- 1、[LG] Using large-scale experiments and machine learning to discover theories of human decision-making
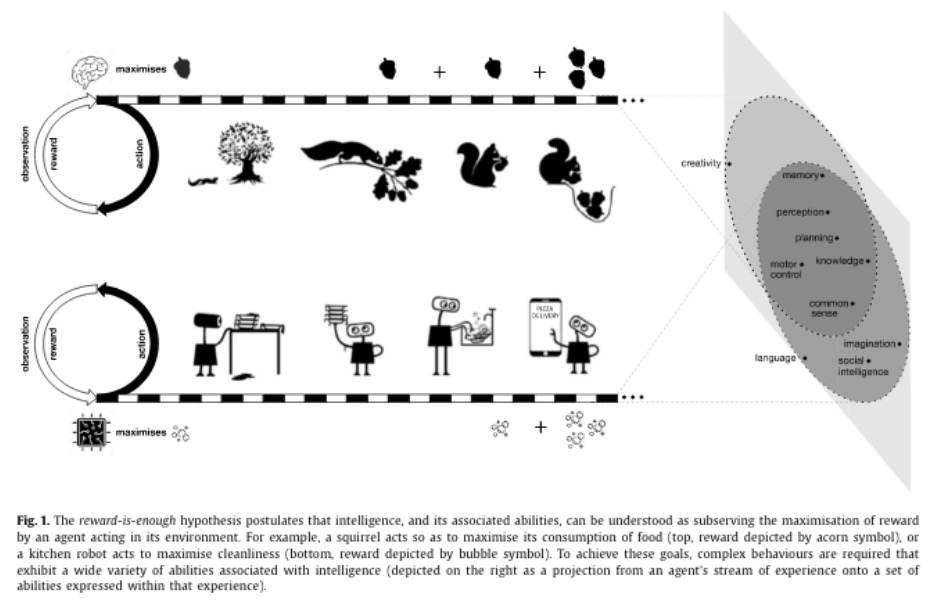
- 2、[LG] Reward is enough
- 3、[LG] Do Transformers Really Perform Bad for Graph Representation?
- 4、[LG] Credit Assignment Through Broadcasting a Global Error Vector
- 5、[CL] Enriching Transformers with Structured Tensor-Product Representations for Abstractive Summarization
- [CV] Space-time Mixing Attention for Video Transformer
- [LG] Self-Supervised Learning with Data Augmentations Provably Isolates Content from Style
- [LG] Learning Gradient Fields for Molecular Conformation Generation
- [CL] On Finding the K-best Non-projective Dependency Trees
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] Using large-scale experiments and machine learning to discover theories of human decision-making
J C. Peterson, D D. Bourgin, M Agrawal, D Reichman, T L. Griffiths
[Princeton University & Worcester Polytechnic Institute]
用大规模实验和机器学习发现人类决策理论。预测和理解人类如何做决策,是许多领域长期以来的目标,人类决策的定量模型,可以为社会科学和工程的研究提供信息。本文展示了如何通过大型数据集为机器学习算法提供动力,来加速实现这一目标的进展,这些算法被限制在产生可解释的心理学理论。进行了迄今为止最大的风险选择实验,用基于梯度的优化,通过人工神经网络实现的可分化决策理论来分析结果,以重述历史上的发现,确定在现有理论上有改进余地,并发现一个新的、更准确的人类决策模型,其形式保留了几个世纪的研究见解。
Predicting and understanding how people make decisions has been a long-standing goal in many fields, with quantitative models of human decision-making informing research in both the social sciences and engineering. We show how progress toward this goal can be accelerated by using large datasets to power machine-learning algorithms that are constrained to produce interpretable psychological theories. Conducting the largest experiment on risky choice to date and analyzing the results using gradient-based optimization of differentiable decision theories implemented through artificial neural networks, we were able to recapitulate historical discoveries, establish that there is room to improve on existing theories, and discover a new, more accurate model of human decision-making in a form that preserves the insights from centuries of research.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kk4YmmlEM
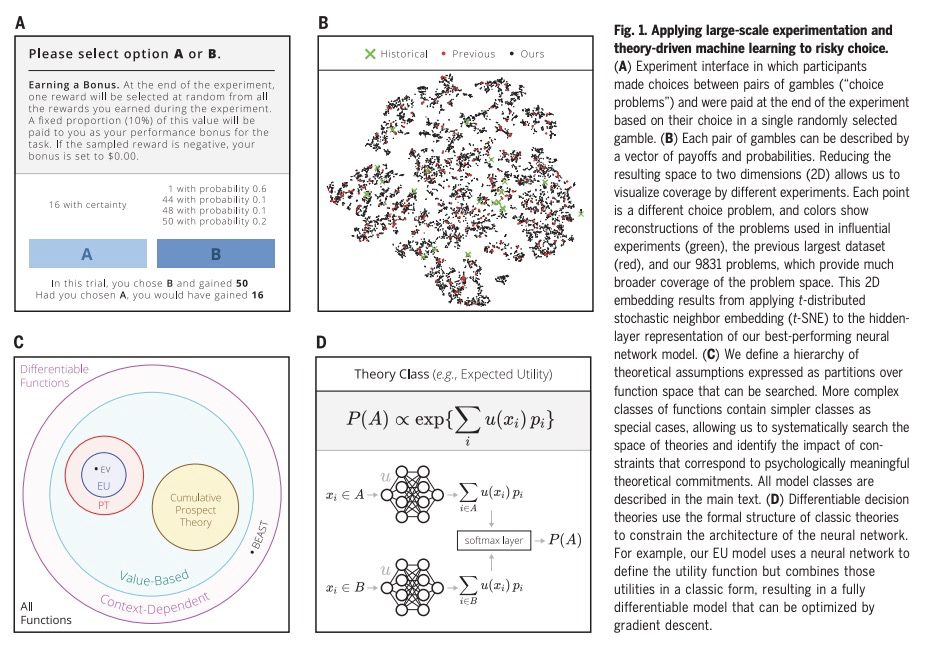
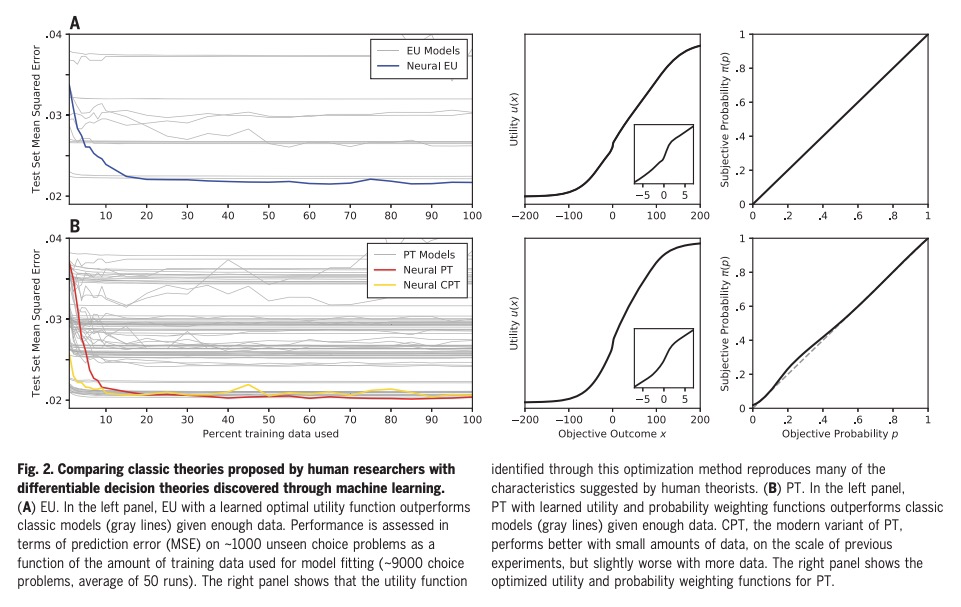
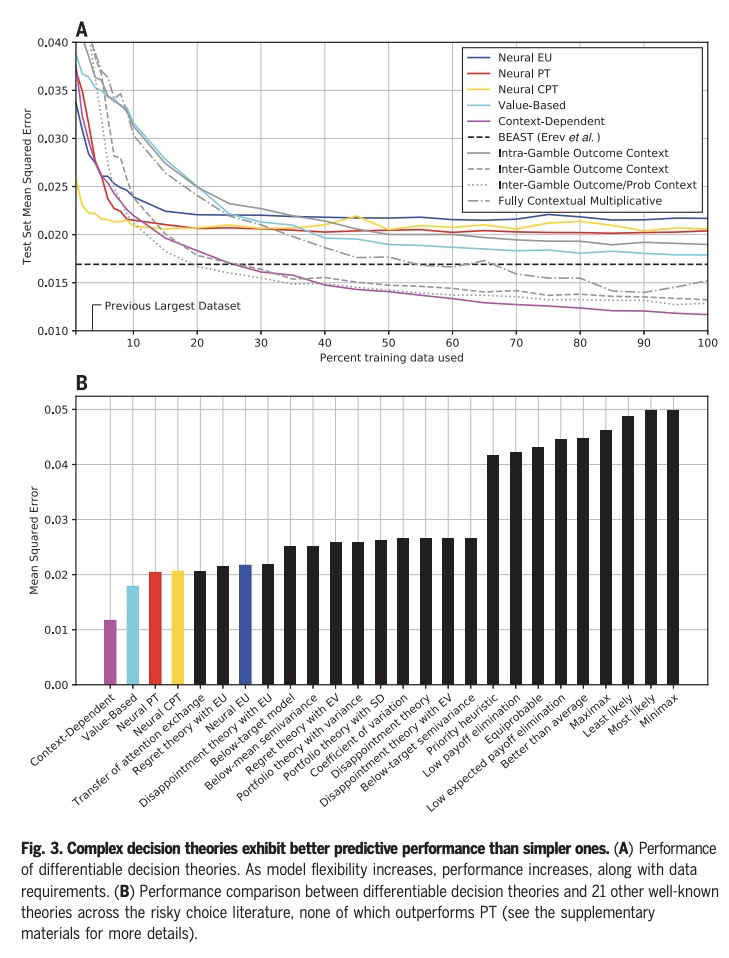
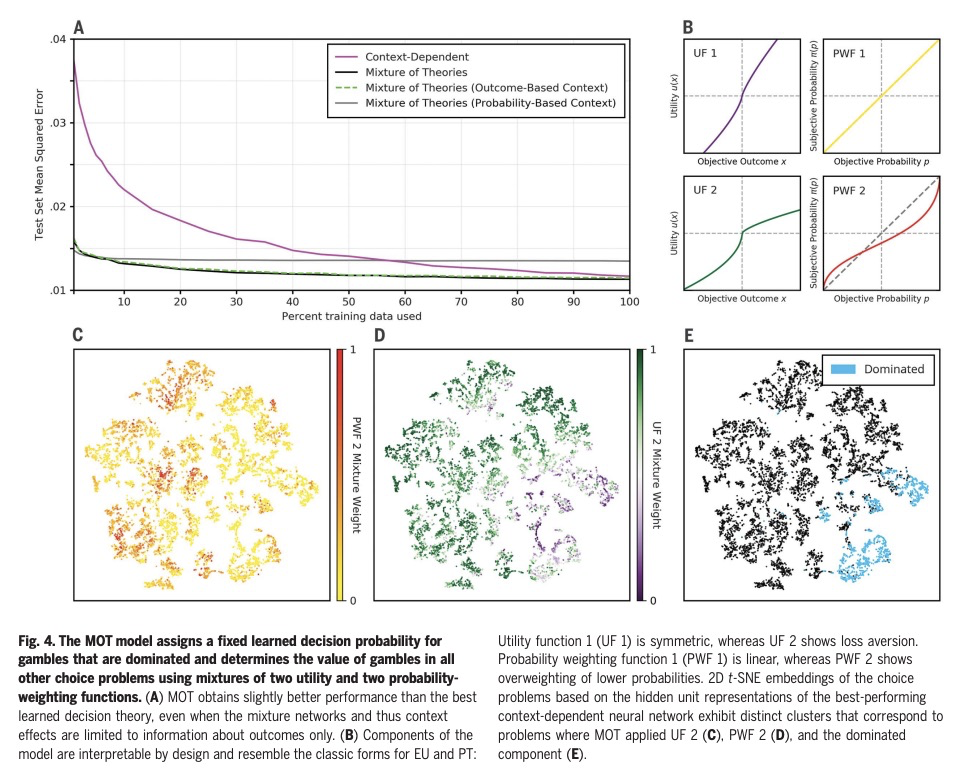
2、[LG] Reward is enough
D Silver, S Singh, D Precup, RS Sutton
[Google]
要智能有奖励就够了。本文假设智力及其相关能力,可以理解为对奖励的最大化,奖励足以驱动表现出自然和人工智能中所研究的能力的行为,包括知识、学习、感知、社会智能、语言、概括和模仿。这与基于其他信号或目标、每种能力都需要专门的问题表述的观点形成鲜明对比。此外,本文建议,通过试错经验进行学习,以获得最大化奖励,智能体可学到表现出大部分(如果不是全部)能力的行为,强大的强化学习智能体可以构成人工通用智能的解决方案。
In this article we hypothesise that intelligence, and its associated abilities, can be understood as subserving the maximisation of reward. Accordingly, reward is enough to drive behaviour that exhibits abilities studied in natural and artificial intelligence, including knowledge, learning, perception, social intelligence, language, generalisation and imitation. This is in contrast to the view that specialised problem formulations are needed for each ability, based on other signals or objectives. Furthermore, we suggest that agents that learn through trial and error experience to maximise reward could learn behaviour that exhibits most if not all of these abilities, and therefore that powerful reinforcement learning agents could constitute a solution to artificial general intelligence.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kk5464oAN
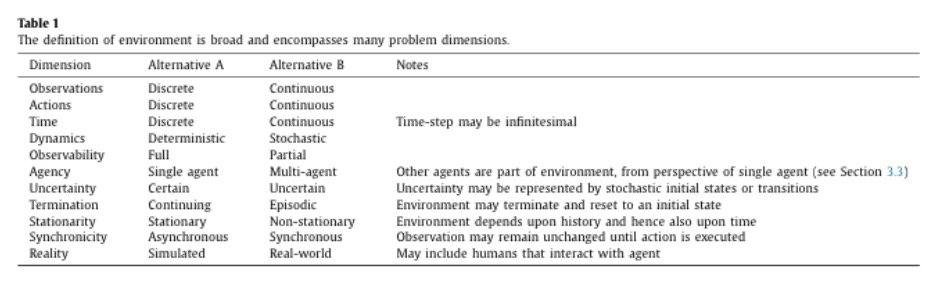
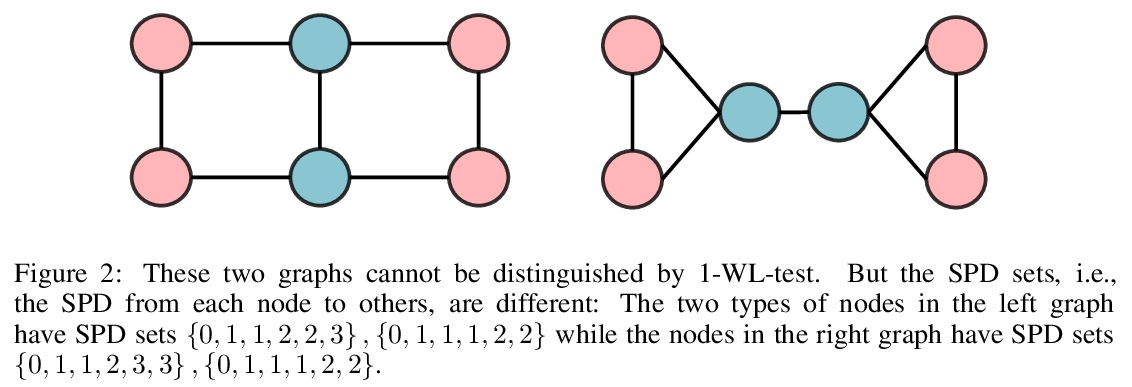
3、[LG] Do Transformers Really Perform Bad for Graph Representation?
C Ying, T Cai, S Luo, S Zheng, G Ke, D He, Y Shen, T Liu
[Dalian University of Technology & Princeton University & Peking University & Microsoft Research Asia]
基于Transformer的图表示学习。Transformer架构已经成为许多领域的首选方案,如自然语言处理和计算机视觉。然而,与主流的GNN变体相比,Transformer在图级别预测的主流排行榜上并没有取得有竞争力的性能。因此,Transformer如何在图表示学习中表现良好仍然是个问题。本文提出Graphormer,以解答该问题,Graphormer建立在标准的Transformer架构之上,可以在广泛的图表示学习任务中取得优异成绩,特别是在最近的OGB大型挑战赛中。本文对在图上利用Transformer的关键见解是,必须将图结构信息有效编码到模型中,为此,提出了几种简单而有效的结构编码方法,以帮助Graphormer更好地建立图结构数据模型。此外,对Graphormer的表达能力进行了数学上的描述,展示了用该方法对图结构信息进行编码,许多流行的GNN变体可以作为Graphormer的特例来涵盖。
The Transformer architecture has become a dominant choice in many domains, such as natural language processing and computer vision. Yet, it has not achieved competitive performance on popular leaderboards of graph-level prediction compared to mainstream GNN variants. Therefore, it remains a mystery how Transformers could perform well for graph representation learning. In this paper, we solve this mystery by presenting Graphormer, which is built upon the standard Transformer architecture, and could attain excellent results on a broad range of graph representation learning tasks, especially on the recent OGB Large-Scale Challenge. Our key insight to utilizing Transformer in the graph is the necessity of effectively encoding the structural information of a graph into the model. To this end, we propose several simple yet effective structural encoding methods to help Graphormer better model graph-structured data. Besides, we mathematically characterize the expressive power of Graphormer and exhibit that with our ways of encoding the structural information of graphs, many popular GNN variants could be covered as the special cases of Graphormer.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kk58jiiyW
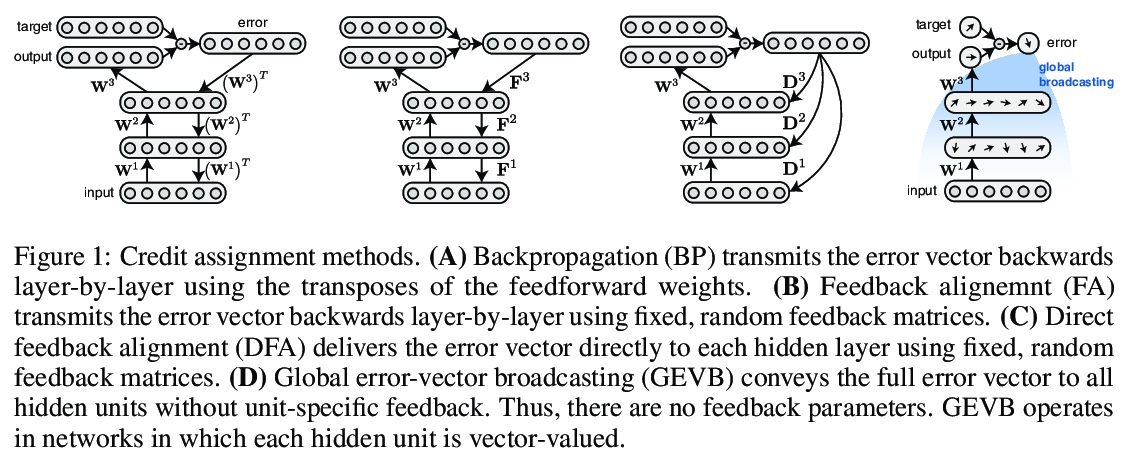
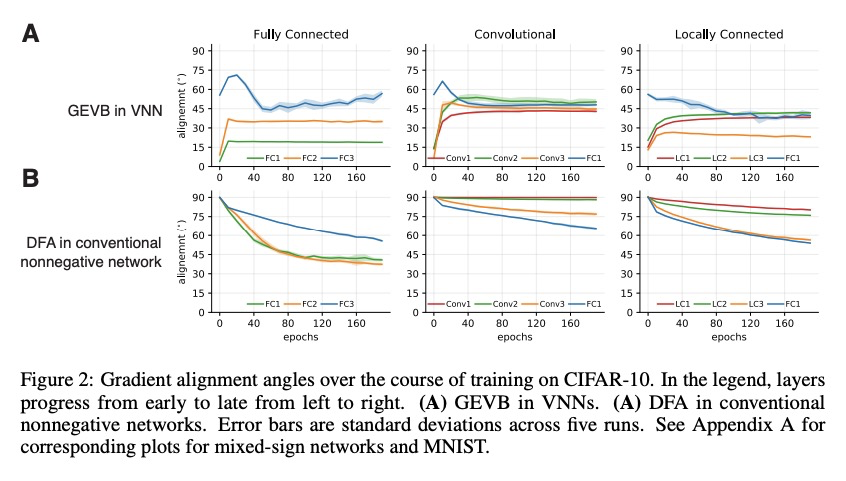
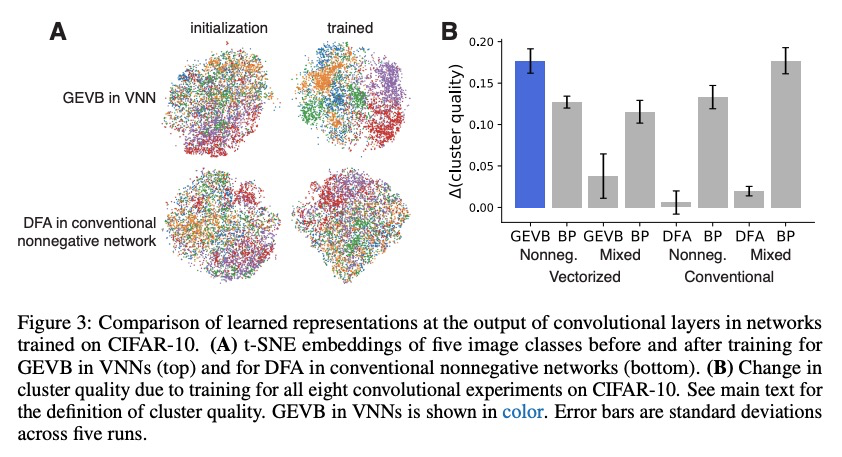
4、[LG] Credit Assignment Through Broadcasting a Global Error Vector
D G. Clark, L. F. Abbott, S Chung
[Columbia University]
基于全局误差向量广播的信用分配。反向传播(BP)用详细的、特定单元的反馈来训练深度神经网络(DNN),并取得了显著成功。生物神经回路似乎可以进行信用分配,但不能实现BP,这意味着存在其他强大的学习算法。本文探讨了全局广播学习信号加上局部权重更新,能否改善DNN的训练。提出了一种学习规则,称为全局误差向量广播(GEVB),以及一类DNN,称为向量非负网络(VNN),学习规则在其中运作。向量非负网络具有第一层后的向量值单元和非负权重。GEVB学习规则概括了三因素Hebbian学习,当突触后单元活跃时,每个权重的更新量与突触前激活和全局广播误差向量的内积成正比。本文证明,这些权重的更新与梯度的正负相匹配,从而实现准确的信用分配。此外,在初始化时,这些更新与无限网络宽度限制下的梯度完全成正比。GEVB与VNN中的BP性能相匹配,在某些情况下优于传统网络中应用的直接反馈调整(DFA)。与DFA不同,GEVB成功地训练了卷积层。本文的理论和经验结果表明,全局学习信号在训练DNN中具有令人惊讶的强大作用。
Backpropagation (BP) uses detailed, unit-specific feedback to train deep neural networks (DNNs) with remarkable success. That biological neural circuits appear to perform credit assignment, but cannot implement BP, implies the existence of other powerful learning algorithms. Here, we explore the extent to which a globally broadcast learning signal, coupled with local weight updates, enables training of DNNs. We present both a learning rule, called global error-vector broadcasting (GEVB), and a class of DNNs, called vectorized nonnegative networks (VNNs), in which this learning rule operates. VNNs have vector-valued units and nonnegative weights past the first layer. The GEVB learning rule generalizes three-factor Hebbian learning, updating each weight by an amount proportional to the inner product of the presynaptic activation and a globally broadcast error vector when the postsynaptic unit is active. We prove that these weight updates are matched in sign to the gradient, enabling accurate credit assignment. Moreover, at initialization, these updates are exactly proportional to the gradient in the limit of infinite network width. GEVB matches the performance of BP in VNNs, and in some cases outperforms direct feedback alignment (DFA) applied in conventional networks. Unlike DFA, GEVB successfully trains convolutional layers. Altogether, our theoretical and empirical results point to a surprisingly powerful role for a global learning signal in training DNNs.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kk5cwyoYP

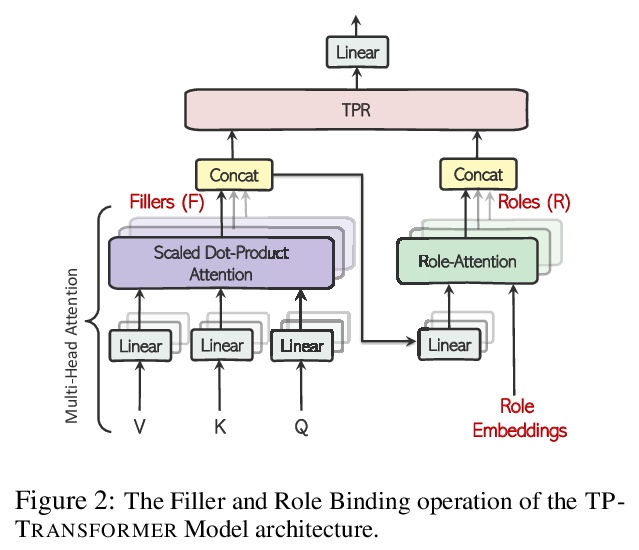
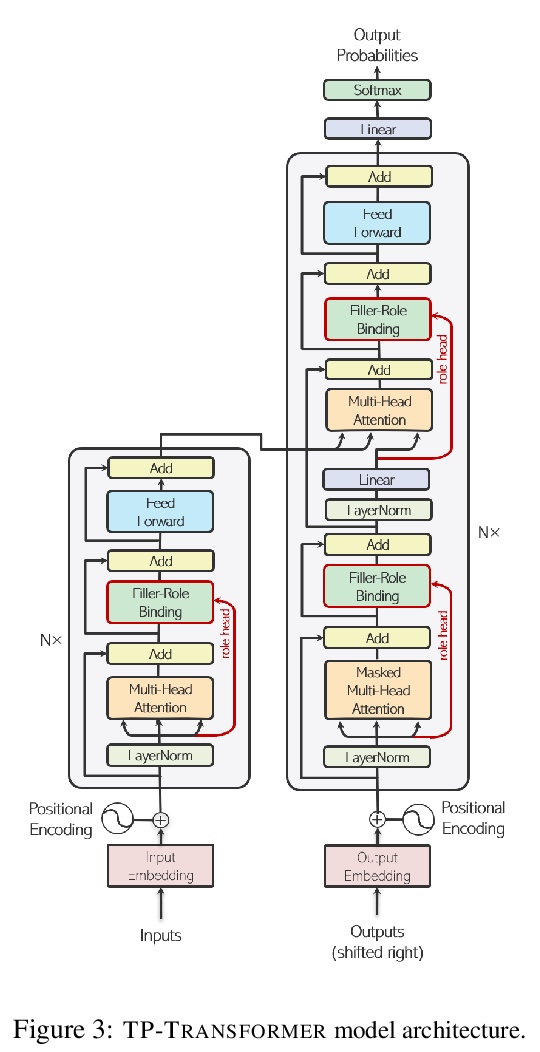
5、[CL] Enriching Transformers with Structured Tensor-Product Representations for Abstractive Summarization
Y Jiang, A Celikyilmaz, P Smolensky, P Soulos, S Rao, H Palangi, R Fernandez, C Smith, M Bansal, J Gao
[UNC Chapel Hill & Microsoft Research & Johns Hopkins University]
面向抽象摘要的结构化张量积表示Transformer。抽象摘要,即生成输入文档的简明摘要的任务,需要:(1)对源文档进行推理,以确定分散在长文件中的突出信息,(2)通过将这些突出事实重构为一个较短摘要,忠实地反映连接这些事实的复杂关系,进而组成一段内部一致的文本。本文面向抽象摘要任务对TP-TRANSFORMER进行了调整,TP-TRANSFORMER用显式组合张量积表示(TPR)来丰富原始Transformer。本文模型的关键特征是结构上的偏差,通过为每个标记编码两种独立表示,分别表示句法结构(用角色向量)和语义内容(用填充向量),将角色向量和填充向量结合到TPR中,作为该层的输出。结构化的中间表征,使模型在生成摘要时能够更好地控制内容(突出的事实)和结构(连接事实的句法)。经验表明,TP-TRANSFORMER在几个基于自动和人工评估的抽象摘要数据集上明显优于Transformer和原始TP-TRANSFORMER。在几个句法和语义探测任务中,证明了角色向量中出现的结构信息和TPR层输出中改进的句法可解释性。
Abstractive summarization, the task of generating a concise summary of input documents, requires: (1) reasoning over the source document to determine the salient pieces of information scattered across the long document, and (2) composing a cohesive text by reconstructing these salient facts into a shorter summary that faithfully reflects the complex relations connecting these facts. In this paper, we adapt TP-TRANSFORMER (Schlag et al., 2019), an architecture that enriches the original Transformer (Vaswani et al., 2017) with the explicitly compositional Tensor Product Representation (TPR), for the task of abstractive summarization. The key feature of our model is a structural bias that we introduce by encoding two separate representations for each token to represent the syntactic structure (with role vectors) and semantic content (with filler vectors) separately. The model then binds the role and filler vectors into the TPR as the layer output. We argue that the structured intermediate representations enable the model to take better control of the contents (salient facts) and structures (the syntax that connects the facts) when generating the summary. Empirically, we show that our TP-TRANSFORMER outperforms the Transformer and the original TPTRANSFORMER significantly on several abstractive summarization datasets based on both automatic and human evaluations. On several syntactic and semantic probing tasks, we demonstrate the emergent structural information in the role vectors and improved syntactic interpretability in the TPR layer outputs.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kk5iQ5865

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
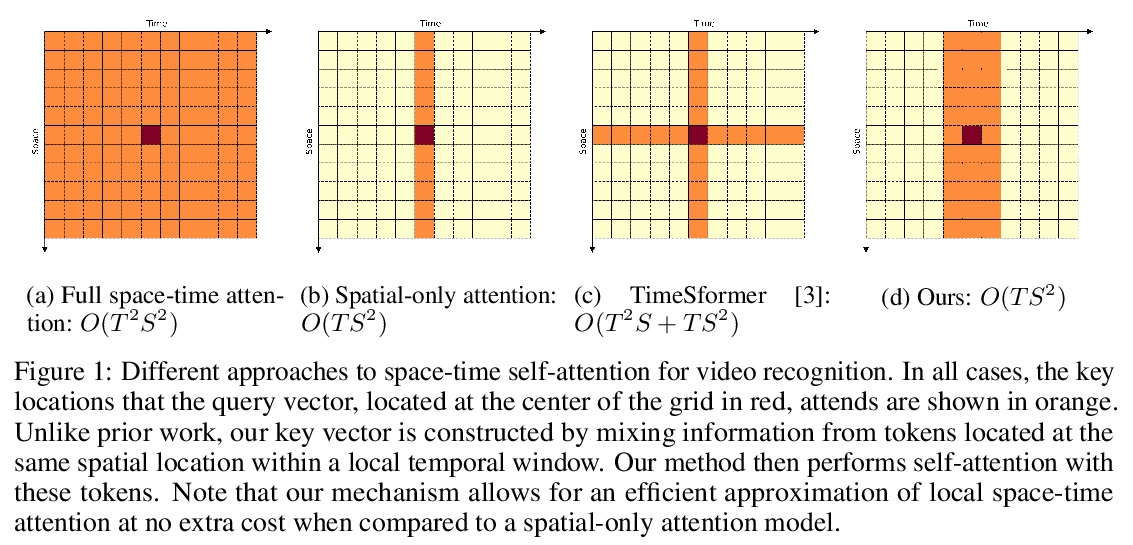
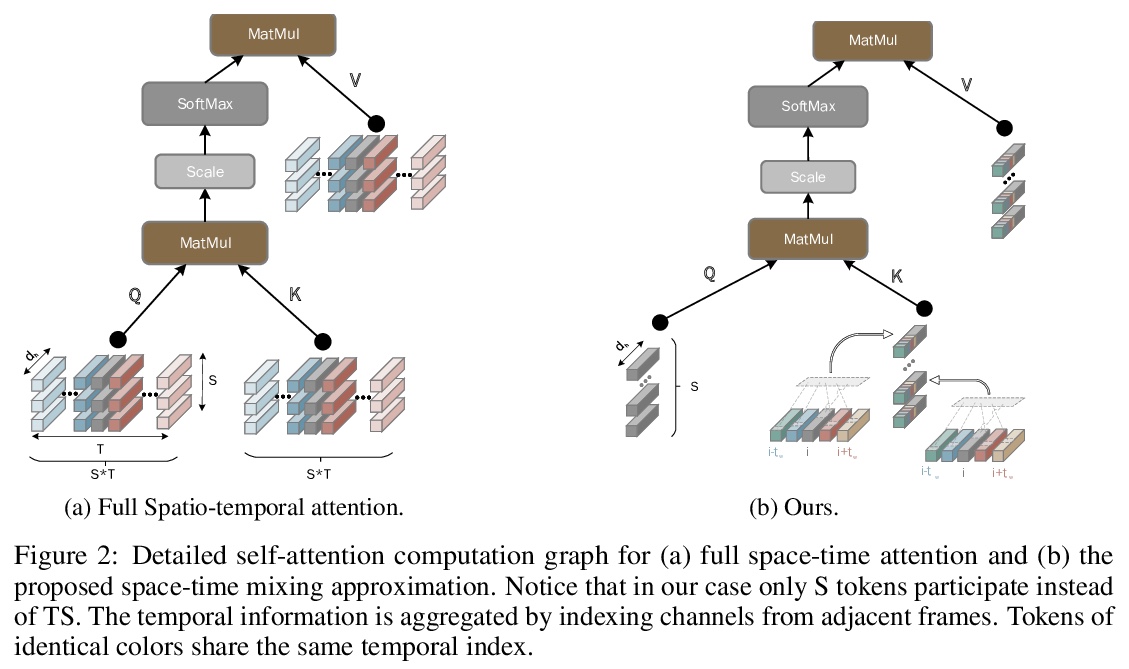
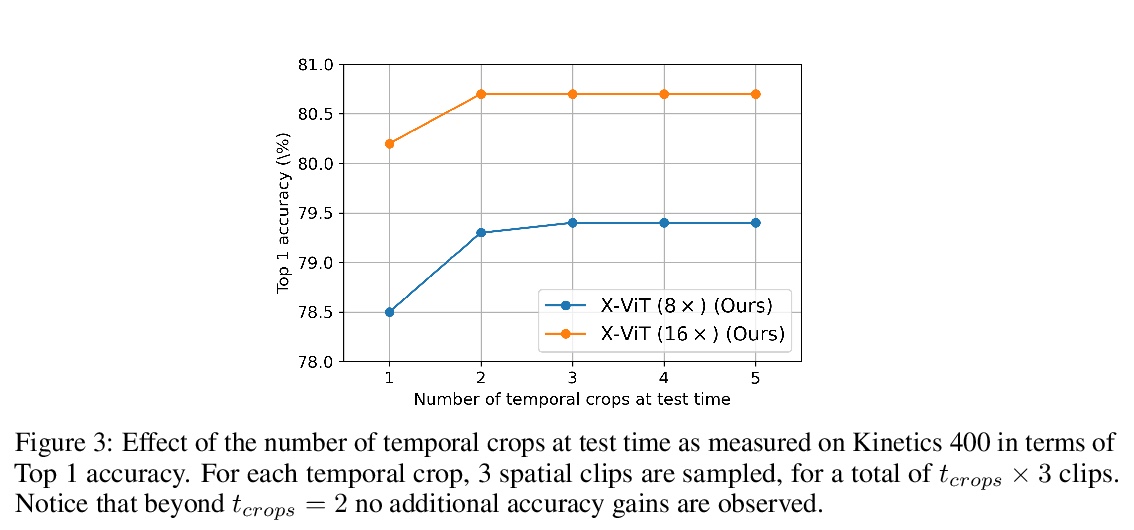
[CV] Space-time Mixing Attention for Video Transformer
视频Transformer的空-时混合注意力
A Bulat, J Perez-Rua, S Sudhakaran, B Martinez, G Tzimiropoulos
[Samsung AI Cambridge]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kk5nDDC0E
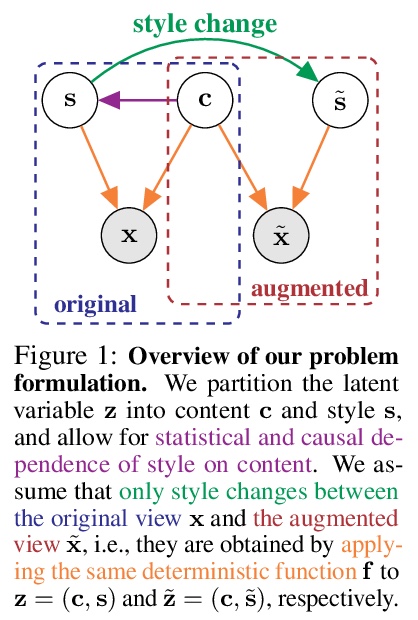
[LG] Self-Supervised Learning with Data Augmentations Provably Isolates Content from Style
基于可证内容风格分离数据增强的自监督学习
J v Kügelgen, Y Sharma, L Gresele, W Brendel, B Schölkopf, M Besserve, F Locatello
[Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems & Tübingen University of Tübingen & Amazon]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kk5psrWuq
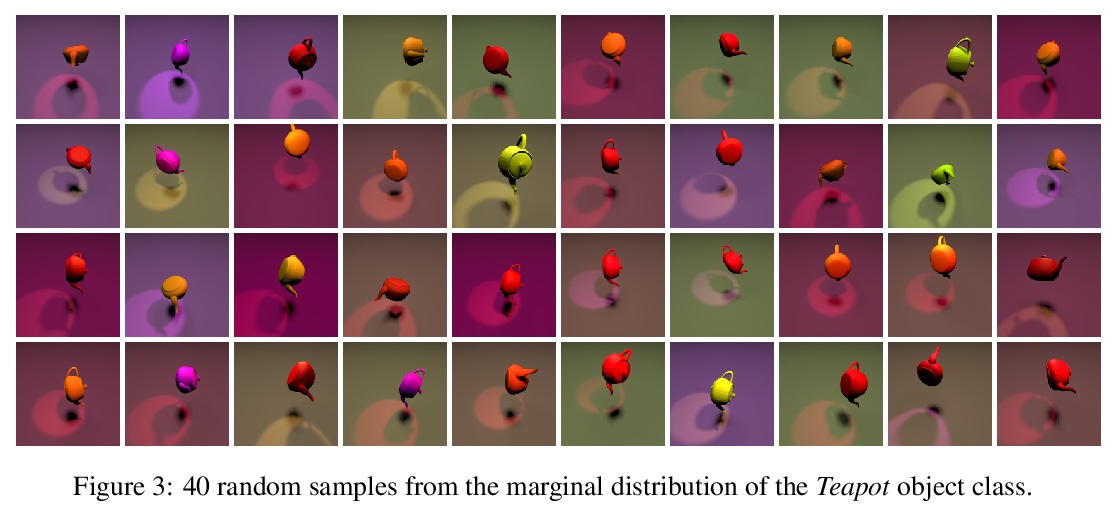
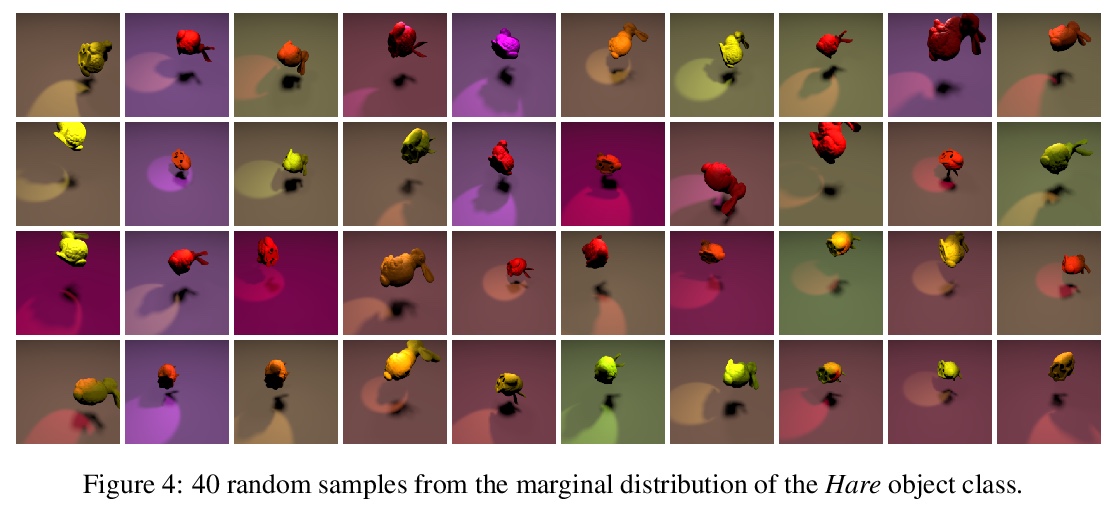


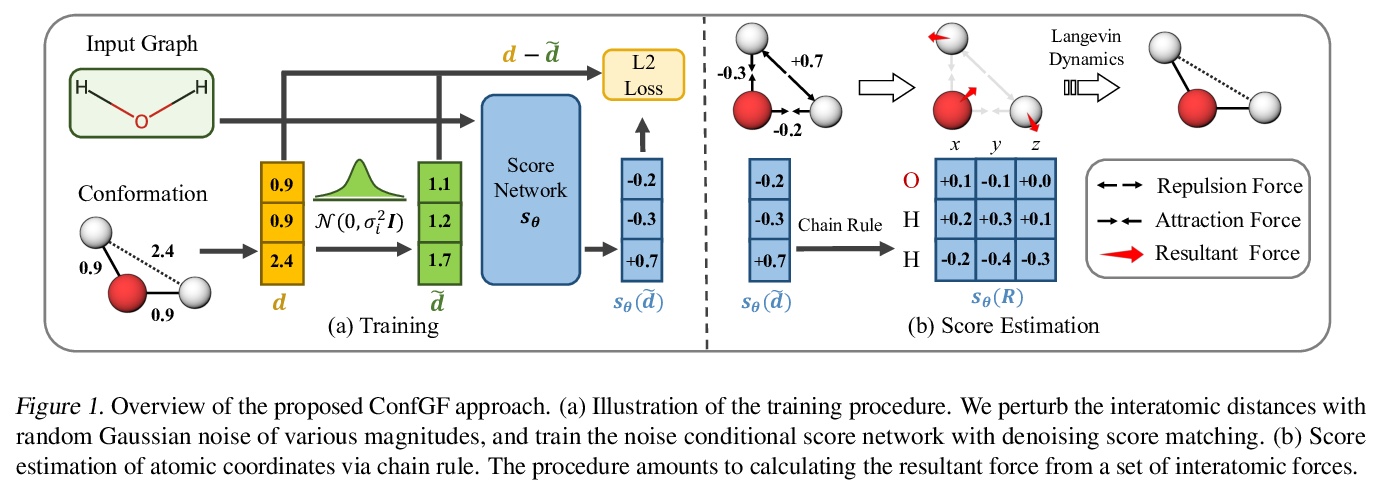
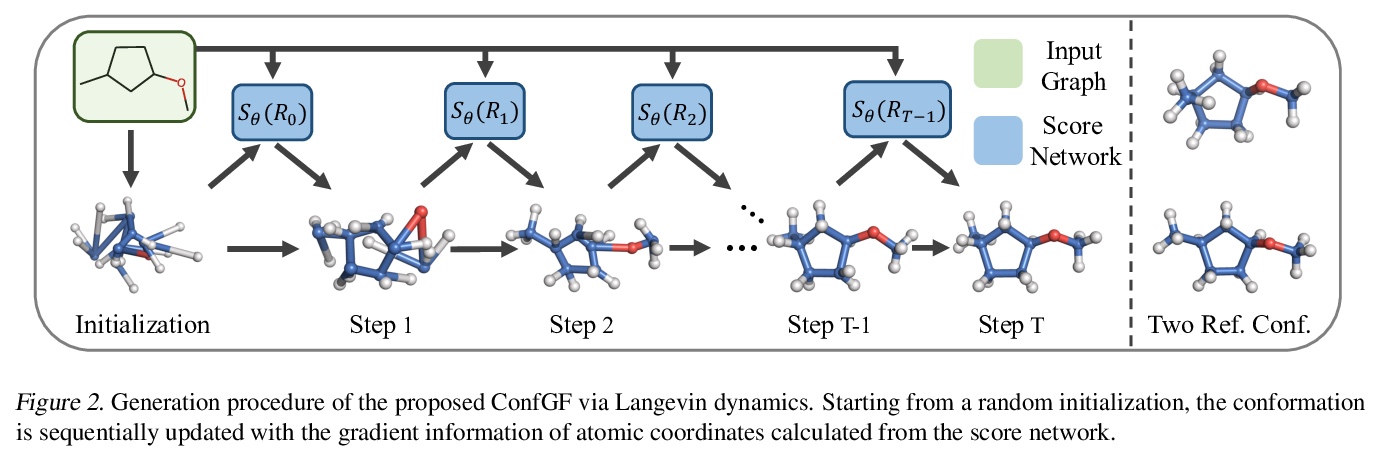
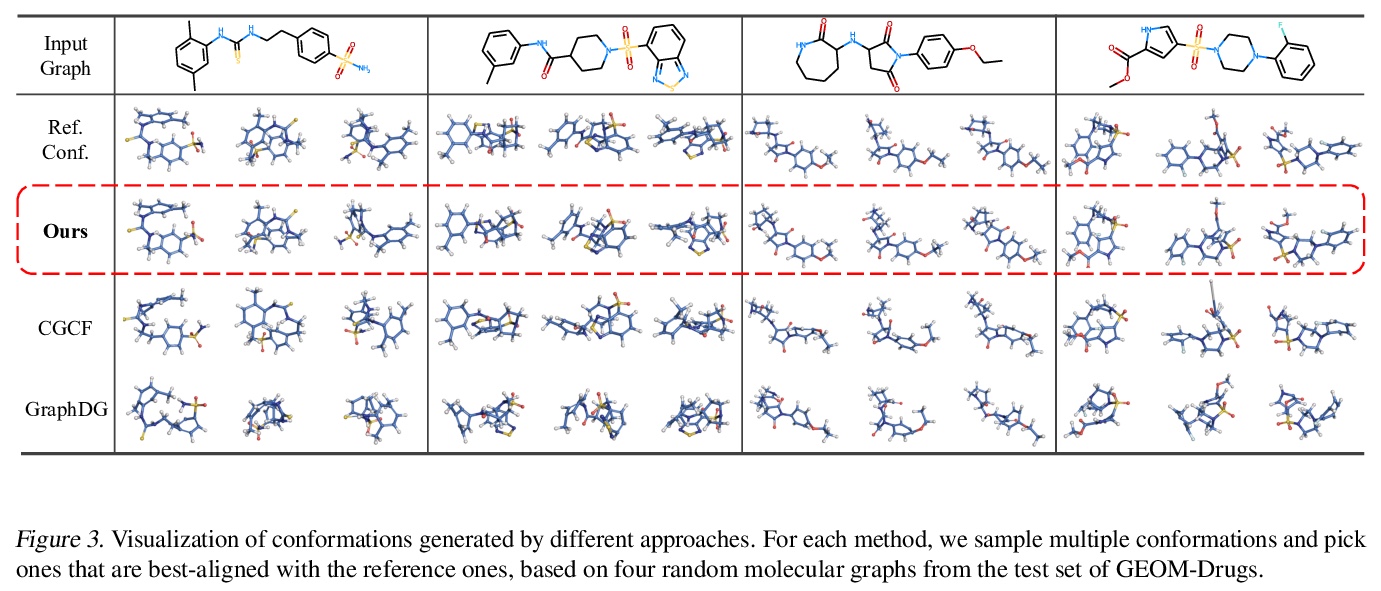
[LG] Learning Gradient Fields for Molecular Conformation Generation
面向分子构象生成的梯度场学习
C Shi, S Luo, M Xu, J Tang
[Mila & Peking University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kk5rSyutt

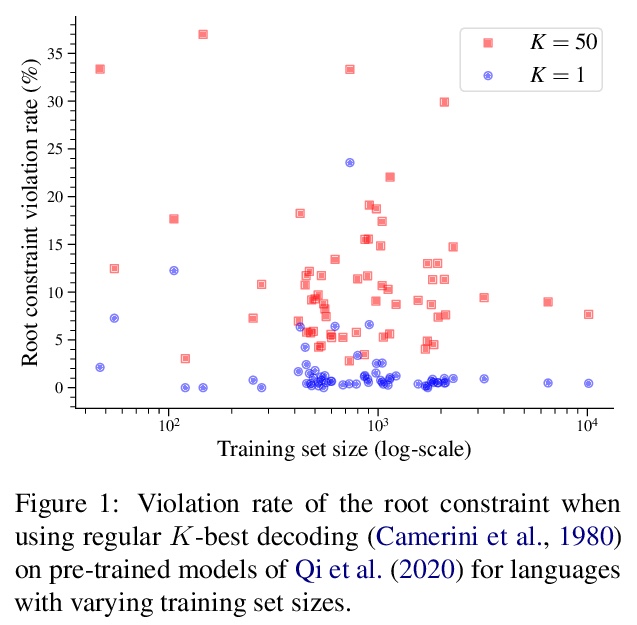
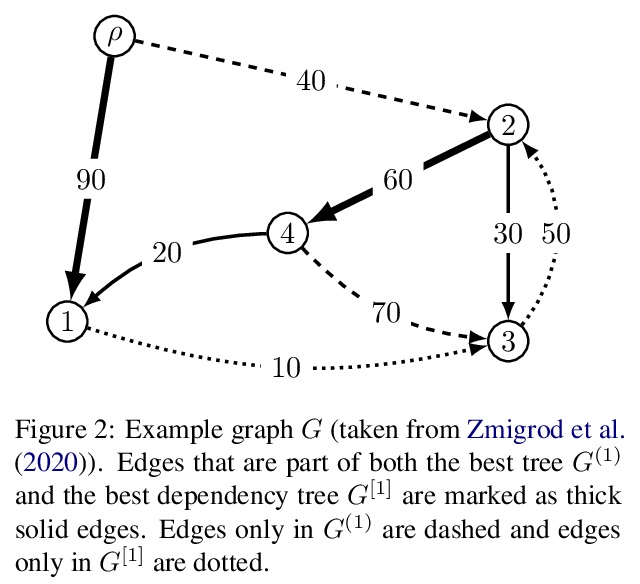
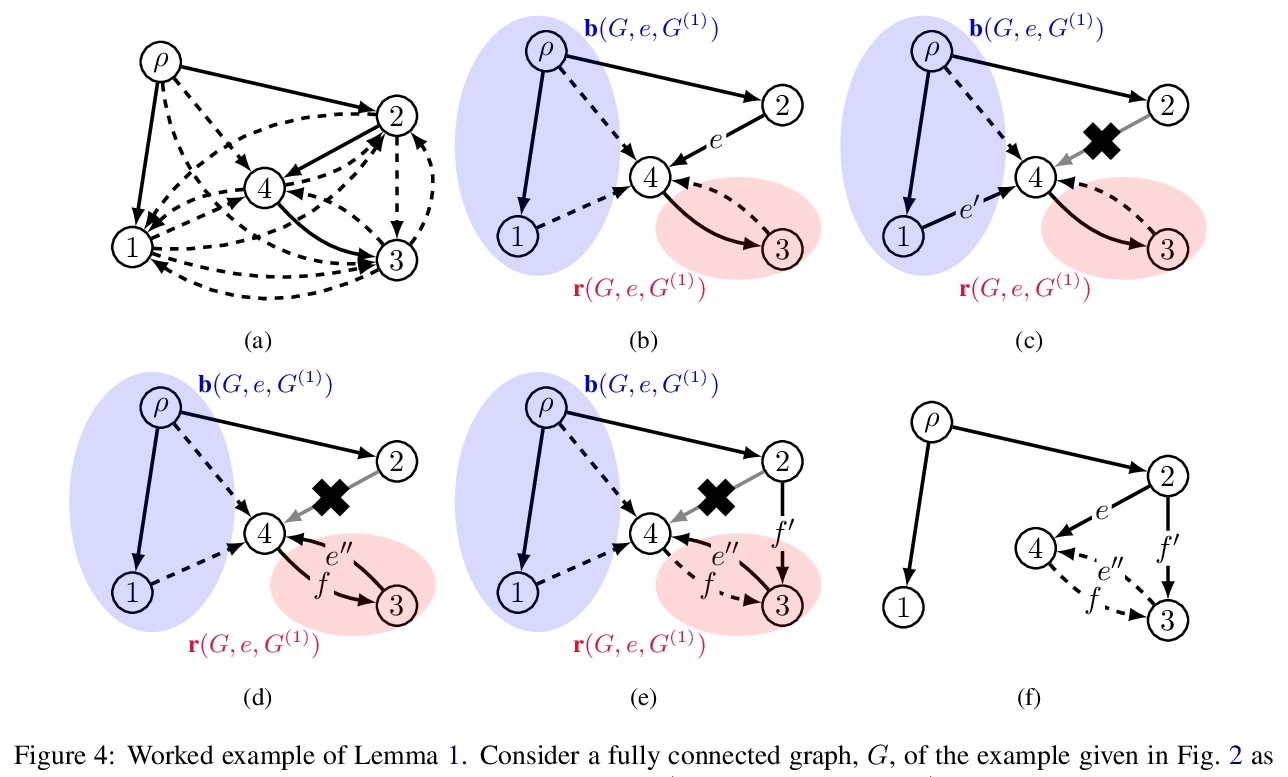
[CL] On Finding the K-best Non-projective Dependency Trees
K最佳非投射依存树探索
R Zmigrod, T Vieira, R Cotterell
[University of Cambridge & Johns Hopkins University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Kk5upwd0G