给定一棵二叉搜索树和其中的一个节点 p ,找到该节点在树中的中序后继。如果节点没有中序后继,请返回 null 。
节点 p 的后继是值比 p.val 大的节点中键值最小的节点,即按中序遍历的顺序节点 p 的下一个节点。
示例 1: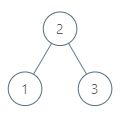
输入:root = [2,1,3], p = 1
输出:2
解释:这里 1 的中序后继是 2。请注意 p 和返回值都应是 TreeNode 类型。
示例 2: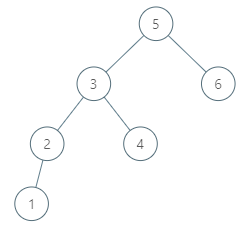
输入:root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], p = 6
输出:null
解释:因为给出的节点没有中序后继,所以答案就返回 null 了。
提示:
树中节点的数目在范围 [1, 104] 内。
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
树中各节点的值均保证唯一。
class Solution {/**中序遍历写法*/public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();int num = 0;List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<>();while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {if (root != null) {stack.push(root);root = root.left;}else {TreeNode node = stack.poll();if (node == p) num = list.size();list.add(node);root = node.right;}}if (list.size() < num+2) return null;return list.get(num+1);}}
利用二叉搜索树特性
class Solution {/**只有在当前节点大于p节点时,当前节点可能是p的下一个节点,我们应该去左子树找可能更小的当前节点小于等于p节点时,是去右子树找p的下一个节点*/public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {TreeNode res = null;int target = p.val;while (root != null) {//当前节点大于target,可能是p的下一个节点,应该去左子树找更小的if (root.val > target) {res = root;root = root.left;}//当前节点小于等于target,应该是去右子树找第一个小的else root = root.right;}return res;}}

