LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[CV] A Note on Data Biases in Generative Models
P Esser, R Rombach, B Ommer
[Heidelberg University]
生成模型的数据偏差。机器学习基于数据计算输出,模型特别容易反映出用于训练的数据集的偏差,其所反映的,未必是世界的真相,而主要是关于数据的真相。本文用条件性可逆神经网络,将不同数据集间共享信息与特定于数据的信息解缠。通过这种方式,将相同的图像投射到不同数据集上,以揭示其固有偏差。用这种方法来:(i)调查数据集质量对生成模型性能的影响,(ii)显示数据集的社会偏见是如何被生成模型复制的,(iii)通过不同数据集(如照片、油画和动画)之间的非配对迁移呈现的创造性应用。
It is tempting to think that machines are less prone to unfairness and prejudice. However, machine learning approaches compute their outputs based on data. While biases can enter at any stage of the development pipeline, models are particularly receptive to mirror biases of the datasets they are trained on and therefore do not necessarily reflect truths about the world but, primarily, truths about the data. To raise awareness about the relationship between modern algorithms and the data that shape them, we use a conditional invertible neural network to disentangle the dataset-specific information from the information which is shared across different datasets. In this way, we can project the same image onto different datasets, thereby revealing their inherent biases. We use this methodology to (i) investigate the impact of dataset quality on the performance of generative models, (ii) show how societal biases of datasets are replicated by generative models, and (iii) present creative applications through unpaired transfer between diverse datasets such as photographs, oil portraits, and animes. Our code and an interactive demonstration are available at > this https URL .
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jxs0Sq5wO

2、** **[CV] BoxInst: High-Performance Instance Segmentation with Box Annotations
Z Tian, C Shen, X Wang, H Chen
[The University of Adelaide]
基于框标记的高性能实例分割。提出BoxInst,只使用框标记,就可实现高质量的实例分割,其核心思想,是用所提出的投影和成对亲和力掩模损失代替原来的像素级掩模损失,无需对分割网络本身进行修改。实验表明,重新设计的掩模损失只用标记框就可产生高质量的实例掩模,显著缩小了弱监督实例分割和全监督实例分割之间的性能差距。
We present a high-performance method that can achieve mask-level instance segmentation with only bounding-box annotations for training. While this setting has been studied in the literature, here we show significantly stronger performance with a simple design (e.g., dramatically improving previous best reported mask AP of 21.1% in Hsu et al. (2019) to 31.6% on the COCO dataset). Our core idea is to redesign the loss of learning masks in instance segmentation, with no modification to the segmentation network itself. The new loss functions can supervise the mask training without relying on mask annotations. This is made possible with two loss terms, namely, 1) a surrogate term that minimizes the discrepancy between the projections of the ground-truth box and the predicted mask; 2) a pairwise loss that can exploit the prior that proximal pixels with similar colors are very likely to have the same category label. Experiments demonstrate that the redesigned mask loss can yield surprisingly high-quality instance masks with only box annotations. For example, without using any mask annotations, with a ResNet-101 backbone and 3x training schedule, we achieve 33.2% mask AP on COCO test-dev split (vs. 39.1% of the fully supervised counterpart). Our excellent experiment results on COCO and Pascal VOC indicate that our method dramatically narrows the performance gap between weakly and fully supervised instance segmentation.Code is available at: > this https URL
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jxs66zj0S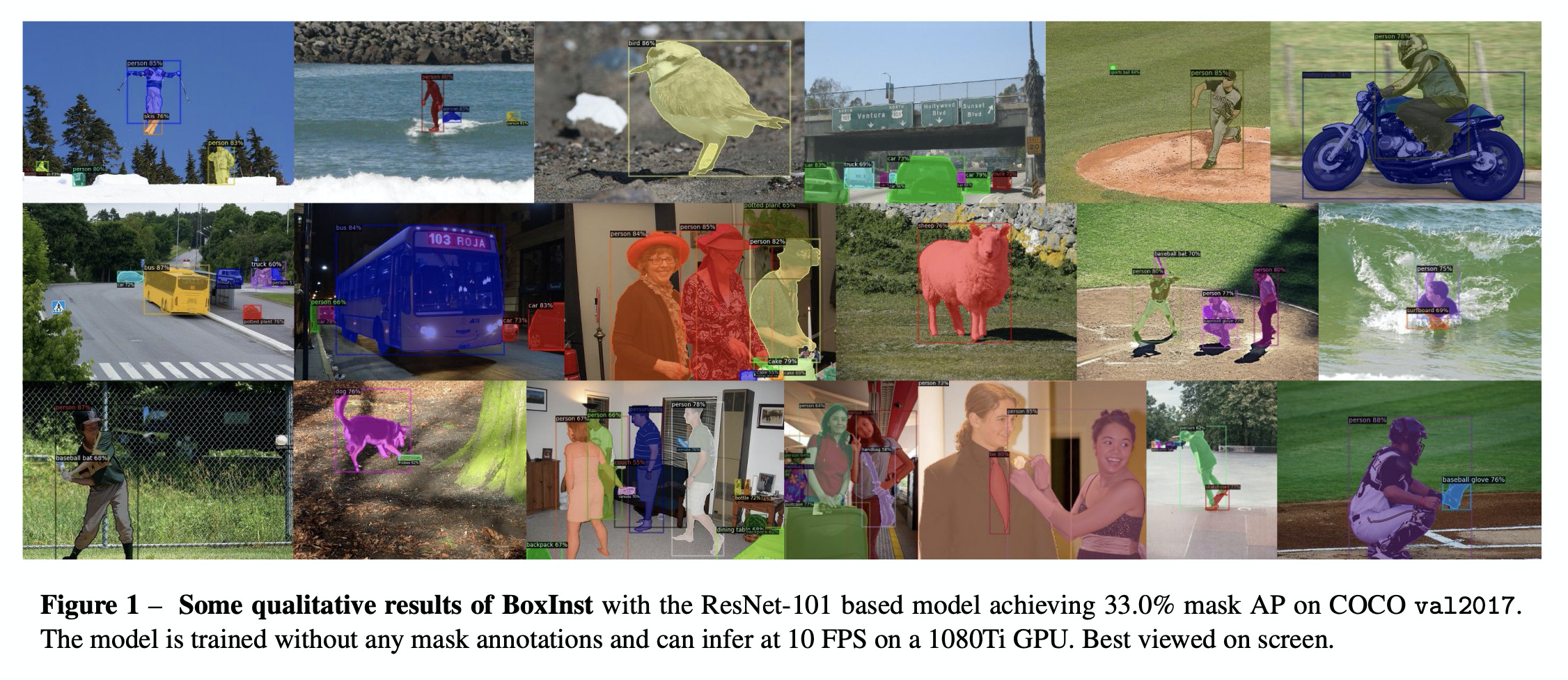

3、** **[CL] Playing Text-Based Games with Common Sense
S Dambekodi, S Frazier, P Ammanabrolu, M O. Riedl
[Georgia Institute of Technology]
用常识玩文字类型游戏。探索用两种技术,将常识整合到玩文本类型游戏的智能体。用COMET常识推理模型,和BERT语言模型,推断世界状态可能存在的隐藏方面。根据语言模型所识别的共同模式,偏置智能体的探索行为。在9to05游戏中进行了测试,这是一个基于文本的游戏的极端版本,需要与日常物品以及场景进行大量交互,得出的结论是,常识性推断可用于增强智能体对世界状态的信念,使智能体对观察失败或文本描述缺失的信息更具鲁棒性。
Text based games are simulations in which an agent interacts with the world purely through natural language. They typically consist of a number of puzzles interspersed with interactions with common everyday objects and locations. Deep reinforcement learning agents can learn to solve these puzzles. However, the everyday interactions with the environment, while trivial for human players, present as additional puzzles to agents. We explore two techniques for incorporating commonsense knowledge into agents. Inferring possibly hidden aspects of the world state with either a commonsense inference model COMET, or a language model BERT. Biasing an agents exploration according to common patterns recognized by a language model. We test our technique in the 9to05 game, which is an extreme version of a text based game that requires numerous interactions with common, everyday objects in common, everyday scenarios. We conclude that agents that augment their beliefs about the world state with commonsense inferences are more robust to observational errors and omissions of common elements from text descriptions.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jxs9C4sUf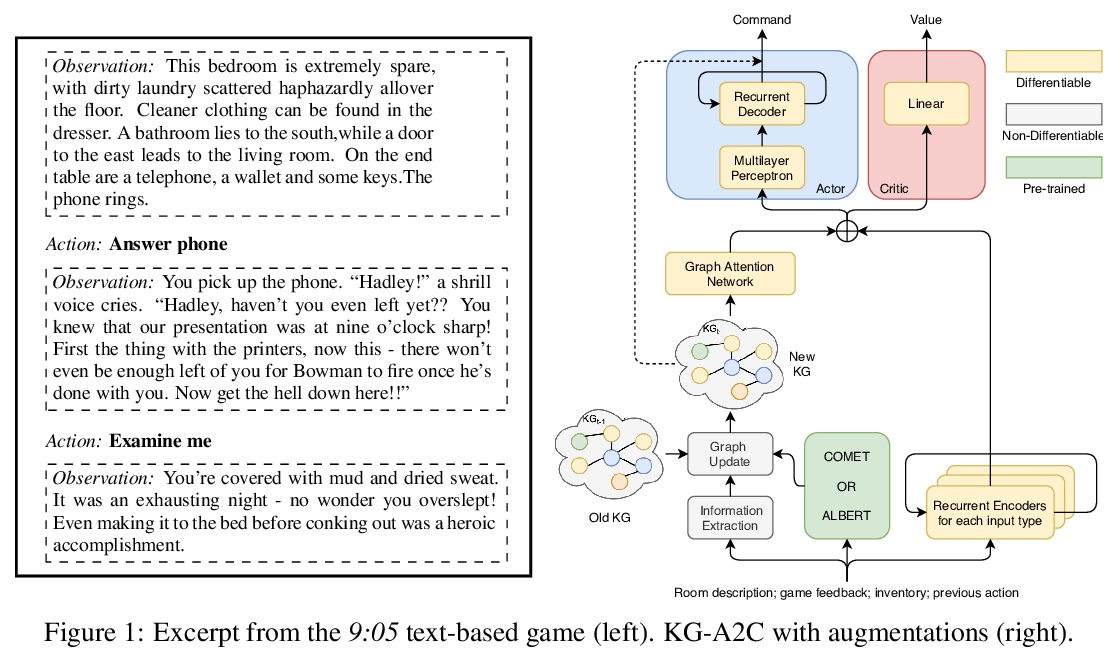
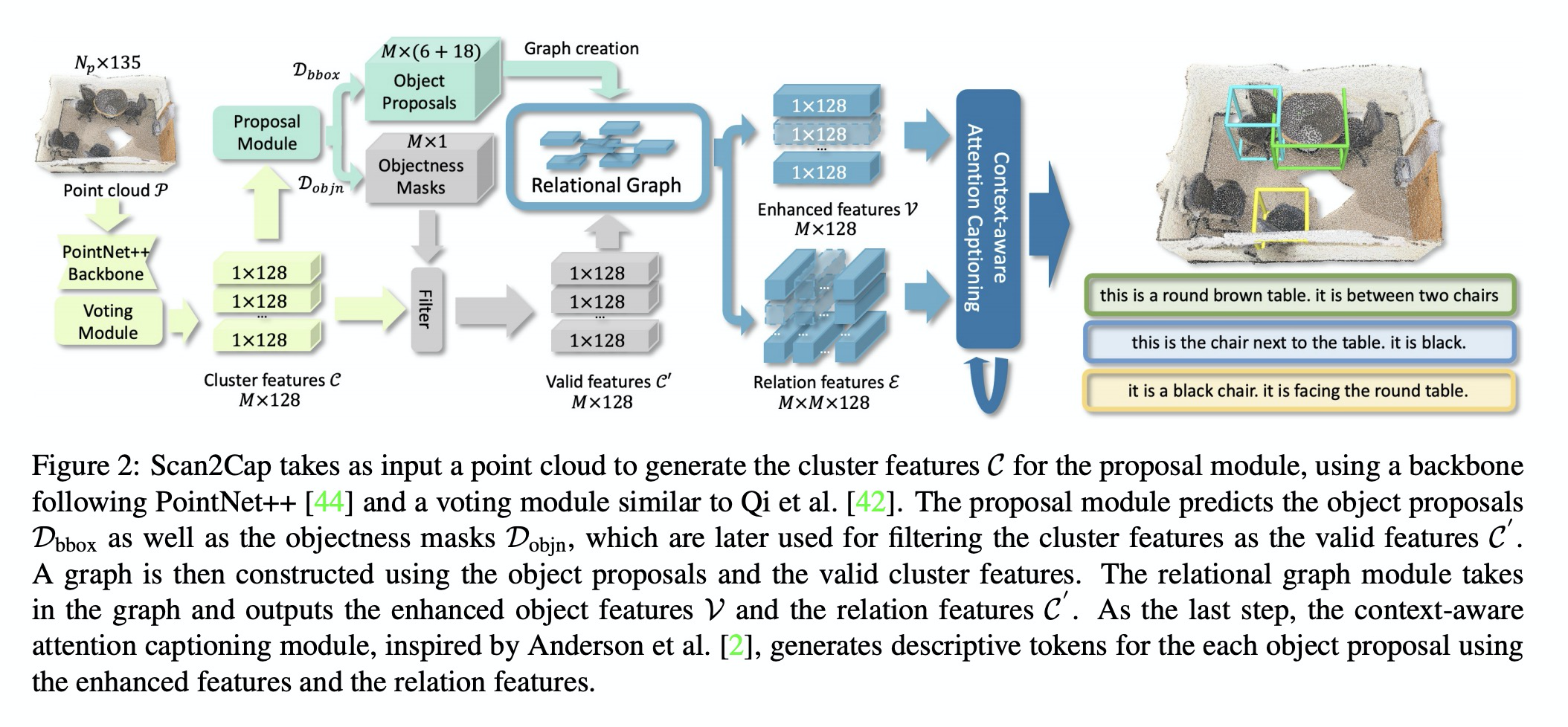
4、[CV] Scan2Cap: Context-aware Dense Captioning in RGB-D Scans
D Z Chen, A Gholami, M Nießner, A X. Chang
[Technical University of Munich & Simon Fraser University]
RGB-D扫描的上下文感知密集描述。引入了RGB-D扫描密集描述生成的新任务,提出一种端到端训练的架构,来定位输入点云中的3D目标,并为其生成自然语言描述,同时解决3D定位和描述问题。用带有消息传递网络的基于注意力的图像描述pipeline,引用局部上下文相关组件,生成描述性词条。该架构能有效对场景中3D目标进行定位和描述,在3D密集描述生成任务上大大优于2D密集描述方法。
We introduce the task of dense captioning in 3D scans from commodity RGB-D sensors. As input, we assume a point cloud of a 3D scene; the expected output is the bounding boxes along with the descriptions for the underlying objects. To address the 3D object detection and description problems, we propose Scan2Cap, an end-to-end trained method, to detect objects in the input scene and describe them in natural language. We use an attention mechanism that generates descriptive tokens while referring to the related components in the local context. To reflect object relations (i.e. relative spatial relations) in the generated captions, we use a message passing graph module to facilitate learning object relation features. Our method can effectively localize and describe 3D objects in scenes from the ScanRefer dataset, outperforming 2D baseline methods by a significant margin (27.61% CiDEr@0.5IoUimprovement).
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JxsgtjlX8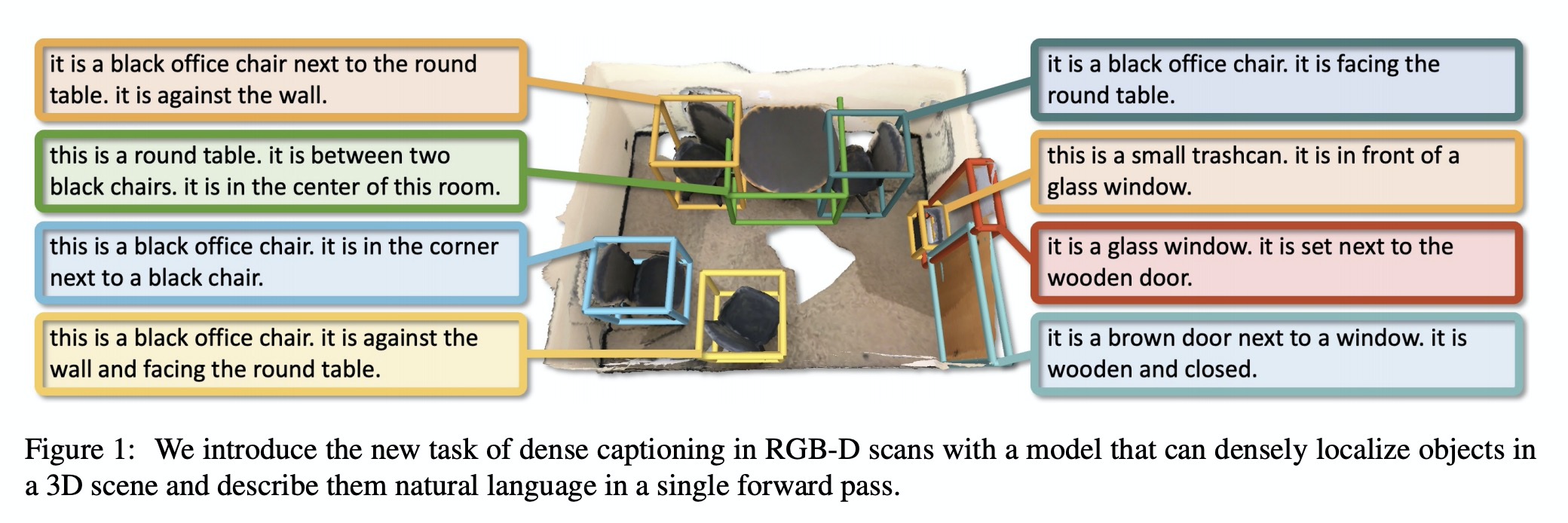
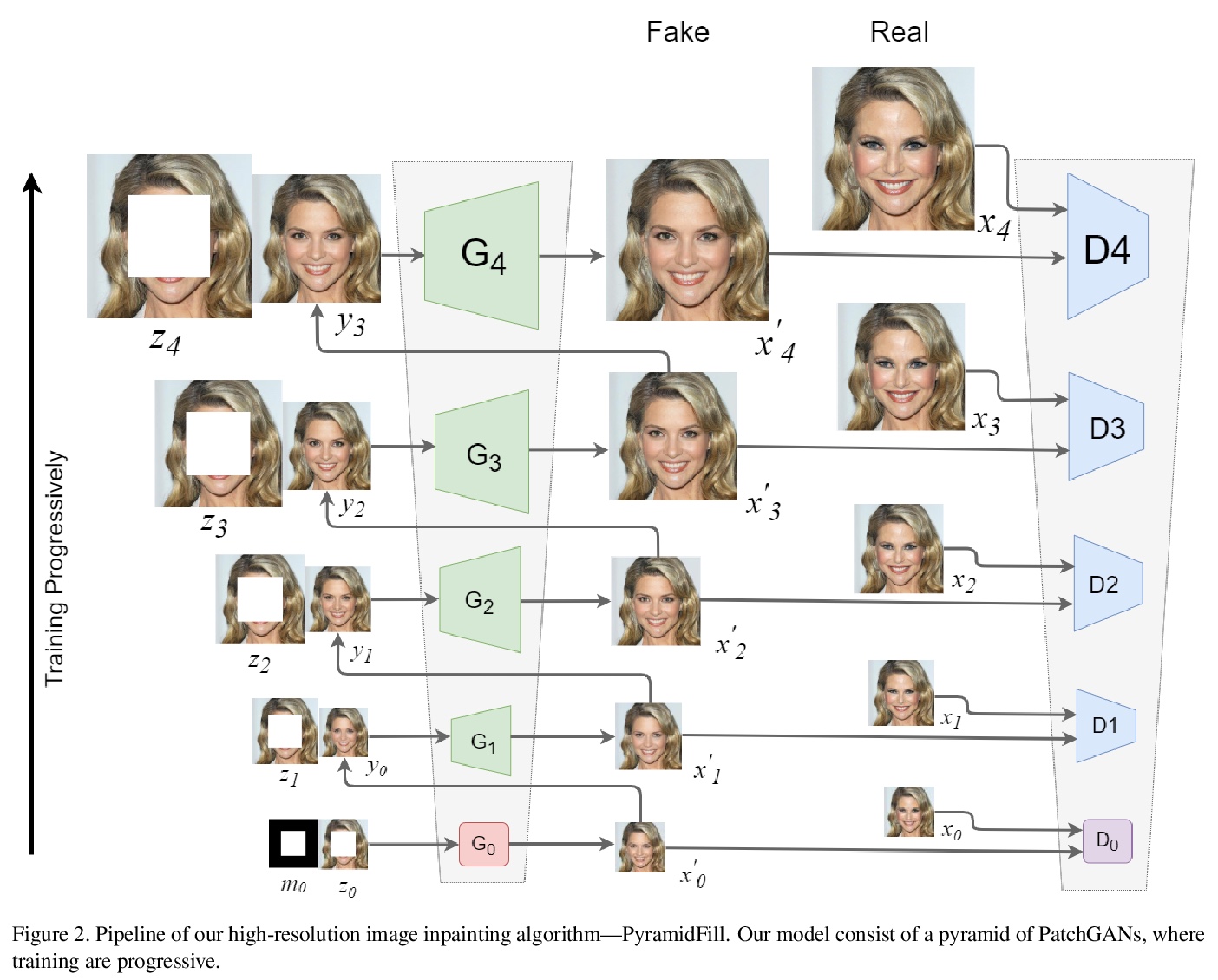
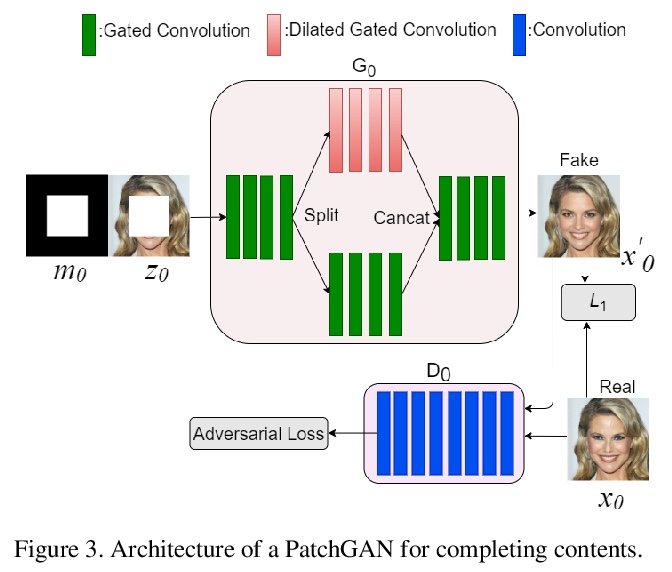
5、** **[CV] Generator Pyramid for High-Resolution Image Inpainting
L Cao, T Yang, Y Wang, B Yan, Y Guo
[OPPO Research & Johns Hopkins University]
生成器金字塔高分辨率图像补全。提出用于高分辨率图像补全的PyramidFill,明确分离内容补全和纹理合成过程——框架由PatchGANs堆叠的金字塔构成,其中内容GAN负责在低分辨率被破坏图像中生成内容,而纹理GAN负责在高分辨率图像中逐步合成细节纹理,为内容GAN和纹理GAN分别定制生成器和鉴别器。在多个数据集上的实验表明,PyramidFill生成的渲染结果比最先进的方法质量更高。
Inpainting high-resolution images with large holes challenges existing deep learning based image inpainting methods. We present a novel framework — PyramidFill for high-resolution image inpainting task, which explicitly disentangles content completion and texture synthesis. PyramidFill attempts to complete the content of unknown regions in a lower-resolution image, and synthesis the textures of unknown regions in a higher-resolution image, progressively. Thus, our model consists of a pyramid of fully convolutional GANs, wherein the content GAN is responsible for completing contents in the lowest-resolution masked image, and each texture GAN is responsible for synthesizing textures in a higher-resolution image. Since completing contents and synthesising textures demand different abilities from generators, we customize different architectures for the content GAN and texture GAN. Experiments on multiple datasets including CelebA-HQ, Places2 and a new natural scenery dataset (NSHQ) with different resolutions demonstrate that PyramidFill generates higher-quality inpainting results than the state-of-the-art methods. To better assess high-resolution image inpainting methods, we will release NSHQ, high-quality natural scenery images with high-resolution 1920> ×1080.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JxskM4MYK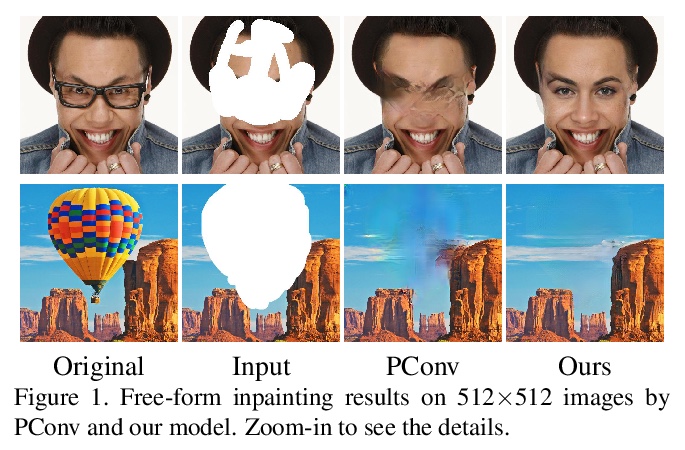
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
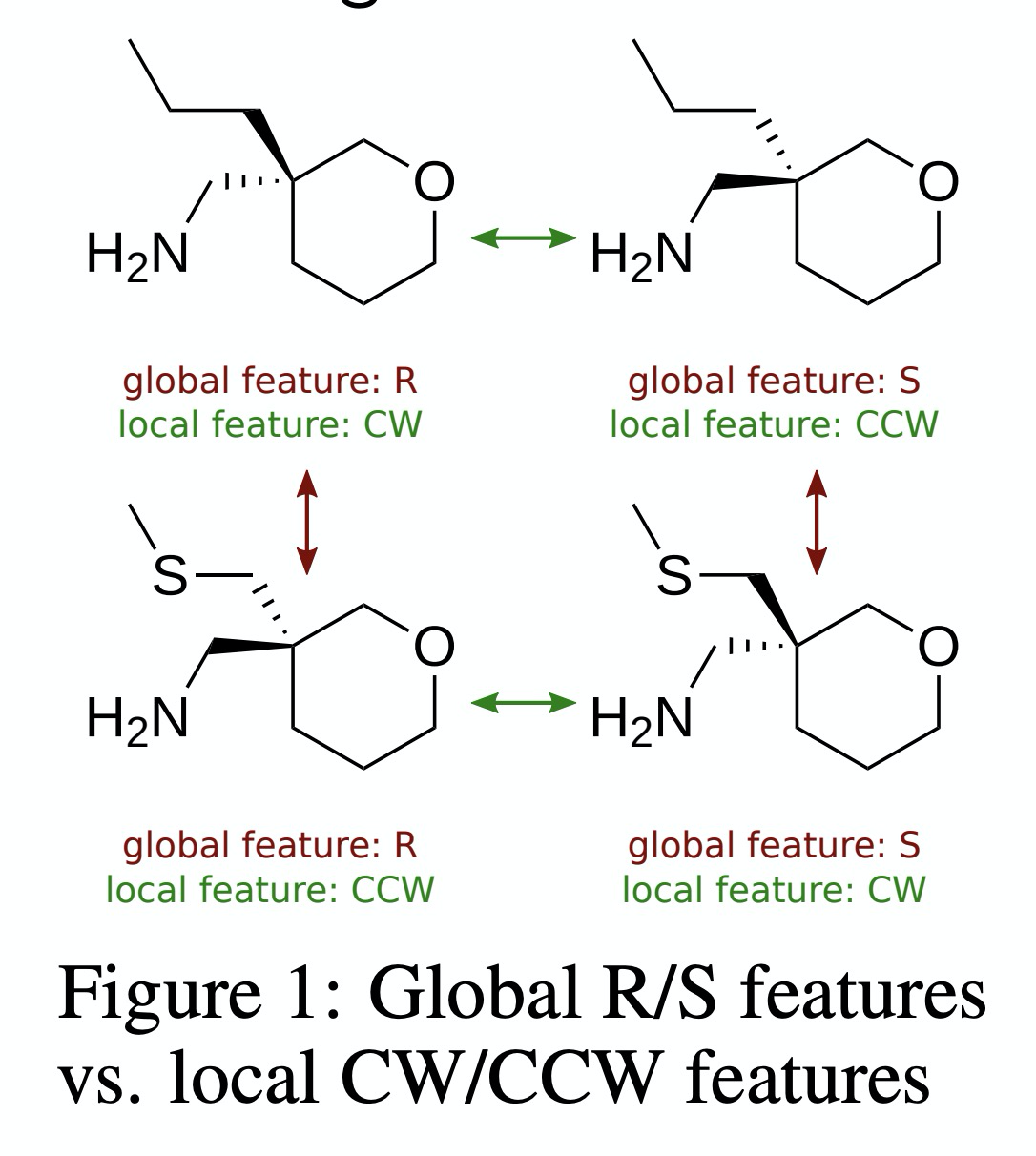
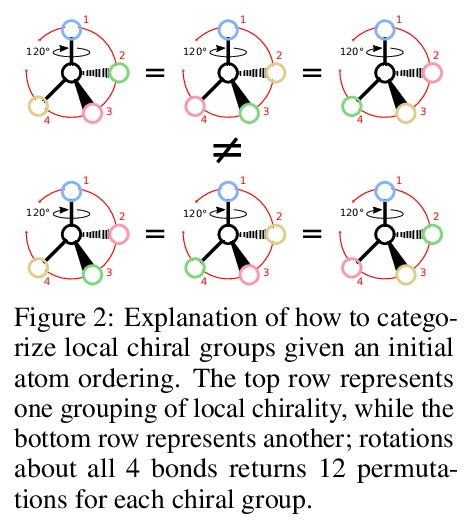
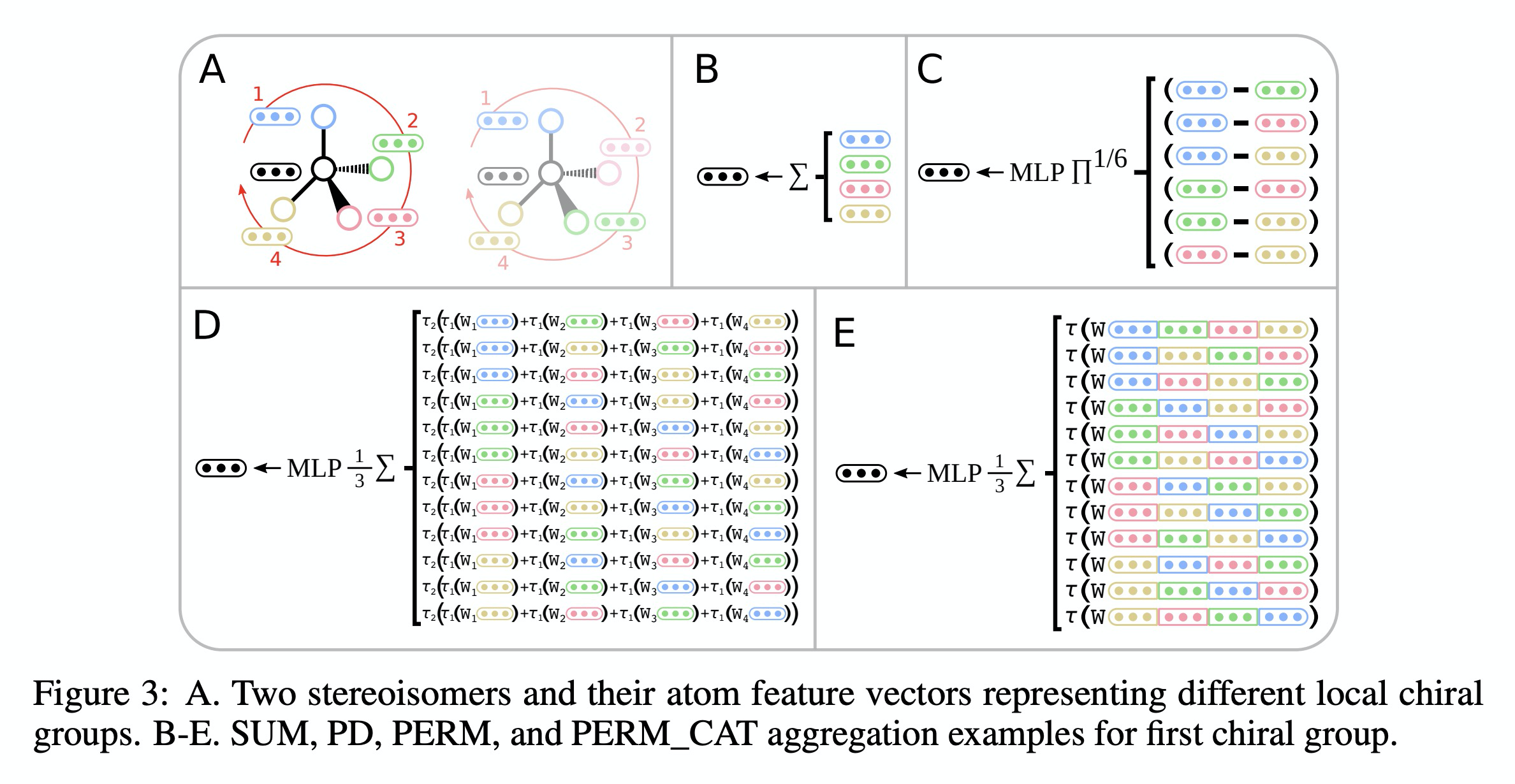
[LG] Message Passing Networks for Molecules with Tetrahedral Chirality
基于信息传递网络的四面体手性分子性质学习
L Pattanaik, O Ganea, I Coley, K F. Jensen, W H. Green, C W. Coley
[MIT & Rutgers University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/Jxspdd7Yv
/
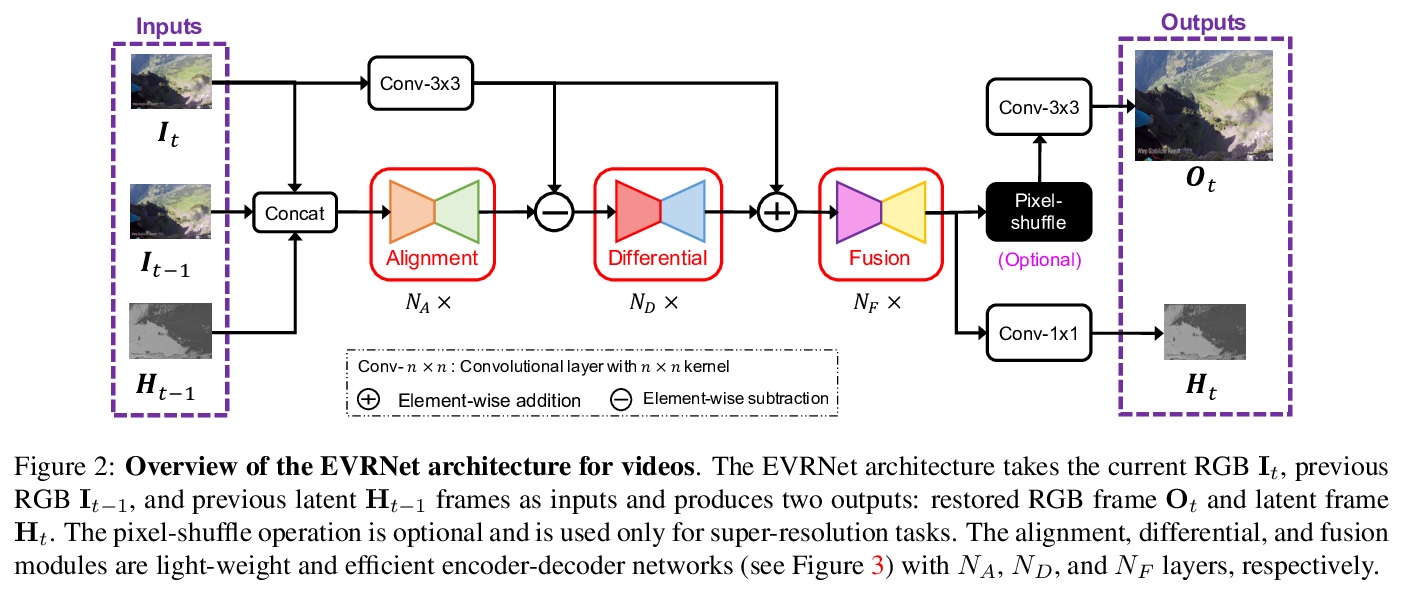
[CV] EVRNet: Efficient Video Restoration on Edge Devices
边缘设备上的高效视频恢复(去块效应、去噪和超分辨率等)
S Mehta, A Kumar, F Reda, V Nasery, V Mulukutla, R Ranjan, V Chandra
[University of Washington & Facebook Inc]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JxssGmn9E
[LG] When does gradient descent with logistic loss find interpolating two-layer networks?
N S. Chatterji, P M. Long, P L. Bartlett
[UC Berkeley & Google]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JxsvBvBGq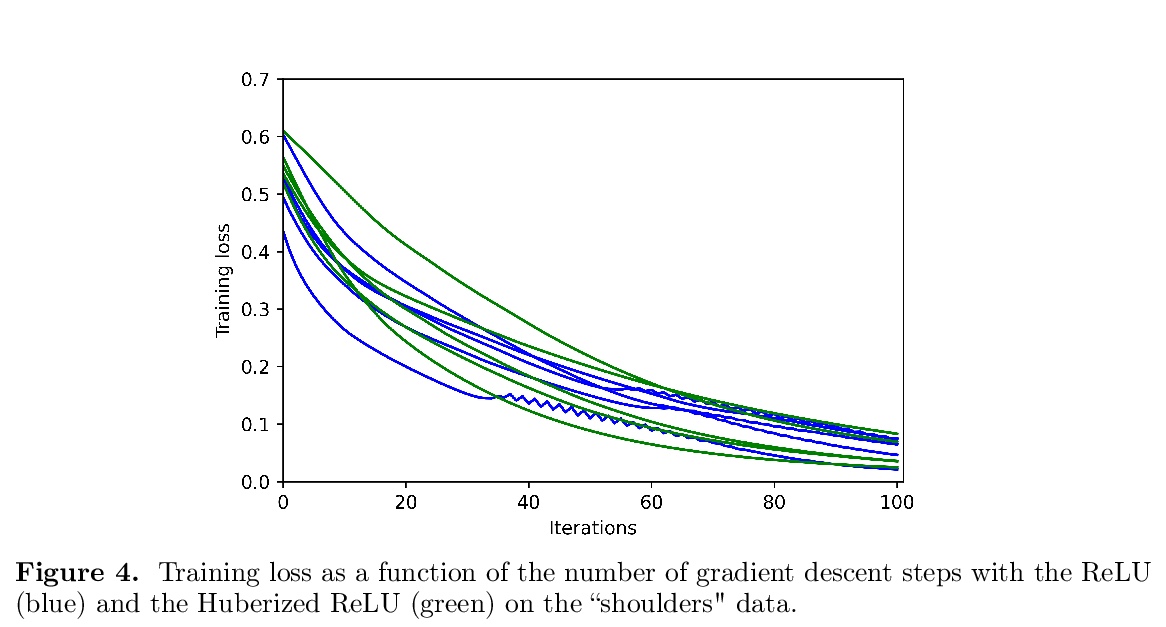
[LG] Universal Approximation Property of Neural Ordinary Differential Equations
神经常微分方程的泛逼近性质
T Teshima, K Tojo, M Ikeda, I Ishikawa, K Oono
[The University of Tokyo & RIKEN]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/JxswP7e6O

