多三角三维曲面
使用三角形网格绘制曲面的另外两个示例。
第一个演示使用plot_trisurf的三角形参数,第二个设置Triangulation对象的蒙版并将对象直接传递给plot_trisurf。
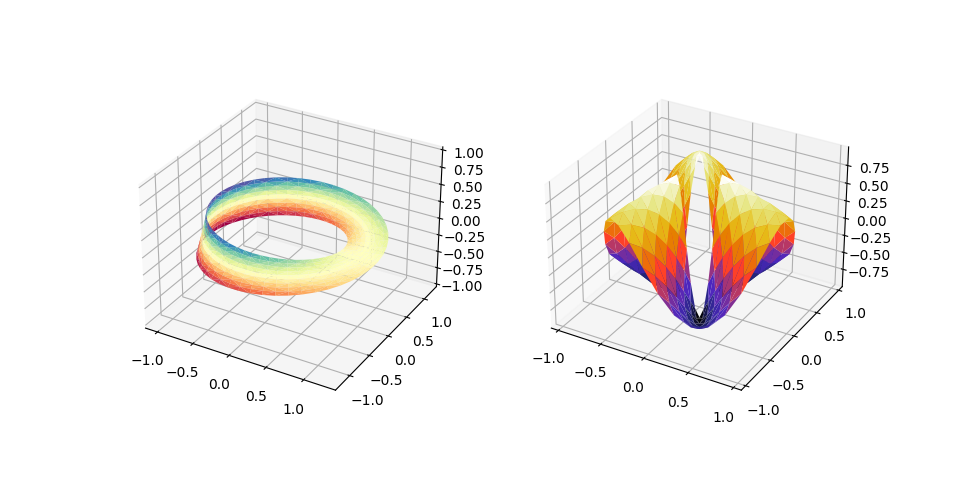
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport matplotlib.tri as mtri# This import registers the 3D projection, but is otherwise unused.from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D # noqa: F401 unused importfig = plt.figure(figsize=plt.figaspect(0.5))#============# First plot#============# Make a mesh in the space of parameterisation variables u and vu = np.linspace(0, 2.0 * np.pi, endpoint=True, num=50)v = np.linspace(-0.5, 0.5, endpoint=True, num=10)u, v = np.meshgrid(u, v)u, v = u.flatten(), v.flatten()# This is the Mobius mapping, taking a u, v pair and returning an x, y, z# triplex = (1 + 0.5 * v * np.cos(u / 2.0)) * np.cos(u)y = (1 + 0.5 * v * np.cos(u / 2.0)) * np.sin(u)z = 0.5 * v * np.sin(u / 2.0)# Triangulate parameter space to determine the trianglestri = mtri.Triangulation(u, v)# Plot the surface. The triangles in parameter space determine which x, y, z# points are connected by an edge.ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1, projection='3d')ax.plot_trisurf(x, y, z, triangles=tri.triangles, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)ax.set_zlim(-1, 1)#============# Second plot#============# Make parameter spaces radii and angles.n_angles = 36n_radii = 8min_radius = 0.25radii = np.linspace(min_radius, 0.95, n_radii)angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, n_angles, endpoint=False)angles = np.repeat(angles[..., np.newaxis], n_radii, axis=1)angles[:, 1::2] += np.pi/n_angles# Map radius, angle pairs to x, y, z points.x = (radii*np.cos(angles)).flatten()y = (radii*np.sin(angles)).flatten()z = (np.cos(radii)*np.cos(3*angles)).flatten()# Create the Triangulation; no triangles so Delaunay triangulation created.triang = mtri.Triangulation(x, y)# Mask off unwanted triangles.xmid = x[triang.triangles].mean(axis=1)ymid = y[triang.triangles].mean(axis=1)mask = np.where(xmid**2 + ymid**2 < min_radius**2, 1, 0)triang.set_mask(mask)# Plot the surface.ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2, projection='3d')ax.plot_trisurf(triang, z, cmap=plt.cm.CMRmap)plt.show()

