- 1、[LG] Deep Probabilistic Graphical Modeling
- 2、[CV] EigenGAN: Layer-Wise Eigen-Learning for GANs
- 3、[CV] Visformer: The Vision-friendly Transformer
- 4、[CV] MDETR — Modulated Detection for End-to-End Multi-Modal Understanding
- 5、[CV] Improve Vision Transformers Training by Suppressing Over-smoothing
- [CV] Towards Good Practices for Efficiently Annotating Large-Scale Image Classification Datasets
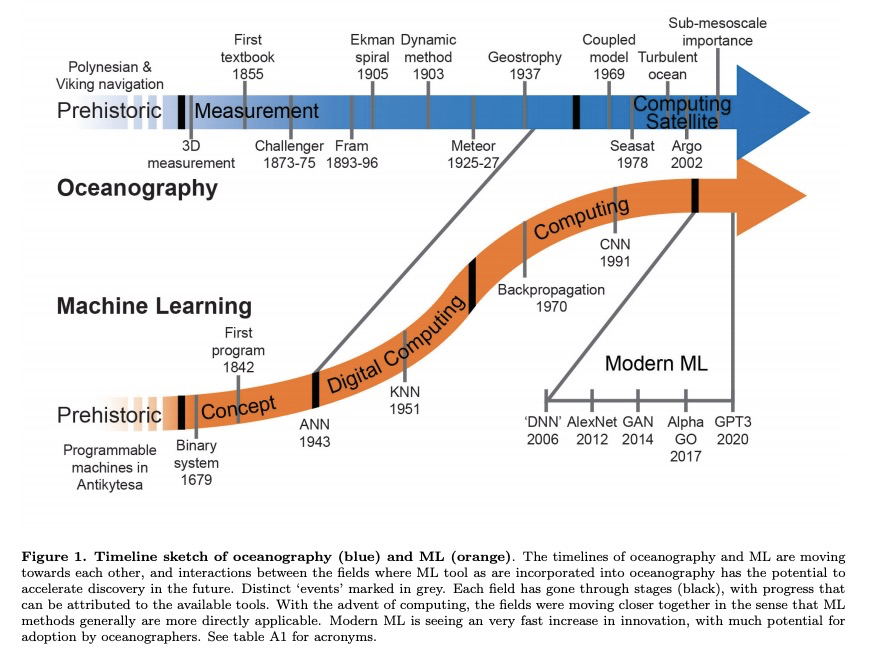
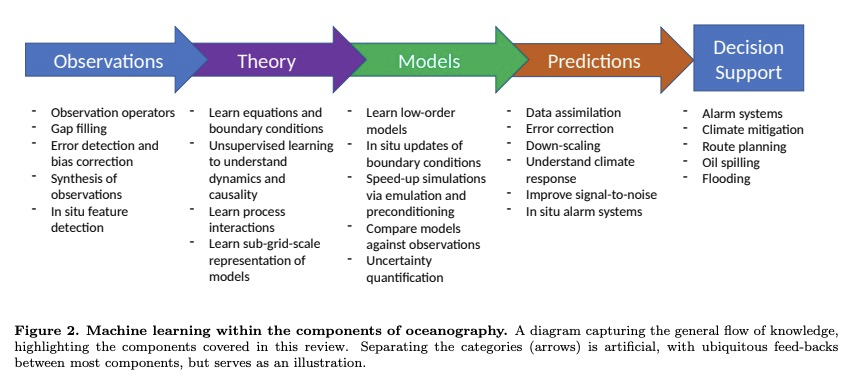
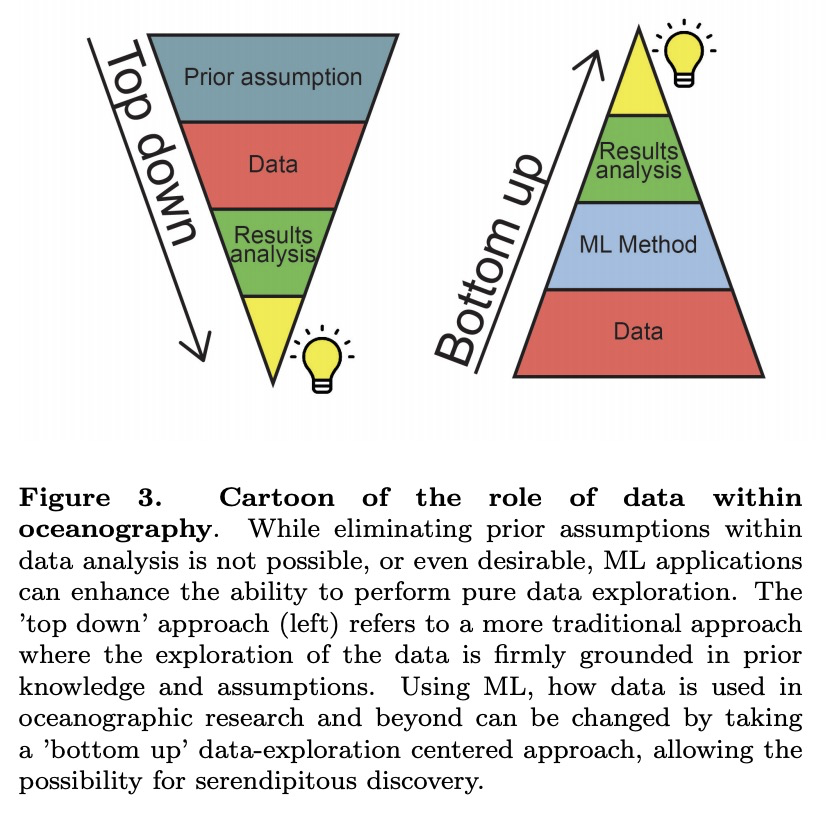
- [LG] Bridging observation, theory and numerical simulation of the ocean using Machine Learning
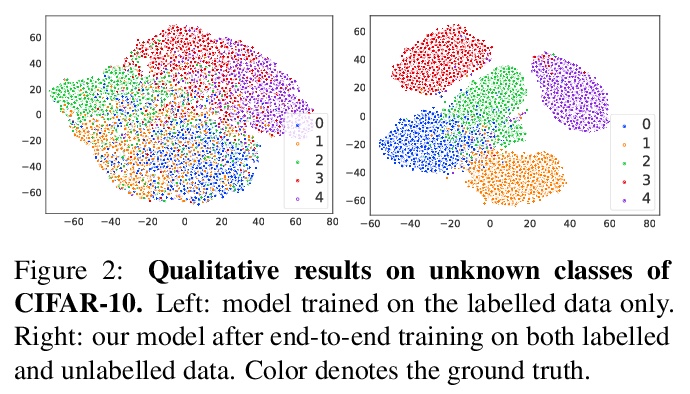
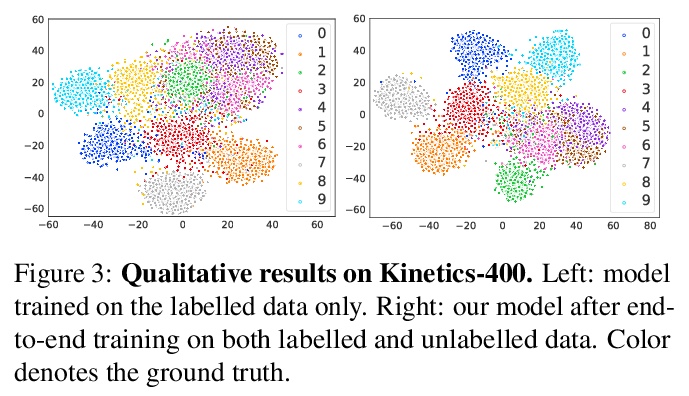
- [CV] Joint Representation Learning and Novel Category Discovery on Single- and Multi-modal Data
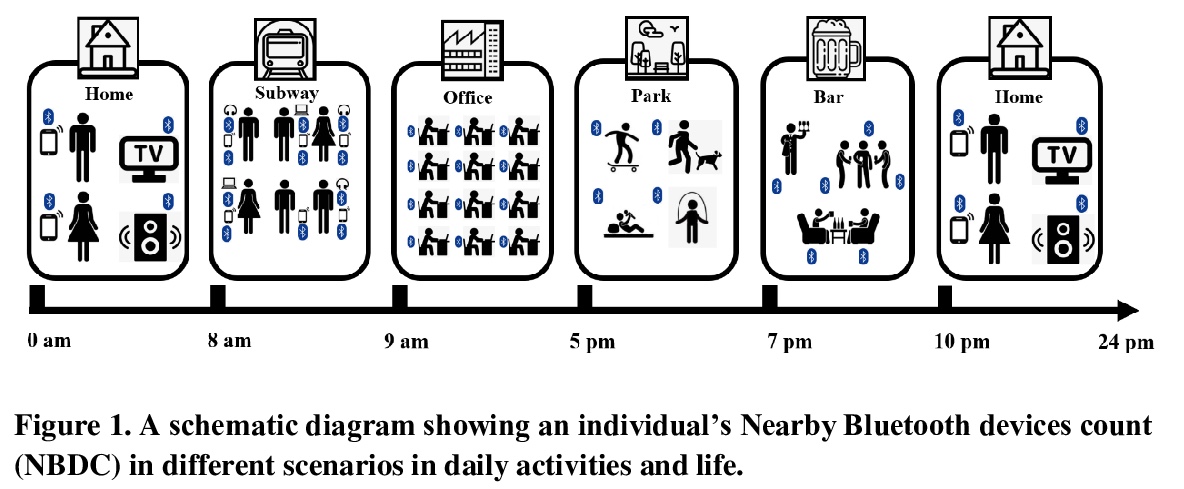
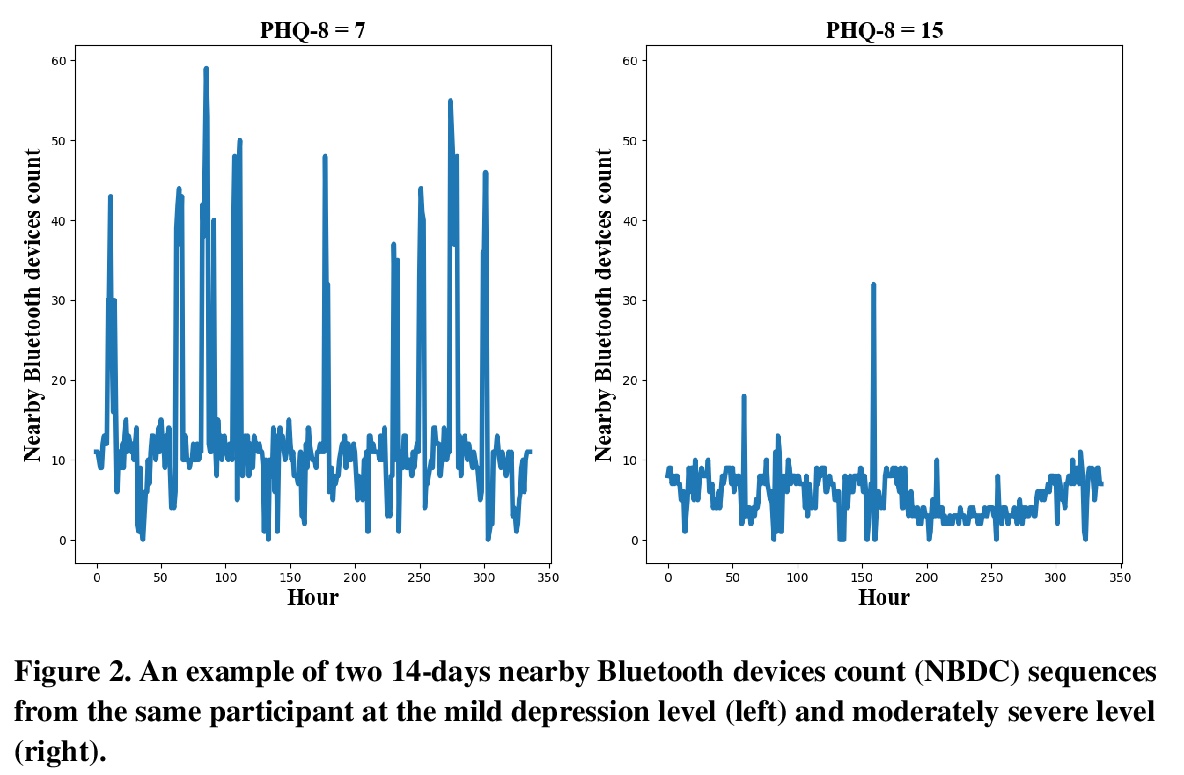
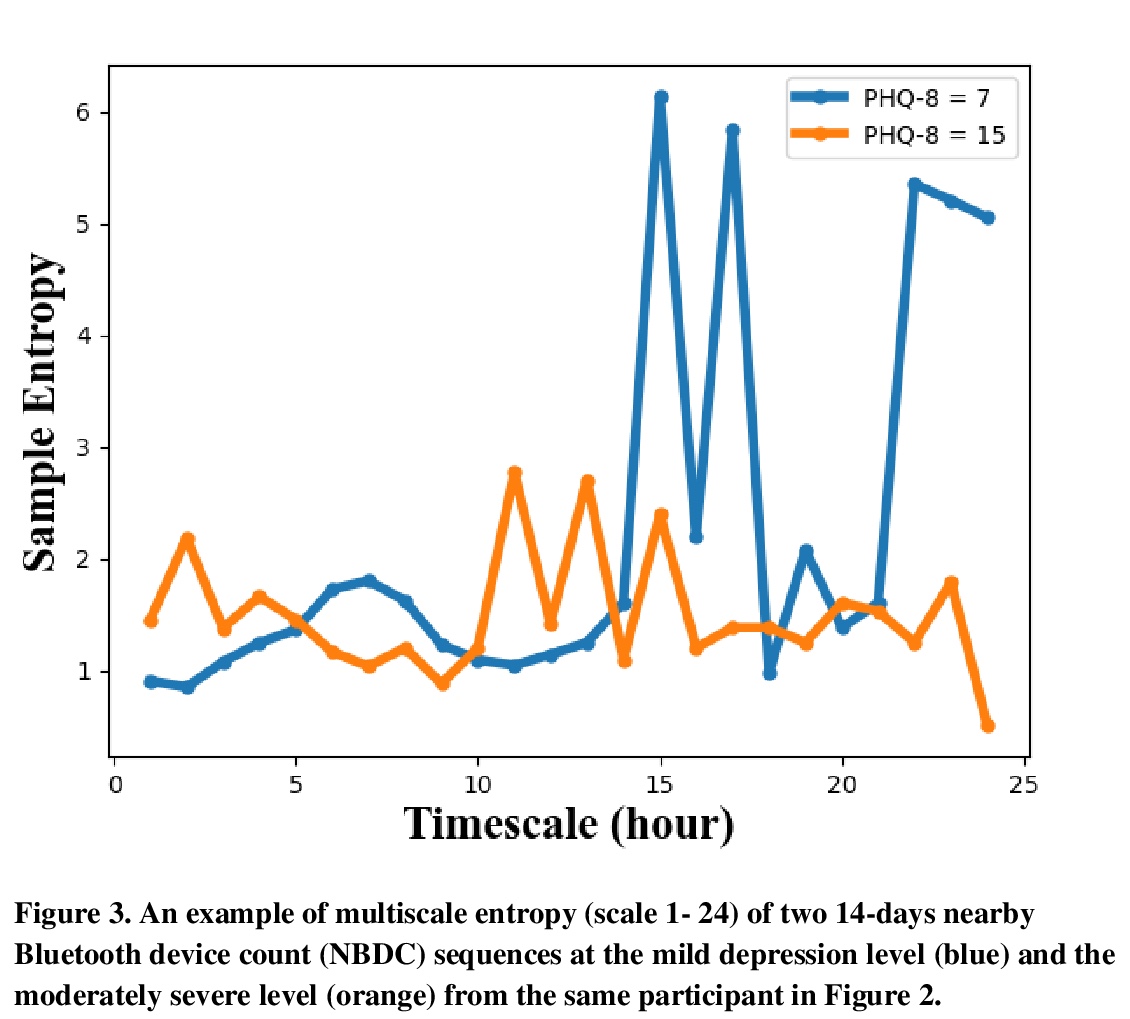
- [LG] Predicting Depressive Symptom Severity through Individuals’ Nearby Bluetooth Devices Count Data Collected by Mobile Phones: A Preliminary Longitudinal Study
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
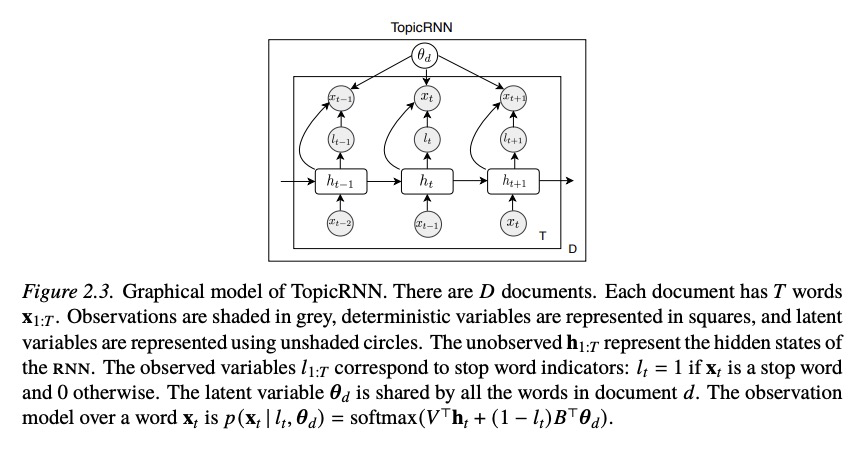
1、[LG] Deep Probabilistic Graphical Modeling
A B. Dieng
[Columbia University]
深度概率图建模。概率图解建模(PGM)提供了一个框架,用于构造数据的可解释生成过程,并表达未知的不确定性。这使得PGM对于理解数据背后的现象和决策非常有用。PGM已经成功地应用于可解释推论非常关键的领域,如市场营销、医学、神经科学和社会科学。然而,PGM往往缺乏灵活性,往往无法用于大规模高维复杂数据的建模和执行需要灵活性的任务,例如视觉和语言应用。深度学习是用于建模和从数据中学习的替代框架,近年来在经验上取得了巨大的成功。深度学习非常强大,提供了很大的灵活性,但缺乏PGM的可解释性和校准性。本文提出深度概率图建模(DPGM),利用深度学习使PGM更灵活,带来了从数据中学习的新方法,结合了PGM和深度学习的优点。在PGM中使用深度学习建立灵活的模型,并赋予其可解释的潜在结构。所提出一个模型族用神经网络扩展了指数族主成分分析(EF-PCA),以提高预测性能,同时强制执行潜在因素的可解释性。所提出的另一个模型族在为连续数据建模时能够考虑到长程依赖性,这在使用纯粹的深度学习或PGM方法时是一个挑战。该用于连续数据的模型族被成功应用于语言建模、面向情感分析的无监督文档表示学习、对话建模和用于医院再入院预测的病人表示学习。最后,DPGM成功解决了概率主题模型的几个突出问题,是一个广泛使用的概率图模型族。在PGM中利用深度学习也带来了新的算法,用于复杂数据的学习。开发了重加权期望最大化(Reweighted Expectation Maximization,REM),统一了现有的几种基于最大似然的算法,用于学习由深度神经网络参数化的模型。这种统一观点是通过期望最大化来实现的,期望最大化是PGM中的一种典型推理算法。开发了熵-正则化对抗学习,一种偏离PGM中使用的传统最大似然法的学习范式。从深度学习的角度,熵-正则化对抗学习为生成对抗网络(GAN)长期存在的模式崩溃问题提供了一个解决方案。
Deep Probabilistic Graphical Modeling Adji Bousso Dieng Probabilistic graphical modeling (pgm) provides a framework for formulating an interpretable generative process of data and expressing uncertainty about unknowns. This makes pgm very useful for understanding the phenomena underlying data and for decision making. pgm has been successfully used in domains where interpretable inferences are key, e.g. marketing, medicine, neuroscience, and the social sciences. However pgm tends to lack flexibility. This lack of flexibility makes pgm often inadequate for modeling large-scale high-dimensional complex data and performing tasks that do require flexibility, e.g. vision and language applications. Deep learning (dl) is an alternative framework for modeling and learning from data that has seen great empirical success in recent years. dl is very powerful and offers great flexibility, but it lacks the interpretability and calibration of pgm. This thesis develops deep probabilistic graphical modeling (dpgm). dpgm consists in leveraging dl to make pgm more flexible. dpgm brings about new methods for learning from data that exhibit the advantages of both pgm and dl. We use dl within pgm to build flexible models endowed with an interpretable latent structure. One family of models we develop extends exponential family principal component analysis (ef-pca) using neural networks to improve predictive performance while enforcing the interpretability of the latent factors. Another model class we introduce enables accounting for long-term dependencies when modeling sequential data, which is a challenge when using purely dl or pgm approaches. This model class for sequential data was successfully applied to language modeling, unsupervised document representation learning for sentiment analysis, conversation modeling, and patient representation learning for hospital readmission prediction. Finally, dpgm successfully solves several outstanding problems of probabilistic topic models, a widely used family of probabilistic graphical models. Leveraging dl within pgm also brings about new algorithms for learning with complex data. We develop reweighted expectation maximization (rem), an algorithm that unifies several existing maximum likelihood-based algorithms for learning models parameterized by deep neural networks. This unifying view is made possible using expectation maximization, a canonical inference algorithm in pgm. We also develop entropy-regularized adversarial learning, a learning paradigm that deviates from the traditional maximum likelihood approach used in pgm. From the dl perspective, entropyregularized adversarial learning provides a solution to the long-standing mode collapse problem of generative adversarial networks (gans), a widely used dl approach.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcVTVbkbr

2、[CV] EigenGAN: Layer-Wise Eigen-Learning for GANs
Z He, M Kan, S Shan
[ICT]
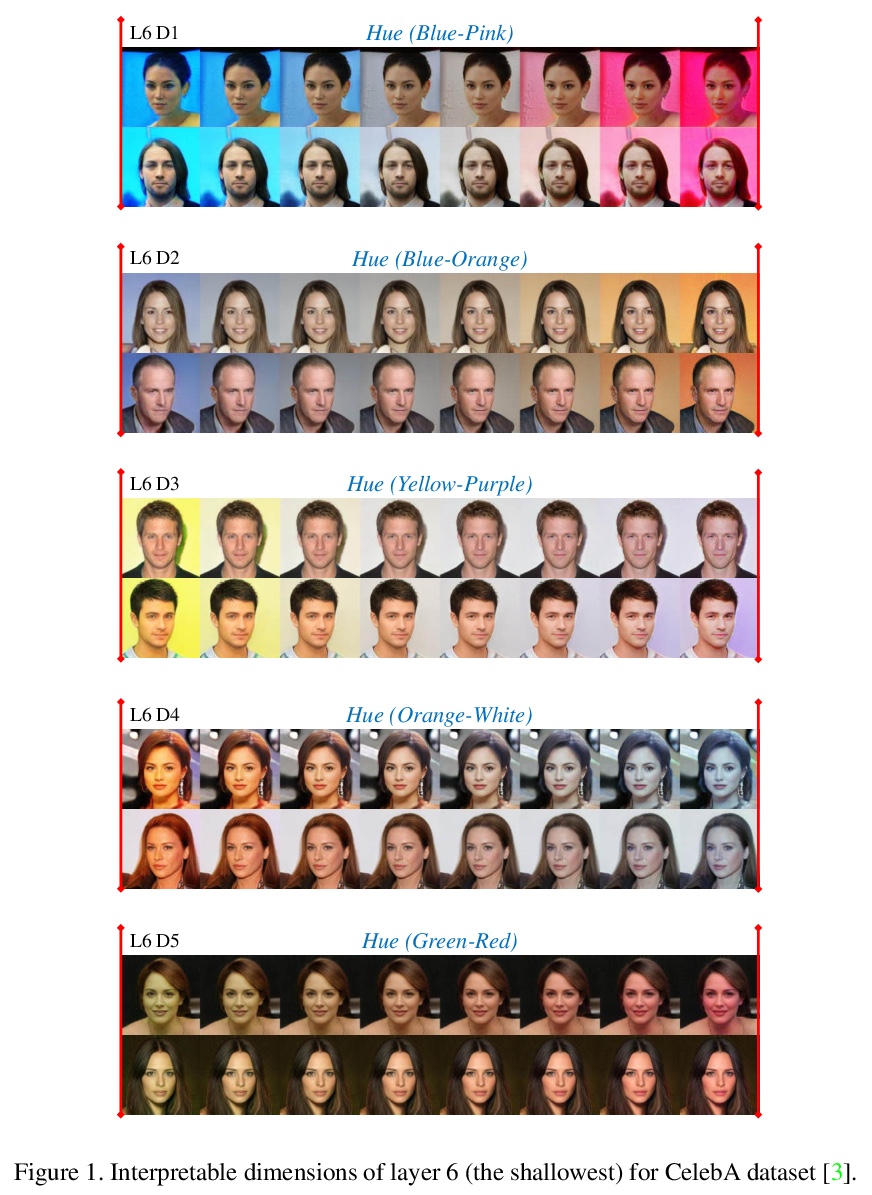
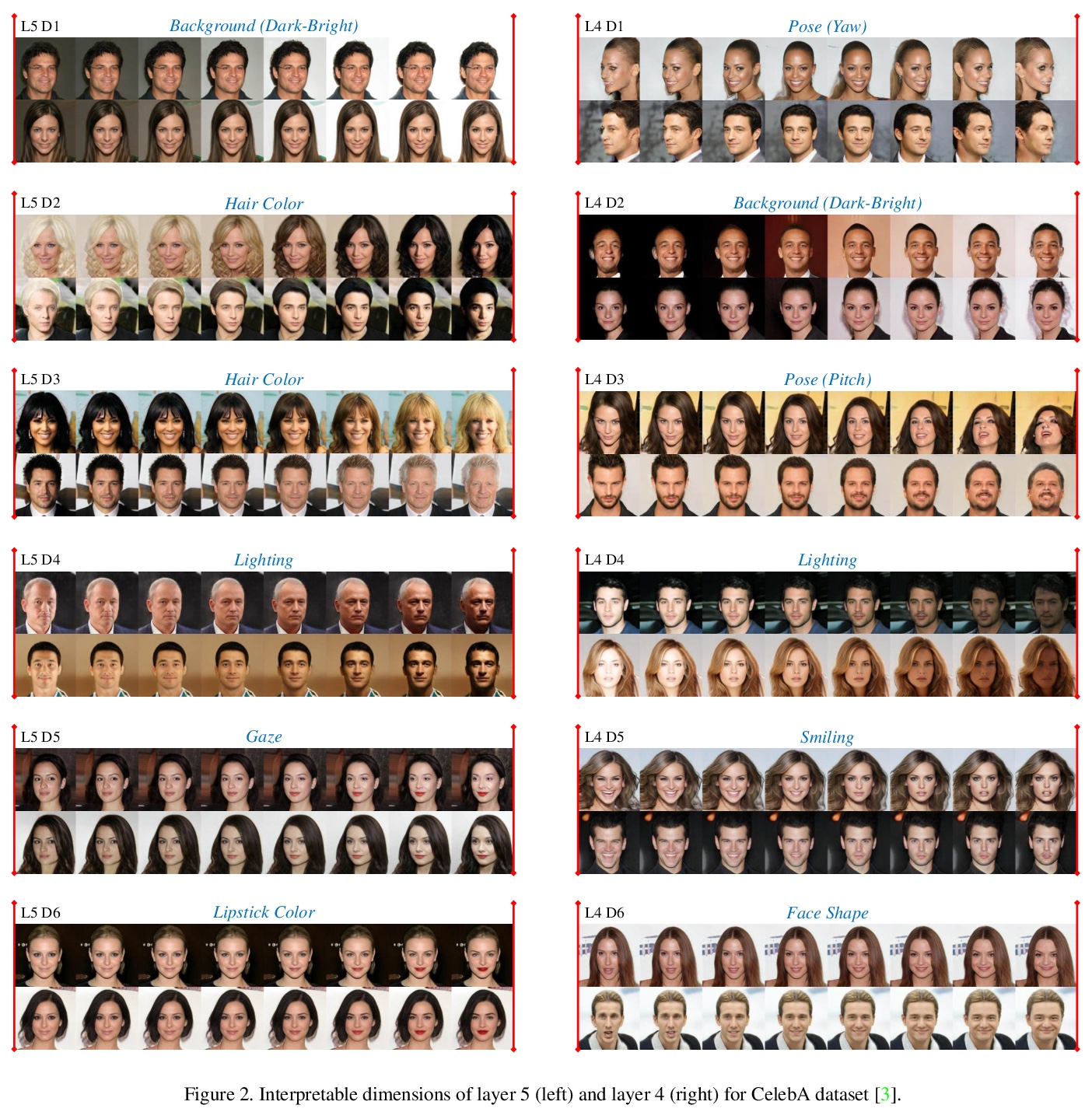
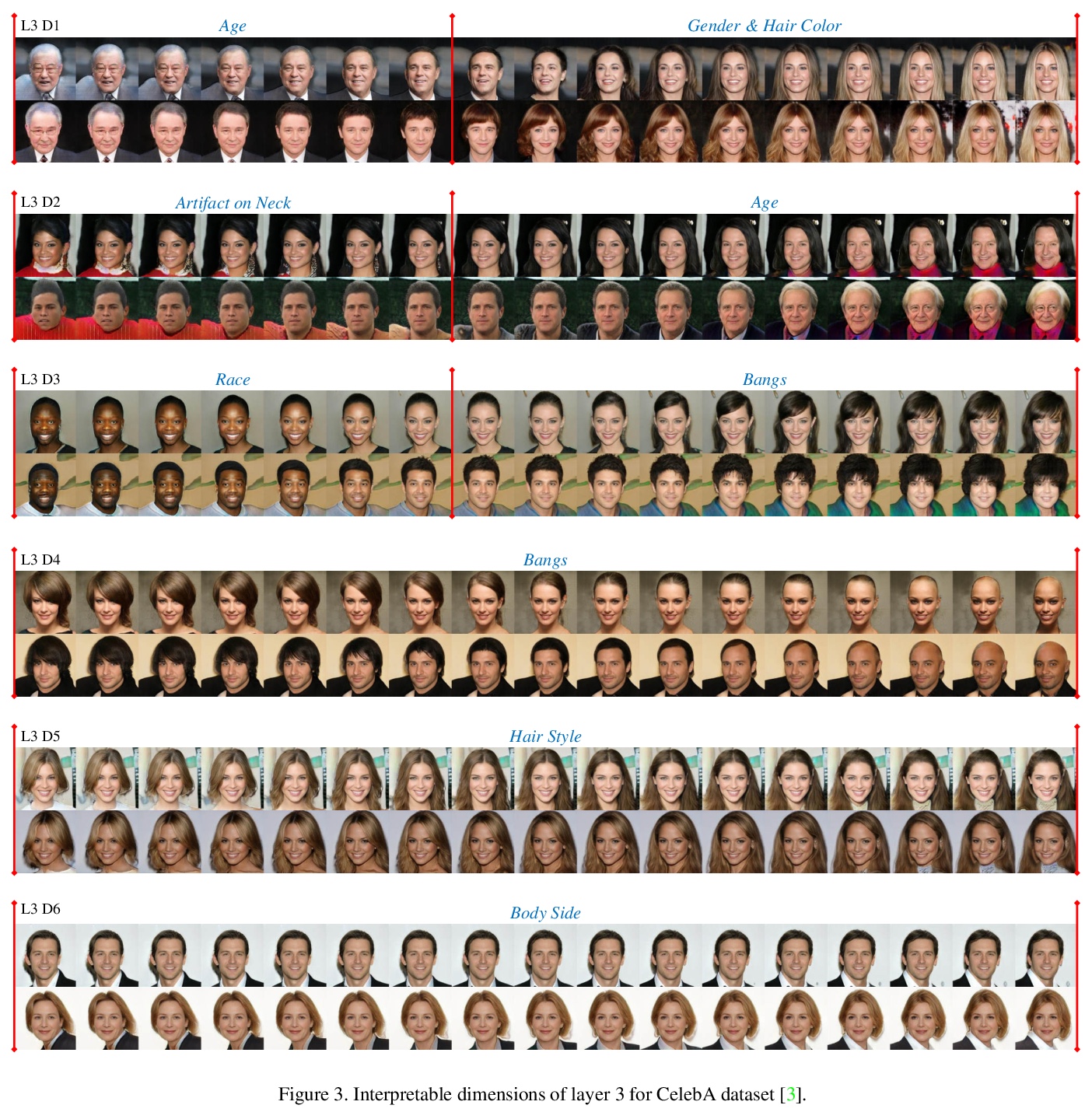
EigenGAN:GAN的分层感知特征学习。最近关于生成式对抗网络(GAN)的研究显示,生成式CNN的不同层对应了合成图像的不同语义。然而,很少有GAN模型有明确的维度来控制特定层中的语义属性。本文提出EigenGAN,能无监督地从不同的生成器层中挖掘可解释和可控制的维度。EigenGAN将一个具有正交基的线性子空间嵌入到每个生成器层。通过对抗训练来学习目标分布,这些层的子空间会在每一层自动发现一组”特征维”,对应于一组语义属性或可解释的变化。通过遍历特定特征维的系数,生成器可产生对应于特定语义属性的具有连续变化的样本。以人脸为例,EigenGAN可发现深层子空间中姿态和性别等高级概念的可控维度,以及浅层子空间中色调和颜色等低级概念。在线性情况下,从理论上证明了该算法能像PCA那样得出主成分。
Recent studies on Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) reveal that different layers of a generative CNN hold different semantics of the synthesized images. However, few GAN models have explicit dimensions to control the semantic attributes represented in a specific layer. This paper proposes EigenGAN which is able to unsupervisedly mine interpretable and controllable dimensions from different generator layers. Specifically, EigenGAN embeds one linear subspace with orthogonal basis into each generator layer. Via the adversarial training to learn a target distribution, these layer-wise subspaces automatically discover a set of “eigen-dimensions” at each layer corresponding to a set of semantic attributes or interpretable variations. By traversing the coefficient of a specific eigen-dimension, the generator can produce samples with continuous changes corresponding to a specific semantic attribute. Taking the human face for example, EigenGAN can discover controllable dimensions for high-level concepts such as pose and gender in the subspace of deep layers, as well as low-level concepts such as hue and color in the subspace of shallow layers. Moreover, under the linear circumstance, we theoretically prove that our algorithm derives the principal components as PCA does. Codes can be found inthis https URL.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcW0f43aD



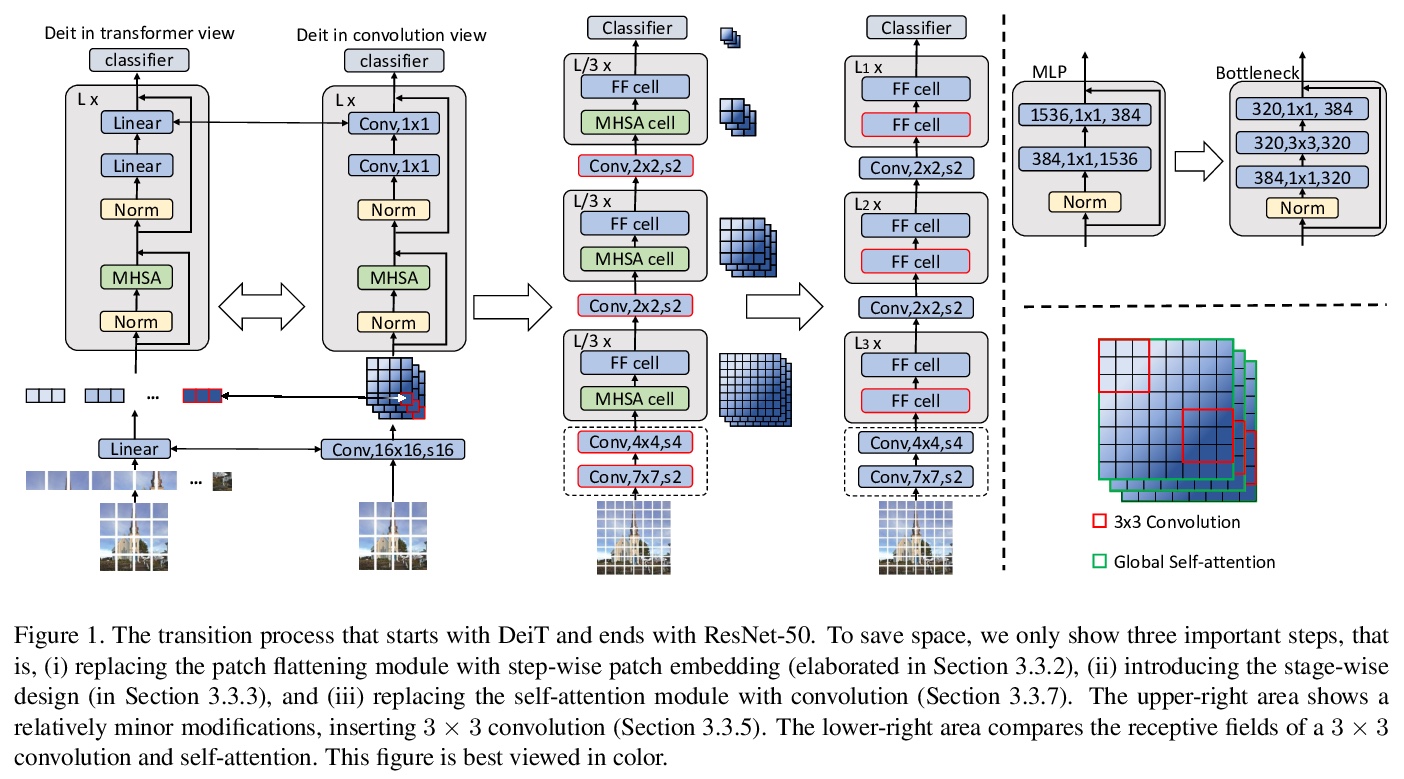
3、[CV] Visformer: The Vision-friendly Transformer
Z Chen, L Xie, J Niu, X Liu, L Wei, Q Tian
[Beihang University & Johns Hopkins University & Peking University & Xidian University]
Visformer:视觉友好Transformer。过去一年里,将Transformer模块应用于视觉问题的研究得到了快速发展。尽管已证明基于Transformer的模型具有良好的数据拟合能力,但越来越多的证据表明,这些模型存在过拟合问题,尤其是在训练数据有限的情况下。本文提供了实证研究,通过一步步操作,将基于Transformer的模型逐步过渡到基于卷积的模型。在转换过程中得到的结果,为改善视觉识别提供了有用的信息。基于这些观察,提出一个新的架构Visformer,”视觉友好型Transformer”。在计算复杂度相同的情况下,Visformer在ImageNet分类准确率方面优于基于Transformer的模型和基于卷积的模型,在模型复杂度较低或训练集较小的情况下,优势变得更加明显。
The past year has witnessed the rapid development of applying the Transformer module to vision problems. While some researchers have demonstrated that Transformer-based models enjoy a favorable ability of fitting data, there are still growing number of evidences showing that these models suffer over-fitting especially when the training data is limited. This paper offers an empirical study by performing step-by-step operations to gradually transit a Transformer-based model to a convolution-based model. The results we obtain during the transition process deliver useful messages for improving visual recognition. Based on these observations, we propose a new architecture named Visformer, which is abbreviated from the `Vision-friendly Transformer’. With the same computational complexity, Visformer outperforms both the Transformer-based and convolution-based models in terms of ImageNet classification accuracy, and the advantage becomes more significant when the model complexity is lower or the training set is smaller. The code is available atthis https URL.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcW3AsSMq
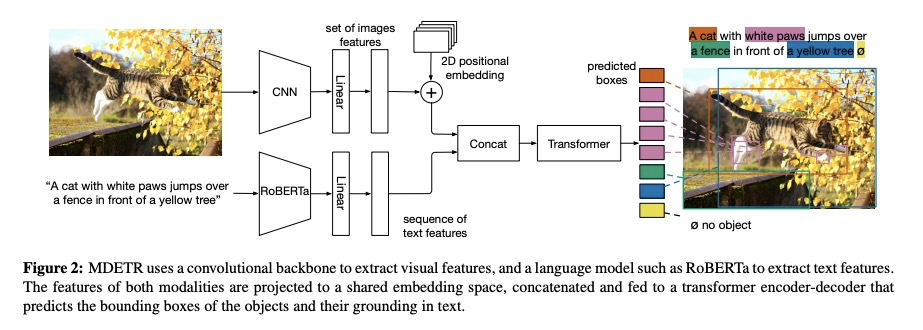
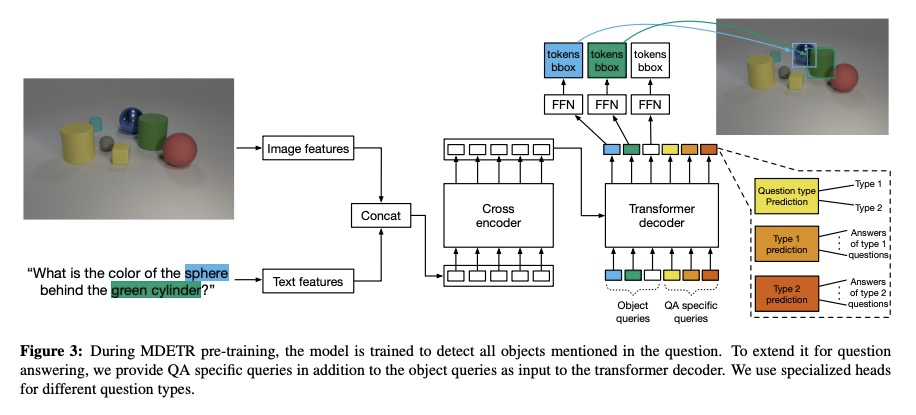
4、[CV] MDETR — Modulated Detection for End-to-End Multi-Modal Understanding
A Kamath, M Singh, Y LeCun, I Misra, G Synnaeve, N Carion
[NYU & Facebook]
MDETR:面向端到端多模态理解的调制检测。多模态推理系统依赖于预训练好的目标检测器,从图像中提取感兴趣区域。然而,该关键模块通常被当作黑箱,独立于下游任务,在固定的目标和属性词上进行训练,使得这类系统在捕捉以自由形式文本表达的视觉概念的长尾方面具有挑战性。本文提出MDETR,一个端到端的调制检测器,根据原始文本查询(如标题或问题)来检测图像中的物体。采用基于transformer的架构,通过在模型早期阶段融合这两种模式共同推理文本和图像。在130万个文本-图像对上对网络进行预训练,这些文本-图像对是从已有的多模态数据集中挖掘出来的,在文本中的短语和图像中的物体之间有明确的一致性。在几个下游任务上进行微调,如短语定位、指代表达理解和分割,在流行基准上取得了最先进结果。所采用的预训练方法提供了一种方法,来处理具有极少标记实例的物体类别的长尾。该方法可以很容易地扩展到视觉问题的回答,在GQA和CLEVR上取得有竞争力的性能。
Multi-modal reasoning systems rely on a pre-trained object detector to extract regions of interest from the image. However, this crucial module is typically used as a black box, trained independently of the downstream task and on a fixed vocabulary of objects and attributes. This makes it challenging for such systems to capture the long tail of visual concepts expressed in free form text. In this paper we propose MDETR, an end-to-end modulated detector that detects objects in an image conditioned on a raw text query, like a caption or a question. We use a transformer-based architecture to reason jointly over text and image by fusing the two modalities at an early stage of the model. We pre-train the network on 1.3M text-image pairs, mined from pre-existing multi-modal datasets having explicit alignment between phrases in text and objects in the image. We then fine-tune on several downstream tasks such as phrase grounding, referring expression comprehension and segmentation, achieving state-of-the-art results on popular benchmarks. We also investigate the utility of our model as an object detector on a given label set when fine-tuned in a few-shot setting. We show that our pre-training approach provides a way to handle the long tail of object categories which have very few labelled instances. Our approach can be easily extended for visual question answering, achieving competitive performance on GQA and CLEVR. The code and models are available atthis https URL.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcW7RfJYd

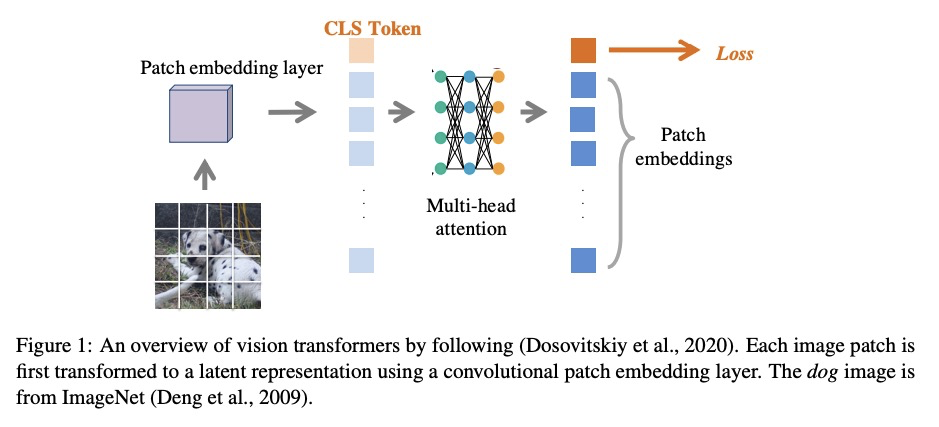
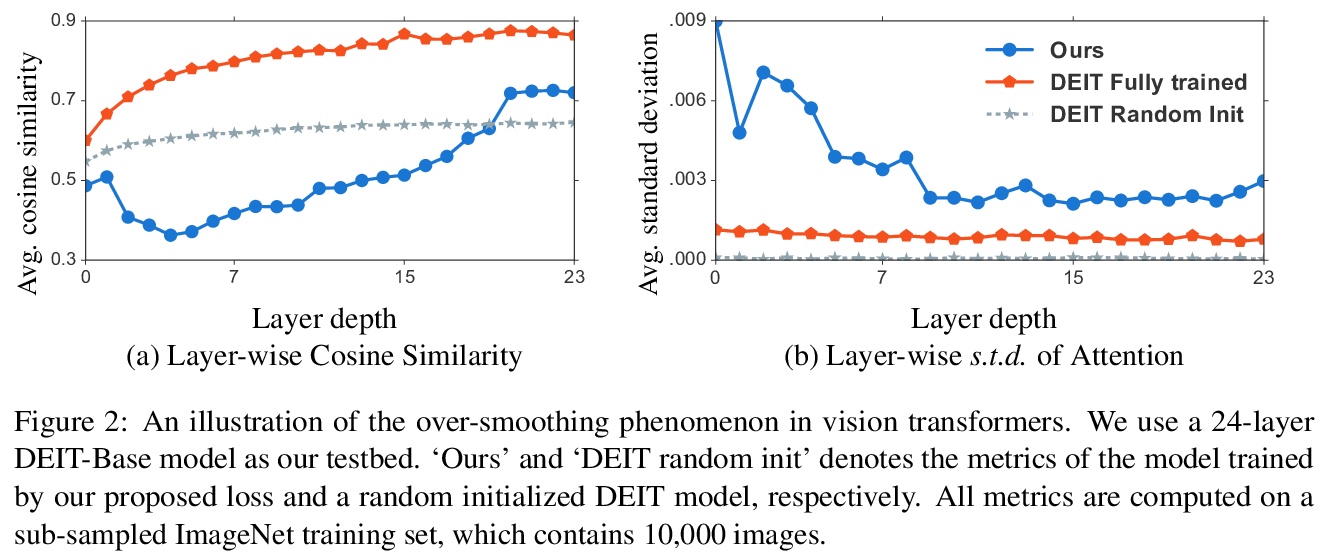
5、[CV] Improve Vision Transformers Training by Suppressing Over-smoothing
C Gong, D Wang, M Li, V Chandra, Q Liu
[University of Texas at Austin & Facebook]
通过抑制过平滑来改善视觉变Transformer训练。在计算机视觉任务中引入Transformer结构,有望产生比传统卷积网络更好的速度-精度权衡。然而,在视觉任务中直接训练vanilla transformer已被证明会产生不稳定和次优的结果。因此,最近的工作建议通过加入卷积层来修改Transformer结构,以提高视觉任务性能。本文研究了如何在不修改特殊结构的情况下稳定视觉Transformer的训练。视觉任务中Transformer训练的不稳定性可归因于过平滑问题,即自注意力层倾向于将输入图像中的不同斑块映射为相似的潜表示,因而产生了信息损失和性能退化,特别是当层数较多时。提出一些技术来缓解该问题,包括引入额外的损失函数来鼓励多样性,防止信息损失,以及通过Cutmix的额外图块分类损失来区分不同的图块。实验表明,所提出的技术稳定了训练,可训练更广泛和更深入的视觉Transformer,在ImageNet验证集上达到85.0%的top-1准确率,而无需引入额外的教师或额外的卷积层。
Introducing the transformer structure into computer vision tasks holds the promise of yielding a better speed-accuracy trade-off than traditional convolution networks. However, directly training vanilla transformers on vision tasks has been shown to yield unstable and sub-optimal results. As a result, recent works propose to modify transformer structures by incorporating convolutional layers to improve the performance on vision tasks. This work investigates how to stabilize the training of vision transformers \emph{without} special structure modification. We observe that the instability of transformer training on vision tasks can be attributed to the over-smoothing problem, that the self-attention layers tend to map the different patches from the input image into a similar latent representation, hence yielding the loss of information and degeneration of performance, especially when the number of layers is large. We then propose a number of techniques to alleviate this problem, including introducing additional loss functions to encourage diversity, prevent loss of information, and discriminate different patches by additional patch classification loss for Cutmix. We show that our proposed techniques stabilize the training and allow us to train wider and deeper vision transformers, achieving 85.0\% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet validation set without introducing extra teachers or additional convolution layers. Our code will be made publicly available atthis https URL.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcWbqxUzQ
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
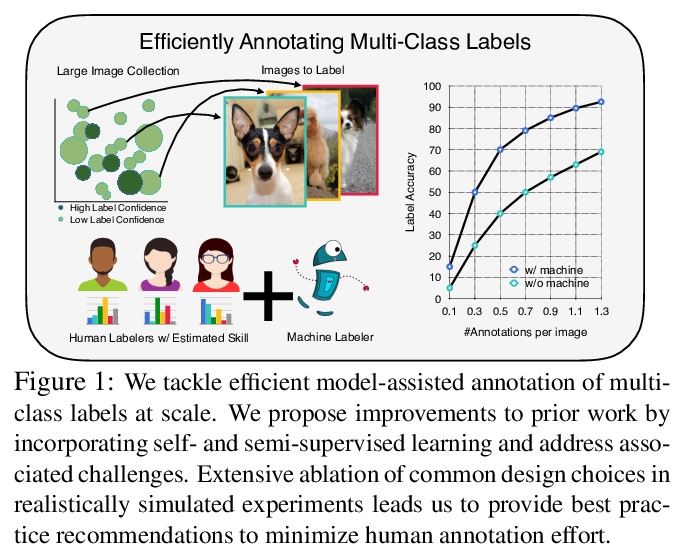
[CV] Towards Good Practices for Efficiently Annotating Large-Scale Image Classification Datasets
大规模图像分类数据集高效标注良好实践探索
Y Liao, A Kar, S Fidler
[University of Toronto]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcWffwZTY

[LG] Bridging observation, theory and numerical simulation of the ocean using Machine Learning
用机器学习弥合海洋观测、理论和数值模拟
M Sonnewald, R Lguensat, D C. Jones, P D. Dueben, J Brajard, V Balaji
[Princeton University & Laboratoire des Sciences du Climat et de l’Environnement (LSCE-IPSL) & Sorbonne Universit´e]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcWhCpJqt
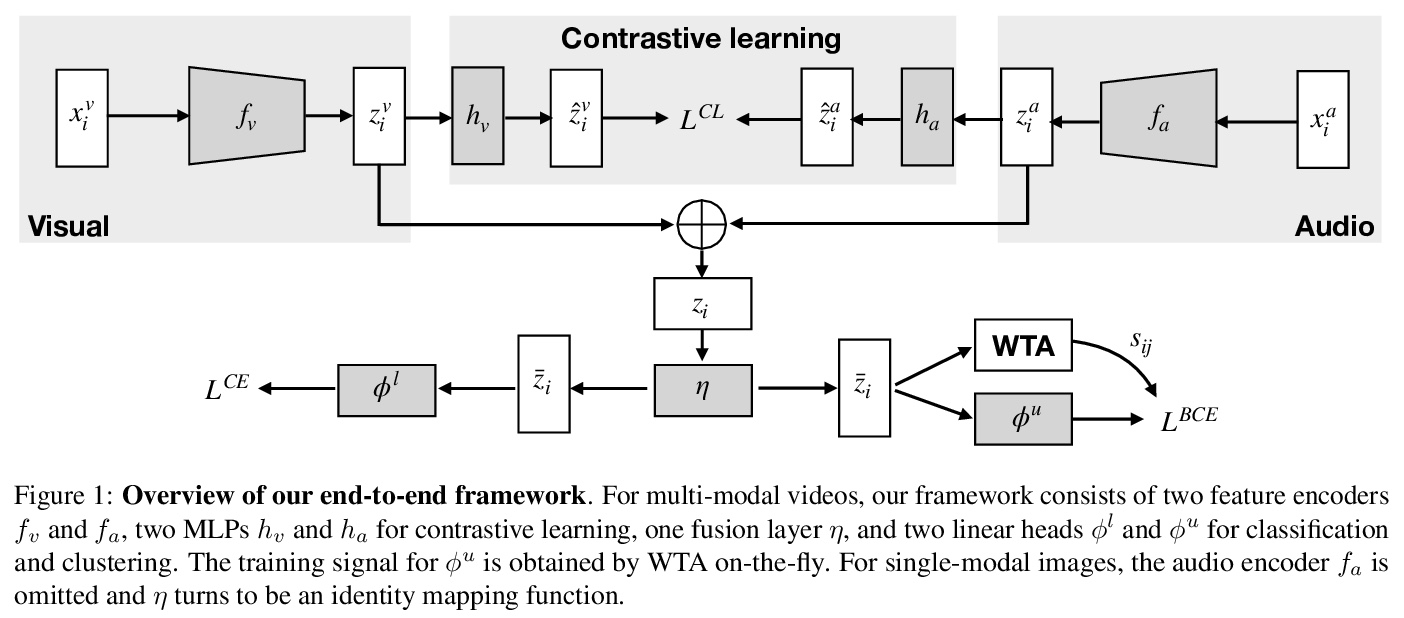
[CV] Joint Representation Learning and Novel Category Discovery on Single- and Multi-modal Data
单模态和多模态数据的联合表示学习和新类别发现
X Jia, K Han, Y Zhu, B Green
[Google & University of Bristol]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcWj6gmnC
[LG] Predicting Depressive Symptom Severity through Individuals’ Nearby Bluetooth Devices Count Data Collected by Mobile Phones: A Preliminary Longitudinal Study
通过手机收集个人附近蓝牙设备计数数据预测抑郁症状严重程度:一项初步纵向研究
Y Zhang, A A Folarin, S Sun, N Cummins, Y Ranjan, Z Rashid, P Conde, C Stewart, P Laiou, F Matcham, C Oetzmann, F Lamers, S Siddi, S Simblett, A Rintala, D C Mohr, I Myin-Germeys, T Wykes, J M Haro, B W Pennix, V A Narayan, P Annas, M Hotopf, R J Dobson
[King’s College London]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KcWkwCqEJ