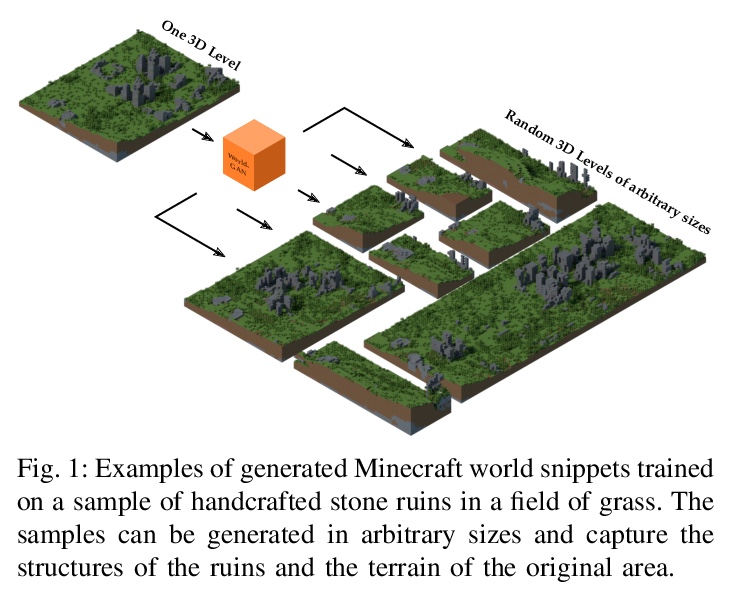
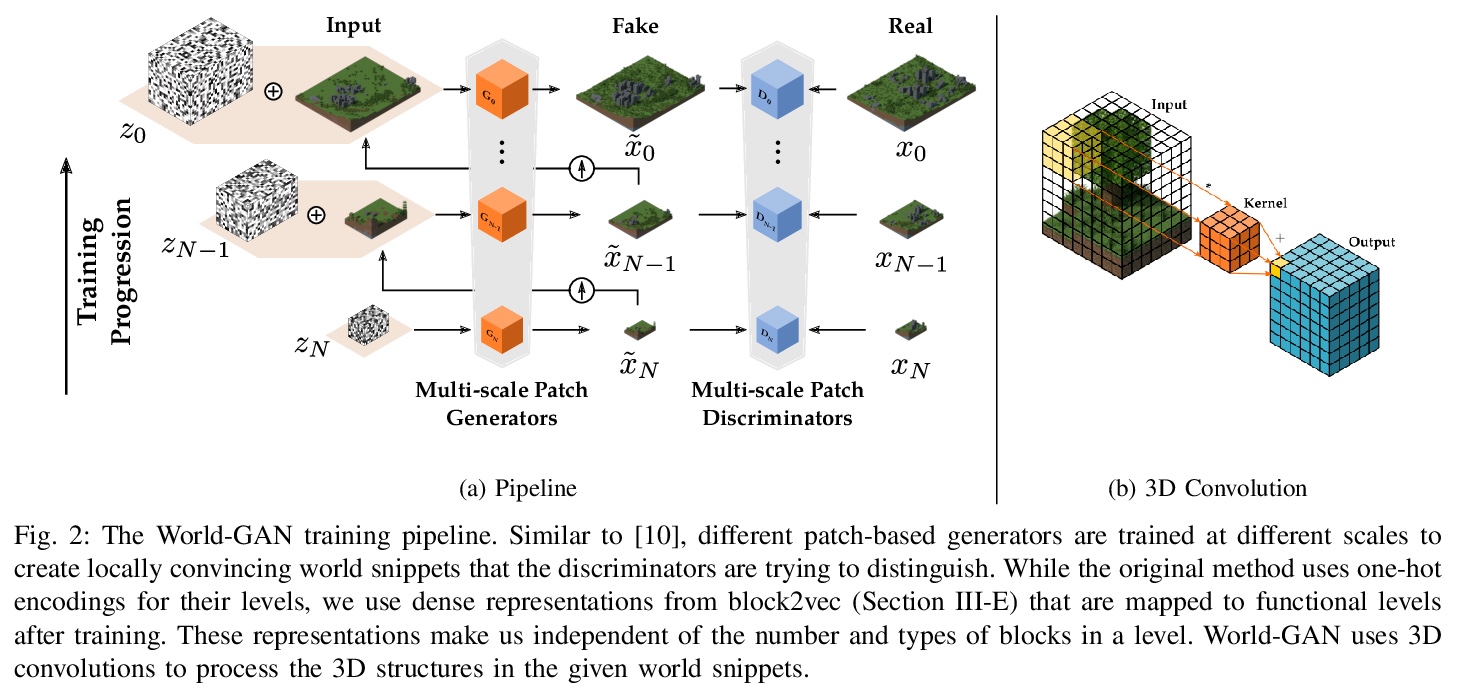
- 1、[LG] World-GAN: a Generative Model for Minecraft Worlds
- 2、[LG] Distributed Deep Learning in Open Collaborations
- 3、[LG] Riemannian Convex Potential Maps
- 4、[CV] How to train your ViT? Data, Augmentation, and Regularization in Vision Transformers
- 5、[CV] HifiFace: 3D Shape and Semantic Prior Guided High Fidelity Face Swapping
- [LG] Non Gaussian Denoising Diffusion Models
- [CL] Memory-efficient Transformers via Top-k Attention
- [CV] Bridging the Gap Between Object Detection and User Intent via Query-Modulation
- [LG] Learning to Generate Code Sketches
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] World-GAN: a Generative Model for Minecraft Worlds
M Awiszus, F Schubert, B Rosenhahn
[Leibniz University Hannover]
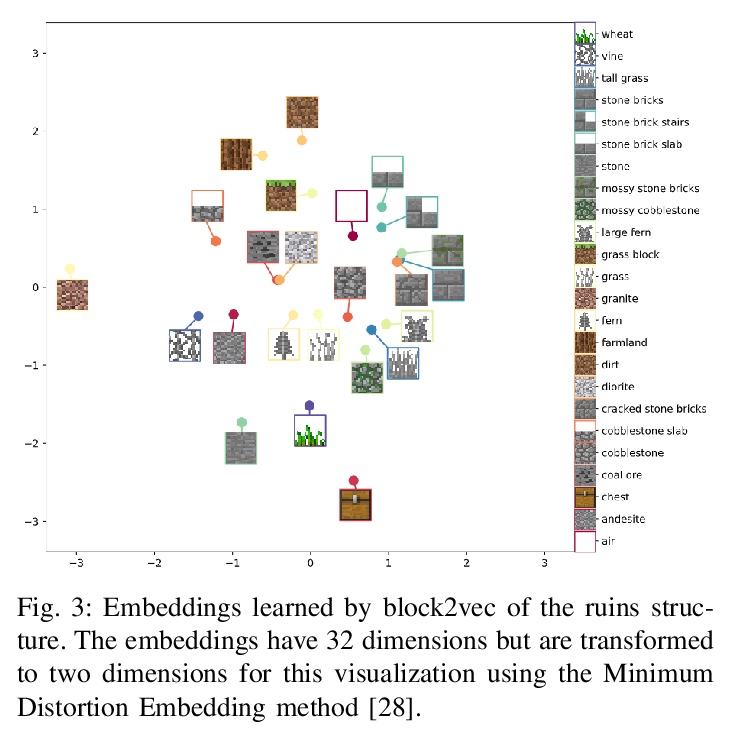
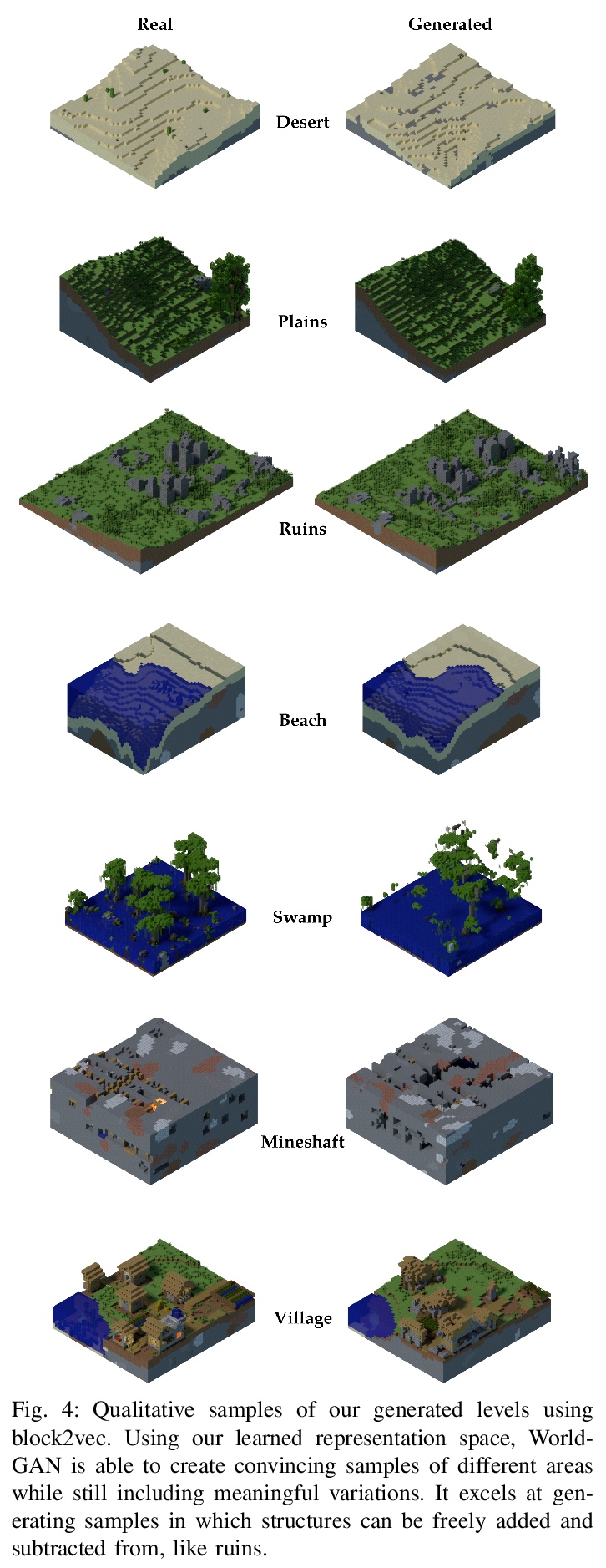
World-GAN:“我的世界”生成模型。本文提出World-GAN,第一个通过机器学习在“我的世界(Minecraft)”中从单一示例进行数据驱动程序化内容生成的方法。基于3D生成对抗网络(GAN)架构,从一个给定的示例创建任意大小的世界片段。该方法是由自然语言处理中使用的密集表示(word2vec)所激发。所提出的block2vec表示,使World-GAN独立于不同块的数量,这在Minecraft中可能变化很大,并能生成更大的层次。改变这个新的表示空间可以改变已经训练好的生成器的生成风格。World-GAN使其用户能够根据他们创作的部分内容来生成Minecraft世界。本文用来自社区的创作以及用Minecraft世界生成器生成的结构进行了评估。
This work introduces World-GAN, the first method to perform data-driven Procedural Content Generation via Machine Learning in Minecraft from a single example. Based on a 3D Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) architecture, we are able to create arbitrarily sized world snippets from a given sample. We evaluate our approach on creations from the community as well as structures generated with the Minecraft World Generator. Our method is motivated by the dense representations used in Natural Language Processing (NLP) introduced with word2vec [1]. The proposed block2vec representations make World-GAN independent from the number of different blocks, which can vary a lot in Minecraft, and enable the generation of larger levels. Finally, we demonstrate that changing this new representation space allows us to change the generated style of an already trained generator. World-GAN enables its users to generate Minecraft worlds based on parts of their creations.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KliqCnLr6
2、[LG] Distributed Deep Learning in Open Collaborations
M Diskin, A Bukhtiyarov, M Ryabinin, L Saulnier, Q Lhoest, A Sinitsin, D Popov, D Pyrkin, M Kashirin, A Borzunov, A V d Moral, D Mazur, I Kobelev, Y Jernite, T Wolf, G Pekhimenko
[Yandex & Hugging Face & HSE University & University of Toronto]
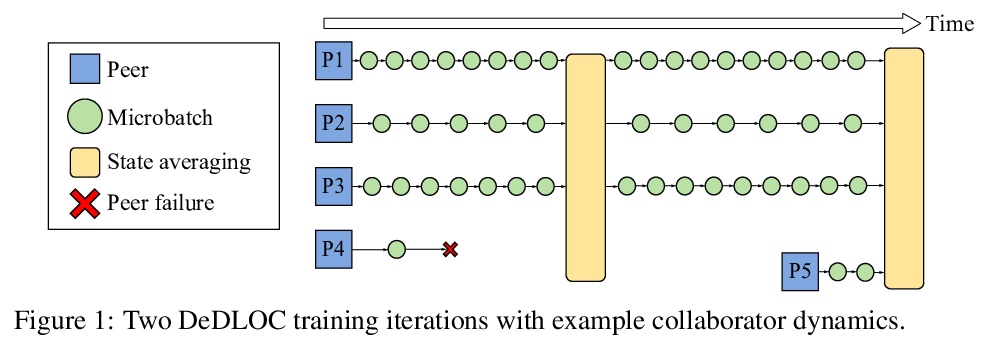
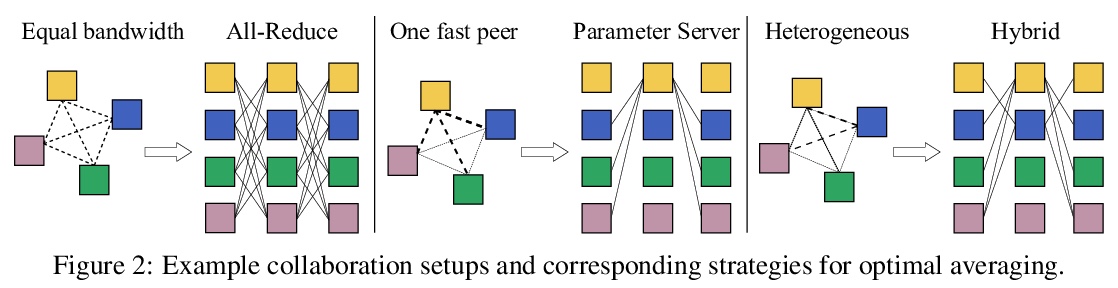
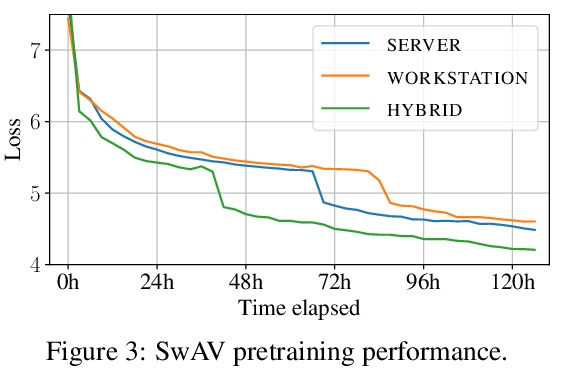
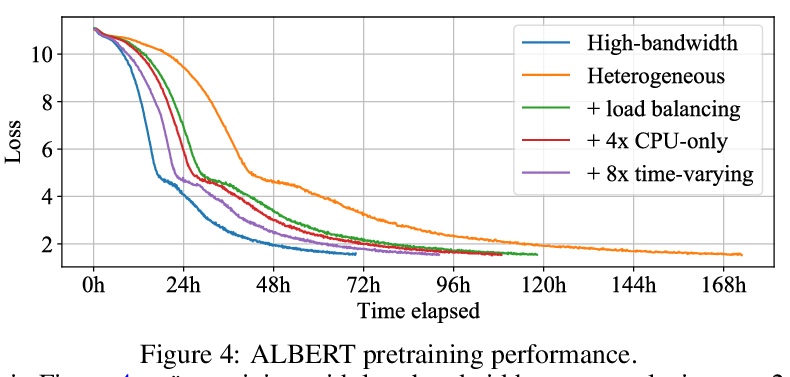
开放协作分布式深度学习。现代深度学习应用需要越来越多的计算来训练最先进的模型。为满足这一需求,大型企业和机构采用专用的高性能计算集群,其建设和维护既不利于环境,也远远超出了大多数组织的预算。因此,一些研究方向成为少数大型工业企业和更少的学术机构的专属领域。为缓解这种差异,较小团体可集中计算资源,进行协作实验,使所有参与者都受益。这种模式被称为网格计算或志愿者计算,已经在许多科学领域得到了成功的应用。然而,由于高延迟、不对称带宽以及志愿者计算所特有的几个挑战,将这种方法用于机器学习是很困难的。本文仔细分析了这些限制因素,提出一种专门为协作训练设计的新型算法框架,证明了该方法在现实条件下对SwAV和ALBERT进行预训练的有效性,并以很小的成本实现了与传统设置相媲美的性能。
Modern deep learning applications require increasingly more compute to train state-of-the-art models. To address this demand, large corporations and institutions use dedicated High-Performance Computing clusters, whose construction and maintenance are both environmentally costly and well beyond the budget of most organizations. As a result, some research directions become the exclusive domain of a few large industrial and even fewer academic actors. To alleviate this disparity, smaller groups may pool their computational resources and run collaborative experiments that benefit all participants. This paradigm, known as gridor volunteer computing, has seen successful applications in numerous scientific areas. However, using this approach for machine learning is difficult due to high latency, asymmetric bandwidth, and several challenges unique to volunteer computing. In this work, we carefully analyze these constraints and propose a novel algorithmic framework designed specifically for collaborative training. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach for SwAV and ALBERT pretraining in realistic conditions and achieve performance comparable to traditional setups at a fraction of the cost. Finally, we provide a detailed report of successful collaborative language model pretraining with 40 participants.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kliv1aqFi
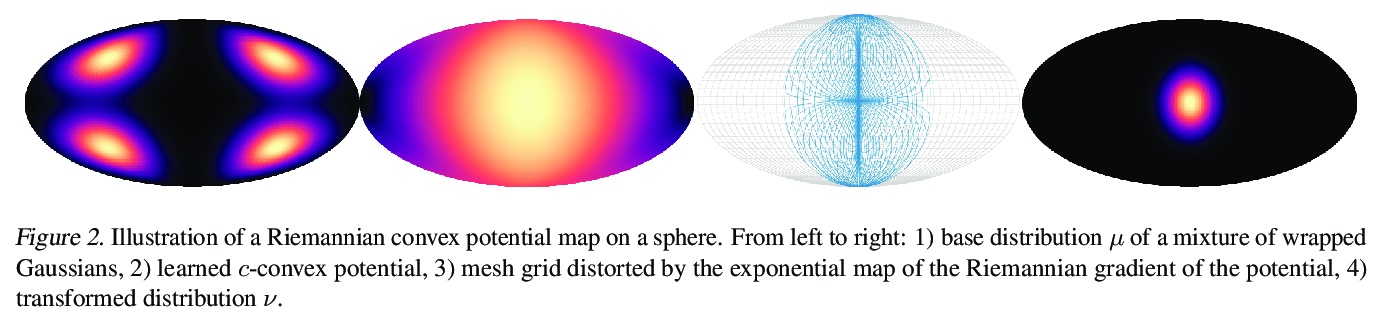
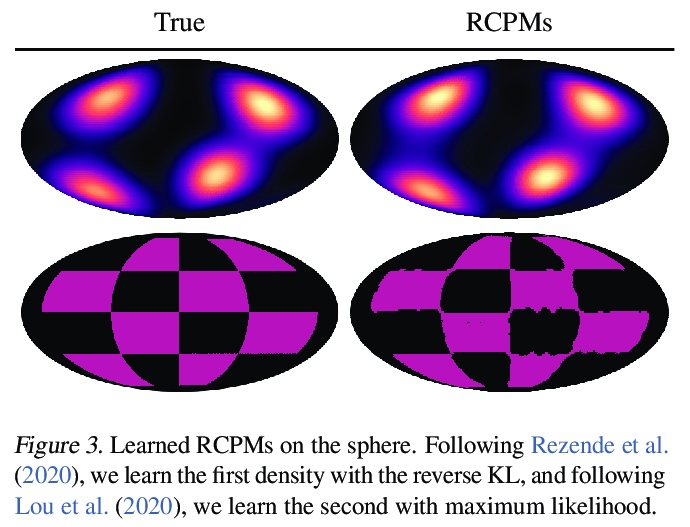
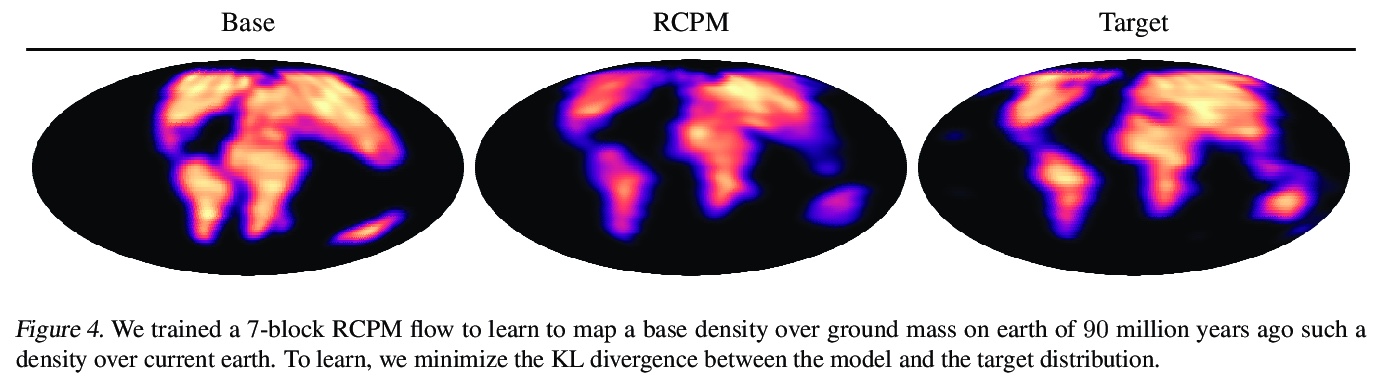
3、[LG] Riemannian Convex Potential Maps
S Cohen, B Amos, Y Lipman
[University College London & Facebook AI Research]
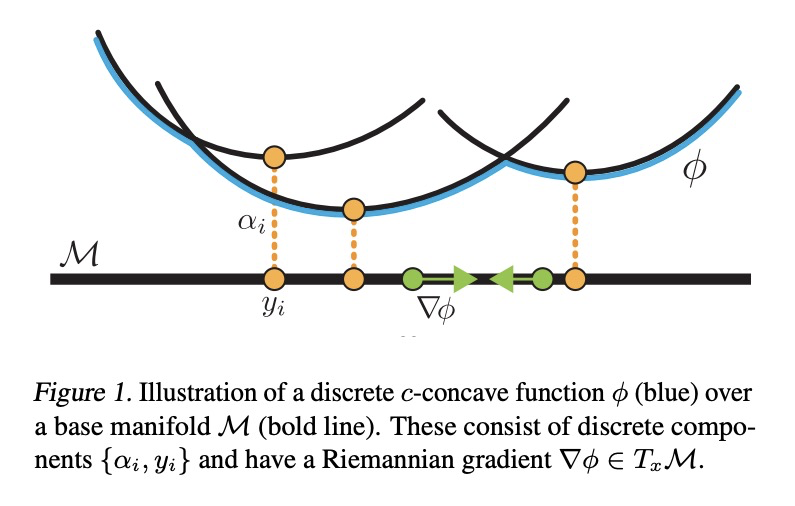
黎曼凸势映射。对黎曼流形上的分布进行建模,是理解非欧几里得数据的一个重要组成部分,例如在物理学和地质学中出现的数据。在这一领域,新兴的方法受到表示和计算权衡的限制。本文提出并研究了一类用黎曼最优传输的凸势的流。该模型是通用的,可以对任意紧凑的黎曼流形上的分布进行建模,而不需要将流形的领域知识整合到架构中。证明了这些流可以在合成和地质数据上模拟球体和环状的标准分布。
Modeling distributions on Riemannian manifolds is a crucial component in understanding nonEuclidean data that arises, e.g., in physics and geology. The budding approaches in this space are limited by representational and computational tradeoffs. We propose and study a class of flows that uses convex potentials from Riemannian optimal transport. These are universal and can model distributions on any compact Riemannian manifold without requiring domain knowledge of the manifold to be integrated into the architecture. We demonstrate that these flows can model standard distributions on spheres, and tori, on synthetic and geological data.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KlixDB2q8
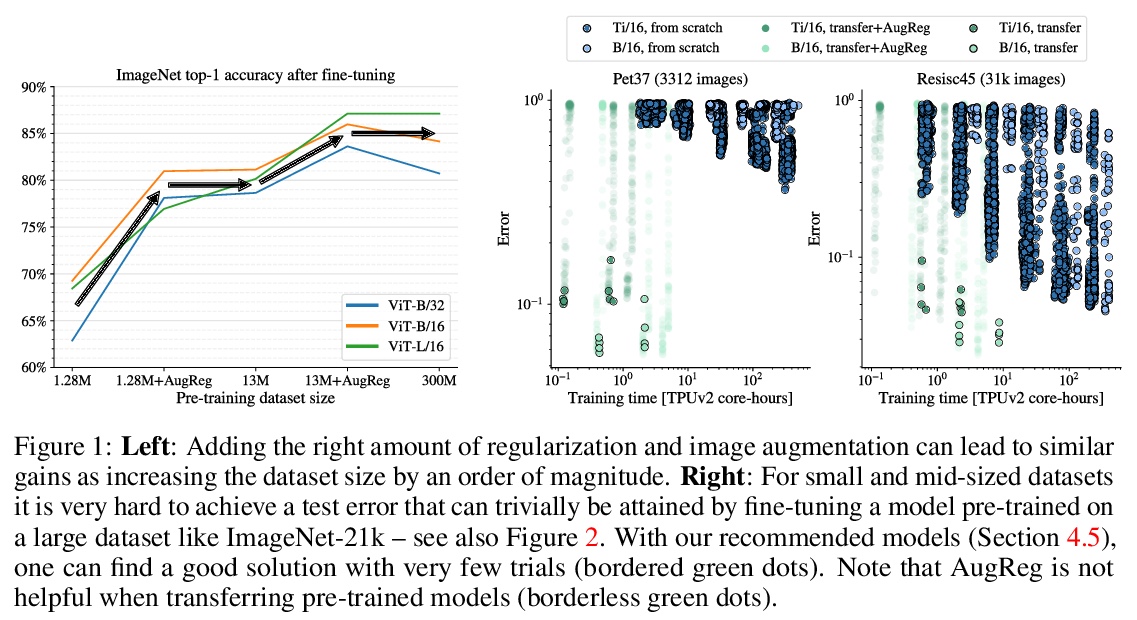
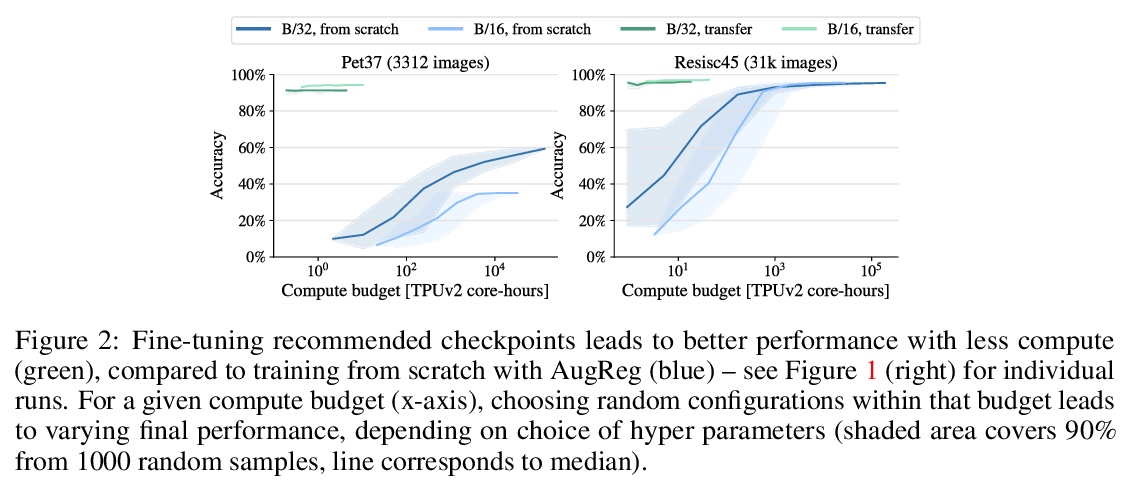
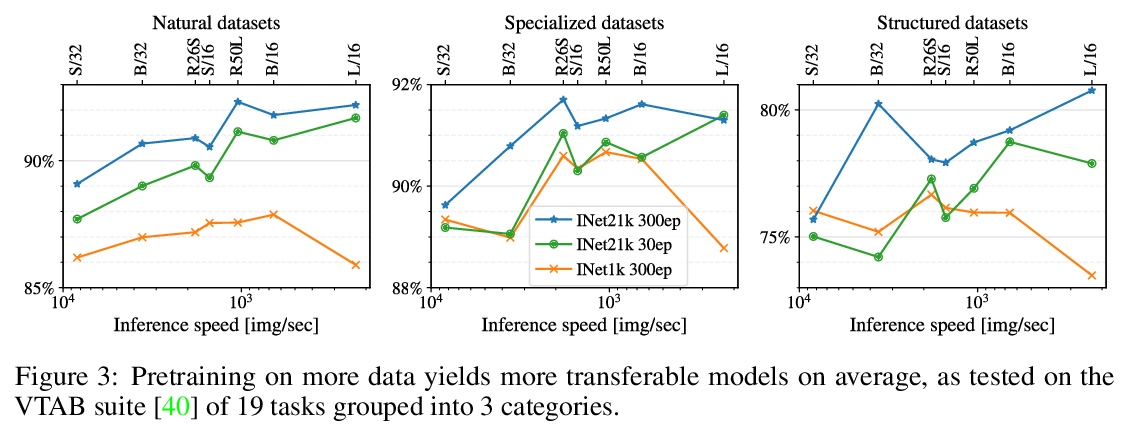
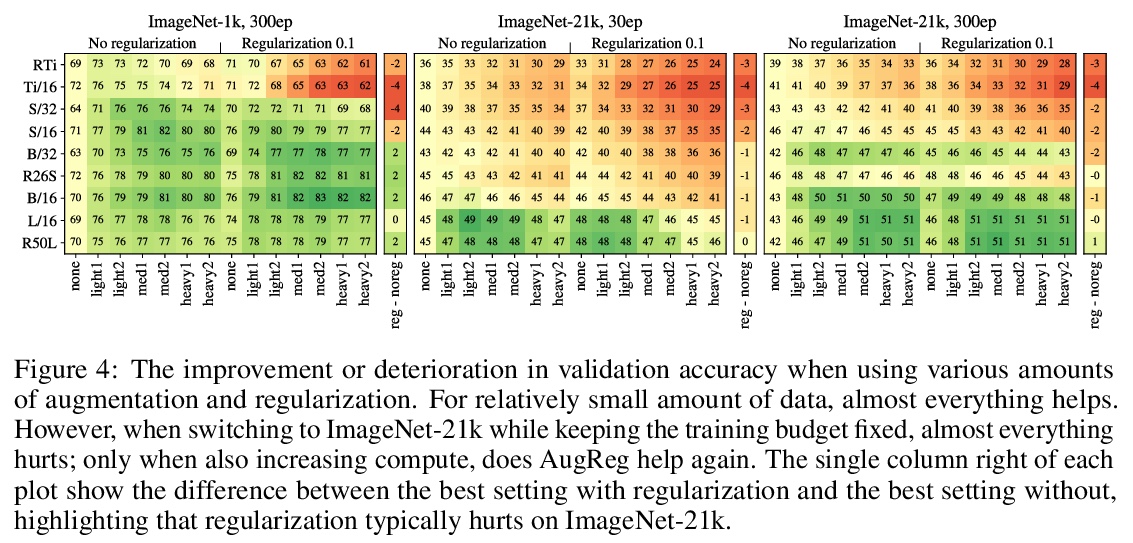
4、[CV] How to train your ViT? Data, Augmentation, and Regularization in Vision Transformers
A Steiner, A Kolesnikov, X Zhai, R Wightman, J Uszkoreit, L Beyer
[Google Research]
如何训练ViT?视觉Transformer的数据、增强和正则化。视觉Transformer(ViT)已被证明在广泛的视觉应用中取得了极具竞争力的性能,如图像分类、目标检测和语义图像分割。与卷积神经网络相比,视觉Transformer较弱的归纳偏差,通常被认为会导致在较小的训练数据集上训练时对模型正则化或数据增强(简称”AugReg”)的依赖性增加。本文进行了系统的实证研究,以便更好地理解训练数据量、AugReg、模型大小和计算预算之间的相互作用。作为这项研究的结果之一,发现增加计算量和AugReg的组合可以产生与在更多数量级的训练数据上训练的模型相同的性能:在公开的ImageNet-21k数据集上训练不同规模的ViT模型,这些模型与在更大的但不公开的JFT-300M数据集上训练的模型相匹配,甚至优于它们的表现。
Vision Transformers (ViT) have been shown to attain highly competitive performance for a wide range of vision applications, such as image classification, object detection and semantic image segmentation. In comparison to convolutional neural networks, the Vision Transformer’s weaker inductive bias is generally found to cause an increased reliance on model regularization or data augmentation (“AugReg” for short) when training on smaller training datasets. We conduct a systematic empirical study in order to better understand the interplay between the amount of training data, AugReg, model size and compute budget. 1 As one result of this study we find that the combination of increased compute and AugReg can yield models with the same performance as models trained on an order of magnitude more training data: we train ViT models of various sizes on the public ImageNet-21k dataset which either match or outperform their counterparts trained on the larger, but not publicly available JFT-300M dataset.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KliB1p5sF
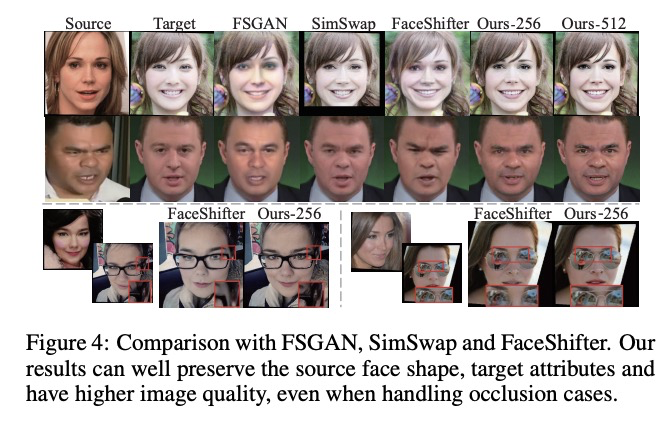
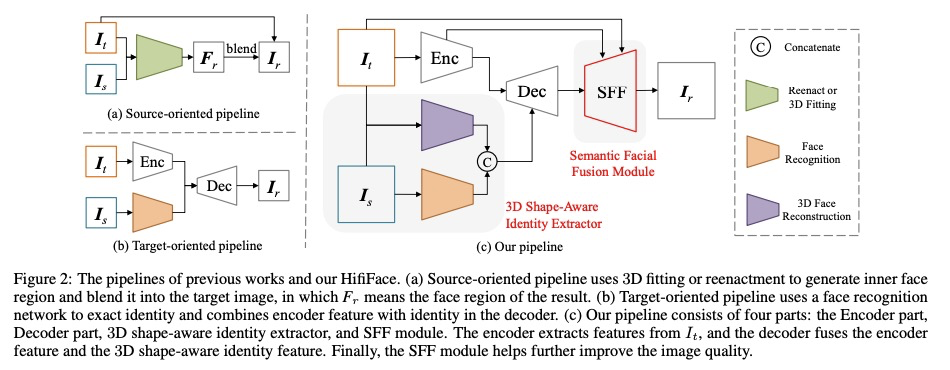
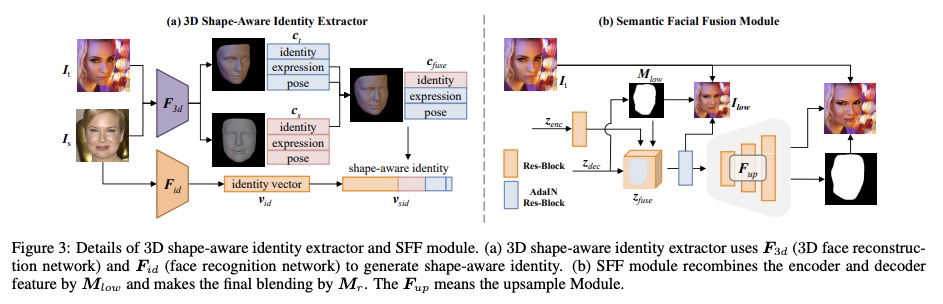
5、[CV] HifiFace: 3D Shape and Semantic Prior Guided High Fidelity Face Swapping
Y Wang, X Chen, J Zhu, W Chu, Y Tai, C Wang, J Li, Y Wu, F Huang, R Ji
[Tencent & Xiamen University]
HifiFace:三维形状和语义先验引导的高保真换脸。本文提出一种高保真的换脸方法HifiFace,可以很好地保留源脸的脸部形状,并产生照片般逼真的结果。与其他现有的只用人脸识别模型来保持身份相似性的换脸工作不同,本文提出了3D形状感知身份,用3DMM的几何监督和3D人脸重建方法来控制人脸形状。引入了语义人脸融合模块,对编码器和解码器的特征进行优化组合,并进行自适应混合,使结果更符合照片的真实性。在现实场景进行的大量人脸实验表明,该方法可以更好地保留身份,特别是在脸部形状上,并且可以比之前的最先进的方法产生更逼真的结果。
In this work, we propose a high fidelity face swapping method, called HifiFace, which can well preserve the face shape of the source face and generate photo-realistic results. Unlike other existing face swapping works that only use face recognition model to keep the identity similarity, we propose 3D shape-aware identity to control the face shape with the geometric supervision from 3DMM and 3D face reconstruction method. Meanwhile, we introduce the Semantic Facial Fusion module to optimize the combination of encoder and decoder features and make adaptive blending, which makes the results more photo-realistic. Extensive experiments on faces in the wild demonstrate that our method can preserve better identity, especially on the face shape, and can generate more photo-realistic results than previous state-of-the-art methods.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KliE57zmV


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
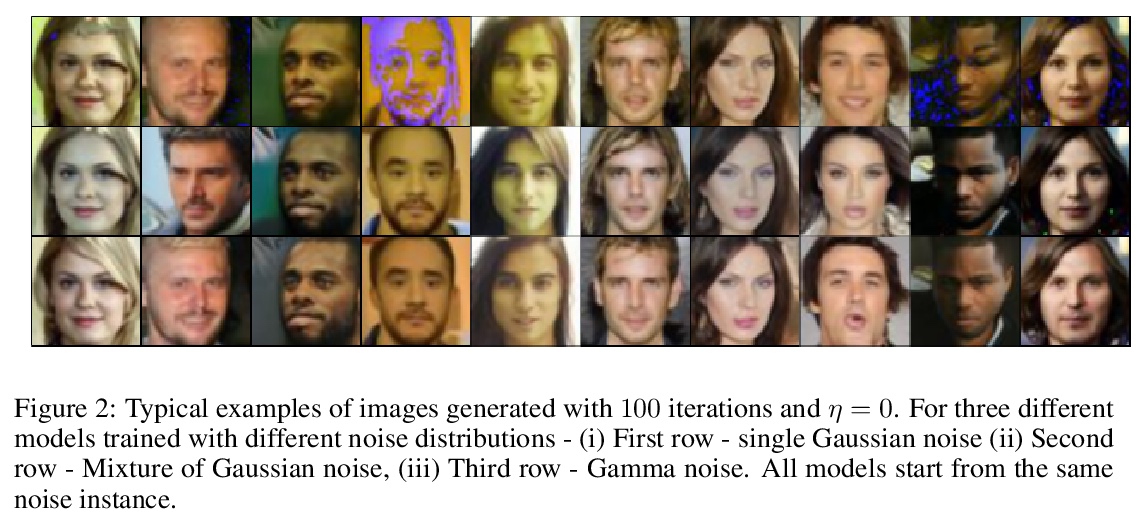
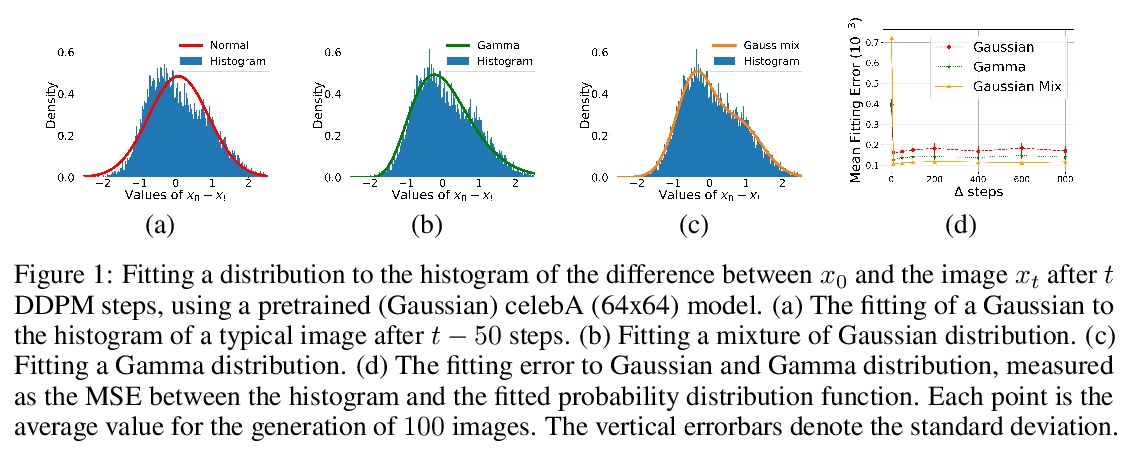
[LG] Non Gaussian Denoising Diffusion Models
非高斯去噪扩散模型
E Nachmani, R S Roman, L Wolf
[Tel-Aviv University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KliHcmzme

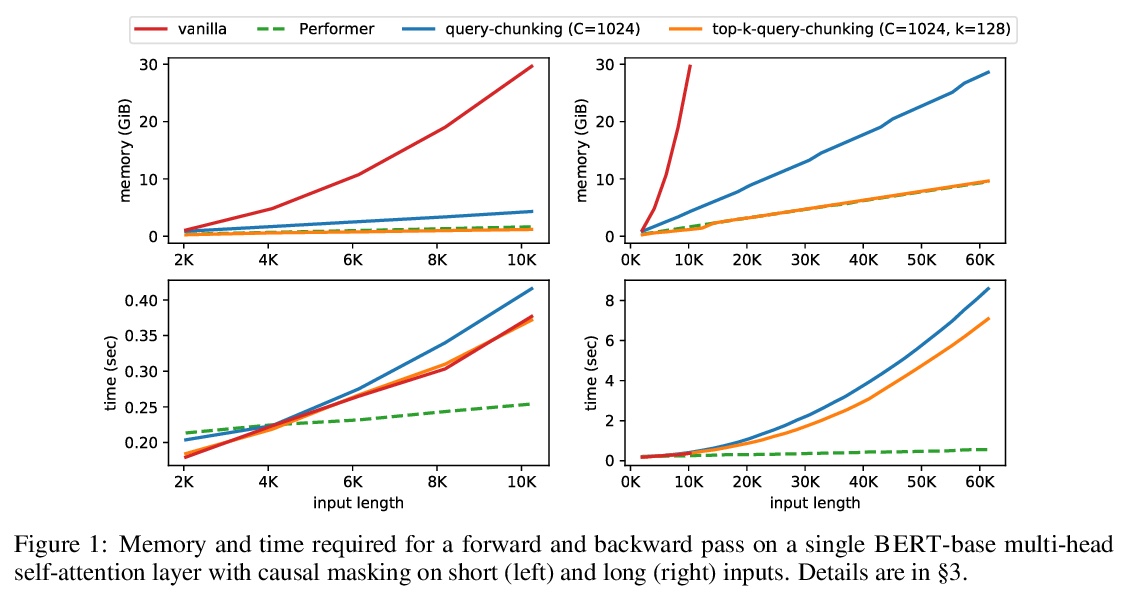
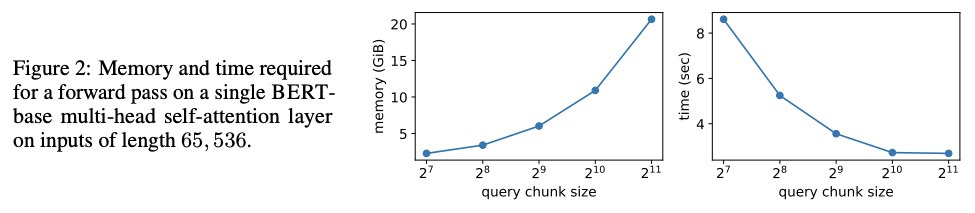
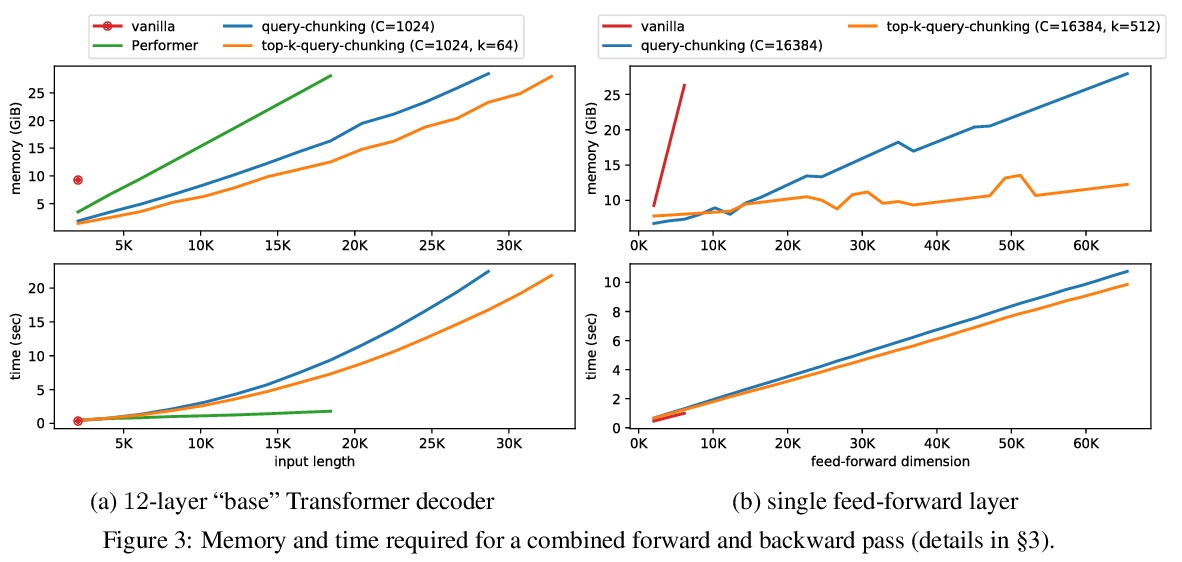
[CL] Memory-efficient Transformers via Top-k Attention
基于Top-k注意力的记忆高效Transformer
A Gupta, G Dar, S Goodman, D Ciprut, J Berant
[IBM Research & Tel Aviv University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KliII44t7
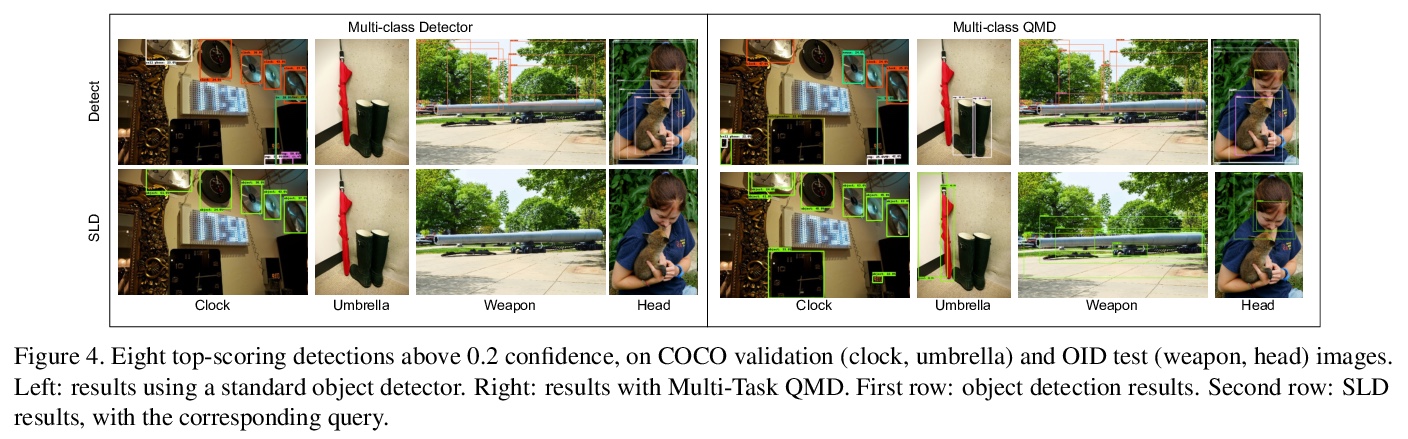
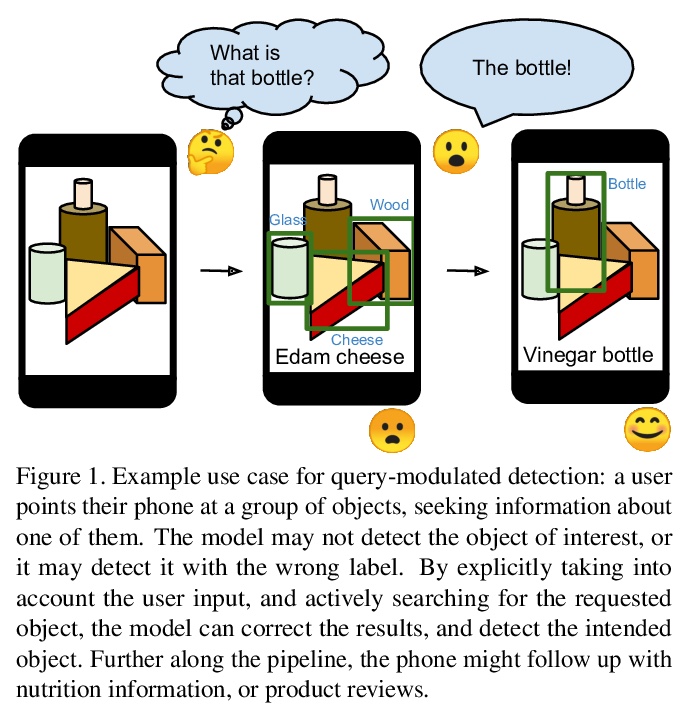
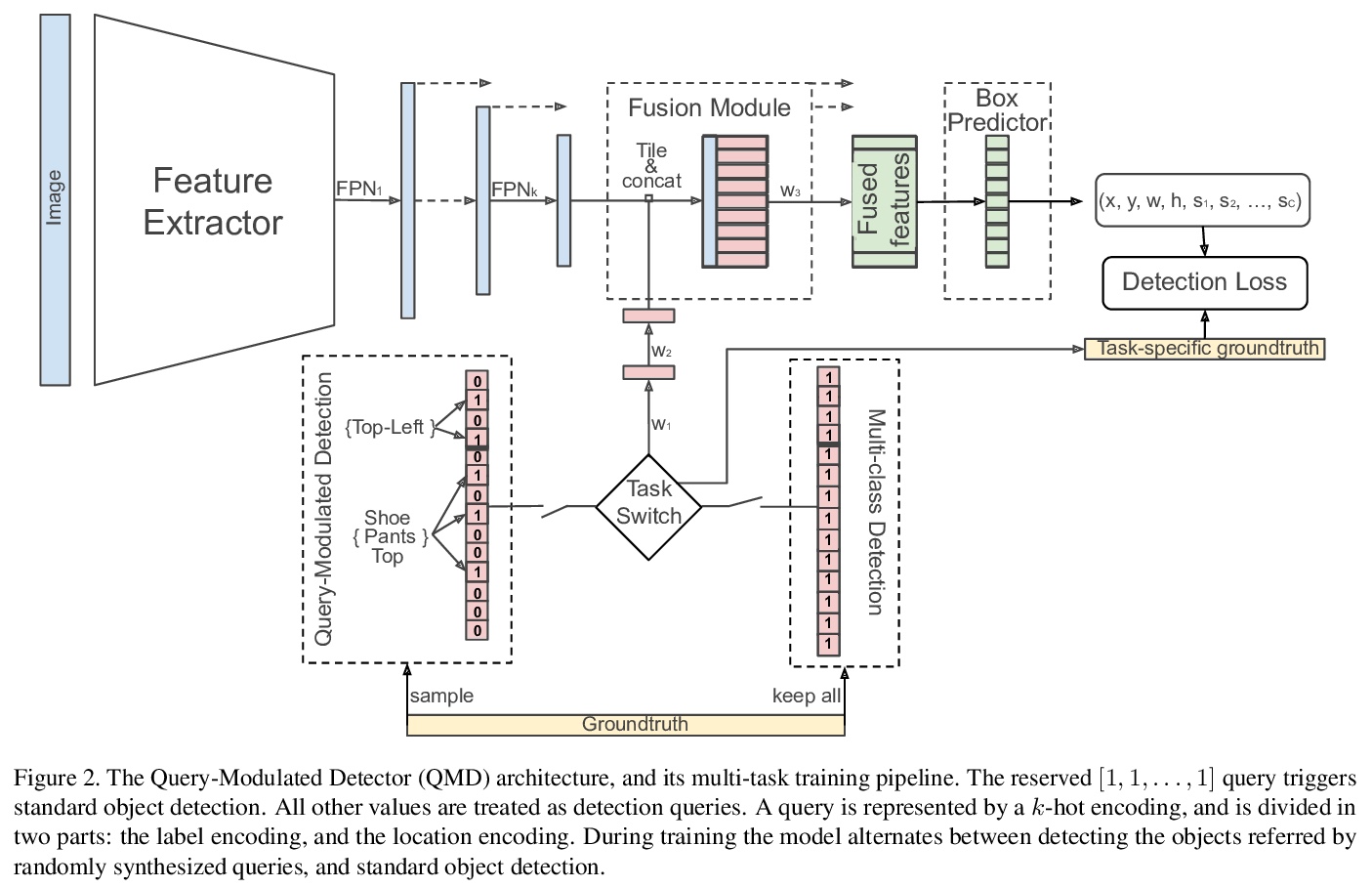
[CV] Bridging the Gap Between Object Detection and User Intent via Query-Modulation
通过查询-调制弥合目标检测和用户意图间的差距
M Fornoni, C Yan, L Luo, K Wilber, A Stark, Y Cui, B Gong, A Howard
[Google Research & University of Texas at Arlington]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KliKDqDbA

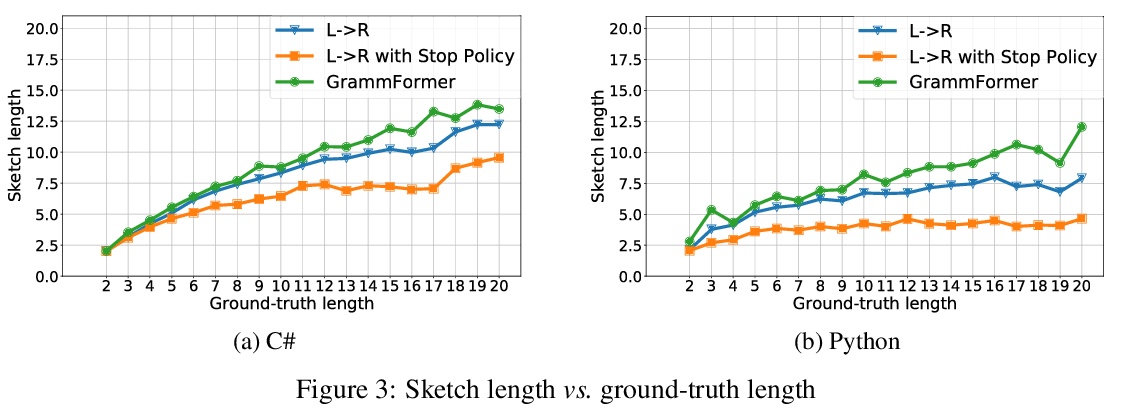
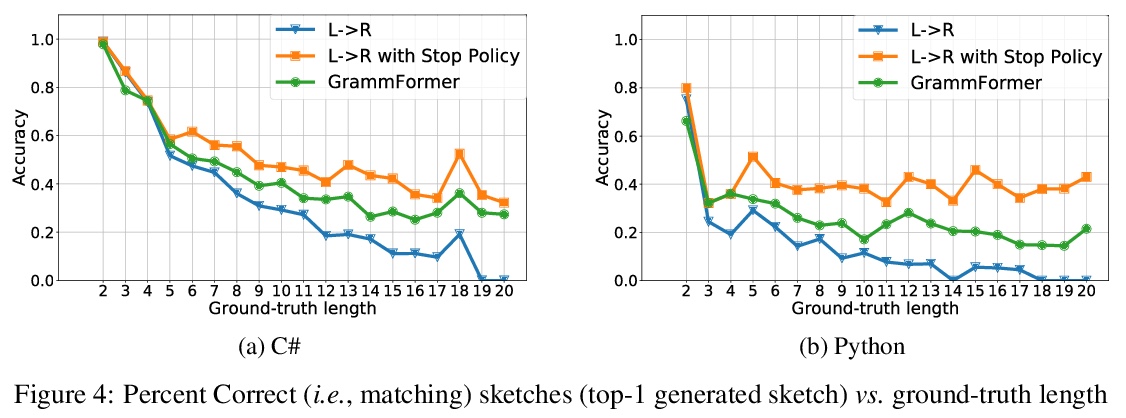
[LG] Learning to Generate Code Sketches
草代码生成学习
D Guo, A Svyatkovskiy, J Yin, N Duan, M Brockschmidt, M Allamanis
[Microsoft Research & Microsoft & Sun Yat-sen University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KliMx6sno