- 1、[CV] CogView: Mastering Text-to-Image Generation via Transformers
- 2、[CV] Stylizing 3D Scene via Implicit Representation and HyperNetwork
- 3、[LG] Drawing Multiple Augmentation Samples Per Image During Training Efficiently Decreases Test Error
- 4、[LG] Encoders and Ensembles for Task-Free Continual Learning
- 5、[LG] SLOE: A Faster Method for Statistical Inference in High-Dimensional Logistic Regression
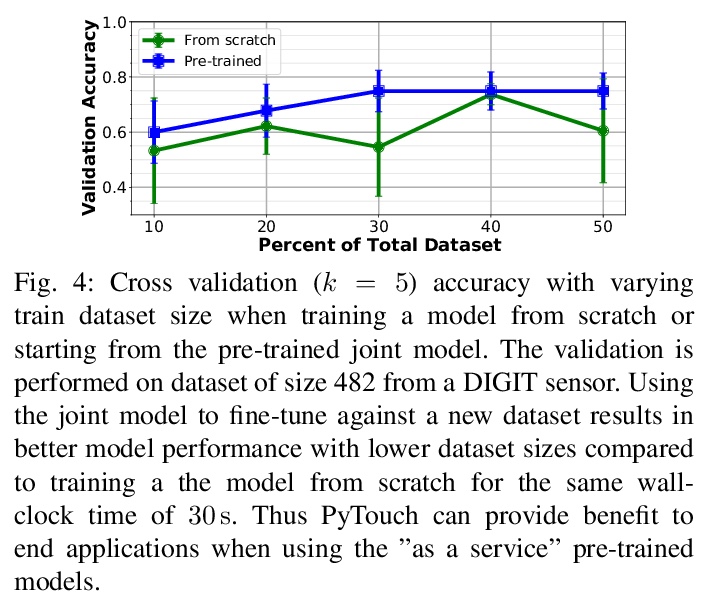
- [RO] PyTouch: A Machine Learning Library for Touch Processing
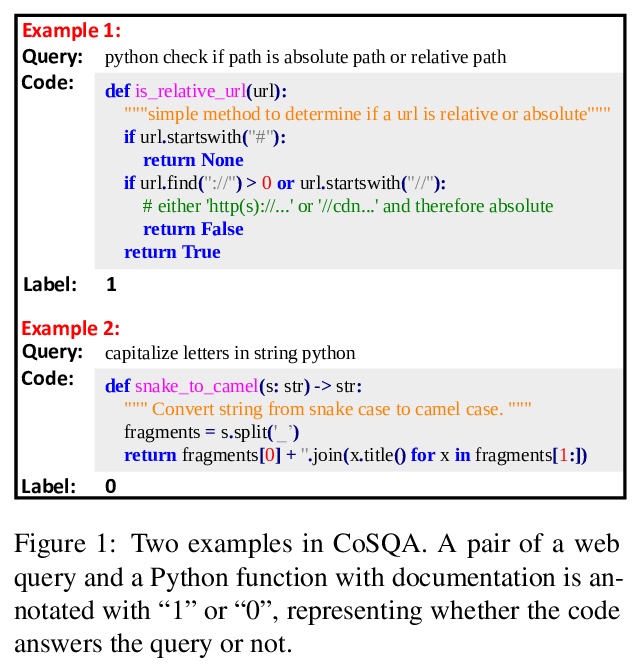
- [CL] CoSQA: 20,000+ Web Queries for Code Search and Question Answering
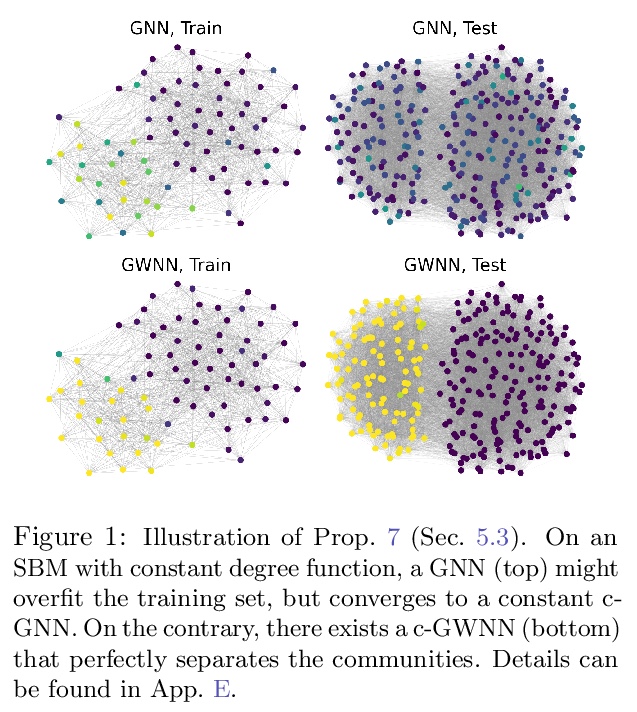
- [LG] On the Universality of Graph Neural Networks on Large Random Graphs
- [RO] Uncertainty-Aware Self-Supervised Target-Mass Grasping of Granular Foods
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
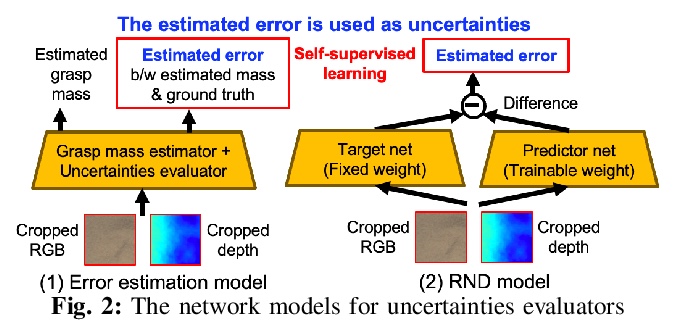
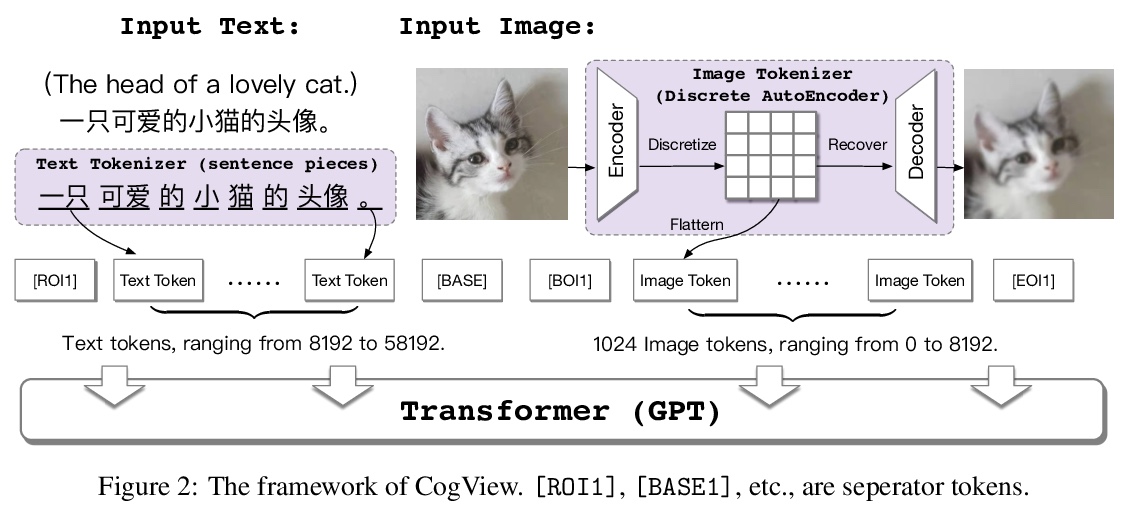
1、[CV] CogView: Mastering Text-to-Image Generation via Transformers
M Ding, Z Yang, W Hong, W Zheng, C Zhou, D Yin, J Lin, X Zou, Z Shao, H Yang, J Tang
[Tsinghua University & DAMO Academy & BAAI]
CogView: 基于Transformer的文本-图像生成。通用领域文本到图像生成一直是个开放问题,需要生成模型和跨模态理解。本文提出CogView,一种带有VQ-VAE标记器的40亿参数的Transformer,将VQVAE和Transformer相结合,用以推动该问题的解决。展示了各种下游任务的微调策略,如画风学习、超分辨率、文本-图像排序和时尚设计,以及稳定预训练的方法,如消除NaN损失。CogView为可扩展的跨模态生成预训练展示了有希望的结果,同时也揭示并解决了可能源于数据异质性的精度问题。CogView(zeroshot)在模糊的MS COCO上实现了新的最先进的FID,超过了之前基于GAN的模型和最近的类似工作DALL-E。
Text-to-Image generation in the general domain has long been an open problem, which requires both generative model and cross-modal understanding. We propose CogView, a 4-billion-parameter Transformer with VQ-VAE tokenizer to advance this problem. We also demonstrate the finetuning strategies for various downstream tasks, e.g. style learning, super-resolution, text-image ranking and fashion design, and methods to stabilize pretraining, e.g. eliminating NaN losses. CogView (zeroshot) achieves a new state-of-the-art FID on blurred MS COCO, outperforms previous GAN-based models and a recent similar work DALL-E.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhEcxuh5c


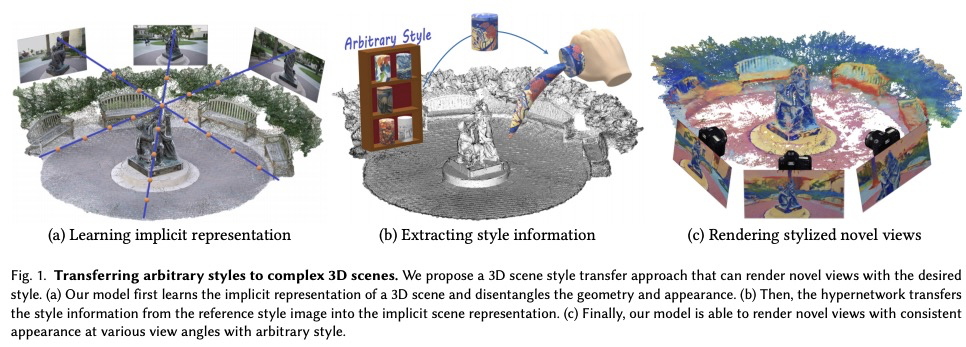
2、[CV] Stylizing 3D Scene via Implicit Representation and HyperNetwork
P Chiang, M Tsai, H Tseng, W Lai, W Chiu
[National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University & University of California, Merced]
基于隐表征和超网络的3D场景风格化。本文旨在解决3D场景风格化问题——在任意新视角下生成场景的风格化图像。一种直接的解决方案,是结合现有的新视图合成和图像/视频画风迁移方法,往往会导致模糊的结果,或不一致的外观。受神经辐射场(NeRF)方法高质量结果的启发,本文提出一种联合框架,直接渲染具有所需风格的新视图。该框架由两部分组成:一个带有神经辐射场模型的3D场景隐表征,以及一个将风格信息迁移到场景表示的超网络。隐表征模型将场景解缠为几何和外观两个分支,超网络则从参考风格图像中学习预测外观分支的参数。为减轻训练的难度和内存的负担,提出一种两阶段的训练程序和一种图块子采样方法,用神经辐射场模型来优化风格和内容损失。经过优化,该模型能在任意视角下以任意风格呈现一致的新视图。定量评估和人工研究表明,所提出方法产生了忠实的风格化结果,在不同的视图中具有一致的外观。
In this work, we aim to address the 3D scene stylization problem - generating stylized images of the scene at arbitrary novel view angles. A straightforward solution is to combine existing novel view synthesis and image/video style transfer approaches, which often leads to blurry results or inconsistent appearance. Inspired by the high quality results of the neural radiance fields (NeRF) method, we propose a joint framework to directly render novel views with the desired style. Our framework consists of two components: an implicit representation of the 3D scene with the neural radiance field model, and a hypernetwork to transfer the style information into the scene representation. In particular, our implicit representation model disentangles the scene into the geometry and appearance branches, and the hypernetwork learns to predict the parameters of the appearance branch from the reference style image. To alleviate the training difficulties and memory burden, we propose a two-stage training procedure and a patch sub-sampling approach to optimize the style and content losses with the neural radiance field model. After optimization, our model is able to render consistent novel views at arbitrary view angles with arbitrary style. Both quantitative evaluation and human subject study have demonstrated that the proposed method generates faithful stylization results with consistent appearance across different views.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhEjOsRvo


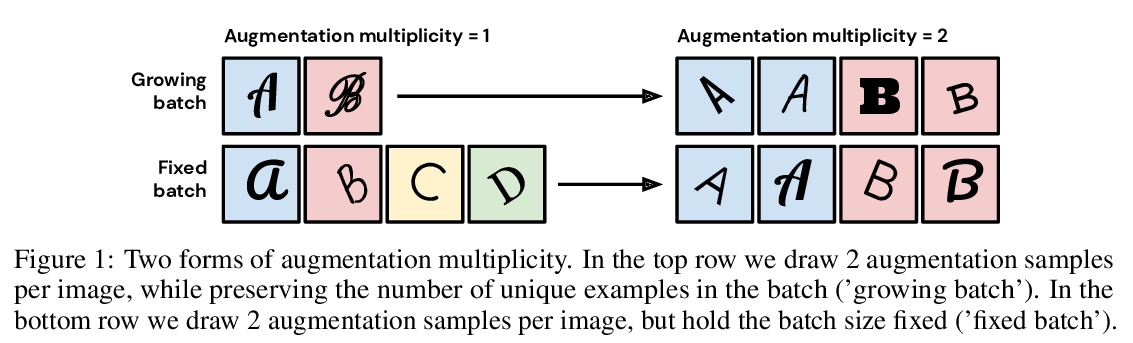
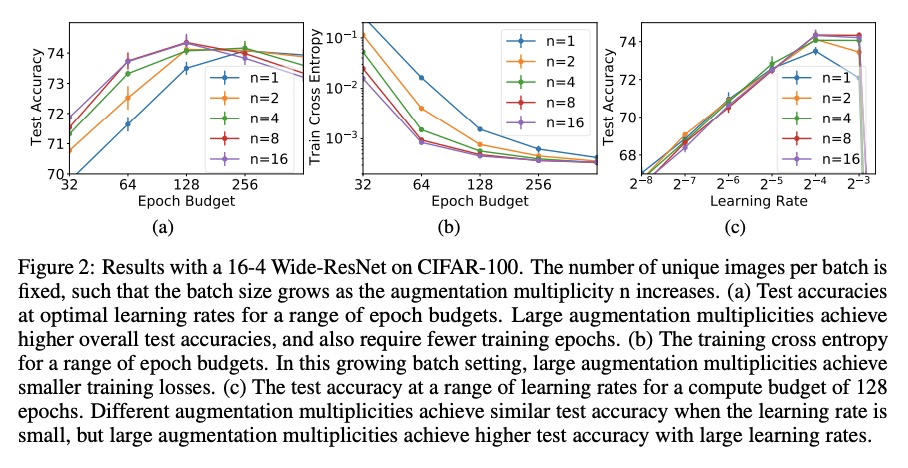
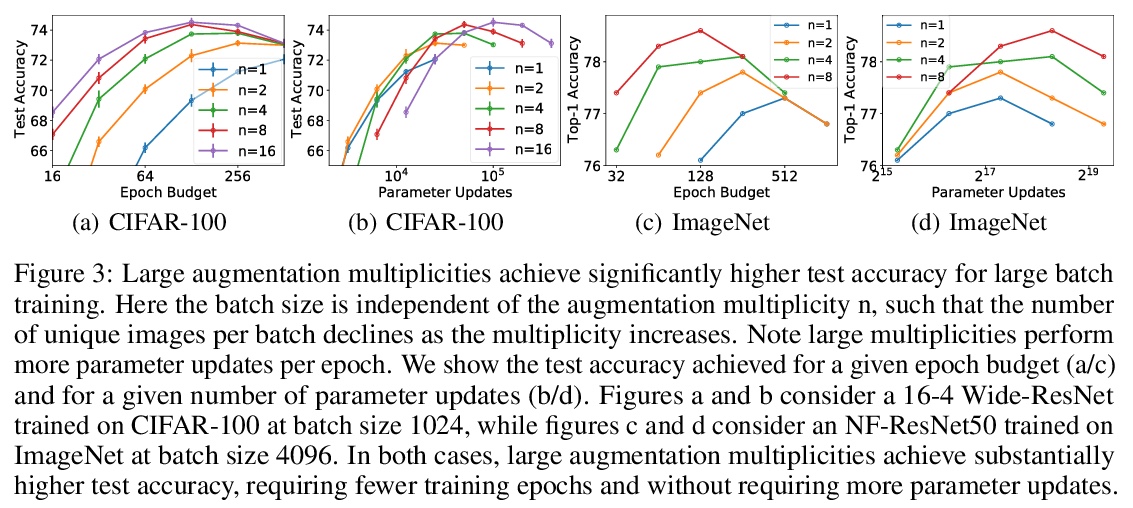
3、[LG] Drawing Multiple Augmentation Samples Per Image During Training Efficiently Decreases Test Error
S Fort, A Brock, R Pascanu, S De, S L. Smith
[Stanford University & DeepMind]
训练过程中每幅图像抽取多个增广样本可有效降低测试误差。计算机视觉中,标准做法是为mini-batch中每张独特图像从数据增强程序中抽取一个样本,然而,目前还不清楚这种选择是否是泛化的最佳选择。本文提供了一个详细的实证评估,即每张独特图像的增强样本的数量会如何影响保留数据的性能。结果发现,尽管在每个mini-batch中减少了独特训练样本的数量,但每张图像抽取多个增广样本,始终能提高小批次和大批次训练的测试精度。即使不同的增广倍数执行相同数量的参数更新和梯度评估,也会有这方面的收益。结果表明,尽管子采样数据集产生的梯度估计方差具有隐含正则化的好处,但数据增广过程中产生的方差会损害测试精度。通过对最近提出的NFNet模型系列进行扩增倍率,达到了86.8%的Top-1(不含额外数据)的ImageNet新技术水平。
In computer vision, it is standard practice to draw a single sample from the data augmentation procedure for each unique image in the mini-batch, however it is not clear whether this choice is optimal for generalization. In this work, we provide a detailed empirical evaluation of how the number of augmentation samples per unique image influences performance on held out data. Remarkably, we find that drawing multiple samples per image consistently enhances the test accuracy achieved for both small and large batch training, despite reducing the number of unique training examples in each mini-batch. This benefit arises even when different augmentation multiplicities perform the same number of parameter updates and gradient evaluations. Our results suggest that, although the variance in the gradient estimate arising from subsampling the dataset has an implicit regularization benefit, the variance which arises from the data augmentation process harms test accuracy. By applying augmentation multiplicity to the recently proposed NFNet model family, we achieve a new ImageNet state of the art of 86.8% top-1 w/o extra data.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhEnAaPKx

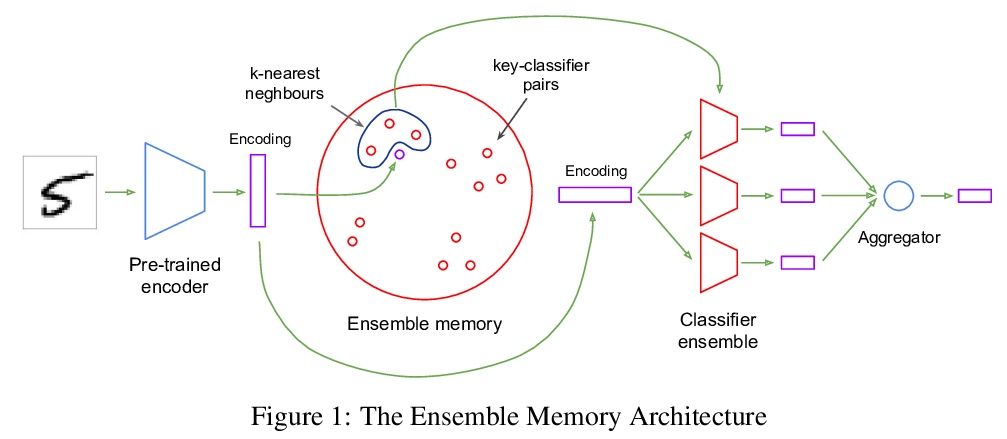
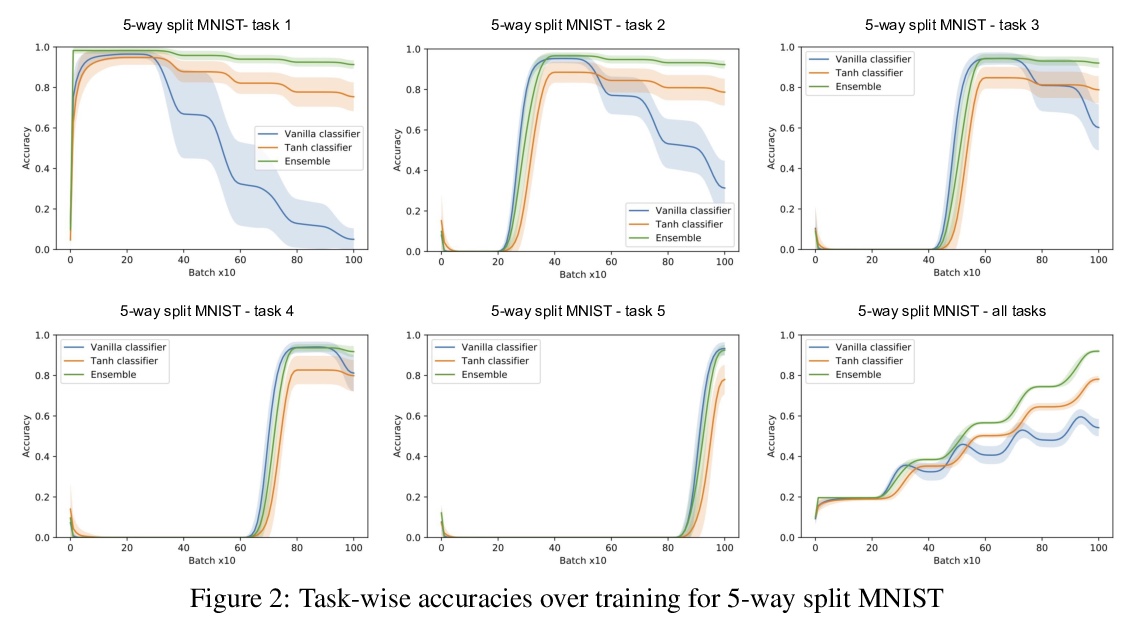
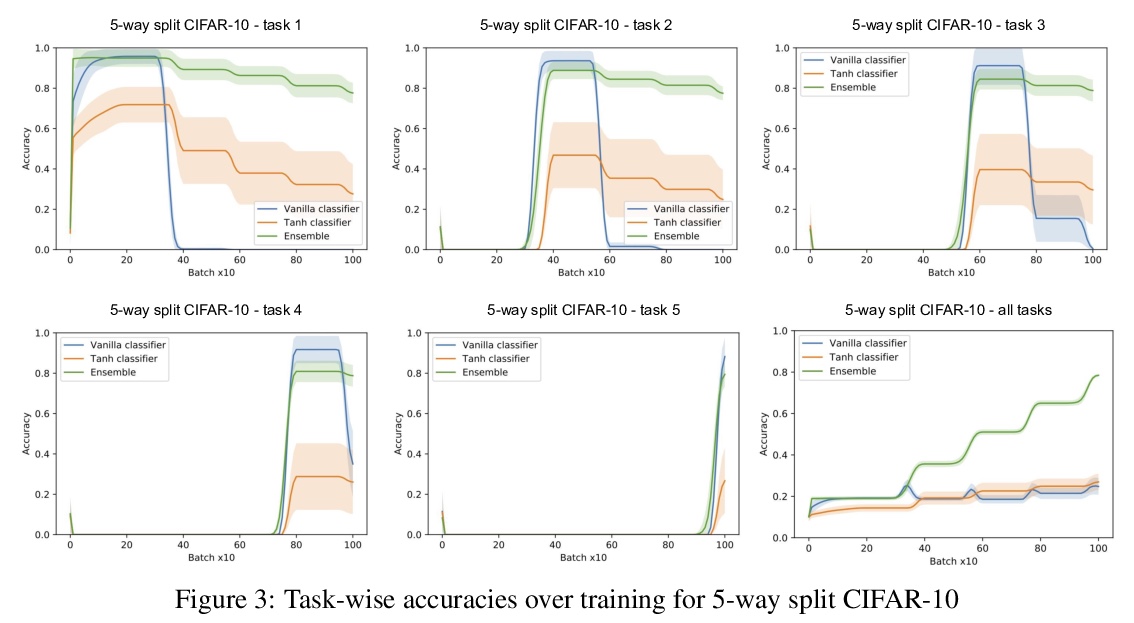
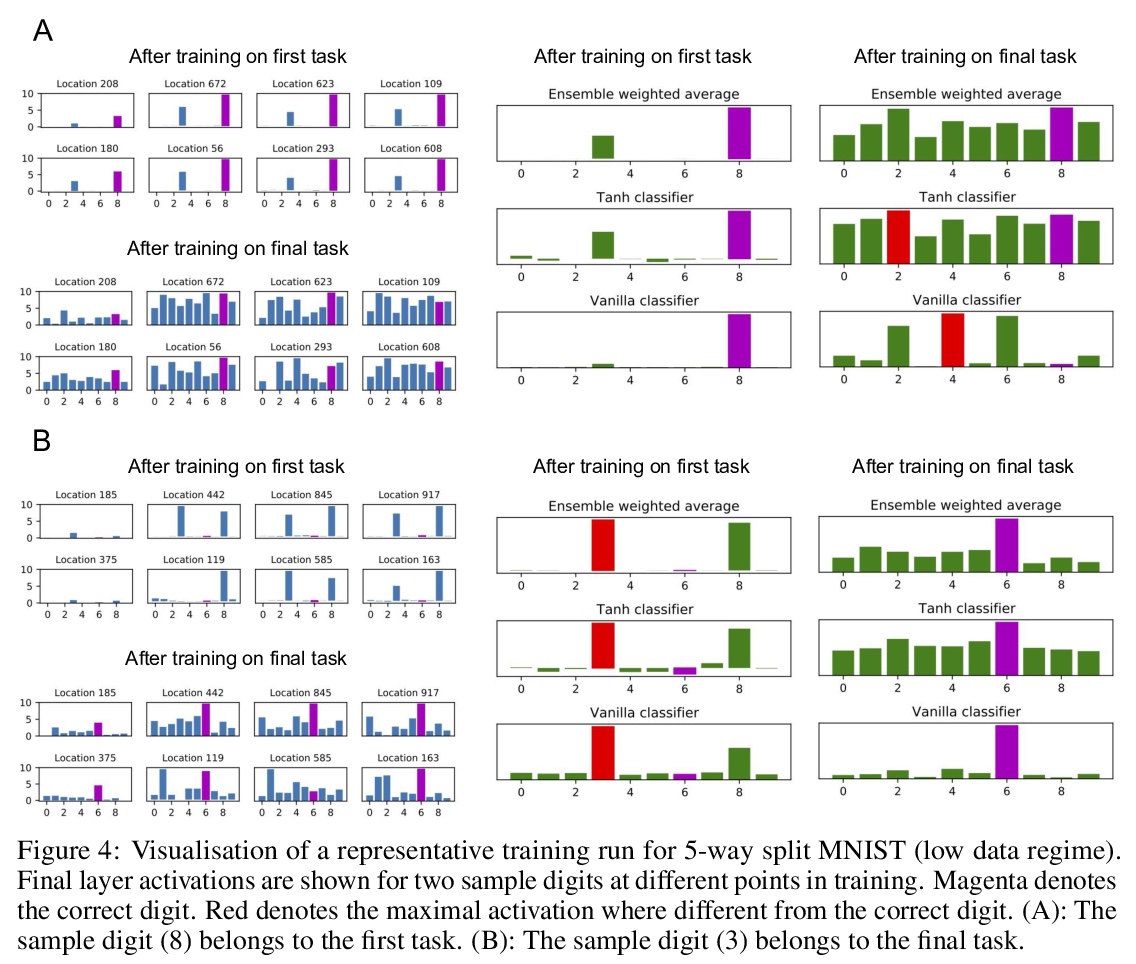
4、[LG] Encoders and Ensembles for Task-Free Continual Learning
M Shanahan, C Kaplanis, J Mitrović
[DeepMind]
面向无任务持续学习的编码器与集成。本提出一种架构,在特别苛刻的环境中有效地持续学习,该环境中不存在或不知道任务的边界。该架构包括在单独数据集上预训练的编码器,以及一个简单的单层分类器的集成。要使这种组合发挥作用,需要两个主要的创新:首先,由于自监督训练方法的最新进展,提供适当的通用预训练编码器已成为可能。其次,将组合中的每个分类器与一个键配对,其中键空间与编码器的潜空间相同,使得它们可以通过最近邻查找来协同选择性使用。在标准图像分类持续学习基准的无任务设置中,用编码器和集成的架构训练的模型是最先进的,并且在最具挑战性的情况下,比之前的最先进水平有很大提高。该架构在完全增量的情况下学习效果很好,即一次学习一个类别,实验证明了在这种情况下对多达100个类别的有效性。展示了该架构在无任务的持续学习环境中的效果,在这种环境中,数据分布逐渐变化,现有的需要了解任务边界的方法无法应用。
We present an architecture that is effective for continual learning in an especially demanding setting, where task boundaries do not exist or are unknown. Our architecture comprises an encoder, pre-trained on a separate dataset, and an ensemble of simple one-layer classifiers. Two main innovations are required to make this combination work. First, the provision of suitably generic pre-trained encoders has been made possible thanks to recent progress in self-supervised training methods. Second, pairing each classifier in the ensemble with a key, where the key-space is identical to the latent space of the encoder, allows them to be used collectively, yet selectively, via k-nearest neighbour lookup. We show that models trained with the encoders-and-ensembles architecture are state-of-the-art for the task-free setting on standard image classification continual learning benchmarks, and improve on prior state-of-the-art by a large margin in the most challenging cases. We also show that the architecture learns well in a fully incremental setting, where one class is learned at a time, and we demonstrate its effectiveness in this setting with up to 100 classes. Finally, we show that the architecture works in a task-free continual learning context where the data distribution changes gradually, and existing approaches requiring knowledge of task boundaries cannot be applied.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhEwMqu0L
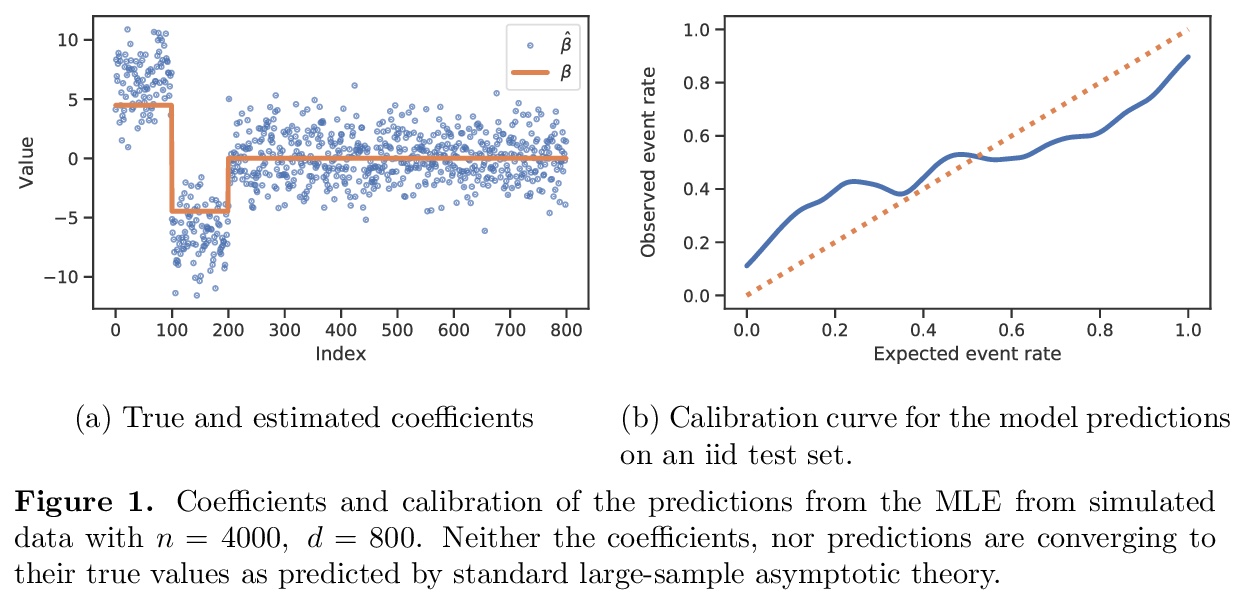
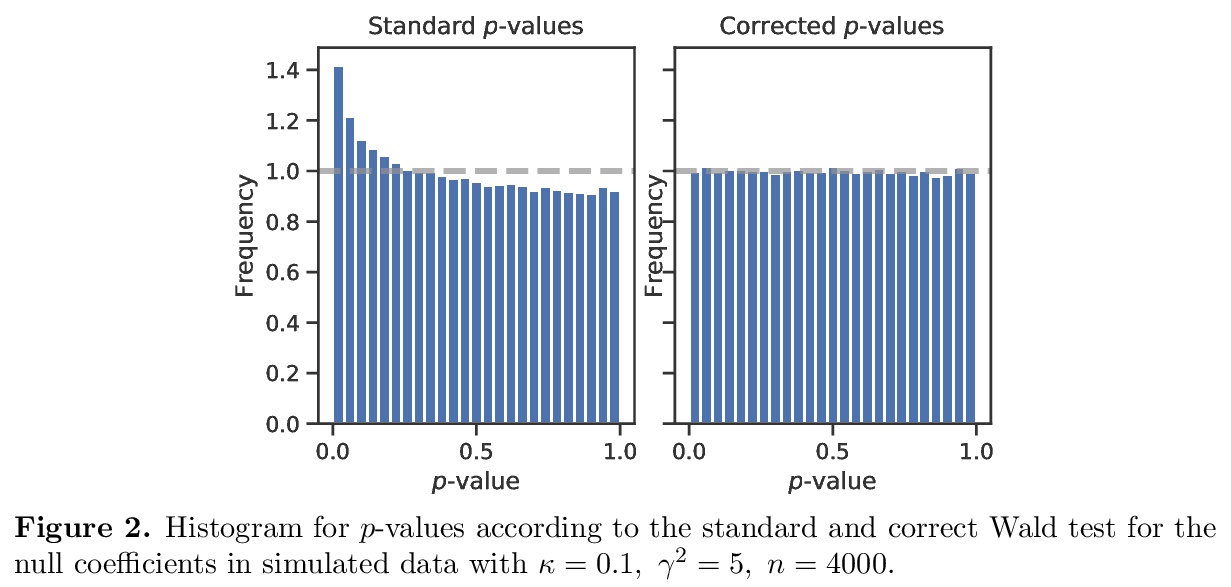
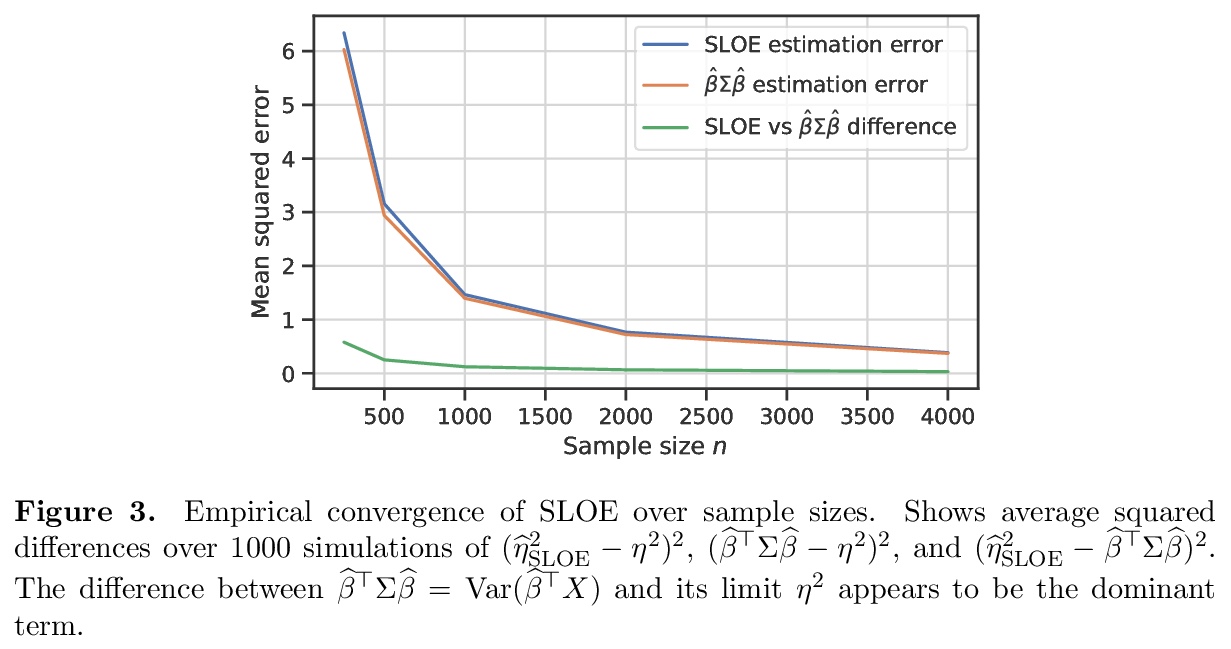
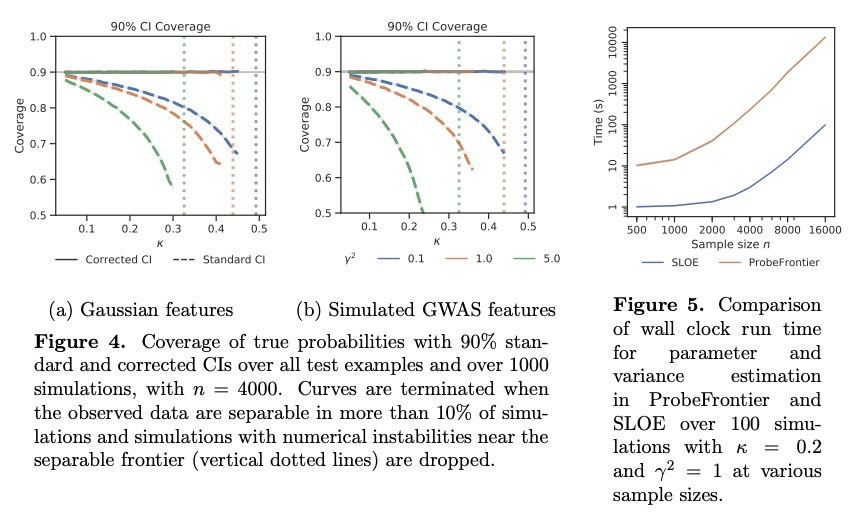
5、[LG] SLOE: A Faster Method for Statistical Inference in High-Dimensional Logistic Regression
S Yadlowsky, T Yun, C McLean, A D’Amour
[Google]
SLOE:更快的高维Logistic回归统计推断方法。Logistic回归仍然是应用统计、机器学习和数据科学中最广泛使用的工具之一。然而,在中等高维问题中,当特征数d相对样本量n是一个不可忽略的部分时,Logistic回归最大似然估计器(MLE)和基于其分布的大样本近似的统计程序表现会很糟糕。最新研究表明,这些问题可以通过应用MLE在这种高维制度下的新近似采样分布来纠正。不幸的是,这些修正在实践中难以实现,因为它们需要对信号强度的估计,而信号强度是Logistic回归基础参数β的函数。为解决这个问题,本文提出SLOE,一种快速、直接的方法,用来估计Logistic回归的信号强度,可根据被破坏的信号强度进行重参数化,只估计参数β̂的函数。提出该量的估计器,证明它在相关的高维场景中是一致的,并表明使用SLOE的维度校正在有限样本中是准确的。与现有的ProbeFrontier启发式方法相比,SLOE在概念上更简单,速度也更快,使其适合于常规使用。在UCI资源库的心脏病数据集和使用英国生物库数据的基因组学应用中证明了常规维度校正的重要性。
Logistic regression remains one of the most widely used tools in applied statistics, machine learning and data science. However, in moderately high-dimensional problems, where the number of features d is a non-negligible fraction of the sample size n, the logistic regression maximum likelihood estimator (MLE), and statistical procedures based the large-sample approximation of its distribution, behave poorly. Recently, Sur and Candès [2019] showed that these issues can be corrected by applying a new approximation of the MLE’s sampling distribution in this high-dimensional regime. Unfortunately, these corrections are difficult to implement in practice, because they require an estimate of the signal strength, which is a function of the underlying parameters β of the logistic regression. To address this issue, we propose SLOE, a fast and straightforward approach to estimate the signal strength in logistic regression. The key insight of SLOE is that the Sur and Candès [2019] correction can be reparameterized in terms of the corrupted signal strength, which is only a function of the estimated parameters β̂. We propose an estimator for this quantity, prove that it is consistent in the relevant high-dimensional regime, and show that dimensionality correction using SLOE is accurate in finite samples. Compared to the existing ProbeFrontier heuristic, SLOE is conceptually simpler and orders of magnitude faster, making it suitable for routine use. We demonstrate the importance of routine dimensionality correction in the Heart Disease dataset from the UCI repository, and a genomics application using data from the UK Biobank.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhEG000JK
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
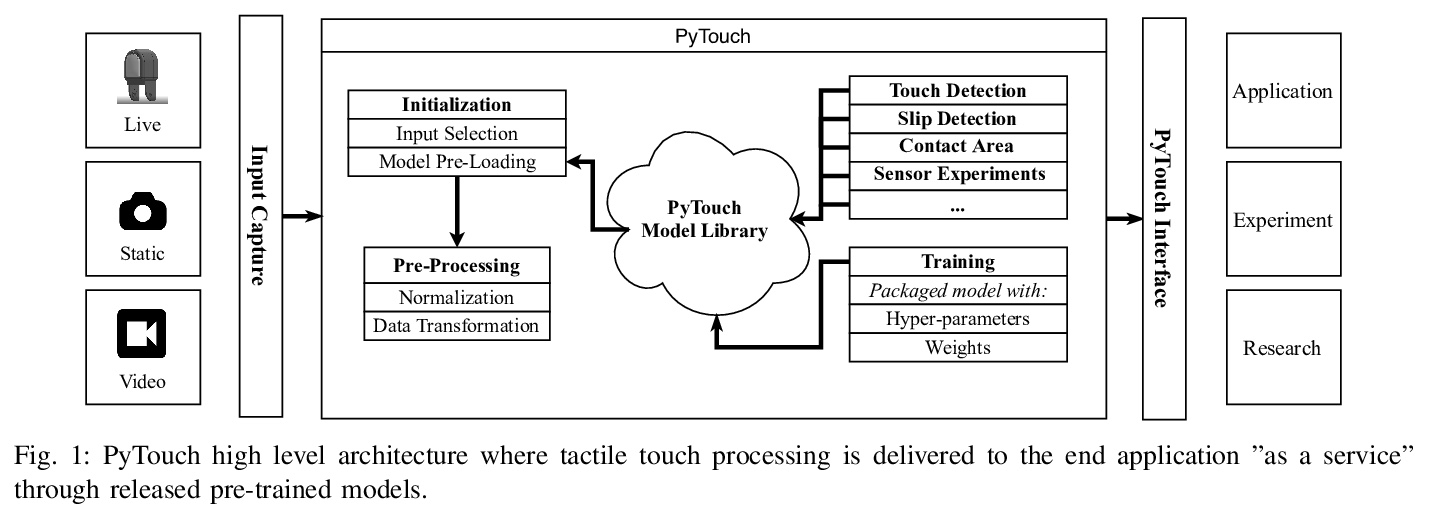
[RO] PyTouch: A Machine Learning Library for Touch Processing
PyTouch:触觉处理机器学习库
M Lambeta, H Xu, J Xu, P Chou, S Wang, T Darrell, R Calandra
[Facebook AI Research & UC Berkeley & Shanghai Jiao Tong University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhEgoxr8v

[CL] CoSQA: 20,000+ Web Queries for Code Search and Question Answering
CoSQA: 包含20,000多代码搜索/问题回答网络查询的数据集
J Huang, D Tang, L Shou, M Gong, K Xu, D Jiang, M Zhou, N Duan
[Beihang University & Microsoft Research Asia & Microsoft STC Asia]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhEt4hsOL
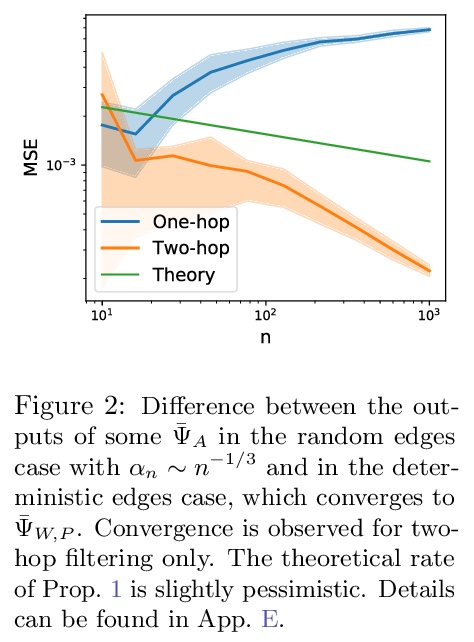
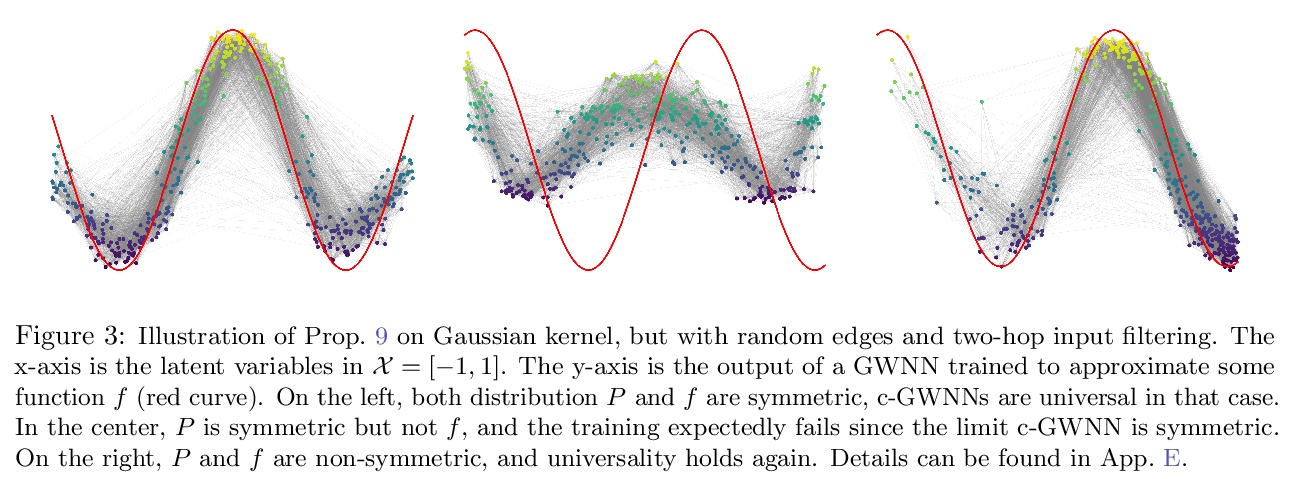
[LG] On the Universality of Graph Neural Networks on Large Random Graphs
大规模随机图上图神经网络的普适性
N Keriven, A Bietti, S Vaiter
[CNRS & NYU Center for Data Science]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhEuVuM6e
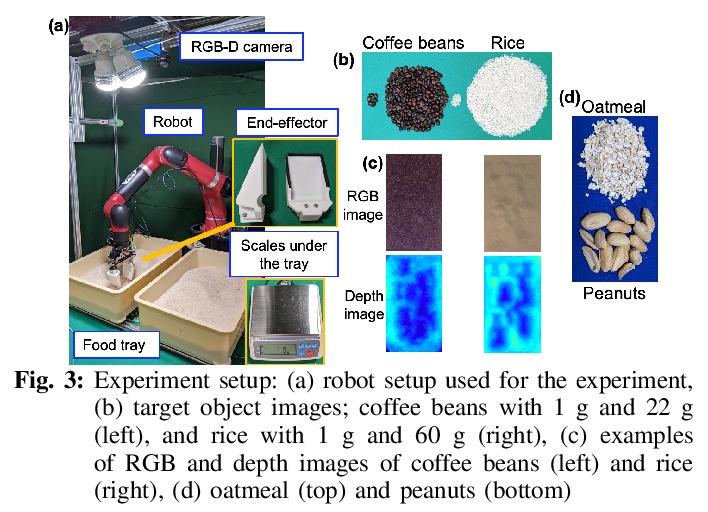
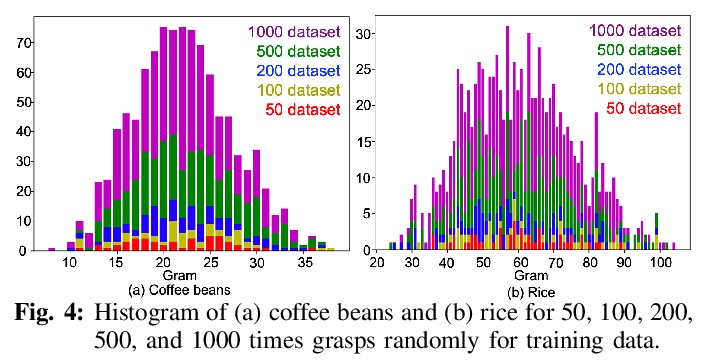
[RO] Uncertainty-Aware Self-Supervised Target-Mass Grasping of Granular Foods
颗粒食品不确定性感知自监督目标质量抓取
K Takahashi, W Ko, A Ummadisingu, S Maeda
[Preferred Networks]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KhENk6UFf