LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、**[AI] Brain Co-Processors: Using AI to Restore and Augment Brain Function
R P. N. Rao
[University of Washington]
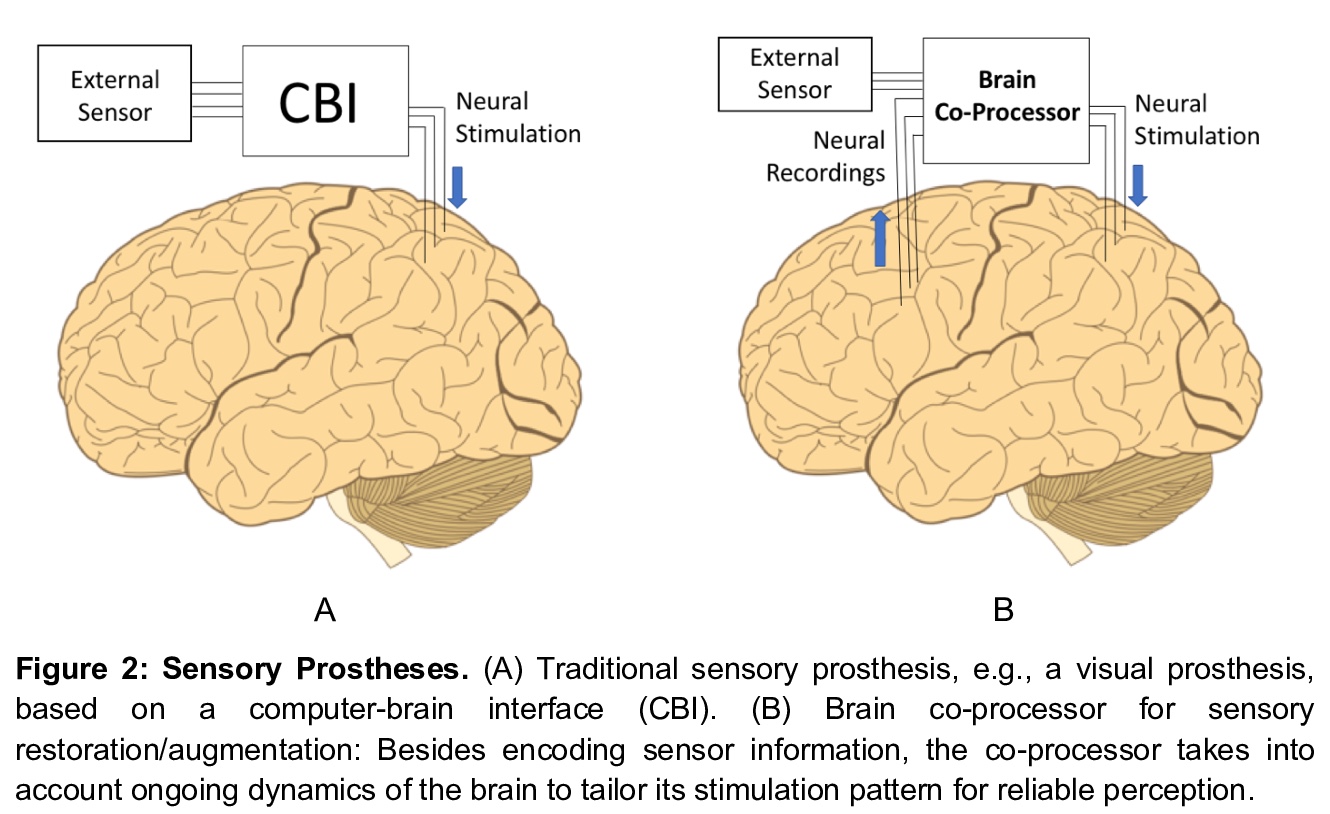
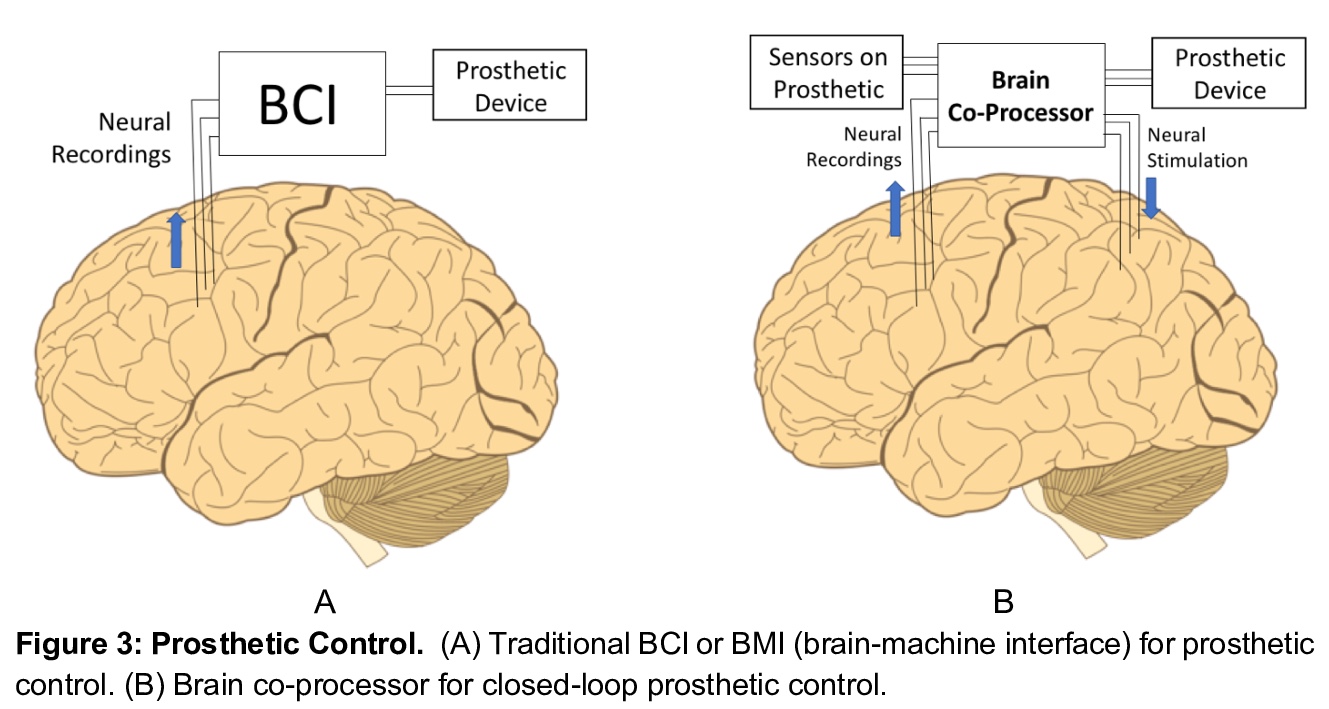
脑协处理器:用人工智能恢复和增强大脑功能。脑协处理器结合了脑-机接口(BCIs)和机-脑接口(CBIs)的概念,用人工智能框架来“闭环”大脑,解码大脑某区域的神经活动的同时,通过刺激将信息传递到另一个区域,这种能力赋予了协处理器很大的通用性。本文回顾了如何用协处理器(a)控制假肢与人工感官反馈触觉传感器;(b)利用来自大脑的运动意向信号,通过刺激控制瘫痪肢体;(c)恢复和增强认知功能和记忆,以及(d)诱导神经可塑性康复。在动物模型和人类的某些情况下,已经获得了有希望的概念验证结果,但大多是在实验室条件下。为了过渡到现实世界,协处理器必须与神经系统协同适应,联合优化行为成本函数。本文引入了神经协处理器,用人工神经网络与神经系统生物神经网络同步联合优化行为成本函数。神经协处理器将大型多维神经活动模式(尖峰、发射率、局部场电位、ECoG、EEG等)映射到复杂的输出刺激模式,以达到预期目标。*
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) use decoding algorithms to control prosthetic devices based on brain signals for restoration of lost function. Computer-brain interfaces (CBIs), on the other hand, use encoding algorithms to transform external sensory signals into neural stimulation patterns for restoring sensation or providing sensory feedback for closed-loop prosthetic control. In this article, we introduce brain co-processors, devices that combine decoding and encoding in a unified framework using artificial intelligence (AI) to supplement or augment brain function. Brain co-processors can be used for a range of applications, from inducing Hebbian plasticity for rehabilitation after brain injury to reanimating paralyzed limbs and enhancing memory. A key challenge is simultaneous multi-channel neural decoding and encoding for optimization of external behavioral or task-related goals. We describe a new framework for developing brain co-processors based on artificial neural networks, deep learning and reinforcement learning. These “neural co-processors” allow joint optimization of cost functions with the nervous system to achieve desired behaviors. By coupling artificial neural networks with their biological counterparts, neural co-processors offer a new way of restoring and augmenting the brain, as well as a new scientific tool for brain research. We conclude by discussing the potential applications and ethical implications of brain co-processors.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jydh5p1SO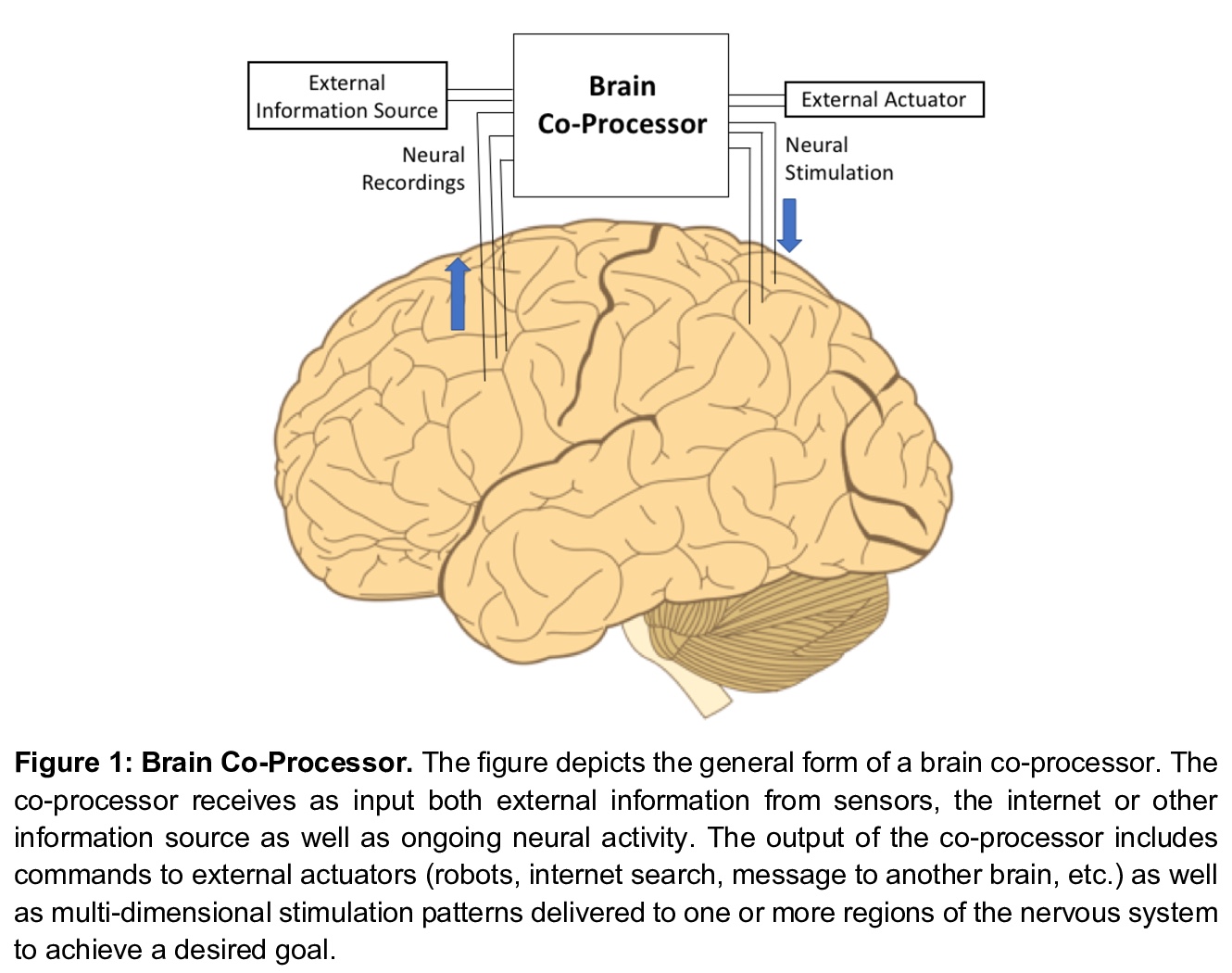
2、** *[AI] EvoCraft: A New Challenge for Open-Endedness
D Grbic, R B Palm, E Najarro, C Glanois, S Risi
[IT University of Copenhagen & Shanghai University]
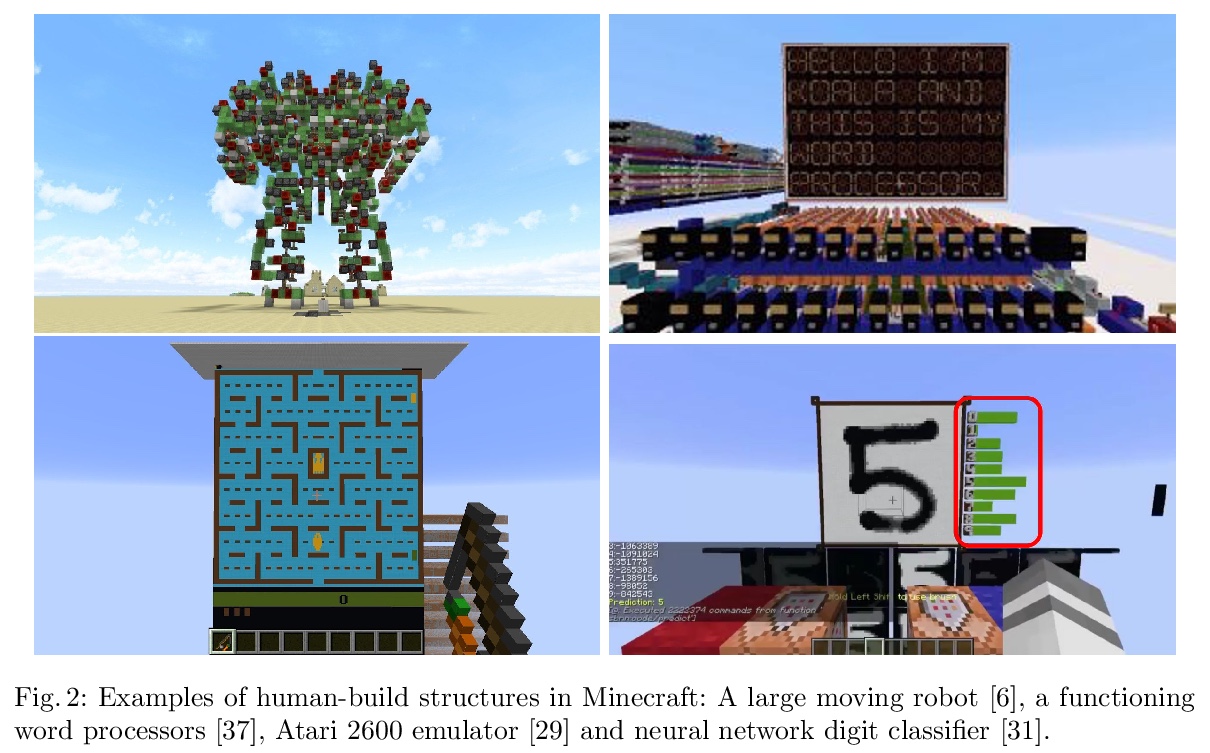
EvoCraft:开放式新挑战。介绍了基于Minecraft的新框架EoCraft,旨在研究开放式算法,引入一个API,提供开源Python接口,用于与Minecraft通信以放置和跟踪块。与之前在Minecraft中专注于学习玩游戏的工作不同,这里提出的宏大挑战,以开放式方式、自动搜索越来越复杂的工件。与其他用于开放性研究的环境相比,Minecraft允许构建几乎任何类型的结构,包括带有电路和机械部件的驱动机器。通过交互和自动进化,呈现了简单Minecraft创作的初步基线结果。虽然当进化的任务是使结构向着特定目标发展时,进化成功了,但当奖励创造一个会移动的简单机器时,它无法找到解决方案。EoCraft为自动搜索方法(如进化)提供了一个具有挑战性的新环境,鼓励用开放式算法探索更复杂的工件。
This paper introduces EvoCraft, a framework for Minecraft designed to study open-ended algorithms. We introduce an API that provides an open-source Python interface for communicating with Minecraft to place and track blocks. In contrast to previous work in Minecraft that focused on learning to play the game, the grand challenge we pose here is to automatically search for increasingly complex artifacts in an open-ended fashion. Compared to other environments used to study open-endedness, Minecraft allows the construction of almost any kind of structure, including actuated machines with circuits and mechanical components. We present initial baseline results in evolving simple Minecraft creations through both interactive and automated evolution. While evolution succeeds when tasked to grow a structure towards a specific target, it is unable to find a solution when rewarded for creating a simple machine that moves. Thus, EvoCraft offers a challenging new environment for automated search methods (such as evolution) to find complex artifacts that we hope will spur the development of more open-ended algorithms. A Python implementation of the EvoCraft framework is available at: > this https URL.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jydqc45jy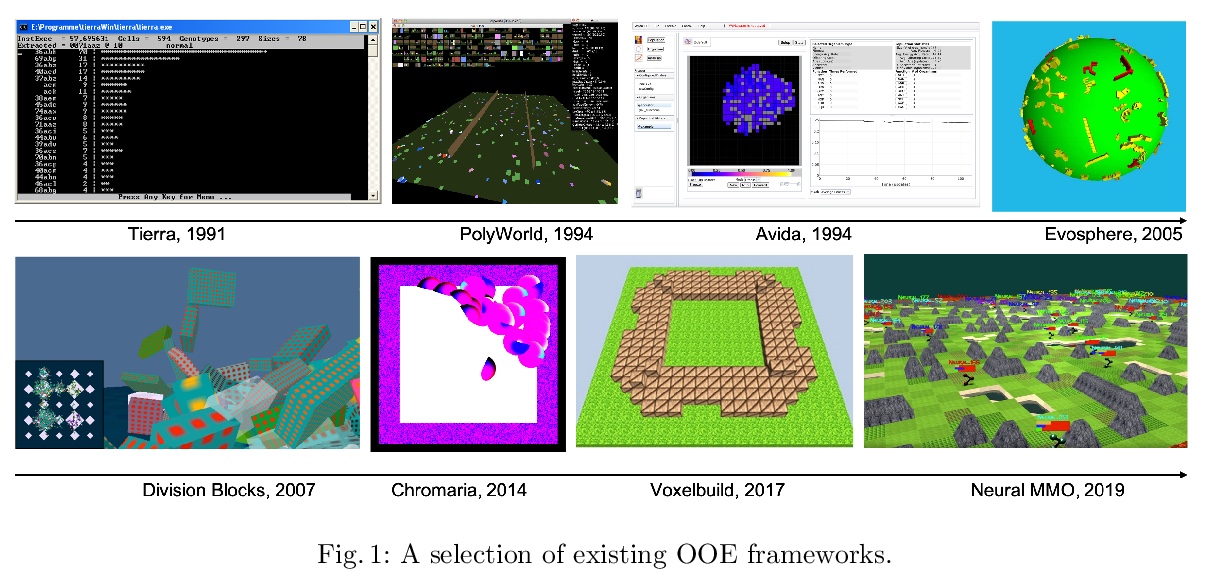


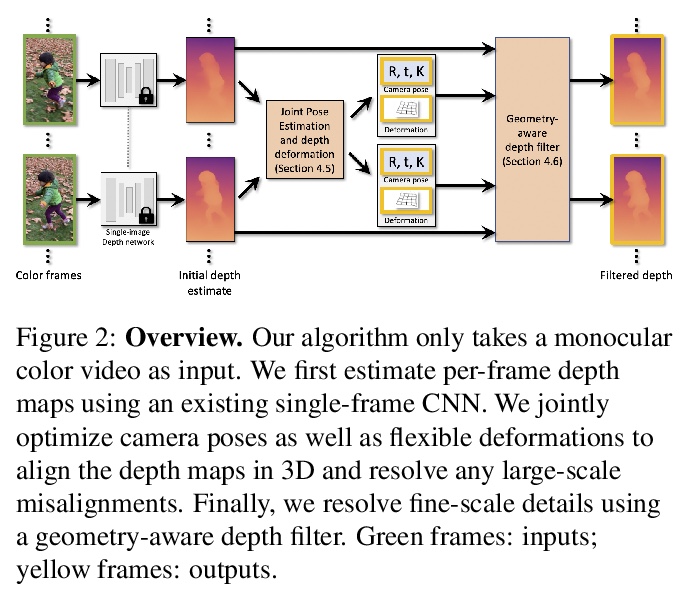
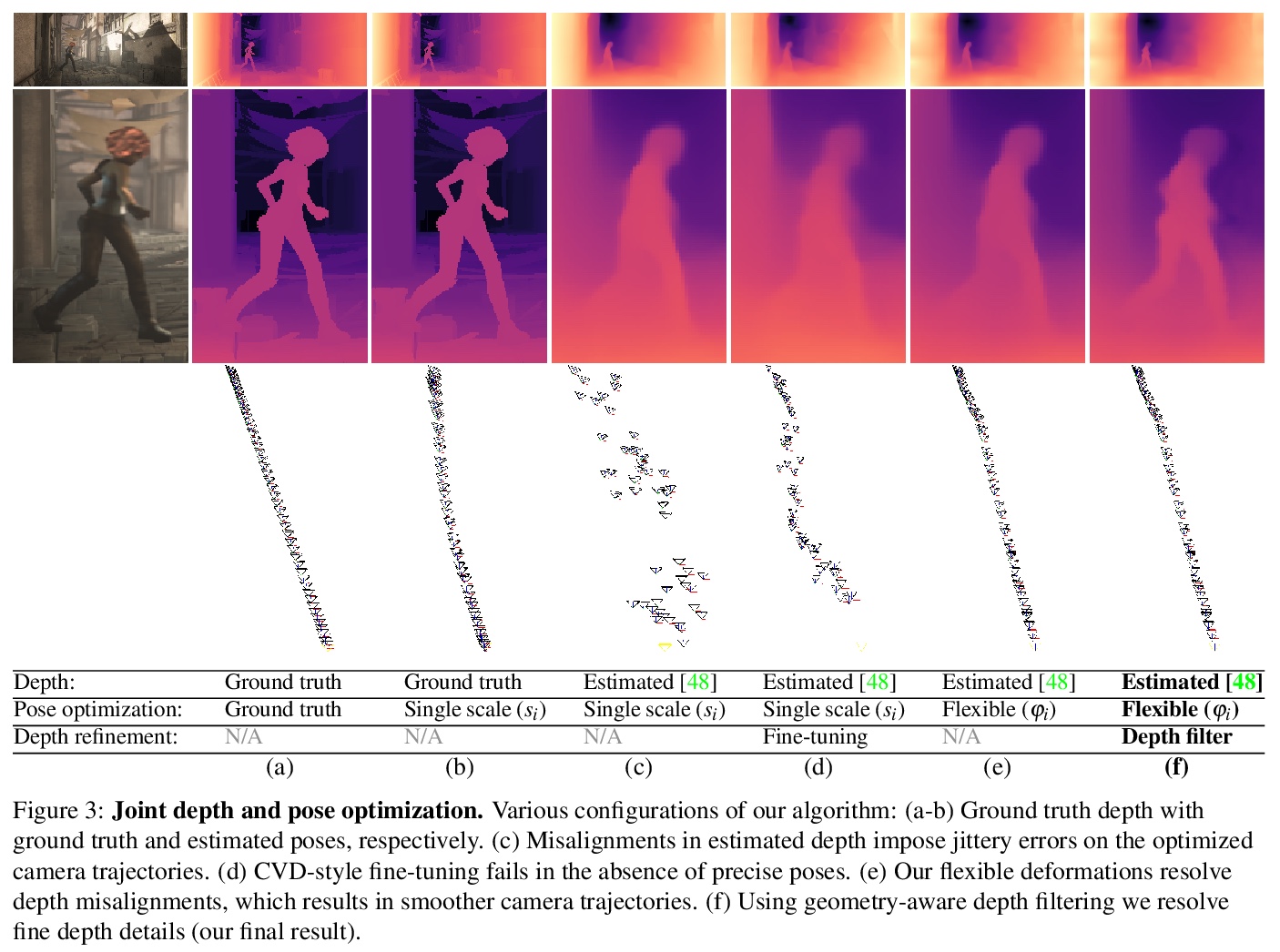
3、** *[CV] Robust Consistent Video Depth Estimation
J Kopf, X Rong, J Huang
[Facebook & Virginia Tech]
鲁棒的一致视频深度估计。提出一种通用优化算法,用于单目视频的一致深度估计,将基于学习的深度先验,与几何优化相结合,为单幅图像深度估计训练卷积神经网络,以估计平滑的摄像机轨迹,以及详细和稳定的深度重建,既不需要输入姿态,也不需要推理时进行微调。与之前方法相比,对手持设备随意拍摄的包含大量噪声、抖动、运动模糊和滚动快门变形的具有挑战性的动态视频进行了鲁棒性重建,在不同测试平台上取得了更好的性能,在质量和数量上都有很好的表现。
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jydx82Lx2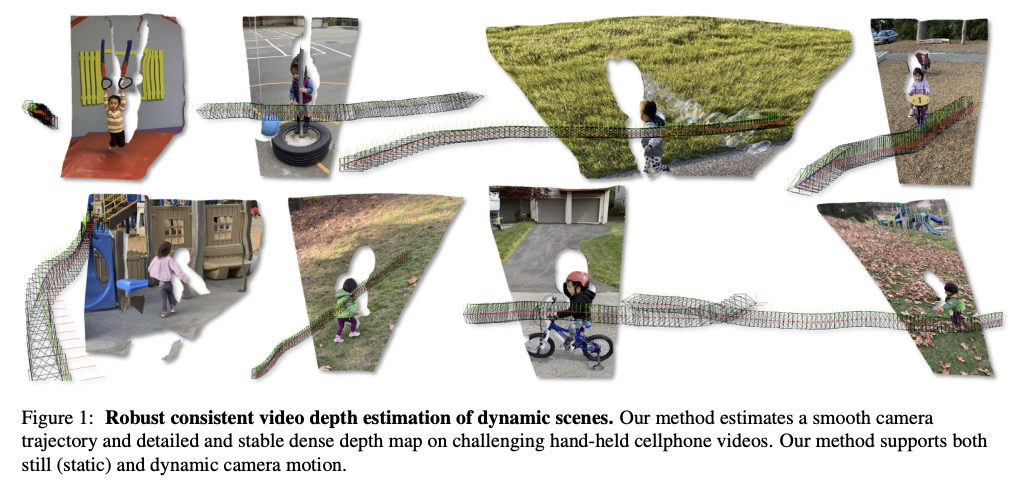
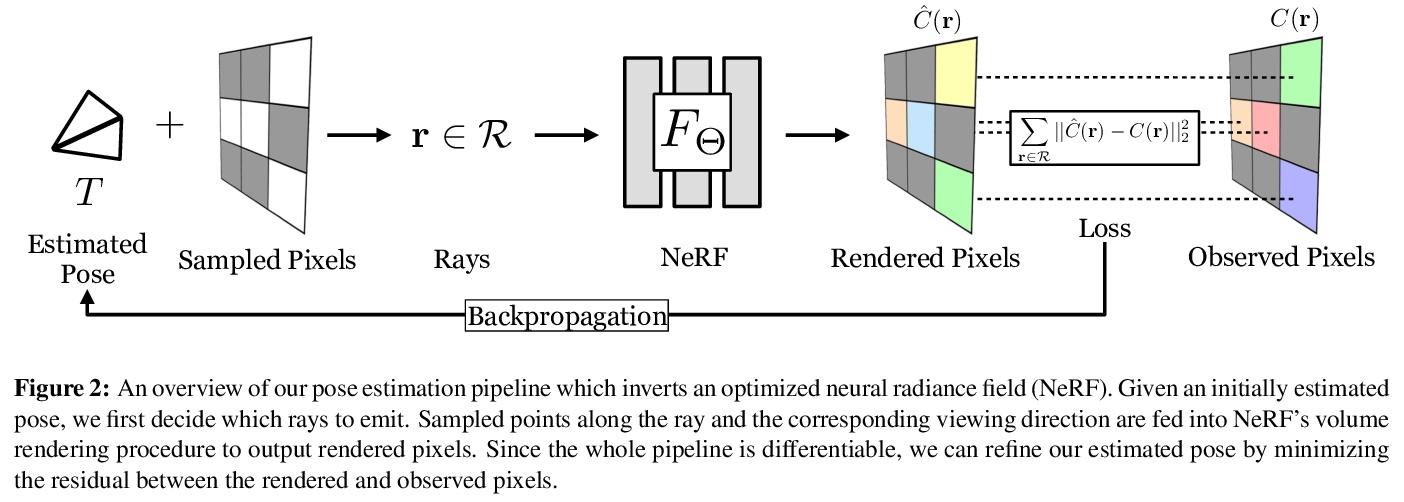
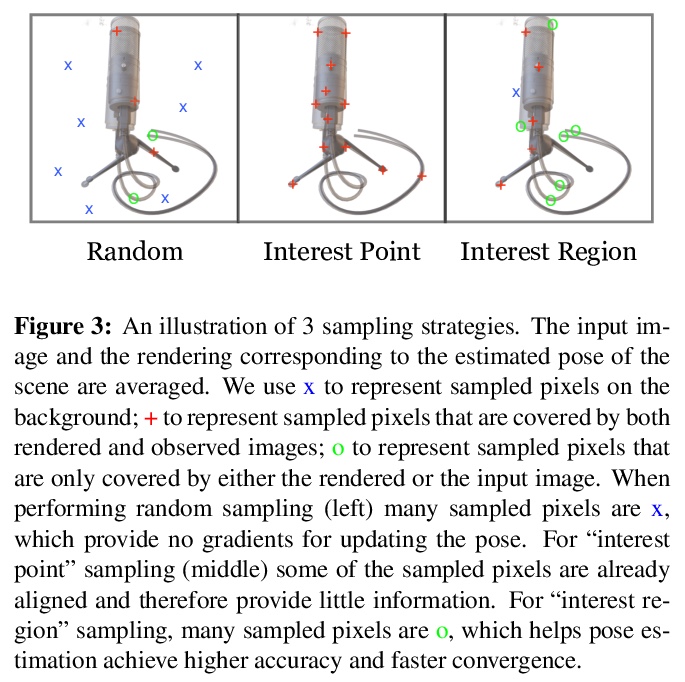
4、**[CV] iNeRF: Inverting Neural Radiance Fields for Pose Estimation
L Yen-Chen, P Florence, J T. Barron, A Rodriguez, P Isola, T Lin
[Google Research & MIT]
逆神经辐射场姿态估计。提出姿势估计框架iNeRF,通过逆向预训练NeRF模型来实现,用梯度优化执行精确的姿态估计。研究了如何将NeRF的合成分析应用于6DoF姿态估计——给定一幅图像,找到摄像机相对于3D模型的平移和旋转。从初始姿势估计开始,用梯度下降法来最小化预训练NeRF渲染的像素和观察图像中的像素间的残差。iNeRF可通过估计新图像的相机姿态,并将这些图像用作NeRF的额外训练数据来改进NeRF。**
We present iNeRF, a framework that performs pose estimation by “inverting” a trained Neural Radiance Field (NeRF). NeRFs have been shown to be remarkably effective for the task of view synthesis - synthesizing photorealistic novel views of real-world scenes or objects. In this work, we investigate whether we can apply analysis-by-synthesis with NeRF for 6DoF pose estimation - given an image, find the translation and rotation of a camera relative to a 3D model. Starting from an initial pose estimate, we use gradient descent to minimize the residual between pixels rendered from an already-trained NeRF and pixels in an observed image. In our experiments, we first study 1) how to sample rays during pose refinement for iNeRF to collect informative gradients and 2) how different batch sizes of rays affect iNeRF on a synthetic dataset. We then show that for complex real-world scenes from the LLFF dataset, iNeRF can improve NeRF by estimating the camera poses of novel images and using these images as additional training data for NeRF. Finally, we show iNeRF can be combined with feature-based pose initialization. The approach outperforms all other RGB-based methods relying on synthetic data on LineMOD.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JydDV8oYo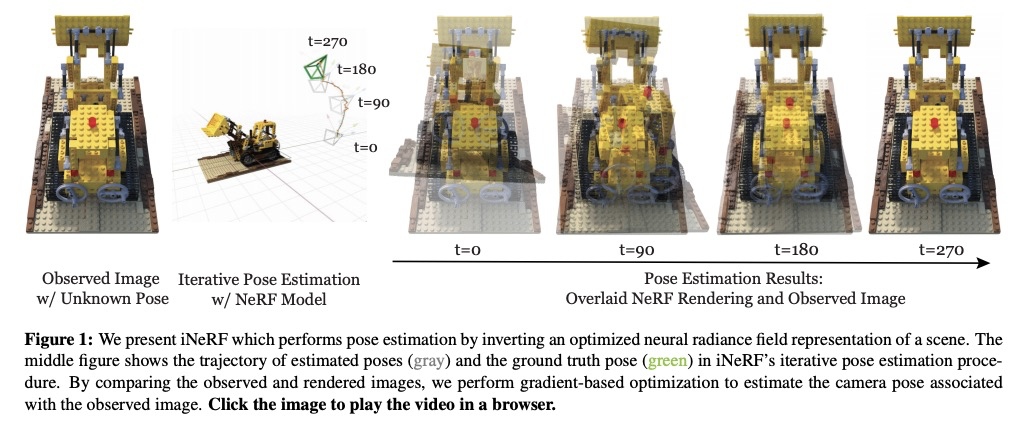
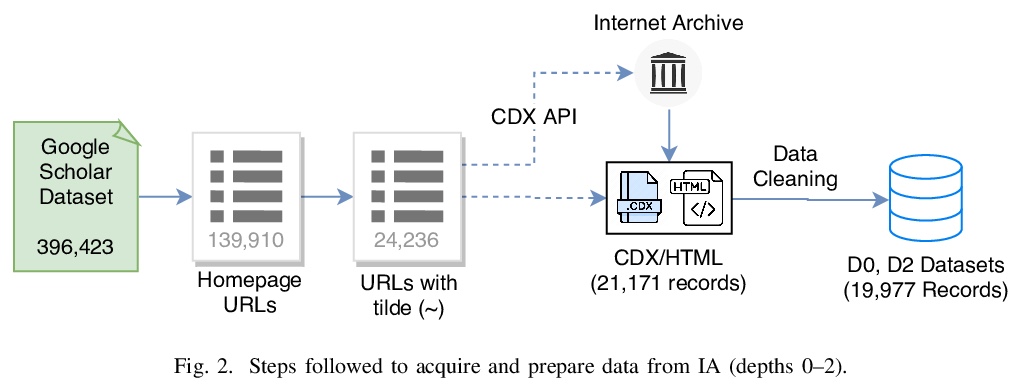
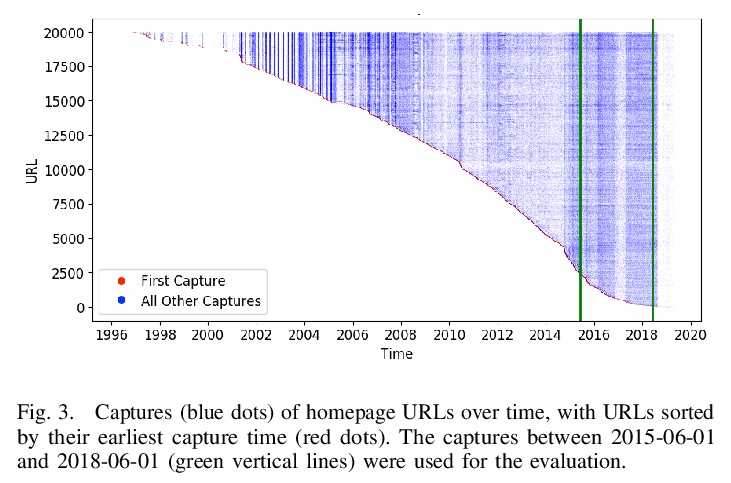
5、** **[IR] Modeling Updates of Scholarly Webpages Using Archived Data
Y Jayawardana, A C. Nwala, G Jayawardena, J Wu, S Jayarathna, M L. Nelson, C. L Giles
[Old Dominion University & Indiana University & Pennsylvania State University]
利用存档数据建立学术网页更新模型。提出一种利用存档拷贝对网页变化动态建模的方法,用谷歌学术作者简介中获得的19,977个种子url,对学术网站进行了初步研究。先从Internet Archive (IA)获取这些网页的存档副本,估计实际更新发生的时间,用最大似然估计它们的平均更新频率λ。实验表明,从存档数据的较短历史数据估计的λ值,可以很好地估计短期内的真实更新频率,与基线模型相比,在资源较少的情况下提供了更好的更新估计。
The vastness of the web imposes a prohibitive cost on building large-scale search engines with limited resources. Crawl frontiers thus need to be optimized to improve the coverage and freshness of crawled content. In this paper, we propose an approach for modeling the dynamics of change in the web using archived copies of webpages. To evaluate its utility, we conduct a preliminary study on the scholarly web using 19,977 seed URLs of authors’ homepages obtained from their Google Scholar profiles. We first obtain archived copies of these webpages from the Internet Archive (IA), and estimate when their actual updates occurred. Next, we apply maximum likelihood to estimate their mean update frequency (> λ) values. Our evaluation shows that > λ values derived from a short history of archived data provide a good estimate for the true update frequency in the short-term, and that our method provides better estimations of updates at a fraction of resources compared to the baseline models. Based on this, we demonstrate the utility of archived data to optimize the crawling strategy of web crawlers, and uncover important challenges that inspire future research directions.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JydJBkNEL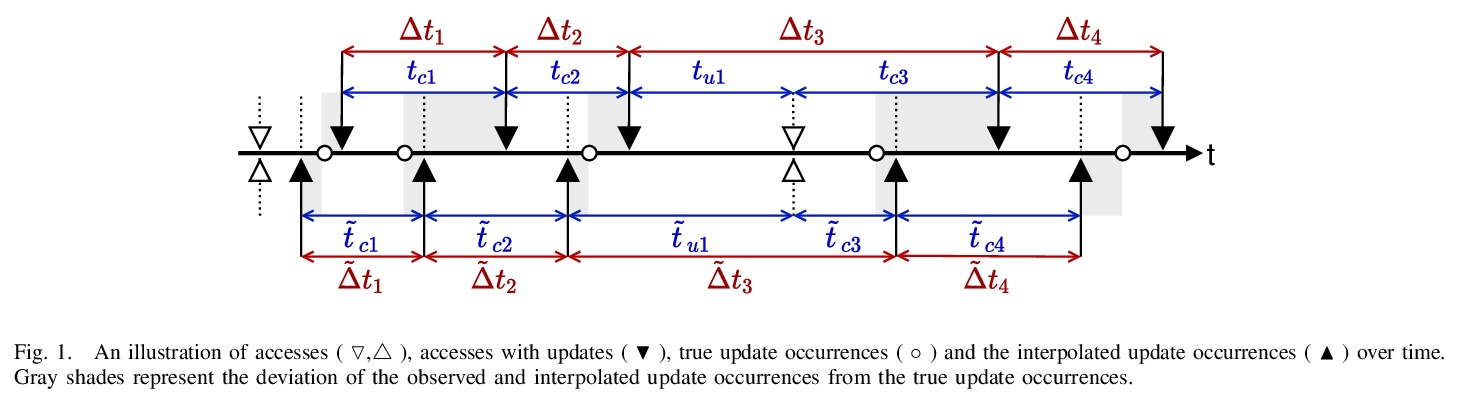
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
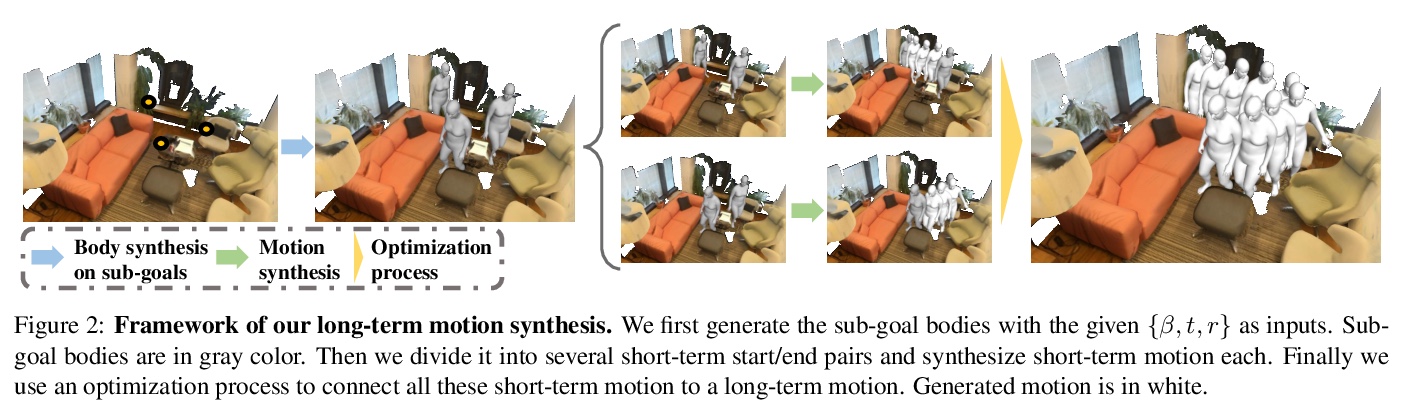
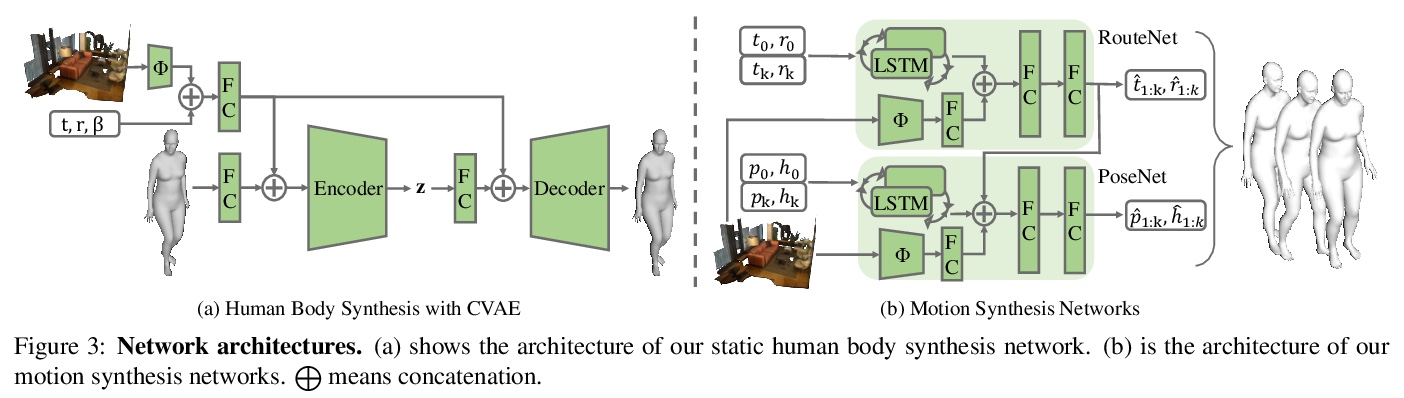
[CV] Synthesizing Long-Term 3D Human Motion and Interaction in 3D Scenes
3D场景中的长期3D人体运动与交互合成
J Wang, H Xu, J Xu, S Liu, X Wang
[UC San Diego & UC Berkeley & Shanghai Jiao Tong University & NVIDIA]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JydPLnWfV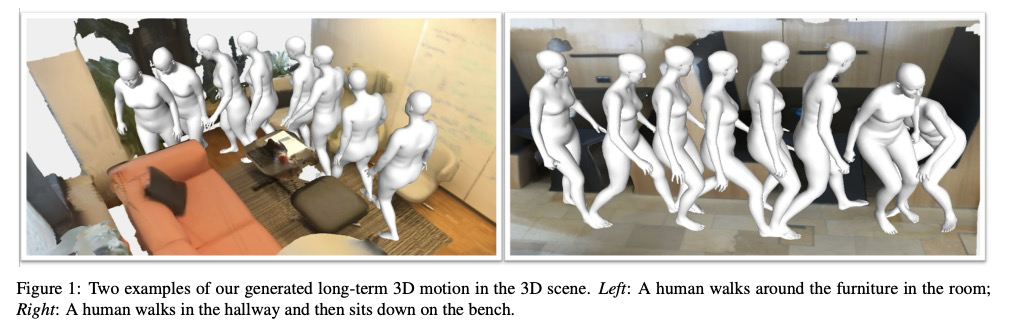
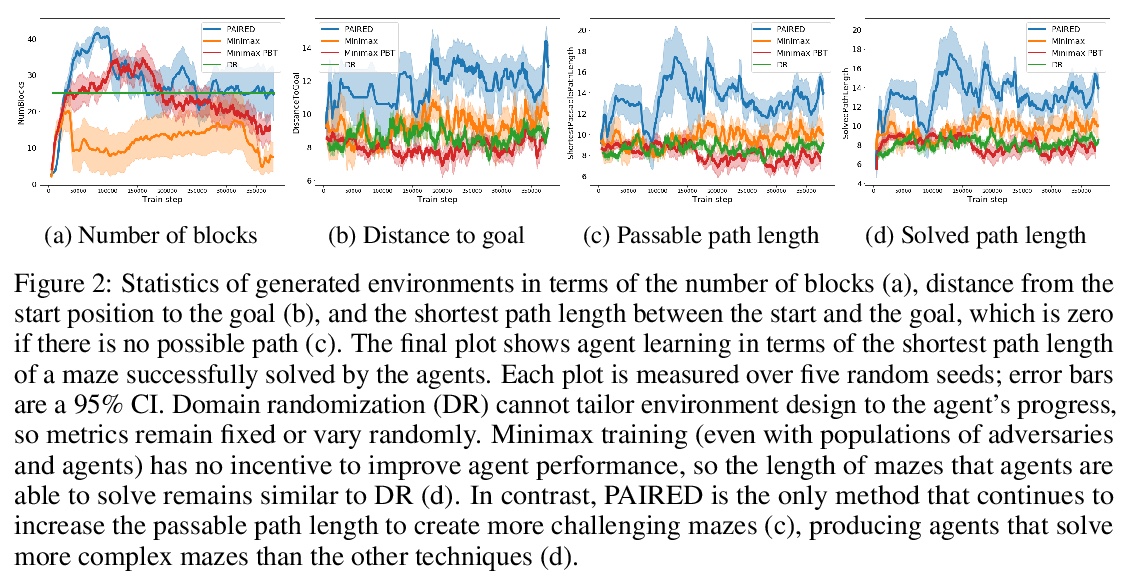
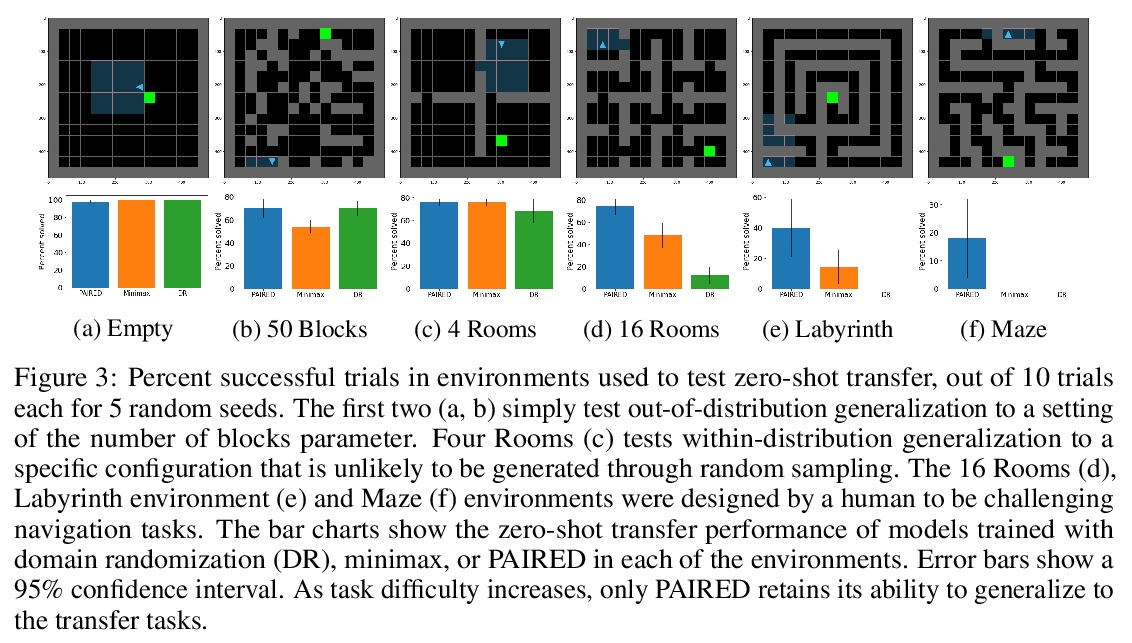
[LG] Emergent Complexity and Zero-shot Transfer via Unsupervised Environment Design
基于无监督环境设计的涌现复杂性与零样本迁移
M Dennis, N Jaques, E Vinitsky, A Bayen, S Russell, A Critch, S Levine
[UC Berkeley & Google Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JydRHolcK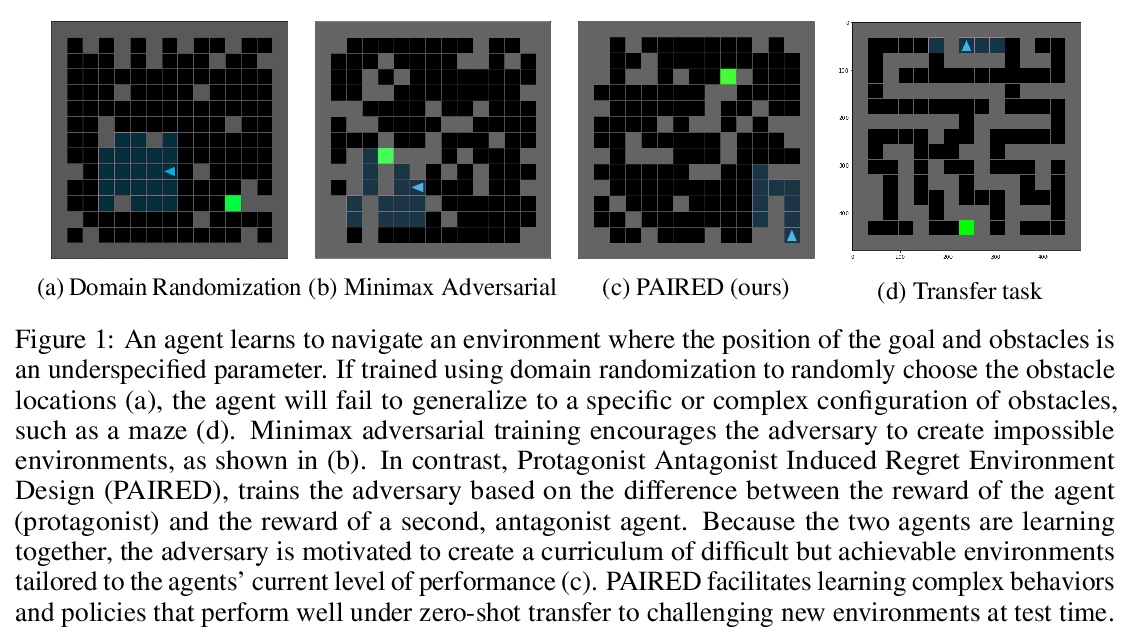
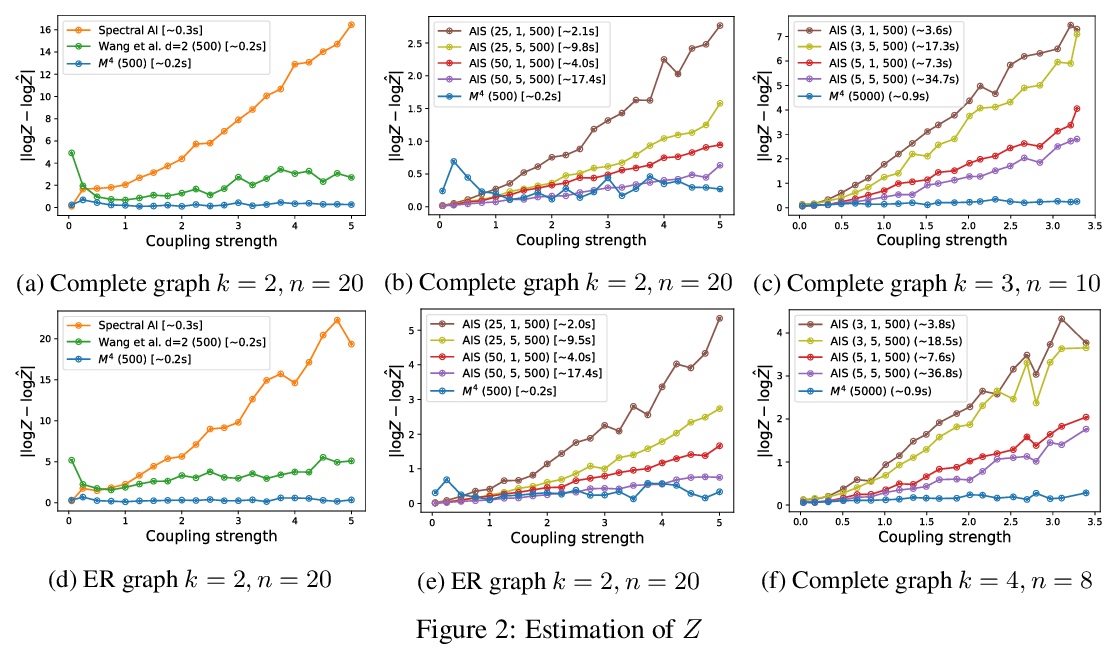
[LG] Efficient semidefinite-programming-based inference for binary and multi-class MRFs
二分和多分类马尔可夫随机场高效半定规划推理
C Pabbaraju, P Wang, J. Z Kolter
[CMU]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JydTdADEp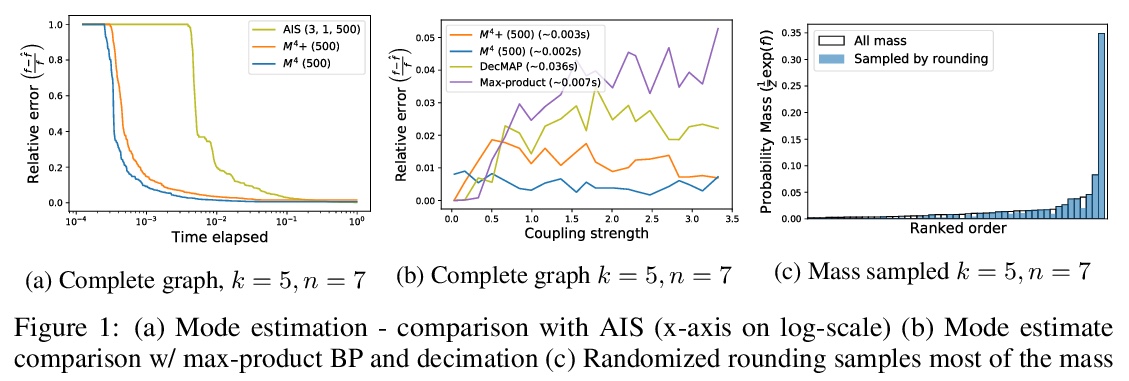
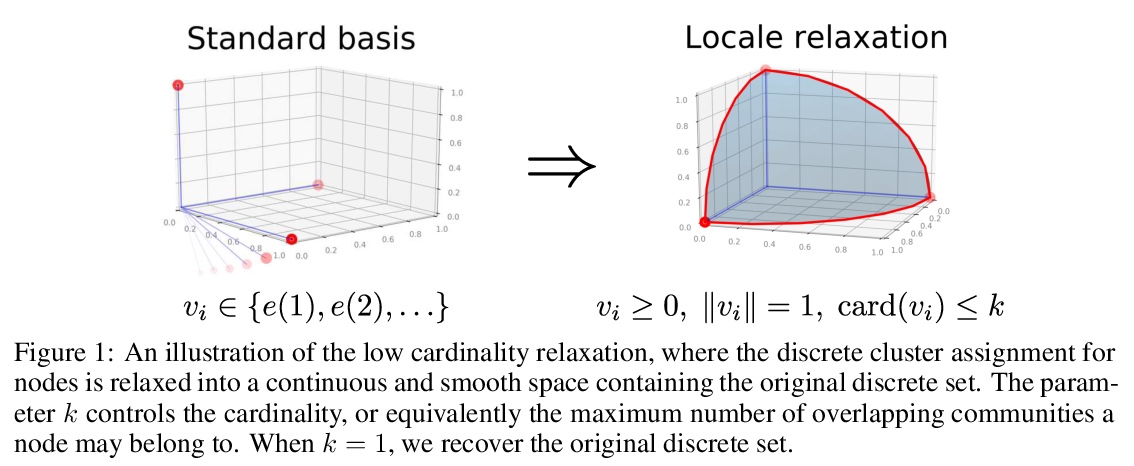
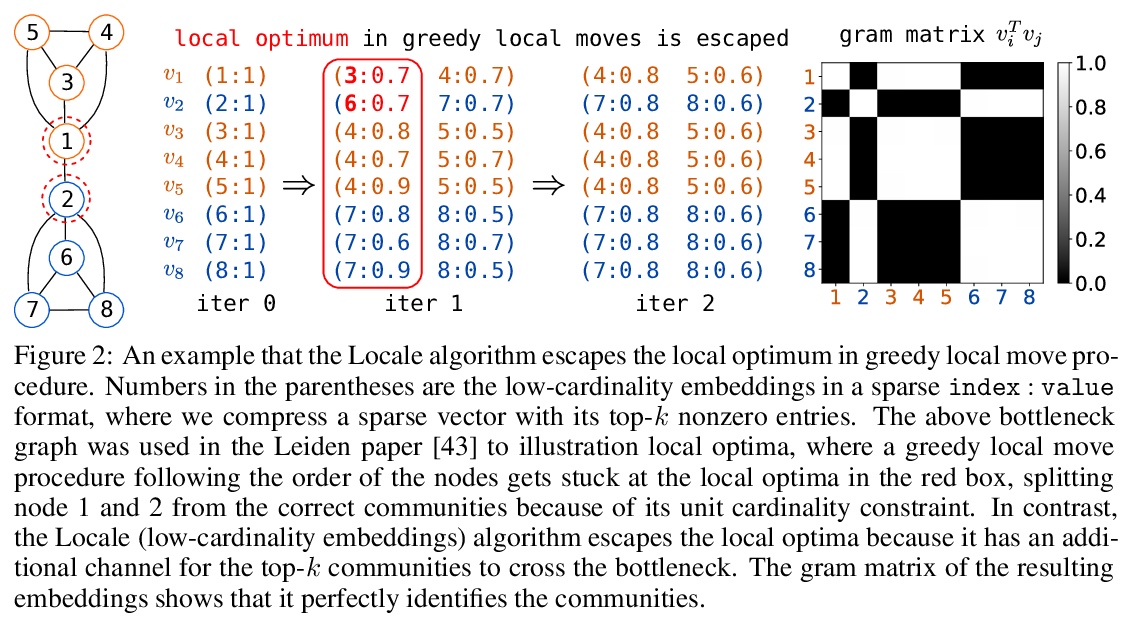
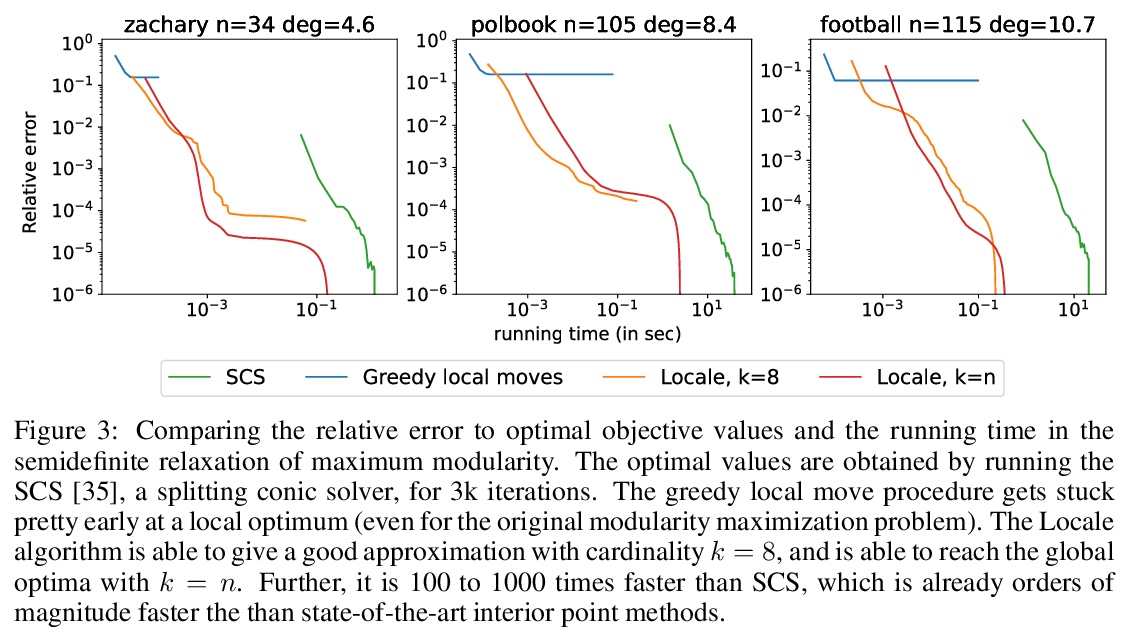
[LG] Community detection using fast low-cardinality semidefinite programming
基于快速低基半定规划的社区检测
P Wang, J. Z Kolter
[CMU]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JydVtq6Ot