- 1、[LG] Coordinate Independent Convolutional Networks — Isometry and Gauge Equivariant Convolutions on Riemannian Manifolds
- 2、[CV] SimSwap: An Efficient Framework For High Fidelity Face Swapping
- 3、[CV] Scaling Vision with Sparse Mixture of Experts
- 4、[CV] MlTr: Multi-label Classification with Transformer
- 5、[CV] Part-aware Panoptic Segmentation
- [CV] View Generalization for Single Image Textured 3D Models
- [AS] Catch-A-Waveform: Learning to Generate Audio from a Single Short Example
- [CL] Zero-Shot Controlled Generation with Encoder-Decoder Transformers
- [LG] Scalable Variational Gaussian Processes via Harmonic Kernel Decomposition
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] Coordinate Independent Convolutional Networks — Isometry and Gauge Equivariant Convolutions on Riemannian Manifolds
M Weiler, P Forré, E Verlinde, M Welling
[University of Amsterdam]
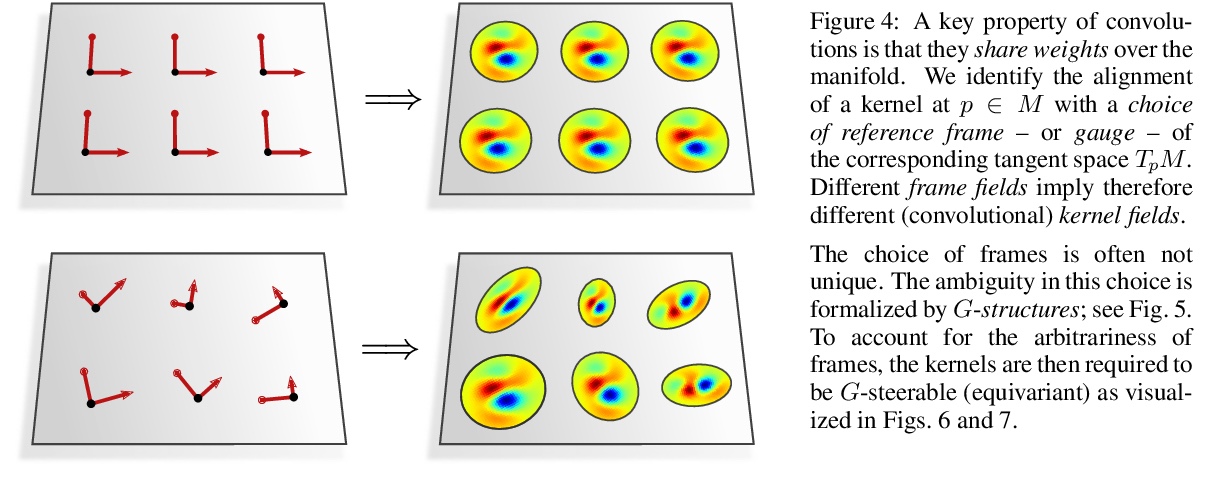
坐标独立卷积网络——黎曼流形上的等值和尺度等变卷积。在深度卷积网络巨大成功的激励下,人们对将卷积推广到非欧几里得流形有很大兴趣。与平坦空间相比,一个主要问题是不清楚卷积核应该在流形上以何种方式应用。这种模糊性的根本原因是,一般流形并没有一个典型的参考框架(尺度)的选择。因此,核和特征必须相对于任意坐标来表达。本文认为,坐标化的特定选择不应影响网络的推理——它应该是坐标独立的。对坐标独立和权重共享的同时要求被证明会导致对网络的要求,即在局部规整变换(局部参考框架的变化)下的等值性。参考框架的模糊性取决于流形的G群结构,因此必要的尺度等变水平是由相应的G群结构规定的。与坐标无关的卷积被证明是与作为G群结构对称等距等变的。由此产生的理论在纤维束方面以无坐标方式表述。为了说明独立于坐标的卷积的设计,在莫比乌斯带上实现了一个卷积网络。对卷积网络的微分几何表述的普遍性通过大量的文献回顾来证明,这些文献解释了大量的欧氏CNN、球形CNN和一般表面上的CNN作为坐标独立卷积的具体实例。
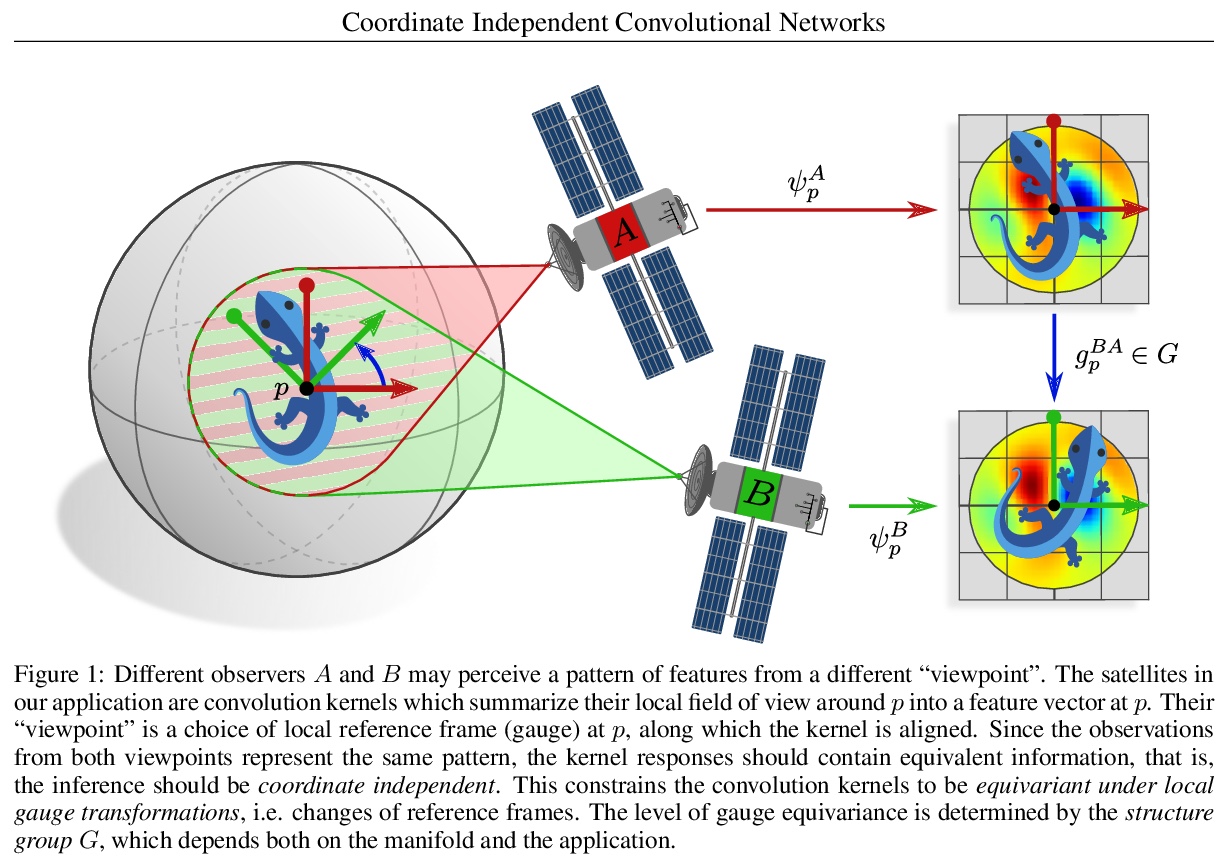
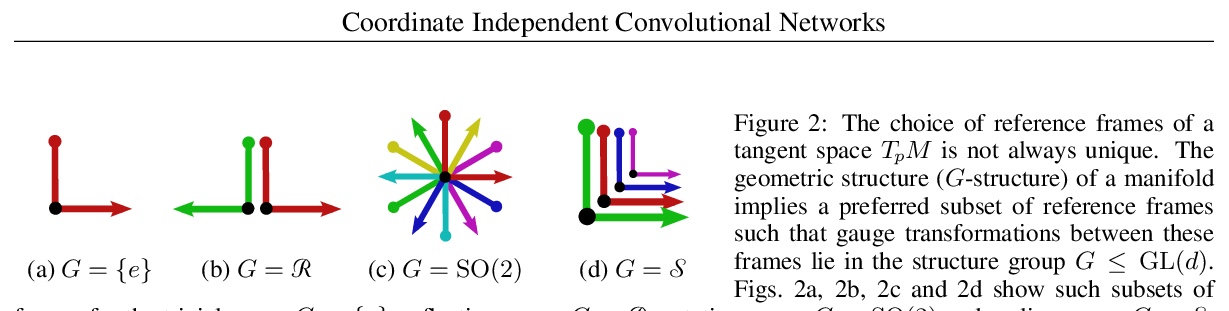
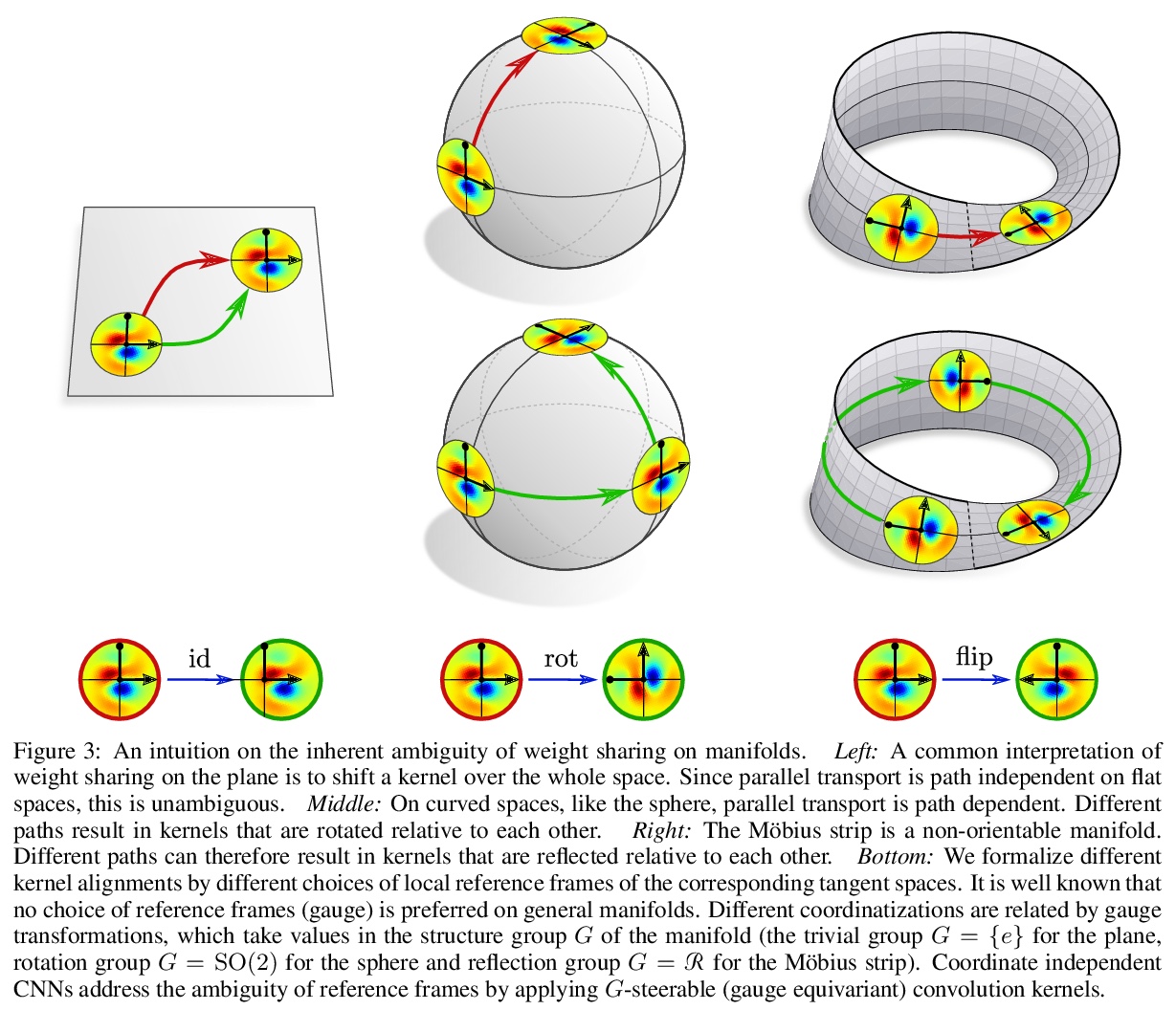
Motivated by the vast success of deep convolutional networks, there is a great interest in generalizing convolutions to non-Euclidean manifolds. A major complication in comparison to flat spaces is that it is unclear in which alignment a convolution kernel should be applied on a manifold. The underlying reason for this ambiguity is that general manifolds do not come with a canonical choice of reference frames (gauge). Kernels and features therefore have to be expressed relative to arbitrary coordinates. We argue that the particular choice of coordinatization should not affect a network’s inference – it should be coordinate independent. A simultaneous demand for coordinate independence and weight sharing is shown to result in a requirement on the network to be equivariant under local gauge transformations (changes of local reference frames). The ambiguity of reference frames depends thereby on the G-structure of the manifold, such that the necessary level of gauge equivariance is prescribed by the corresponding structure group G. Coordinate independent convolutions are proven to be equivariant w.r.t. those isometries that are symmetries of the G-structure. The resulting theory is formulated in a coordinate free fashion in terms of fiber bundles. To exemplify the design of coordinate independent convolutions, we implement a convolutional network on the Möbius strip. The generality of our differential geometric formulation of convolutional networks is demonstrated by an extensive literature review which explains a large number of Euclidean CNNs, spherical CNNs and CNNs on general surfaces as specific instances of coordinate independent convolutions.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kkesz2BQL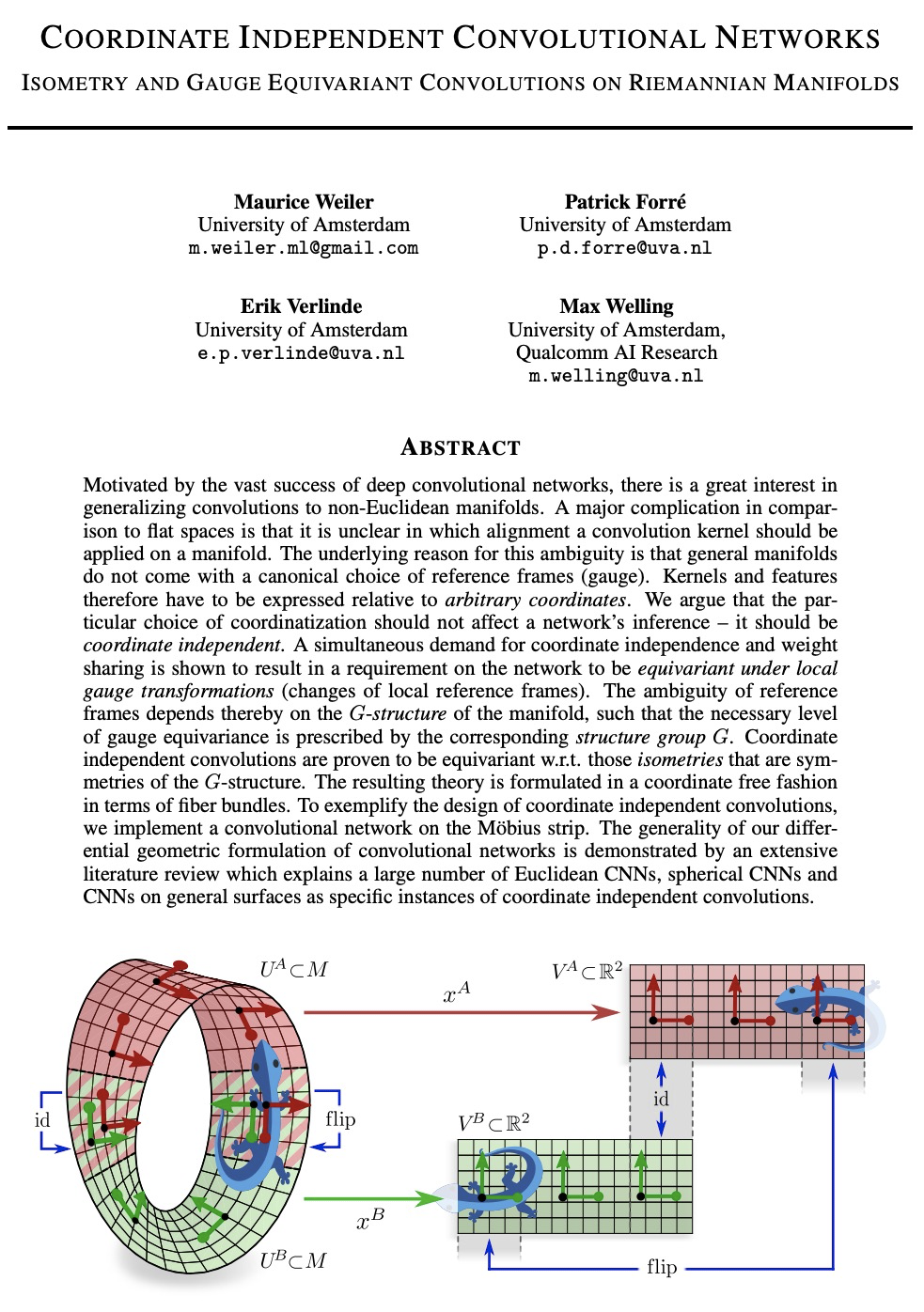
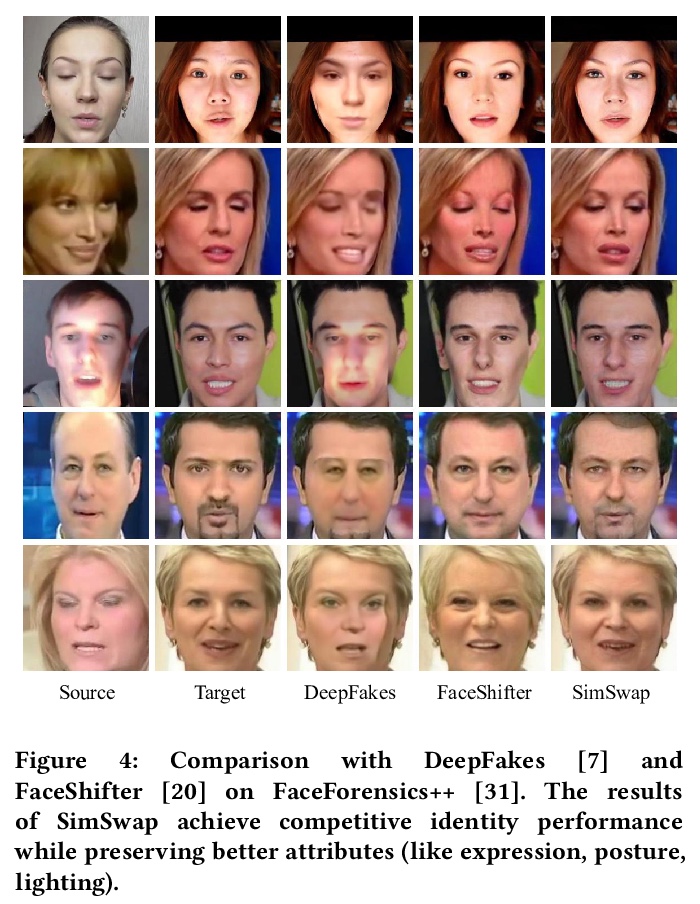
2、[CV] SimSwap: An Efficient Framework For High Fidelity Face Swapping
R Chen, X Chen, B Ni, Y Ge
[Shanghai Jiao Tong University & Tencent]
SimSwap:高效的高保真换脸框架。本文提出一种叫做简单交换(SimSwap)的高效框架,旨在实现通用的高保真换脸。之前的方法或者缺乏泛化到任意身份的能力,或者无法保留面部表情和注视方向等属性,相比之下,本框架能将任意源脸身份迁移到任意目标脸,同时保留目标脸属性。通过以下两种方式克服上述缺陷。首先,提出了ID注入模块(IIM),在特征层面将源脸的身份信息迁移到目标脸。通过该模块,将特定身份的人脸互换算法的结构扩展到任意人脸互换框架。其次,提出了弱特征匹配损失,帮助框架以隐式方式保留人脸属性。对真实人脸的广泛实验表明,SimSwap能实现有竞争力的身份识别性能,同时比以前最先进的方法更好地保留属性。
We propose an efficient framework, called Simple Swap (SimSwap), aiming for generalized and high fidelity face swapping. In contrast to previous approaches that either lack the ability to generalize to arbitrary identity or fail to preserve attributes like facial expression and gaze direction, our framework is capable of transferring the identity of an arbitrary source face into an arbitrary target face while preserving the attributes of the target face. We overcome the above defects in the following two ways. First, we present the ID Injection Module (IIM) which transfers the identity information of the source face into the target face at feature level. By using this module, we extend the architecture of an identityspecific face swapping algorithm to a framework for arbitrary face swapping. Second, we propose the Weak Feature Matching Loss ∗Equal contribution. ⊠Corresponding author: Bingbing Ni. Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page. Copyrights for components of this work owned by others than ACM must be honored. Abstracting with credit is permitted. To copy otherwise, or republish, to post on servers or to redistribute to lists, requires prior specific permission and/or a fee. Request permissions from permissions@acm.org. MM ’20, October 12–16, 2020, Seattle, WA, USA © 2020 Association for Computing Machinery. ACM ISBN 978-1-4503-7988-5/20/10. . . $15.00 https://doi.org/10.1145/3394171.3413630 which efficiently helps our framework to preserve the facial attributes in an implicit way. Extensive experiments on wild faces demonstrate that our SimSwap is able to achieve competitive identity performance while preserving attributes better than previous state-of-the-art methods.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkexG8yHw





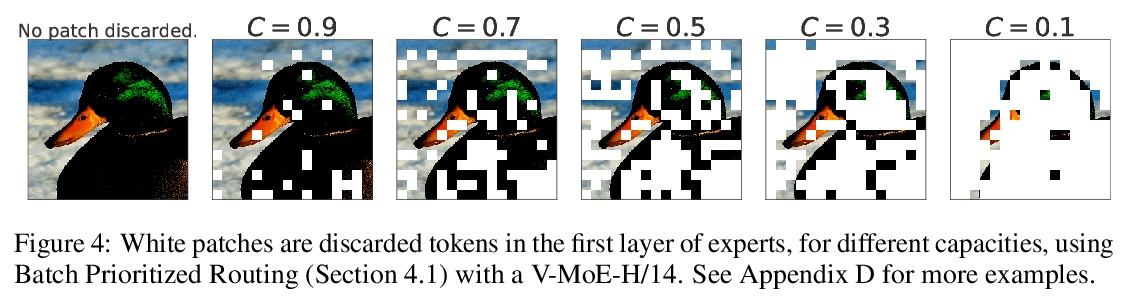
3、[CV] Scaling Vision with Sparse Mixture of Experts
C Riquelme, J Puigcerver, B Mustafa, M Neumann, R Jenatton, A S Pinto, D Keysers, N Houlsby
[Google Brain]
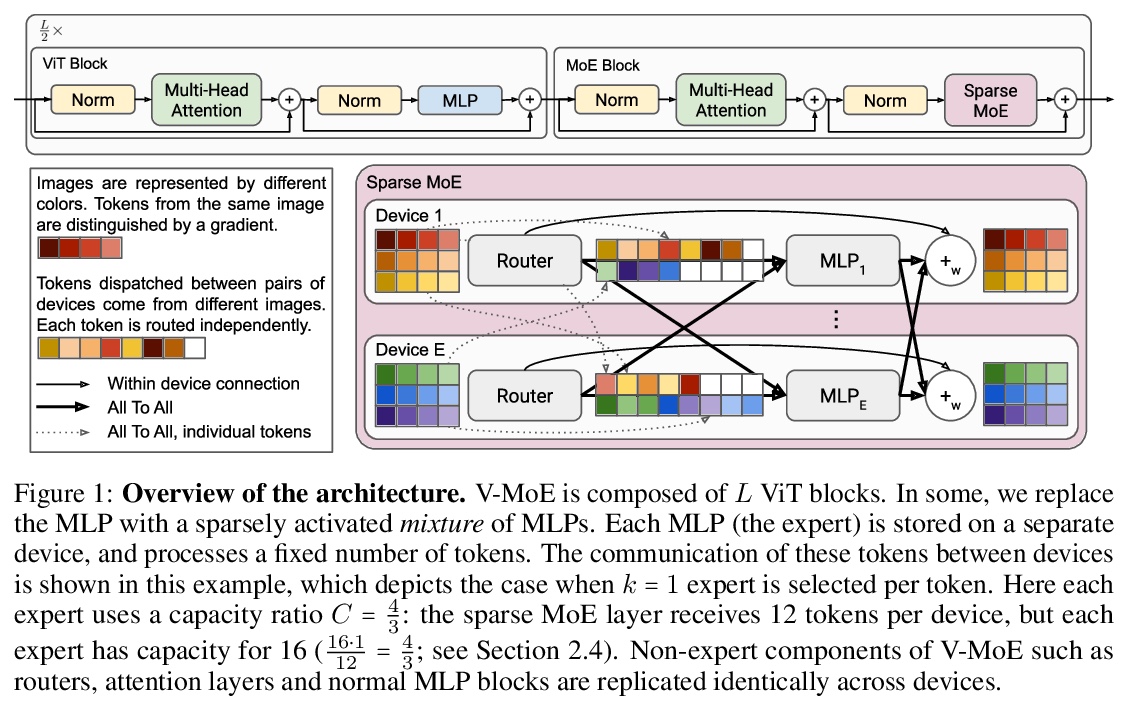
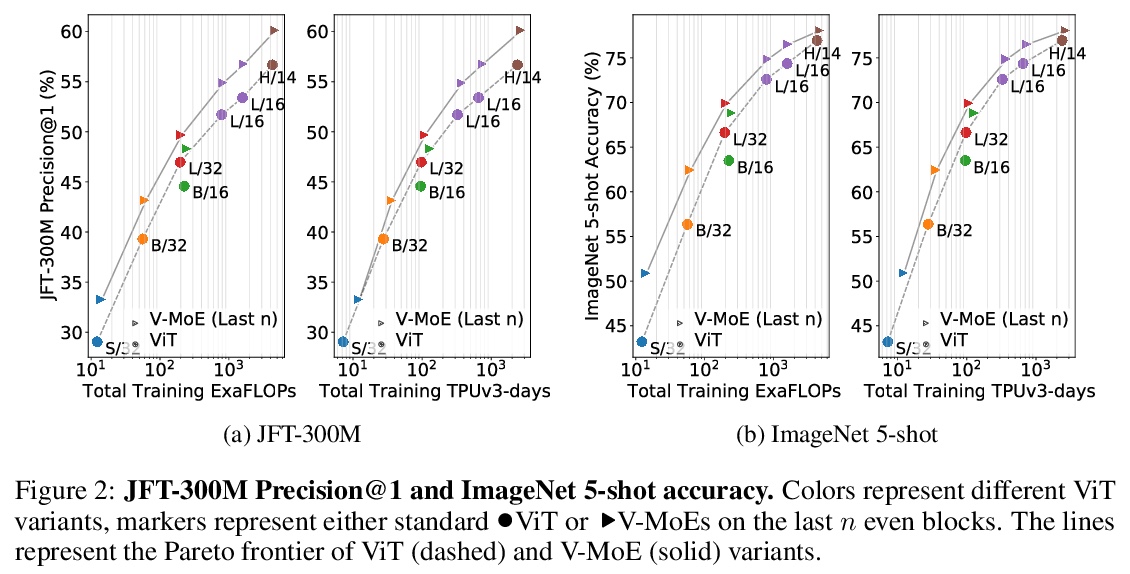
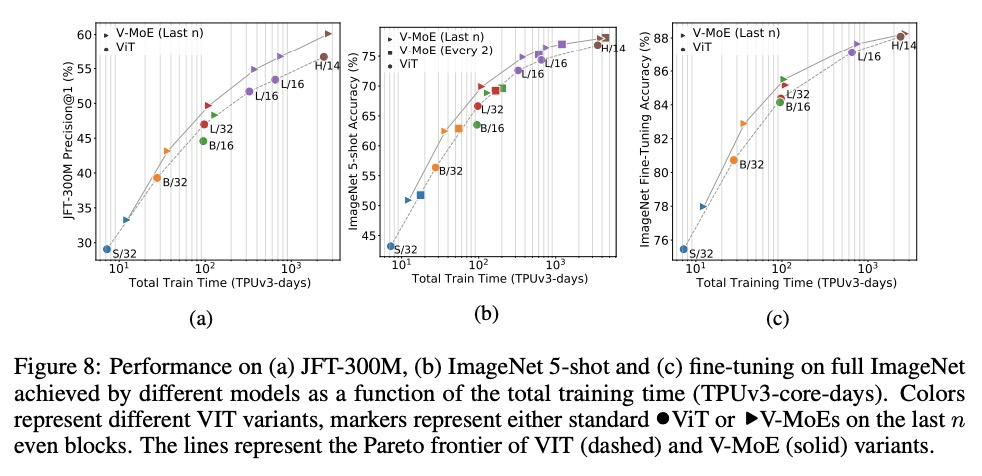
基于专家稀疏混合的视觉扩展。稀疏门控的专家混合网络(MoE)在自然语言处理中表现出卓越的可扩展性。然而,在计算机视觉中,几乎所有的高性能网络都是”密集”的,也就是说,每个输入都由每个参数来处理。本文提出Vision MoE(V-MoE),Vision Transformer的一种稀疏版本,具有可扩展性,能与最大的密集网络竞争。当应用于图像识别时,V-MoE与最先进的网络性能匹配,而在推理时只需要一半的计算。提出了对路由算法的扩展,可以在整个批次中优先考虑每个输入的子集,从而实现每个图像的自适应计算。这使得V-MoE能够在测试时平稳地权衡性能和计算。展示了V-MoE扩展视觉模型的潜力,并训练了一个15B参数的模型,在ImageNet上达到了90.35%。
Sparsely-gated Mixture of Experts networks (MoEs) have demonstrated excellent scalability in Natural Language Processing. In Computer Vision, however, almost all performant networks are “dense”, that is, every input is processed by every parameter. We present a Vision MoE (V-MoE), a sparse version of the Vision Transformer, that is scalable and competitive with the largest dense networks. When applied to image recognition, V-MoE matches the performance of state-ofthe-art networks, while requiring as little as half of the compute at inference time. Further, we propose an extension to the routing algorithm that can prioritize subsets of each input across the entire batch, leading to adaptive per-image compute. This allows V-MoE to trade-off performance and compute smoothly at test-time. Finally, we demonstrate the potential of V-MoE to scale vision models, and train a 15B parameter model that attains 90.35% on ImageNet.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkeBz1uWA
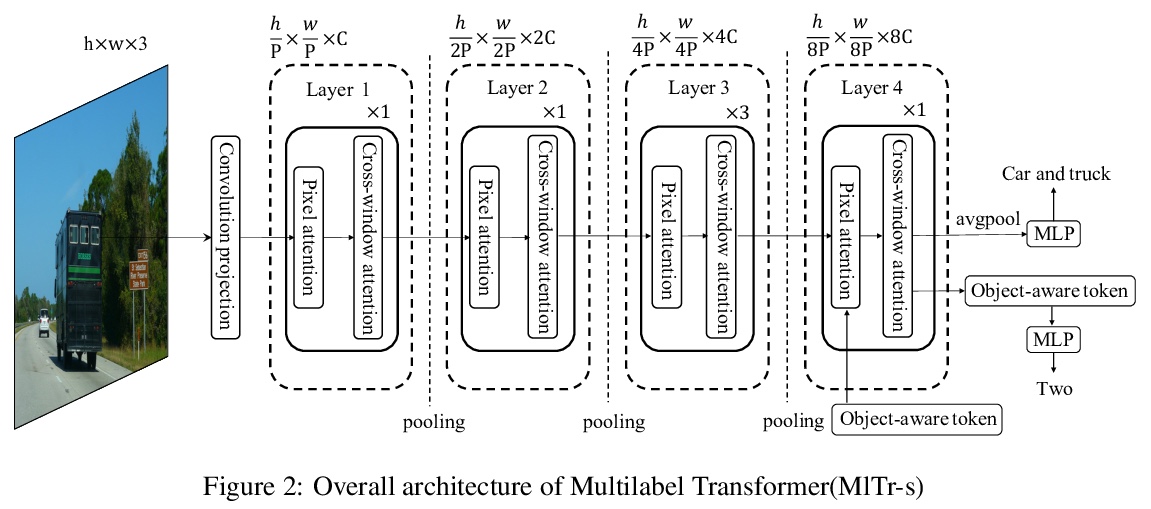
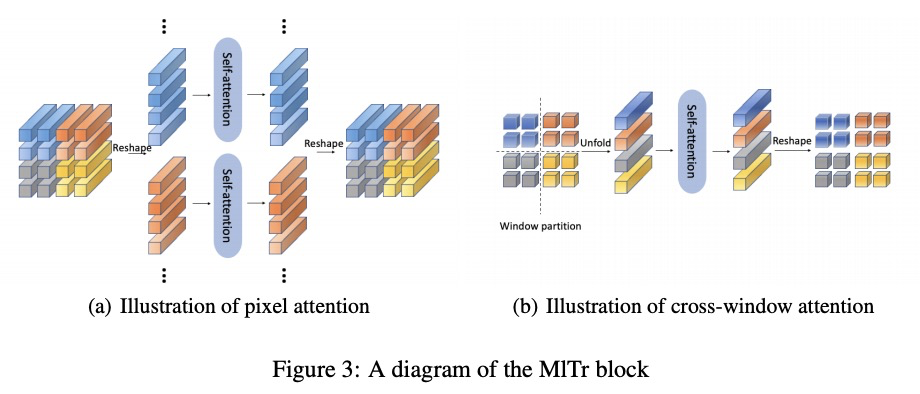
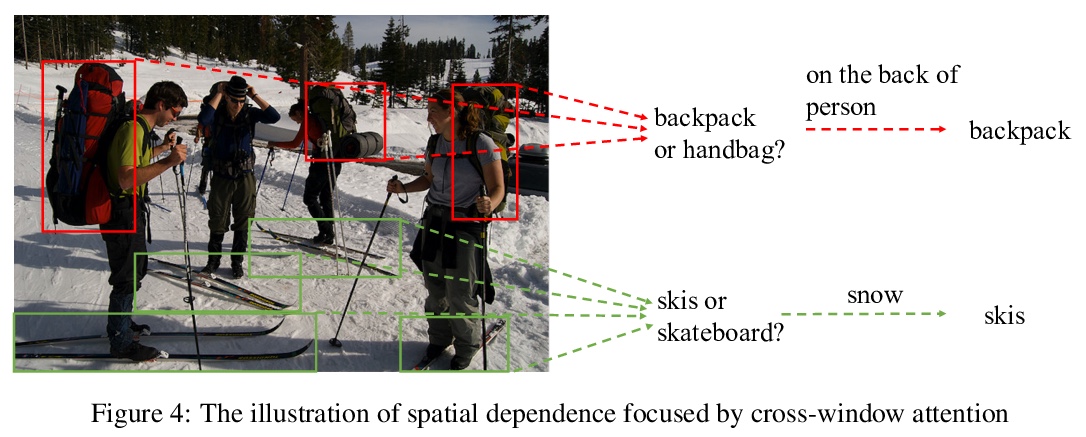
4、[CV] MlTr: Multi-label Classification with Transformer
X Cheng, H Lin, X Wu, F Yang, D Shen, Z Wang, N Shi, H Liu
[KuaiShou Inc]
MlTr: 基于Transformer的多标签分类。多标签图像分类的任务,是识别图像中出现的所有物体标签。尽管多年来一直在进步,但受卷积核表征能力的限制,小目标、相似物体和具有高条件概率的物体,仍然是之前基于卷积神经网络(CNN)模型的主要瓶颈问题。最近的视觉Transformer网络,利用自注意力机制来提取像素颗粒度的特征,表达了更丰富的局部语义信息,但对于挖掘全局的空间依赖是不够的。本文指出了基于CNN方法所遇到的三个关键问题,并探讨了用特定Transformer模块来解决这些问题的可能性。提出一种多标签Transformer架构(MlTr),由窗口划分、窗口内像素注意力、跨窗口注意力构成,改善了多标签图像分类任务的性能。所提出的MlTr在各种流行的多标签数据集上显示出最先进的结果,如MS-COCO、Pascal-VOC、NUSWIDE,分别为88.5%、95.8%、65.5%。
The task of multi-label image classification is to recognize all the object labels presented in an image. Though advancing for years, small objects, similar objects and objects with high conditional probability are still the main bottlenecks of previous convolutional neural network(CNN) based models, limited by convolutional kernels’ representational capacity. Recent vision transformer networks utilize the self-attention mechanism to extract the feature of pixel granularity, which expresses richer local semantic information, while is insufficient for mining global spatial dependence. In this paper, we point out the three crucial problems that CNN-based methods encounter and explore the possibility of conducting specific transformer modules to settle them. We put forward a Multi-label Transformer architecture(MlTr) constructed with windows partitioning, in-window pixel attention, cross-window attention, particularly improving the performance of multilabel image classification tasks. The proposed MlTr shows state-of-the-art results on various prevalent multi-label datasets such as MS-COCO, Pascal-VOC, NUSWIDE with 88.5%, 95.8%, 65.5% respectively.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkeEfkReK

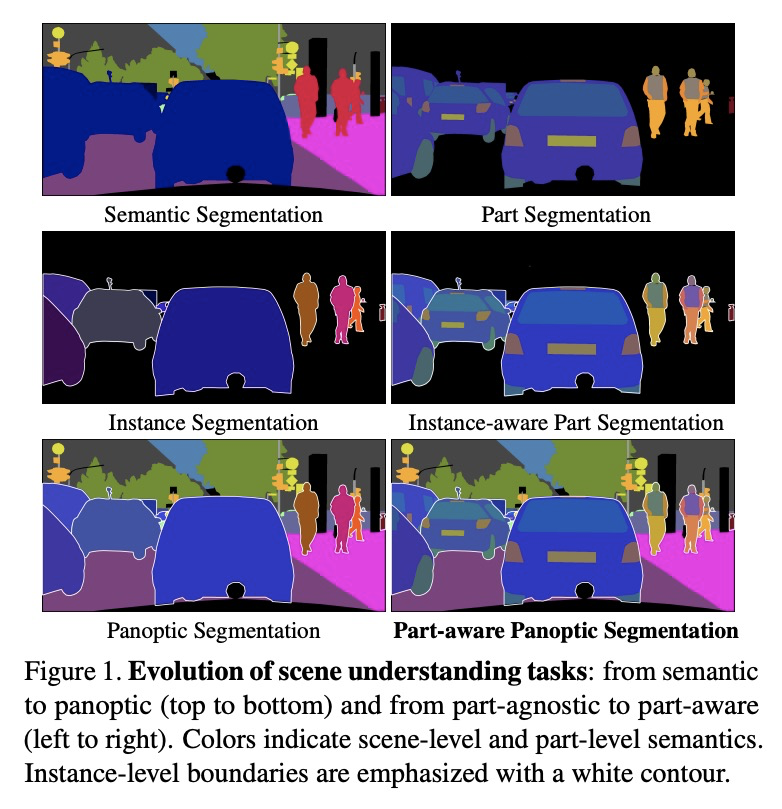
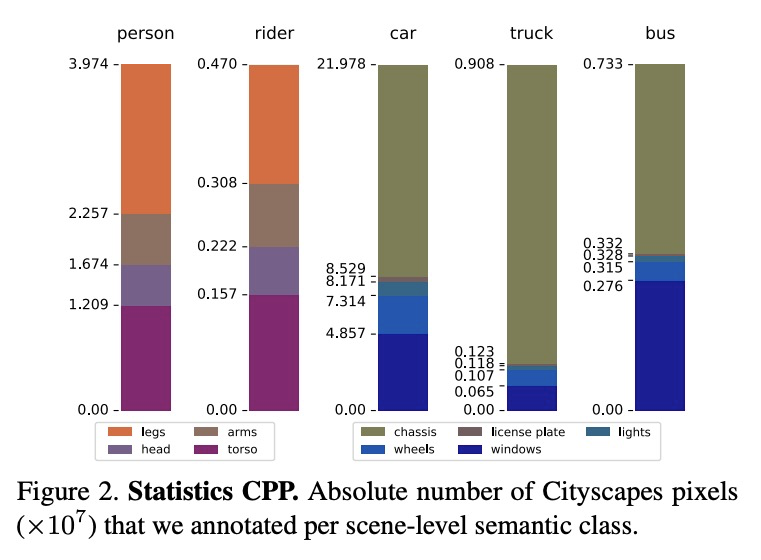
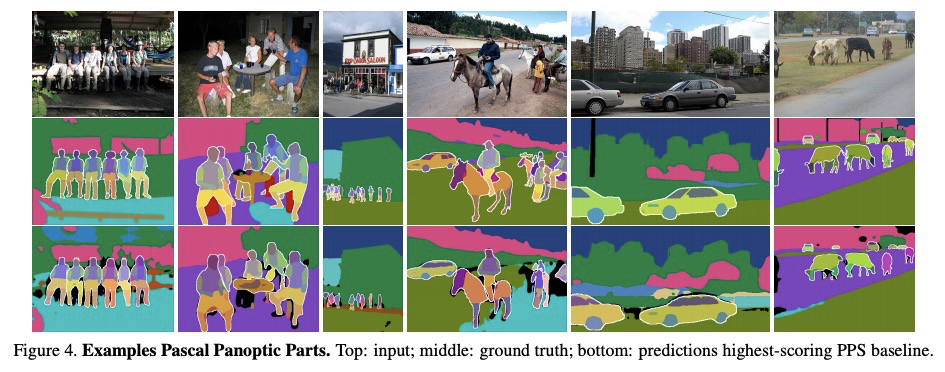
5、[CV] Part-aware Panoptic Segmentation
D d Geus, P Meletis, C Lu, X Wen, G Dubbelman
[Eindhoven University of Technology & University of Amsterdam]
部分感知全景分割。本文提出新的场景理解任务——部分感知全景分割(PPS),目的是在多个抽象层次上理解单个场景,并将场景解析和部分解析的任务统一起来。对于这项新任务,在两个常用的数据集上提供一致的标注:Cityscapes和Pascal VOC。提出一项评估PPS的指标,称为部分感知全景质量(PartPQ)。对于这项新任务,使用该指标和标注,通过合并现有的最先进的全景分割和部分分割方法的结果来设置多个基线。最后,进行了几个实验,评估不同的抽象层次在这个单一任务中的重要性。
In this work, we introduce the new scene understanding task of Part-aware Panoptic Segmentation (PPS), which aims to understand a scene at multiple levels of abstraction, and unifies the tasks of scene parsing and part parsing. For this novel task, we provide consistent annotations on two commonly used datasets: Cityscapes and Pascal VOC. Moreover, we present a single metric to evaluate PPS, called Part-aware Panoptic Quality (PartPQ). For this new task, using the metric and annotations, we set multiple baselines by merging results of existing state-of-the-art methods for panoptic segmentation and part segmentation. Finally, we conduct several experiments that evaluate the importance of the different levels of abstraction in this single task.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkeH6n2LJ

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
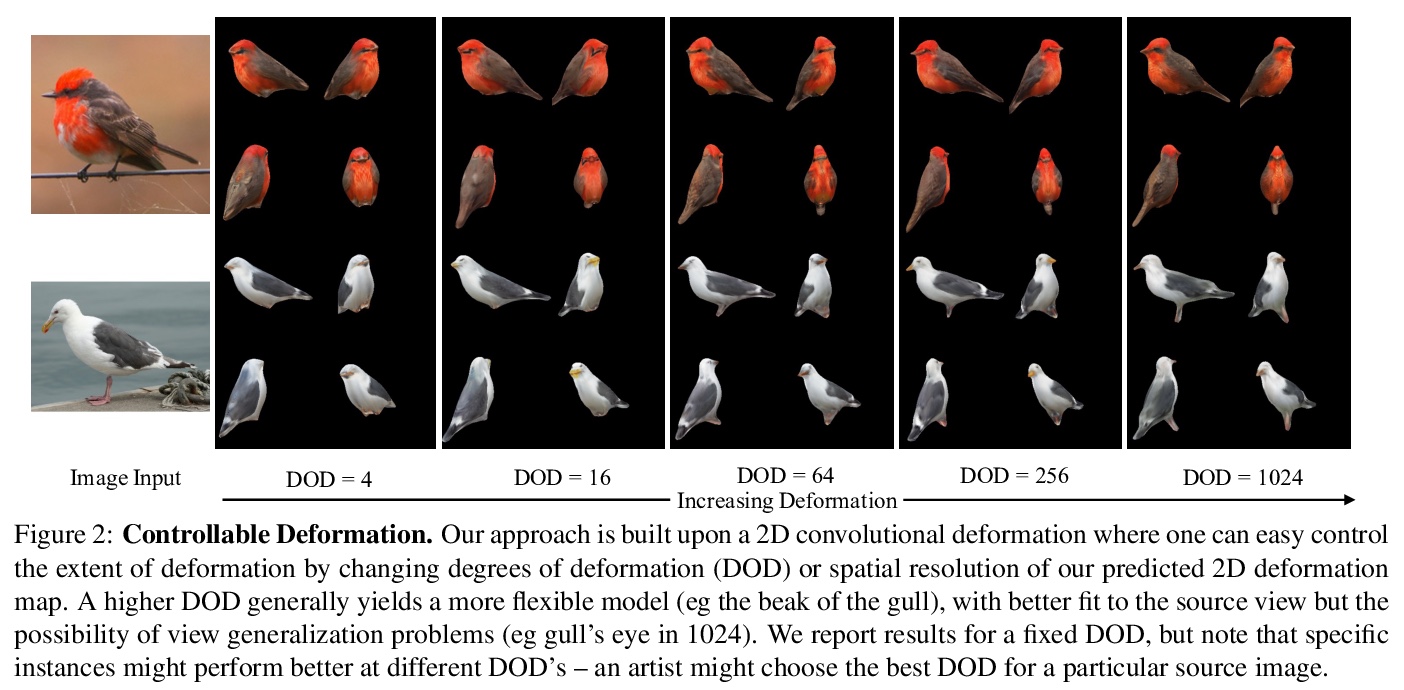
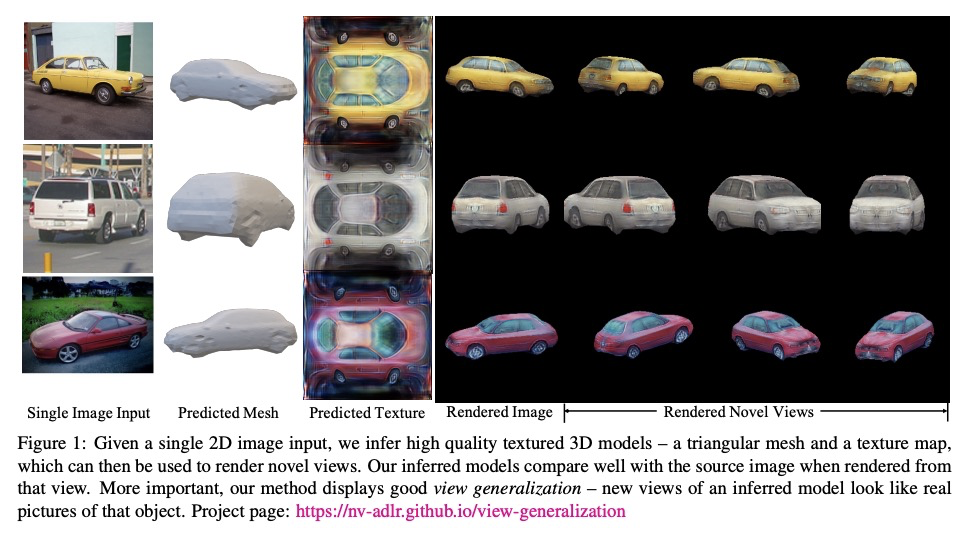
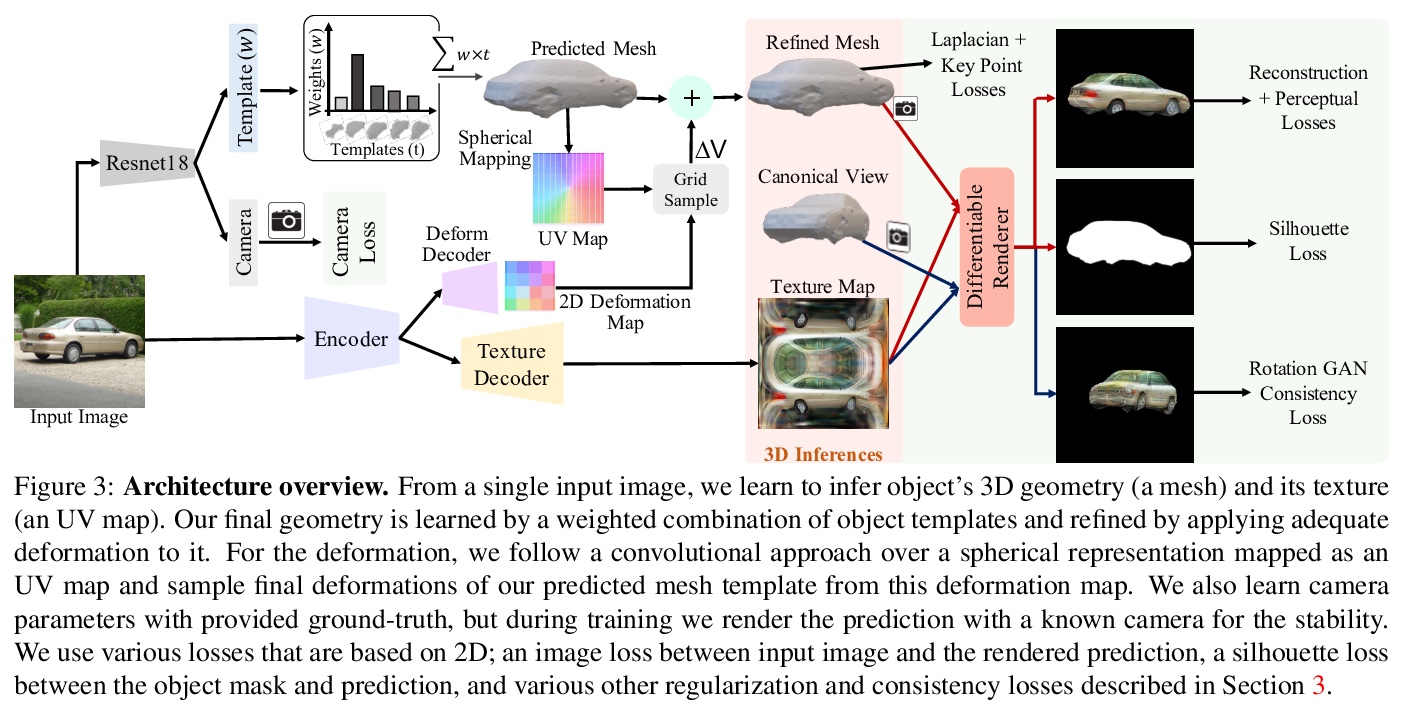
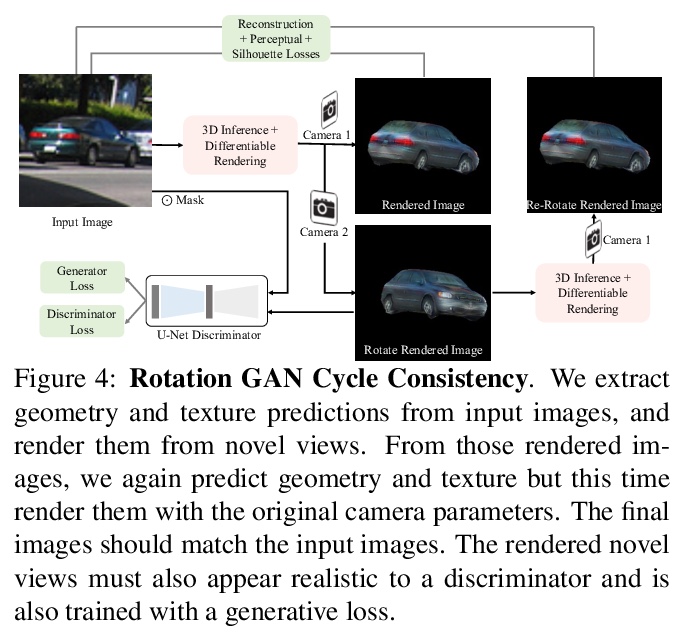
[CV] View Generalization for Single Image Textured 3D Models
单图像3D纹理模型的视图泛化
A Bhattad, A Dundar, G Liu, A Tao, B Catanzaro
[University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign & Bilkent University & NVIDIA]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkeKI2ejS

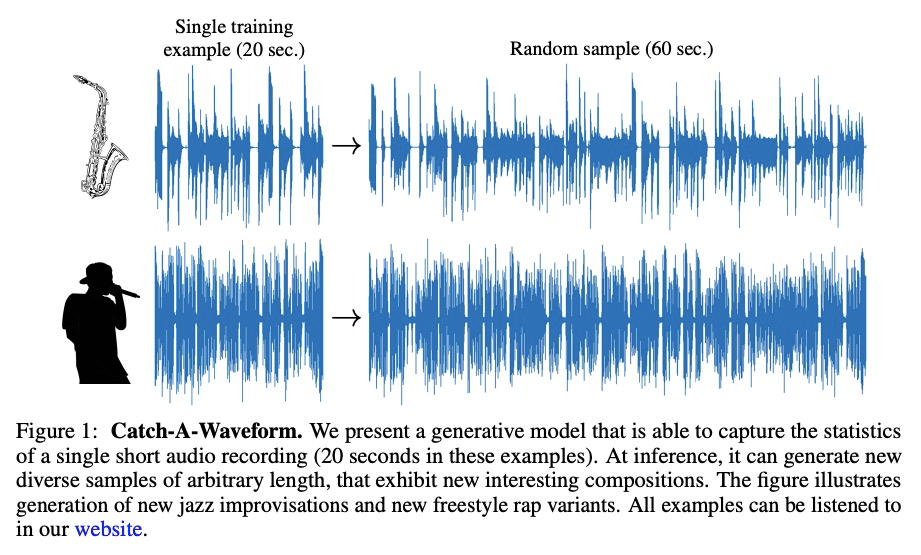
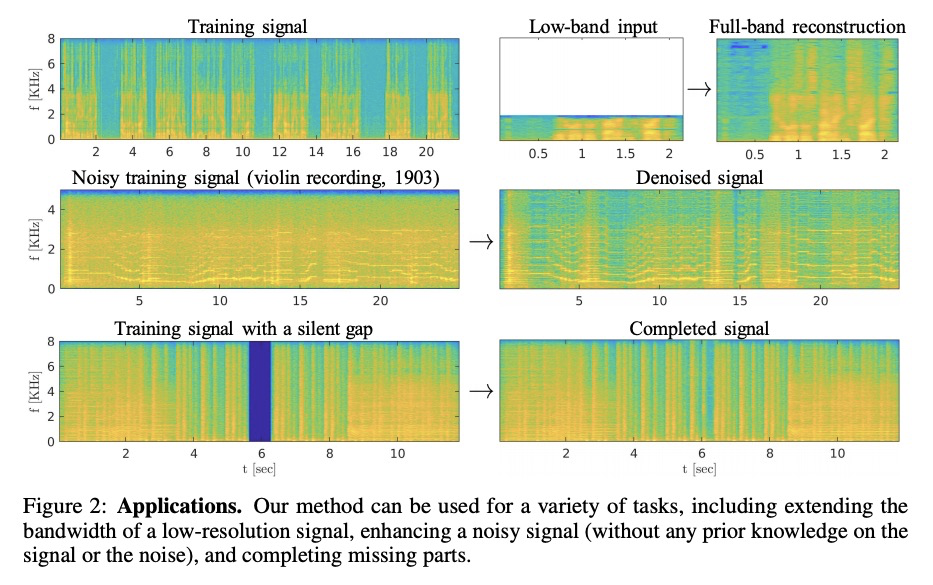
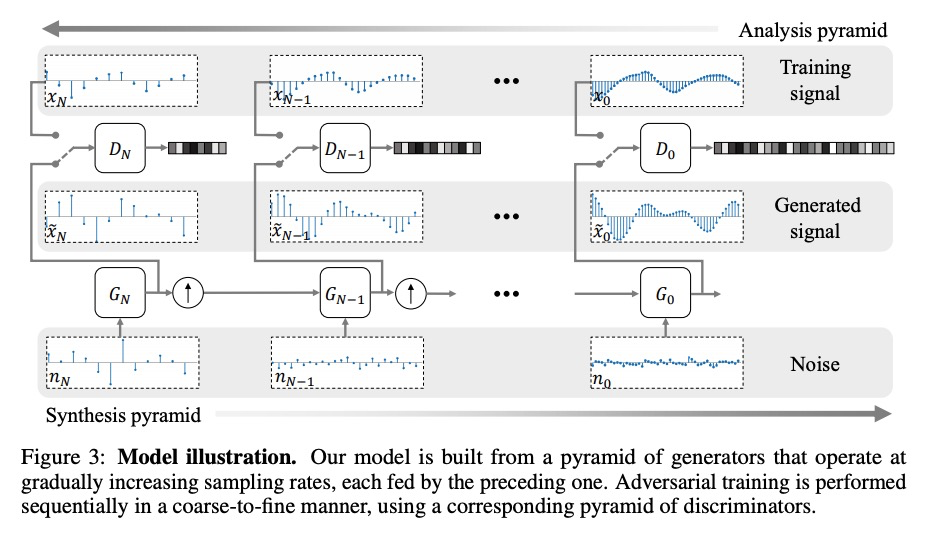
[AS] Catch-A-Waveform: Learning to Generate Audio from a Single Short Example
Catch-A-Waveform:从单个简单样本学习生成音频
G Greshler, T R Shaham, T Michaeli
[Technion – Israel Institute of Technology]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkeMDEbXO
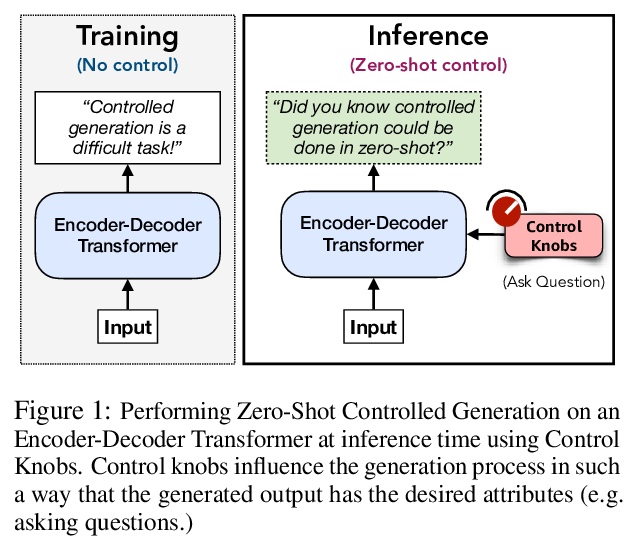
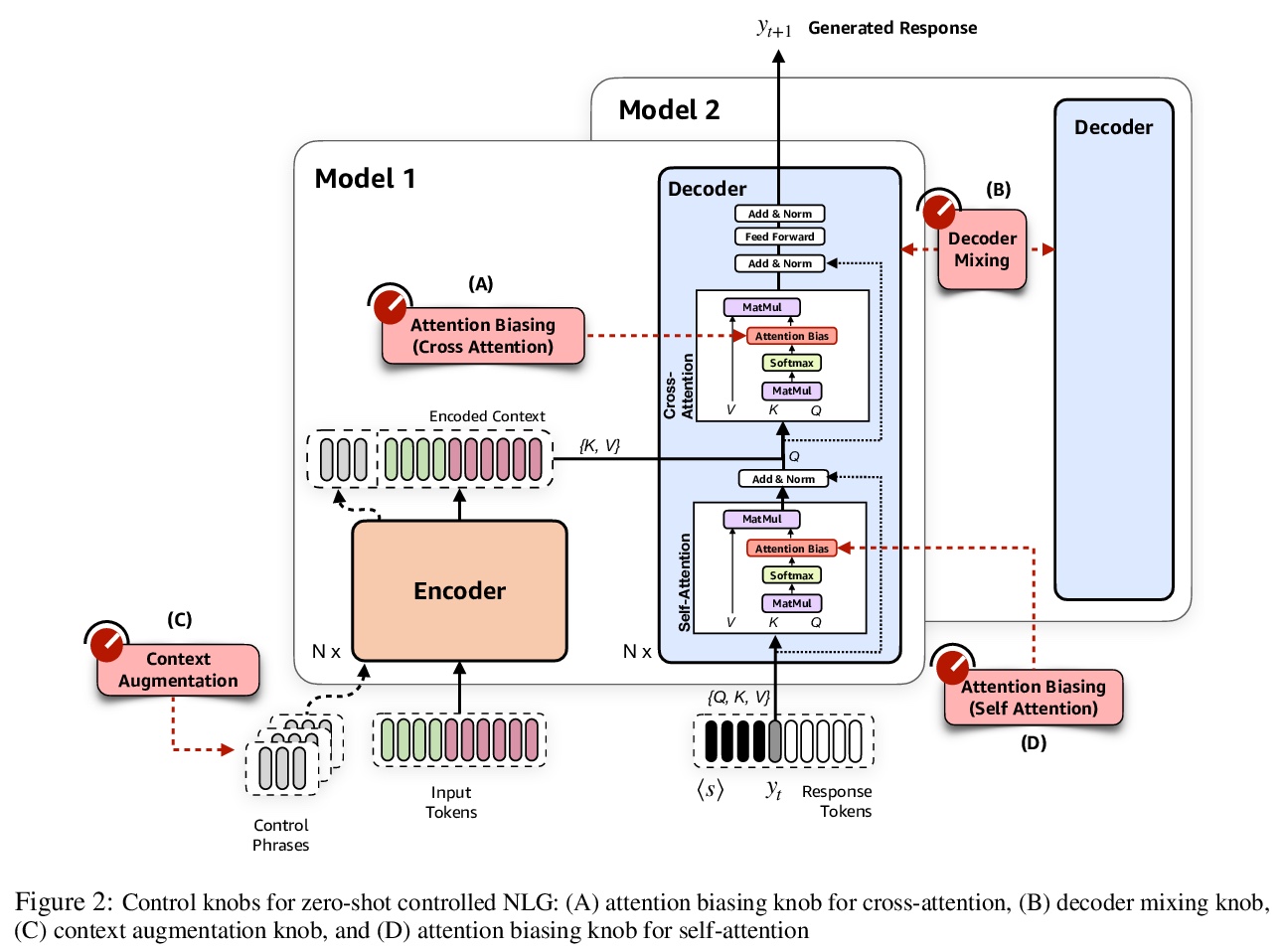
[CL] Zero-Shot Controlled Generation with Encoder-Decoder Transformers
基于编码器-解码器Transformer的零样本控制生成
D Hazarika, M Namazifar, D Hakkani-Tür
[Amazon Alexa AI]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkeO6onsD
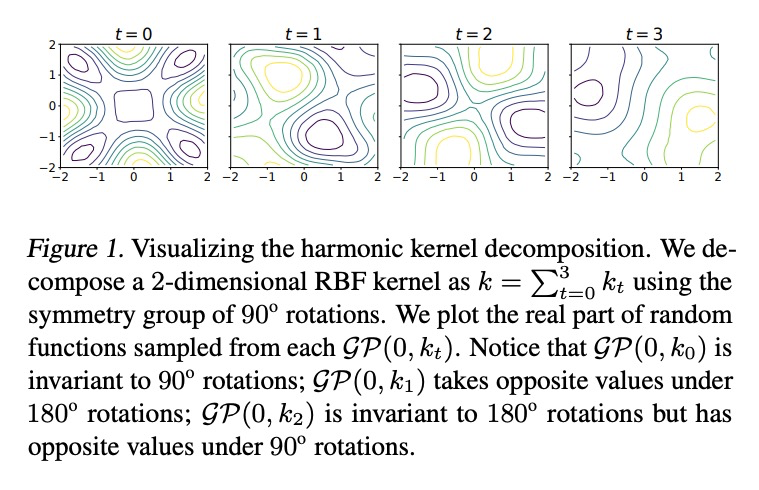
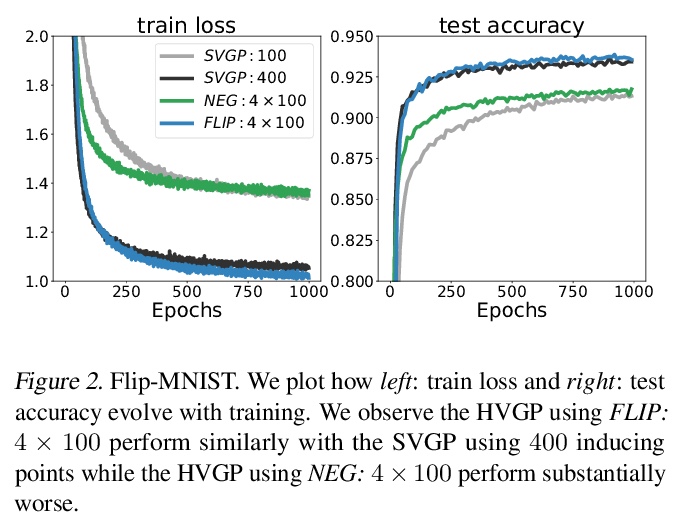
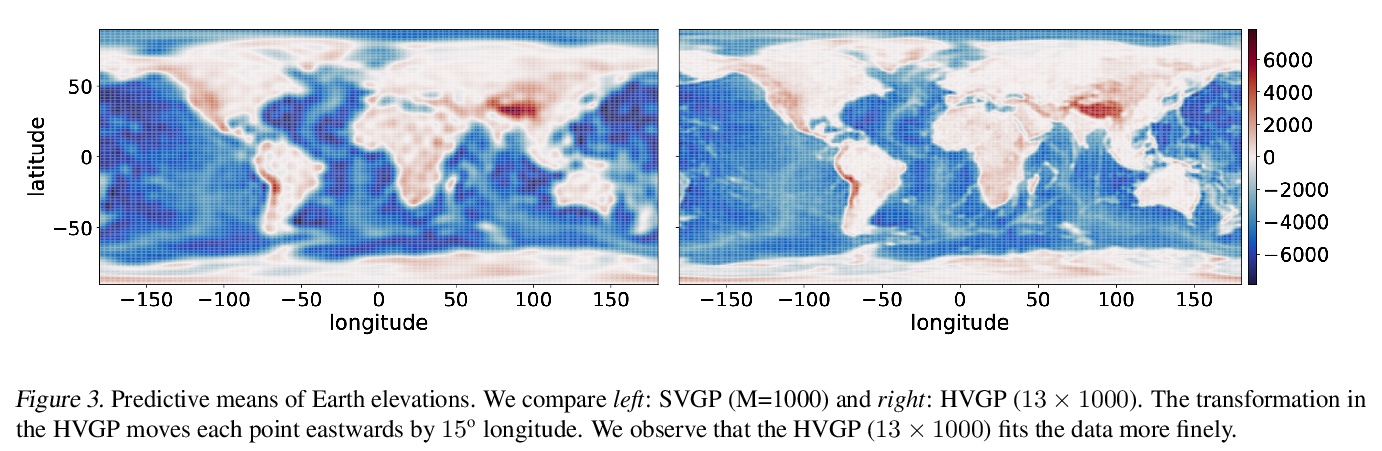
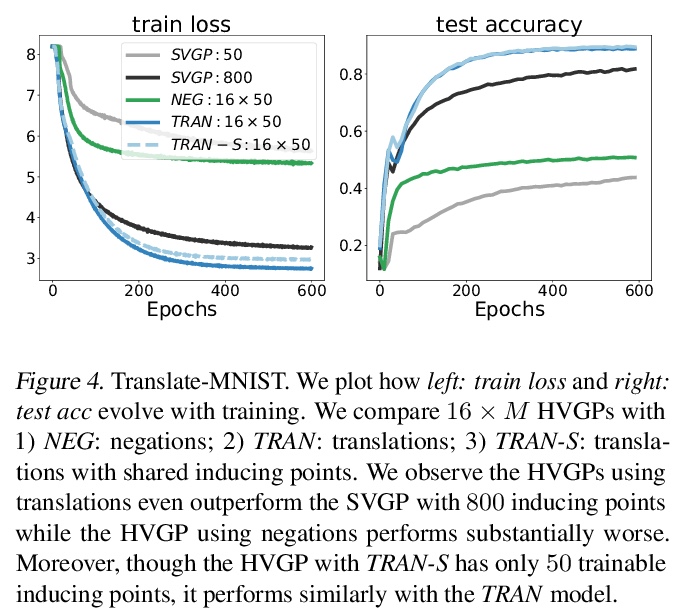
[LG] Scalable Variational Gaussian Processes via Harmonic Kernel Decomposition
基于调和核分解的可扩展变分高斯过程
S Sun, J Shi, A G Wilson, R Grosse
[University of Toronto & Microsoft Research New England & New York University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KkePSCuJh