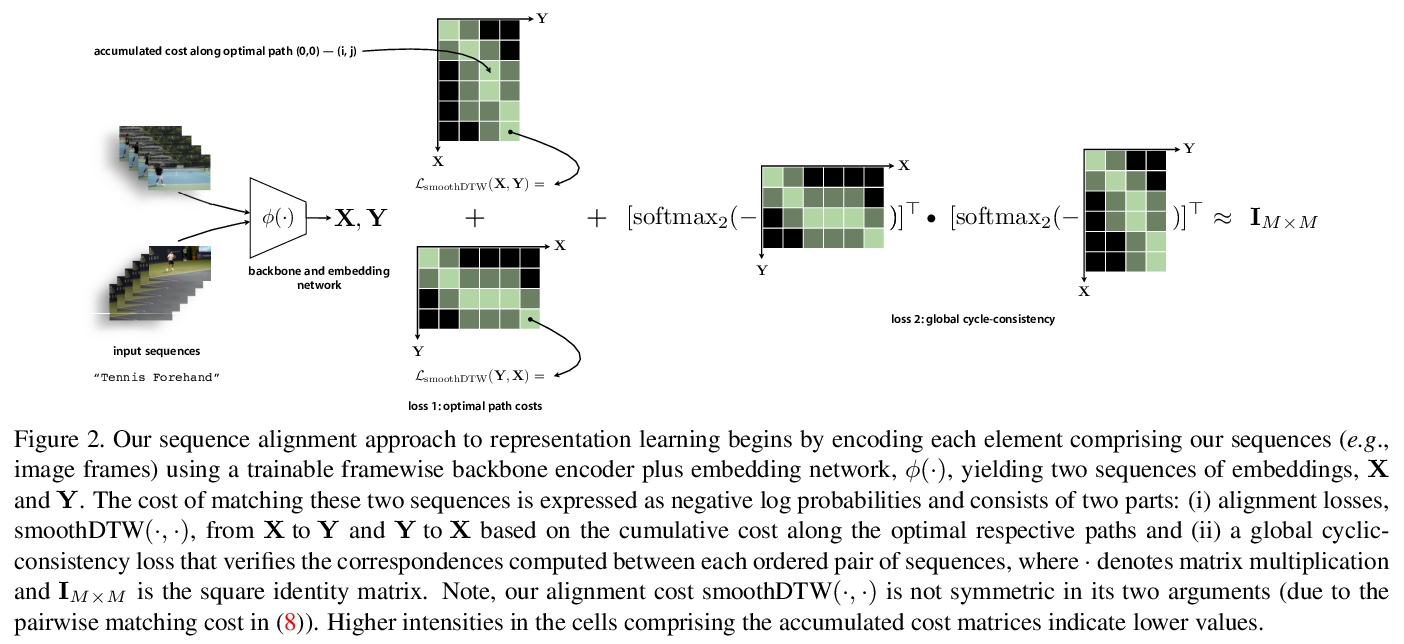
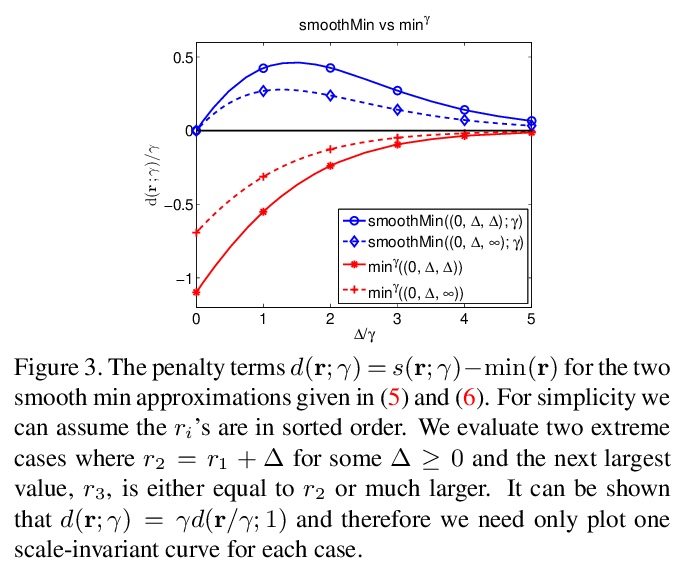
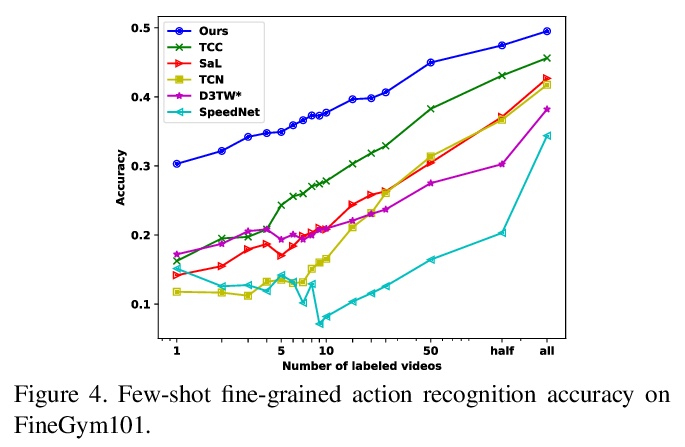
4、[CV] Representation Learning via Global Temporal Alignment and Cycle-Consistency
I Hadji, K G. Derpanis, A D. Jepson
[Samsung AI Centre Toronto]
基于全局时间对齐和循环一致性的表示学习。提出一种弱监督方法,用于基于同一过程(如人类行动)的时间序列(如视频)对齐的表示学习。其主要思想是用跨序列对的潜在对应关系的全局时间排序作为监督信号。提出了一个基于对最佳序列排列的评分的损失,以训练嵌入网络,损失从动态时间扭曲(DTW)的新型概率路径寻找的角度,包含以下三个关键特征:(i)局部路径路由决定是对比性的和可微的,(ii)成对距离也是对比性的概率,以及(iii)该表述自然接受一个验证对应关系的全局循环一致性损失。为了评估,考虑了细粒度动作分类、少样本学习和视频同步等任务。与之前方法相比,性能显著提高。还报告了时间对齐框架的两个应用,即3D姿势重建和细粒度的音频/视觉检索。
We introduce a weakly supervised method for representation learning based on aligning temporal sequences (e.g., videos) of the same process (e.g., human action). The main idea is to use the global temporal ordering of latent correspondences across sequence pairs as a supervisory signal. In particular, we propose a loss based on scoring the optimal sequence alignment to train an embedding network. Our loss is based on a novel probabilistic path finding view of dynamic time warping (DTW) that contains the following three key features: (i) the local path routing decisions are contrastive and differentiable, (ii) pairwise distances are cast as probabilities that are contrastive as well, and (iii) our formulation naturally admits a global cycleconsistency loss that verifies correspondences. For evaluation, we consider the tasks of fine-grained action classification, few shot learning, and video synchronization. We report significant performance increases over previous methods. In addition, we report two applications of our temporal alignment framework, namely 3D pose reconstruction and fine-grained audio/visual retrieval.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kfwj5tEpA
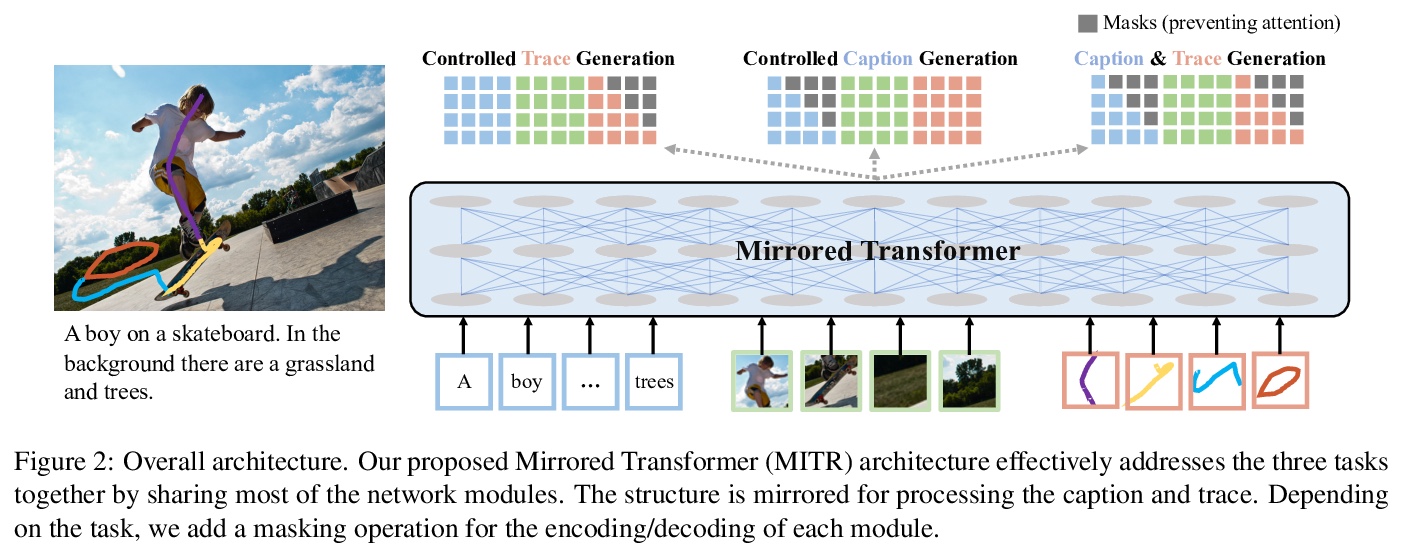
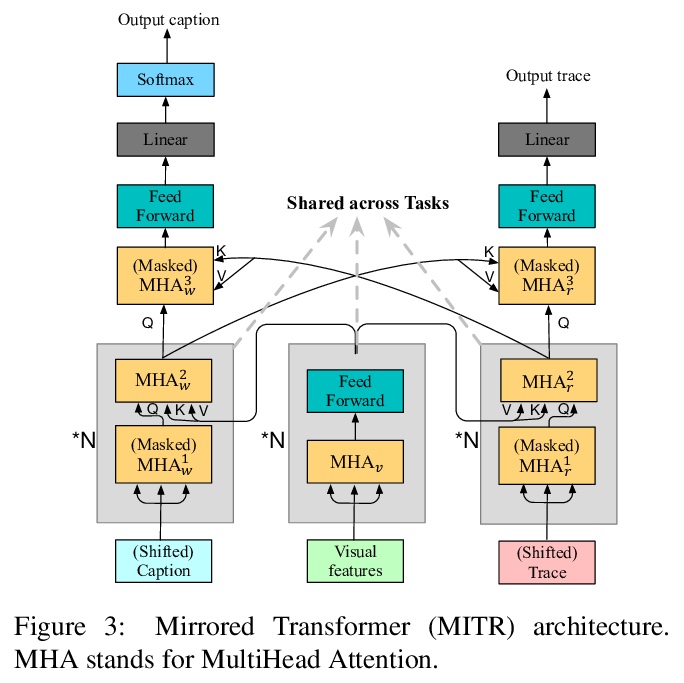
5、[CV] Connecting What to Say With Where to Look by Modeling Human Attention Traces
Z Meng, L Yu, N Zhang, T Berg, B Damavandi, V Singh, A Bearman
[University of Wisconsin Madison & Facebook AI]
对图像、文本和注意力轨迹的联合建模。提出一个统一的框架对图像、文本和人类注意力轨迹进行联合建模。该工作建立在最近的Localized Narratives标注框架之上,其中给定标题的每个词都与鼠标轨迹段配对。本文提出两个新任务:(1)预测给定图像和标题的轨迹(即视觉事实),以及(2)仅给定图像预测标题和轨迹。由于人工提供的轨迹中存在噪音,以及存在无法进行有意义视觉标记的单词,学习每个词的事实是具有挑战性的。提出一种新的模型结构,在双重任务(受控轨迹生成和受控标题生成)上联合训练的。为评估生成轨迹的质量,提出了一个局部双点匹配(LBM)距离指标,对两个不同长度的轨迹进行比较。实验表明,模型对不完善的训练数据具有鲁棒性,并以明显优势胜过基线。
We introduce a unified framework to jointly model images, text, and human attention traces. Our work is built on top of the recent Localized Narratives annotation framework [30], where each word of a given caption is paired with a mouse trace segment. We propose two novel tasks: (1) predict a trace given an image and caption (i.e., visual grounding), and (2) predict a caption and a trace given only an image. Learning the grounding of each word is challenging, due to noise in the human-provided traces and the presence of words that cannot be meaningfully visually grounded. We present a novel model architecture that is jointly trained on dual tasks (controlled trace generation and controlled caption generation). To evaluate the quality of the generated traces, we propose a local bipartite matching (LBM) distance metric which allows the comparison of two traces of different lengths. Extensive experiments show our model is robust to the imperfect training data and outperforms the baselines by a clear margin. Moreover, we demonstrate that our model pre-trained on the proposed tasks can be also beneficial to the downstream task of COCO’s guided image captioning. Our code1 and project page2 are publicly available.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kfwo3oXpV


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
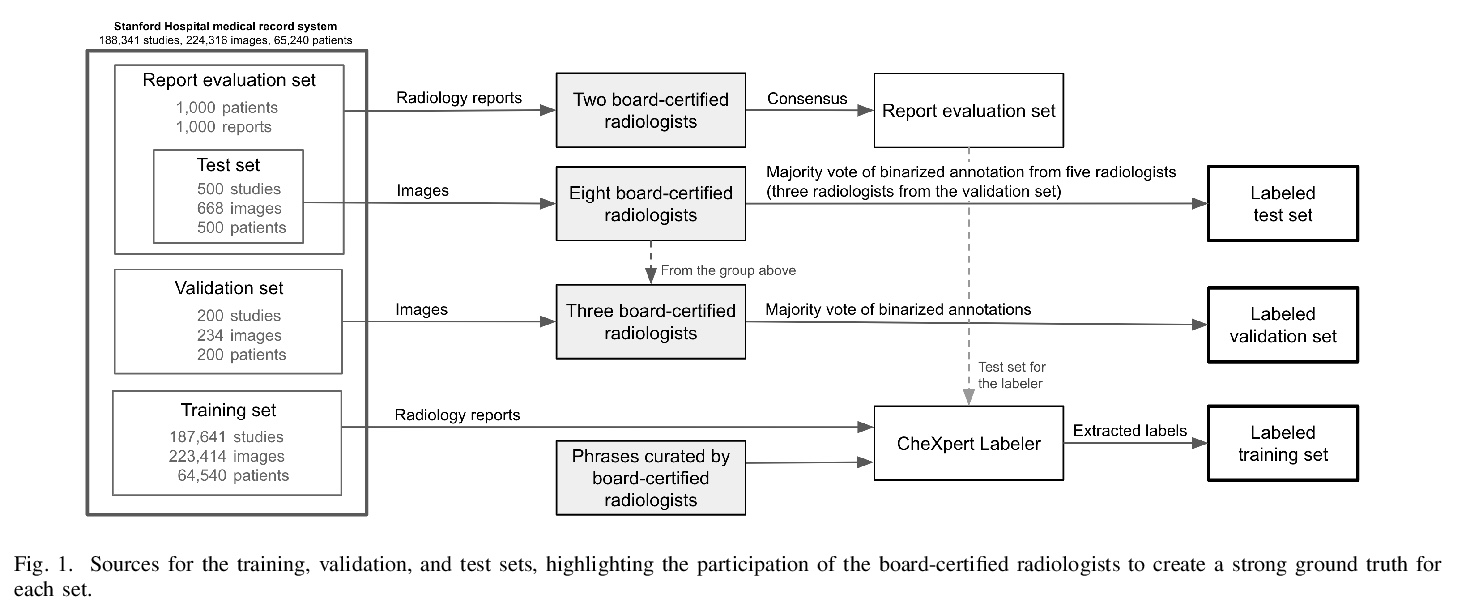
[CV] Structured dataset documentation: a datasheet for CheXpert
结构化数据集文档:CheXpert数据表
C Garbin, P Rajpurkar, J Irvin, M P. Lungren, O Marques
[Florida Atlantic University & Stanford University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfwlVkZNL
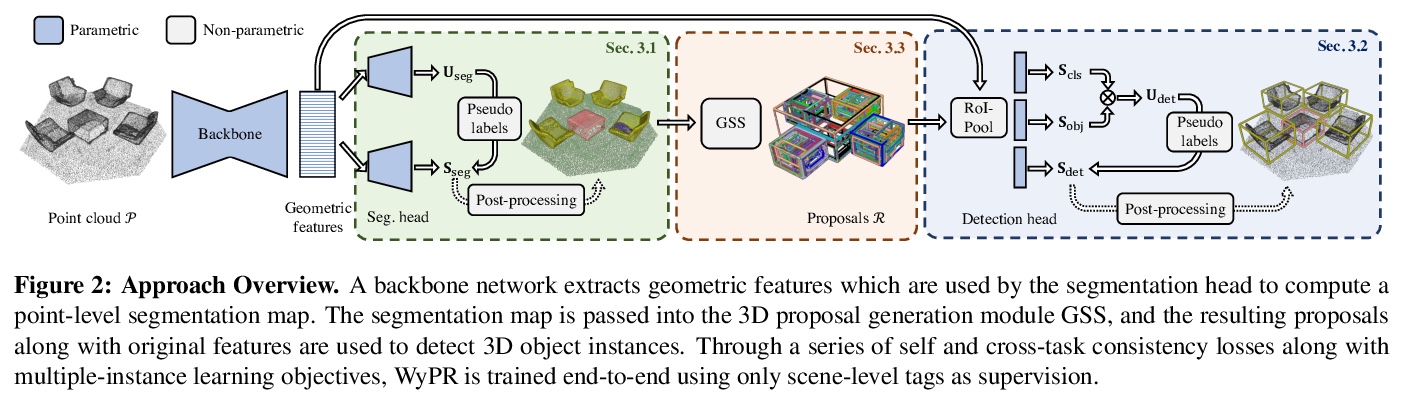
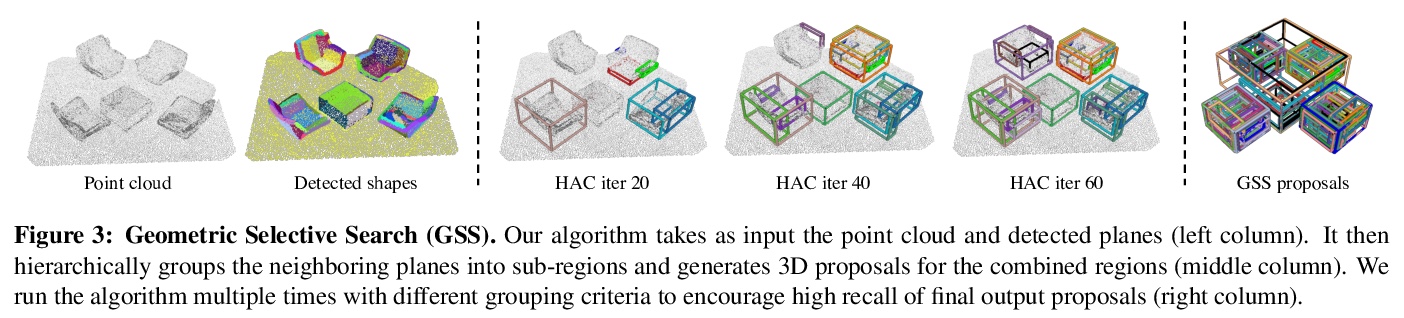
[CV] 3D Spatial Recognition without Spatially Labeled 3D
无空间标记3D空间识别
Z Ren, I Misra, A G. Schwing, R Girdhar
[Facebook AI Research & University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfwsYjElT

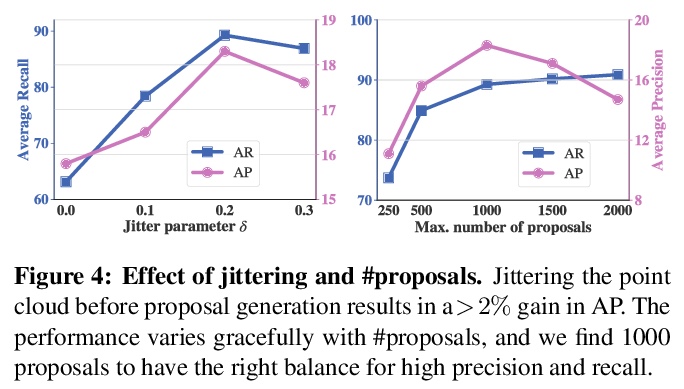
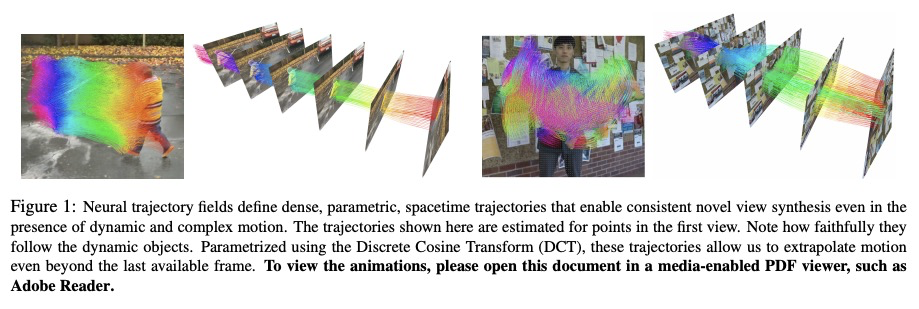
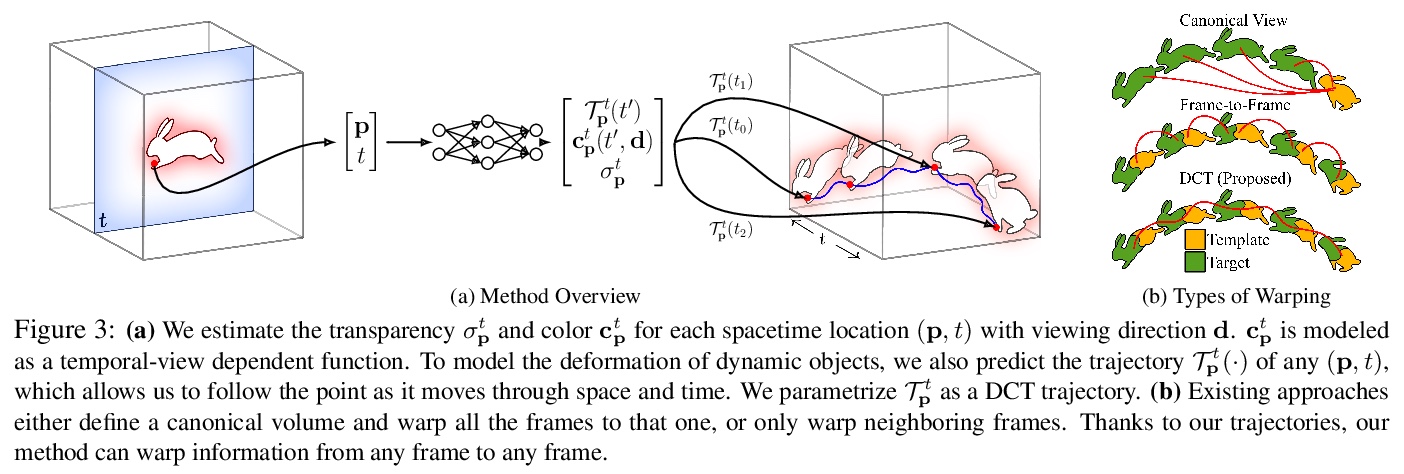
[CV] Neural Trajectory Fields for Dynamic Novel View Synthesis
神经轨迹场动态新视图合成
C Wang, B Eckart, S Lucey, O Gallo
[NVIDIA & CMU]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfwuUk2Qa


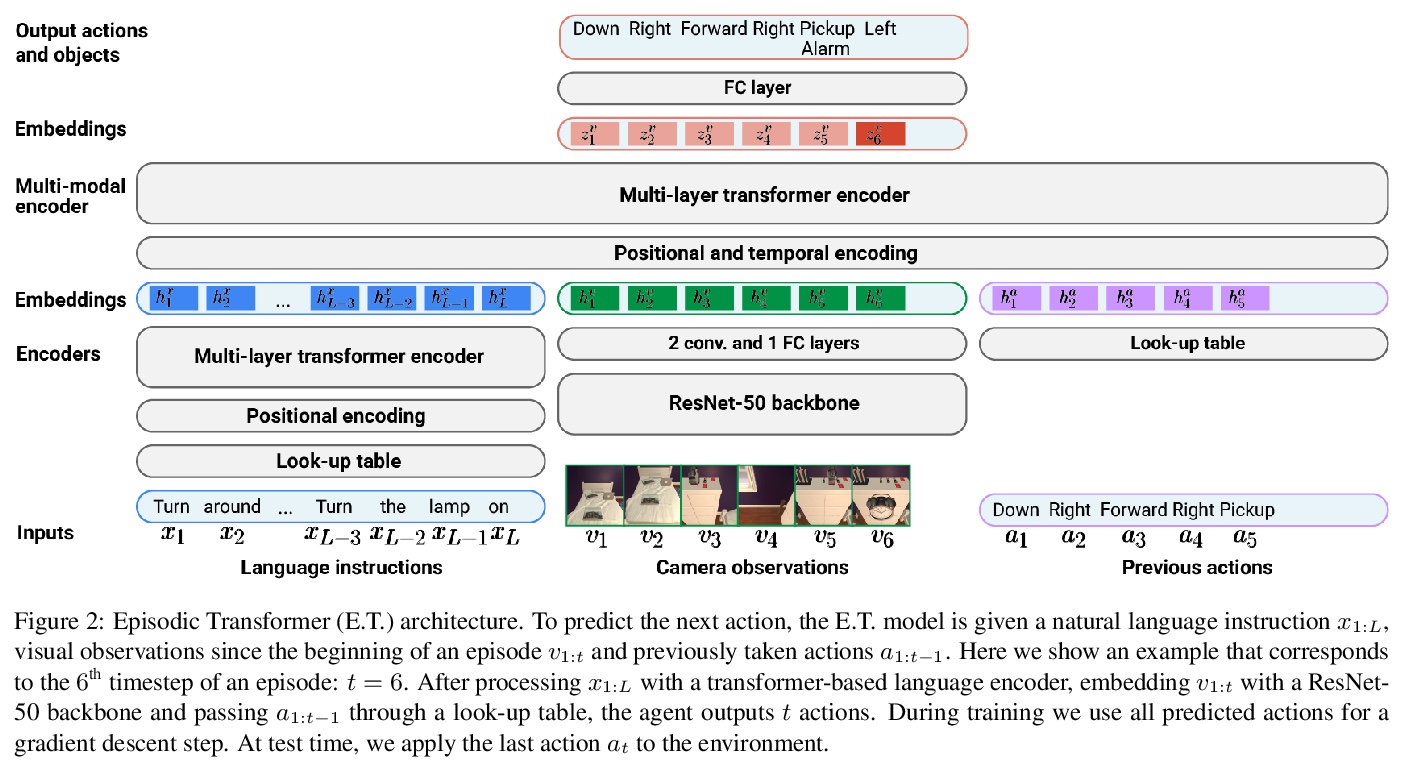
[CV] Episodic Transformer for Vision-and-Language Navigation
基于情景Transformer的视觉-语言导航
A Pashevich, C Schmid, C Sun
[Inria & Google Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfwwTx9Vl