- 1、[CV] Alias-Free Generative Adversarial Networks
- 2、[LG] Very Deep Graph Neural Networks Via Noise Regularisation
- 3、[LG] Why Do Pretrained Language Models Help in Downstream Tasks? An Analysis of Head and Prompt Tuning
- 4、[LG] Real-time gravitational-wave science with neural posterior estimation
- 5、[LG] LocoProp: Enhancing BackProp via Local Loss Optimization
- [LG] GraphiT: Encoding Graph Structure in Transformers
- [CL] Parameter-efficient Multi-task Fine-tuning for Transformers via Shared Hypernetworks
- [CV] Discovering Relationships between Object Categories via Universal Canonical Maps
- [LG] Iterative Feature Matching: Toward Provable Domain Generalization with Logarithmic Environments
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
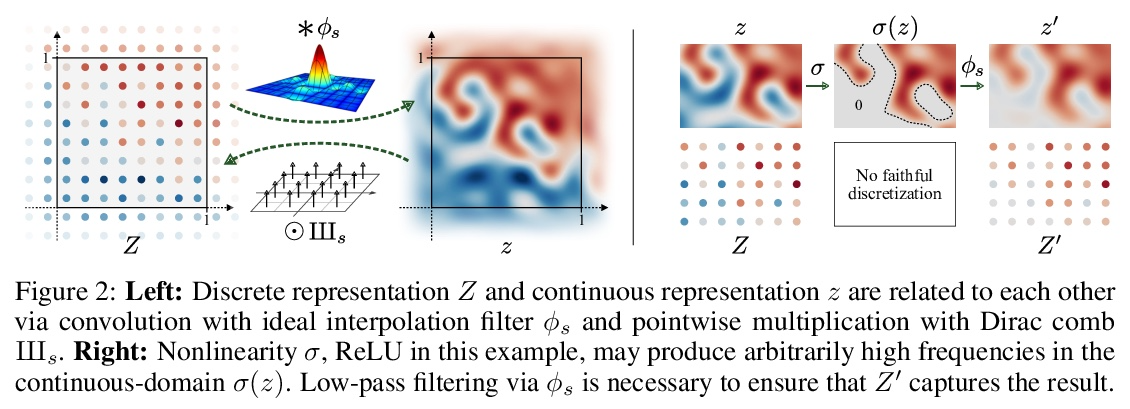
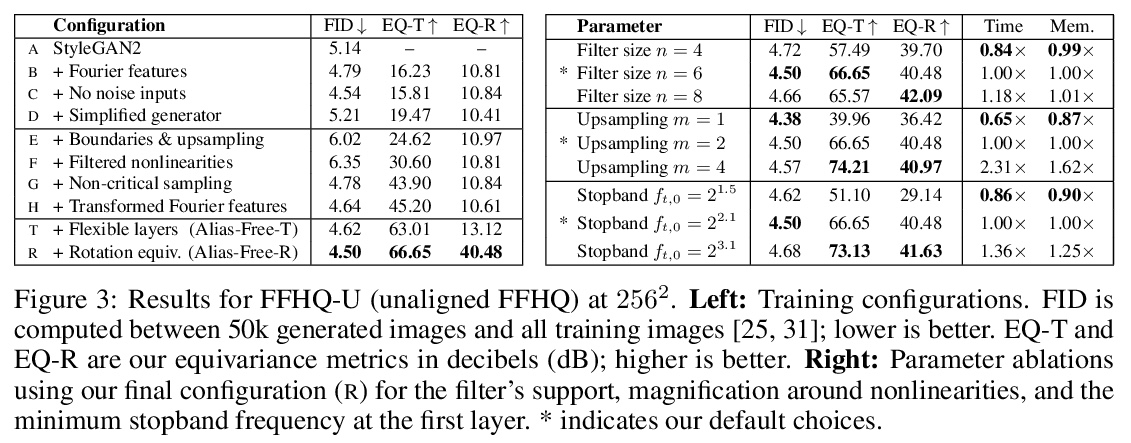
1、[CV] Alias-Free Generative Adversarial Networks
T Karras, M Aittala, S Laine, E Härkönen, J Hellsten, J Lehtinen, T Aila
[NVIDIA & Aalto University]
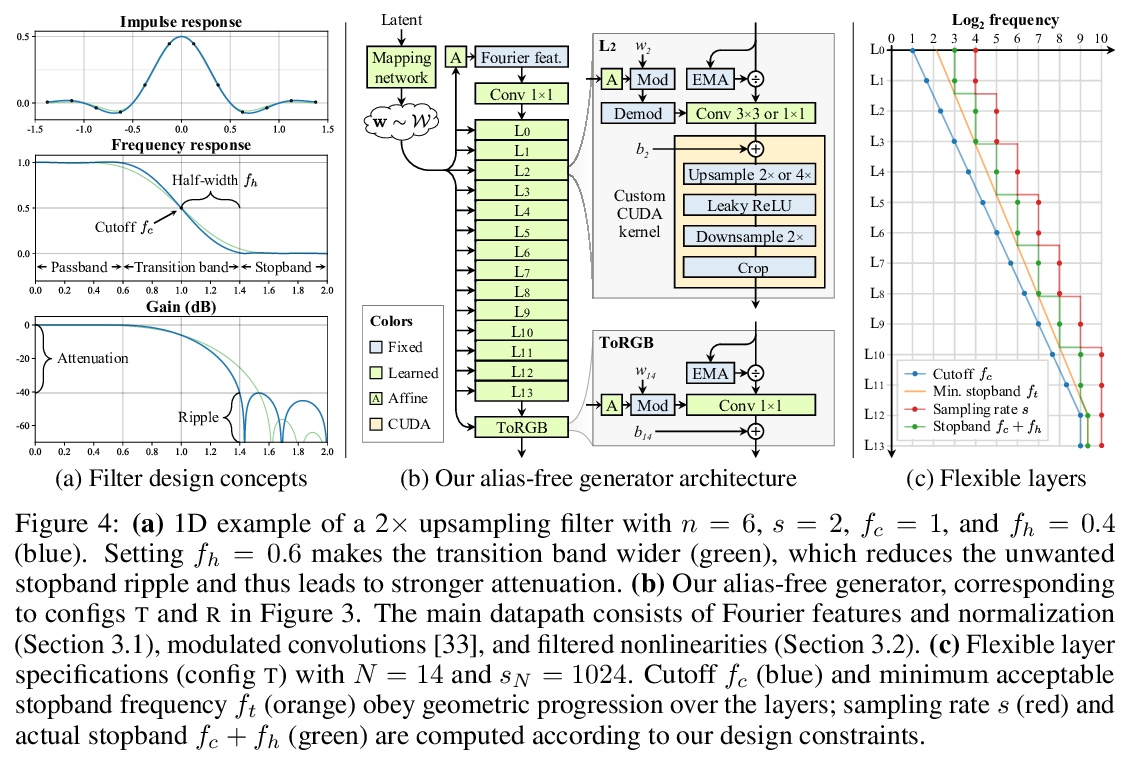
无走样生成对抗网络。尽管具有分层卷积的性质,但典型的生成对抗网络的合成过程以一种非健康方式依赖于绝对像素坐标。这表现为,例如,细节似乎依附于图像坐标而不是所描绘对象的表面上。本文将根本原因追溯到导致生成器网络中出现混叠的不细致的信号处理上,将网络中所有信号解释为连续的,得出普遍适用的小架构变化,以保证不需要的信息不会泄漏到分层合成过程中。由此产生的网络与 StyleGAN2 的 FID 相匹配,但内部表示有很大的不同,即使在亚像素尺度下,也完全等同于平移和旋转。本文的结果为更适合视频和动画的生成模型铺平了道路。
We observe that despite their hierarchical convolutional nature, the synthesis process of typical generative adversarial networks depends on absolute pixel coordinates in an unhealthy manner. This manifests itself as, e.g., detail appearing to be glued to image coordinates instead of the surfaces of depicted objects. We trace the root cause to careless signal processing that causes aliasing in the generator network. Interpreting all signals in the network as continuous, we derive generally applicable, small architectural changes that guarantee that unwanted information cannot leak into the hierarchical synthesis process. The resulting networks match the FID of StyleGAN2 but differ dramatically in their internal representations, and they are fully equivariant to translation and rotation even at subpixel scales. Our results pave the way for generative models better suited for video and animation.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmcTA0Nai 

2、[LG] Very Deep Graph Neural Networks Via Noise Regularisation
J Godwin, M Schaarschmidt, A Gaunt, A Sanchez-Gonzalez, Y Rubanova, P Veličković, J Kirkpatrick, P Battaglia
[DeepMind]
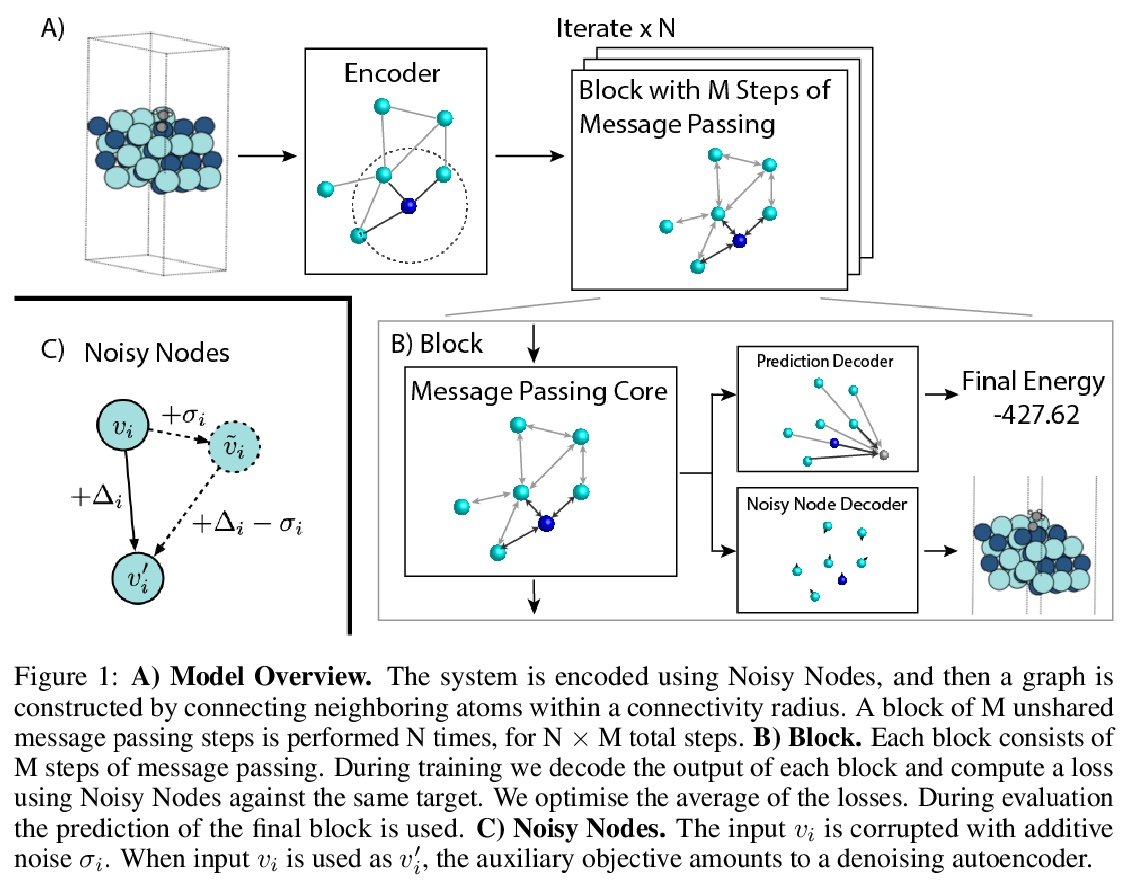
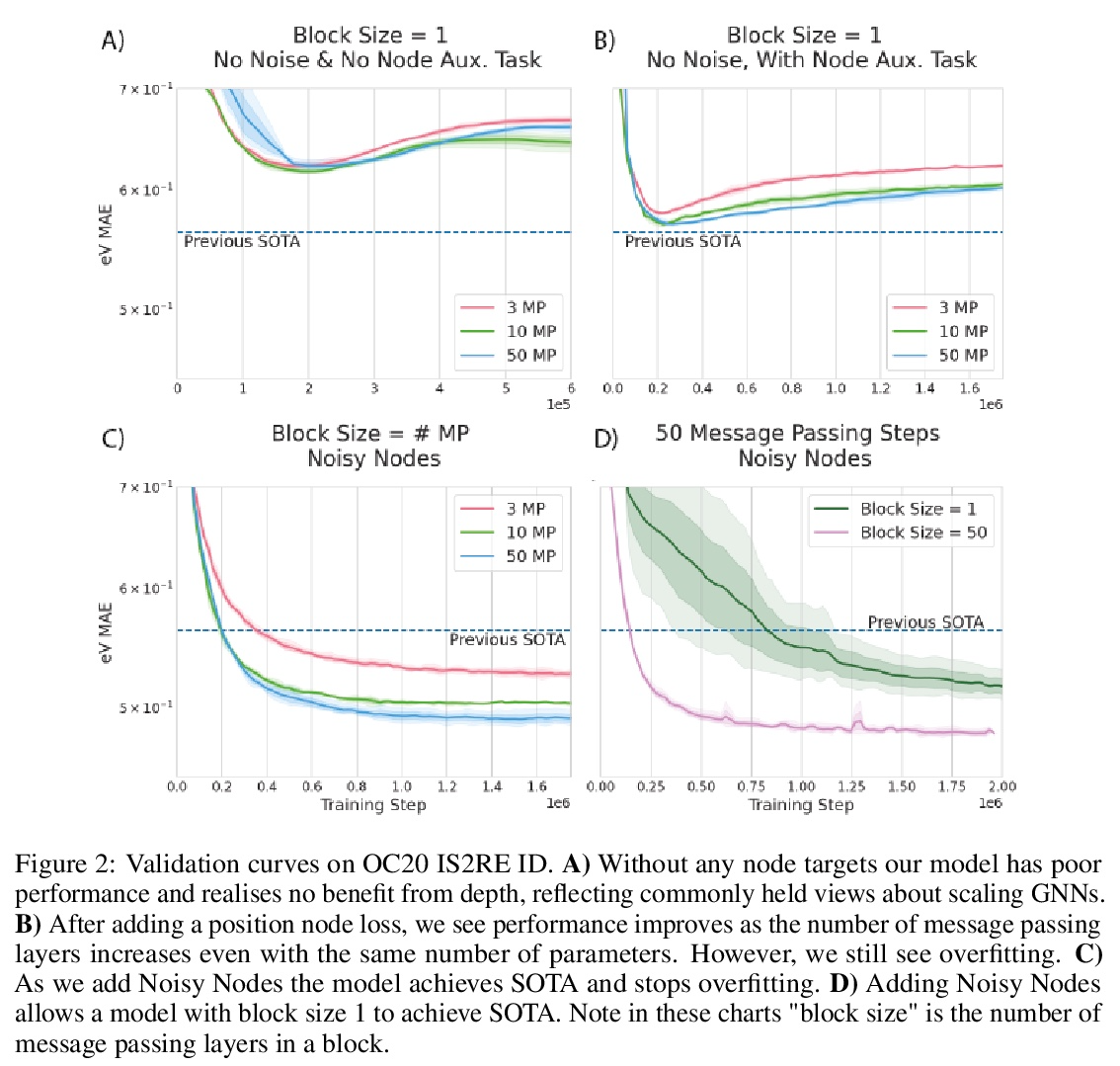
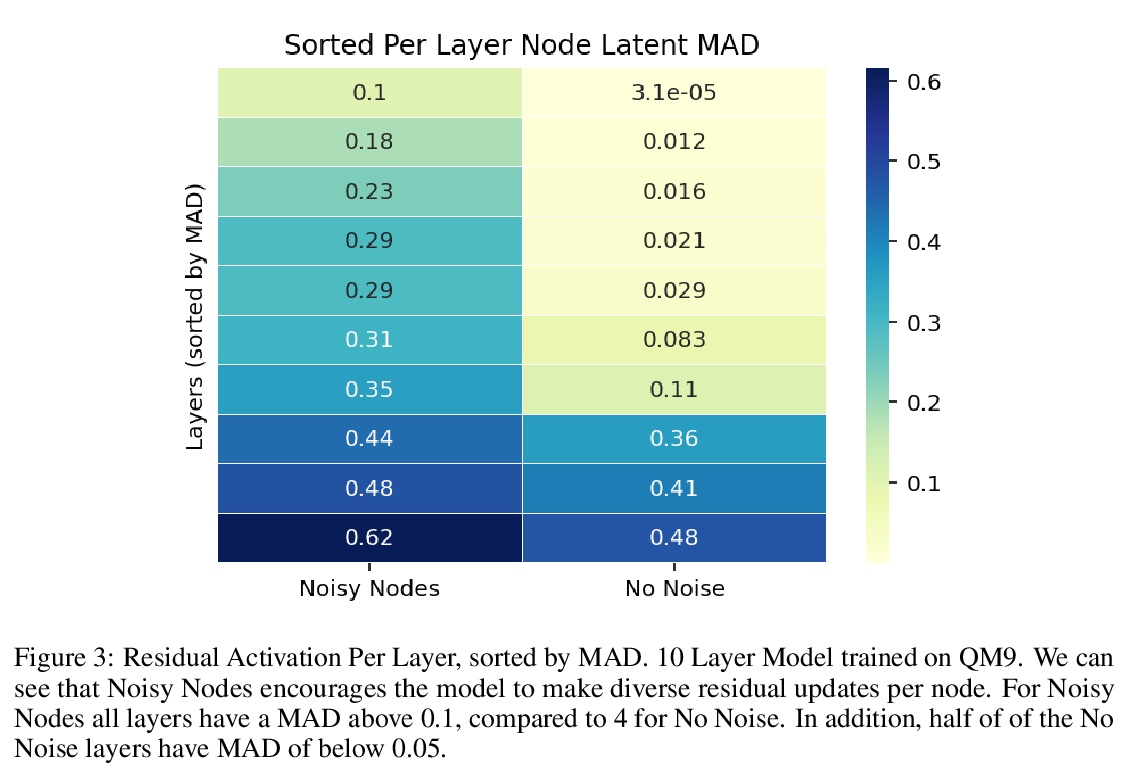
基于噪声正则化的非常深图神经网络。图神经网络 (GNN) 在输入图上执行习得消息传递,但传统观点认为,执行超过少数几个步骤会使训练变得困难,并且不会提高性能。本文展示了相反的情况,训练了一个具有多达 100 个消息传递步骤的深度 GNN,并在两个具有挑战性的分子特性预测基准 Open Catalyst 2020 IS2RE 和 QM9 上取得了多项最先进的结果。该方法主要依赖于一种新的简单正则化方法“噪声节点”,如果任务是图属性预测,就用噪声破坏输入图并添加辅助节点自编码器损失。结果表明,该正则化方法允许模型随着消息传递步骤的增加而单调提高性能。
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) perform learned message passing over an input graph, but conventional wisdom says performing more than handful of steps makes training difficult and does not yield improved performance. Here we show the contrary. We train a deep GNN with up to 100 message passing steps and achieve several state-of-the-art results on two challenging molecular property prediction benchmarks, Open Catalyst 2020 IS2RE and QM9. Our approach depends crucially on a novel but simple regularisation method, which we call “Noisy Nodes”, in which we corrupt the input graph with noise and add an auxiliary node autoencoder loss if the task is graph property prediction. Our results show this regularisation method allows the model to monotonically improve in performance with increased message passing steps. Our work opens new opportunities for reaping the benefits of deep neural networks in the space of graph and other structured prediction problems.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmcZakKMJ 
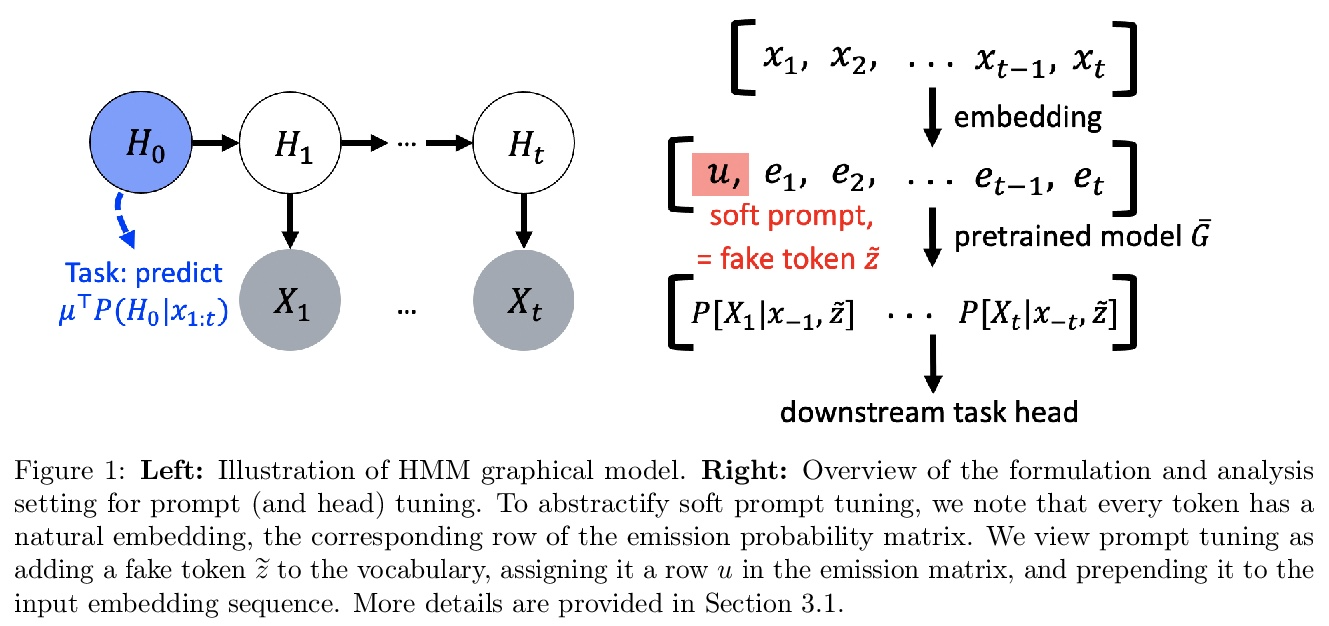
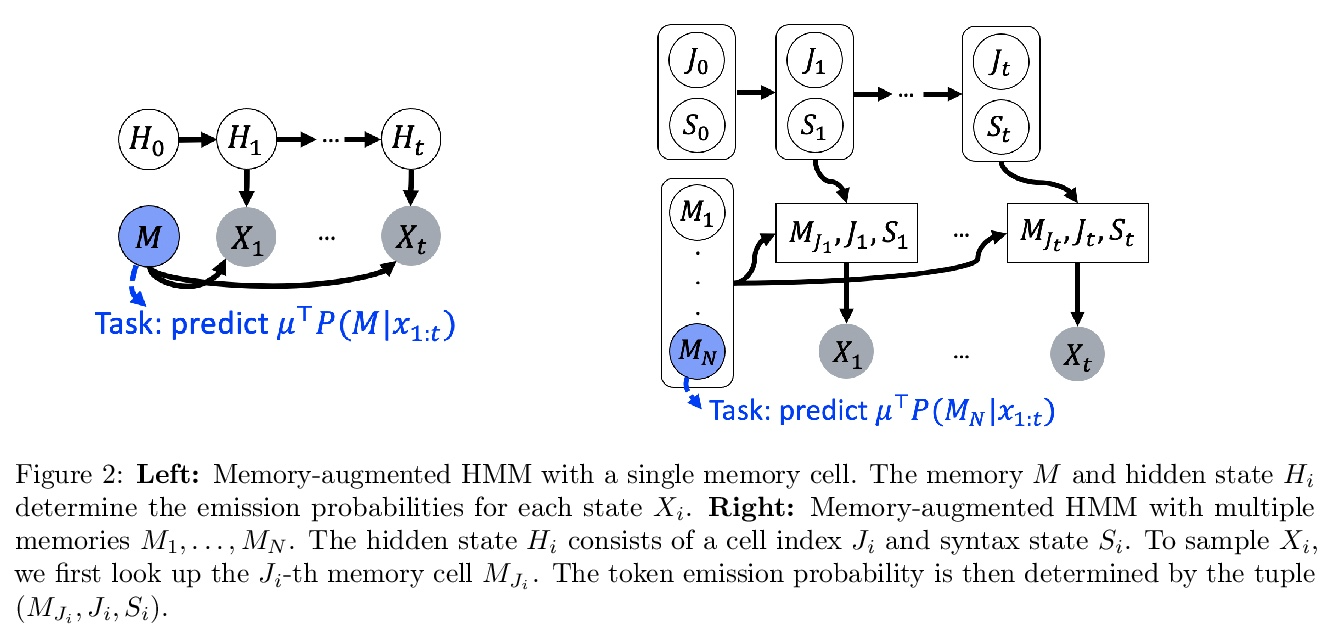
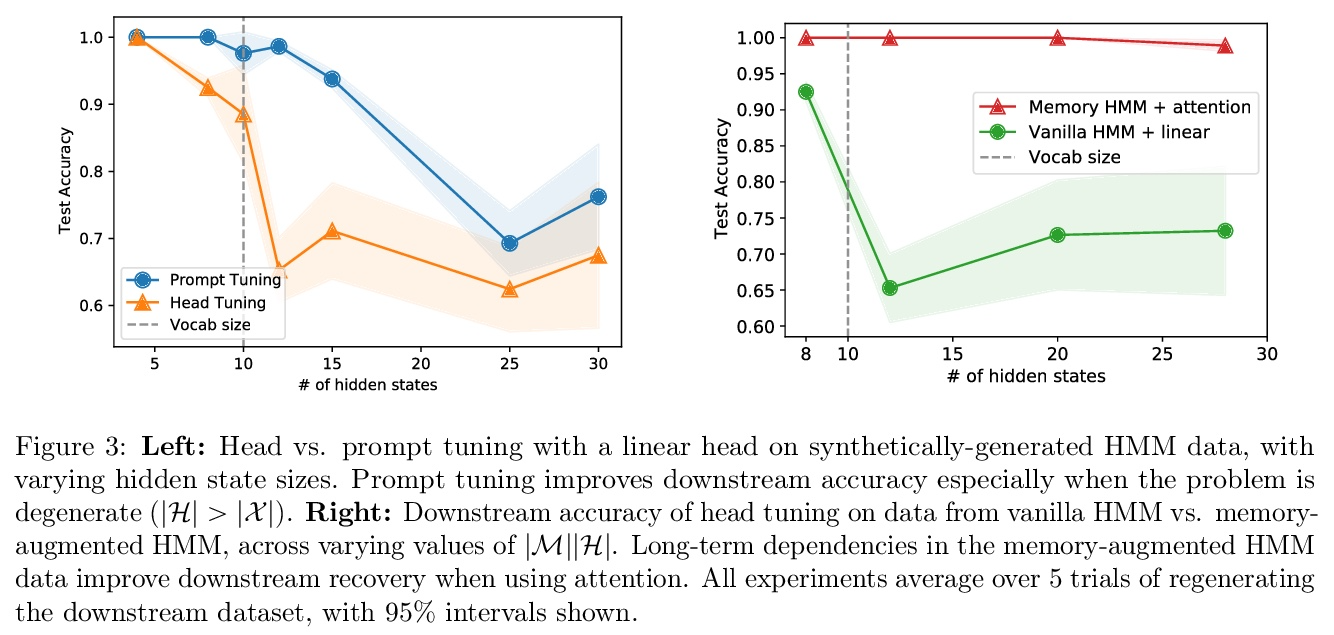
3、[LG] Why Do Pretrained Language Models Help in Downstream Tasks? An Analysis of Head and Prompt Tuning
C Wei, S M Xie, T Ma
[Stanford University]
为什么预训练语言模型有助于下游任务?头和提示微调分析。当适应下游 NLP 任务时,预训练语言模型已经实现了最先进的性能。然而,这些模型的理论分析很少且具有挑战性,因为预训练和下游任务可能非常不同。本文提出了一种分析框架,将预训练和下游任务与文本的底层潜变量生成模型联系起来——下游分类器必须恢复潜变量的后验分布函数。分析头微调(在冻结预训练模型基础上学习分类器)并在该设置下进行提示微调。分析中的生成模型或者是隐马尔可夫模型 (HMM) ,或者是由自然语言中的长程依赖关系驱动的由潜记忆组件增强的 HMM。本文表明 1)在 HMM 上的某些非退化性条件下,简单的分类头可以解决下游任务,2)提示微调可获得具有较弱非退化性条件的下游保证,以及 3)对记忆增强 HMM 的恢复保证比普通 HMM 更强,因为与任务相关的信息更容易从长期记忆中恢复。
Pretrained language models have achieved state-of-the-art performance when adapted to a downstream NLP task. However, theoretical analysis of these models is scarce and challenging since the pretraining and downstream tasks can be very different. We propose an analysis framework that links the pretraining and downstream tasks with an underlying latent variable generative model of text — the downstream classifier must recover a function of the posterior distribution over the latent variables. We analyze head tuning (learning a classifier on top of the frozen pretrained model) and prompt tuning in this setting. The generative model in our analysis is either a Hidden Markov Model (HMM) or an HMM augmented with a latent memory component, motivated by long-term dependencies in natural language. We show that 1) under certain non-degeneracy conditions on the HMM, simple classification heads can solve the downstream task, 2) prompt tuning obtains downstream guarantees with weaker non-degeneracy conditions, and 3) our recovery guarantees for the memory-augmented HMM are stronger than for the vanilla HMM because task-relevant information is easier to recover from the long-term memory. Experiments on synthetically generated data from HMMs back our theoretical findings.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kmd2Z2eO5 
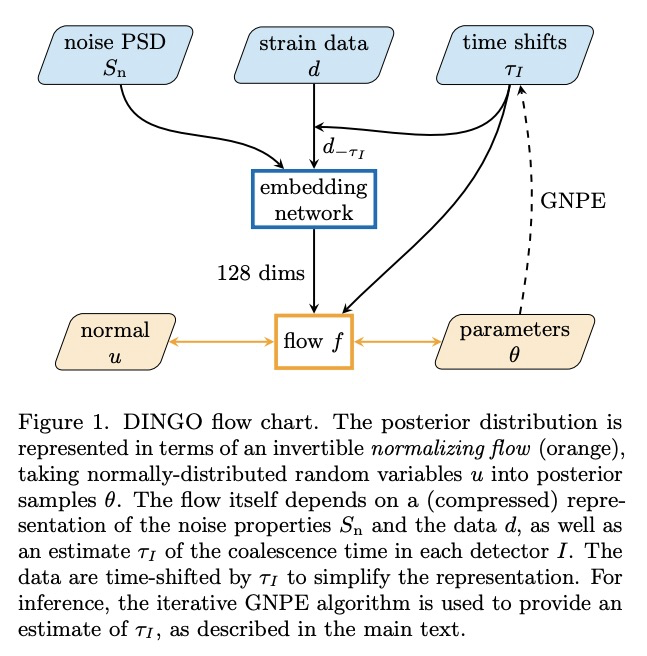
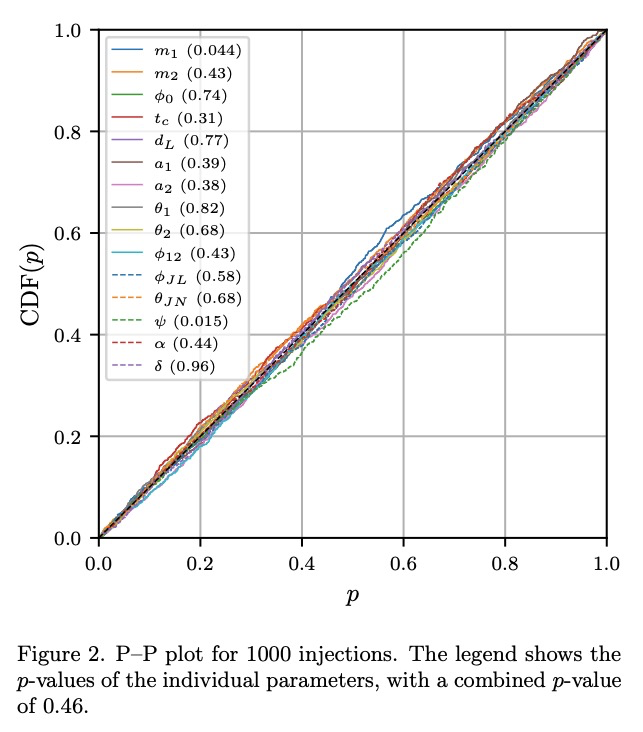
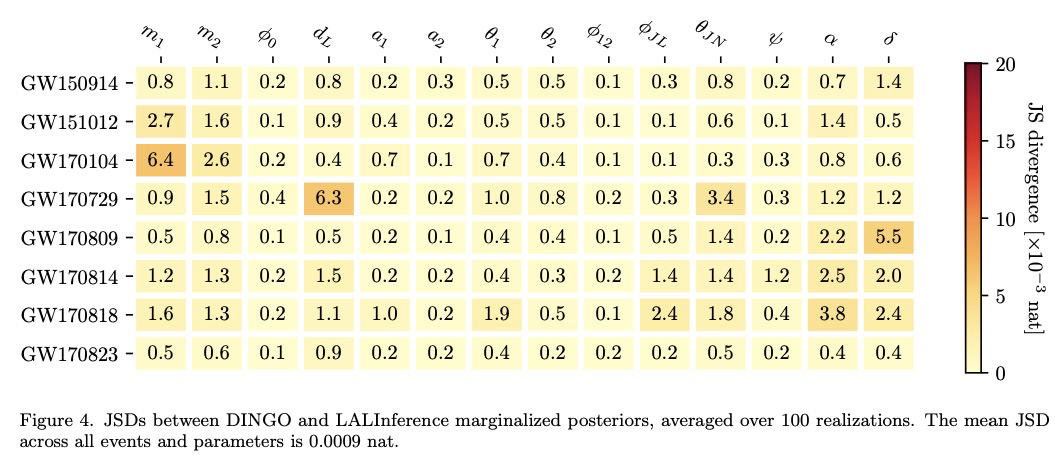
4、[LG] Real-time gravitational-wave science with neural posterior estimation
M Dax, S R. Green, J Gair, J H. Macke, A Buonanno, B Schölkopf
[Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems & Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics]
基于神经后验估计的实时引力波科学。本文展示了基于深度学习进行快速引力波参数估计的前所未有的准确性。用神经网络替代贝叶斯后验分布,分析了第一个 LIGO-Virgo 引力波瞬态目录中的八个引力波事件,并发现与标准推理代码非常接近的定量一致性,但推理时间从 O(day) 减少到每事件一分钟。所用网络基于仿真数据进行训练,包括对事件附近检测器噪声特性的估计。在数百万个神经网络参数中对信号和噪声模型进行编码,并能够对与训练分布一致的任何观察到的数据进行推断,从而解释事件之间的噪声非平稳性。所提出的算法——称为“DINGO”——为检测到的引力波事件的物理参数的快速准确推断设立了一个新标准,能在不牺牲准确性的情况下进行实时数据分析。
We demonstrate unprecedented accuracy for rapid gravitational-wave parameter estimation with deep learning. Using neural networks as surrogates for Bayesian posterior distributions, we analyze eight gravitational-wave events from the first LIGO-Virgo Gravitational-Wave Transient Catalog and find very close quantitative agreement with standard inference codes, but with inference times reduced from O(day) to a minute per event. Our networks are trained using simulated data, including an estimate of the detector-noise characteristics near the event. This encodes the signal and noise models within millions of neural-network parameters, and enables inference for any observed data consistent with the training distribution, accounting for noise nonstationarity from event to event. Our algorithm — called “DINGO” — sets a new standard in fast-and-accurate inference of physical parameters of detected gravitational-wave events, which should enable real-time data analysis without sacrificing accuracy.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kmd8MhTOD 

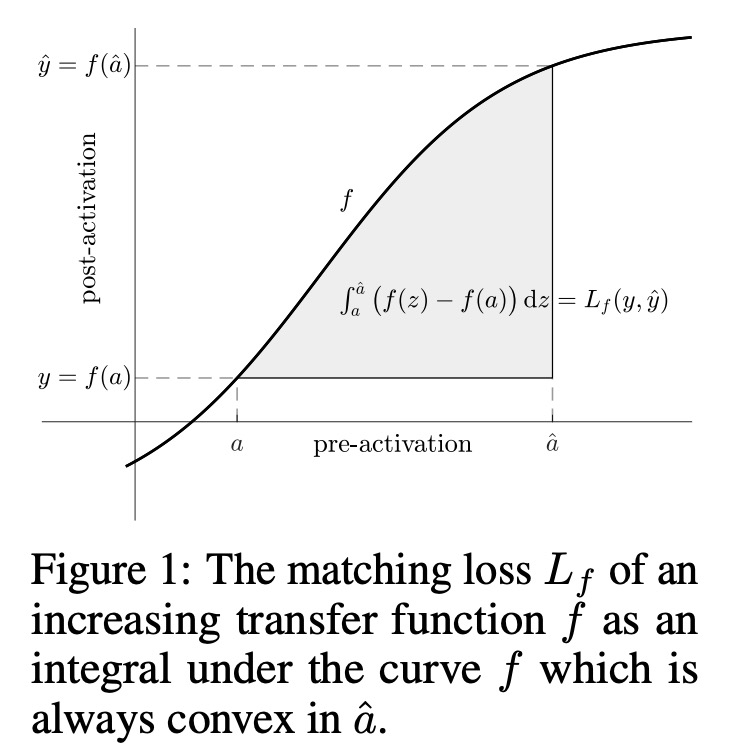
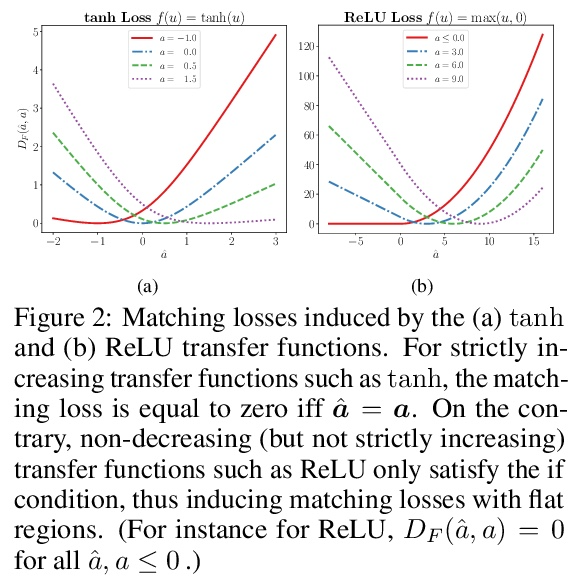
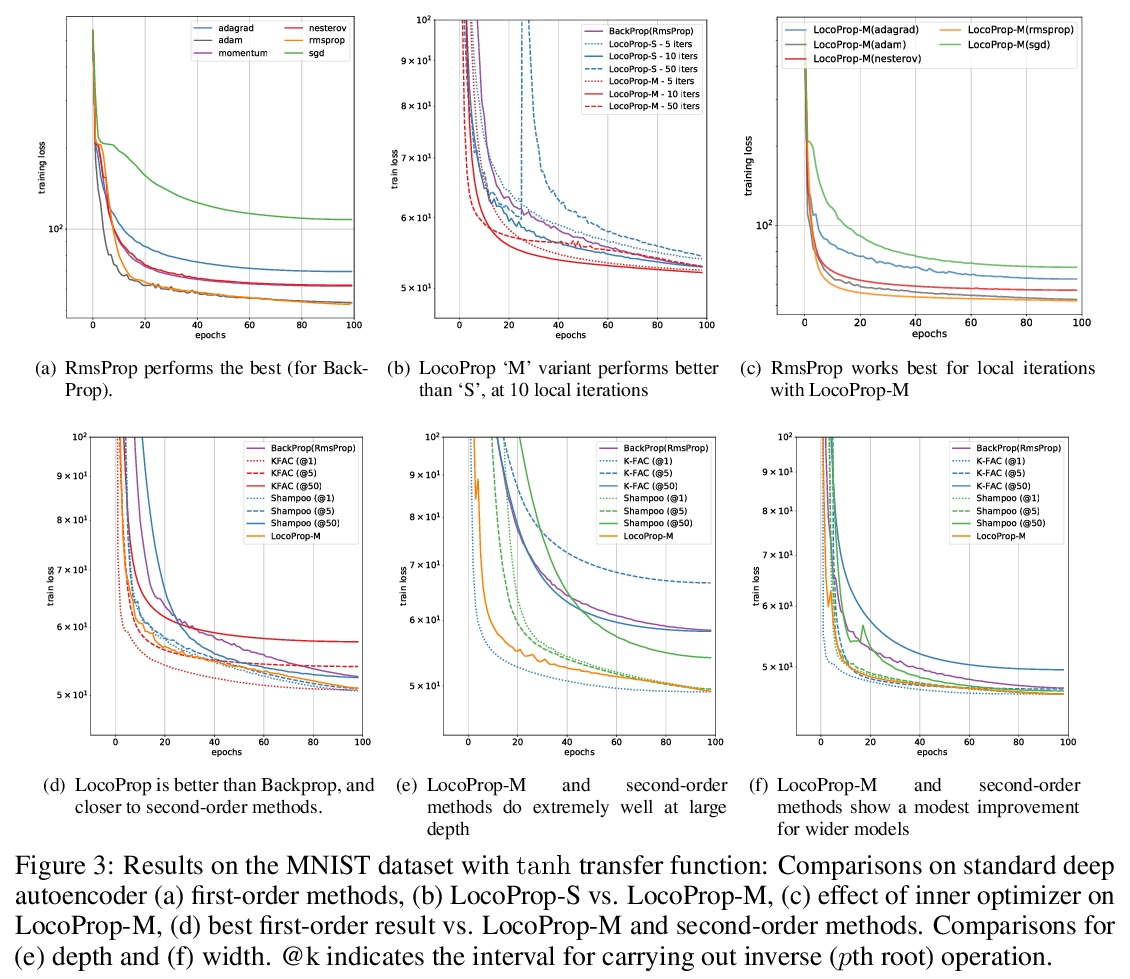
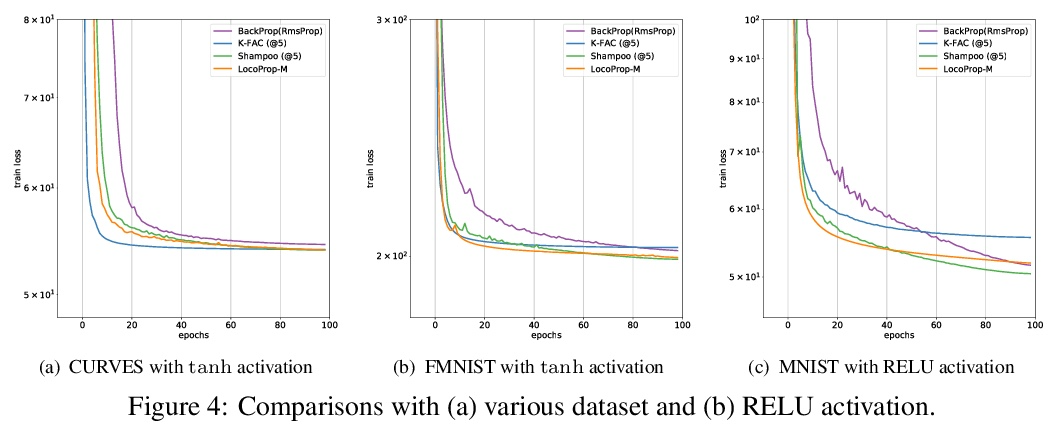
5、[LG] LocoProp: Enhancing BackProp via Local Loss Optimization
E Amid, R Anil, M K. Warmuth
[Google Research]
LocoProp:基于局部损失优化改善反向传播。本文研究了一种用于优化神经网络的局部损失构建方法。将问题作为最小化每层的预激活和局部目标之间的平方损失,加上权重的正则化项来解决。选择目标,使得局部目标上的第一个梯度下降步骤恢复vanilla反向传播,而每个问题的精确解会导致预处理梯度更新。通过在每一层形成一个 Bregman 散度来改进局部损失构造,该散度适合于传递函数,保持局部问题相对于权重是凸的。通过对权重采取小的梯度下降步骤,再次迭代解决广义局部问题,第一步恢复反向传播。实验表明该构造一致地提高了收敛性,减少了一阶和二阶方法之间的差距。
We study a local loss construction approach for optimizing neural networks. We start by motivating the problem as minimizing a squared loss between the preactivations of each layer and a local target, plus a regularizer term on the weights. The targets are chosen so that the first gradient descent step on the local objectives recovers vanilla BackProp, while the exact solution to each problem results in a preconditioned gradient update. We improve the local loss construction by forming a Bregman divergence in each layer tailored to the transfer function which keeps the local problem convex w.r.t. the weights. The generalized local problem is again solved iteratively by taking small gradient descent steps on the weights, for which the first step recovers BackProp. We run several ablations and show that our construction consistently improves convergence, reducing the gap between first-order and second-order methods.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kmdc8incX 
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[LG] GraphiT: Encoding Graph Structure in Transformers
GraphiT:用Transformer编码图结构
G Mialon, D Chen, M Selosse, J Mairal
[Inria]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kmdh8zlQ1 

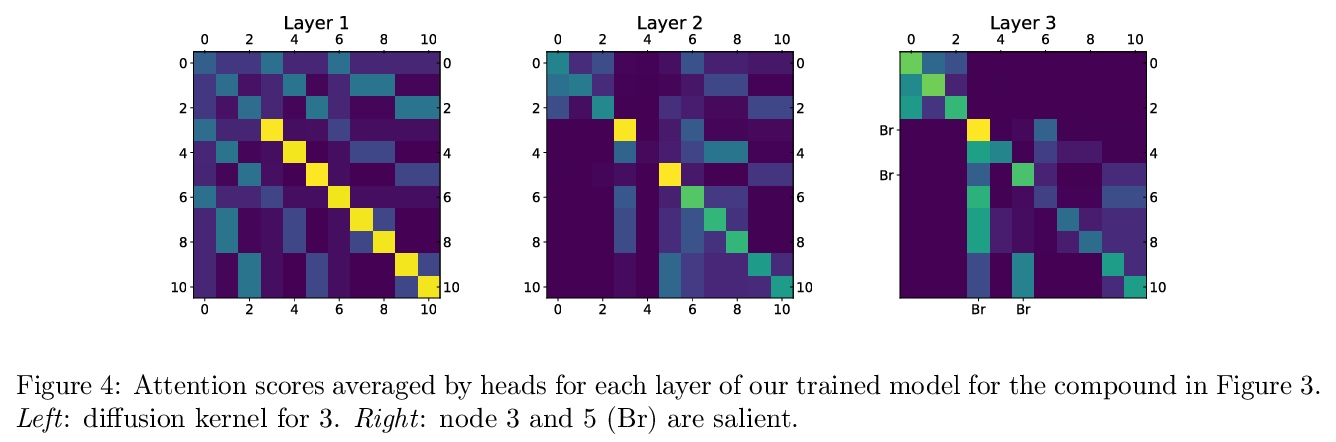
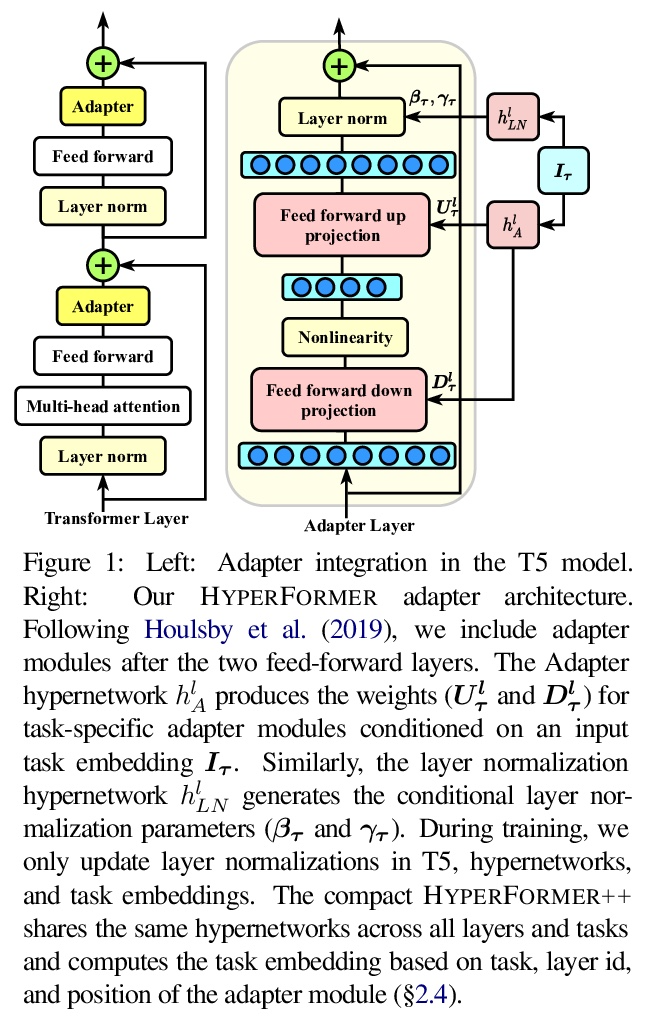
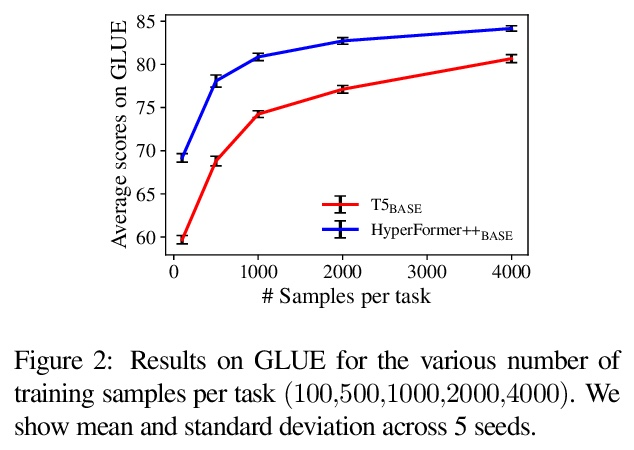
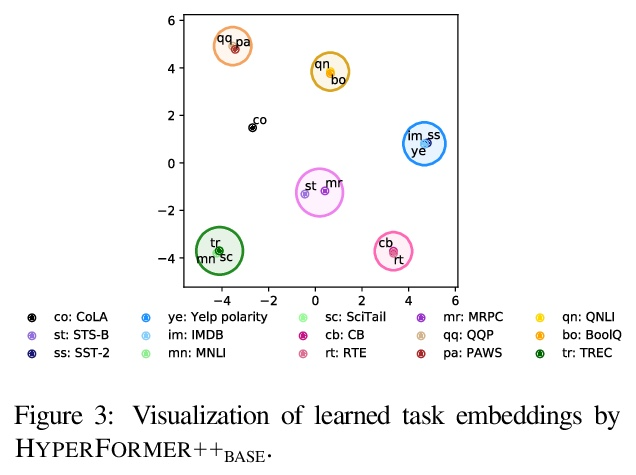
[CL] Parameter-efficient Multi-task Fine-tuning for Transformers via Shared Hypernetworks
基于共享超网络的Transformer参数高效多任务微调
R K Mahabadi, S Ruder, M Dehghani, J Henderson
[EPFL University & DeepMind & Google Brain & Idiap Research Institute]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KmdiE0mmw 
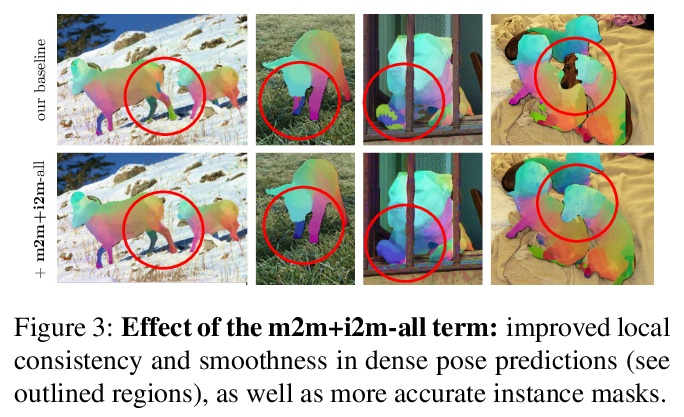
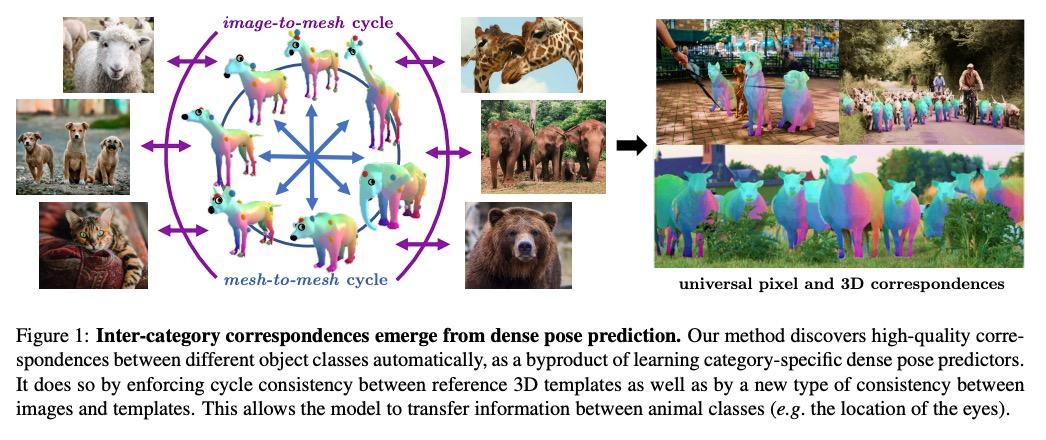
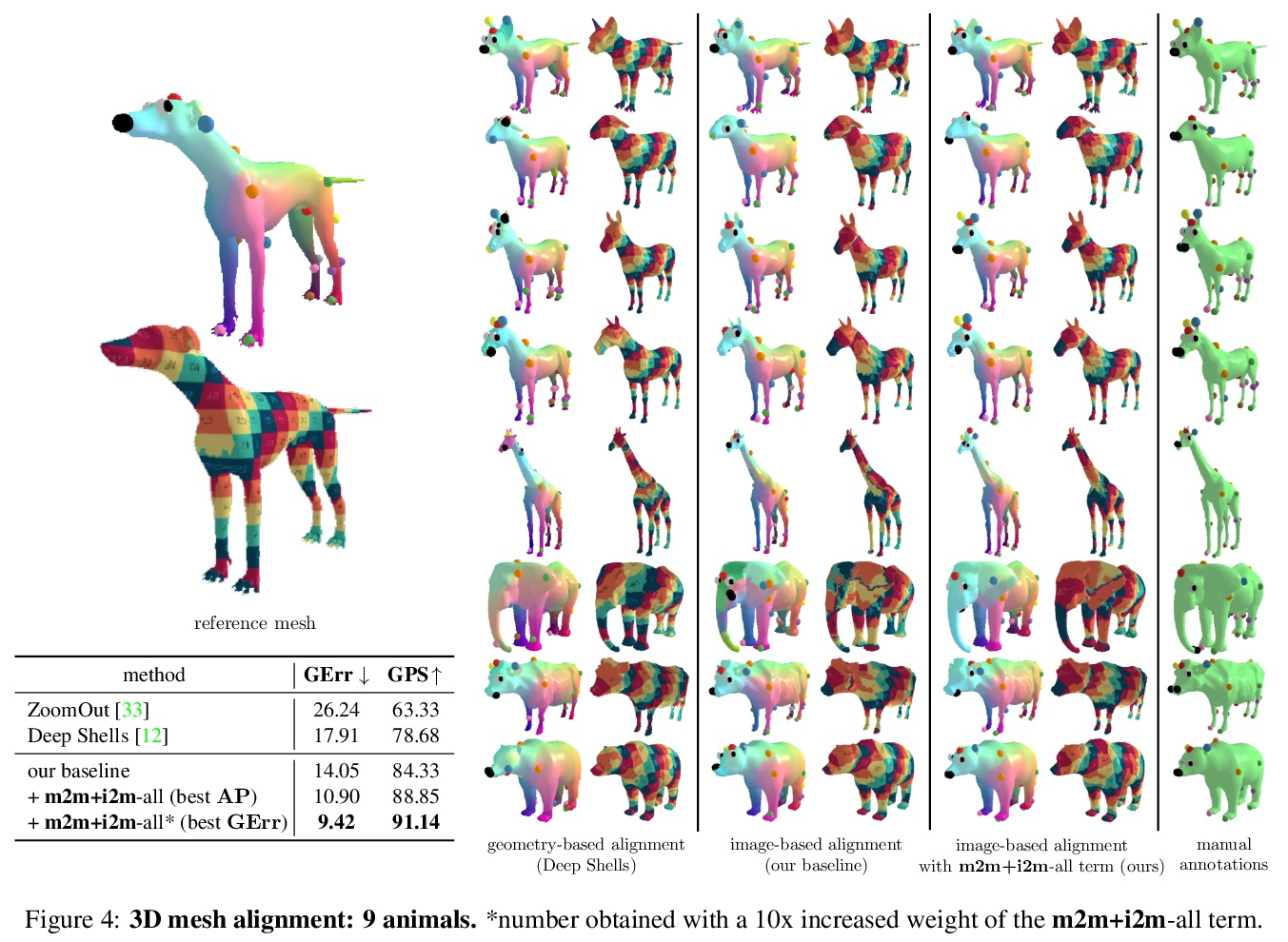
[CV] Discovering Relationships between Object Categories via Universal Canonical Maps
基于通用规范化映射发现对象类间关系
N Neverova, A Sanakoyeu, P Labatut, D Novotny, A Vedaldi
[Facebook AI Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kmdk3oN3Y 


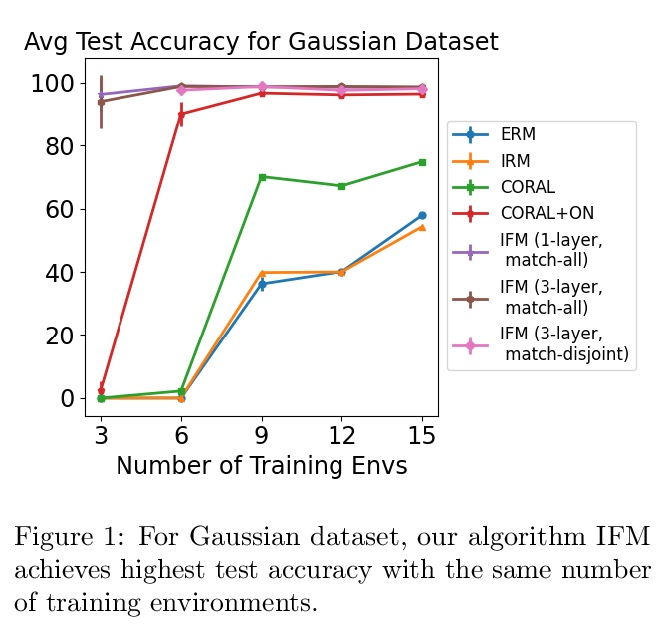
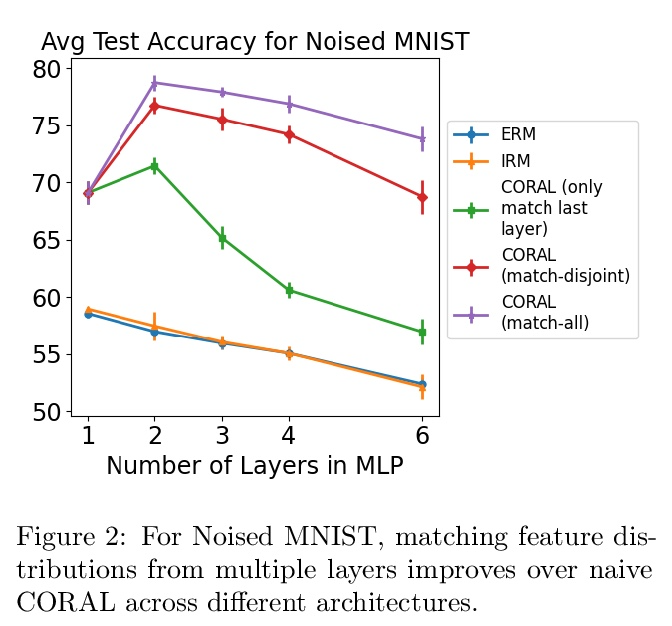
[LG] Iterative Feature Matching: Toward Provable Domain Generalization with Logarithmic Environments
迭代特征匹配:对数环境可证域泛化
Y Chen, E Rosenfeld, M Sellke, T Ma, A Risteski
[Stanford University & CMU]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kmdmn0pDl