题目
有一个 m × n 的矩形岛屿,与 太平洋 和 大西洋 相邻。 “太平洋” 处于大陆的左边界和上边界,而 “大西洋” 处于大陆的右边界和下边界。
这个岛被分割成一个由若干方形单元格组成的网格。给定一个 m x n 的整数矩阵 heights , heights[r][c] 表示坐标 (r, c) 上单元格 高于海平面的高度 。
岛上雨水较多,如果相邻单元格的高度 小于或等于 当前单元格的高度,雨水可以直接向北、南、东、西流向相邻单元格。水可以从海洋附近的任何单元格流入海洋。
返回 网格坐标 result 的 2D列表 ,其中 result[i] = [ri, ci] 表示雨水可以从单元格 (ri, ci) 流向 太平洋和大西洋 。
示例 1:
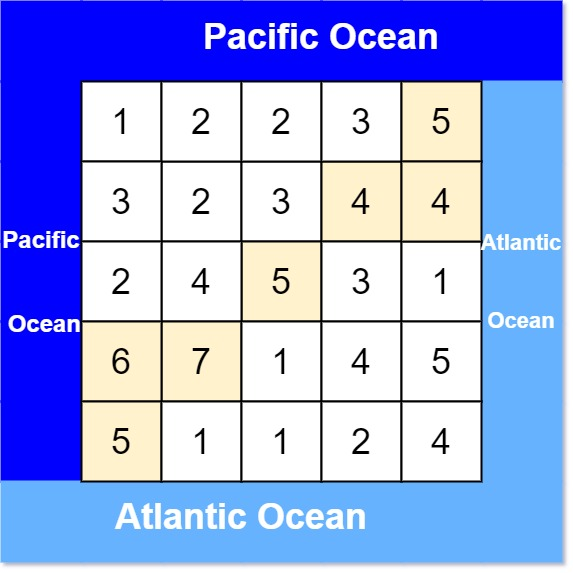
输入: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]]
输出: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]示例 2:
输入: heights = [[2,1],[1,2]]
输出: [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]提示:
m == heights.length
n == heights[r].length
1 <= m, n <= 200
0 <= heights[r][c] <= 10^5来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pacific-atlantic-water-flow
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
题目很好理解,要求和太平洋、大西洋都连通的坐标点。
如果按常规思路对每一个点进行
遍历,在时间上,有
个点,每个点要遍历
时间,时间复杂度为
#card=math&code=O%28m%5E2%2An%5E2%29&id=ICkhF),会超时。在空间上,除了遍历时常用到的
数组外,还需要空间记录
点搜索的结果,即是否同时与太平洋、大西洋都连通。所以需要转变思路。
如果逆向考虑,从边界开始搜索,即分别从太平洋、大西洋进行搜索,分别记录两个水域可以到达的位置,最后返回两个集合的交集即可。重点是,从四个边界分别搜索一遍矩阵,时间复杂度是#card=math&code=O%28m%2An%29&id=D6BSj)。
代码
class Solution {int[][] dirs = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {int m = heights.length;int n = heights[0].length;// pacific[i][j] 表示[i,j]这一坐标能否流到太平洋boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[m][n];// atlantic[i][j] 表示[i,j]这一坐标能否流到大西洋boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[m][n];for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {// 从第一列边界开始搜索,能搜到的位置就表示和太平洋连通,pacific数组可以和下面循环内第一个dfs共用dfs(i, 0, m, n, heights, pacific);// 从第n-1列边界开始搜索,能搜到的位置就表示和大西洋连通,atlantic数组可以和下面循环内第二个dfs共用dfs(i, n - 1, m, n, heights, atlantic);}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// 从第一行边界开始搜索,能搜到的位置就表示和太平洋连通dfs(0, i, m, n, heights, pacific);// 从第m-1行边界开始搜索,能搜到的位置就表示和大西洋连通dfs(m - 1, i, m, n, heights, atlantic);}List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {// 将和太平洋、大西洋都连通的点添加到结果集if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {ans.add(List.of(i, j));}}}return ans;}private void dfs(int row, int col, int m, int n, int[][] heights, boolean[][] reachable) {reachable[row][col] = true;for (int[] dir : dirs) {int nr = dir[0] + row;int nc = dir[1] + col;if (nr < 0 || nr >= m || nc < 0 || nc >= n || reachable[nr][nc] || heights[nr][nc] < heights[row][col]) {continue;}dfs(nr, nc, m, n, heights, reachable);}}}