- 1、[LG] Momentum Residual Neural Networks
- 2、[LG] Neural Rough Differential Equations for Long Time Series
- 3、[CV] Dynamic View Synthesis from Dynamic Monocular Video
- 4、[CL] AdapterFusion: Non-Destructive Task Composition for Transfer Learning
- 5、[CV] GAN Prior Embedded Network for Blind Face Restoration in the Wild
- [CV] Home Action Genome: Cooperative Compositional Action Understanding
- [CL] EL-Attention: Memory Efficient Lossless Attention for Generation
- [CL] Measuring and Increasing Context Usage in Context-Aware Machine Translation
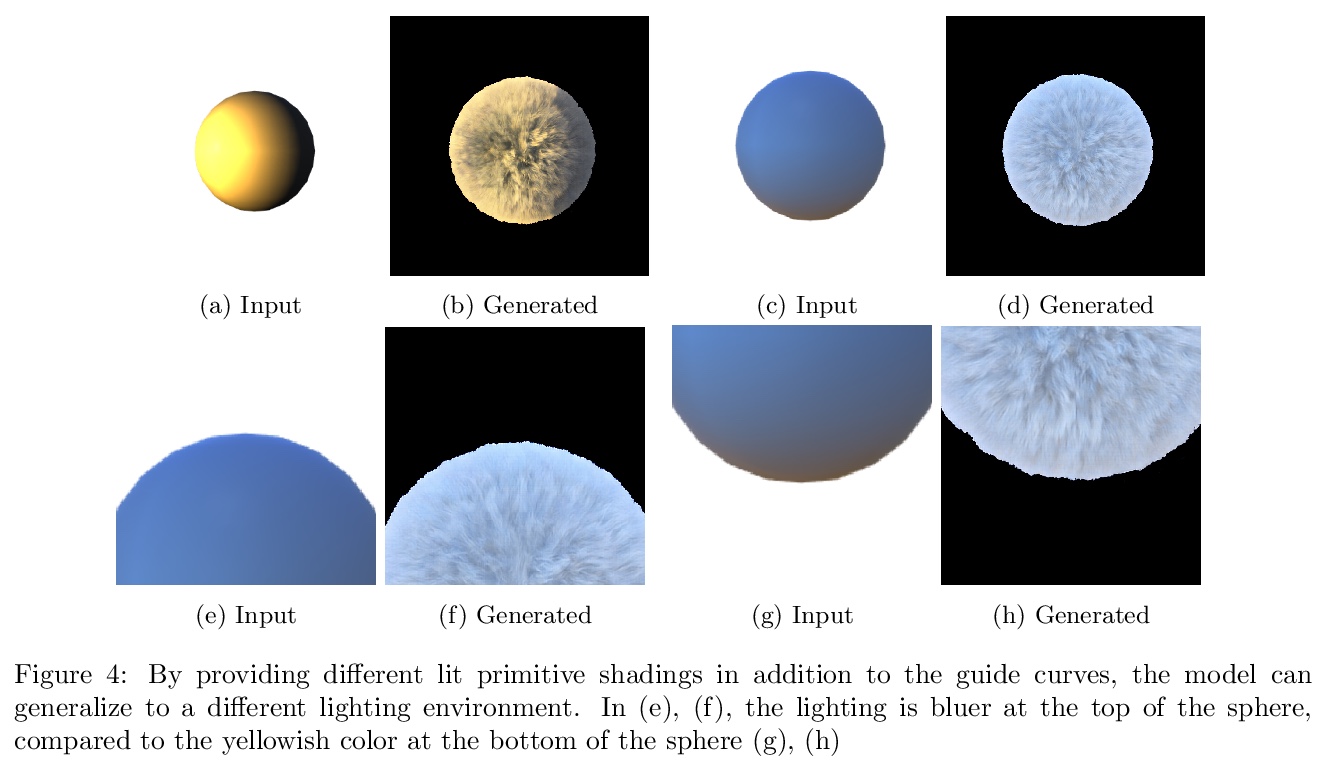
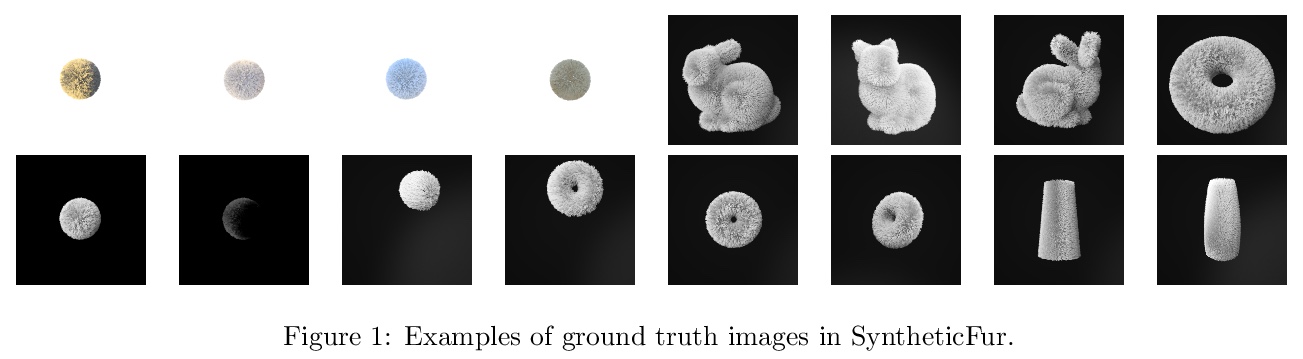
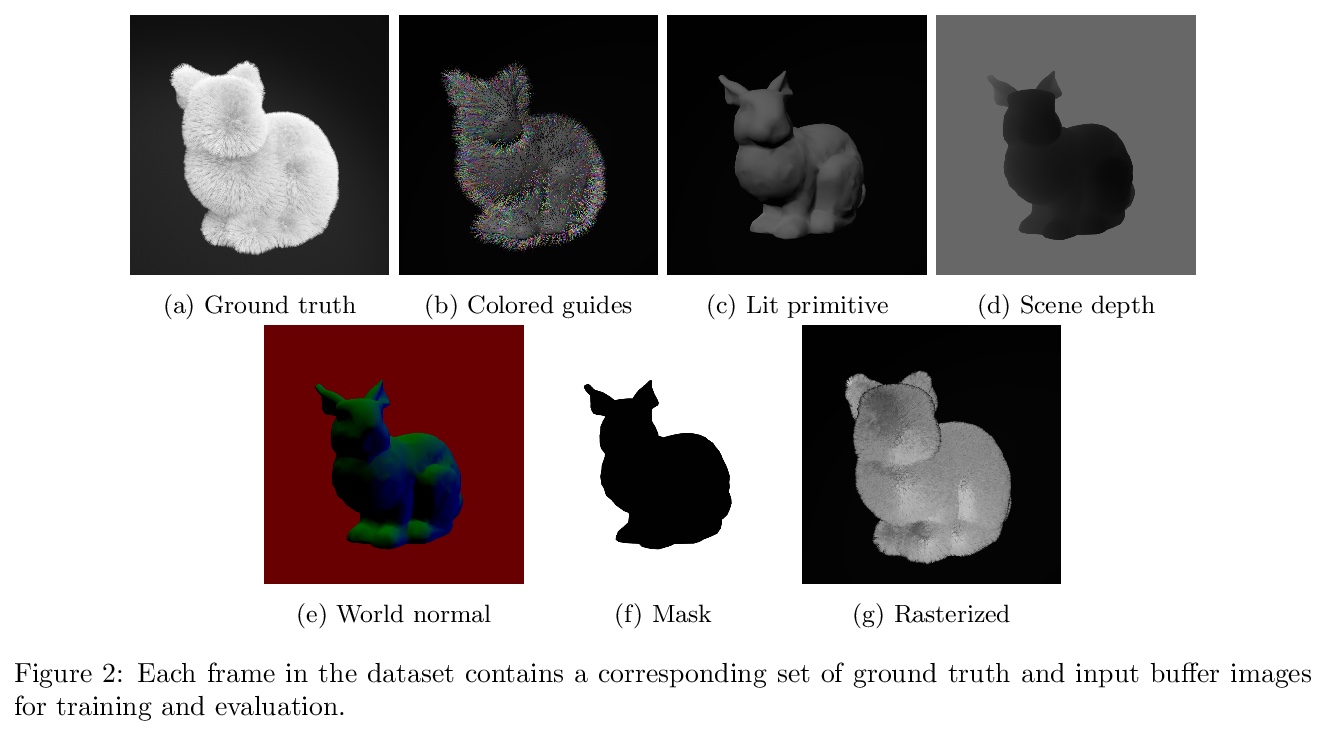
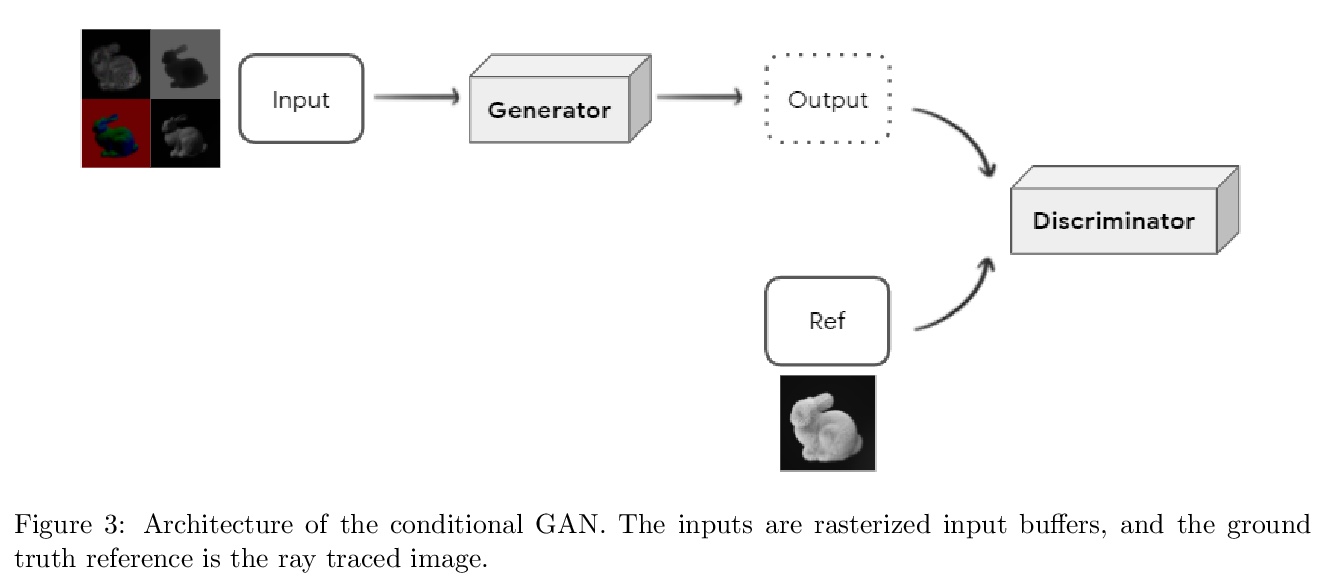
- [LG] SyntheticFur dataset for neural rendering
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
1、[LG] Momentum Residual Neural Networks
M E. Sander, P Ablin, M Blondel, G Peyré
[Ecole Normale Superieure]
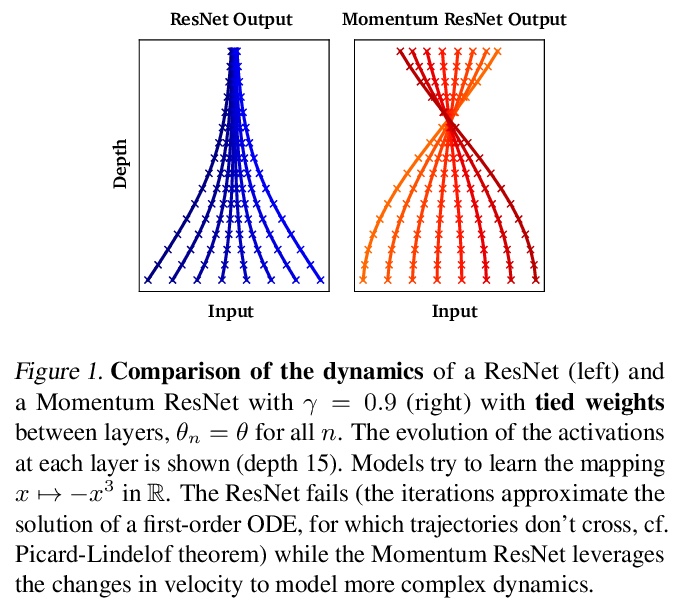
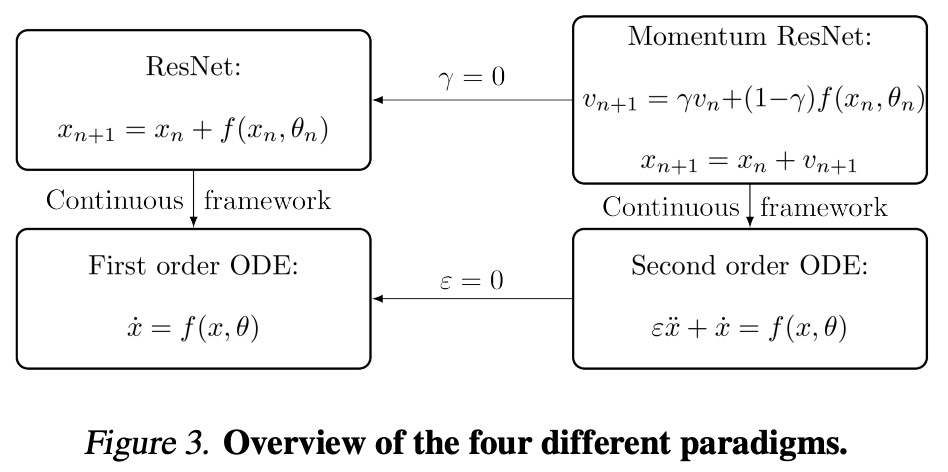
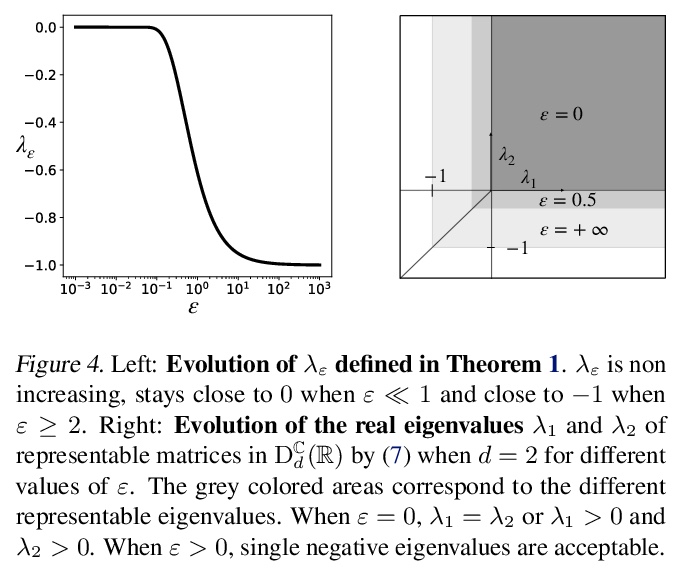
动量残差神经网络。用反向传播方法训练深度残差神经网络(ResNets),其内存成本随网络深度而线性增加。规避这一问题的方法是使用可逆架构。本文建议通过增加一个动量项来改变ResNet的前进规则。由此产生的网络,即动量残差神经网络(Momentum ResNets),是可逆的,与之前的可逆结构不同,它们可以直接替换任何现有ResNet块。Momentum ResNets既提供了理论上的优势(更好的表示能力,对线性动力学的可行分析),也提供了实际的优势(直接替换,模型微调速度和内存改进)。在无限小的步长下,动量残差网络可解释为二阶常微分方程(ODE),且确切描述了增加动量如何逐步增加动量残差网络的表示能力。分析显示,动量残差网络可学习任何线性映射,而残差网络不能。我们在CIFAR和ImageNet上显示,Momentum ResNets具有与ResNets相同的准确性,同时内存占用更小。
The training of deep residual neural networks (ResNets) with backpropagation has a memory cost that increases linearly with respect to the depth of the network. A way to circumvent this issue is to use reversible architectures. In this paper, we propose to change the forward rule of a ResNet by adding a momentum term. The resulting networks, momentum residual neural networks (Momentum ResNets), are invertible. Unlike previous invertible architectures, they can be used as a dropin replacement for any existing ResNet block. We show that Momentum ResNets can be interpreted in the infinitesimal step size regime as secondorder ordinary differential equations (ODEs) and exactly characterize how adding momentum progressively increases the representation capabilities of Momentum ResNets. Our analysis reveals that Momentum ResNets can learn any linear mapping up to a multiplicative factor, while ResNets cannot. In a learning to optimize setting, where convergence to a fixed point is required, we show theoretically and empirically that our method succeeds while existing invertible architectures fail. We show on CIFAR and ImageNet that Momentum ResNets have the same accuracy as ResNets, while having a much smaller memory footprint, and show that pre-trained Momentum ResNets are promising for fine-tuning models.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfFAU0Yq1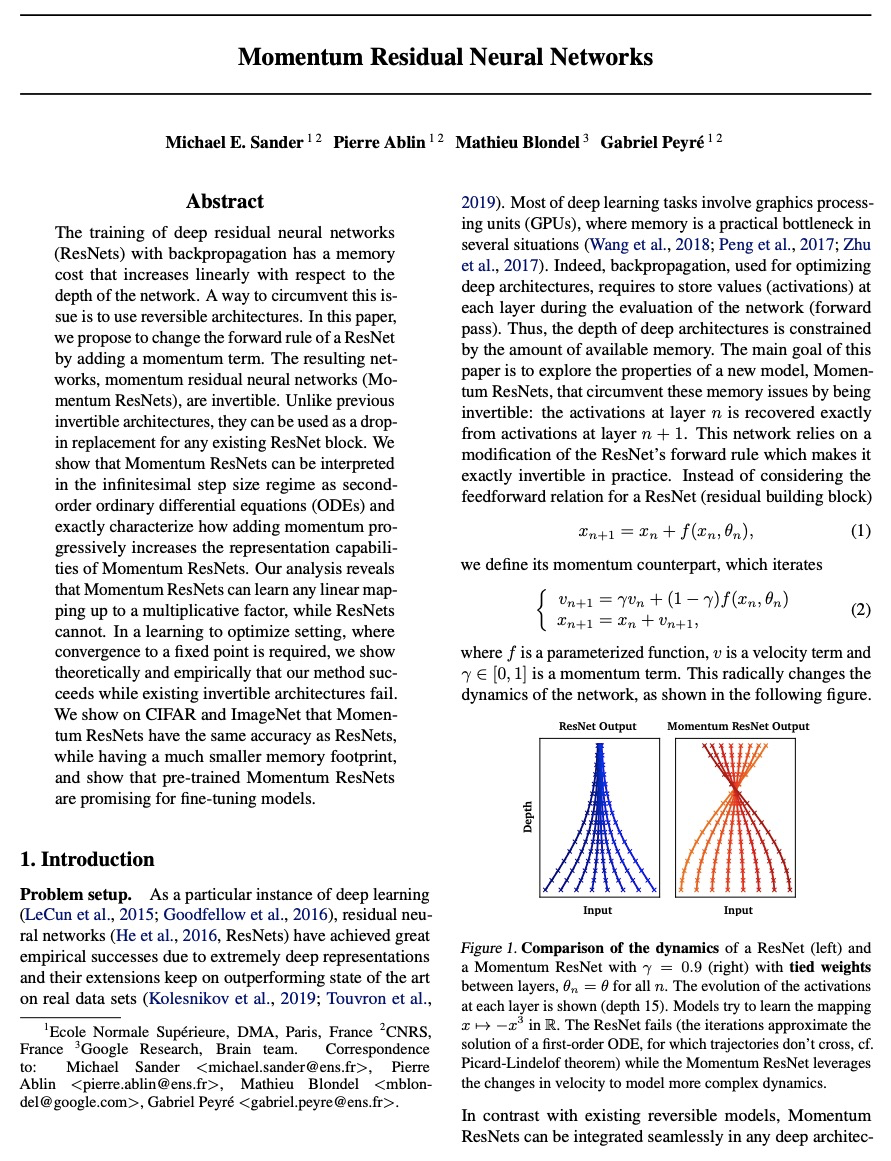

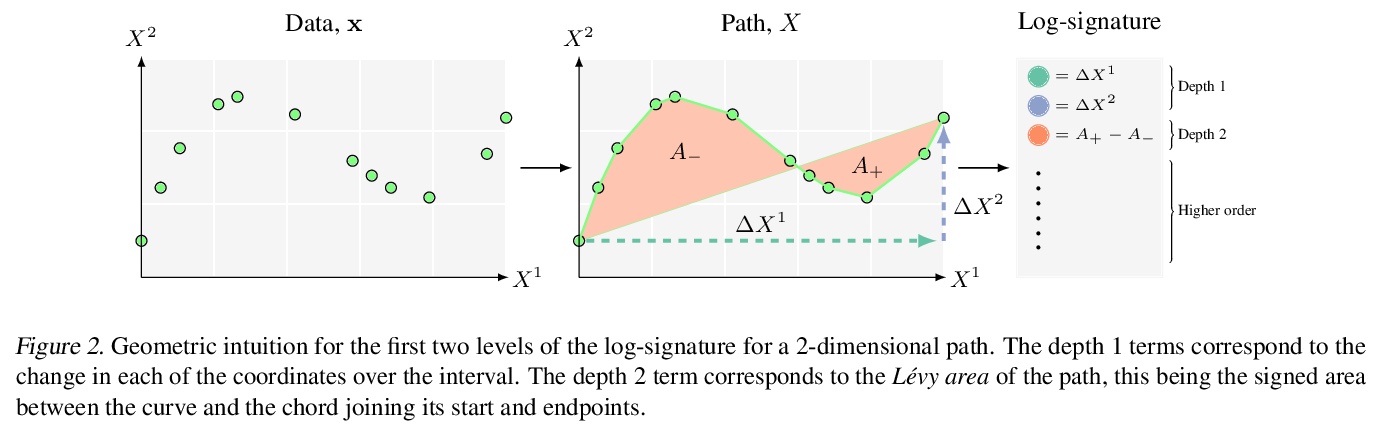
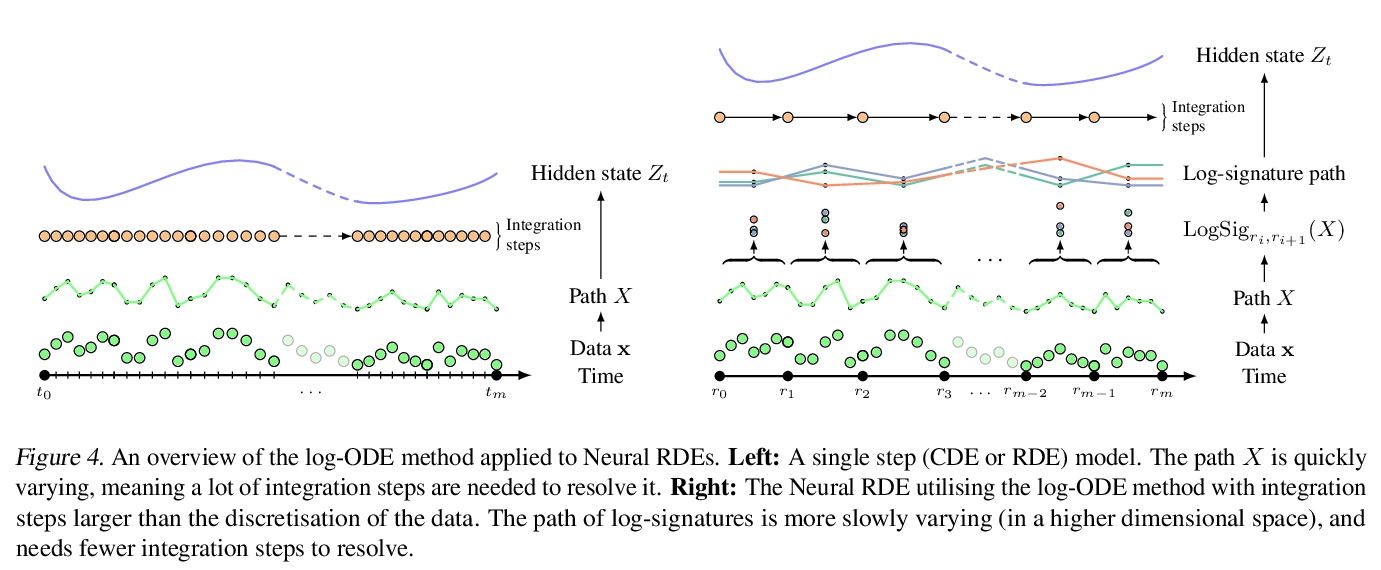
2、[LG] Neural Rough Differential Equations for Long Time Series
J Morrill, C Salvi, P Kidger, J Foster, T Lyons
[University of Oxford]
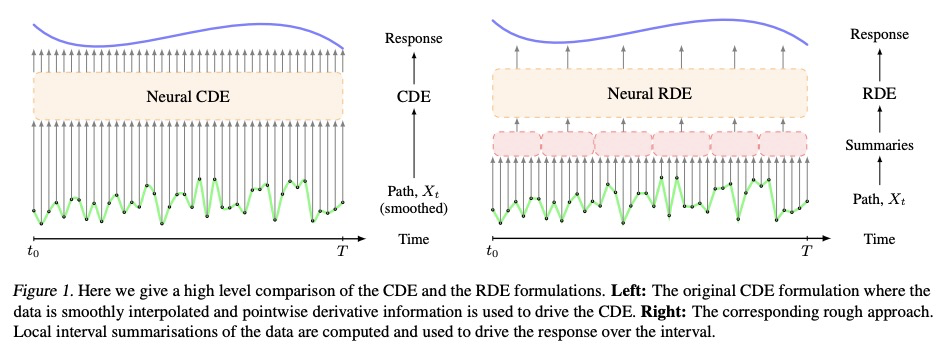
长时间序列神经粗微分方程。神经控制微分方程(CDE)是递归神经网络的连续时间对应架构,就像神经ODE对残差网络一样,为潜在不规则时间序列的函数建模提供了一种高效的连续时间方式。现有的计算神经CDE前向传播的方法,包括将传入的时间序列嵌入路径空间,通常是通过插值,并使用该路径的评估来驱动隐状态。本文用粗糙路径理论扩展这种表述,通过对数符号来表示小时间间隔内的输入信号,这些符号是描述信号如何驱动CDE的统计数据。通过将神经CDE方法推广到更广泛的驱动信号类别,展示了处理长时间序列的特殊优势,与现有方法相比,训练速度明显加快,模型性能得到改善,内存需求减少。
Neural controlled differential equations (CDEs) are the continuous-time analogue of recurrent neural networks, as Neural ODEs are to residual networks, and offer a memory-efficient continuoustime way to model functions of potentially irregular time series. Existing methods for computing the forward pass of a Neural CDE involve embedding the incoming time series into path space, often via interpolation, and using evaluations of this path to drive the hidden state. Here, we use rough path theory to extend this formulation. Instead of directly embedding into path space, we instead represent the input signal over small time intervals through its log-signature, which are statistics describing how the signal drives a CDE. This is the approach for solving rough differential equations (RDEs), and correspondingly we describe our main contribution as the introduction of Neural RDEs. This extension has a purpose: by generalising the Neural CDE approach to a broader class of driving signals, we demonstrate particular advantages for tackling long time series. In this regime, we demonstrate efficacy on problems of length up to 17k observations and observe significant training speed-ups, improvements in model performance, and reduced memory requirements compared to existing approaches.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfFIerFN5

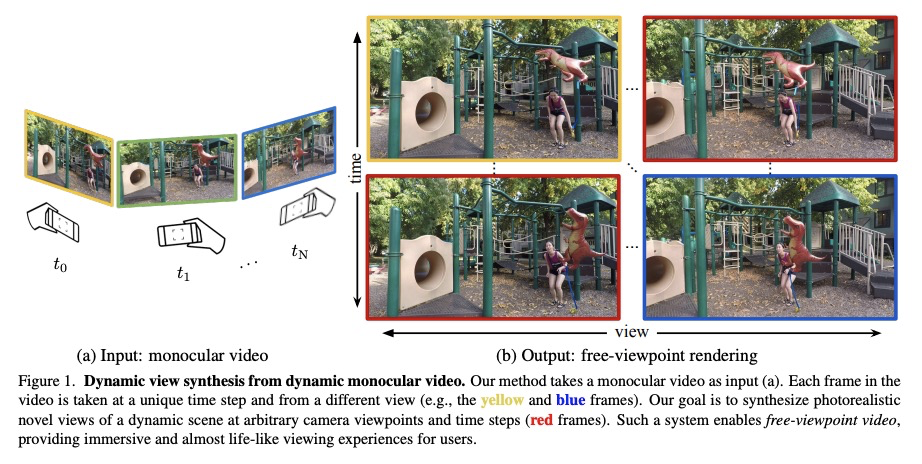
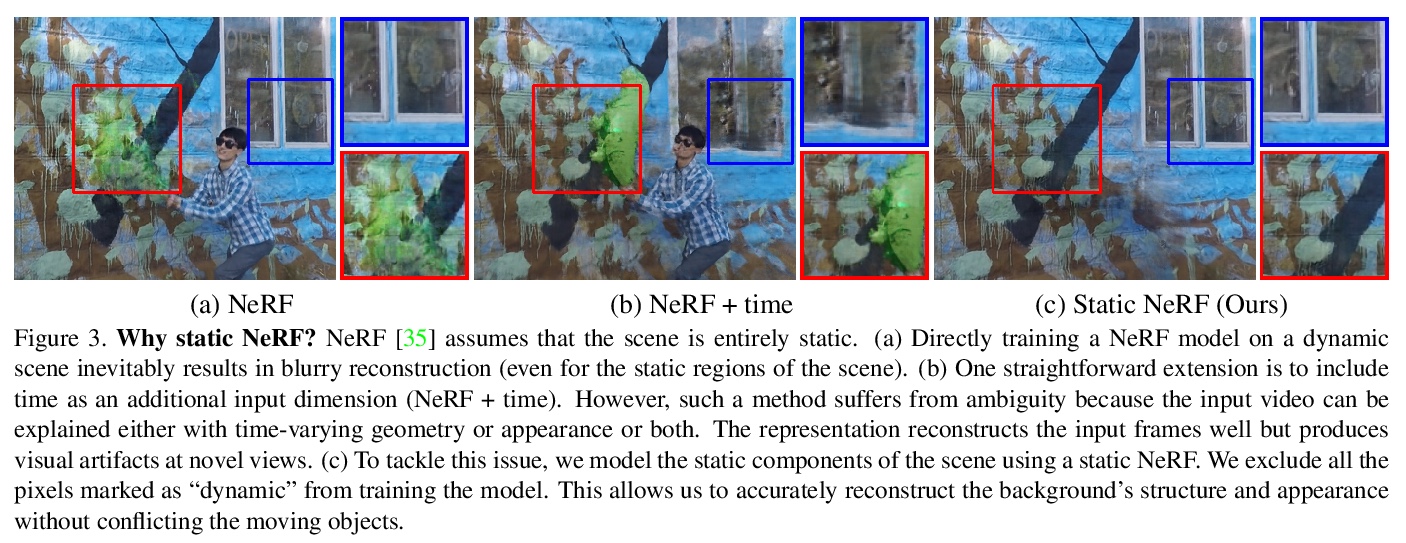
3、[CV] Dynamic View Synthesis from Dynamic Monocular Video
C Gao, A Saraf, J Kopf, J Huang
[Virginia Tech & Facebook]
动态场景单目视频的动态视图合成。提出一种算法,用于在给定动态场景单目视频的情况下,在任意视点和输入时间步长上生成新的视图。该工作建立在神经隐性表征的最新进展之上,用连续和可微分的函数对场景的时变结构和外观进行建模。联合训练一个时间不变的静态NeRF和一个时间变化的动态NeRF,并学习如何以无监督方式混合结果。从单一视频中学习这个隐含函数是高度不确定的(有无限多与输入视频匹配的解决方案)。为解决这种模糊性,引入了正则化损失,以鼓励更多物理上合理的解决方案。
We present an algorithm for generating novel views at arbitrary viewpoints and any input time step given a monocular video of a dynamic scene. Our work builds upon recent advances in neural implicit representation and uses continuous and differentiable functions for modeling the time-varying structure and the appearance of the scene. We jointly train a time-invariant static NeRF and a timevarying dynamic NeRF, and learn how to blend the results in an unsupervised manner. However, learning this implicit function from a single video is highly ill-posed (with infinitely many solutions that match the input video). To resolve the ambiguity, we introduce regularization losses to encourage a more physically plausible solution. We show extensive quantitative and qualitative results of dynamic view synthesis from casually captured videos.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfFNTvqz3
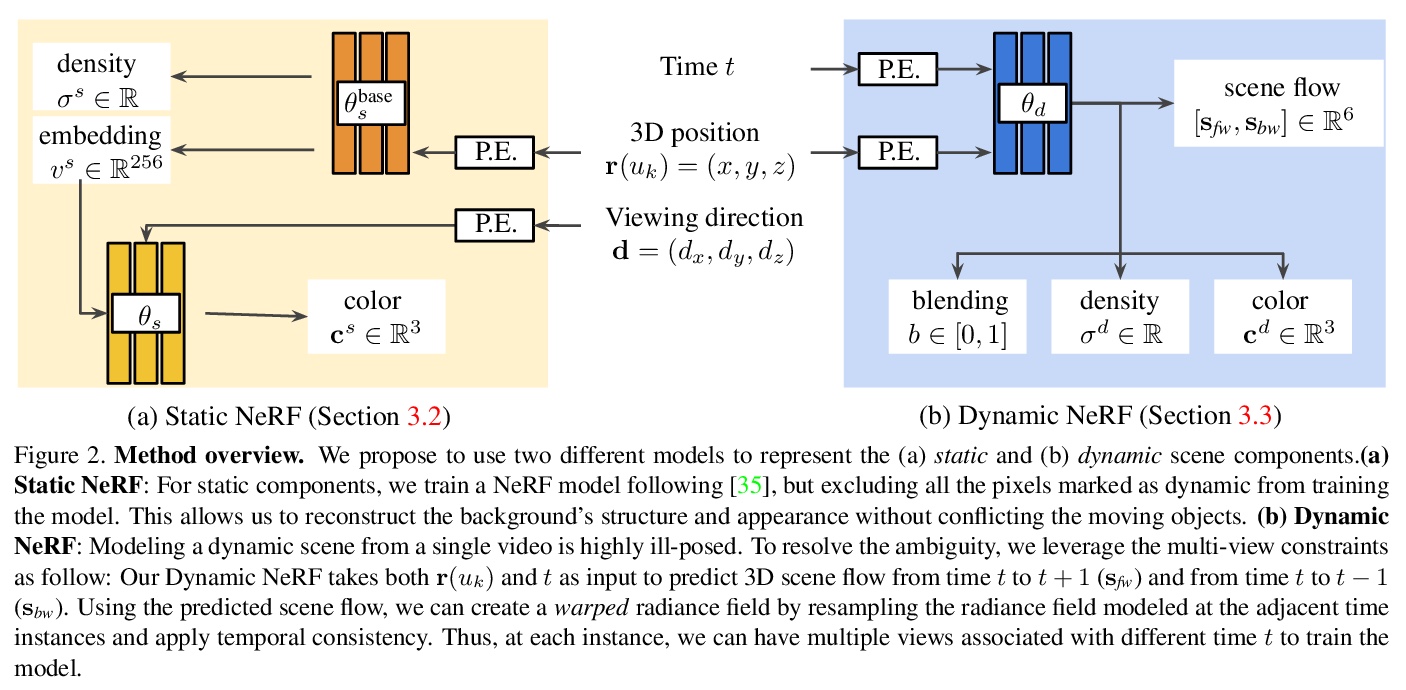

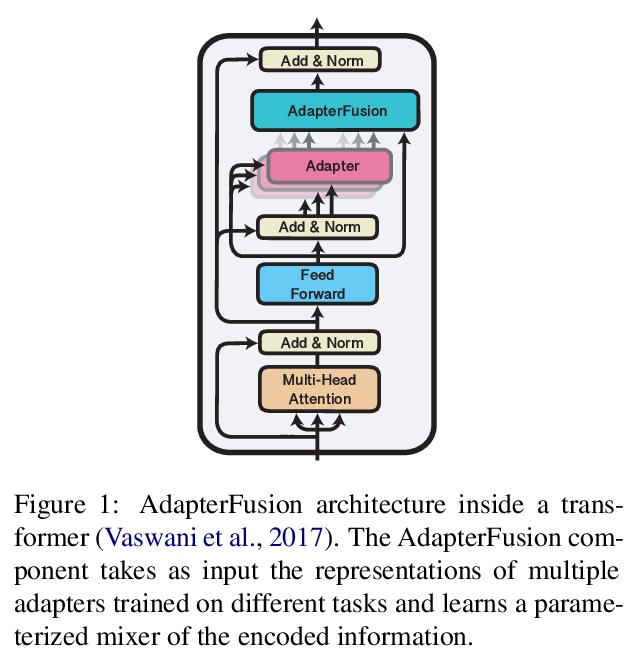
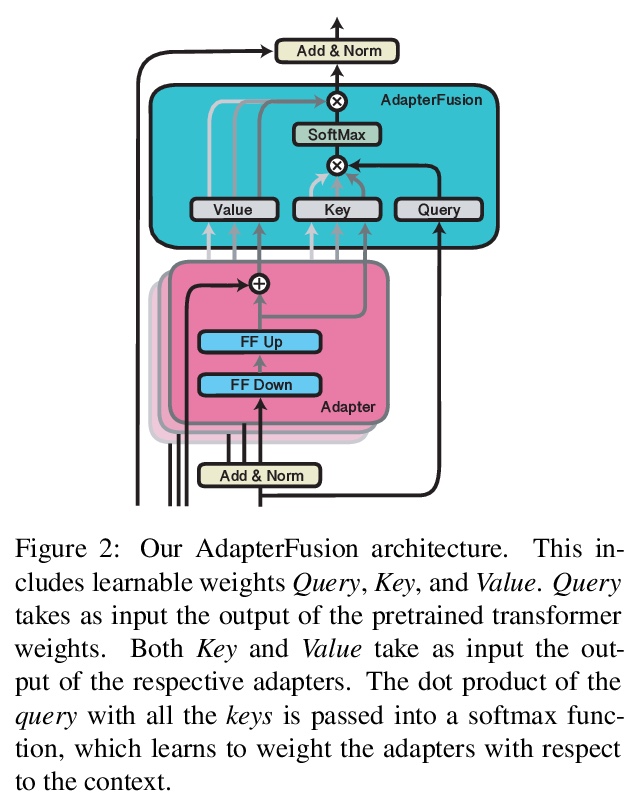
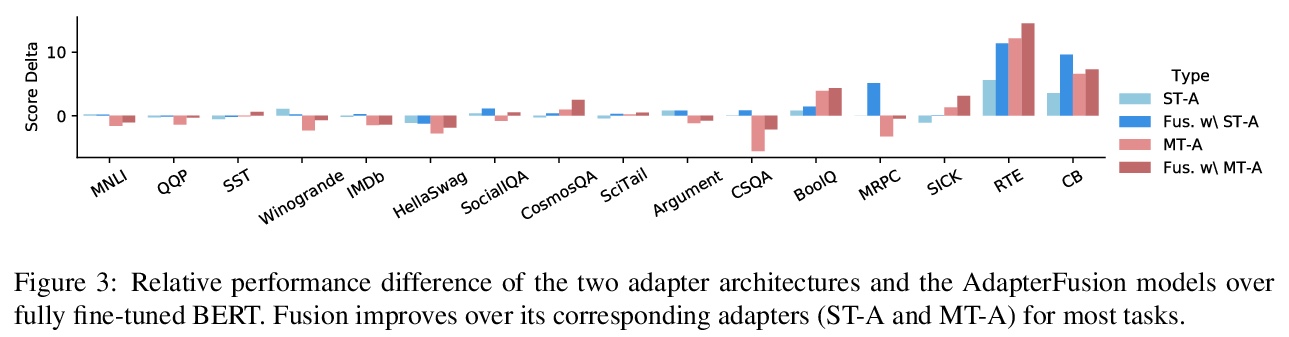
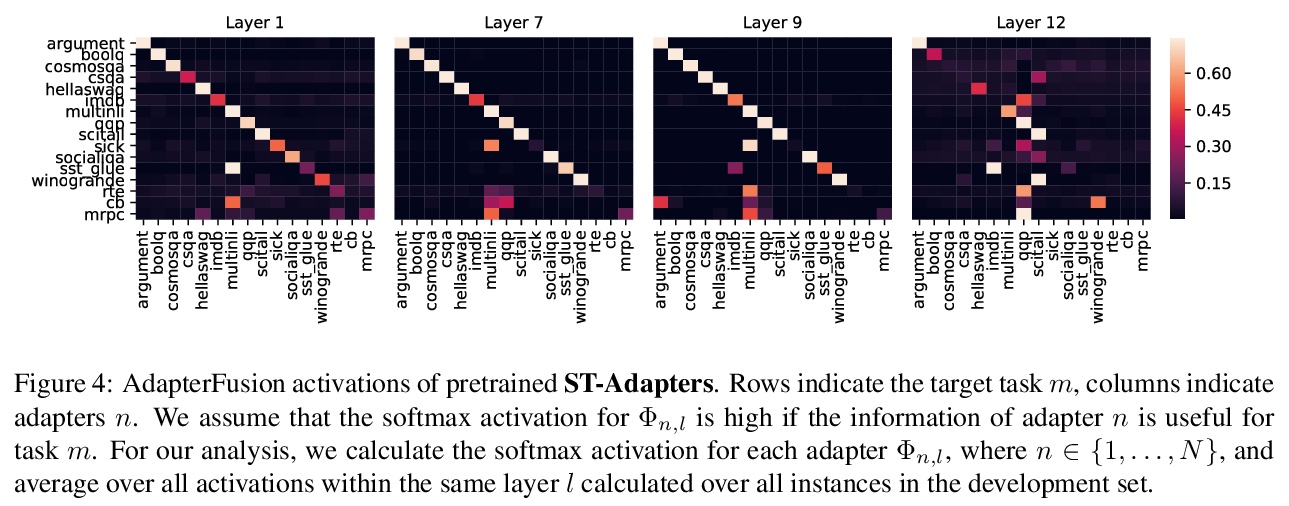
4、[CL] AdapterFusion: Non-Destructive Task Composition for Transfer Learning
J Pfeiffer, A Kamath, A Rücklé, K Cho, I Gurevych
[Technical University of Darmstadt & New York University]
AdapterFusion: 面向迁移学习的非破坏性任务组合。顺序微调和多任务学习是旨在纳入多任务知识的方法;然而,它们受到灾难性遗忘和数据集平衡困难的影响。为解决这些缺点,本文提出一种新的两阶段学习算法AdapterFusion,以利用来自多个任务的知识。在知识提取阶段,学习被称为适配器的特定任务参数,这些参数封装了特定任务信息。在一个单独的知识构成步骤中结合适配器。通过分离这两个阶段,即知识提取和知识组合,分类器可以以非破坏性的方式有效地利用从多个任务学到的表征。在16个不同的NLU任务上对AdapterFusion进行了实证评估,发现它在模型的不同层有效地结合了各种类型的知识,优于传统的策略,如全微调以及多任务学习。
Sequential fine-tuning and multi-task learning are methods aiming to incorporate knowledge from multiple tasks; however, they suffer from catastrophic forgetting and difficulties in dataset balancing. To address these shortcomings, we propose AdapterFusion, a new two stage learning algorithm that leverages knowledge from multiple tasks. First, in the knowledge extraction stage we learn task specific parameters called adapters, that encapsulate the task-specific information. We then combine the adapters in a separate knowledge composition step. We show that by separating the two stages, i.e., knowledge extraction and knowledge composition, the classifier can effectively exploit the representations learned from multiple tasks in a non-destructive manner. We empirically evaluate AdapterFusion on 16 diverse NLU tasks, and find that it effectively combines various types of knowledge at different layers of the model. We show that our approach outperforms traditional strategies such as full fine-tuning as well as multi-task learning. Our code and adapters are available at AdapterHub.ml.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfFRkyogZ
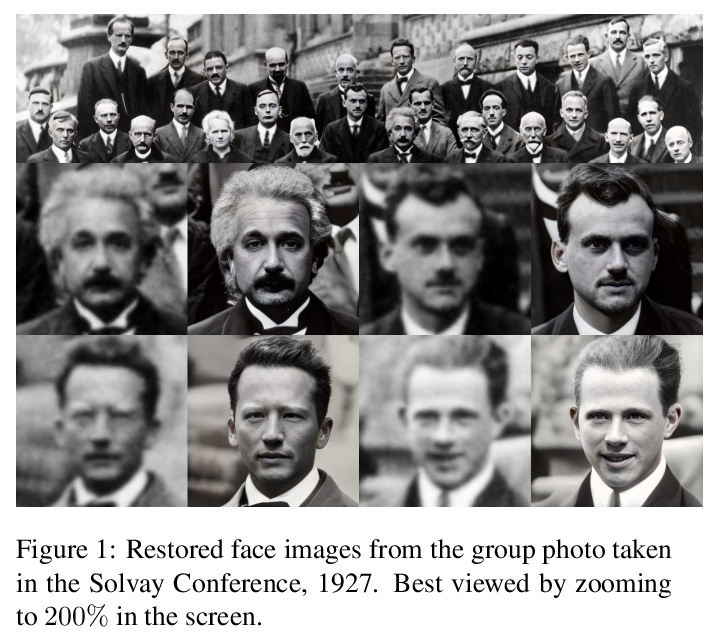
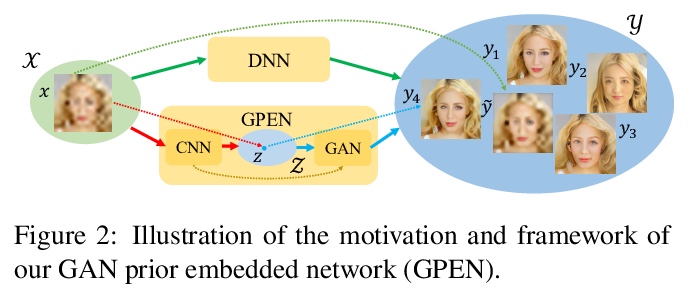
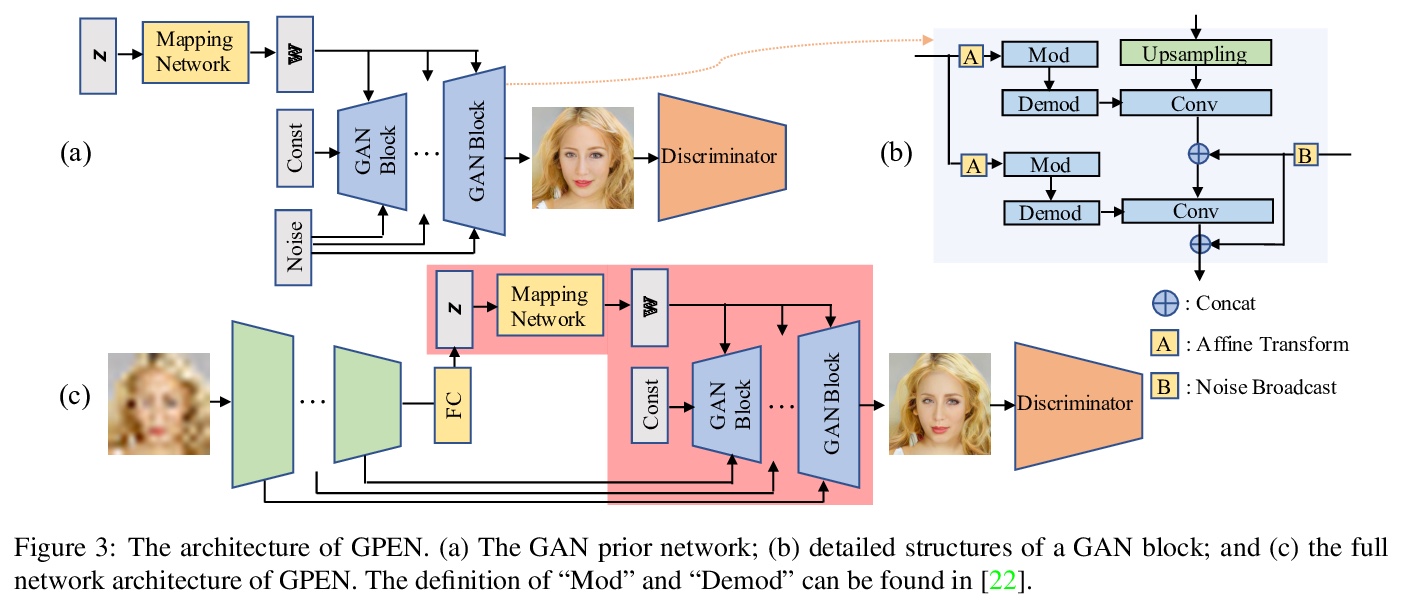
5、[CV] GAN Prior Embedded Network for Blind Face Restoration in the Wild
T Yang, P Ren, X Xie, L Zhang
[DAMO Academy]
基于GAN先验嵌入网络的真实场景人脸修复。从真实场景的退化人脸图像中进行盲人脸修复(BFR)是一个非常具有挑战性的问题。由于问题的高发性和复杂的未知退化,直接训练一个深度神经网络通常无法得到可接受的结果。现有的基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的方法可以产生更好的结果,但往往会产生过度平滑的修复。本文提出一种新方法,首先学习用于生成高质量人脸图像的GAN,并将其嵌入到U型DNN中作为先验解码器,用一组合成的低质量人脸图像对GAN先验嵌入式DNN进行微调。GAN块的设计是为了保证GAN的潜码和噪声输入可以分别由DNN的深层和浅层特征产生,控制重建图像的全局人脸结构、局部人脸细节和背景。所提出的GAN先验嵌入网络(GPEN)易于实现,并能产生视觉上的照片级逼真的结果。实验表明,所提出的GPEN在数量和质量上都取得了明显优于最先进的BFR方法的结果,特别是对真实场景严重退化的人脸图像的修复。
Blind face restoration (BFR) from severely degraded face images in the wild is a very challenging problem. Due to the high illness of the problem and the complex unknown degradation, directly training a deep neural network (DNN) usually cannot lead to acceptable results. Existing generative adversarial network (GAN) based methods can produce better results but tend to generate over-smoothed restorations. In this work, we propose a new method by first learning a GAN for high-quality face image generation and embedding it into a U-shaped DNN as a prior decoder, then fine-tuning the GAN prior embedded DNN with a set of synthesized low-quality face images. The GAN blocks are designed to ensure that the latent code and noise input to the GAN can be respectively generated from the deep and shallow features of the DNN, controlling the global face structure, local face details and background of the reconstructed image. The proposed GAN prior embedded network (GPEN) is easy-to-implement, and it can generate visually photo-realistic results. Our experiments demonstrated that the proposed GPEN achieves significantly superior results to state-of-the-art BFR methods both quantitatively and qualitatively, especially for the restoration of severely degraded face images in the wild.
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfG1Ymi30


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
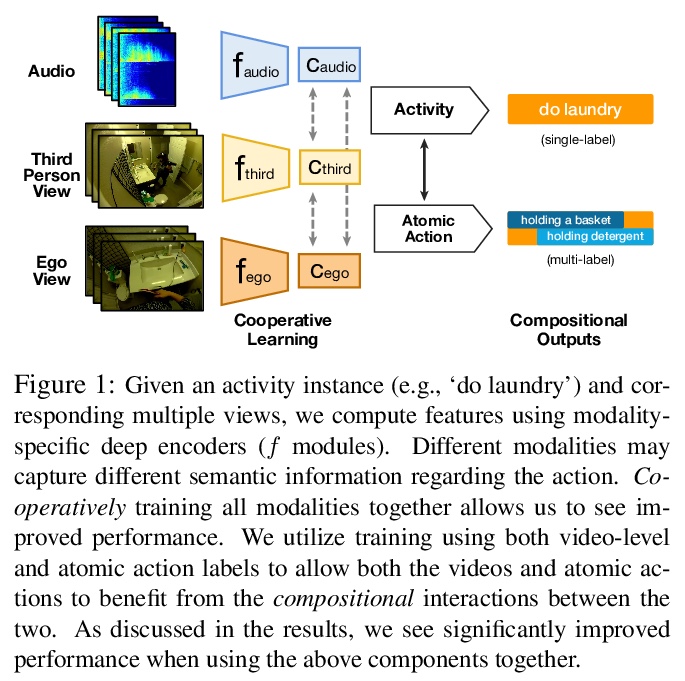
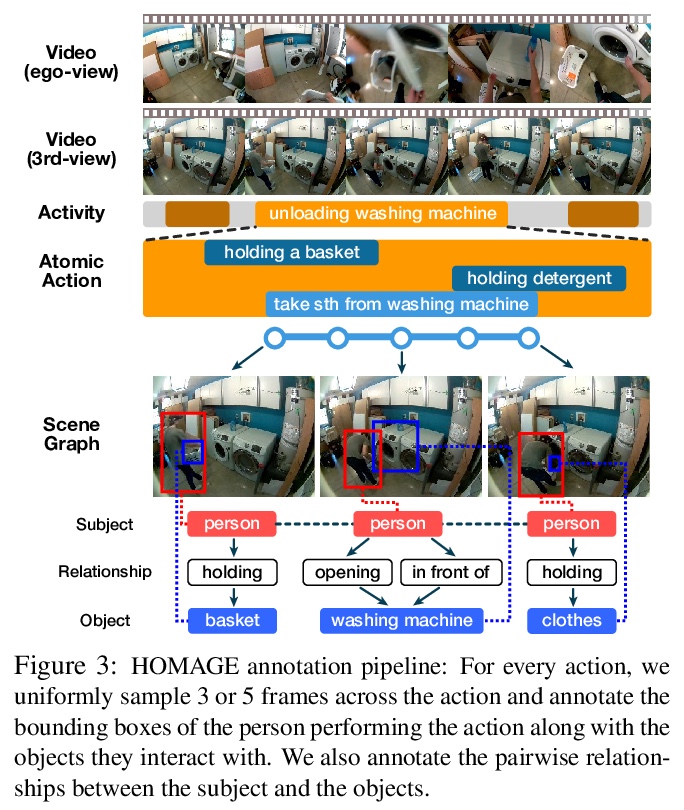
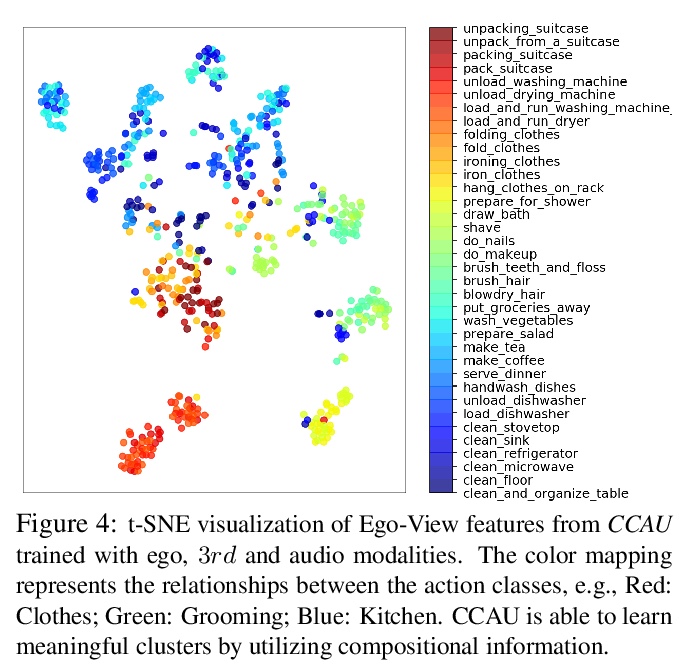
[CV] Home Action Genome: Cooperative Compositional Action Understanding
Home Action Genome:面向合作构成行为理解的多视角行为数据集
N Rai, H Chen, J Ji, R Desai, K Kozuka, S Ishizaka, E Adeli, J C Niebles
[Stanford University & Panasonic Corporation]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfG6pd26x

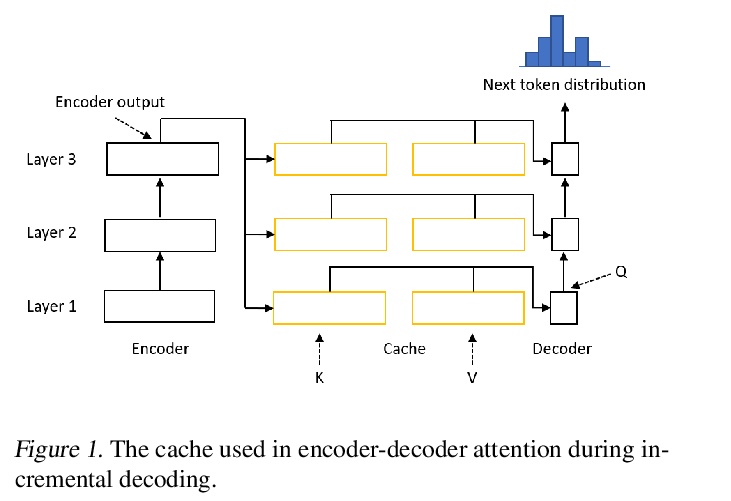
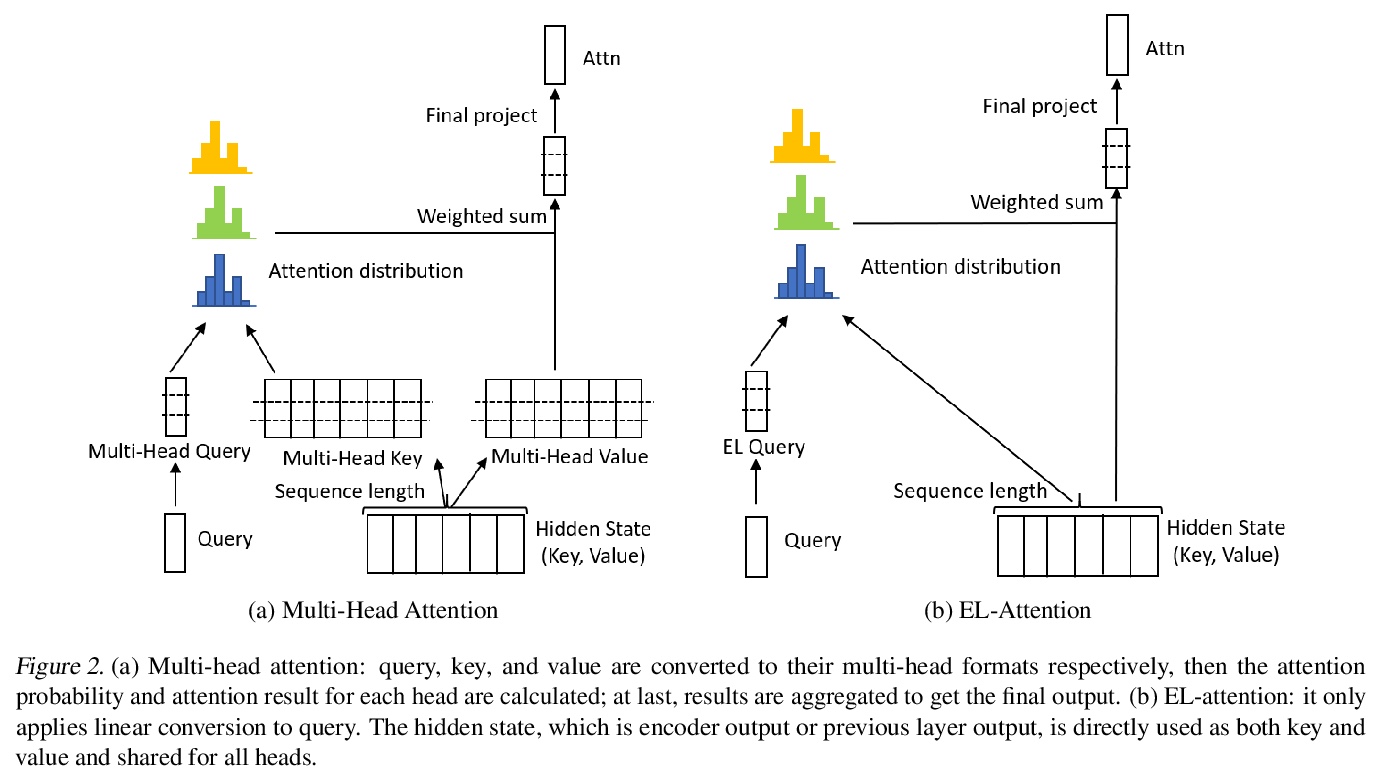
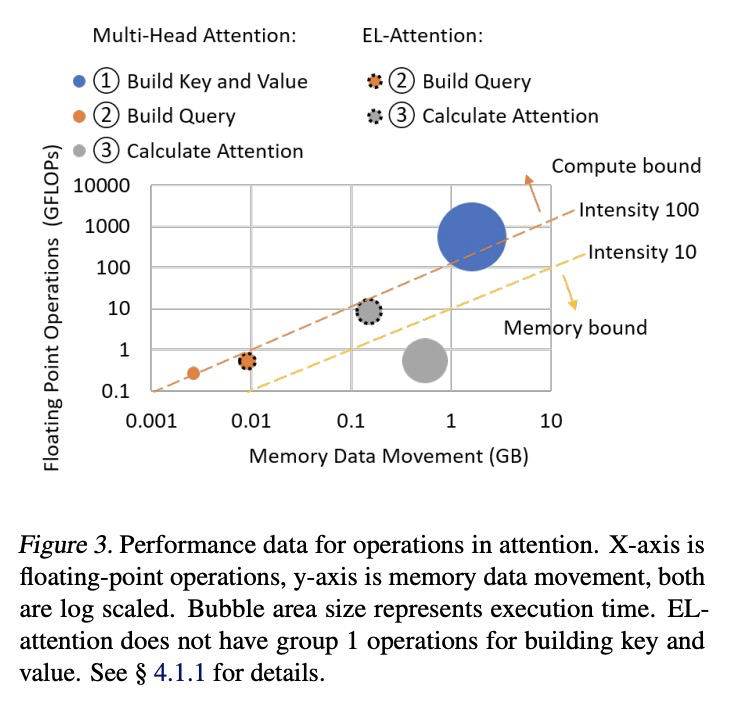
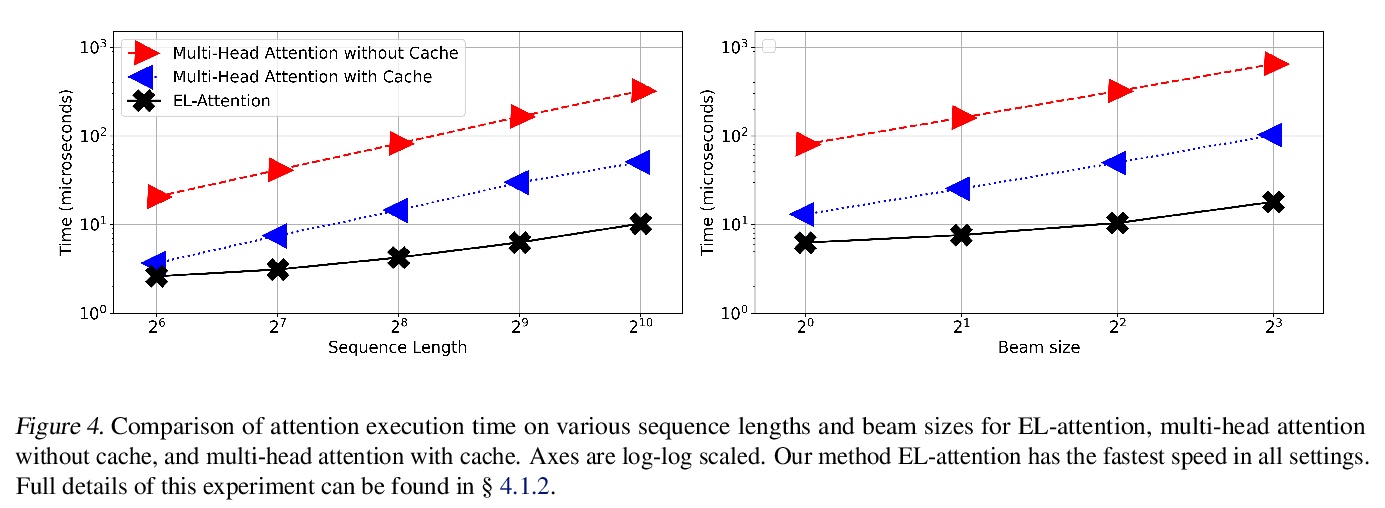
[CL] EL-Attention: Memory Efficient Lossless Attention for Generation
EL-Attention:面向生成的记忆高效无损注意力
Y Yan, J Chen, W Qi, N Bhendawade, Y Gong, N Duan, R Zhang
[Microsoft & University of Science and Technology of China & Microsoft Research Asia]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfG8Brlpt
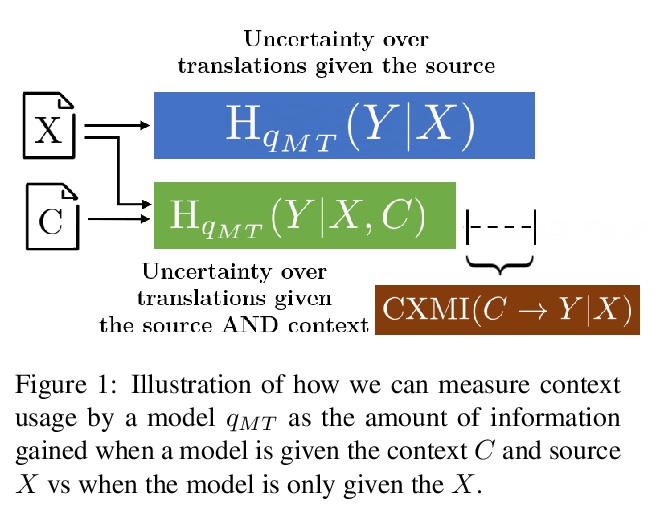
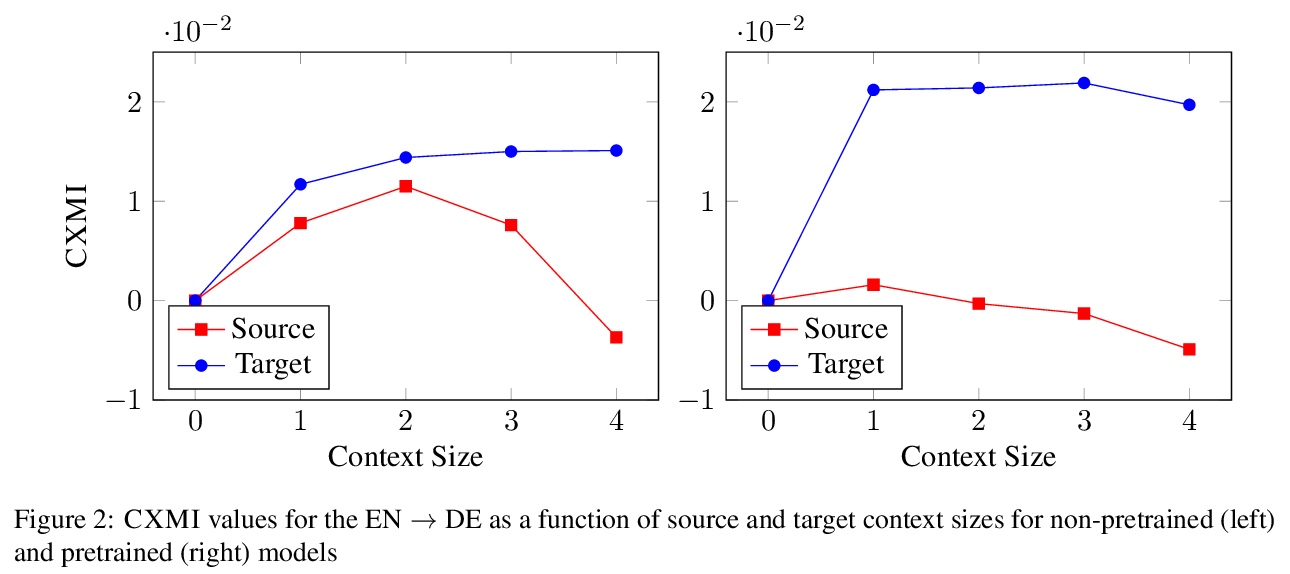
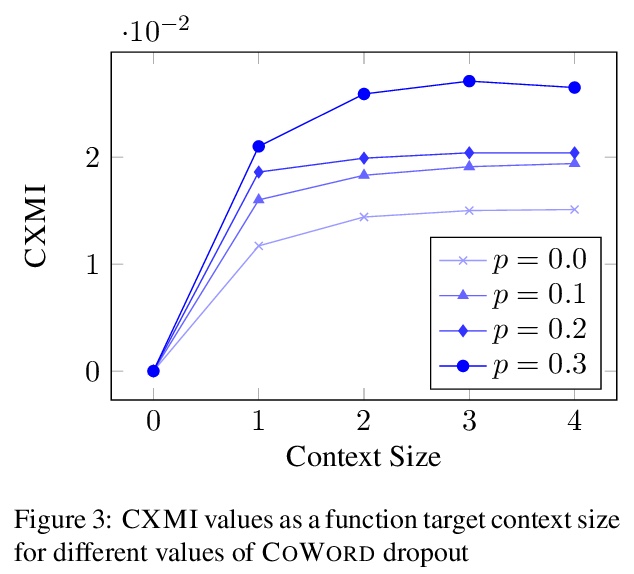
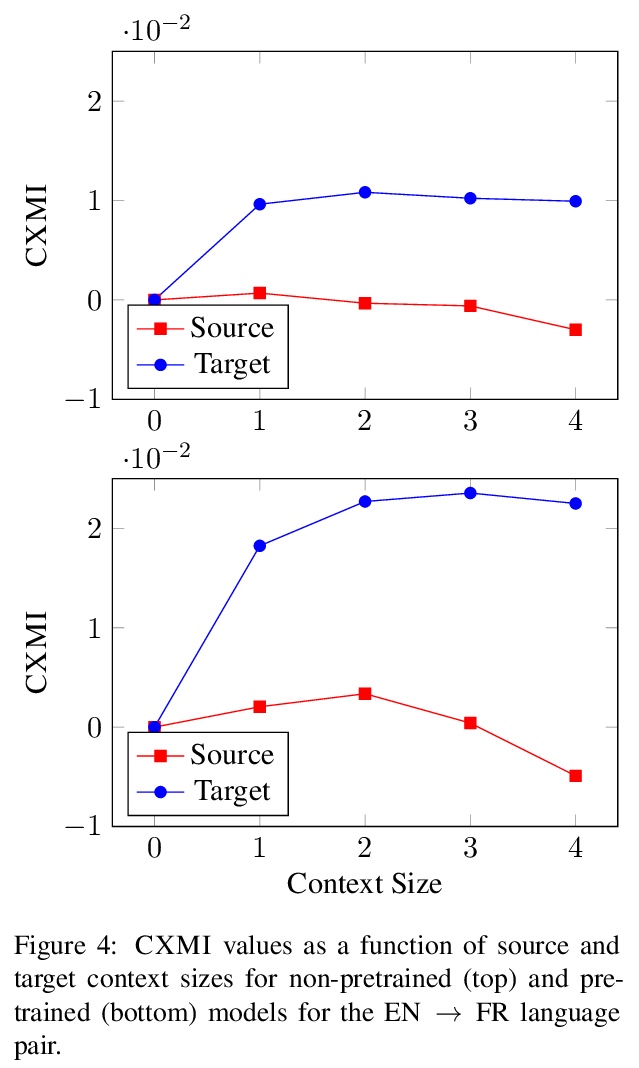
[CL] Measuring and Increasing Context Usage in Context-Aware Machine Translation
在上下文感知机器翻译中测量和增加上下文使用
P Fernandes, K Yin, G Neubig, A F. T. Martins
[CMU & Instituto de Telecomunicacoes]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfG9VcZor
[LG] SyntheticFur dataset for neural rendering
面向神经渲染的合成毛发数据集
T Le, R Poplin, F Bertsch, A S Toor, M L. Oh
[Google]
https://weibo.com/1402400261/KfGhw1K5D