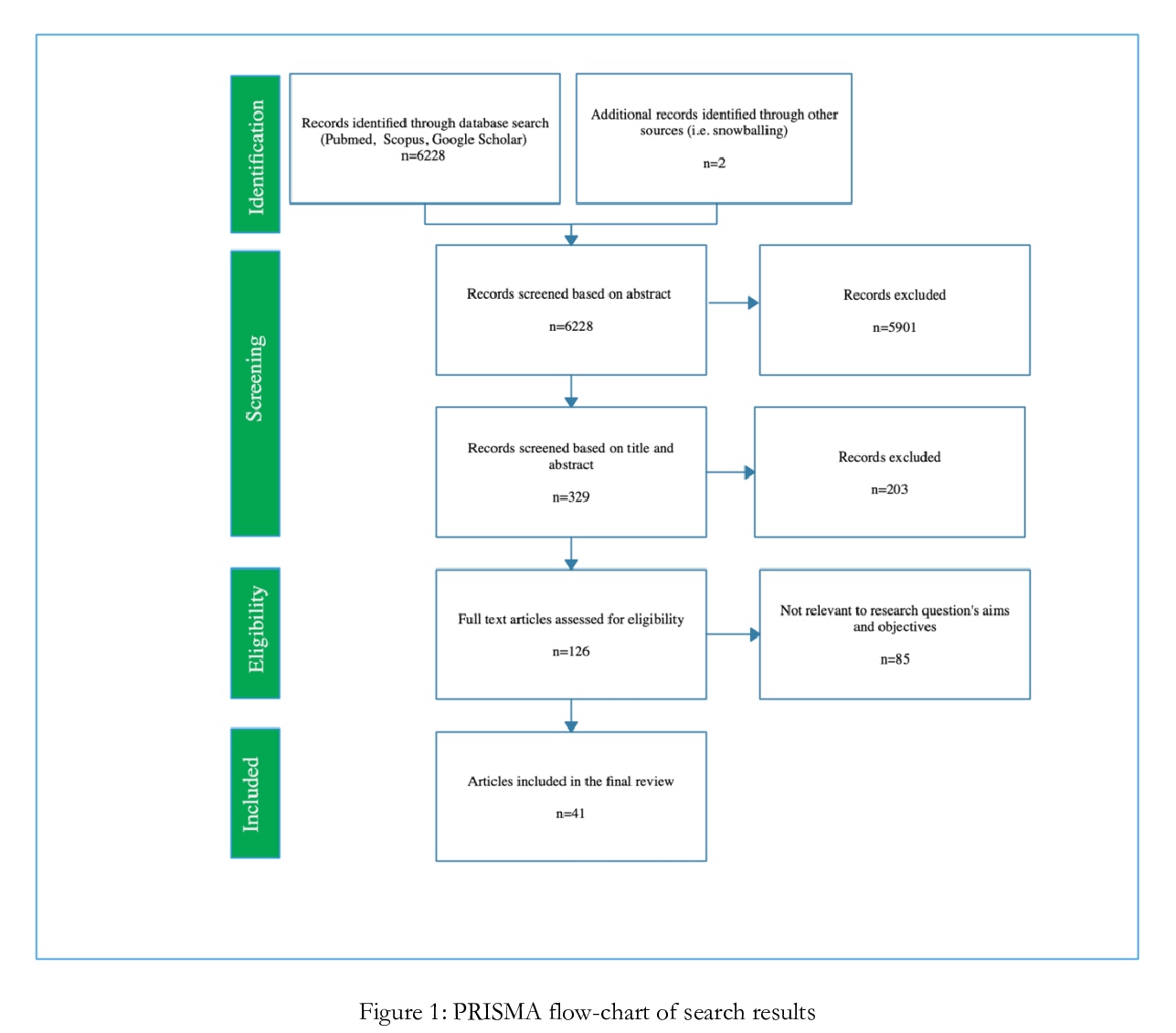
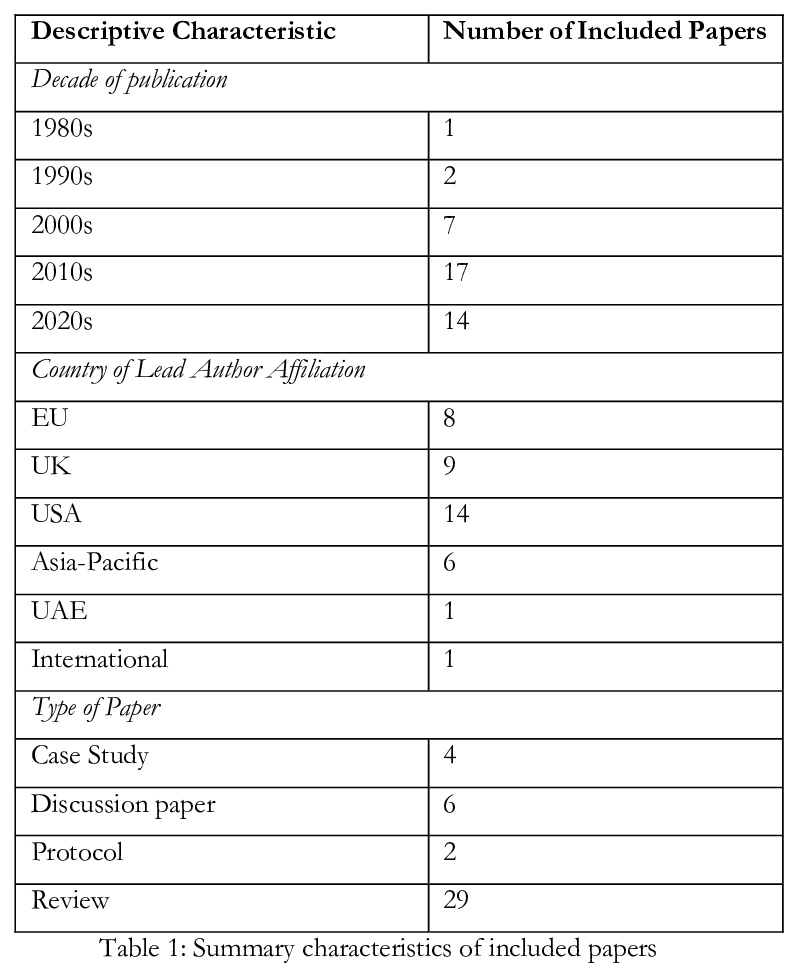
- 1、[CV] DatasetGAN: Efficient Labeled Data Factory with Minimal Human Effort
- 2、[CL] Masked Language Modeling and the Distributional Hypothesis: Order Word Matters Pre-training for Little
- 3、[CV] Aligning Latent and Image Spaces to Connect the Unconnectable
- 4、[CV] Few-shot Image Generation via Cross-domain Correspondence
- 5、[CL] Large-Scale Self- and Semi-Supervised Learning for Speech Translation
- [AS] Non-autoregressive sequence-to-sequence voice conversion
- [CL] Modeling Framing in Immigration Discourse on Social Media
- [CV] Revisiting Hierarchical Approach for Persistent Long-Term Video Prediction
- [AI] Towards a framework for evaluating the safety, acceptability and efficacy of AI systems for health: an initial synthesis
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[CV] DatasetGAN: Efficient Labeled Data Factory with Minimal Human Effort
Y Zhang, H Ling, J Gao, K Yin, J Lafleche, A Barriuso, A Torralba, S Fidler
[NVIDIA & MIT]
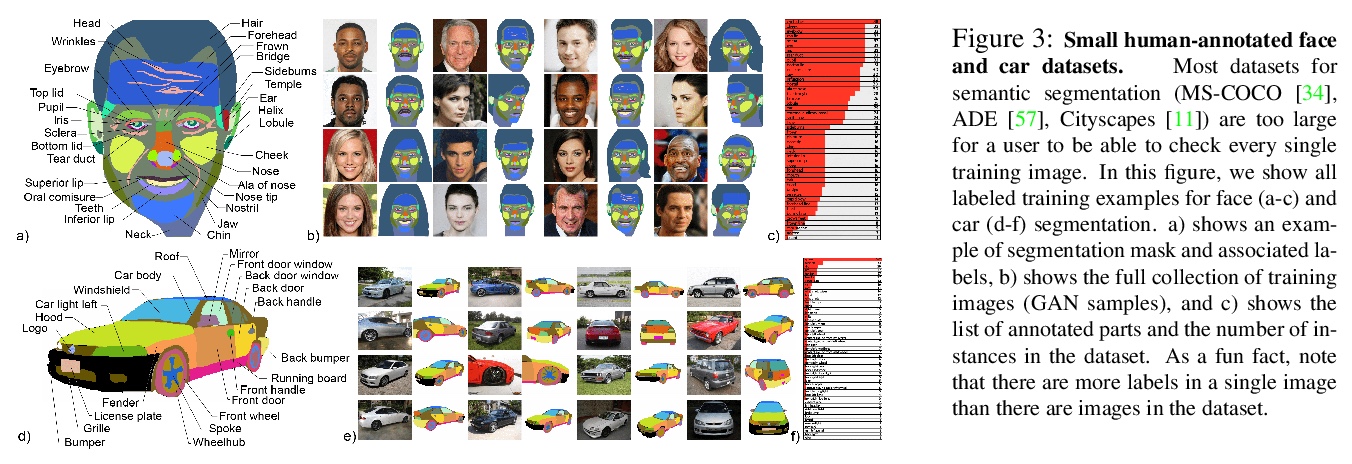
DatasetGAN:人力投入最少化的高效标注数据工厂。目前的深度网络主要得益于对大规模数据集的训练,数据需求非常大,而构造具有像素级标注的图像数据集,如语义分割或实例分割的数据集,是非常费力且昂贵的。本文的目标,是通过只对少量样本的标注,来合成大型高质量的标注数据集。提出了DatasetGAN,只需要最少的人力,就能生成高质量语义分割图像的海量数据集。该方法利用了最先进的生成模型StyleGAN来学习潜空间,训练一个浅层解码器对GAN潜码进行解码,来产生图像的语义分割。训练解码器只需要少数标注样本,就能泛化到潜空间的其他位置,产生一个无限标注数据集生成器。这些生成的数据集,可以像真实数据集一样,用于训练任意计算机视觉架构。由于只需要对少数图像进行手动分割,因此可以对图像进行极其详细的标注,生成具有丰富对象和部件分割的数据集。手工标注了对应于7个不同任务的微小数据集,每个数据集的细节都很高,包括34个人脸组件的像素级标记,以及32个汽车部件。在这些数据集上进行训练,用DATASETGAN合成了大型的图像分割任务数据集。该方法明显优于所有半监督基线,与全监督方法相当,在某些情况下,全监督方法需要的标注数据是该方法的100倍之多。
We introduce DatasetGAN: an automatic procedure to generate massive datasets of high-quality semantically segmented images requiring minimal human effort. Current deep networks are extremely data-hungry, benefiting from training on large-scale datasets, which are time consuming to annotate. Our method relies on the power of recent GANs to generate realistic images. We show how the GAN latent code can be decoded to produce a semantic segmentation of the image. Training the decoder only needs a few labeled examples to generalize to the rest of the latent space, resulting in an infinite annotated dataset generator! These generated datasets can then be used for training any computer vision architecture just as real datasets are. As only a few images need to be manually segmented, it becomes possible to annotate images in extreme detail and generate datasets with rich object and part segmentations. To showcase the power of our approach, we generated datasets for 7 image segmentation tasks which include pixel-level labels for 34 human face parts, and 32 car parts. Our approach outperforms all semi-supervised baselines significantly and is on par with fully supervised methods, which in some cases require as much as 100x more annotated data as our method.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kb6JgDShl

2、[CL] Masked Language Modeling and the Distributional Hypothesis: Order Word Matters Pre-training for Little
K Sinha, R Jia, D Hupkes, J Pineau, A Williams, D Kiela
[Facebook AI Research]
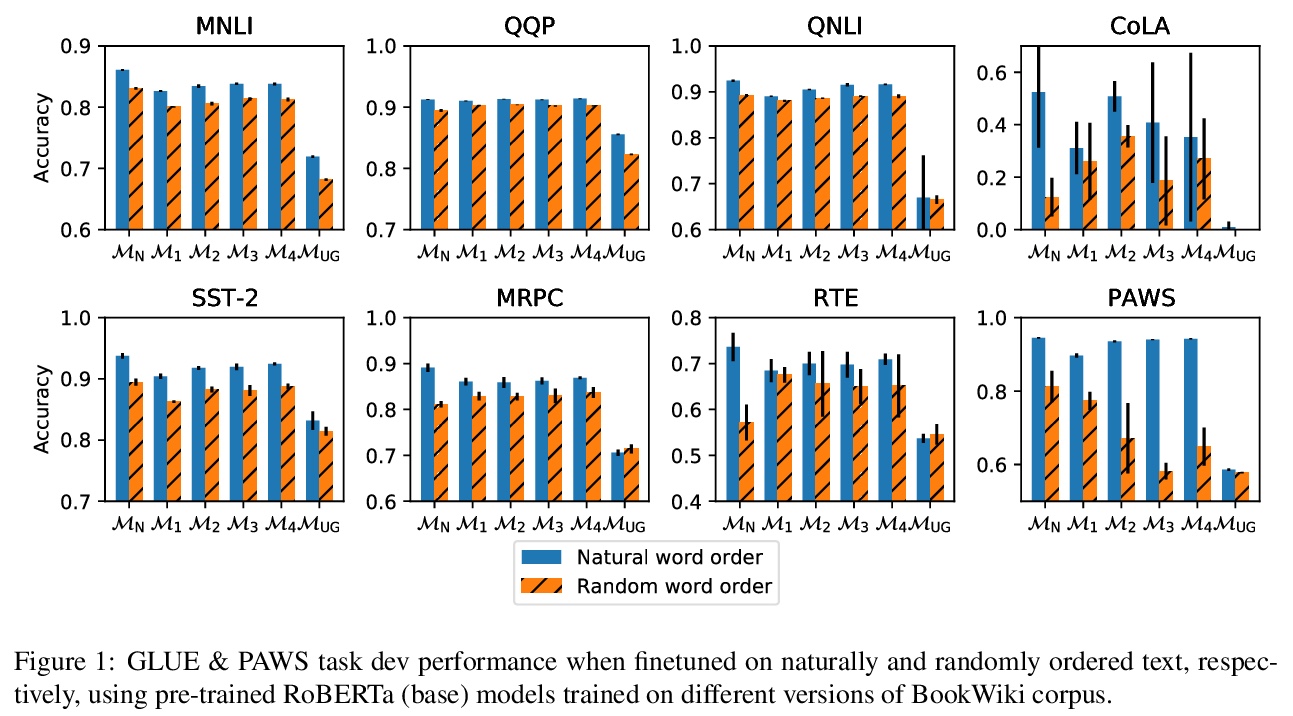
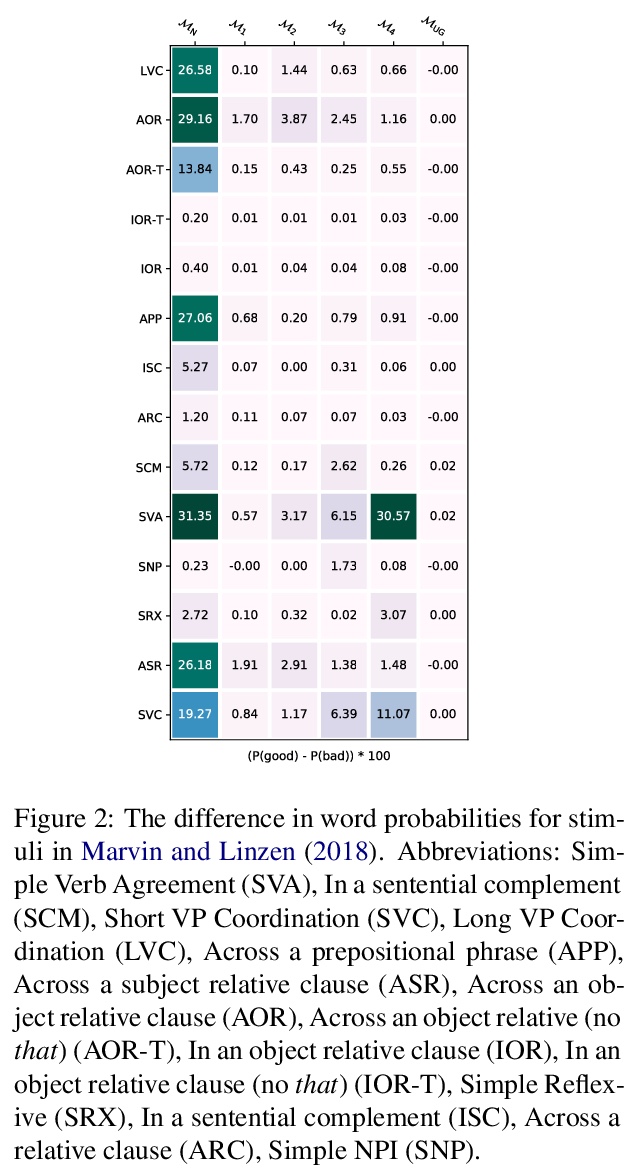
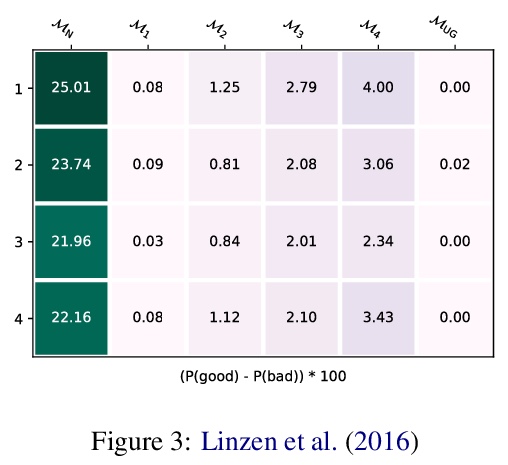
掩码语言模型与分布假说:次序对预训练影响微乎其微。自然语言处理已经被“预训练-微调”的范式所主导,在该范式中,首先要获得一个良好的参数化先验,以便随后对下游任务进行准确建模。特别是以BERT为代表的掩码语言模型(MLM),其预训练被证明是非常成功的,但背后的确切原因仍然不清楚。关于掩码语言模型(MLM)预训练,令人印象深刻的一种可能的解释是,模型学会了如何表示经典NLP流水线中普遍存在的语法结构。本文提出了一种不同的解释。掩码语言模型在下游任务上的成功,很可能不是因为能够发现传统语言处理流水线所必需的语法和语义机制,而几乎完全是由于其对高阶词共现统计的建模能力,为后续的微调提供了有用的分布先验。为证明这一点,在具有随机重排词序的句子上对掩码语言模型进行预训练,并表明这些模型在许多下游任务上—包括在专门为忽略词序的模型设计的具有挑战性的任务上—进行微调后,仍然达到了很高的准确度。模型用一些参数化句法探针进行测试表现出奇的好,表明测试句法信息表征的方式可能存在缺陷。实验结果表明,单纯的分布信息在很大程度上解释了预训练的成功,同时也强调了策划具有挑战性的评价数据集的重要性,这些数据集需要更深入的语言学知识。
A possible explanation for the impressive performance of masked language model (MLM) pre-training is that such models have learned to represent the syntactic structures prevalent in classical NLP pipelines. In this paper, we propose a different explanation: MLMs succeed on downstream tasks almost entirely due to their ability to model higher-order word co-occurrence statistics. To demonstrate this, we pre-train MLMs on sentences with randomly shuffled word order, and show that these models still achieve high accuracy after fine-tuning on many downstream tasks — including on tasks specifically designed to be challenging for models that ignore word order. Our models perform surprisingly well according to some parametric syntactic probes, indicating possible deficiencies in how we test representations for syntactic information. Overall, our results show that purely distributional information largely explains the success of pre-training, and underscore the importance of curating challenging evaluation datasets that require deeper linguistic knowledge.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kb6Ujh8iV
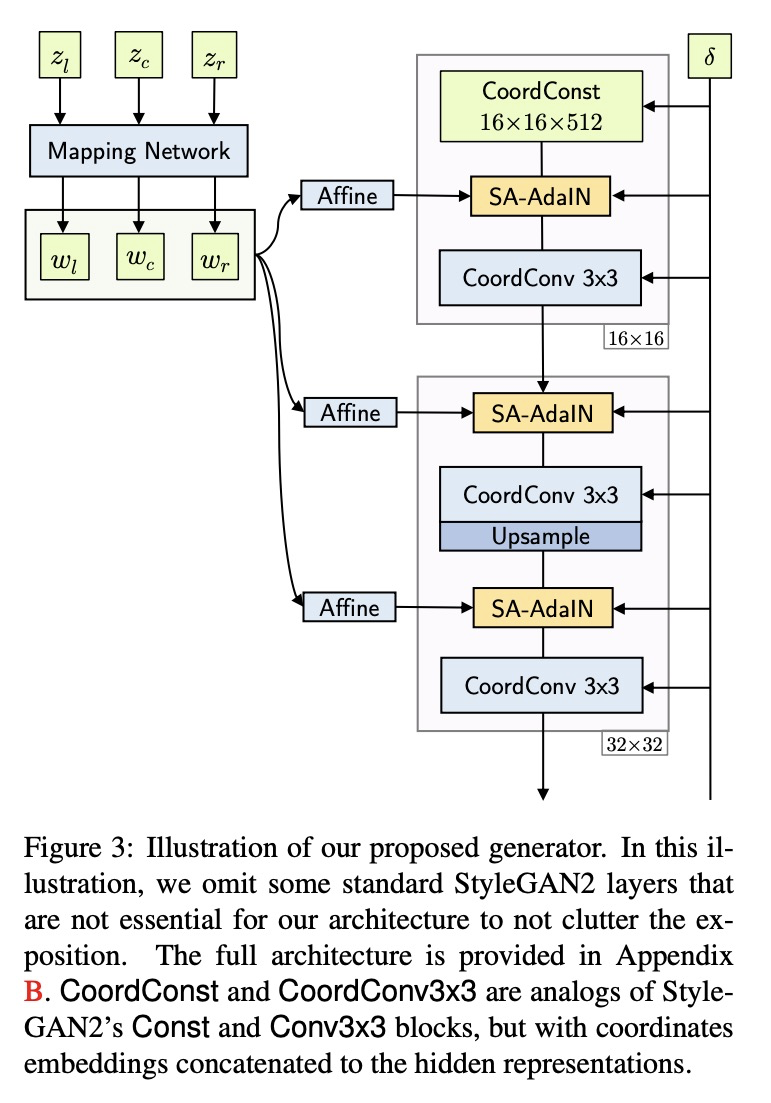
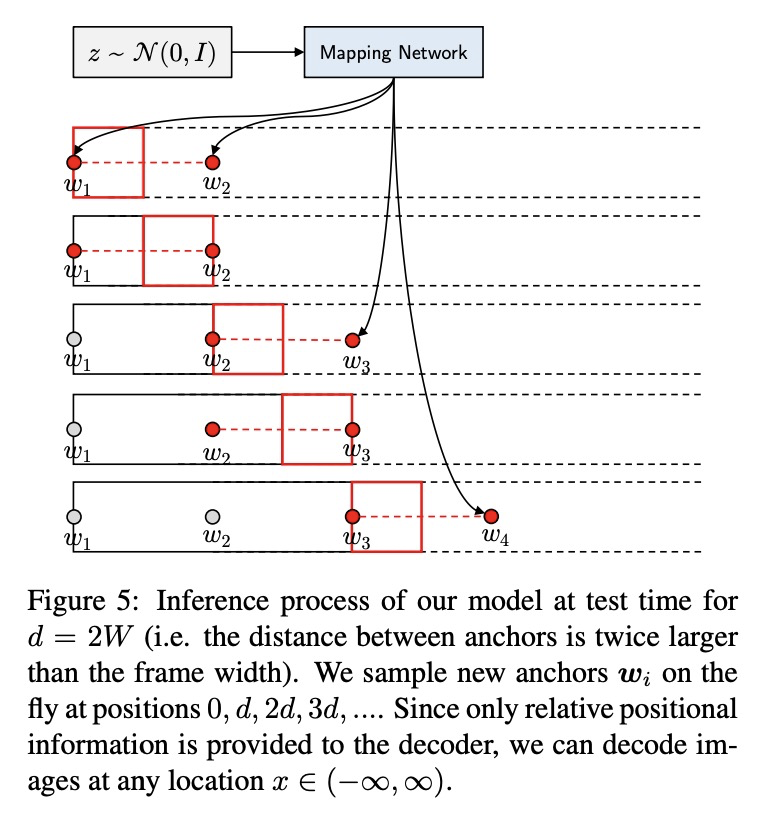
3、[CV] Aligning Latent and Image Spaces to Connect the Unconnectable
I Skorokhodov, G Sotnikov, M Elhoseiny
[KAUST & HSE]
对齐潜空间和图像空间以拼接不可拼接图像。现代图像生成器,通常被设计为合成一些固定尺寸和长宽比的图片。而现实世界在任何捕获到的照片边界之外仍会无线延续,为匹配这种行为,本文提出一种将潜空间和图像空间对齐的思想,GAN生成器经过训练,可从空间任何位置生成可信的图像,用来构建最先进的无限图像生成模型,生成具有多样化和复杂内容的无限高分辨率图像。基于在图像空间和潜空间同步插值的全等价发生器,潜码在采样时被定位在坐标网格上,每个像素由附近的样式码插值计算而成。修改了AdaIN机制,使其能在这样的设置中工作,并在对抗性环境中训练生成器,以生成定位在任意两个潜向量之间的图像。测试时,可生成复杂多样的无限图像,并将任意两个不相关场景拼接成一张任意大的全景图。引入了LHQ,一个由90k高分辨率自然景观组成的新计算机视觉数据集。实验表明,该方法在生成的无限图像的质量和多样性方面相比基线至少好4倍。
In this work, we develop a method to generate infinite high-resolution images with diverse and complex content. It is based on a perfectly equivariant generator with synchronous interpolations in the image and latent spaces. Latent codes, when sampled, are positioned on the coordinate grid, and each pixel is computed from an interpolation of the nearby style codes. We modify the AdaIN mechanism to work in such a setup and train the generator in an adversarial setting to produce images positioned between any two latent vectors. At test time, this allows for generating complex and diverse infinite images and connecting any two unrelated scenes into a single arbitrarily large panorama. Apart from that, we introduce LHQ: a new dataset of \lhqsize high-resolution nature landscapes. We test the approach on LHQ, LSUN Tower and LSUN Bridge and outperform the baselines by at least 4 times in terms of quality and diversity of the produced infinite images. The project page is located atthis https URL.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kb74iEfXJ


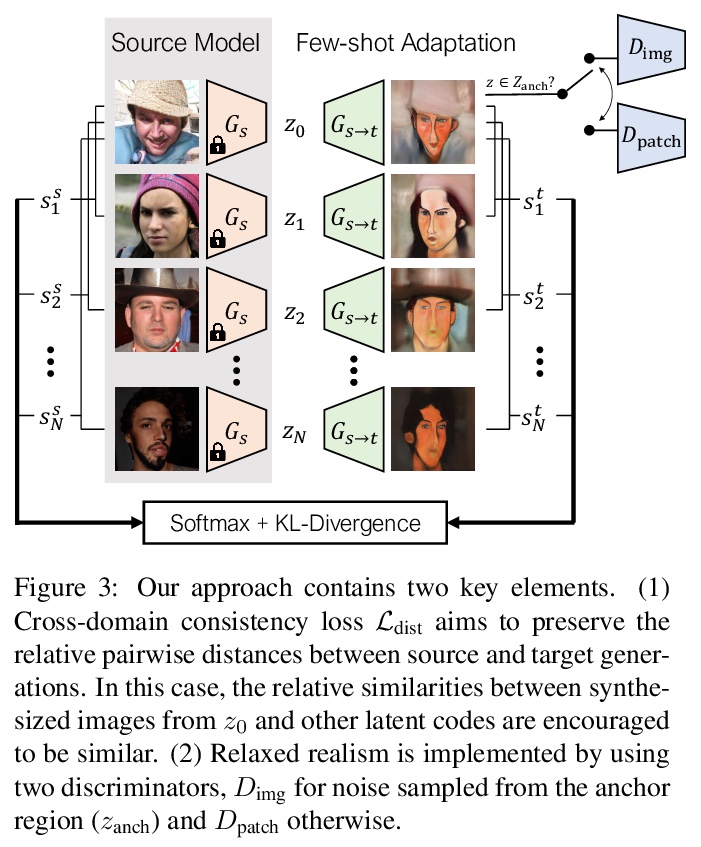
4、[CV] Few-shot Image Generation via Cross-domain Correspondence
U Ojha, Y Li, J Lu, A A. Efros, Y J Lee, E Shechtman, R Zhang
[Adobe Research & UC Davis]
基于跨域对应的少样本图像生成。在包含有限样本(如10个)的目标域上,训练生成式模型(如GAN),很容易导致过拟合。本文寻求利用一个大的源域进行预训练,将多样性信息从源域迁移到目标域。提出一中新的GAN自适应框架,通过一种新的跨域距离一致性损失,来保存源中实例间的相对相似性和差异性。为进一步减少过拟合,提出一种基于锚的策略,以鼓励在潜空间不同区域上实现不同的真实度水平。通过在光逼真和非光逼真领域的广泛结果,定性和定量地证明了该少样本模型可自动发现源域和目标域之间的对应关系,并生成比之前方法更多样化、更逼真的图像。
Training generative models, such as GANs, on a target domain containing limited examples (e.g., 10) can easily result in overfitting. In this work, we seek to utilize a large source domain for pretraining and transfer the diversity information from source to target. We propose to preserve the relative similarities and differences between instances in the source via a novel cross-domain distance consistency loss. To further reduce overfitting, we present an anchor-based strategy to encourage different levels of realism over different regions in the latent space. With extensive results in both photorealistic and non-photorealistic domains, we demonstrate qualitatively and quantitatively that our few-shot model automatically discovers correspondences between source and target domains and generates more diverse and realistic images than previous methods.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kb7bccRBd



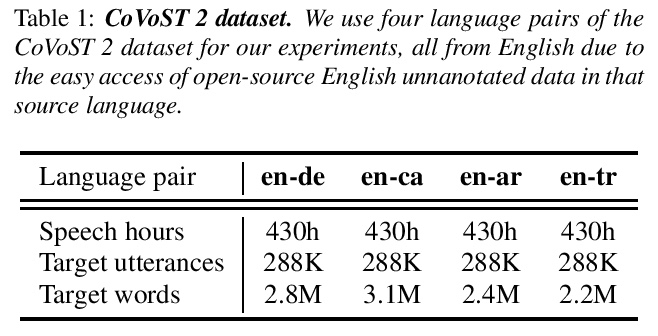
5、[CL] Large-Scale Self- and Semi-Supervised Learning for Speech Translation
C Wang, A Wu, J Pino, A Baevski, M Auli, A Conneau
[Facebook AI]
面向语音翻译的大规模自监督和半监督学习。通过以不同的互补方式有效利用大量未标记的语音和文本数据来改进语音翻译(ST)。通过用大型Libri-Light语音音频语料库和CommonCrawl的语言建模,探索预训练和自训练。通过利用wav2vec 2.0的预训练和自训练,推动了语音翻译的自监督和半监督学习的极限。这些技术可以在不使用CoVoST 2数据以外的任何类型监督的情况下,在四个语言方向上以平均1.3 BLEU的成绩超越之前的技术水平。证明了无监督预训练、自训练和语言模型解码的互补性,比之前方法高出2.6 BLEU。为语音翻译提供了更强、更简单的基线,并证明了wav2vec 2.0无监督预训练对语音翻译的有效性。
In this paper, we improve speech translation (ST) through effectively leveraging large quantities of unlabeled speech and text data in different and complementary ways. We explore both pretraining and self-training by using the large Libri-Light speech audio corpus and language modeling with CommonCrawl. Our experiments improve over the previous state of the art by 2.6 BLEU on average on all four considered CoVoST 2 language pairs via a simple recipe of combining wav2vec 2.0 pretraining, a single iteration of self-training and decoding with a language model. Different to existing work, our approach does not leverage any other supervision than ST data. Code and models will be publicly released.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kb7g63jOW
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
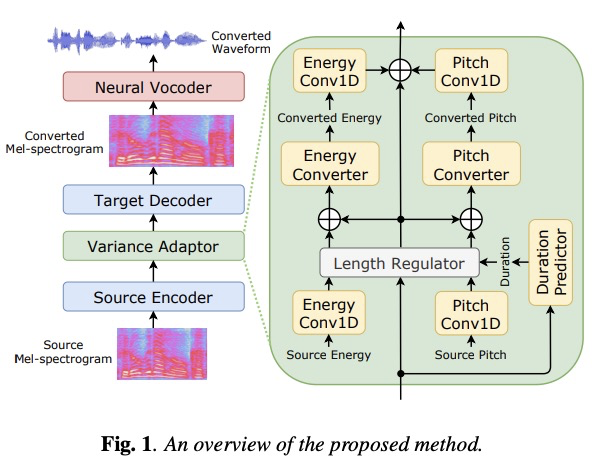
[AS] Non-autoregressive sequence-to-sequence voice conversion
非自回归序列到序列语音转换
T Hayashi, W Huang, K Kobayashi, T Toda
[TARVO Inc & Nagoya University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kb7jKBblb
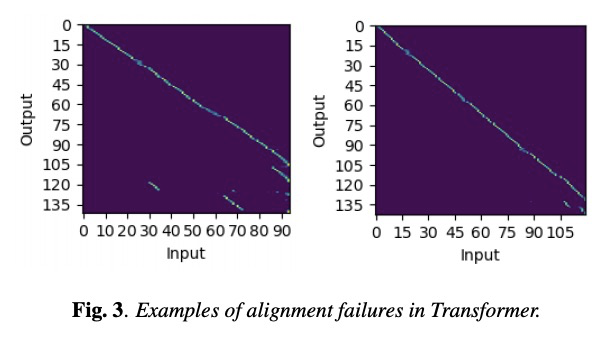
[CL] Modeling Framing in Immigration Discourse on Social Media
社交媒体移民话语框架建模
J Mendelsohn, C Budak, D Jurgens
[University of Michigan]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kb7lqEajm
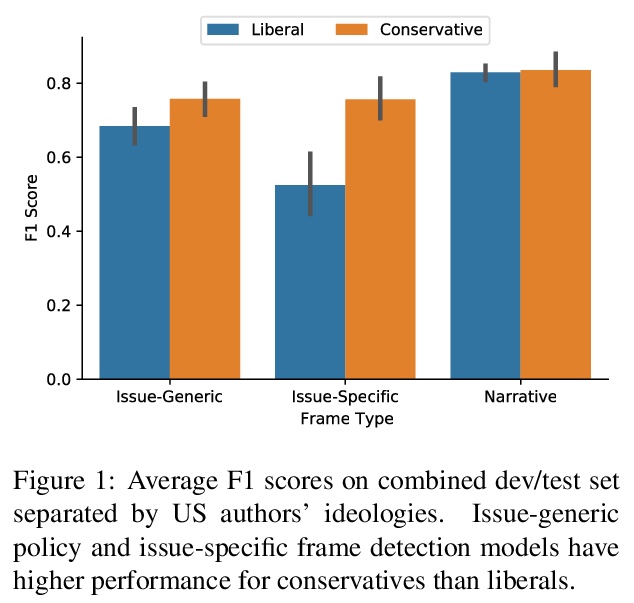
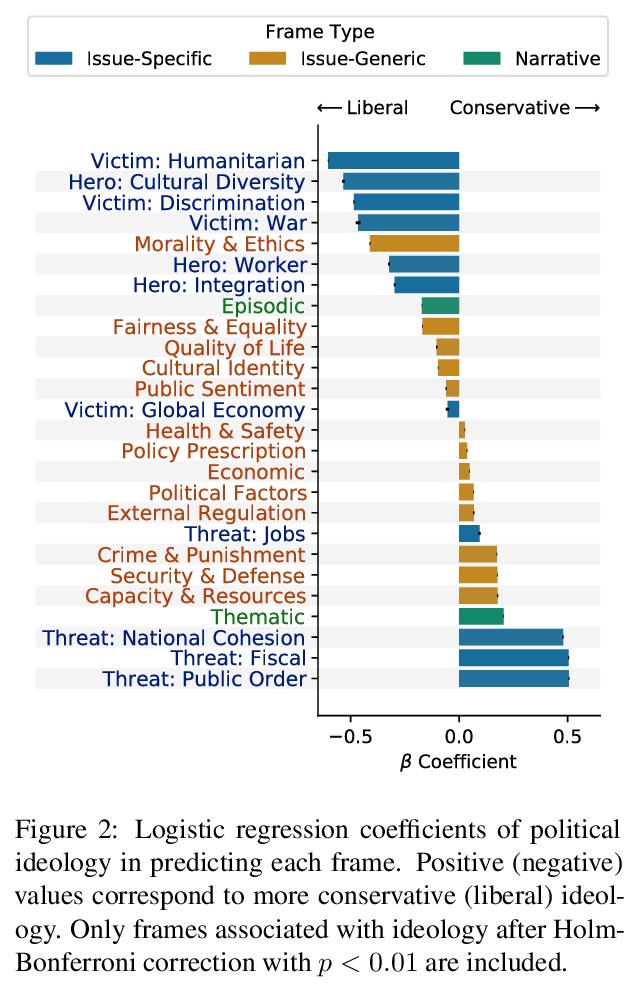
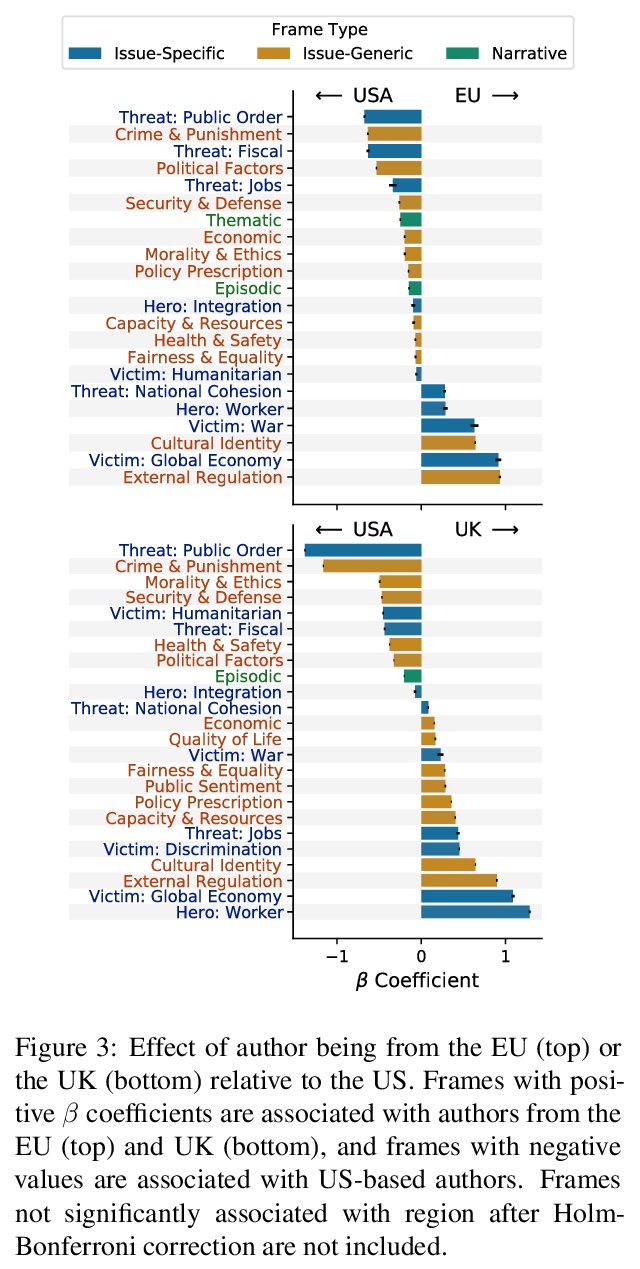
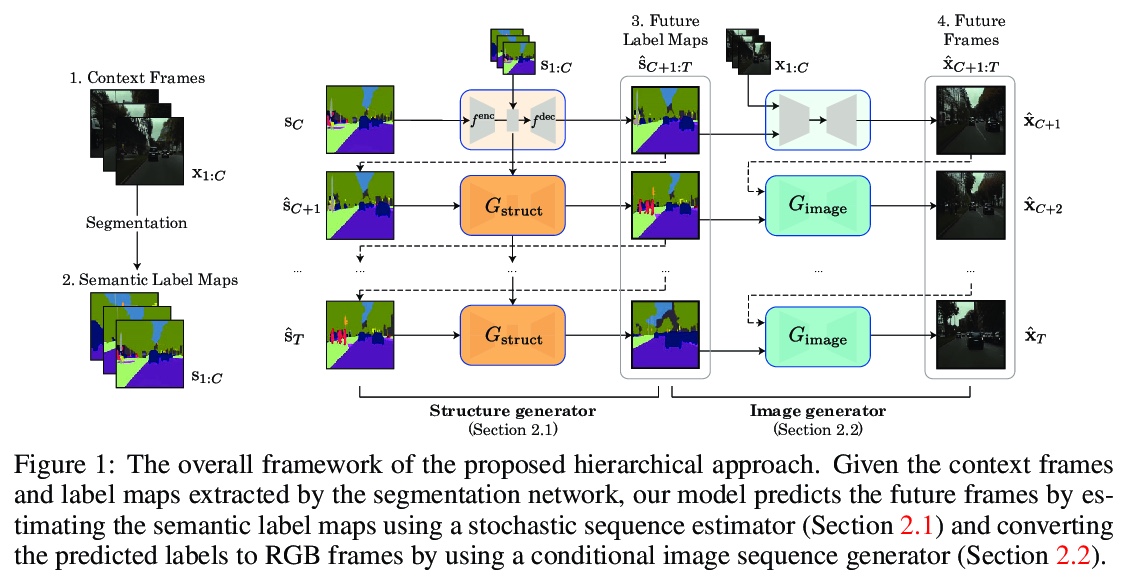
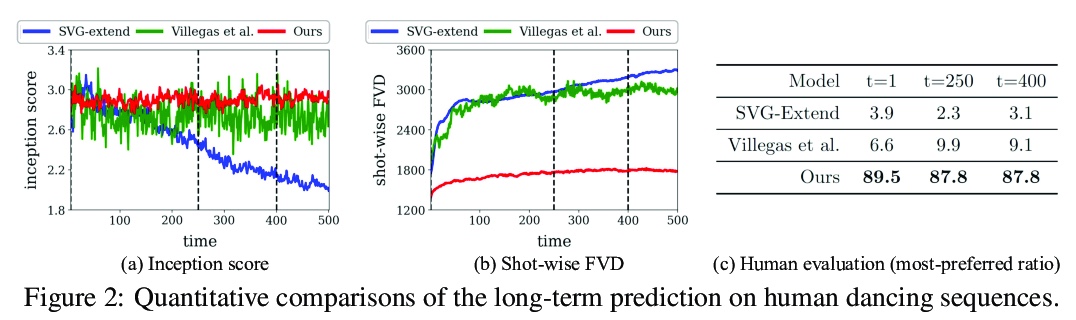
[CV] Revisiting Hierarchical Approach for Persistent Long-Term Video Prediction
再论视频持续长程预测的层次方法
W Lee, W Jung, H Zhang, T Chen, J Y Koh, T Huang, H Yoon, H Lee, S Hong
[KAIST & Google Research & University of Michigan]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kb7oXDXk2

[AI] Towards a framework for evaluating the safety, acceptability and efficacy of AI systems for health: an initial synthesis
人工智能系统安全性、可接受性和有效性评估框架:初步综述
J Morley, C Morton, K Karpathakis, M Taddeo, L Floridi
[University of Oxford]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kb7tSzKMp