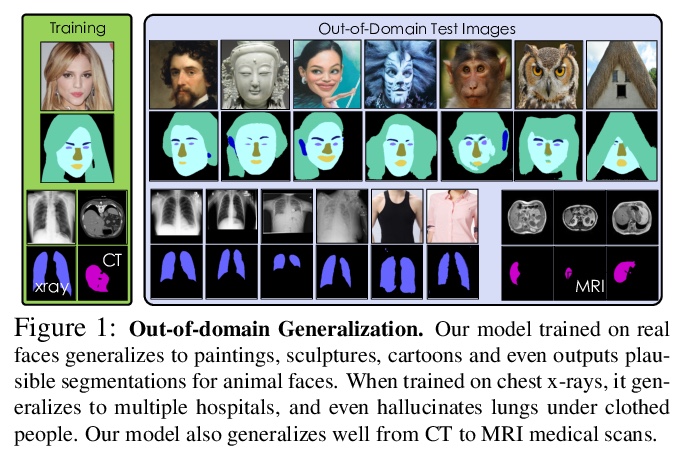
- 1、[CV] Semantic Segmentation with Generative Models: Semi-Supervised Learning and Strong Out-of-Domain Generalization
- 2、[CV] BARF: Bundle-Adjusting Neural Radiance Fields
- 3、[CV] Self-supervised object detection from audio-visual correspondence
- 4、[CL] What’s in your Head? Emergent Behaviour in Multi-Task Transformer Models
- 5、[LG] Online and Offline Reinforcement Learning by Planning with a Learned Model
- [LG] Learning and Planning in Complex Action Spaces
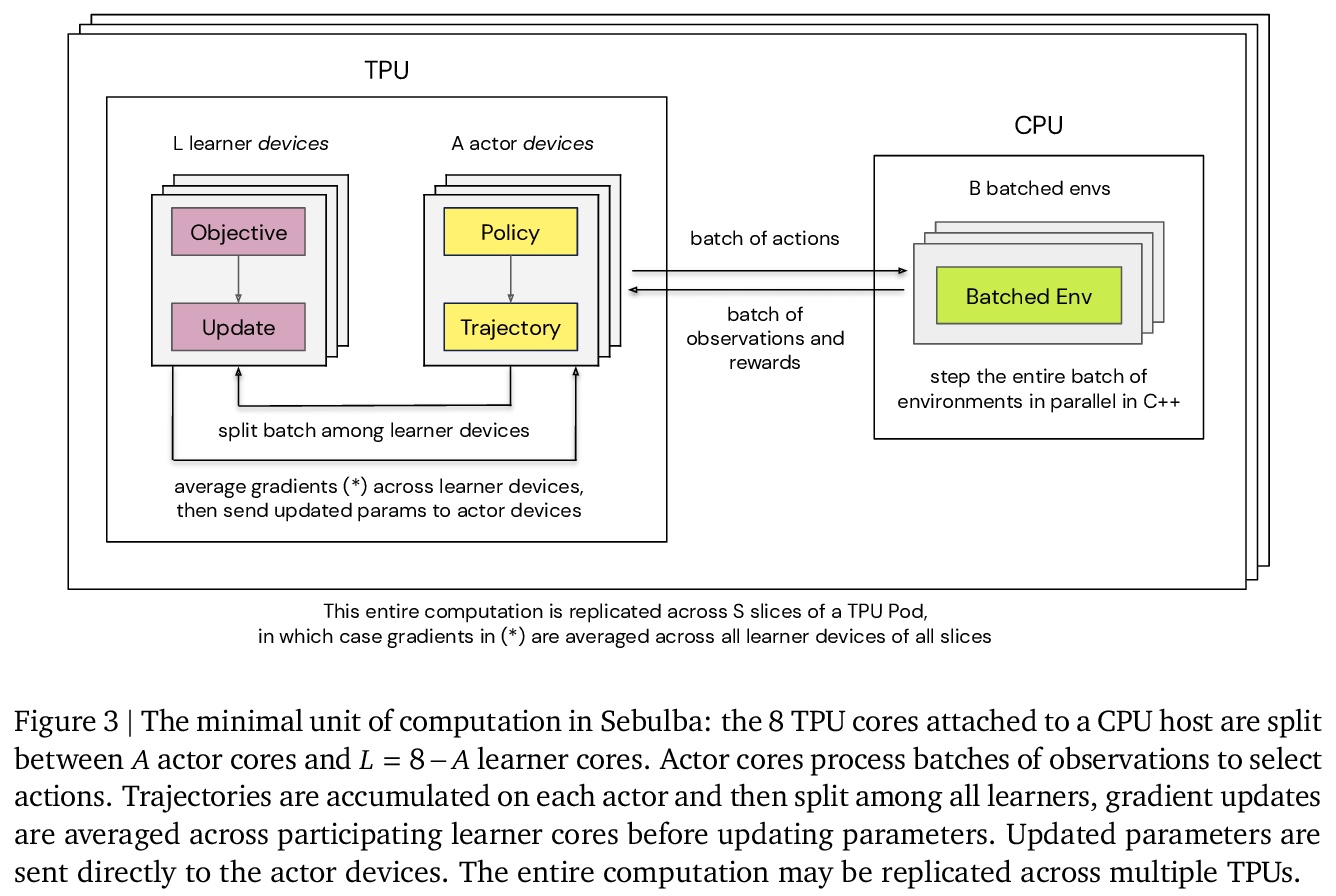
- [LG] Podracer architectures for scalable Reinforcement Learning
- [CV] DropLoss for Long-Tail Instance Segmentation
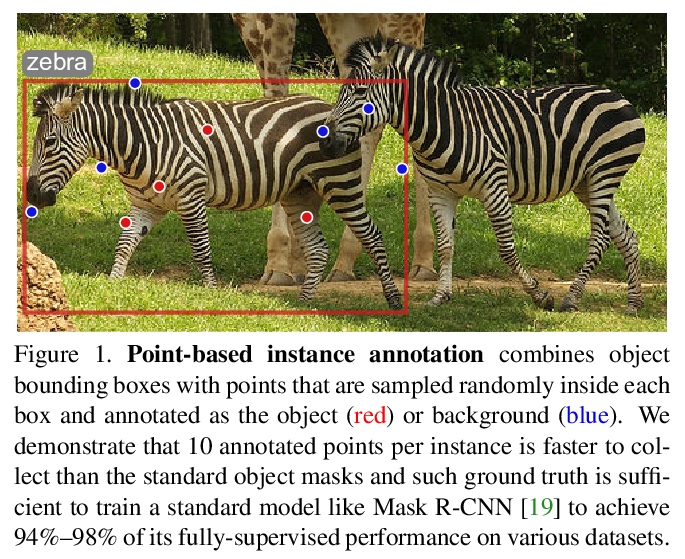
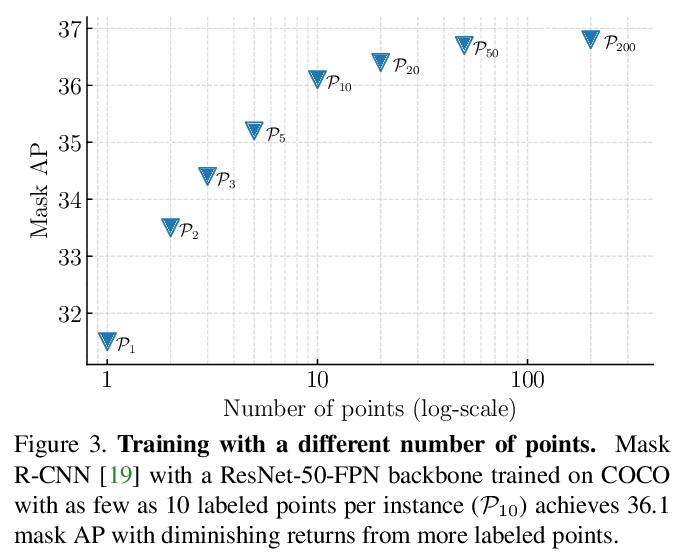
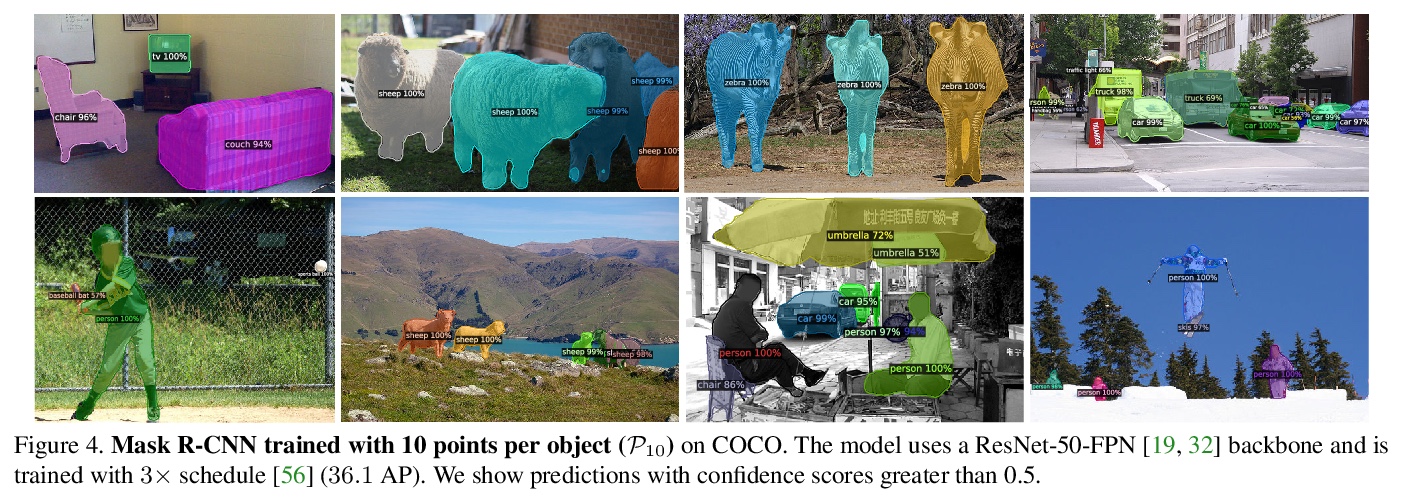
- [CV] Pointly-Supervised Instance Segmentation
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 (*表示值得重点关注)
1、[CV] Semantic Segmentation with Generative Models: Semi-Supervised Learning and Strong Out-of-Domain Generalization
D Li, J Yang, K Kreis, A Torralba, S Fidler
[NVIDIA & MIT]
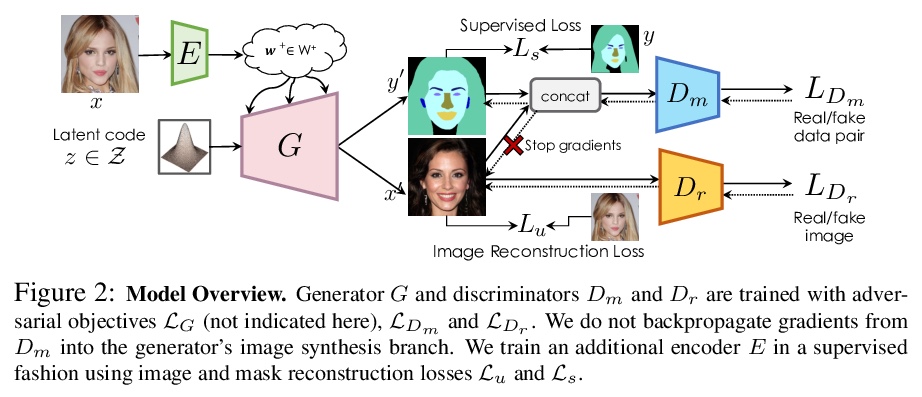
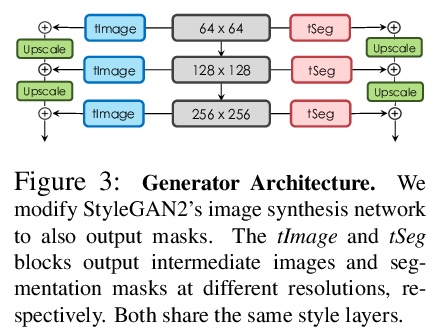
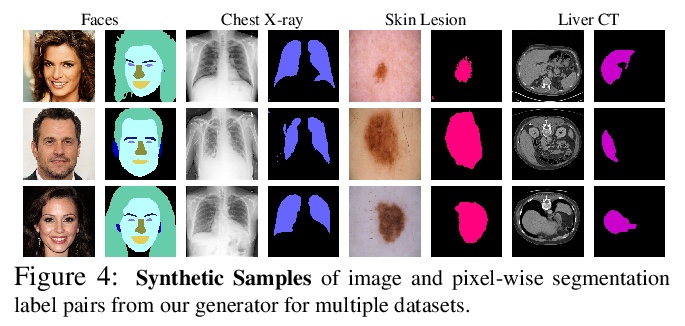
基于生成式模型的语义分割:半监督学习和强大的域外泛化。用有限的标注数据训练深度网络,同时实现强大的泛化能力,是寻求减少人类标注工作量的关键,也是半监督学习的目标,半监督学习利用更广泛可用的未标注数据,来补充小型标注数据集。本文提出一种新框架,用图像和标记的生成模型,完成判别式像素级任务。通过学习一个生成式对抗网络,以捕捉图像和标记的联合分布,用大量的未标记图像和少量的标记图像进行有效训练。在StyleGAN2的基础上进行架构,增加了一个标记合成分支,先通过编码器网络和测试时优化,将目标图像嵌入到联合潜空间,再从推断嵌入中生成标记,从而在测试时获得图像标记。在医疗领域和人脸图像上进行了广泛验证,在半监督环境下,展示了同等于或优于现有竞争基线的结果,展示出强大的泛化能力,在域外分割任务上以较大优势超越了基线。即使在极端的域外实例上,也能展示出合理的性能,例如在医学成像中从CT迁移到核磁共振,从真实面孔照片转移到绘画、雕塑,甚至卡通和动物面孔。
Training deep networks with limited labeled data while achieving a strong generalization ability is key in the quest to reduce human annotation efforts. This is the goal of semi-supervised learning, which exploits more widely available unlabeled data to complement small labeled data sets. In this paper, we propose a novel framework for discriminative pixel-level tasks using a generative model of both images and labels. Concretely, we learn a generative adversarial network that captures the joint image-label distribution and is trained efficiently using a large set of unlabeled images supplemented with only few labeled ones. We build our architecture on top of StyleGAN2, augmented with a label synthesis branch. Image labeling at test time is achieved by first embedding the target image into the joint latent space via an encoder network and test-time optimization, and then generating the label from the inferred embedding. We evaluate our approach in two important domains: medical image segmentation and part-based face segmentation. We demonstrate strong in-domain performance compared to several baselines, and are the first to showcase extreme out-of-domain generalization, such as transferring from CT to MRI in medical imaging, and photographs of real faces to paintings, sculptures, and even cartoons and animal faces. Project Page: this https URL
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaXgExI2Y
2、[CV] BARF: Bundle-Adjusting Neural Radiance Fields
C Lin, W Ma, A Torralba, S Lucey
[CMU & MIT]
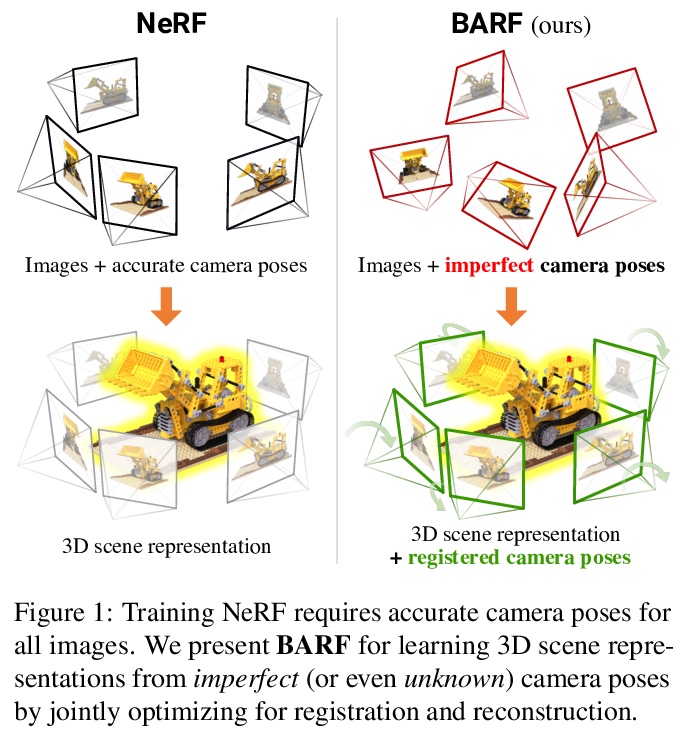
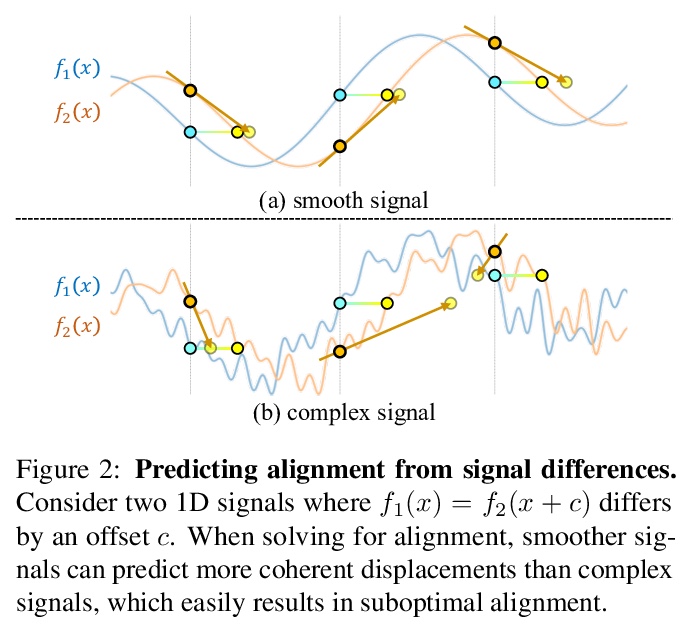
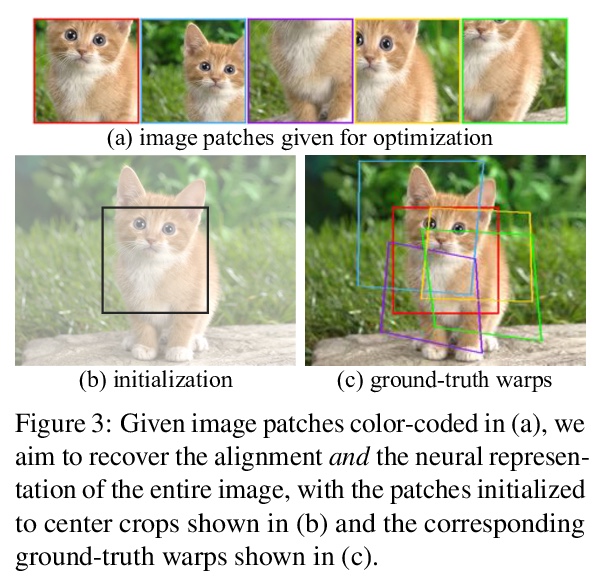
BARF : 绑定-调整神经辐射场。神经辐射场(NeRF)最近在计算机视觉领域引起了极大兴趣,因为它能够合成真实世界场景的照片般逼真的新视角。然而,NeRF的一个局限性是需要准确的相机姿态来学习场景表示。本文提出绑定-调整神经辐射场(BARF),一种简单有效的策略,用于从不完美(甚至未知)的相机姿态训练NeRF——即神经3D表示学习和相机帧配准的联合问题。建立了与经典图像对齐的理论联系,表明从粗到细的配准也适用于NeRF。在NeRF中天真地应用位置编码对基于综合目标的配准有负面影响。在合成和真实世界数据上的实验表明,BARF可以有效地优化神经场景表示,同时解决大的相机姿态错位问题,使得从未知摄像机姿态获得的视频序列的视图合成和定位成为可能,为视觉定位系统(如SLAM)开辟了新途径,并为密集的3D映射和重建提供了潜在的应用基础。
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have recently gained a surge of interest within the computer vision community for its power to synthesize photorealistic novel views of real-world scenes. One limitation of NeRF, however, is its requirement of accurate camera poses to learn the scene representations. In this paper, we propose Bundle-Adjusting Neural Radiance Fields (BARF) for training NeRF from imperfect (or even unknown) camera poses — the joint problem of learning neural 3D representations and registering camera frames. We establish a theoretical connection to classical image alignment and show that coarse-to-fine registration is also applicable to NeRF. Furthermore, we show that naïvely applying positional encoding in NeRF has a negative impact on registration with a synthesis-based objective. Experiments on synthetic and real-world data show that BARF can effectively optimize the neural scene representations and resolve large camera pose misalignment at the same time. This enables view synthesis and localization of video sequences from unknown camera poses, opening up new avenues for visual localization systems (e.g. SLAM) and potential applications for dense 3D mapping and reconstruction.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaXpdxF3R
3、[CV] Self-supervised object detection from audio-visual correspondence
T Afouras, Y M. Asano, F Fagan, A Vedaldi, F Metze
[University of Oxford & Facebook AI]
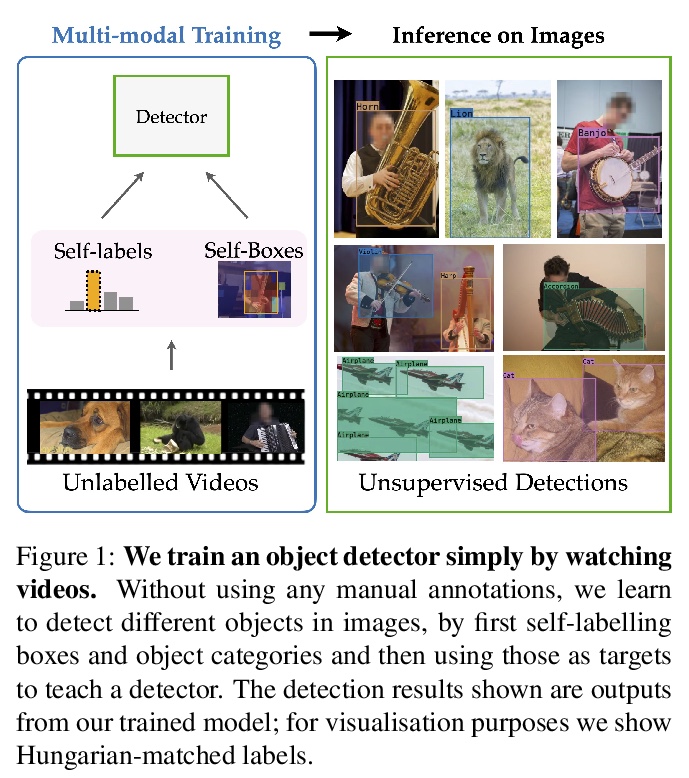
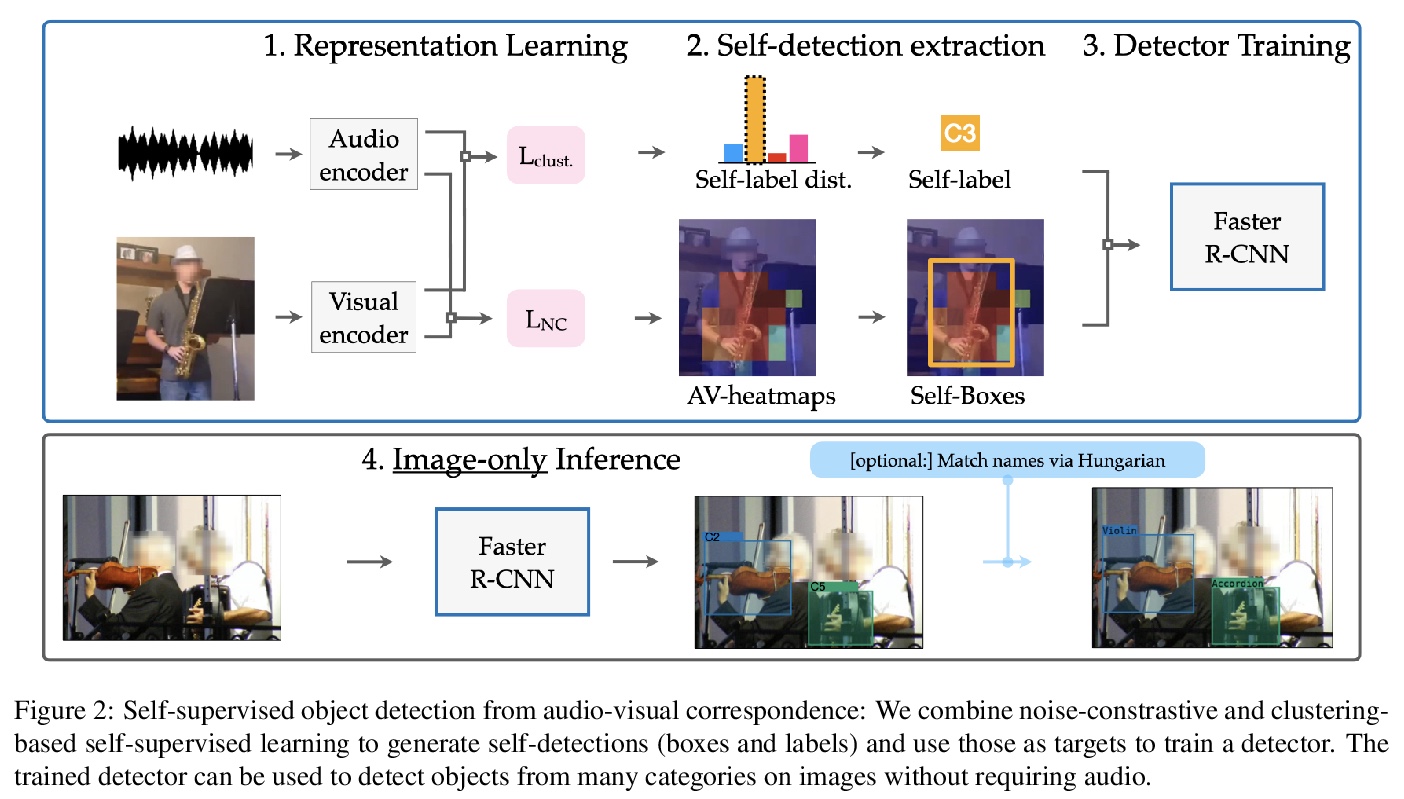
基于从视-听对应的自监督目标检测。考虑在没有任何人工监督的情况下,学习可解释性概念的问题。特别的,专注于完全无需人工标注的情况下,学习同时检测和分类目标。提出了一种通过观看未标注视频,纯粹用自监督来训练强目标检测器的方法。与弱监督目标检测不同,该方法不假设图像级的类标签,而是从视-听数据中提取监督信号,利用音频成分”教”目标检测器。设计了一个具有对比性目标的自监督框架,联合学习对目标的分类和定位。在不使用任何监督的情况下,简单使用这些自监督的标签和框,来训练基于图像的目标检测器。实验表明在目标检测和声源定位任务中,该方法表现优于之前的无监督和弱监督检测器。
We tackle the problem of learning object detectors without supervision. Differently from weakly-supervised object detection, we do not assume image-level class labels. Instead, we extract a supervisory signal from audio-visual data, using the audio component to “teach” the object detector. While this problem is related to sound source localisation, it is considerably harder because the detector must classify the objects by type, enumerate each instance of the object, and do so even when the object is silent. We tackle this problem by first designing a self-supervised framework with a contrastive objective that jointly learns to classify and localise objects. Then, without using any supervision, we simply use these self-supervised labels and boxes to train an image-based object detector. With this, we outperform previous unsupervised and weakly-supervised detectors for the task of object detection and sound source localization. We also show that we can align this detector to ground-truth classes with as little as one label per pseudo-class, and show how our method can learn to detect generic objects that go beyond instruments, such as airplanes and cats.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaXuE8SH4

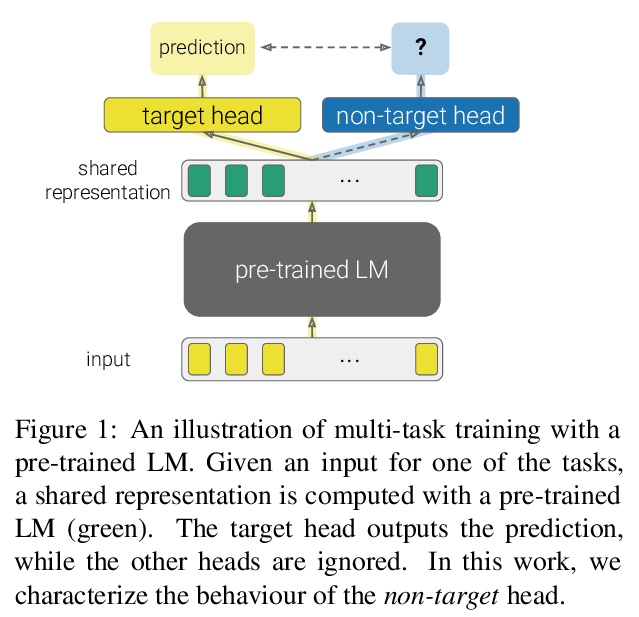
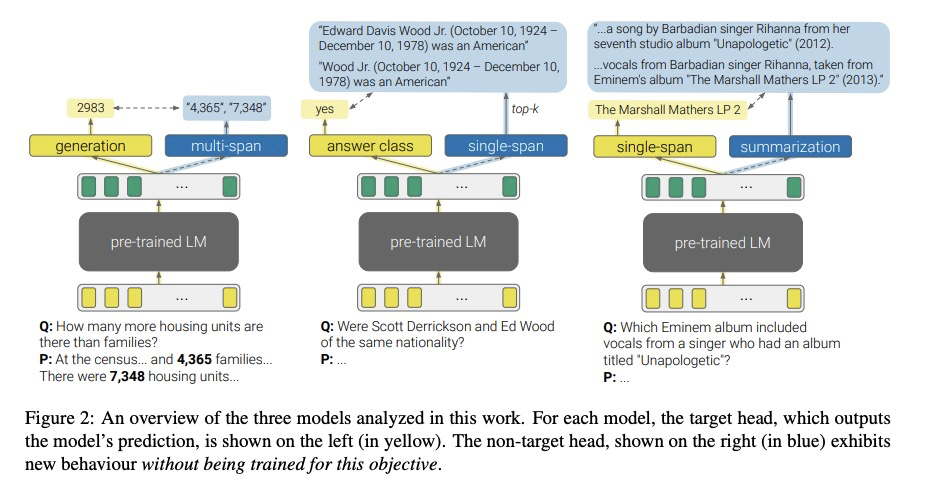
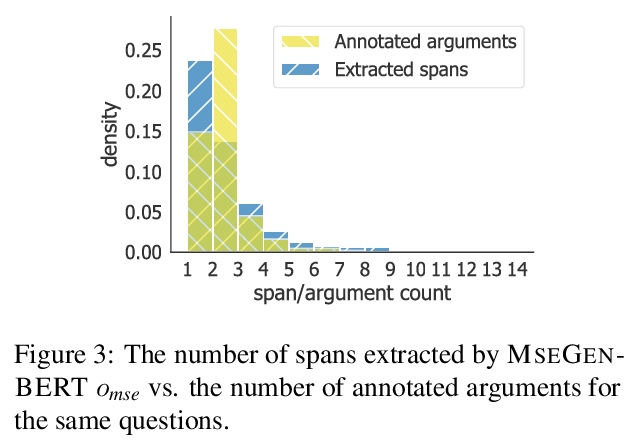
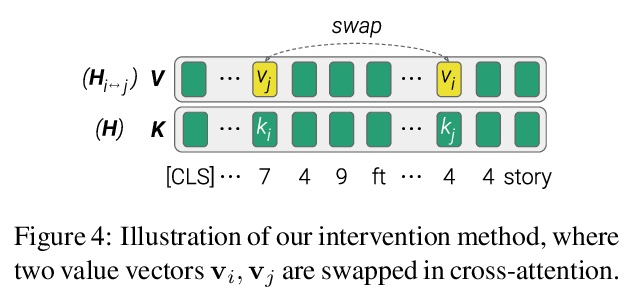
4、[CL] What’s in your Head? Emergent Behaviour in Multi-Task Transformer Models
M Geva, U Katz, A Ben-Arie, J Berant
[Tel-Aviv University]
多任务Transformer模型中的突发行为。自然语言处理中多任务训练的主要范式,是用一个共享的预训练语言模型来表示输入,并在每个任务中增加一个小而浅的网络(头)。给定一个输入,目标头是选择输出最终预测的那个头。本文研究了三个多任务transformer模型中非目标头的行为,即当给定输入属于不同于它们所训练的任务时,头的输出。发现在没有任何专门训练的情况下,非目标头表现出了突发行为,这些行为可能解释了目标任务,也可能泛化到它们原来的任务之外。这种新出现的行为表明,多任务训练会导致技能的非平凡外推,可利用这些技能来实现可解释性和通用性。
The primary paradigm for multi-task training in natural language processing is to represent the input with a shared pre-trained language model, and add a small, thin network (head) per task. Given an input, a target head is the head that is selected for outputting the final prediction. In this work, we examine the behaviour of non-target heads, that is, the output of heads when given input that belongs to a different task than the one they were trained for. We find that non-target heads exhibit emergent behaviour, which may either explain the target task, or generalize beyond their original task. For example, in a numerical reasoning task, a span extraction head extracts from the input the arguments to a computation that results in a number generated by a target generative head. In addition, a summarization head that is trained with a target question answering head, outputs query-based summaries when given a question and a context from which the answer is to be extracted. This emergent behaviour suggests that multi-task training leads to non-trivial extrapolation of skills, which can be harnessed for interpretability and generalization.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaXzIwUUn
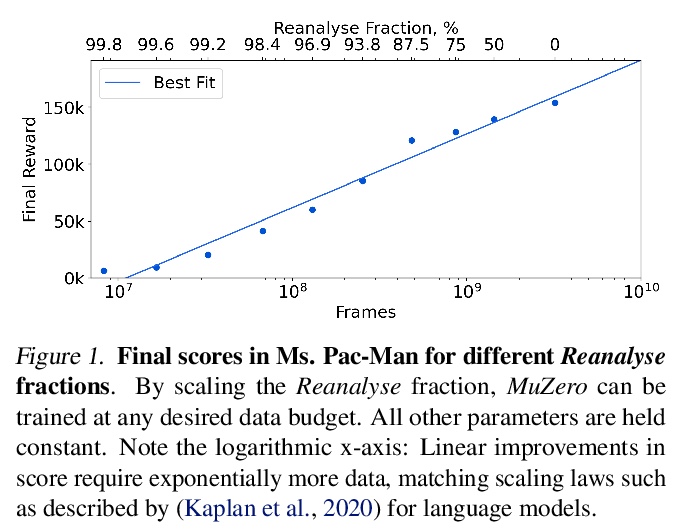
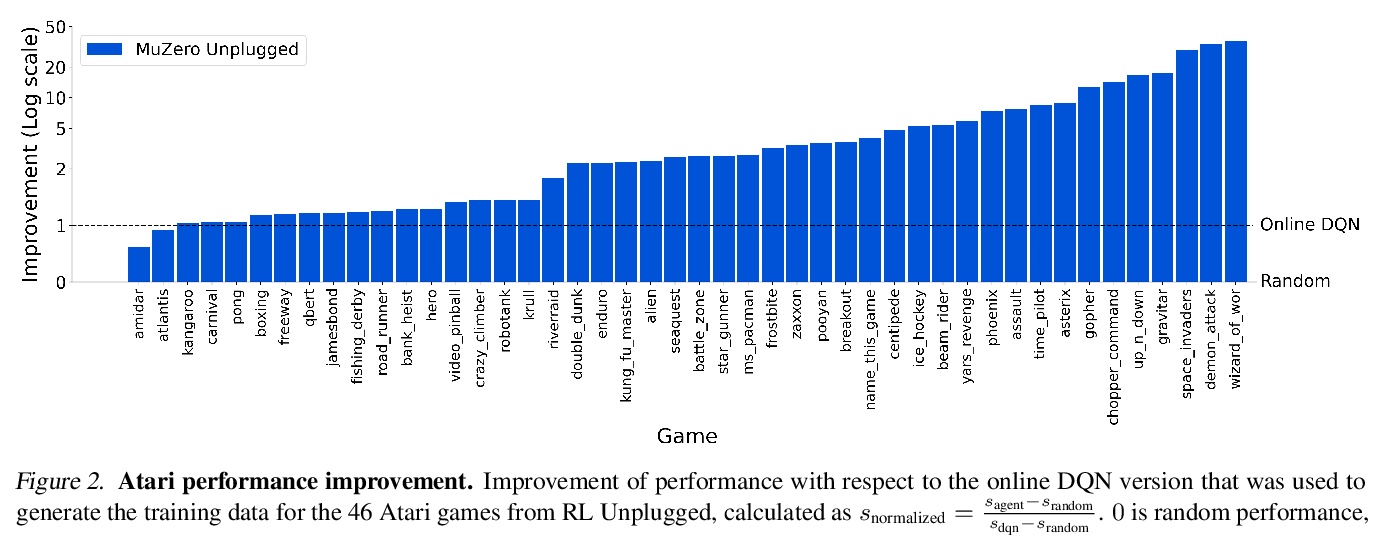
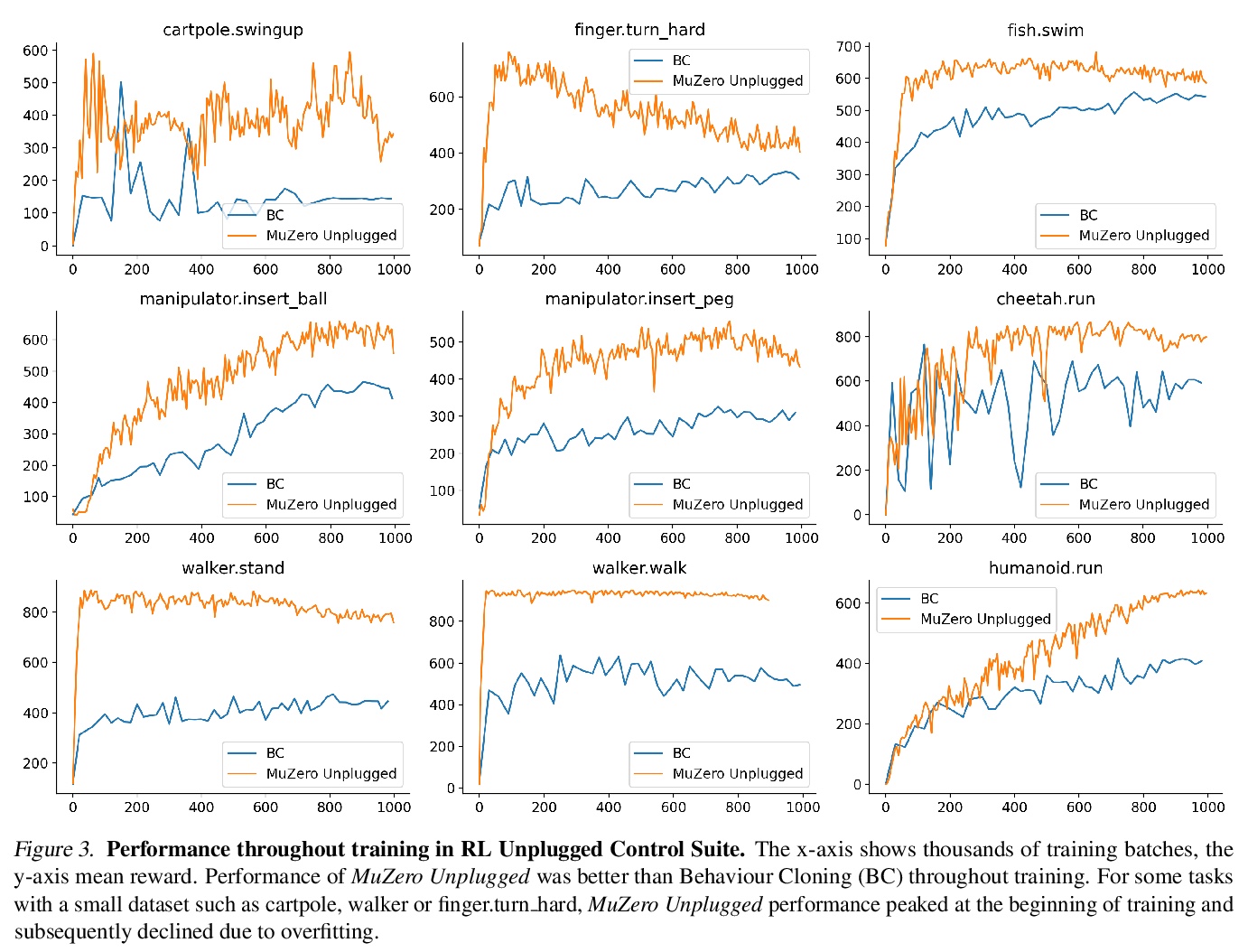
5、[LG] Online and Offline Reinforcement Learning by Planning with a Learned Model
J Schrittwieser, T Hubert, A Mandhane, M Barekatain, I Antonoglou, D Silver
[DeepMind]
基于习得模型规划的在线/离线强化学习。长期以来,从少量数据中高效学习,一直是基于模型的强化学习的重点,无论是与环境交互的在线情况,还是从固定数据集学习的离线情况。然而,到目前为止,还没有一个统一的算法能在这两种情况下展示最先进结果。本文提出了Reanalyse算法,该算法用基于模型的策略和价值改进算子,在现有数据点上计算新的改进训练目标,可对变化数个数量级的数据预算进行高效学习。Reanalyse也可用于完全从演示中学习,而不需要任何环境交互,就像离线强化学习一样。将Reanalyse与MuZero算法相结合,引入了MuZero Unplugged,一种适用于任何数据预算的单一统一算法,包括离线强化学习。与之前工作相比,该算法不需要对off-policy或离线强化学习设置进行任何特殊调整。MuZero Unplugged在RL Unplugged离线强化学习基准以及Atari的标准2亿帧设置的在线强化学习基准中创造了新的最先进的结果。
Learning efficiently from small amounts of data has long been the focus of model-based reinforcement learning, both for the online case when interacting with the environment and the offline case when learning from a fixed dataset. However, to date no single unified algorithm could demonstrate state-of-the-art results in both settings. In this work, we describe the Reanalyse algorithm which uses model-based policy and value improvement operators to compute new improved training targets on existing data points, allowing efficient learning for data budgets varying by several orders of magnitude. We further show that Reanalyse can also be used to learn entirely from demonstrations without any environment interactions, as in the case of offline Reinforcement Learning (offline RL). Combining Reanalyse with the MuZero algorithm, we introduce MuZero Unplugged, a single unified algorithm for any data budget, including offline RL. In contrast to previous work, our algorithm does not require any special adaptations for the off-policy or offline RL settings. MuZero Unplugged sets new state-of-the-art results in the RL Unplugged offline RL benchmark as well as in the online RL benchmark of Atari in the standard 200 million frame setting.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaXDoqR4a
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
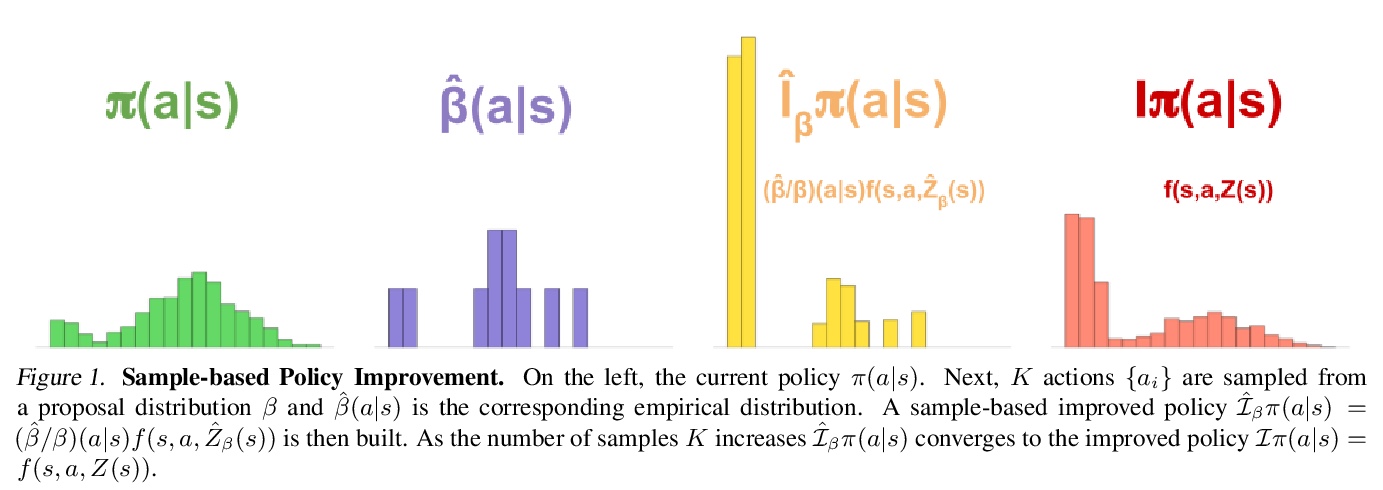
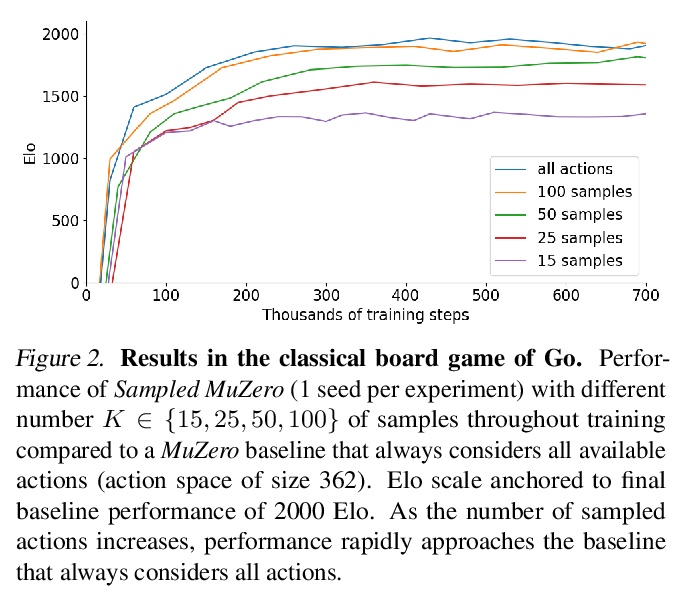
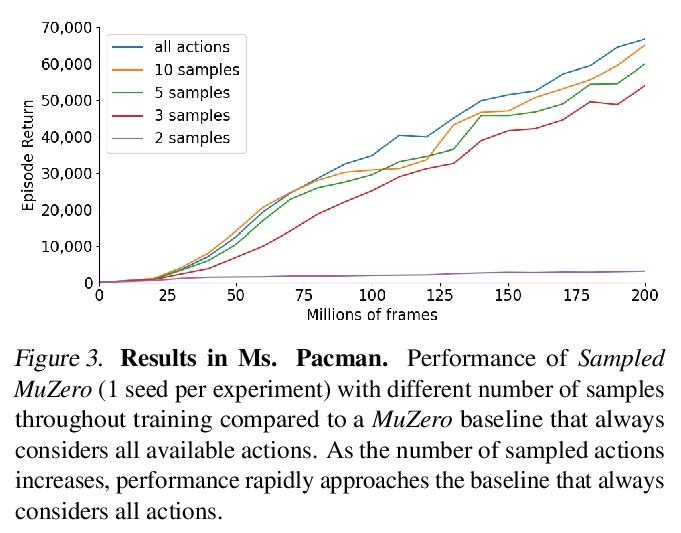
[LG] Learning and Planning in Complex Action Spaces
复杂行动空间中的学习与规划
T Hubert, J Schrittwieser, I Antonoglou, M Barekatain, S Schmitt, D Silver
[DeepMind]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaXI6AQx8
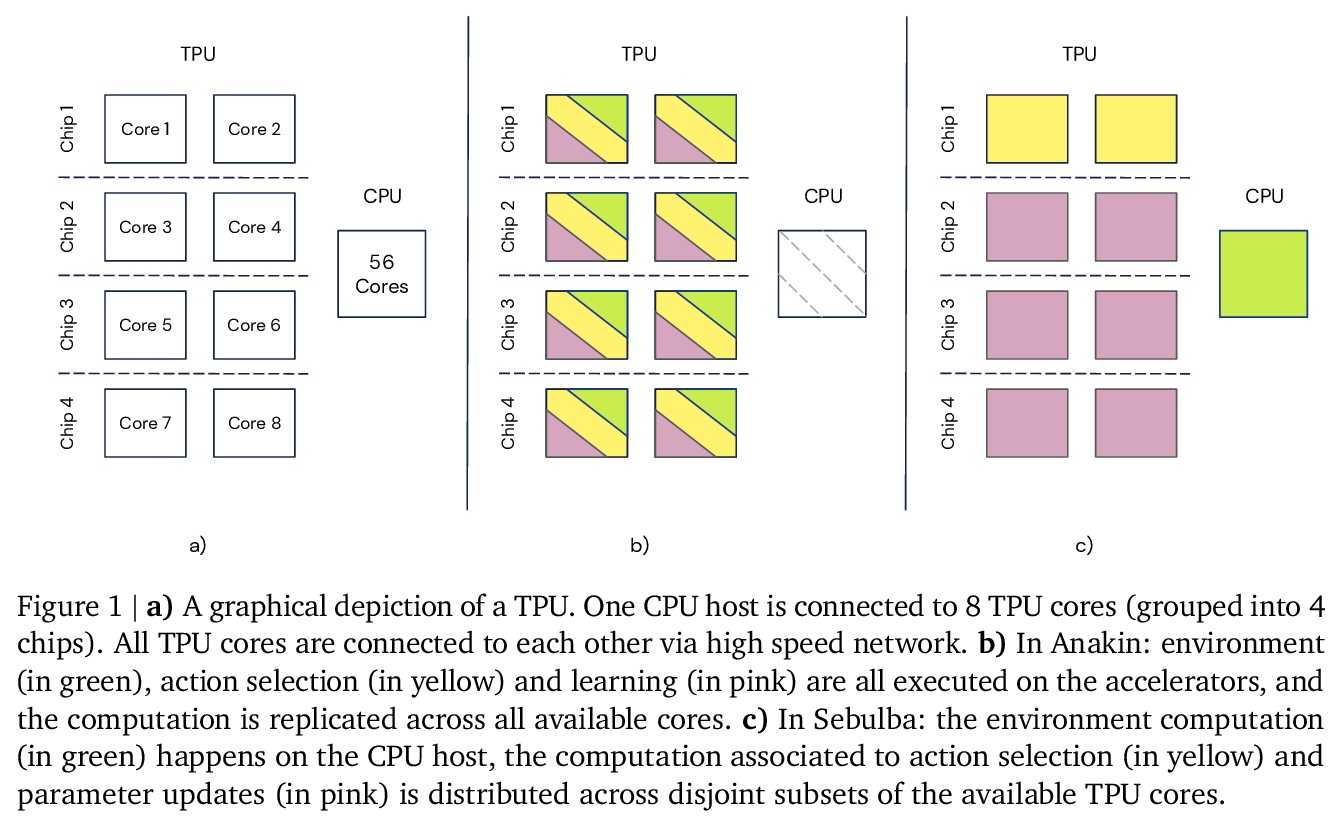
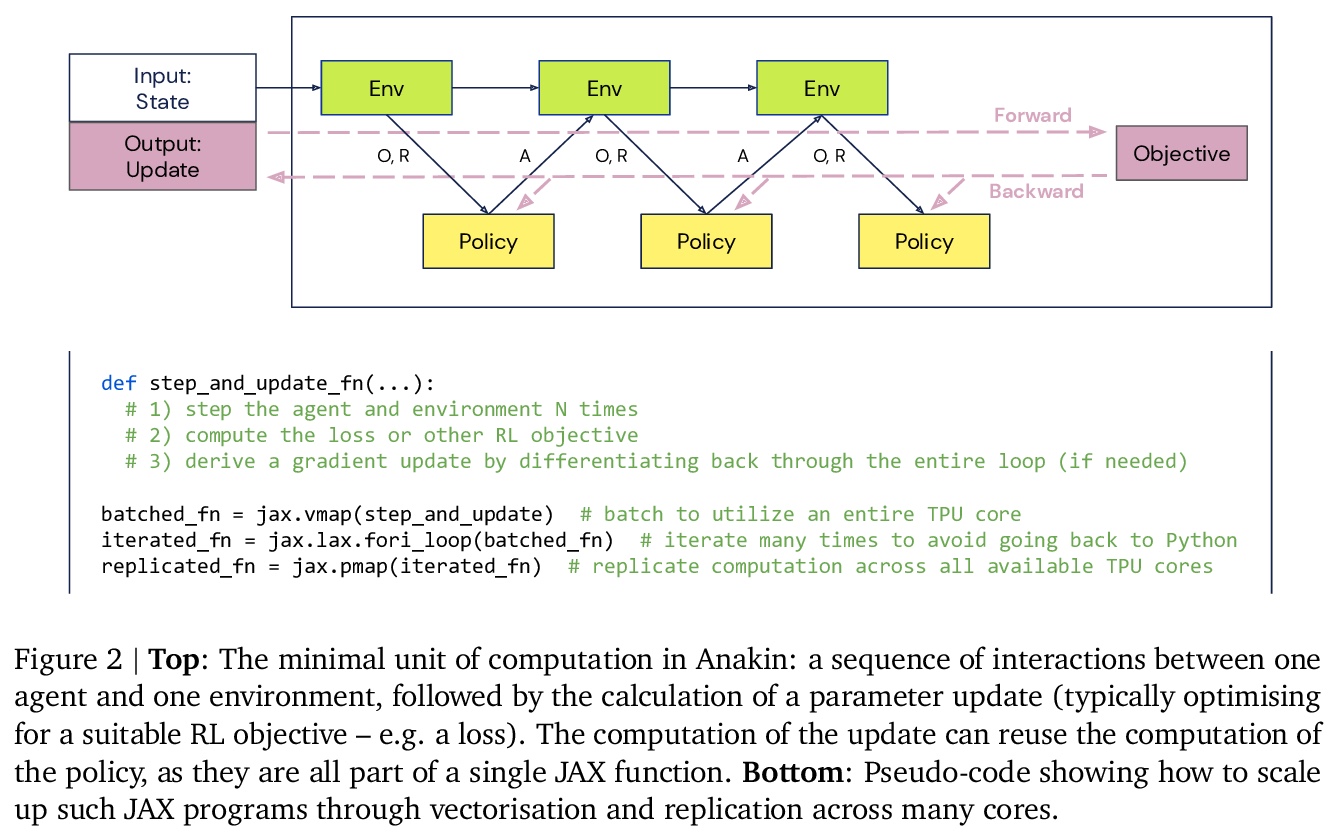
[LG] Podracer architectures for scalable Reinforcement Learning
面向可扩展强化学习的Podracer架构
M Hessel, M Kroiss, A Clark, I Kemaev, J Quan, T Keck, F Viola, H v Hasselt
[DeepMind]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaXJUkWq7
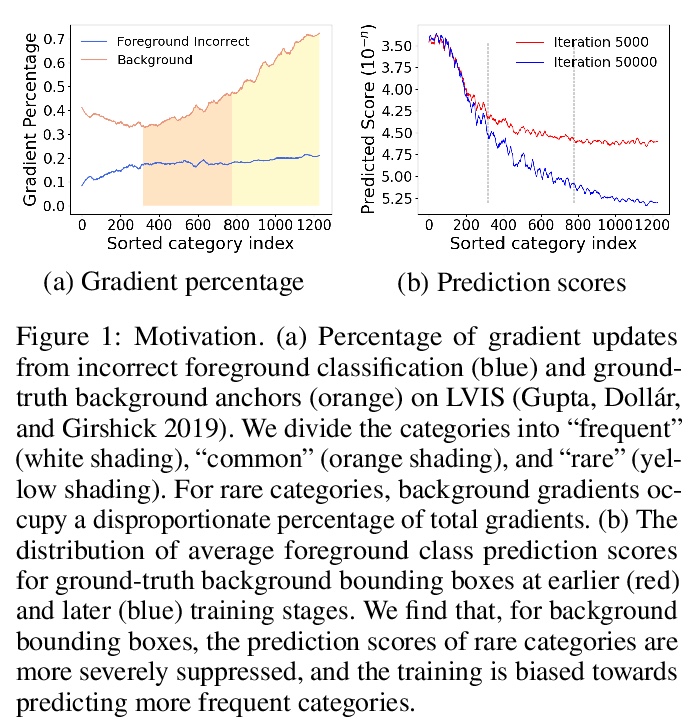
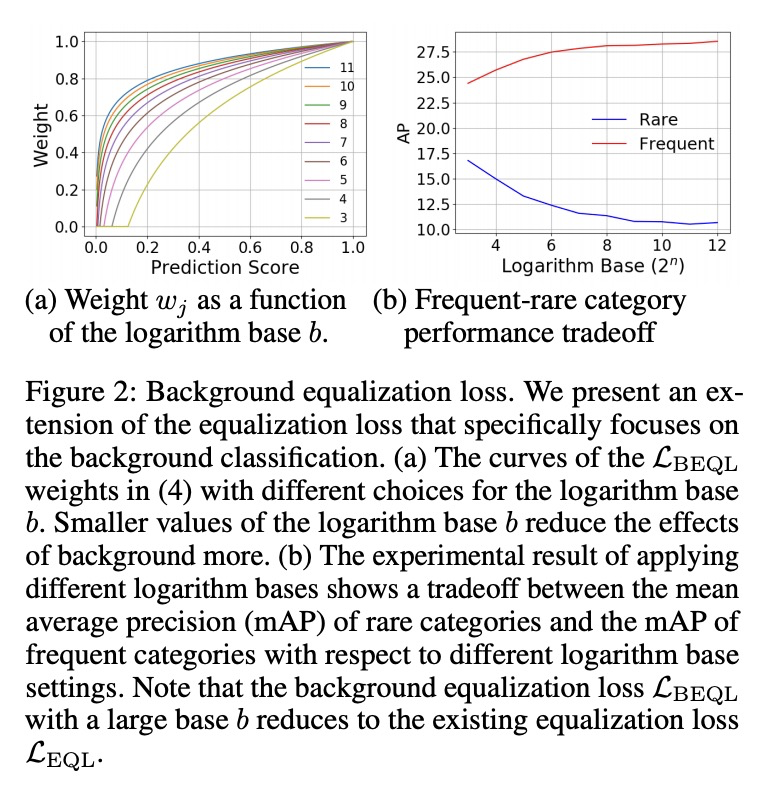
[CV] DropLoss for Long-Tail Instance Segmentation
DropLoss长尾实例分割
T Hsieh, E Robb, H Chen, J Huang
[National Tsing Hua University & Virginia Tech]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaXM26cy8

[CV] Pointly-Supervised Instance Segmentation
点监督实例分割
B Cheng, O Parkhi, A Kirillov
[UIUC & Facebook AI]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KaXNQ6NnN