- 1、[CV] SphereFace2: Binary Classification is All You Need for Deep Face Recognition
- 2、[CV] CBNetV2: A Composite Backbone Network Architecture for Object Detection
- 3、[CV] Polarized Self-Attention: Towards High-quality Pixel-wise Regression
- 4、[CV] On The State of Data In Computer Vision: Human Annotations Remain Indispensable for Developing Deep Learning Models
- 5、[LG] Toward Spatially Unbiased Generative Models
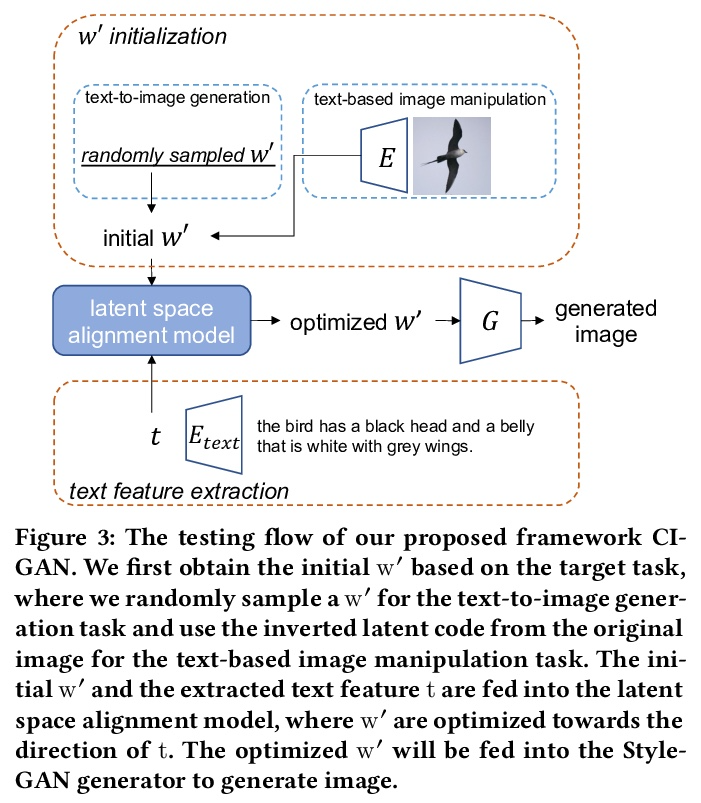
- [CV] Cycle-Consistent Inverse GAN for Text-to-Image Synthesis
- [CV] Where do Models go Wrong? Parameter-Space Saliency Maps for Explainability
- [CV] Evo-ViT: Slow-Fast Token Evolution for Dynamic Vision Transformer
- [CV] Consistent Depth of Moving Objects in Video
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[CV] SphereFace2: Binary Classification is All You Need for Deep Face Recognition
Y Wen, W Liu, A Weller, B Raj, R Singh
[CMU & University of Cambridge]
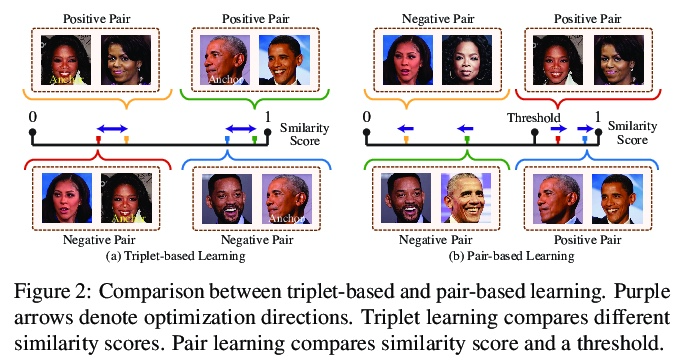
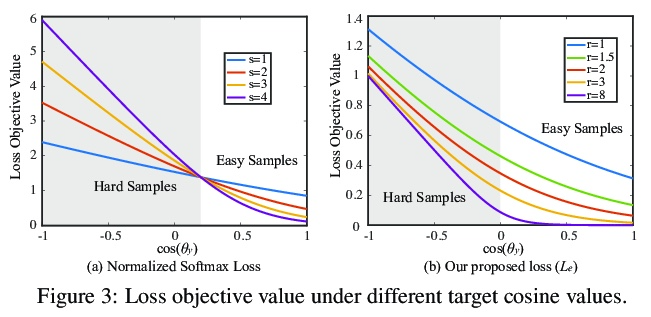
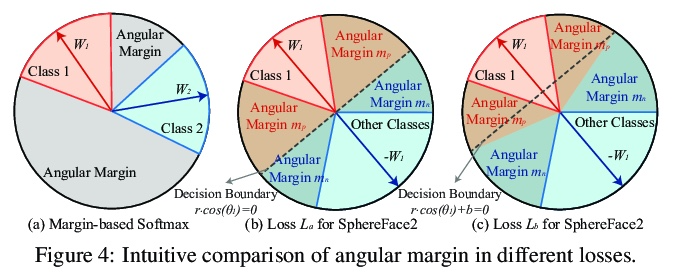
SphereFace2: 深度人脸识别二元分类就够了。最先进的深度人脸识别方法,大多采用基于softmax的多类分类框架进行训练。尽管很受欢迎,也很有效,但这些方法仍然存在一些缺点,限制了其实际表现。本文首先确定了现有多类分类框架中训练和评估之间的差异,讨论了softmax归一化的”竞争”性造成的潜在限制。在这些限制的激励下,本文提出了一种新的二元分类训练框架SphereFace2。与现有方法相比,SphereFace2规避了softmax归一化,以及相应的封闭集假设,有效地弥补了训练和评估之间的差距,使表示能通过每个二元分类任务单独改进。除了设计一个特定的性能良好的损失函数,还为这个”一比一”的二元分类框架总结了一些一般原则,以便它能胜过目前的竞争方法。SphereFace2在具有挑战性的基准上显示出有希望的通用性,对标签噪声的鲁棒性和模型并行化的效率。
State-of-the-art deep face recognition methods are mostly trained with a softmax-based multi-class classification framework. Despite being popular and effective, these methods still have a few shortcomings that limit empirical performance. In this paper, we first identify the discrepancy between training and evaluation in the existing multi-class classification framework and then discuss the potential limitations caused by the “competitive” nature of softmax normalization. Motivated by these limitations, we propose a novel binary classification training framework, termed SphereFace2. In contrast to existing methods, SphereFace2 circumvents the softmax normalization, as well as the corresponding closed-set assumption. This effectively bridges the gap between training and evaluation, enabling the representations to be improved individually by each binary classification task. Besides designing a specific well-performing loss function, we summarize a few general principles for this “one-vs-all” binary classification framework so that it can outperform current competitive methods. We conduct comprehensive experiments on popular benchmarks to demonstrate that SphereFace2 can consistently outperform current state-of-the-art deep face recognition methods.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrZhzpNFP 

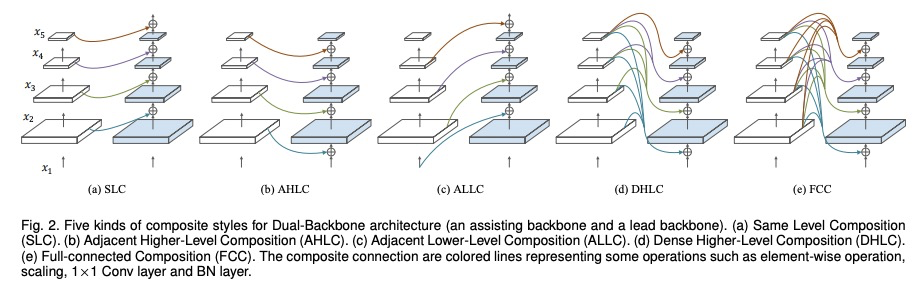
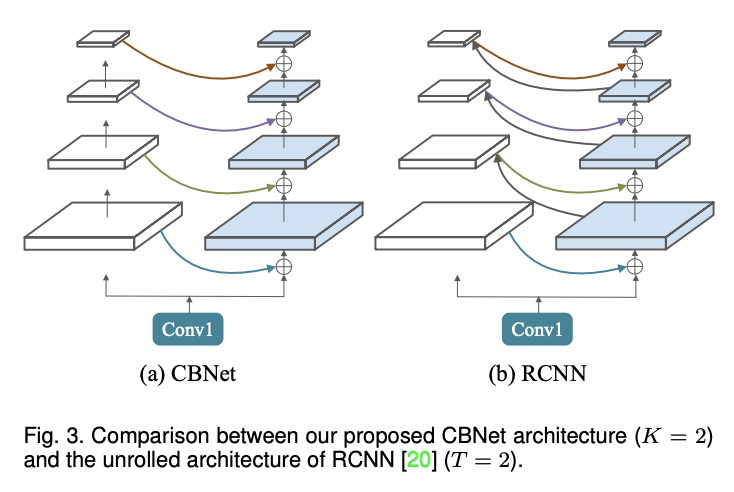
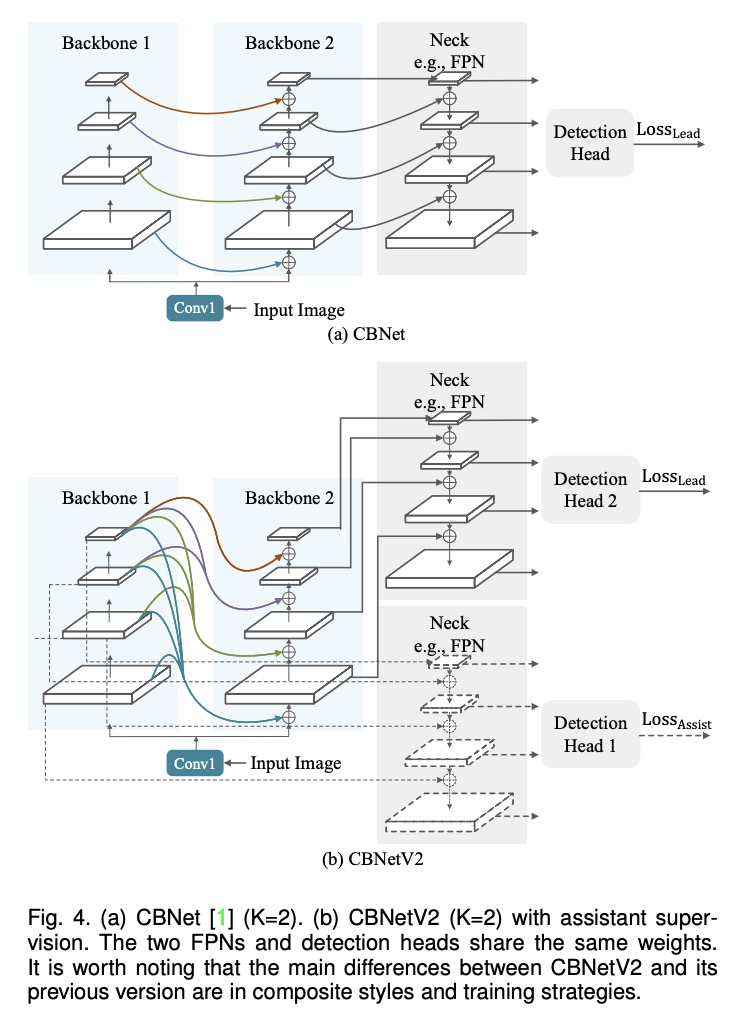
2、[CV] CBNetV2: A Composite Backbone Network Architecture for Object Detection
T Liang, X Chu, Y Liu, Y Wang, Z Tang, W Chu, J Chen, H Ling
[Peking University & Data and Platform Technology Devision of Ant Group]
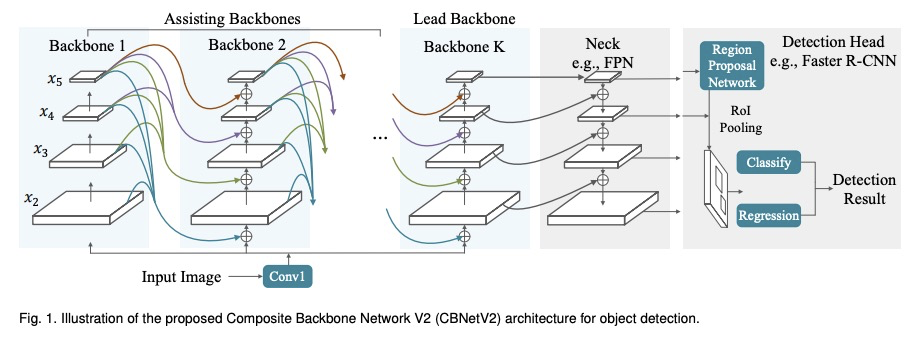
CBNetV2:用于目标检测的复合骨干网络架构。现代性能优异的目标检测器,在很大程度上依赖于骨干网络,骨干网络的进步,通过探索更有效的网络架构带来了持续的性能提升。本文提出一种新的灵活的骨干网络框架CBNetV2,在预训练微调范式下,利用现有开源预训练骨干网络来构建高性能检测器。CBNetV2架构将多个相同的骨干网络分组,通过复合连接进行连接,整合了多个骨干网络的高低层特征,并逐渐扩大感受野,以更有效地进行目标检测。为基于CBNet的检测器提出了一种更好的带有辅助监督的训练策略。CBNetV2对于不同骨干网络和检测器结构的头设计具有很强的泛化能力。无需对复合骨干进行额外预训练,CBNetV2可以适应各种骨干(基于CNN与基于Transformer)和大多数主流检测器的头设计(单阶段与双阶段,基于锚与无锚)。实验表明,与简单地增加网络的深度和宽度相比,CBNetV2引入了一种更高效、有效和资源友好的方式,来构建高性能骨干网络。Dual-Swin-L在COCO test-dev上实现了59.4%的框AP和51.6%的掩膜AP的新记录,超过了之前的单模型单尺度结果。通过多尺度测试,在没有额外训练数据的情况下取得了60.1%的框AP和52.3%的掩膜AP的新的最先进结果。
Modern top-performing object detectors depend heavily on backbone networks, whose advances bring consistent performance gains through exploring more effective network structures. In this paper, we propose a novel and flexible backbone framework, namely CBNetV2, to construct high-performance detectors using existing open-sourced pre-trained backbones under the pre-training fine-tuning paradigm. In particular, CBNetV2 architecture groups multiple identical backbones, which are connected through composite connections. Specifically, it integrates the highand low-level features of multiple backbone networks and gradually expands the receptive field to more efficiently perform object detection. We also propose a better training strategy with assistant supervision for CBNet-based detectors. CBNetV2 has strong generalization capabilities for different backbones and head designs of the detector architecture. Without additional pre-training of the composite backbone, CBNetV2 can be adapted to various backbones (i.e., CNNbased vs. Transformer-based) and head designs of most mainstream detectors (i.e., one-stage vs. two-stage, anchor-based vs. anchorfree-based). Experiments provide strong evidence that, compared with simply increasing the depth and width of the network, CBNetV2 introduces a more efficient, effective, and resource-friendly way to build high-performance backbone networks. Particularly, our DualSwin-L achieves 59.4% box AP and 51.6% mask AP on COCO test-dev under the single-model and single-scale testing protocol, which is significantly better than the state-of-the-art result (i.e., 57.7% box AP and 50.2% mask AP) achieved by Swin-L, while the training schedule is reduced by 6×. With multi-scale testing, we push the current best single model result to a new record of 60.1% box AP and 52.3% mask AP without using extra training data.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrZoI9blx 
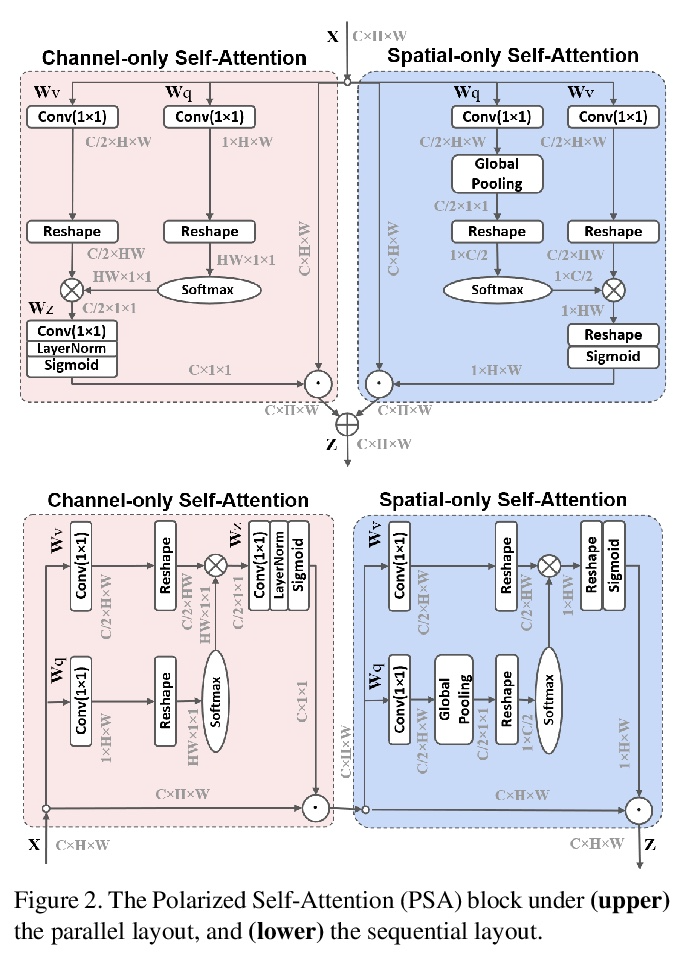
3、[CV] Polarized Self-Attention: Towards High-quality Pixel-wise Regression
H Liu, F Liu, X Fan, D Huang
[Nanjing University of Science and Technology & CMU]
极化自注意力:高质量逐像素回归探索。逐像素回归可能是细粒度计算机视觉任务中最常见的问题,如估计关键点热图和分割掩膜。这些回归问题非常具有挑战性,特别是因为它们需要在低计算开销的情况下,对高分辨率输入/输出的长程依赖性进行建模,以估计高度非线性的像素化语义。虽然深度卷积神经网络(DCNN)中的注意力机制在提高长程依赖性方面很受欢迎,但特定元素的注意力,如非局部块,学习起来非常复杂且对噪音敏感,大多数简化的注意力混合体,都试图在多种类型的任务中达到最佳折衷。本文提出了极化自注意力(PSA)块,包含两个关键设计,以实现高质量像素级回归。(1) 极化滤波:在通道和空间注意力计算中保持高的内部分辨率,同时沿其对应维度完全折叠输入张量。(2)增强:合成非线性,直接拟合典型的细粒度回归的输出分布,如2D高斯分布(关键点热图),或2D二项分布(二元分割掩膜)。PSA似乎已经用尽了其纯通道和纯空间分支内的表示能力,因此其顺序和平行布局之间只有边际的度量差异。实验结果显示,PSA将标准基线提高了2-4个点,并将2D姿势估计和语义分割基准的最新水平提高了1-2个点。
Pixel-wise regression is probably the most common problem in fine-grained computer vision tasks, such as estimating keypoint heatmaps and segmentation masks. These regression problems are very challenging particularly because they require, at low computation overheads, modeling long-range dependencies on high-resolution inputs/outputs to estimate the highly nonlinear pixel-wise semantics. While attention mechanisms in Deep Convolutional Neural Networks(DCNNs) has become popular for boosting long-range dependencies, element-specific attention, such as Nonlocal blocks, is highly complex and noise-sensitive to learn, and most of simplified attention hybrids try to reach the best compromise among multiple types of tasks. In this paper, we present the Polarized Self-Attention(PSA) block that incorporates two critical designs towards highquality pixel-wise regression: (1) Polarized filtering: keeping high internal resolution in both channel and spatial attention computation while completely collapsing input tensors along their counterpart dimensions. (2) Enhancement: composing non-linearity that directly fits the output distribution of typical fine-grained regression, such as the 2D Gaussian distribution (keypoint heatmaps), or the 2D Binormial distribution (binary segmentation masks). PSA appears to have exhausted the representation capacity within its channel-only and spatial-only branches, such that there is only marginal metric differences between its sequential and parallel layouts. Experimental results show that PSA boosts standard baselines by 2− 4 points, and boosts stateof-the-arts by 1 − 2 points on 2D pose estimation and semantic segmentation benchmarks.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrZvBD96K 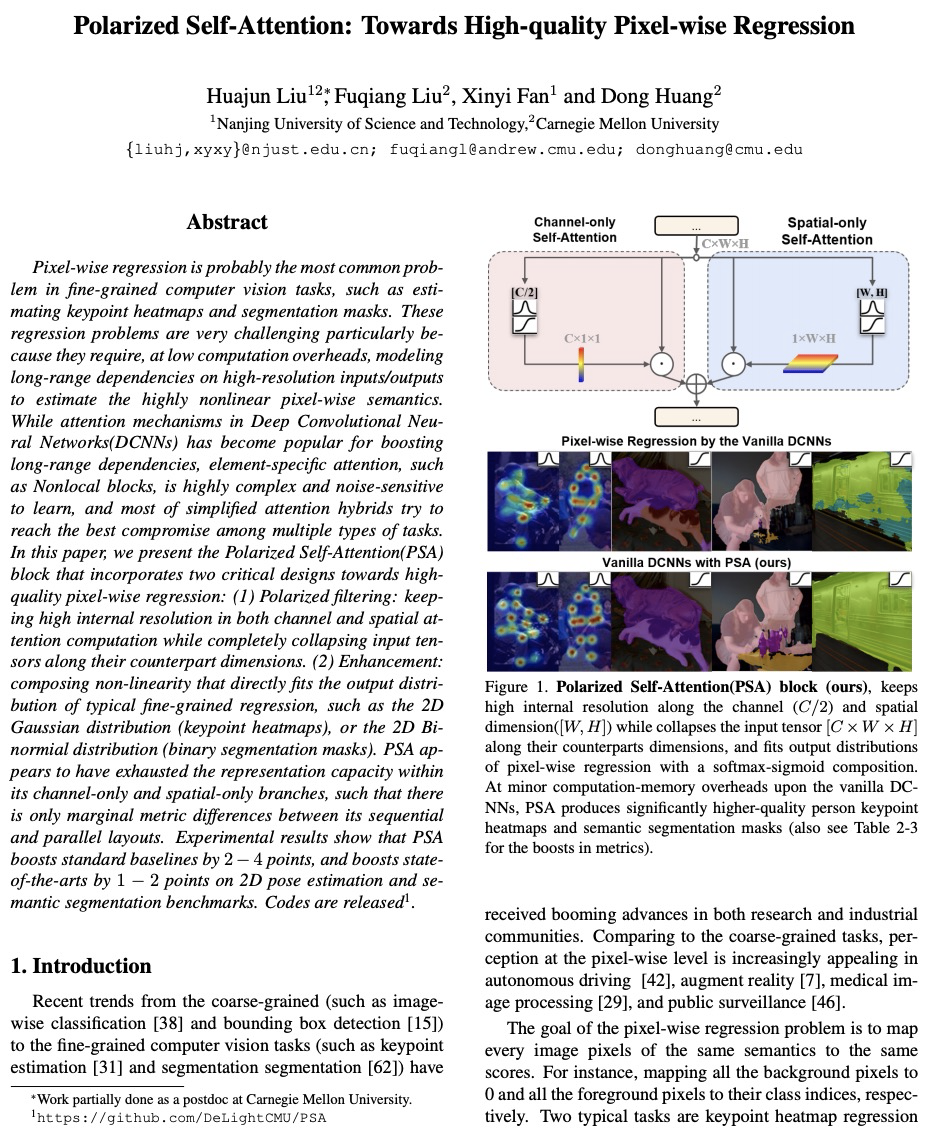


4、[CV] On The State of Data In Computer Vision: Human Annotations Remain Indispensable for Developing Deep Learning Models
Z Emam, A Kondrich, S Harrison, F Lau, Y Wang, A Kim, E Branson
[Scale AI]
计算机视觉数据现状综述:开发深度学习模型人工标注仍然必不可少。高质量标注数据集在推动机器学习(ML)的发展,特别是深度学习(DL)的发展中起着关键作用。然而,自从2012年ImageNet数据集和AlexNet模型出现后,新的开源标注视觉数据集的规模基本保持不变。在计算机视觉界,只有少数工作解决了比Imagenet大几个数量级的数据集上的监督学习。本文调研了计算机视觉研究领域,在这些领域研究了大数据集对不同视觉任务的模型性能的影响。本文总结了社区目前对这些影响的理解,并强调了一些与海量数据集训练有关的开放性问题。特别的,聚焦于 (a) 目前在计算机视觉研究中使用的最大的数据集,以及在这些数据集上训练的有趣收获;(b) 在大数据集上预训练的有效性;(c) 合成数据集的最新进展和面临的障碍;(d) 双重下降和样本非单调性现象的概述;最后,(e) 对终身/持续学习的简要讨论,以及它与在离线环境下从巨大标注数据集学习相比的表现。总的来说,本文的发现是,关于深度学习的优化研究主要集中在完善训练程序,从而使DL模型的数据饥渴度降低,而关于合成数据集的研究旨在抵消数据标注的成本。然而,就目前而言,获得非合成标记的数据对于提升性能仍然是不可或缺的。
High-quality labeled datasets play a crucial role in fueling the development of machine learning (ML), and in particular the development of deep learning (DL). However, since the emergence of the ImageNet dataset and the AlexNet model in 2012, the size of new open-source labeled vision datasets has remained roughly constant. Consequently, only a minority of publications in the computer vision community tackle supervised learning on datasets that are orders of magnitude larger than Imagenet. In this paper, we survey computer vision research domains that study the effects of such large datasets on model performance across different vision tasks. We summarize the community’s current understanding of those effects, and highlight some open questions related to training with massive datasets. In particular, we tackle: (a) The largest datasets currently used in computer vision research and the interesting takeaways from training on such datasets; (b) The effectiveness of pretraining on large datasets; (c) Recent advancements and hurdles facing synthetic datasets; (d) An overview of double descent and sample nonmonotonicity phenomena; and finally, (e) A brief discussion of lifelong/continual learning and how it fares compared to learning from huge labeled datasets in an offline setting. Overall, our findings are that research on optimization for deep learning focuses on perfecting the training routine and thus making DL models less data hungry, while research on synthetic datasets aims to offset the cost of data labeling. However, for the time being, acquiring non-synthetic labeled data remains indispensable to boost performance.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrZzX9NIs 
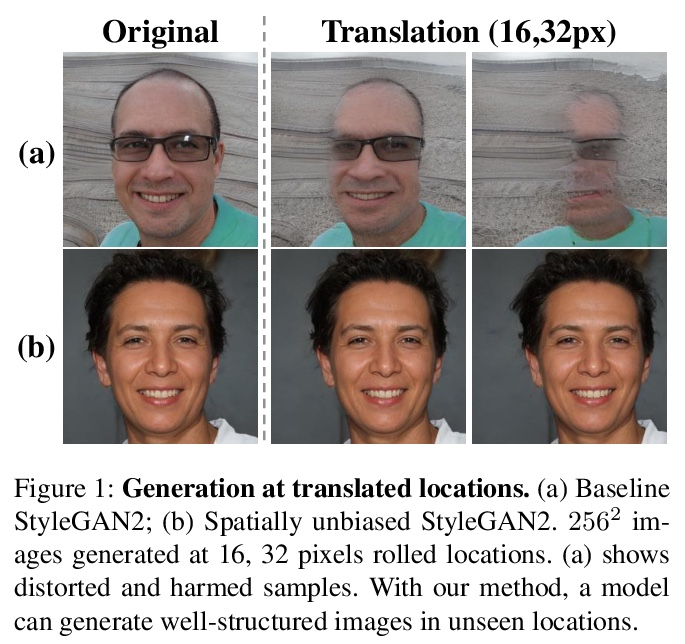
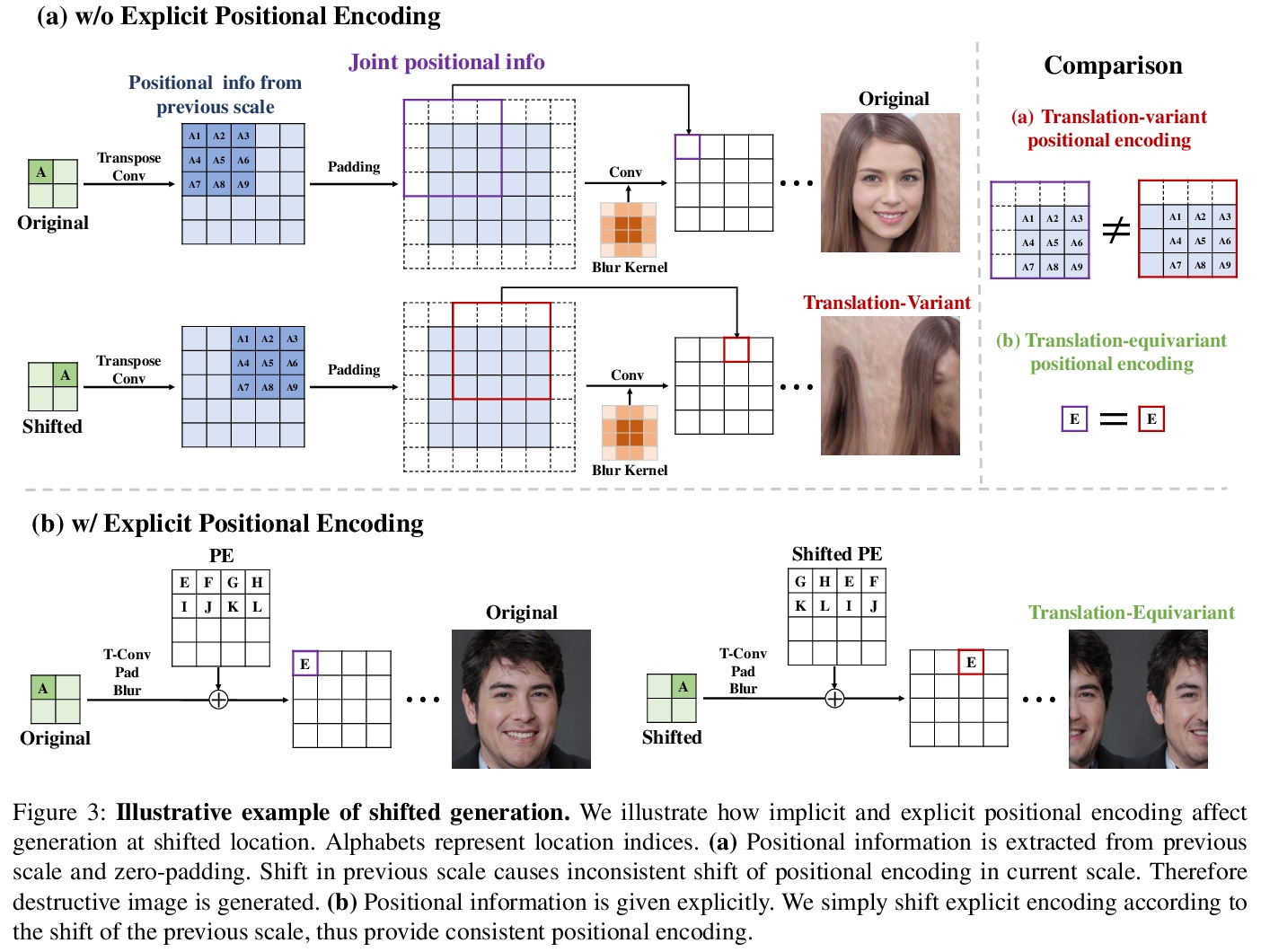
5、[LG] Toward Spatially Unbiased Generative Models
J Choi, J Lee, Y Jeong, S Yoon
[Seoul National University & Samsung]
空间无偏生成模型探索。最近的图像生成模型显示了显著的生成性能。然而,它们反映了数据集中强烈的位置偏好,即空间偏差。生成器在未见的位置和尺度上呈现出很差的样本。本文认为,生成器依靠其隐含位置编码来呈现空间内容,生成器的隐性位置编码是映射可变的,使得生成器在空间上有偏差。为解决这个问题,本文建议在生成器的每个尺度上注入显性位置编码。通过学习空间无偏的生成器,促进了生成器在多种任务中的鲁棒应用,如GAN反演、多尺度生成、任意尺寸和长宽比的生成,该方法也可应用于去噪扩散概率模型。
Recent image generation models show remarkable generation performance. However, they mirror strong location preference in datasets, which we call spatial bias. Therefore, generators render poor samples at unseen locations and scales. We argue that the generators rely on their implicit positional encoding to render spatial content. From our observations, the generator’s implicit positional encoding is translation-variant, making the generator spatially biased. To address this issue, we propose injecting explicit positional encoding at each scale of the generator. By learning the spatially unbiased generator, we facilitate the robust use of generators in multiple tasks, such as GAN inversion, multi-scale generation, generation of arbitrary sizes and aspect ratios. Furthermore, we show that our method can also be applied to denoising diffusion probabilistic models.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrZCXAVAo 



另外几篇值得关注的论文:
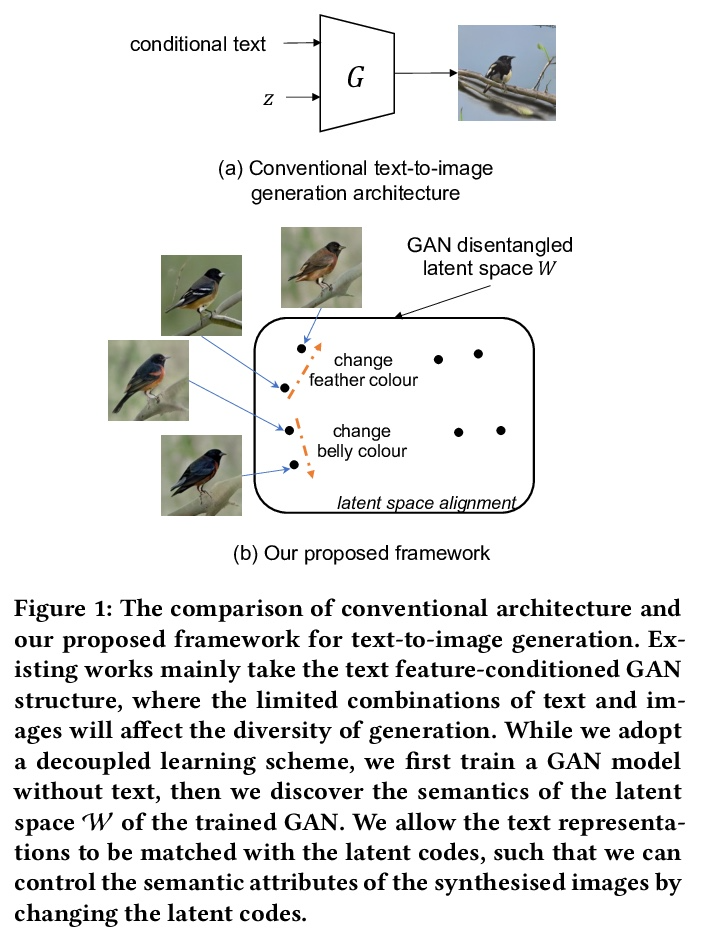
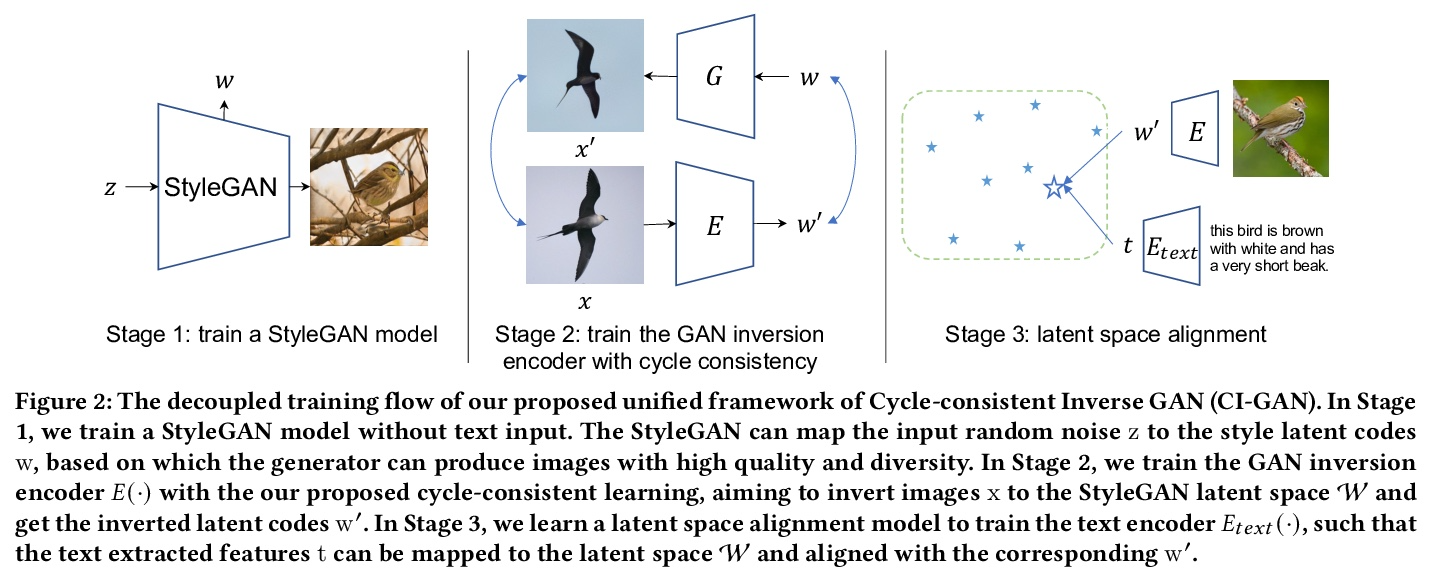
[CV] Cycle-Consistent Inverse GAN for Text-to-Image Synthesis
基于循环一致逆GAN的文本-图像合成
H Wang, G Lin, S C. H. Hoi, C Miao
[Nanyang Technological University (NTU) & Singapore Management University]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrZIfAHmy 

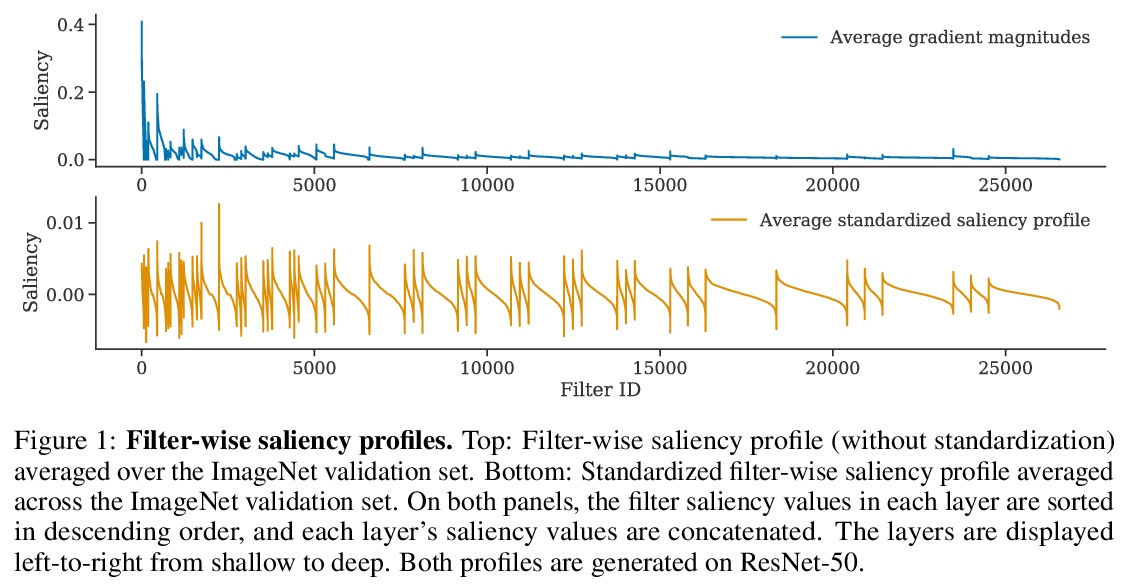
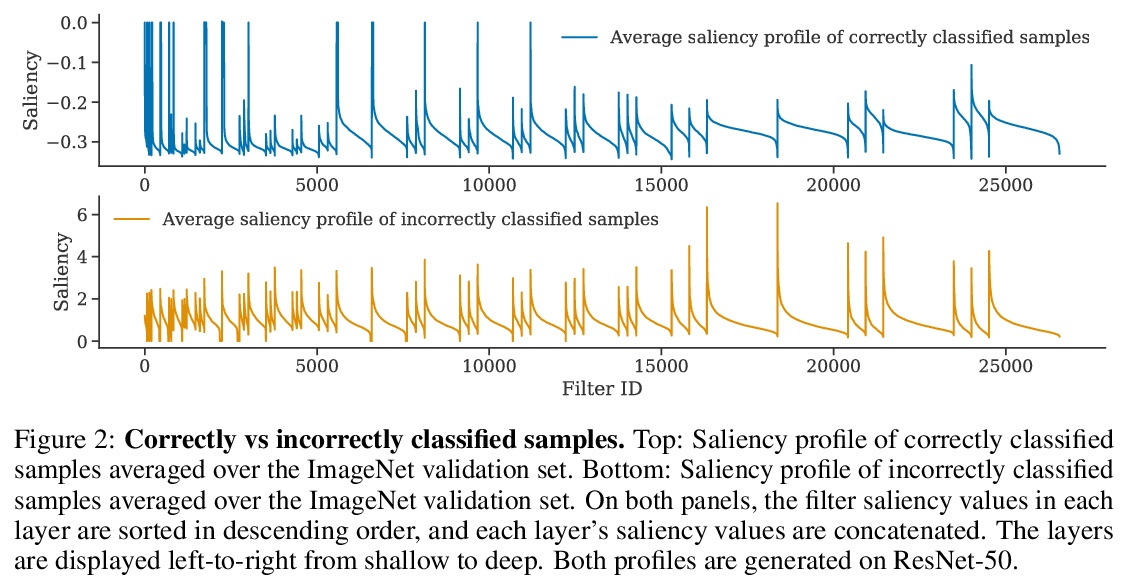
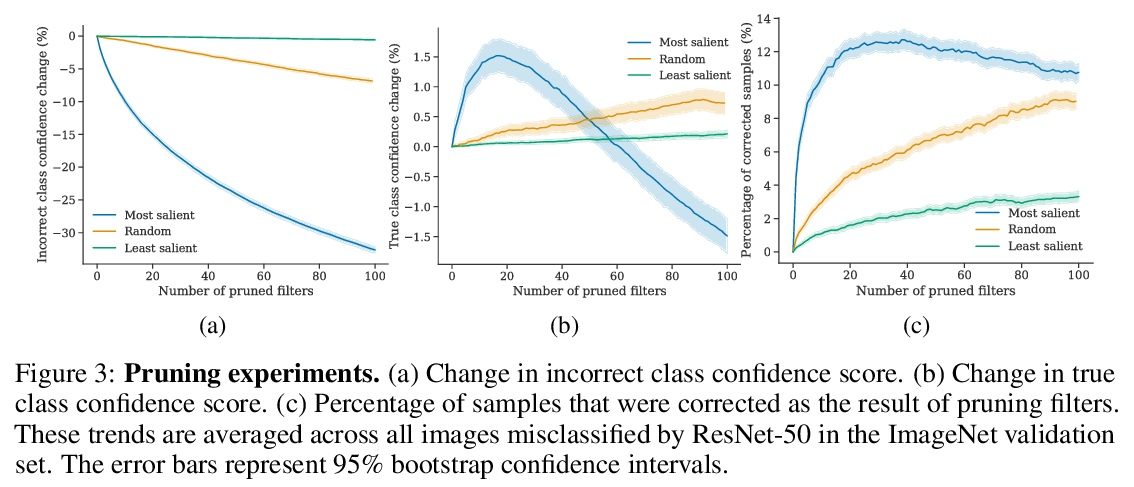
[CV] Where do Models go Wrong? Parameter-Space Saliency Maps for Explainability
模型哪里出错了?面向可解释性的参数-空间显著图
R Levin, M Shu, E Borgnia, F Huang, M Goldblum, T Goldstein
[University of Washington & University of Maryland]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrZKd2Gsy 

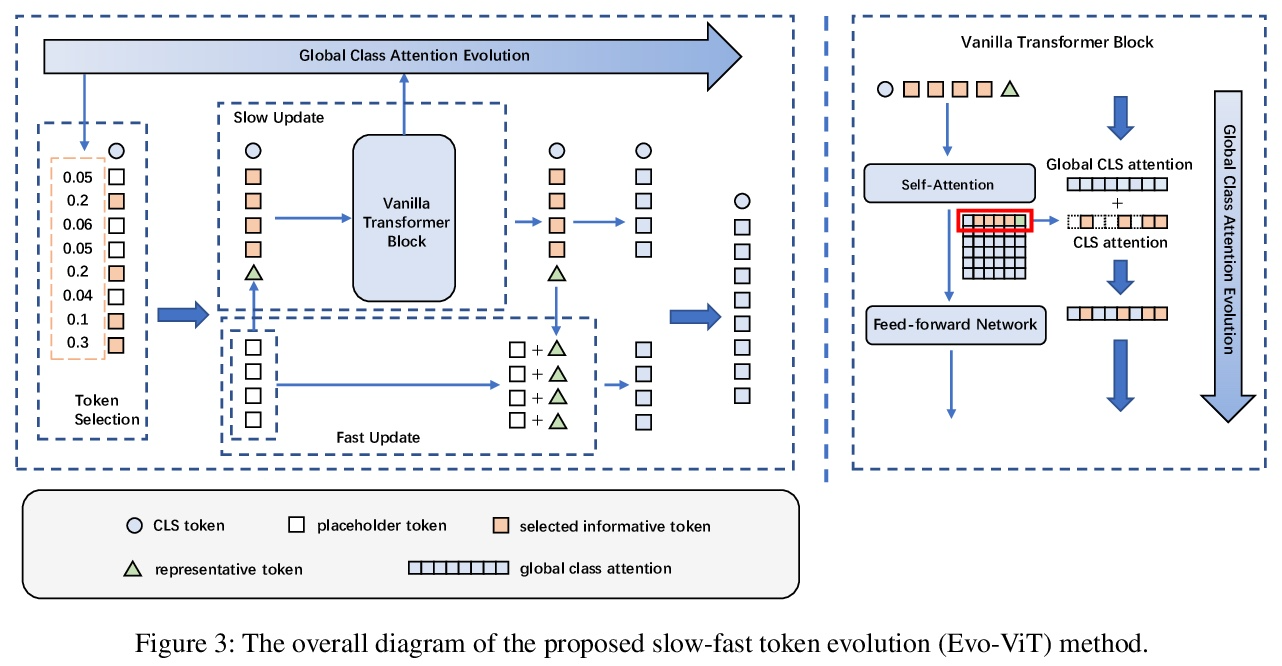
[CV] Evo-ViT: Slow-Fast Token Evolution for Dynamic Vision Transformer
Evo-ViT:动态视觉Transformer的慢-快Token进化
Y Xu, Z Zhang, M Zhang, K Sheng, K Li, W Dong, L Zhang, C Xu, X Sun
[Chinese Academy of Sciences & Shanghai Jiao Tong University & Tencent Youtu Lab]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrZLG3n1t 

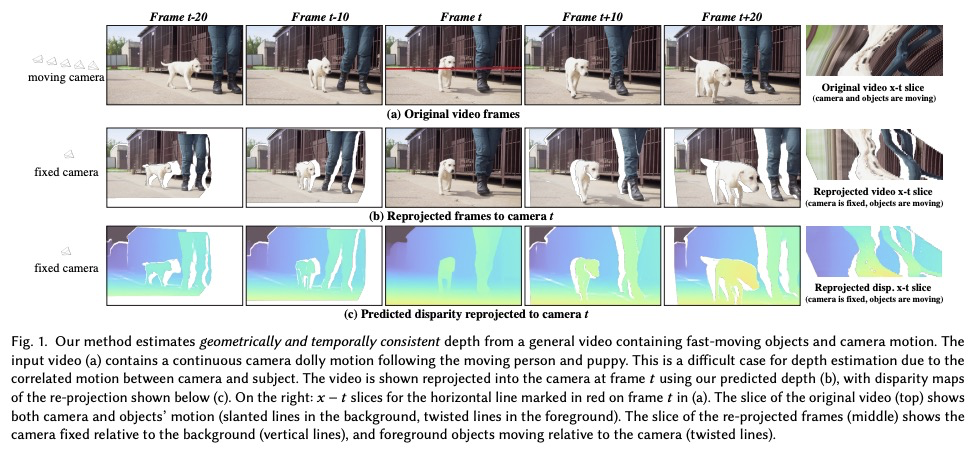
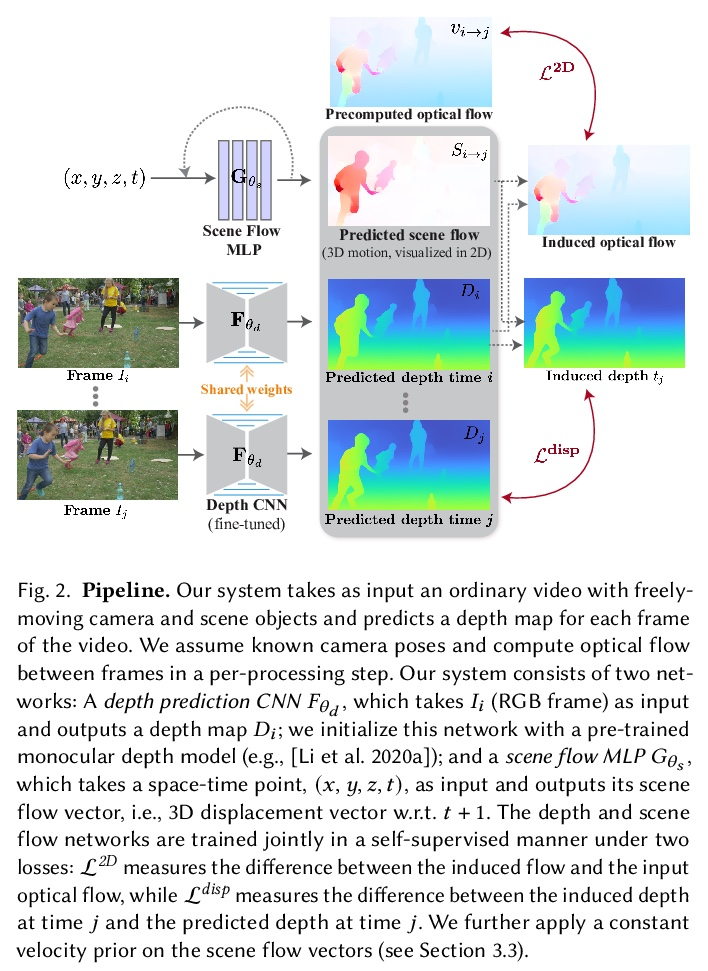
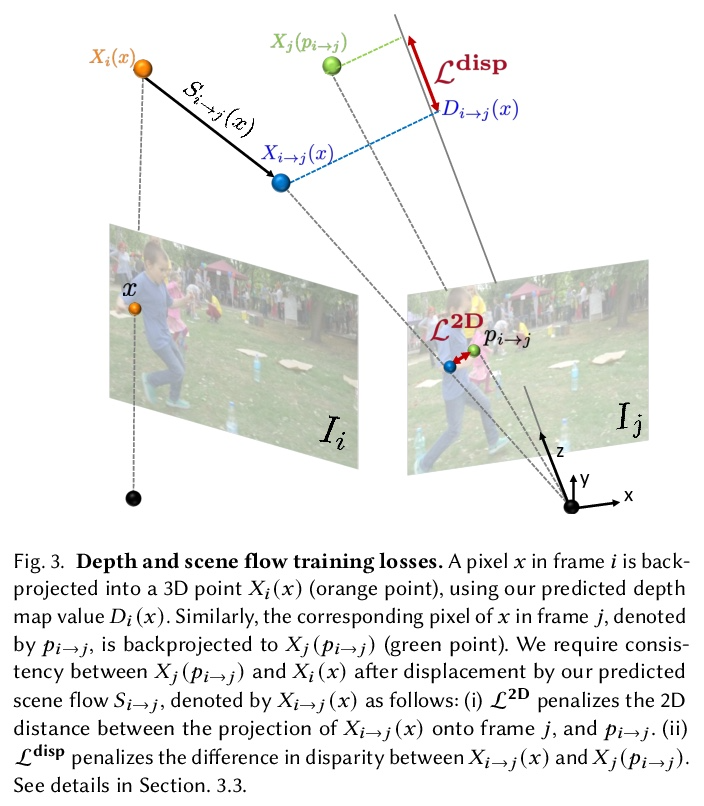
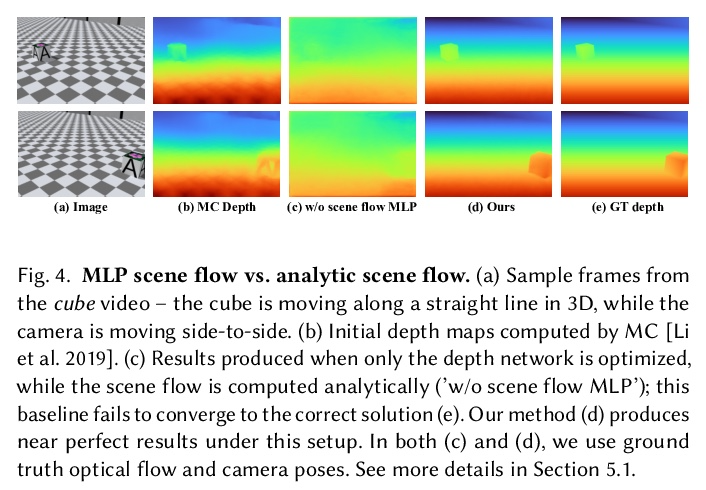
[CV] Consistent Depth of Moving Objects in Video
视频运动目标一致深度
Z Zhang, F Cole, R Tucker, W T. Freeman, T Dekel
[Google Research]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KrZNEa2Gd