- 1、[LG] Geometric Deep Learning: Grids, Groups, Graphs, Geodesics, and Gauges
- 2、[CV] Zero-Shot Detection via Vision and Language Knowledge Distillation
- 3、[CL] Gradient-based Adversarial Attacks against Text Transformers
- 4、[CV] Neural Ray-Tracing: Learning Surfaces and Reflectance for Relighting and View Synthesis
- 5、[LG] An optical neural network using less than 1 photon per multiplication
- [CV] Extreme Rotation Estimation using Dense Correlation Volumes
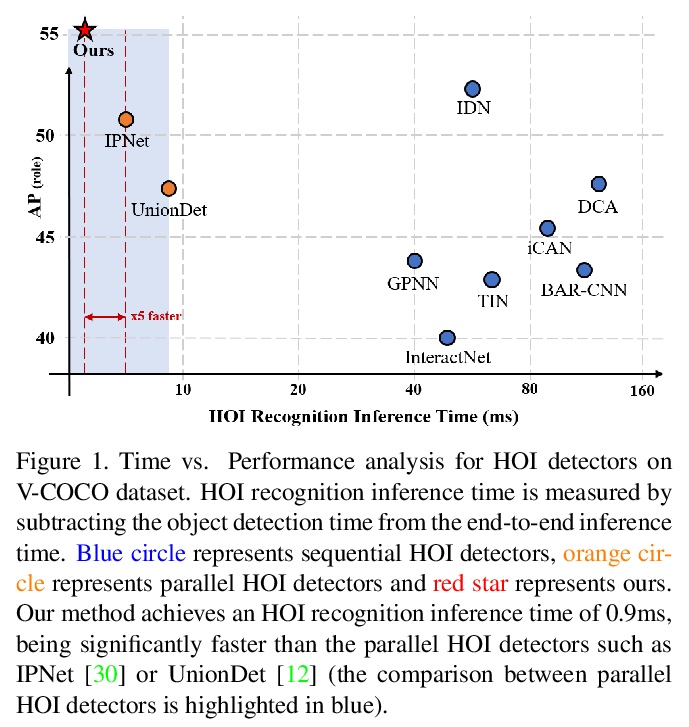
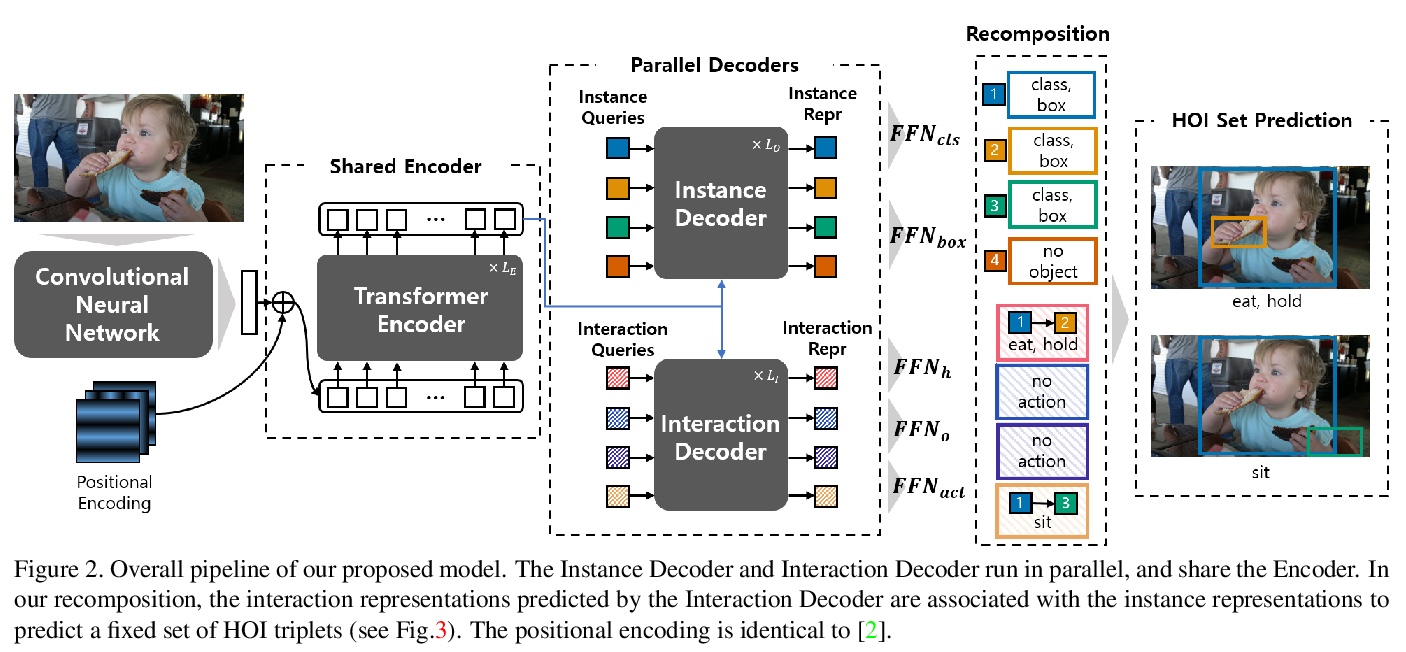
- [CV] HOTR: End-to-End Human-Object Interaction Detection with Transformers
- [CV] Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation with Self-Supervised Depth Estimation
- [CV] PAFNet: An Efficient Anchor-Free Object Detector Guidance
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[LG] Geometric Deep Learning: Grids, Groups, Graphs, Geodesics, and Gauges
M M. Bronstein, J Bruna, T Cohen, P Veličković
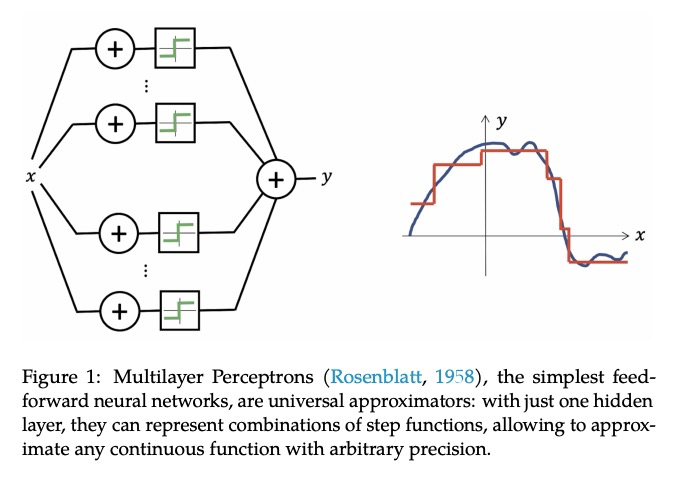
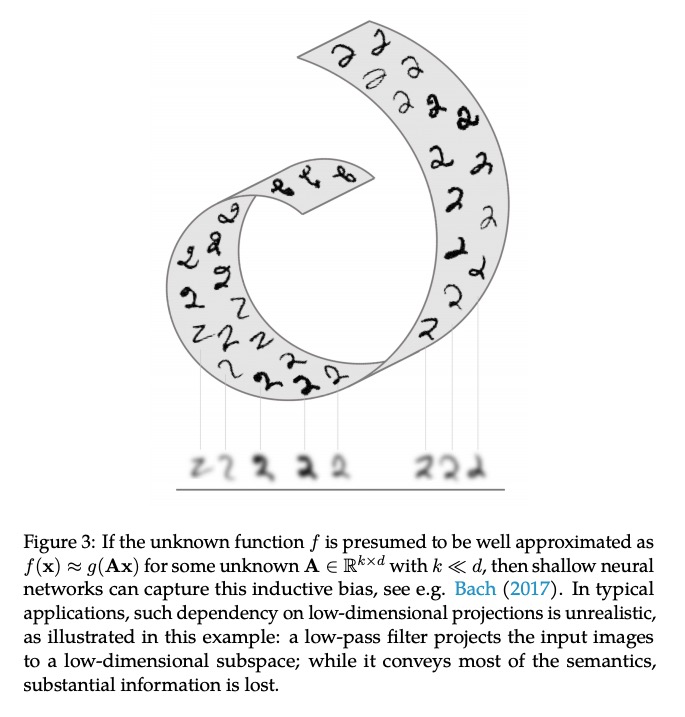
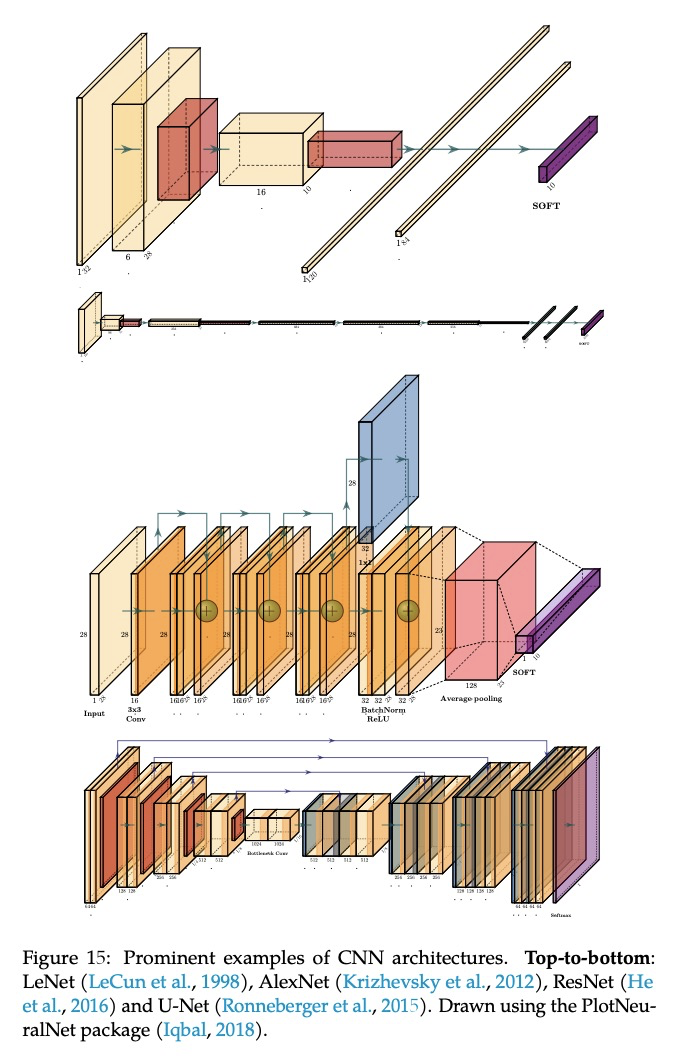
几何深度学习——网格、群、图、测地线和测量仪。过去十年,我们见证了数据科学和机器学习的实验性革命,深度学习方法就是其中的代表,许多以前被认为是遥不可及的高维学习任务——如计算机视觉、下围棋或蛋白质折叠——在适当的计算规模下,在实践中变为可行。深度学习的本质,建立在两个简单的算法原则之上:第一,表示或特征学习的概念,即自适应的,通常是分层的特征,为每个任务捕获适当的规则性概念;第二,通过局部梯度下降类的方法进行学习,通常以反向传播的方式实现。虽然在高维度上学习通用函数,是一个被诅咒的估计问题,但大多数感兴趣的任务都是不通用的,具有从物理世界的底层低维度和结构中产生的基本预定义的规律性。本文关注的,是通过统一的几何原理,来揭示这些规律性,这些原理可以在广泛的场景中得到应用。这种”几何统一”的努力,有两个目标:一方面,提供一个共同的数学框架来研究最成功的神经网络架构,如CNNs、RNNs、GNNs和Transformer。另一方面,提供一个建设性的程序,将先前的物理知识纳入神经架构,并为建立未来的架构提供原则性的方法。
The last decade has witnessed an experimental revolution in data science and machine learning, epitomised by deep learning methods. Indeed, many high-dimensional learning tasks previously thought to be beyond reach — such as computer vision, playing Go, or protein folding — are in fact feasible with appropriate computational scale. Remarkably, the essence of deep learning is built from two simple algorithmic principles: first, the notion of representation or feature learning, whereby adapted, often hierarchical, features capture the appropriate notion of regularity for each task, and second, learning by local gradient-descent type methods, typically implemented as backpropagation.While learning generic functions in high dimensions is a cursed estimation problem, most tasks of interest are not generic, and come with essential pre-defined regularities arising from the underlying low-dimensionality and structure of the physical world. This text is concerned with exposing these regularities through unified geometric principles that can be applied throughout a wide spectrum of applications.Such a ‘geometric unification’ endeavour, in the spirit of Felix Klein’s Erlangen Program, serves a dual purpose: on one hand, it provides a common mathematical framework to study the most successful neural network architectures, such as CNNs, RNNs, GNNs, and Transformers. On the other hand, it gives a constructive procedure to incorporate prior physical knowledge into neural architectures and provide principled way to build future architectures yet to be invented.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KdeJToEOJ

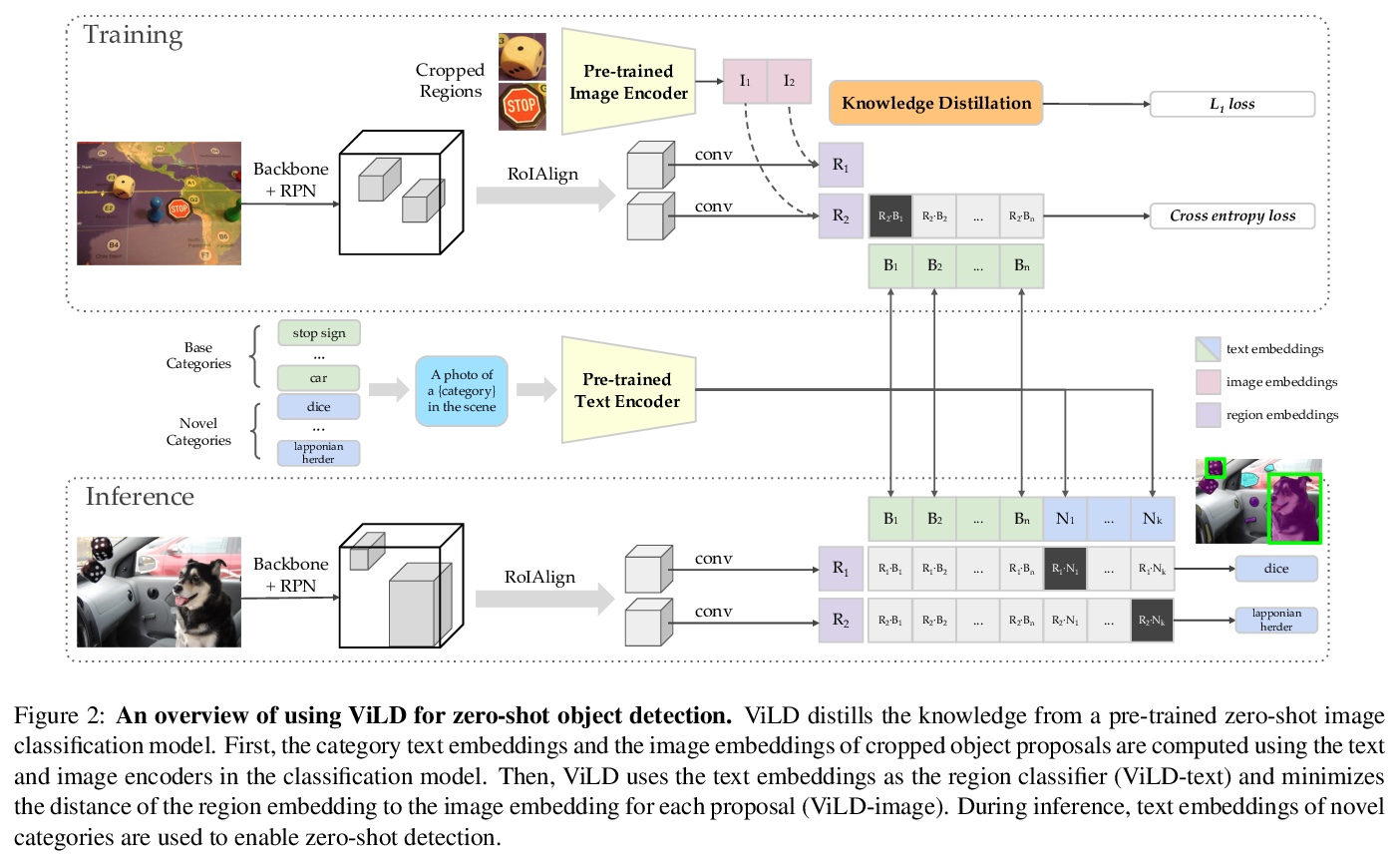
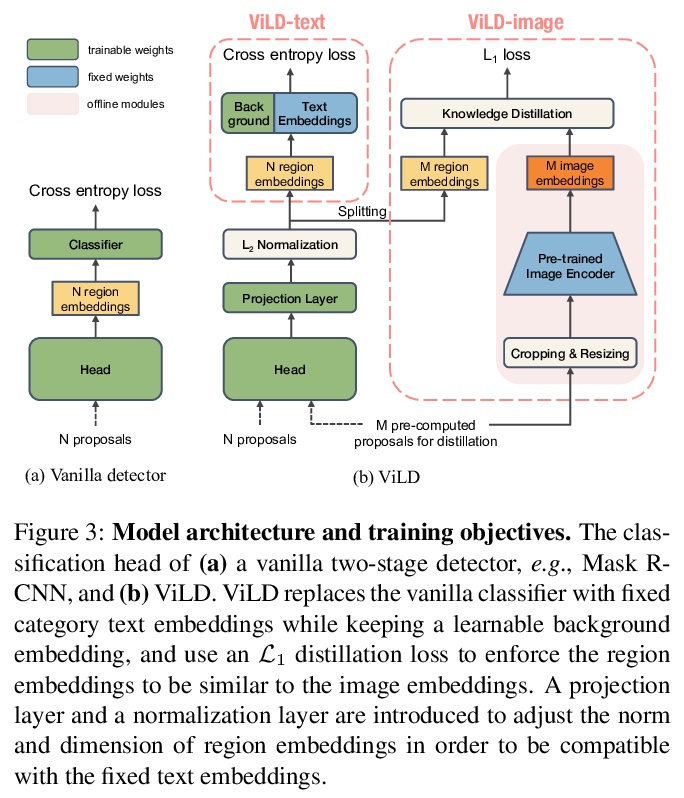
2、[CV] Zero-Shot Detection via Vision and Language Knowledge Distillation
X Gu, T Lin, W Kuo, Y Cui
[Google Research]
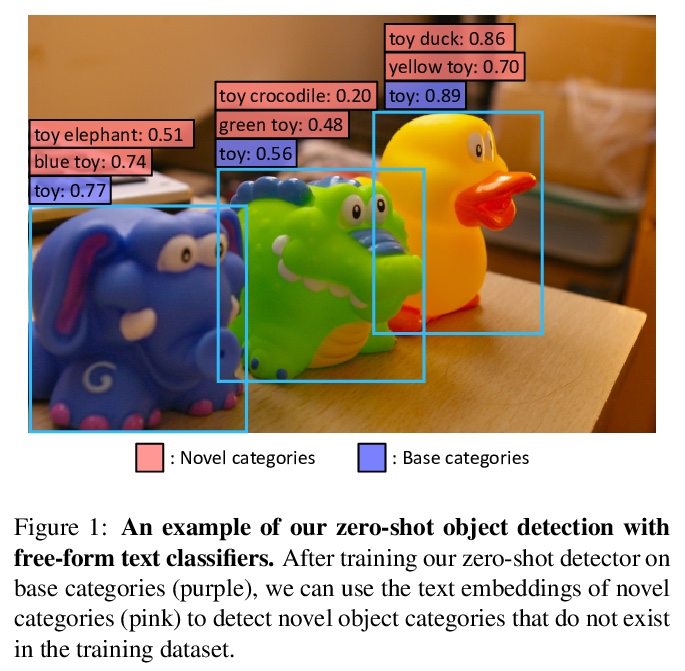
基于视觉和语言知识蒸馏的零样本检测。通过训练对齐的图像和文本编码器,零样本图像分类已经取得了可喜的进展。本工作的目标是推进零样本目标检测,其目的是检测没有边框或掩模标注的新目标。提出了ViLD,一种通过视觉和语言知识蒸馏的训练方法。将预训练的零样本图像分类模型(如CLIP)的知识,蒸馏到两阶段检测器(如Mask R-CNN),将检测器中的区块嵌入与预训练模型推断出的文本和图像嵌入对齐。用文本嵌入作为检测分类器,通过向预训练的文本编码器输入类别名获得。最小化区块嵌入和图像嵌入之间的距离,该距离是通过将候选目标区块输入预训练图像编码器获得的。在推理过程中,将新类别的文本嵌入到检测分类器中,进行零样本检测。以LVIS数据集为基准,将所有罕见类别作为新类别。ViLD通过Mask R-CNN(ResNet-50 FPN)获得了16.1的掩模APr,比有监督的对应模型高出3.8。该模型可以直接迁移到其他数据集,在PASCAL VOC、COCO和Objects365上分别得到了72.2 AP50、36.6 AP和11.8 AP。
Zero-shot image classification has made promising progress by training the aligned image and text encoders. The goal of this work is to advance zero-shot object detection, which aims to detect novel objects without bounding box nor mask annotations. We propose ViLD, a training method via Vision and Language knowledge Distillation. We distill the knowledge from a pre-trained zero-shot image classification model (e.g., CLIP) into a two-stage detector (e.g., Mask R-CNN). Our method aligns the region embeddings in the detector to the text and image embeddings inferred by the pre-trained model. We use the text embeddings as the detection classifier, obtained by feeding category names into the pre-trained text encoder. We then minimize the distance between the region embeddings and image embeddings, obtained by feeding region proposals into the pre-trained image encoder. During inference, we include text embeddings of novel categories into the detection classifier for zero-shot detection. We benchmark the performance on LVIS dataset by holding out all rare categories as novel categories. ViLD obtains 16.1 mask APrwith a Mask R-CNN (ResNet-50 FPN) for zero-shot detection, outperforming the supervised counterpart by 3.8. The model can directly transfer to other datasets, achieving 72.2 AP50, 36.6 AP and 11.8 AP on PASCAL VOC, COCO and Objects365, respectively.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KdeOgC2QB

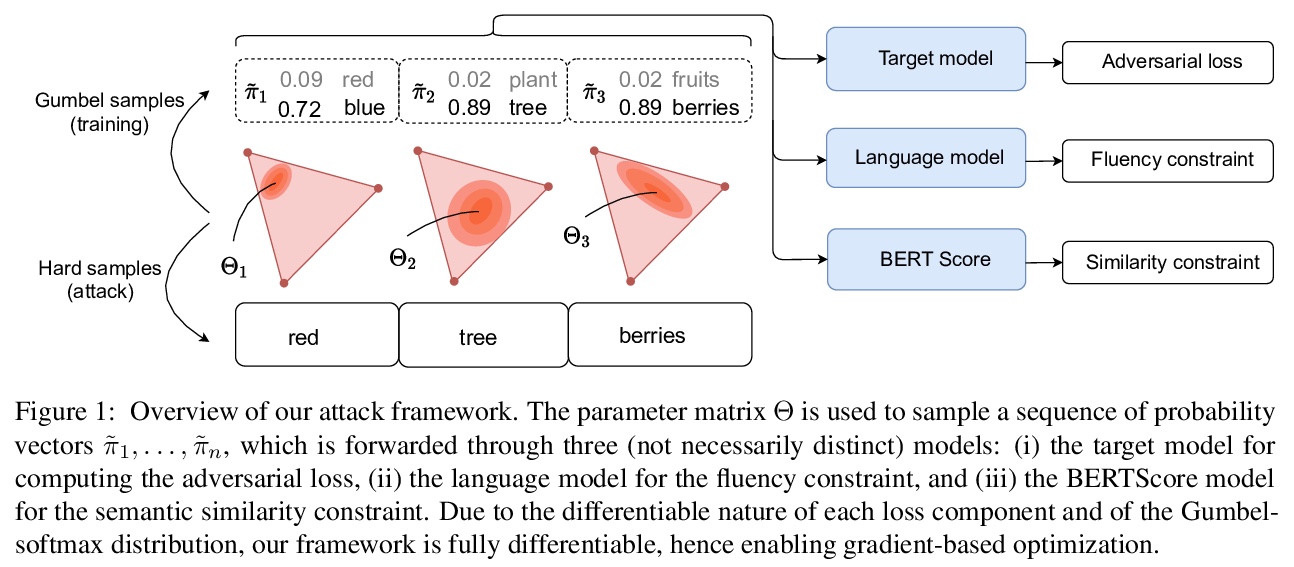
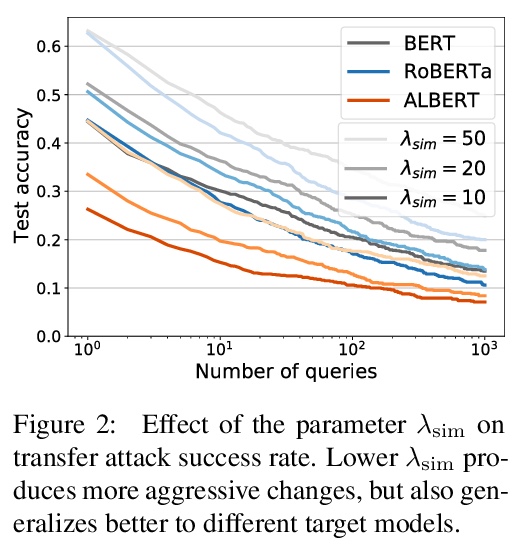
3、[CL] Gradient-based Adversarial Attacks against Text Transformers
C Guo, A Sablayrolles, H Jégou, D Kiela
[Facebook AI Research]
针对文本Transformer的基于梯度对抗性攻击。提出了通用的基于梯度的攻击Transformer模型的GBDA框架,不是搜索单一的对抗性样本,而是搜索由连续值矩阵参数化的对抗性样本的分布,从而实现基于梯度的优化。通过将可微的流畅性和语义相似性约束纳入对抗性损失,该白盒攻击产生了更自然的对抗性文本,同时创造了新的最先进的成功率,在各种自然语言任务中达到了最先进的攻击性能。此外,还展示了一个强大的黑盒迁移攻击,通过从对抗性分布中采样,达到或超过现有方法,只需要硬标签的输出。
We propose the first general-purpose gradient-based attack against transformer models. Instead of searching for a single adversarial example, we search for a distribution of adversarial examples parameterized by a continuous-valued matrix, hence enabling gradient-based optimization. We empirically demonstrate that our white-box attack attains state-of-the-art attack performance on a variety of natural language tasks. Furthermore, we show that a powerful black-box transfer attack, enabled by sampling from the adversarial distribution, matches or exceeds existing methods, while only requiring hard-label outputs.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KdeRN1xz4
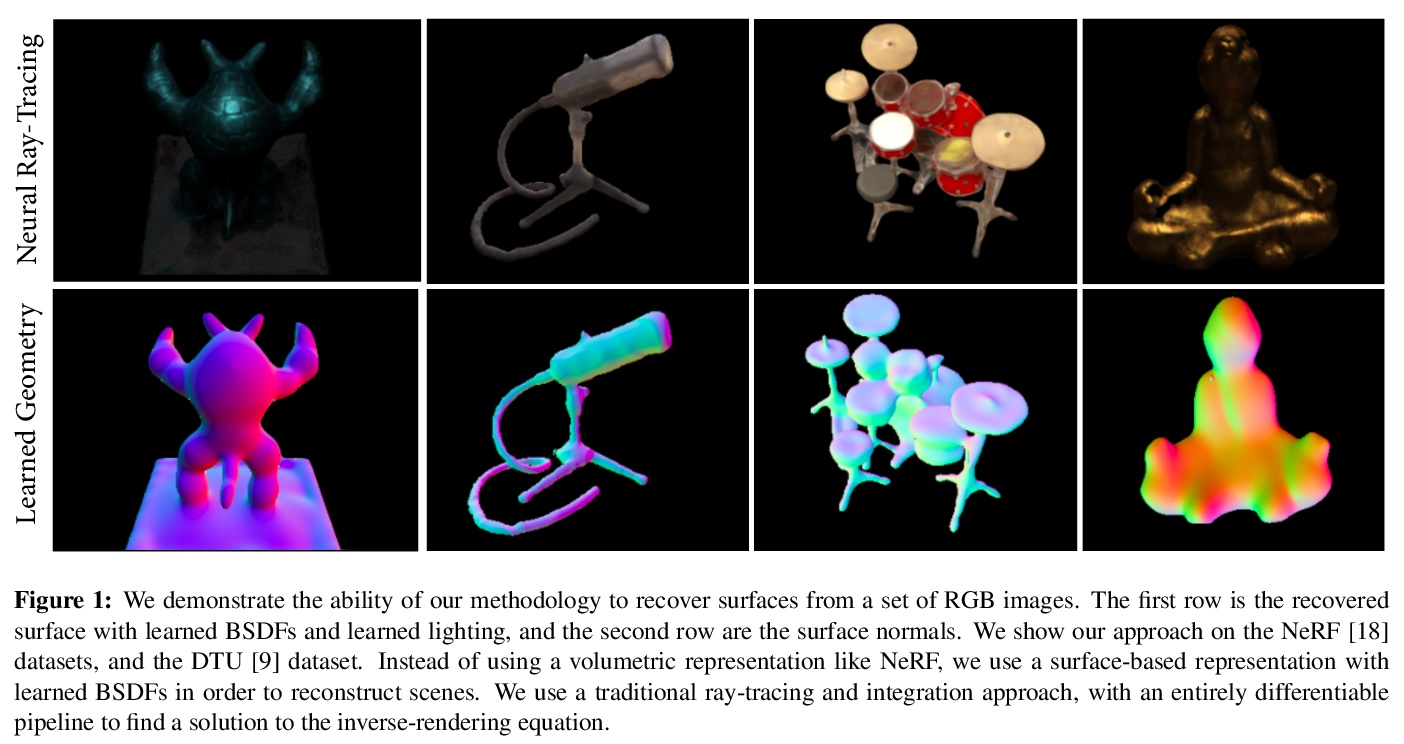
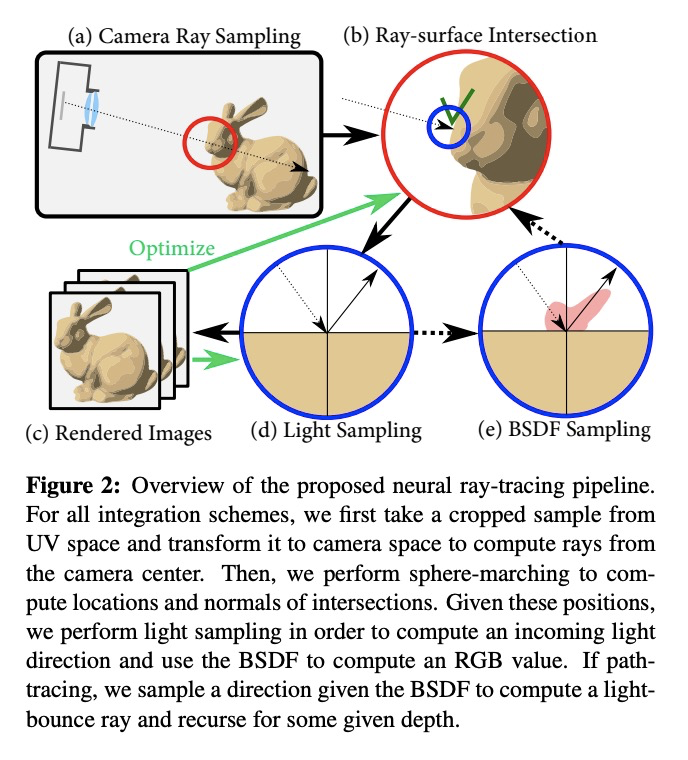
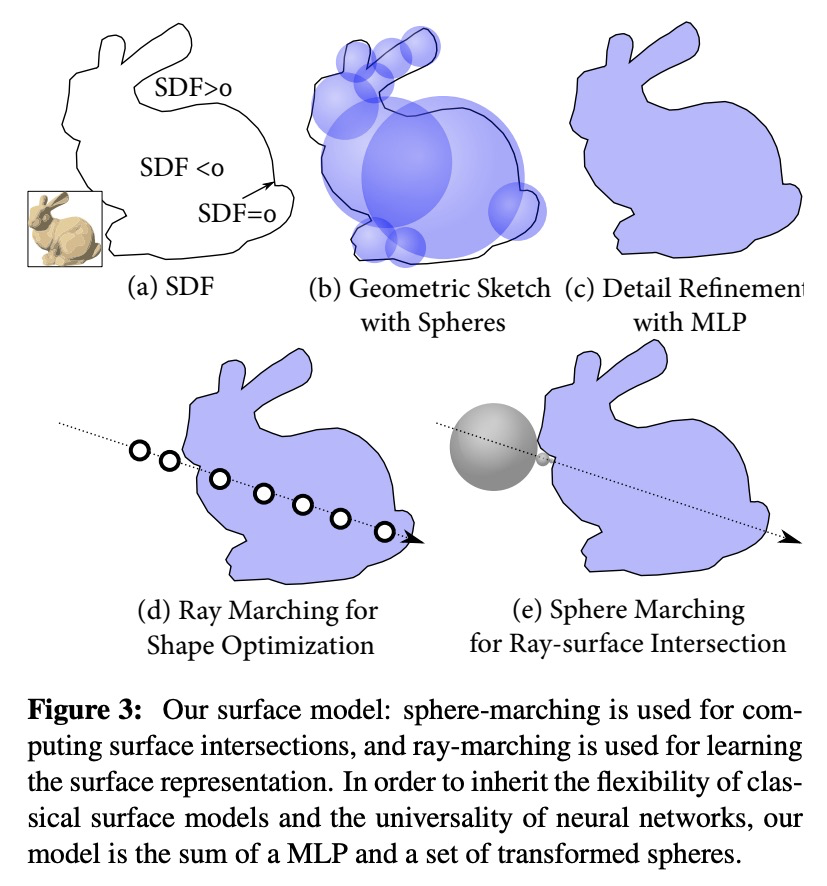
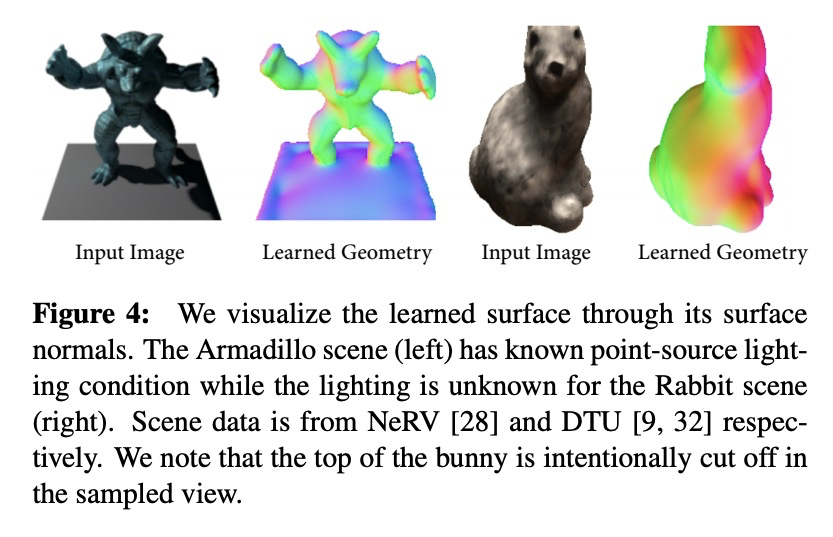
4、[CV] Neural Ray-Tracing: Learning Surfaces and Reflectance for Relighting and View Synthesis
J Knodt, S Baek, F Heide
[Princeton University & Algolux]
神经光线追踪:面向重打光和视图合成的表面和反射率学习。最近的神经渲染方法,通过用神经网络预测体密度和颜色来实现精确的视图插值。尽管这种体表示可以在静态和动态场景中进行监督,但现有的方法隐含地将完整的场景光传输整合到特定场景的单一神经网络中,包括表面建模、双向散射分布函数和间接照明效果。与传统的渲染管道相比,无法进行表面反射率、照度或合成场景中的其他物体的编辑。本文明确地对场景表面之间的光传输进行建模,依靠传统的集成方案和渲染方程来重建场景。所提出的方法允许在未知的光照条件下进行反射率恢复,允许经典的光传输,如pathtracing。通过学习传统渲染方法中建立的表面表征的分解传输,该方法自然有利于编辑形状、反射率、照明和场景构成。在已知光照条件下的重打光表现优于现有的神经渲染方法,并为重打光和编辑的场景产生真实的重建。验证了所提出的用于场景编辑、重打光和反射率估计的方法,该方法是在现有数据集上从合成和捕获的视图中学习的。
Recent neural rendering methods have demonstrated accurate view interpolation by predicting volumetric density and color with a neural network. Although such volumetric representations can be supervised on static and dynamic scenes, existing methods implicitly bake the complete scene light transport into a single neural network for a given scene, including surface modeling, bidirectional scattering distribution functions, and indirect lighting effects. In contrast to traditional rendering pipelines, this prohibits editing surface reflectance, illumination, or composing other objects in the scene. In this work, we explicitly model the light transport between scene surfaces and we rely on traditional integration schemes and the rendering equation to reconstruct a scene. The proposed method allows reflectance recovery with unknown light conditions and classic light transports such as pathtracing. By learning decomposed transport with surface representations established in conventional rendering methods, the method naturally facilitates editing shape, reflectance, lighting and scene composition. The method outperforms existing neural rendering methods for relighting under known lighting conditions, and produces realistic reconstructions for relit and edited scenes. We validate the proposed approach for scene editing, relighting and reflectance estimation learned from synthetic and captured views on existing datasets.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KdeVvtfUC
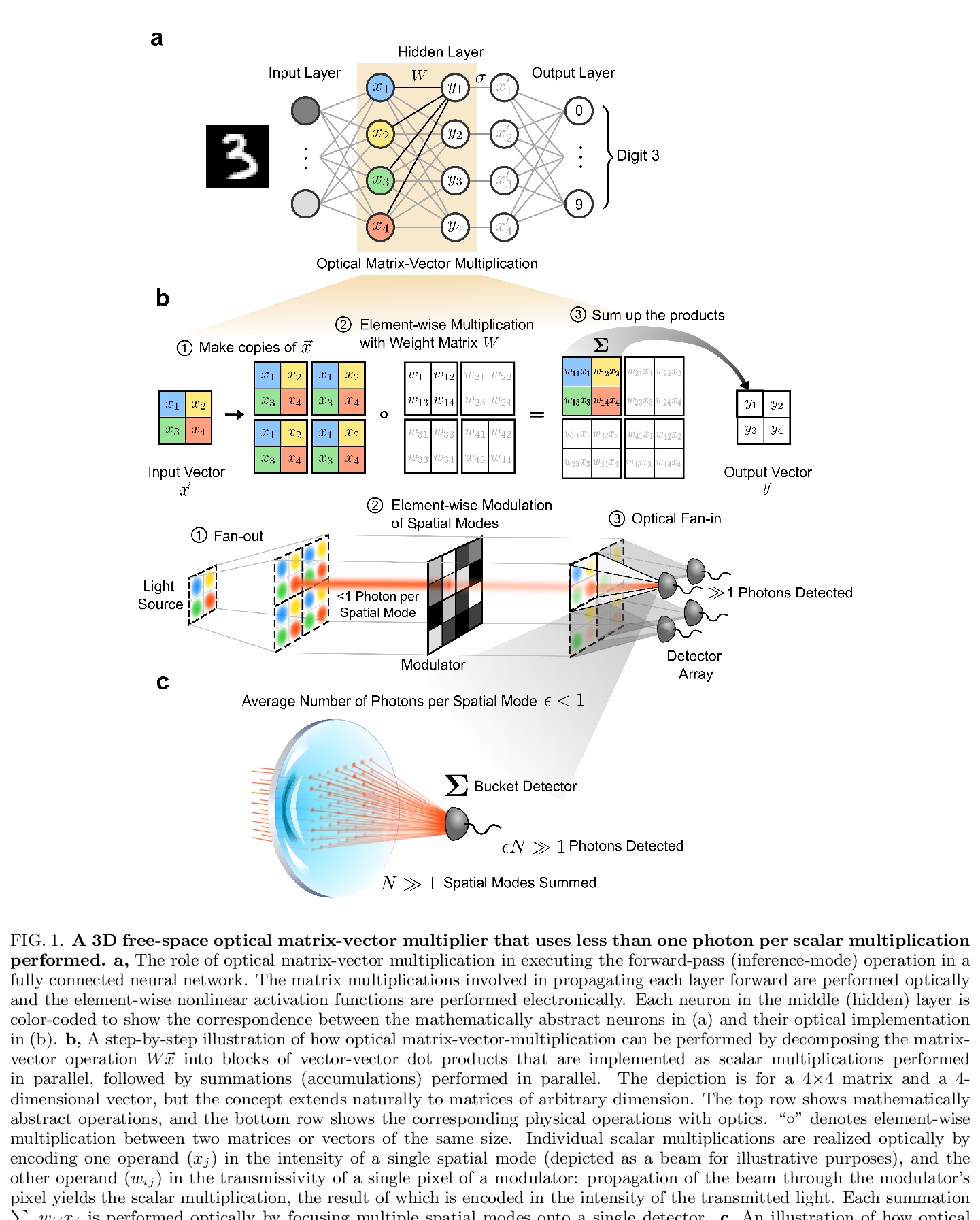
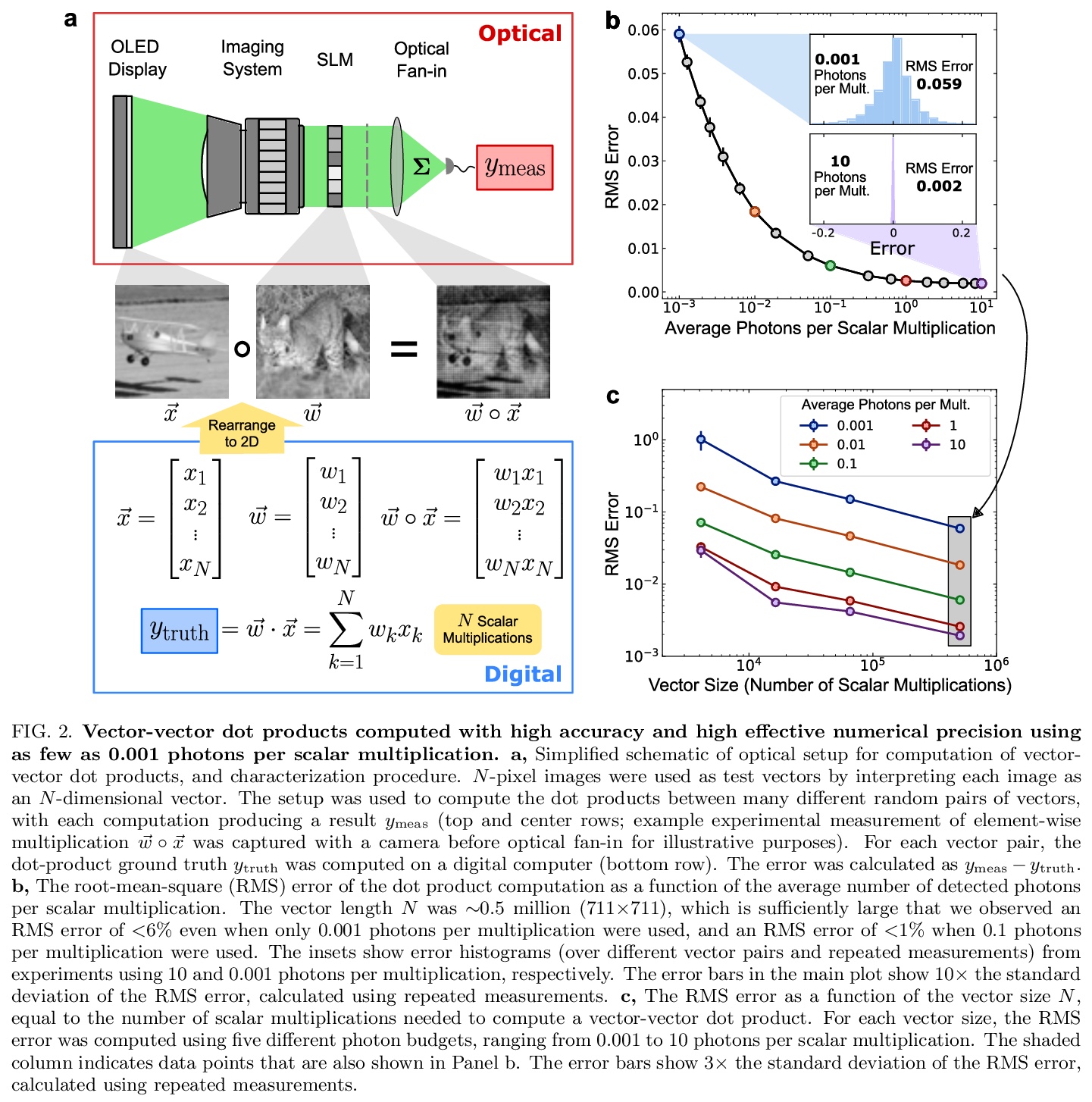
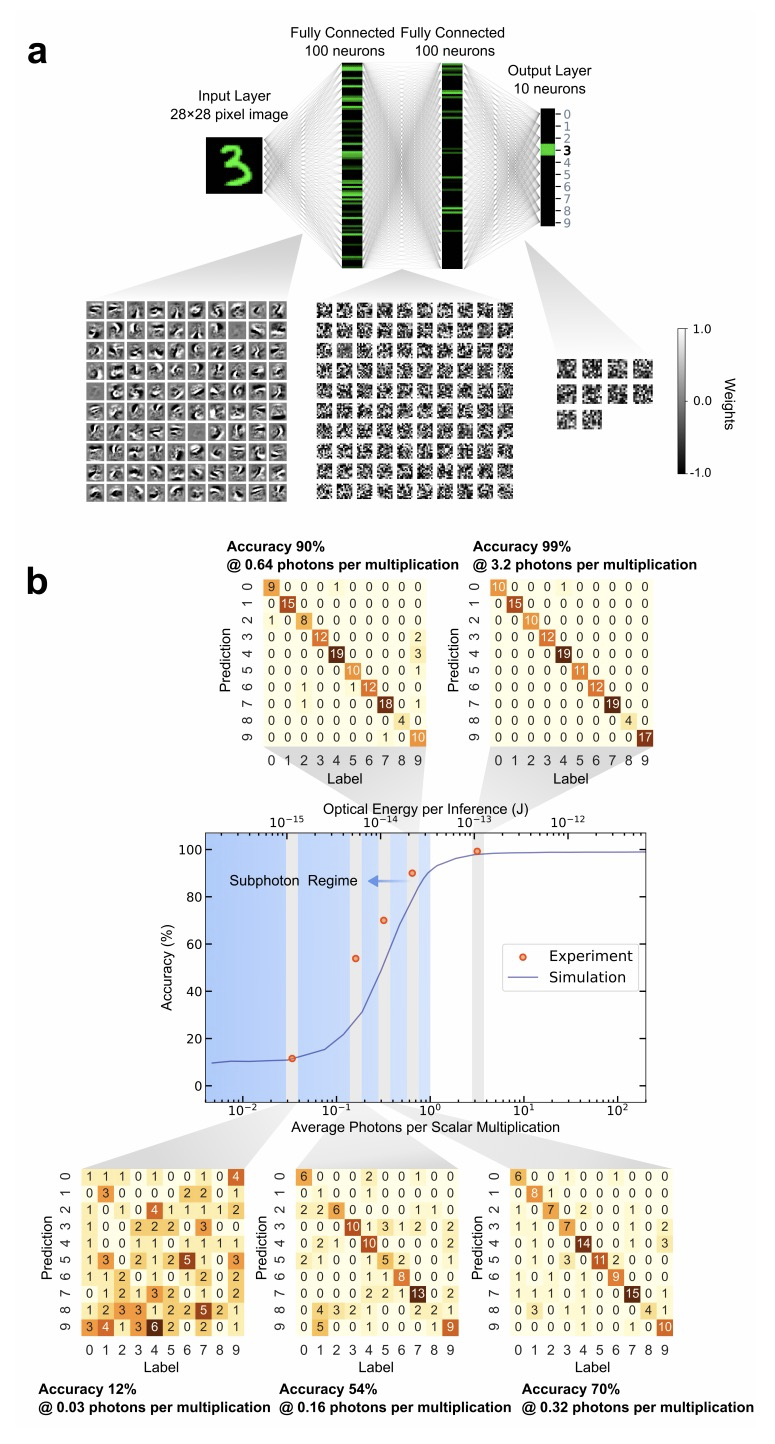
5、[LG] An optical neural network using less than 1 photon per multiplication
T Wang, S Ma, L G. Wright, T Onodera, B Richard, P L. McMahon
[Cornell University]
每次乘法使用少于1个光子的光学神经网络。深度学习已经迅速成为科学和商业领域的一个广泛的工具。过去几年里,越来越多的任务已经实现了深度学习超过人类性能的里程碑,涉及的领域包括玩游戏、自然语言翻译和医学图像分析。然而,由于在电子处理器上训练和运行深度神经网络所需的高能量成本,持续的进展越来越受到阻碍。光学神经网络,作为深度学习的替代物理平台引起了人们的关注,因为从理论上预测,它们可以从根本上实现比部署在传统数字计算机上的神经网络更高的能源效率。本文通过实验,证明了一个光学神经网络在手写数字分类上,每次权重相乘用到3.2个检测到的光子,可以达到99%的准确率,每次权重乘法使用0.64个光子(2.4×10-19J的光能),准确率能达到90%。这一性能是通过一个定制的自由空间光学处理器实现的,该处理器以大规模并行方式执行矩阵-向量乘法,同时进行多达50万次标量(权重)乘法。使用市售的光学元件和标准的神经网络训练方法,证明了光学神经网络可以在接近标准量子极限的情况下以极低的光功率运行,且仍然可以实现高精度。该结果为低光功率操作提供了一个原则性证明,通过仔细的系统设计,包括用于数据存储和控制的周边电子器件,开辟了一条实现光学处理器的道路,每个标量乘法只需要10-16焦耳的总能量——比目前的数字处理器要高效几个数量级。
Deep learning has rapidly become a widespread tool in both scientific and commercial endeavors [1]. Milestones of deep learning exceeding human performance have been achieved for a growing number of tasks over the past several years, across areas as diverse as game-playing, natural-language translation, and medical-image analysis. However, continued progress is increasingly hampered by the high energy costs associated with training and running deep neural networks on electronic processors [2]. Optical neural networks have attracted attention as an alternative physical platform for deep learning [3, 4], as it has been theoretically predicted that they can fundamentally achieve higher energy efficiency than neural networks deployed on conventional digital computers [5, 6]. Here, we experimentally demonstrate an optical neural network achieving 99% accuracy on handwrittendigit classification using ∼3.2 detected photons per weight multiplication and ∼90% accuracy using ∼0.64 photons (∼2.4 × 10−19 J of optical energy) per weight multiplication. This performance was achieved using a custom free-space optical processor that executes matrix-vector multiplications in a massively parallel fashion, with up to ∼0.5 million scalar (weight) multiplications performed at the same time. Using commercially available optical components and standard neural-network training methods, we demonstrated that optical neural networks can operate near the standard quantum limit with extremely low optical powers and still achieve high accuracy. Our results provide a proof-ofprinciple for low-optical-power operation, and with careful system design including the surrounding electronics used for data storage and control, open up a path to realizing optical processors that require only 10−16 J total energy per scalar multiplication—which is orders of magnitude more efficient than current digital processors.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kdf0UfNyo
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
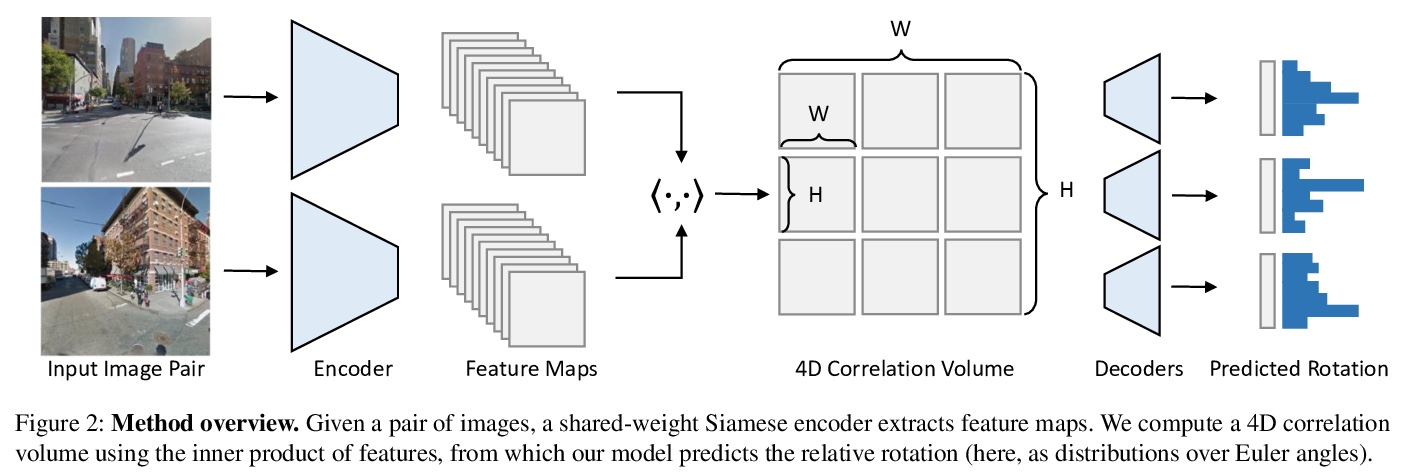
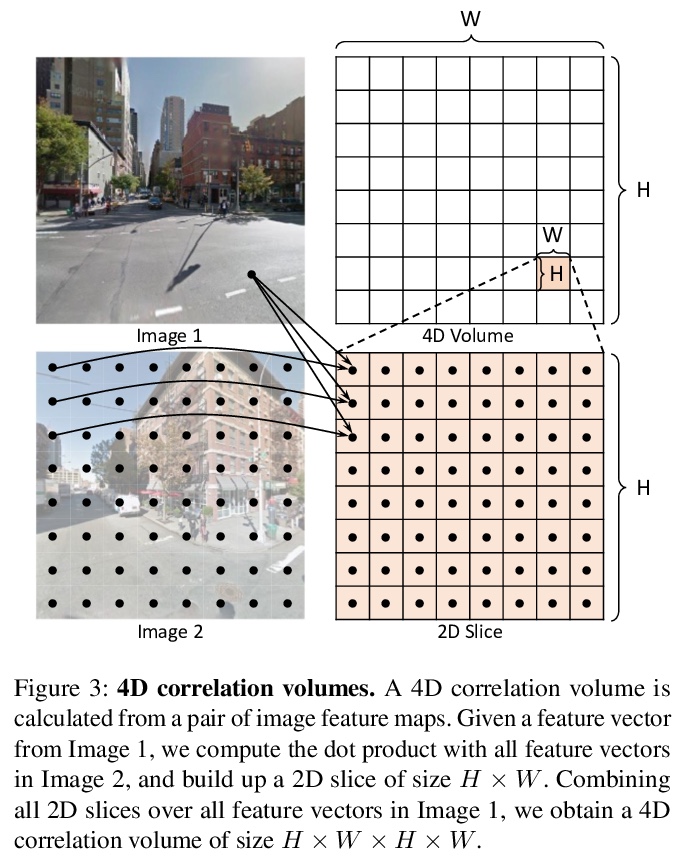
[CV] Extreme Rotation Estimation using Dense Correlation Volumes
基于密集相关体的极端旋转估计
R Cai, B Hariharan, N Snavely, H Averbuch-Elor
[Cornell University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kdf4XapXf


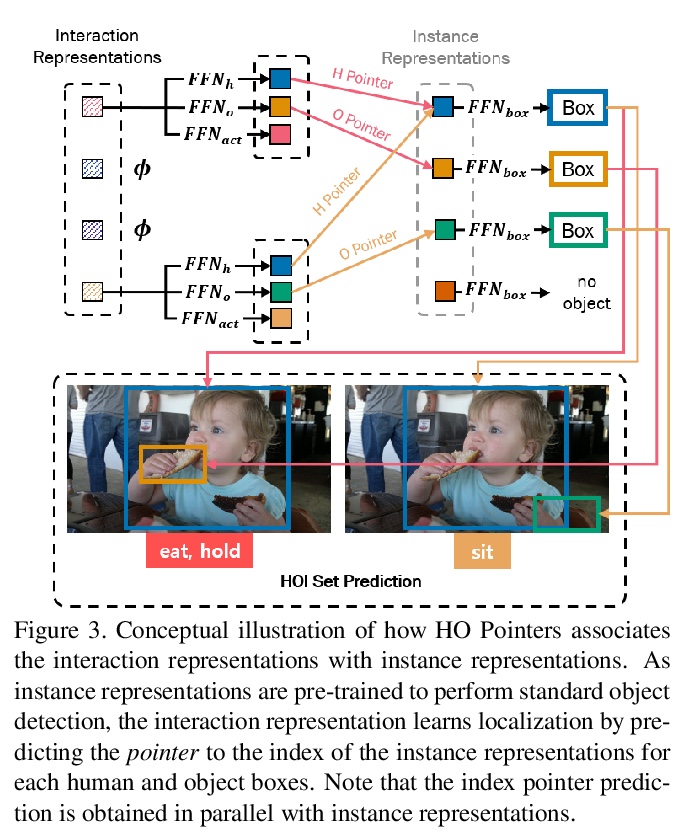
[CV] HOTR: End-to-End Human-Object Interaction Detection with Transformers
HOTR:基于Transformer的端到端人-物互动检测
B Kim, J Lee, J Kang, E Kim, H J. Kim
[Kakao Brain & Korea University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kdf6b822h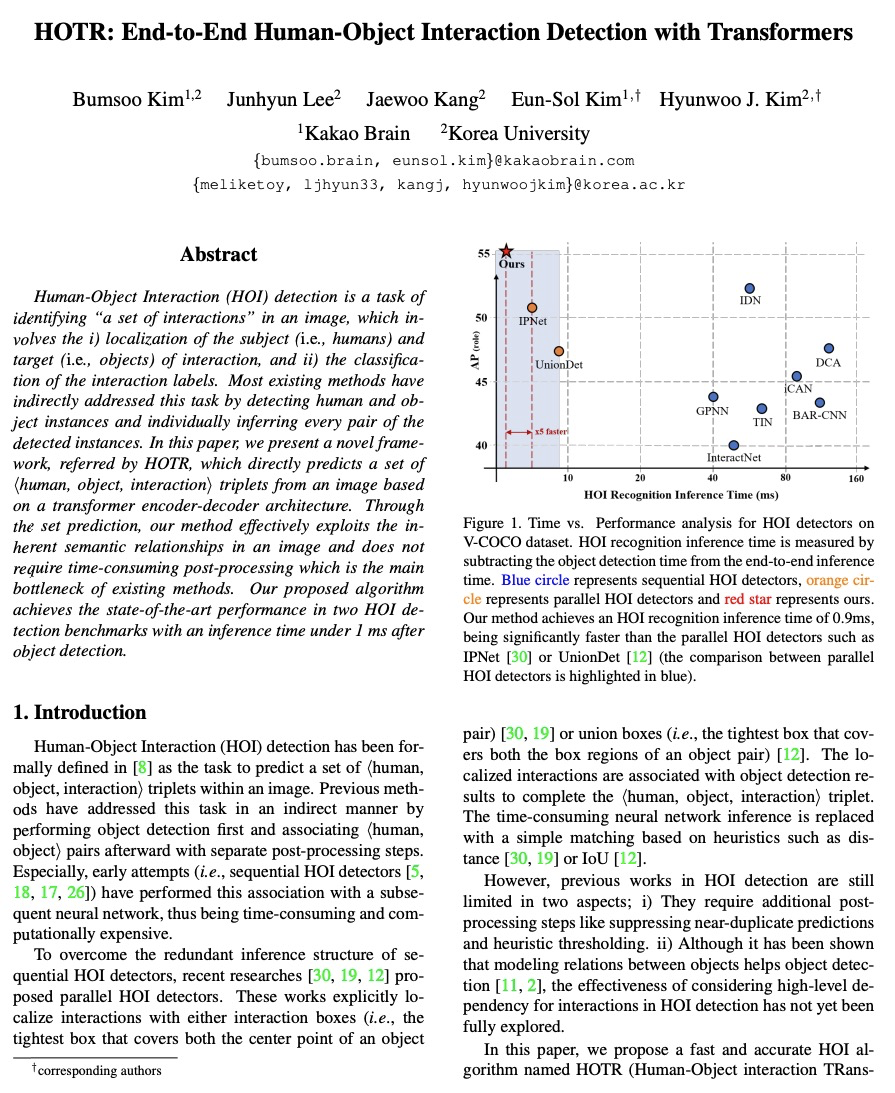
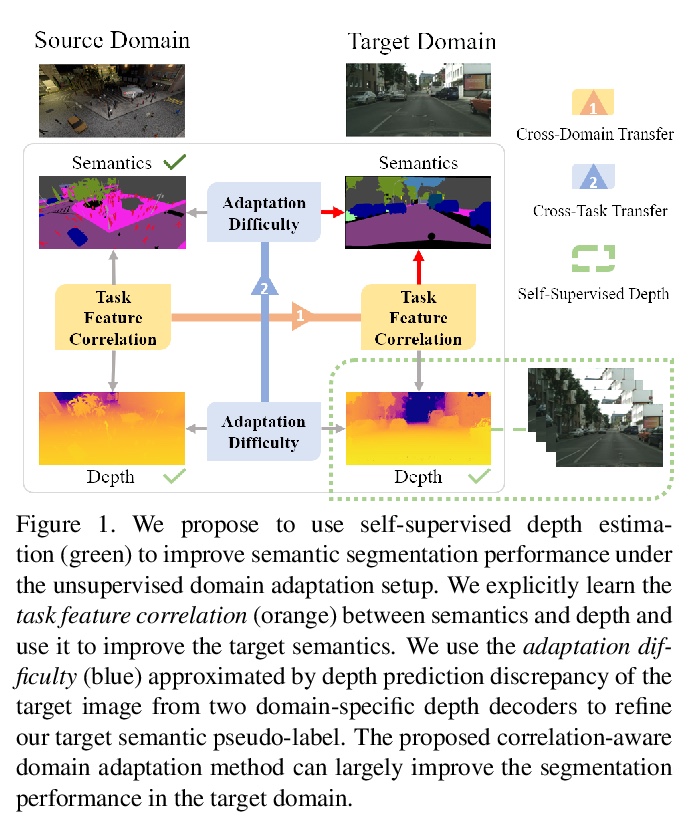
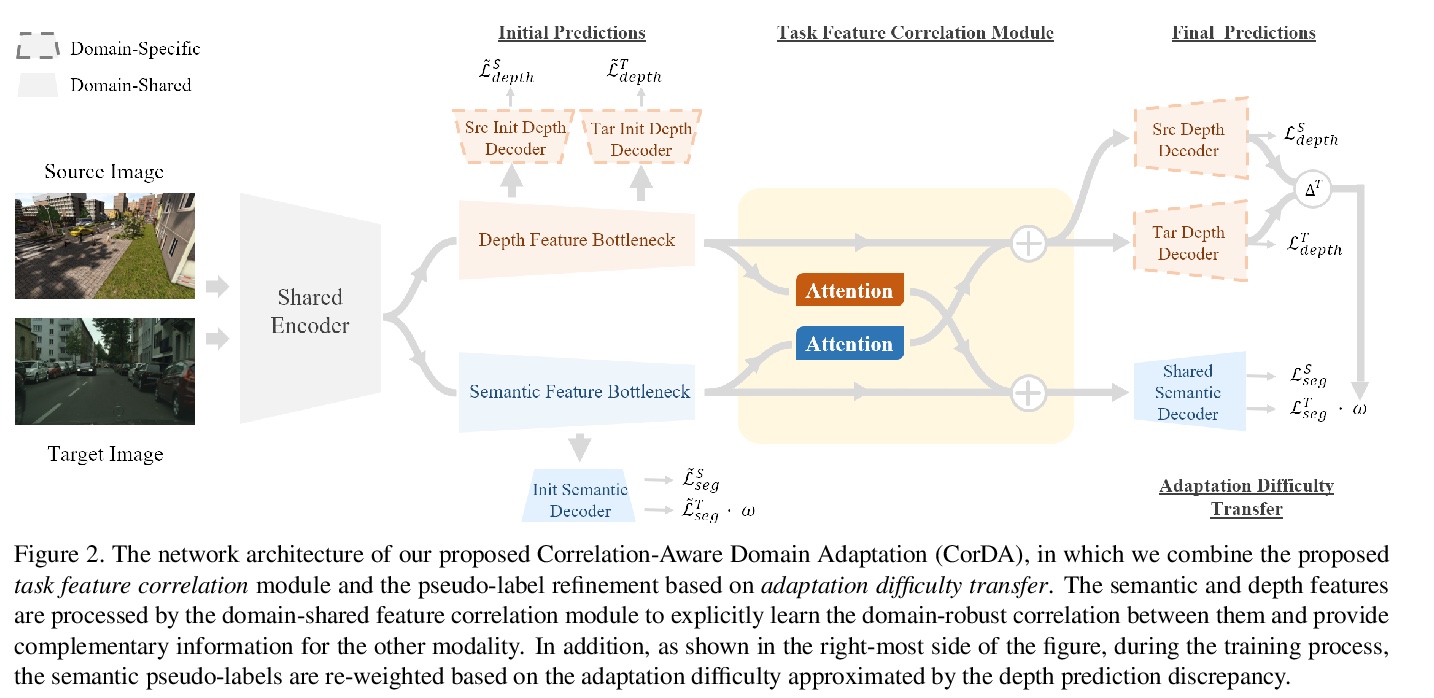
[CV] Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation with Self-Supervised Depth Estimation
基于自监督深度估计的域自适应语义分割
Q Wang, D Dai, L Hoyer, O Fink, L V Gool
[ETH Zurich]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kdf7luuzl
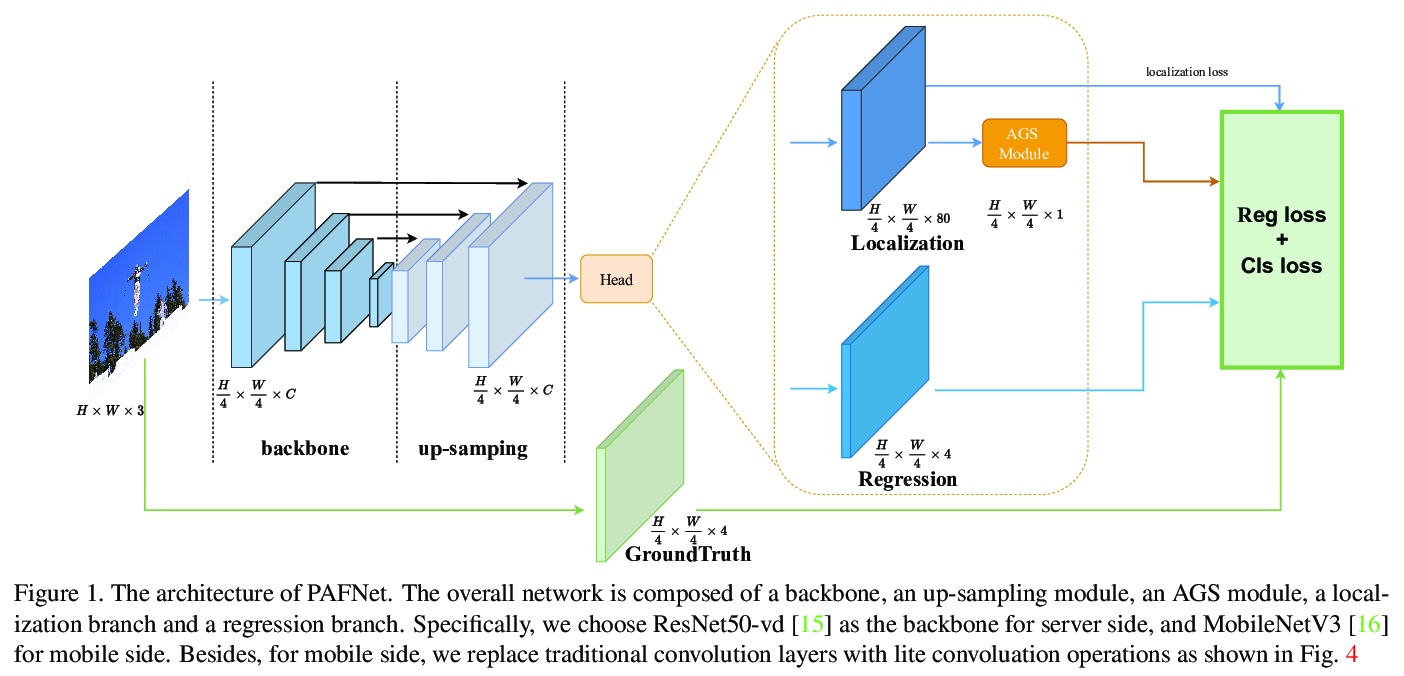
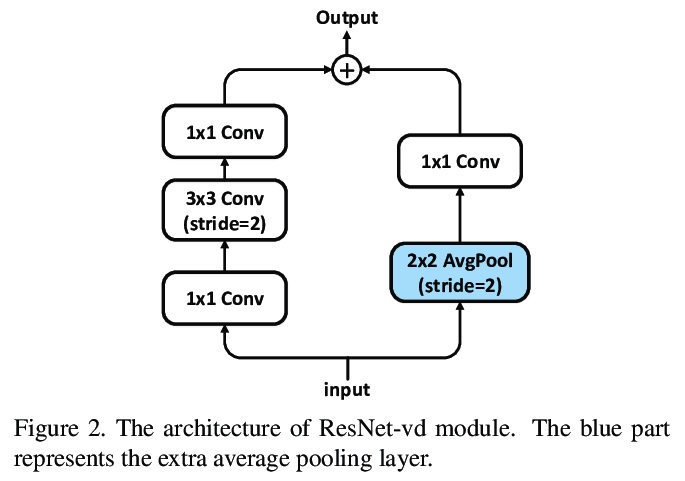
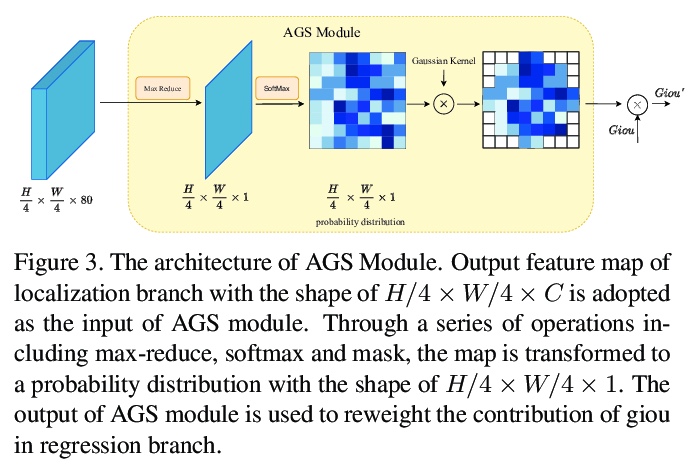
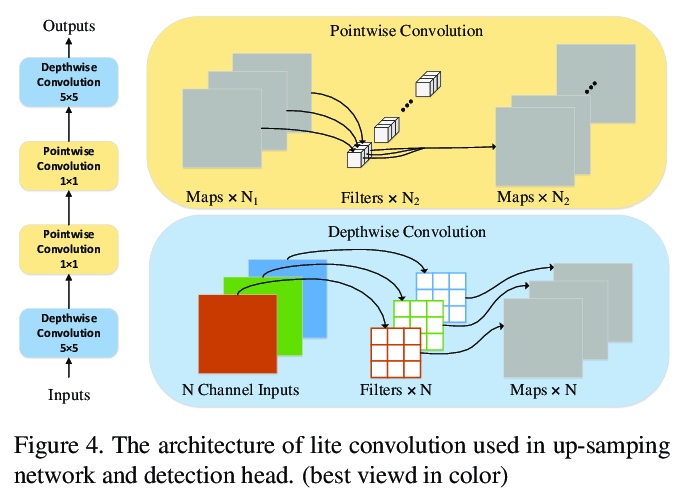
[CV] PAFNet: An Efficient Anchor-Free Object Detector Guidance
PAFNet:一种高效的无锚目标检测器指导
Y Xin, G Wang, M Mao, Y Feng, Q Dang, Y Ma, E Ding, S Han
[Baidu Inc]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KdfauyanM